Isolation and Antibiotic Resistant Research of Tetragenococcus halophilus from Xuanwei Ham, A China High-Salt-Fermented Meat Products
Abstract
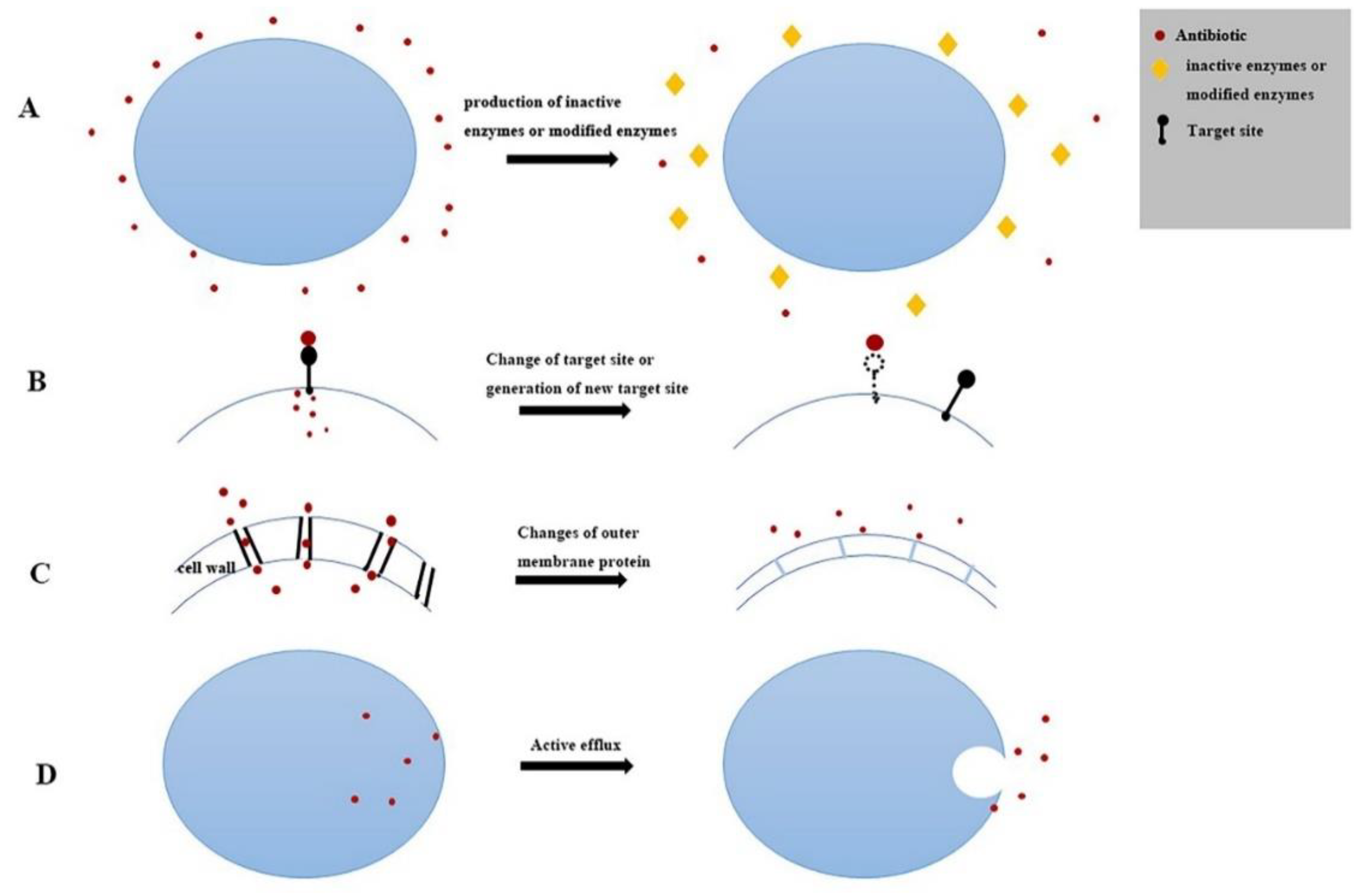
:1. Introduction
2. Results
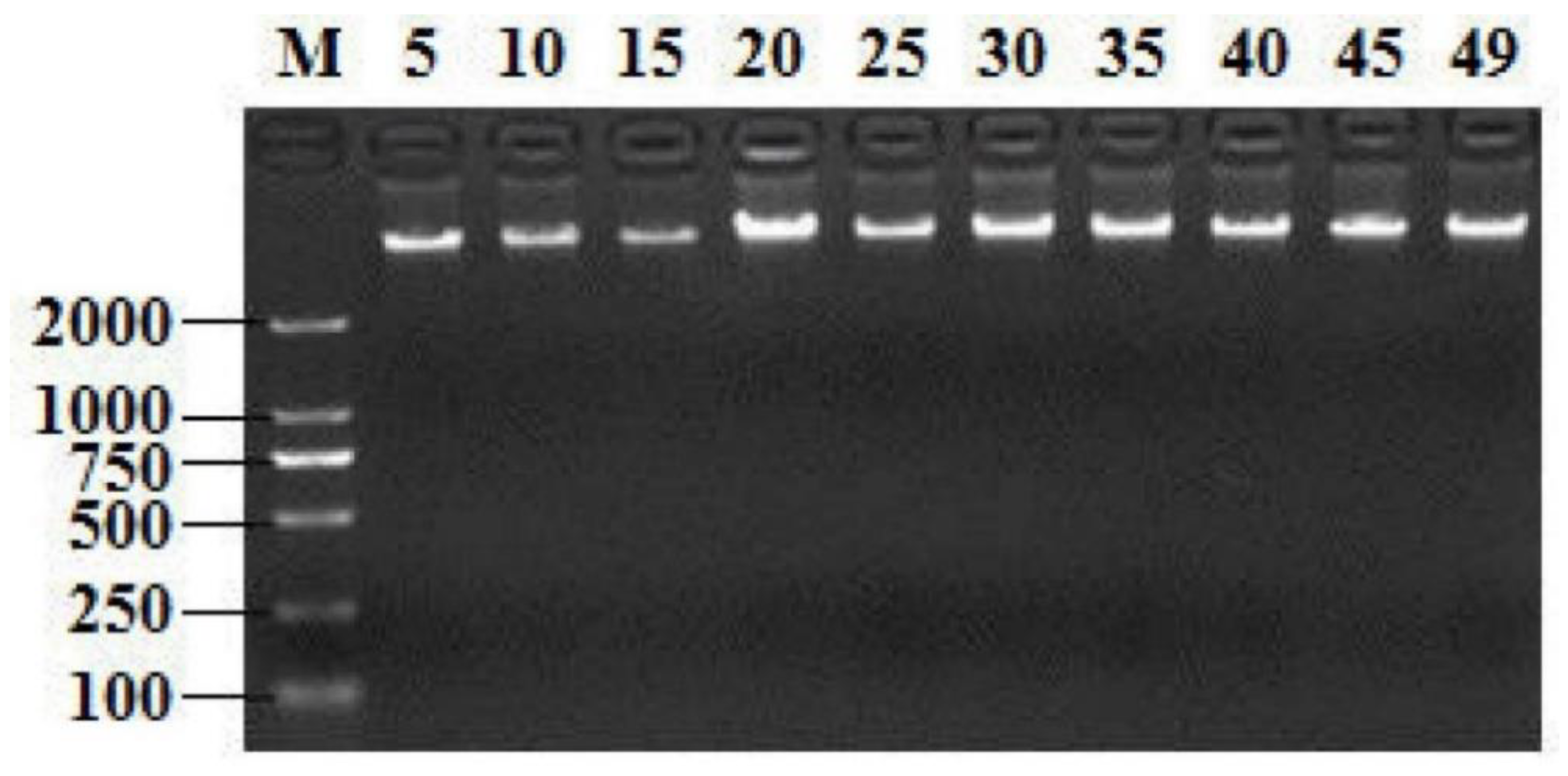
2.1. Screening T. Halophilus Isolates by GroEL Gene and 16S rRNA Gene
2.2. Identification of the Selected Bacteria
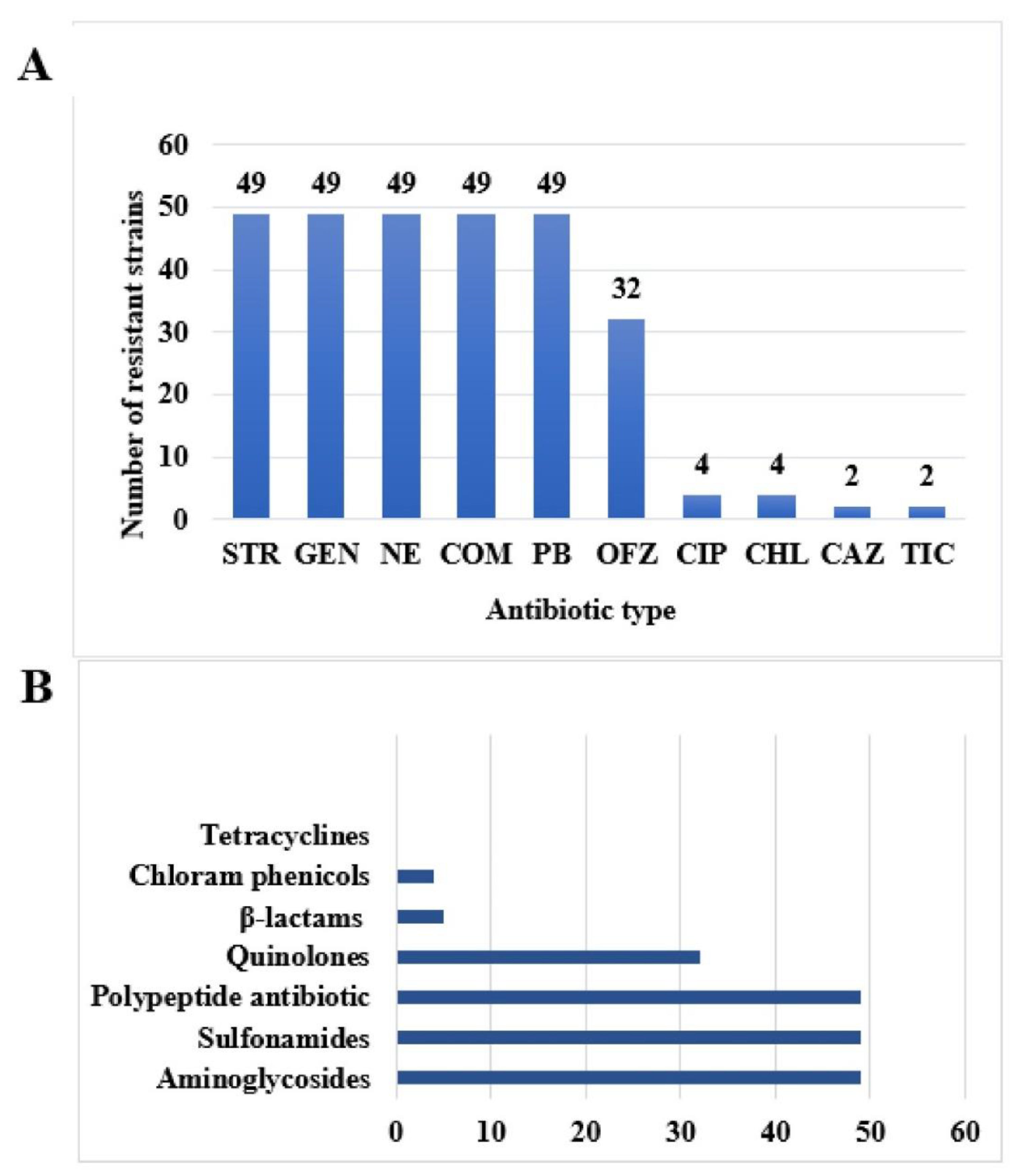
2.3. Experimental Results of Drug resistance Phenotype of 49 Isolates of T. Halophilus
2.4. Drug Resistance Spectrum of 49 Strains of T. Halophilus
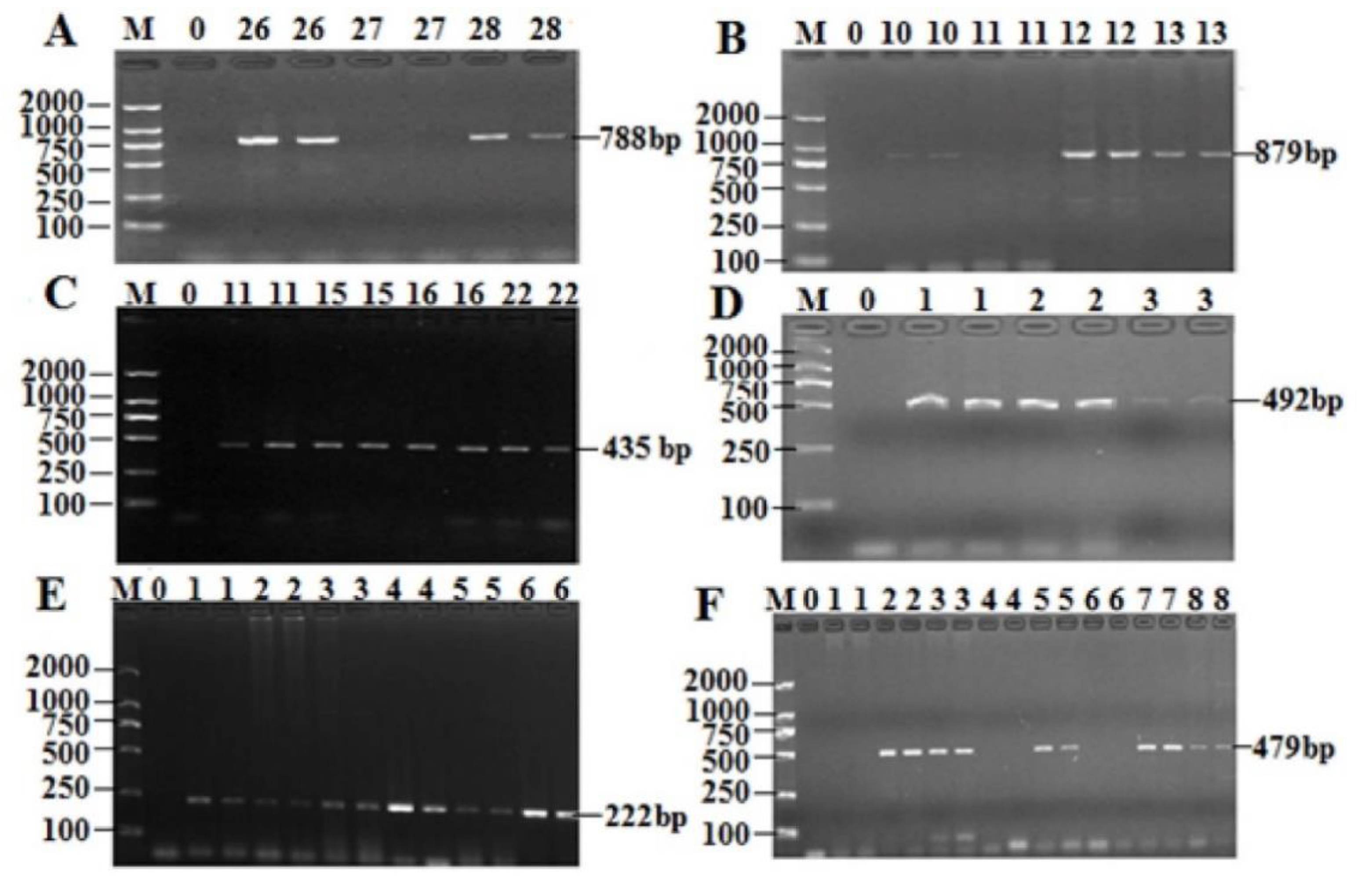
2.5. Prevalence of the AR Genes Among 49 Isolates of T. Halophilus
2.6. Analysis of Drug Resistance Phenotype and Genotype Matching Rate of Isolates of T. Halophilus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
4.2. Xuanwei Ham Samples and Bacterial Strain Isolation
4.3. Identification of Isolates by groEL Gene and 16S rRNA Gene
4.4. Antibiotic Sensitivity Tests of Isolates
4.5. Antibiotic Resistance Gene Detection of Isolates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, M.D.; Williams, A.M.; Wallbanks, S. The phylogeny of Aerococcus and Pediococcus as determined by 16S rRNA sequence analysis: Description of Tetragenococcus gen. nov. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 58, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtler, M.; Ganzle, M.G.; Wolf, G.; Hammes, W.P. Physiological diversity among strains of Tetragenococcus halophilus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Fang, F.; Chen, J.; Du, G.; Liu, L. Isolation and Arginine Metabolism Detection of a Tetragenococcus halophilus Strain. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 35, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, K.R.; Deka, M.; Jeyaram, K. Bacterial dynamics during yearlong spontaneous fermentation for production of ngari, a dry fermented fish product of Northeast India. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 199, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanagata, H.; Shida, O.; Takagi, H. Taxonomic homogeneity of a salt-tolerant lactic acid bacteria isolated from shoyu mash. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juste, A.; Lievens, B.; Frans, I.; Marsh, T.L.; Klingeberg, M.; Michiels, C.W.; Willems, K.A. Genetic and physiological diversity of Tetragenococcus halophilus strains isolated from sugar- and salt-rich environments. Microbiology 2008, 154, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.H.; Ki, H.Y. Analysis of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Japanese- and Chinese-Fermented Soybean Pastes Using Nested PCR-DGGE. Curr. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, T.; Yanagida, F.; Uchimura, T.; Tsuji, M.; Ogino, S.; Shinohara, T.; Yokotsuka, K. Widespread distribution of the bacteriocin-producing lactic acid cocci in Miso-paste products. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roling, W.; van Verseveld, H.W. Characterization of Tetragenococcus halophila Populations in Indonesian Soy Mash (Kecap) Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Udomsil, N.; Rodtong, S.; Tanasupawat, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Proteinase-producing halophilic lactic acid bacteria isolated from fish sauce fermentation and their ability to produce volatile compounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsil, N.; Rodtong, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Hua, Y.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Use of Tetragenococcus halophilus as a Starter Culture for Flavor Improvement in Fish Sauce Fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8401–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, C.D.; Zhou, R.Q. Effect of different halophilic microbial fermentation patterns on the volatile compound profiles and sensory properties of soy sauce moromi (vol 239, pg 321, 2014). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Huang, J.; Liang, R.; Wu, C.; Zhou, R. Comparing the differences of characteristic flavour between natural maturation and starter culture for Mucor-type Douchi. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuda, T.; Izawa, Y.; Ishii, S.; Takahashi, H.; Torido, Y.; Kimura, B. Suppressive effect of Tetragenococcus halophilus, isolated from fish-nukazuke, on histamine accumulation in salted and fermented fish. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuko, N.; Toshinori, I.; Tadao, E.; Yoshihiro, D.; Yoshiaki, O.; Akio, O. Clinical efficacy of halophilic lactic acid bacterium Tetragenococcus halophilus Th221 from soy sauce moromi for perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergol. Int. 2009, 58, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.R. Safety of industrial lactic acid bacteria. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 68, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkers, D.M.A.E. Microbial perturbations and modulation in conditions associated with malnutrition and malabsorption. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Fan, M.; Wei, X. Antibiotic Resistance of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Naturally Fermented Chinese Cured Beef. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 2054–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, G.; Ducci, B.; Comodo, N.; Lo Nostro, A. Antimicrobial resistance profile of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw meat: A research for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Food Control 2007, 18, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorum, H.; L’Abee-Lund, T.M. Antibiotic resistance in food-related bacteria—A result of interfering with the global web of bacterial genetics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graveland, H.; Duim, B.; van Duijkeren, E.; Heederik, D.; Wagenaar, J.A. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in animals and humans. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.W.; Heo, S.; Lee, J.H. Safety assessment of Tetragenococcus halophilus isolates from doenjang, a Korean high-salt-fermented soybean paste. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundsfjord, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Courvalin, P. Human infections caused by glycopeptide-resistant Enterococcus spp.: Are they a zoonosis? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuber, M. Spread of antibiotic resistance with food-borne pathogens. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 56, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berends, B.R.; van den Bogaard, A.E.; van Knapen, F.L.; Snijders, J.M. Human health hazards associated with the administration of antimicrobials to slaughter animals. Part II. An assessment of the risks of resistant bacteria in pigs and pork. Vet. Q. 2001, 23, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, S.; Ma, C.; Li, Z.; Li, S. Antibiotic resistance in fermented food lactic acid bacteria-a review. Microbiol. China 2015, 42, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Casado Muñoz Mdel, C.; Benomar, N.; Lerma, L.L.; Gálvez, A.; Abriouel, H. Antibiotic resistance of Lactobacillus pentosus and Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides isolated from naturally-fermented Aloreña table olives throughout fermentation process. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 172, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Zhou, H. Two kinds of antibiotics resistance of lactic acid bacteria isolated from yogurt. China Public Health 2010, 26, 511–512. [Google Scholar]
- Hummel, A.S.; Hertel, C.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Franz, C.M. Antibiotic resistances of starter and probiotic strains of lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Gao, K.; Zhu, B.; Lv, N. Identification of lactic acid bacteria in commercial yogurt and their antibiotic resistance. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2013, 53, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.K. The Role of Tetragenococcus halophilus’ Gene clpB, dnaK, hrcA in Saline Adaption. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Tian, T.; Yue, X. Isolation, Identification and Preliminary Screening of Acid-Tolerant Lactic Acid Bacteria from Naturally Fermented Pickle Juices from Daqing. Food Sci. 2014, 35, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.L. Analysis of Prosciutto Microflora and the Effect of Superior Strains on the Composition of Microflora in Fermented Sausage. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C. Detection and Sequence Analysis of Correlative Virulence Gene and Drug Resistance Genes of Superiority Escherichia Coli Serotypes Isolated from Cow Mastitis. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Ningxia, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S. Detection and Analysis of Drug Resistance Genes and Virulence Genes of E. coli in Beef Cattle in Parts of Heilongjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes of Pathogenic Salmonella from Swine. Acta Vet. Et Zootech. Sin. 2006, 37, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Shen, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C. Expression of marA, soxS and ramA genes and efflux pump genes acrA and acrB in ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella. Vet. Sci. China 2009, 39, 928–932. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Yang, Q. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance and vancomycin resistance genes in Enterococcus species. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. 2007, 17, 2244–2246. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Emergence of Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-1 in Enterobacteriacea; South China University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]


| Antibiotic | Isolates of Resistant | Isolates of Susceptible | Resistance Rate (R) | Intermediate Rate (I) | Susceptible Rate (S) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEN | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (49/49) |
| AMO | 0 | 47 | 0% | (0/49) | 4.08% | (2/49) | 95.90% | (47/49) |
| AMP | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (49/49) |
| TIC | 2 | 47 | 4.08% | (2/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 95.9% | (47/49) |
| CE | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (49/49) |
| CAZ | 2 | 42 | 4.08% | (2/49) | 10.20% | (5/49) | 85.70% | (42/49) |
| CTX | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (49/49) |
| GEN | 49 | 0 | 100% | (49/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) |
| STR | 49 | 0 | 100% | (49/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) |
| NE | 49 | 0 | 100% | (49/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) |
| TET | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (0/49) |
| MH | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (0/49) |
| DO | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (0/49) |
| PB | 49 | 0 | 100% | (49/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) |
| VA | 0 | 49 | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 100% | (0/49) |
| COM | 49 | 0 | 100% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) | 0% | (0/49) |
| CHL | 4 | 40 | 8.16% | (0/49) | 10.20% | (5/49) | 81.63% | (40/49) |
| OFZ | 32 | 2 | 65.31% | (32/49) | 30.61% | (15/49) | 4.08% | (2/49) |
| CIP | 4 | 33 | 8.16% | (4/49) | 24.49% | (12/49) | 67.35% | (33/49) |
| Type of Resistance | Resistant Spectrum | Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM | 49 |
| 6 | GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ | 32 |
| 7 | GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ-CIP | 4 |
| GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ-CAZ | 2 | |
| GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ-TLC | 2 | |
| GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ-CHL | 2 | |
| 8 | GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ-CIP-CHL | 4 |
| GEN-STR-NEO-PB-COM-OFZ-CIP-CAZ | 1 |
| Type of Resistance | Number of Isolates | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 49 | 100% |
| 2 | 49 | 100% |
| 3 | 49 | 100% |
| 4 | 49 | 100% |
| 5 | 49 | 100% |
| 6 | 32 | 65.31% |
| 7 | 12 | 24.50% |
| 8 | 5 | 10.20% |
| Antibiotic | AR Gene | Positive Isolates | Totally Isolates | Positive Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracyclines | tet(K) | 0 | 49 | 0% |
| tet(L) | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| tet(M) | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| tet(O) | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| tet(S) | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| tet(W) | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| β-lactams | blaTEM | 8 | 49 | 16.33% |
| bl3-vim | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| blaOXA | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| blaSHV | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| Sulfonamides | Sul1 | 0 | 49 | 0% |
| Sul2 | 38 | 49 | 77.55% | |
| Sul3 | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| Aminoglycosides | aac(3′)-IIa | 0 | 49 | 0% |
| acrB | 44 | 49 | 89.79% | |
| aadB | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| aadA1 | 14 | 49 | 28.57% | |
| Chloram Phenicols | floR | 0 | 49 | 0% |
| Cat1 | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| Quinolones | GyrA | 0 | 49 | 0% |
| GyrB | 37 | 49 | 75.51% | |
| ParC | 0 | 49 | 0% | |
| Polypeptide Antibiotic | VanC1 | 0 | 49 | 0% |
| EmgrB | 30 | 49 | 61.22% |
| Antibiotic | Resistant Phenotype | Resistant Gene | Compliance Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracyclines | 0 | 0 | (0/0) | 100% |
| β-lactams | 5 | 8 | (5/8) | 62.5% |
| Sulfonamides | 49 | 38 | (38/49) | 79.17% |
| Aminoglycosides | 49 | 45 | (45/49) | 91.84% |
| Chloram phenicols | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Quinolones | 32 | 37 | (32/37) | 86.49% |
| Polypeptide Antibiotic | 49 | 30 | (30/49) | 61.22% |
| Primers | Gene Sequences (5’–3’) | References |
|---|---|---|
| 27-F | AGATTTGATCCTGGCTCAG | [32] |
| 1492-R | CTACGGCTACCTTGTTACGA | |
| GroEL-F | CGTCGTCAATGCTYAATGG | [33] |
| GroEL-R | TGCTGCCAGAAGAAACTTCA |
| Antibiotic | AR Gene | Gene Sequences (5‘–3‘) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Product Size (bp) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracyclines | tet(K) | F: TTAGGTGAAGGGTTAGGTCC R: GCAAACTCATTCCAGAAGCA | 59 | 697 | [30] |
| tet(O) | F: AACTTAGGCATTCTGGCTCAC R: TCCCACTGTTCCATATCGTCA | 55 | 515 | [30] | |
| tet(S) | F: CATTTGGTCTTATTGGATCG R: ATTACACTTCCGATTTCGG | 55 | 456 | [30] | |
| tet(W) | F: GAGAGCCTGCTATATGCCAGC R: GGGCGTATCCACAATGTTAAC | 58 | 168 | [30] | |
| tet(L) | F: TCATCATCTCCTGATTTTAC R: AGTAAAAACAAGCAGAGCAT | 60 | 1464 | This study | |
| tet(M) | F: GTTAAATAGTGTTCTTGGAG R: CTAAGATATGGCTCTAACAA | 53 | 501 | This study | |
| β-lactams | blaTEM | F: CAGAAACGCTGGTGAAAG R: TTACCAATGGTTAATCAGTGAG | 54 | 788 | [34] |
| bl3-vimF | F: TTGGTCTACATGACCGCGTCTGTA R: AGATCGGCATCGGCCACGTT | 59 | 623 | This study | |
| blaOXA | F: TTTTCTGTTGTTTGGGTTTC R: TTTCTTGGCTTTTATGCTTG | 53 | 447 | [35] | |
| blaSHV | F: TGTATTATCTCCCTGTTAGC R: TTAGCGTTGCCAGTGCTC | 55 | 843 | [35] | |
| Sulfonamides | Sul1 | F: TCGGACAGGGCGTCTAAG R: GGGTATCGGAGCGTTTGC | 63 | 925 | [35] |
| Sul2 | F: CCTGTTTCGTCCGACACAGA R: GAAGCGCAGCCGCAATTCAT | 55 | 435 | This study | |
| Sul3 | F: ATGAGCAAGATTTTTGGAATCGTA R: CTAACCTAGGGCTTTGGATATTT | 59 | 792 | [36] | |
| Aminoglycosides | aac (3′)-IIa | F: GGCGACTTCACCGTTTCT R: GGACCGATCACCCTACGAG | 54 | 412 | [35] |
| acrB | F: CGTGAGCGTTGAGAAGTCCT R: GGCGTCAGTTGGTATTTGGT | 58 | 222 | [37] | |
| aadB | F: GAGGAGTTGGACTATGGATT R: CTTCATCGGCATAGTAAAA | 53 | 208 | This study | |
| aadA1 | F: TTTGCTGGTTACGGTGAC R: GCTCCATTGCCCAGTCG | 58 | 497 | [36] | |
| Chloramphenicols | floR | F: GAACACGACGCCCGCTAT R: TTCCGCTTGGCCTATGAG | 54 | 601 | [35] |
| Cat1 | F: AGTGGAATAACGAACGAGC R: TCAGCAAGCGATATACGCAG | 57 | 470 | This study | |
| Quinolones | GyrA | F: GGTGACGTAATCGGTAAATA R: ACCATGGTGCAATGCCACCA | 53 | 810 | [35] |
| GyrB | F: GGACAAAGAAGGCTACAGCA R: CGTCGCGTTGTACTCAGATA | 53 | 879 | [35] | |
| ParC | F: CTGGGTAAATACCATCCGCAC R: CGGTTCATCTTCATTACGAA | 53 | 987 | [35] | |
| Polypeptides | VanC1 | F: GGTATCAAGGAAACCTC R: CTTCCGCCATCATAGCT | 55 | 822 | [38] |
| EmgrB | F: CCGCTGAGTAATAATCCTAT R: TACAACCAAAGACGCAAT | 48 | 492 | [39] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Shan, L.; Zhang, C.; Lei, Z.; Shang, Y. Isolation and Antibiotic Resistant Research of Tetragenococcus halophilus from Xuanwei Ham, A China High-Salt-Fermented Meat Products. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030151
Li Y, Shan L, Zhang C, Lei Z, Shang Y. Isolation and Antibiotic Resistant Research of Tetragenococcus halophilus from Xuanwei Ham, A China High-Salt-Fermented Meat Products. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(3):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030151
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yinjiao, Luying Shan, Chen Zhang, Zhan Lei, and Ying Shang. 2019. "Isolation and Antibiotic Resistant Research of Tetragenococcus halophilus from Xuanwei Ham, A China High-Salt-Fermented Meat Products" Antibiotics 8, no. 3: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030151
APA StyleLi, Y., Shan, L., Zhang, C., Lei, Z., & Shang, Y. (2019). Isolation and Antibiotic Resistant Research of Tetragenococcus halophilus from Xuanwei Ham, A China High-Salt-Fermented Meat Products. Antibiotics, 8(3), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030151





