Peri-Implant Diseases: Diagnosis, Clinical, Histological, Microbiological Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Criteria for Implant Success
3. Peri-Implant Health and Diseases: Case Definitions
4. Epidemiology of Peri-Implant Diseases
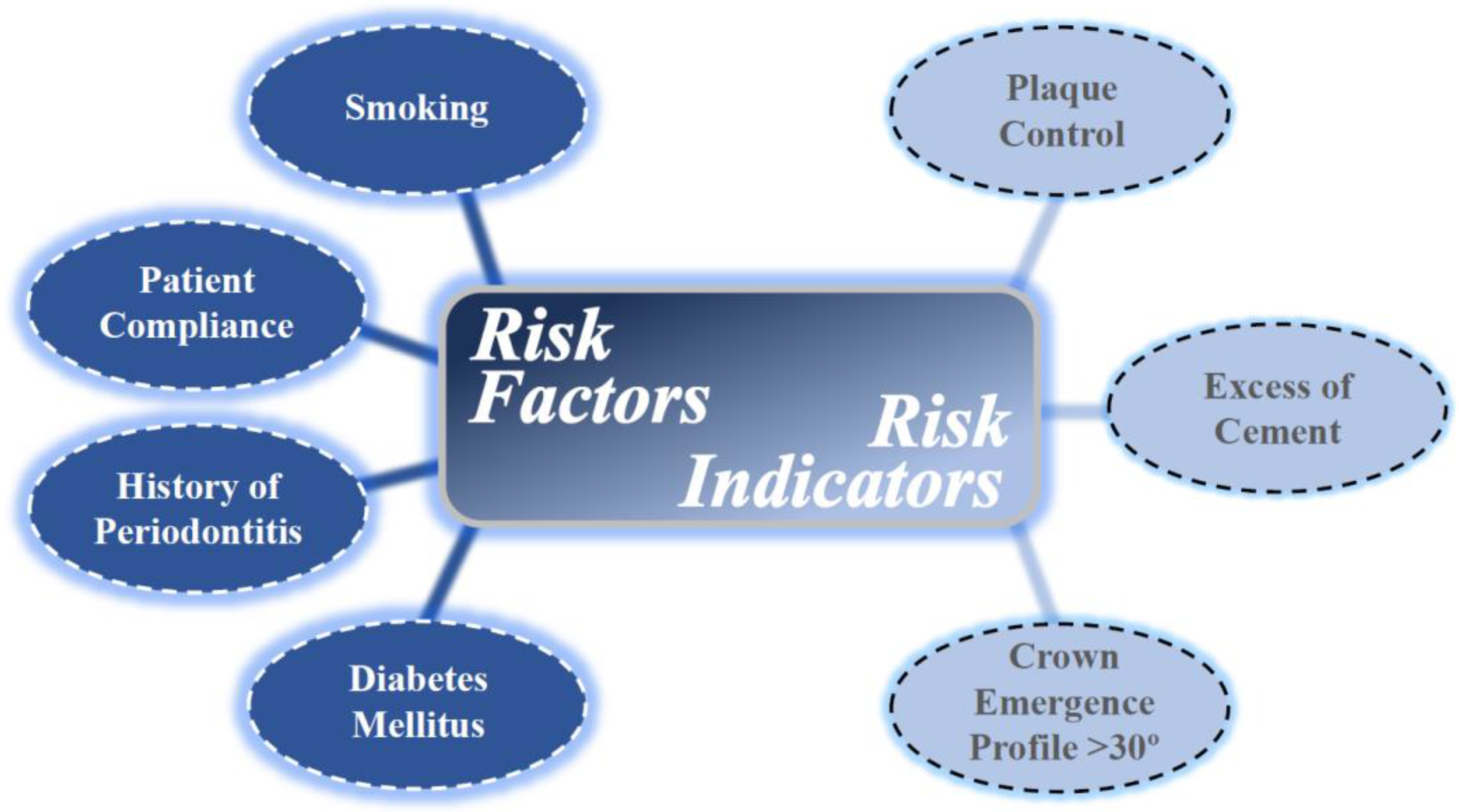
5. Risk Factors and Risk Indicators for Peri-Implant Diseases
6. Implant Prognosis
7. Clinical and Radiographic Analysis of Peri-Implantitis
8. Histopathology and Microbiology of Peri-Implantitis
9. Biomarkers of Peri-Implantitis
10. Treatment of Peri-Implant Diseases
10.1. Mechanical Decontamination of Implant Surface
10.2. Laser Implant Treatment and Combination Therapy
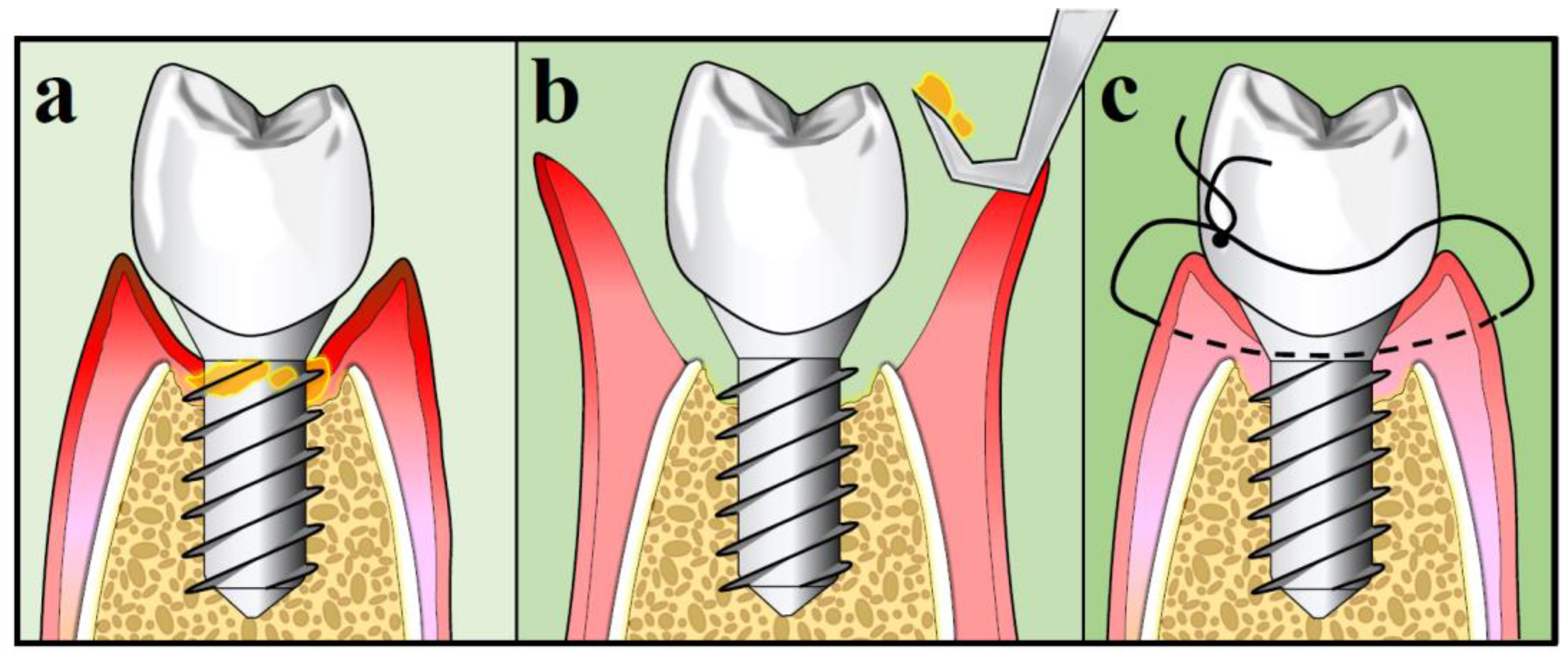
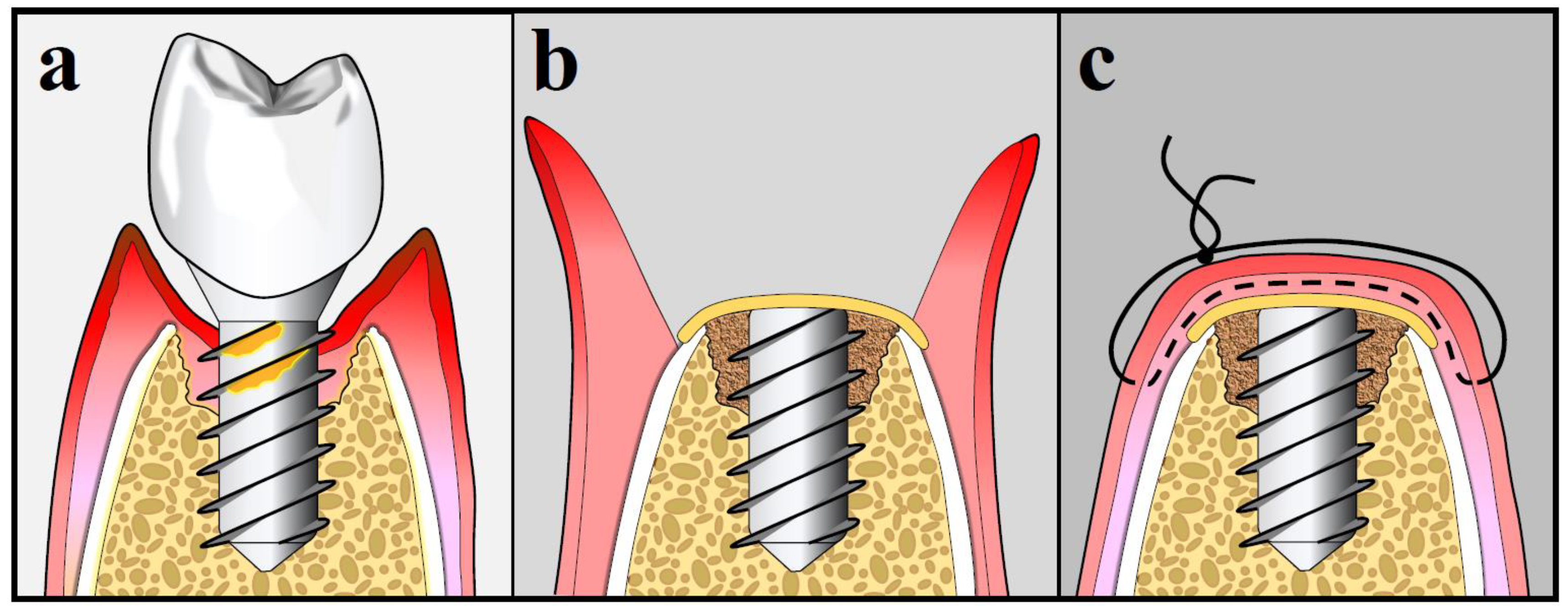
10.3. Surgical Treatment Strategies for Peri-Implantitis
10.4. Success Rate of Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment
11. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Bernabé, E.; Dahiya, M.; Bhandari, B.; Murray, C.J.L.; Marcenes, W. Global burden of severe tooth loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93 (Suppl. 7), 20S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrecht, J.T.; Cardone, E.; Kühl, S. Status report on dental implantology in Switzerland in 2006. A cross-sectional survey. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 3, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sekerci, E.; Lambrecht, J.T.; Mukaddam, K.; Kühl, S. Status report on dental implantology in Switzerland. An updated cross-sectional survey. Swiss Dent. J. 2020, 130, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elani, H.W.; Starr, J.R.; Da Silva, J.D.; Gallucci, G.O. Trends in dental implant use in the U.S., 1999–2016, and projections to 2026. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraschini, V.; Poubel, L.A.; Ferreira, V.F.; Barboza Edos, S. Evaluation of survival and success rates of dental implants reported in longitudinal studies with a follow-up period of at least 10 years: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.W. Titanium alloys for dental implants: A review. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Iannello, G.; Santonocito, D.; Risitano, G.; Cicciù, M. Sandblasted and acid etched titanium dental implant surfaces systematic review and confocal microscopy evaluation. Materials 2019, 12, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, D.; Weber, H.P.; Lang, N.P. Tissue integration of non-submerged implants. 1-year results of a prospective study with 100 ITI hollow-cylinder and hollow-screw implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1990, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misch, C.E.; Perel, M.L.; Wang, H.-L.; Sammartino, G.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Trisi, P.; Steigmann, M.; Rebaudi, A.; Palti, A.; Pikos, M.A.; et al. Implant success, survival, and failure: The International Congress of Oral Implantologists (ICOI) Pisa Consensus Conference. Implant. Dent. 2008, 17, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Chen, C.J.; Singh, M.; Weber, H.P.; Gallucci, G.O. Success criteria in implant dentistry: A systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, M.G.; Lindhe, J. Peri-implant health. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S249–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renvert, S.; Persson, G.R.; Pirih, F.Q.; Camargo, P.M. Peri-implant health, peri-implant mucositis, and peri-implantitis: Case definitions and diagnostic considerations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S304–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-implant mucositis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S257–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.-L. Peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S267–S290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Tarnow, D. The etiology of hard- and soft-tissue deficiencies at dental implants: A narrative review. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S291–S303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. 16), S158–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Zhu, L.; Weltman, R. Prevalences of peri-implantitis and peri-implant mucositis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2017, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, M.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Monje, A.; Randovanovic, S.; Wang, H.-L.; Cochran, D.; Sculean, A.; Canullo, L. How frequent does peri-implantitis occur? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, H.; Grischke, J.; Tiede, C.; Eberhard, J.; Schweitzer, A.; Toikkanen, S.E.; Glöckner, S.; Krause, G.; Stiesch, M. Epidemiology and risk factors of peri-implantitis: A systematic review. J. Periodontal. Res. 2018, 53, 657–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgarea, R.; Sculean, A.; Shibli, J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Prevalence of peri-implant diseases—A critical review on the current evidence. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33 (Suppl. 1), e063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, J.D. Risk revisited. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1998, 26, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgolastra, F.; Petrucci, A.; Severino, M.; Gatto, R.; Monaco, A. Smoking and the risk of peri-implantitis. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, e62–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.; Haimböck, W.; Mailath, G.; Watzek, G. The relationship of smoking on peri-implant tissue: A retrospective study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 76, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.R.; Rajan, M. Effects of smoking on the outcome of implant treatment: A literature review. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2007, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, J.; Callaway, A.; Kwon, Y.D.; d’Hoedt, B.; Al-Nawas, B. Comparison of five parameters as risk factors for peri-mucositis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Gürlek, Ö.; Gümüş, P.; Buduneli, N. Smokers have a higher risk of inflammatory peri-implant disease than non-smokers. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Joo, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y. Prevalence and risk factors of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis after at least 7 years of loading. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2019, 49, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, P.L.; Aguiar, T.; Fernandes Pinheiro, M.P.; Machado, A.; da Rosa Pinheiro, A. Smoking as a risk factor for the development of Periimplant Diseases. Implant. Dent. 2019, 28, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, D.M.; Weinstein, B.F.; Bordin, S.; Leroux, B.G.; Flemming, T.F. Prevalence and predictive factors for peri-implant disease and implant failure: A cross-sectional analysis. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Catena, A.; Borgnakke, W.S. Association between diabetes mellitus/hyperglycaemia and peri-implant diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papi, P.; Letizia, C.; Pilloni, A.; Petramala, L.; Saracino, V.; Rosella, D.; Pompa, G. Peri-implant diseases and metabolic syndrome components: A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.G.F.P.; Bonfante, E.A.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; de Souza, S.L.S.; Riella, L.; Torroni, A.; Benalcazar Jalkh, E.B.; Witek, L.; Lopez, C.D.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; et al. Obesity/metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus on peri-implantitis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renvert, S.; Aghazadeh, A.; Hallström, H.; Persson, G.R. Factors related to peri-implantitis—A retrospective study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacchi, C.; Berton, F.; Perinetti, G.; Frassetto, A.; Lombardi, T.; Khoury, A.; Andolsek, F.; Di Lenarda, R. Risk factors for peri-implantitis: Effect of history of periodontal disease and smoking habits. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2016, 7, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, T.J.; Drake, R.B.; Naylor, J.E. The plaque control record. J. Periodontol. 1972, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameno, T.; Wada, M.; Onodera, Y.; Fujita, D.; Sato, H.; Ikebe, K. Longitudinal study on risk indicators for peri-implantitis using survival-time analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katafuchi, M.; Weinstein, B.F.; Leroux, B.G.; Chen, Y.W.; Daubert, D.M. Restoration contour is a risk indicator for peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional radiographic analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.G., Jr. The positive relationship between excess cement and peri-implant disease: A prospective clinical endoscopic study. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Vindasiute, E.; Linkeviciene, L.; Apse, P. Does residual cement around implant-supported restorations cause peri-implant disease? A retrospective case analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renvert, S.; Quirynen, M. Risk indicators for peri-implantitis. A narrative review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26 (Suppl. 11), 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubli, N.; Walter, C.; Schmidt, J.C.; Weiger, R.; Zitzmann, N.U. Excess cement and the risk of peri-implant disease—A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatta, A.; Bissada, N.F.; Ricchetti, P.; Paes, A.; Demko, C. Impact of implant and site characteristics on the pattern of bone loss in peri-implantitis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenstein, G.; Cavallaro, J. The clinical significance of keratinized gingiva around dental implants. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2011, 32, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B.; Kheirieh, P.; Torabi, A.; Cappetta, E.G.; Najafi, A.; Singh, S.M. A new prognostication system for dental implants. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2018, 38, e17–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobre, M.A.; Salvado, F.; Nogueira, P.; Rocha, E.; Ilg, P.; Maló, P. A prognostic model for the outcome of nobel biocare dental implants with peri-implant disease after one year. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Becker, K.; Schwarz, F. Clinical characteristics of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, S.; Idrees, M.; Alissa, R.; Kujan, O. Ailing and failing oral implants: Initial therapy and surgical management. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2013, 4, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, G.; Sato, H.; Holmes, P.; Turri, A. Intra-surgical vs. radiographic bone level assessments in measuring peri-implant bone loss. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natto, Z.S.; Almeganni, N.; Alnekeeb, E.; Bukhari, Z.; Jan, R.; Iacono, V.J. Peri-implantitis and peri-implant mucositis case definitions in dental research: A systematic assessment. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 45, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransson, C.; Tomasi, C.; Sundén, P.S.; Gröndahl, K.; Wennström, J.L.; Leyland, A.H.; Berglundh, T. Severity and pattern of peri-implantitis-associated bone loss. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papantonopoulos, G.; Gogos, C.; Housos, E.; Bountis, T.; Loos, B.G. Peri-implantitis: A complex condition with non-linear characteristics. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derks, J.; Schaller, D.; Håkansson, J.; Wennström, J.L.; Tomasi, C.; Berglundh, T. Peri-implantitis—Onset and pattern of progression. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhe, J.; Berglundh, T.; Ericsson, I.; Liljenberg, B.; Marinello, C. Experimental breakdown of peri-implant and periodontal tissues. A study in the beagle dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1992, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, S.; Holmstrup, P.; Stoltze, K.; Hjørting-Hansen, E.; Kornman, K.S. Ligature-induced marginal inflammation around osseointegrated implants and ankylosed teeth. Clinical and radiographic observations in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1993, 4, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinello, C.P.; Berglundh, T.; Ericsson, I.; Klinge, B.; Glantz, P.O.; Lindhe, J. Resolution of ligature-induced peri-implantitis lesions in the dog. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcuac, O.; Abrahamsson, I.; Albouy, J.P.; Linder, E.; Larsson, L.; Berglundh, T. Experimental periodontitis and peri-implantitis in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Gislason, O.; Lekholm, U.; Sennerby, L.; Lindhe, J. Histopathological observations of human periimplantitis lesions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2004, 31, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcuac, O.; Berglundh, T. Composition of human peri-implantitis and periodontitis lesions. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, T.G., Jr.; Valderrama, P.; Burbano, M.; Blansett, J.; Levine, R.; Kessler, H.; Rodrigues, D.C. Foreign bodies associated with peri-implantitis human biopsies. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J.; Ericsson, I.; Marinello, C.P.; Liljenberg, B.; Thomsen, P. The soft tissue barrier at implants and teeth. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1991, 2, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonhardt, Å.; Renvert, S.; Dahlén, G. Microbial findings at failing implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1990, 10, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, M.; López-Cerero, L.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Chereguini, C.F.; Ballesta, S.; Ríos, V.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Bullon, P. Assessment of periodontal and opportunistic flora in patients with peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, G.R.; Renvert, S. Cluster of bacteria associated with peri-implantitis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Becker, K.; Rahn, S.; Hegewald, A.; Pfeffer, K.; Henrich, B. Real-time PCR analysis of fungal organisms and bacterial species at peri-implantitis sites. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2015, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankovic, S.; Aleksic, Z.; Dimitrijevic, B.; Lekovic, V.; Camargo, P.; Kenney, B. Prevalence of human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in subgingival plaque at peri-implantitis, mucositis and healthy sites. A pilot study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, S.P.; Williams, R.; Offenbacher, S.; Morelli, T. Gingival crevicular fluid as a source of biomarkers for periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000 2016, 70, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassy, H.; Parachuru, P.; Wolff, L. Peri-implantitis diagnosis and prognosis using biomarkers in peri-implant crevicular fluid: A narrative review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Lee, H.M.; Wolff, M.S.; Golub, L.M.; Sorsa, T.; Kuula, H. Characteristics of collagenase-2 from gingival crevicular fluid and peri-implant sulcular fluid in periodontitis and peri-implantitis patients: Pilot study. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2008, 66, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramseier, C.A.; Eick, S.; Bronnimann, C.; Buser, D.; Bragger, U.; Salvi, G.E. Host-derived biomarkers at teeth and implants in partially edentulous patients. A 10-year retrospective study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakic, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Canullo, L. The microbiologic profile associated with peri-implantitis in humans: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Mi, W.; Wu, T.; Gu, Q.; Huang, H. MicroRNA sequence analysis identifies microRNAs associated with peri-implantitis in dogs. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Gu, Q.; Chen, X.; Mi, W.; Wu, T.; Huang, H. MiR-27a targets DKK2 and SFRP1 to promote reosseointegration in the regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asa’ad, F.; Garaicoa-Pazmiño, C.; Dahlin, C.; Larsson, L. Expression of MicroRNAs in periodontal and peri-implant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menini, M.; Pesce, P.; Baldi, D.; Coronel Vargas, G.; Pera, P.; Izzotti, A. Prediction of Titanium implant success by analysis of microRNA expression in peri-implant tissue. A 5-year follow-up study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Padial-Molina, M.; López-Martínez, J.; O’Valle, F.; Galindo-Moreno, P. Microbial profiles and detection techniques in peri-implant disease: A systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figuero, E.; Graziani, F.; Sanz, I.; Herrera Sanz, M. Management of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 66, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.G., Jr.; Valderrama, P.; Rodrigues, D.B. The case for routine maintenance of dental implants. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Samuelsson, E.; Lindahl, C.; Persson, G.R. Mechanical non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A double-blind randomized longitudinal clinical study. I: Clinical results. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, K.; Wismeijer, D. Decontamination of titanium implant surface and re-osseointegration to treat peri-implantitis: A literature review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Tastepe, C.S.; van Waas, R.; Liu, Y.; Wismeijer, D. Air powder abrasive treatment as an implant surface cleaning method: A literature review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Sirinirund, B.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Wang, H.-L. Effects of mechanical instrumentation with commercially available instruments used in supportive peri-implant therapy: An in vitro study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubasiewicz-Ross, P.; Fleischer, M.; Pitułaj, A.; Hadzik, J.; Nawrot-Hadzik, I.; Bortkiewicz, O.; Dominiak, M.; Jurczyszyn, K. Evaluation of the three methods of bacterial decontamination on implants with three different surfaces. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.E.; Auschill, T.M.; Heumann, C.; Frankenberger, R.; Eick, S.; Sculean, A.; Arweiler, N.B. Influence of different instrumentation modalities on the surface characteristics and biofilm formation on dental implant neck, in vitro. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.C.; Moriarty, J.D.; Kusy, R.P. The effects of scaling a titanium implant surface with metal and plastic instruments: An in vitro study. J. Periodontol. 1990, 61, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, C.; Lusuardi, D.; Battarra, F.; Sassatelli, P.; Spinato, S.; Zaffe, D. The maintenance of inserted titanium implants: In-vitro evaluation of exposed surfaces cleaned with three different instruments. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaglia, L.; di Lauro, A.E.; Morgese, F.; Squillace, A. Profilometric and standard error of the mean analysis of rough implant surfaces treated with different instrumentations. Implant. Dent. 2006, 15, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Becker, K.; Renvert, S. Efficacy of air polishing for the non-surgical treatment of peri-implant diseases: A systematic review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, D.; Nickles, K.; Dannewitz, B.; Ratka, C.; Eickholz, P.; Petsos, H. In vitro efficacy of three different implant surface decontamination methods in three different defect configurations. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhe, J.; Meyle, J. Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35 (Suppl. 8), 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, F.; Schmucker, A.; Becker, J. Efficacy of alternative or adjunctive measures to conventional treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2015, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romanos, G.E.; Nentwig, G.H. Regenerative therapy of deep peri-implant infrabony defects after CO2 laser implant surface decontamination. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2008, 28, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, A.; Tanabe, T. Treatment of peri-implantitis around TiUnite-surface implants using Er:YAG laser microexplosions. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamel, M.S.; Khosa, A.; Tawse-Smith, A.; Leichter, J. The use of laser therapy for dental implant surface decontamination: A narrative review of in vitro studies. Lasers Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Lindahl, C.; Roos Jansåker, A.M.; Persson, G.R. Treatment of peri-implantitis using Er:YAG laser or an air-abrasive device: A randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettraux, G.R.; Sculean, A.; Bürgin, W.B.; Salvi, G.E. Two-year clinical outcomes following non-surgical mechanical therapy of peri-implantitis with adjunctive diode laser application. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Roos-Jansåker, A.M.; Claffey, N. Non-surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A literature review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35 (Suppl. 8), 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukuru, M.; Zainvi, A.; Esplugues, E.O.; Flemmig, T.F. Non- surgical therapy for the management of peri-implantitis: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 6), 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcuac, O.; Derks, J.; Charalampakis, G.; Abrahamsson, I.; Wennström, J.; Berglundh, T. Adjunctive systemic and local antimicrobial therapy in the surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E.; Javed, F.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L. Peri-implant diseases: A review of treatment interventions. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 59, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibli, J.A.; Ferrari, D.S.; Siroma, R.S.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Faveri, M.; Feres, M. Microbiological and clinical effects of adjunctive systemic metronidazole and amoxicillin in the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: 1 year follow-up. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33 (Suppl. 1), e080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verdugo, F.; Laksmana, T.; Uribarri, A. Systemic antibiotics and the risk of superinfection in peri-implantitis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2016, 64, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, G.E.; Persson, G.R.; Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.; Frei, M.; Lang, N.P. Adjunctive local antibiotic therapy in the treatment of peri-implantitis II: Clinical and radiographic outcomes. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, A.; Feloutzis, A.; Brägger, U.; Lang, N.P. Treatment of peri-implantitis by local delivery of tetracycline. Clinical, microbiological and radiological results. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Lessem, J.; Dahlén, G.; Renvert, H.; Lindahl, C. Mechanical and repeated antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system in the treatment of peri-implantitis: A randomized clinical trial. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Kim, H.J.; Joo, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J. Simplified nonsurgical treatment of peri-implantitis using chlorhexidine and minocycline hydrochloride. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2018, 48, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsovilis, S.; Karoussis, I.K.; Trianti, M.; Fourmousis, I. Therapy of peri-implantitis: A systematic review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Coulthard, P.; Worthington, H.V. The efficacy of interventions to treat peri-implantitis: A Cochrane systematic review of randomised controlled clinical trials. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 1), 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- van Winkelhoff, A.J. Antibiotics in the treatment of peri-implantitis. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, S43–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Worthington, H.V. Treatment of peri-implantitis: What interventions are effective? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, S21–S41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Ahmed, A.; Mikami, T.; Ahmed, H.B.; Tenenbaum, H.C. Clinical efficacy of antibiotics in the treatment of peri-implantitis. Int. Dent. J. 2013, 63, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machtei, E.E. Treatment alternatives to negotiate peri-implantitis. Adv. Med. 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schär, D.; Ramseier, C.A.; Eick, S.; Arweiler, N.B.; Sculean, A.; Salvi, G.E. Anti-infective therapy of peri-implantitis with adjunctive local drug delivery or photodynamic therapy: Six-month outcomes of a prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Schär, D.; Wicki, B.; Eick, S.; Ramseier, C.A.; Arweiler, N.B.; Sculean, A.; Salvi, G.E. Anti-infective therapy of peri-implantitis with adjunctive local drug delivery or photodynamic therapy: 12-month outcomes of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambrone, L.; Wang, H.-L.; Romanos, G.E. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for the treatment of periodontitis and peri-implantitis: An American Academy of Periodontology best evidence review. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Sinjab, K.; Wang, H.-L. Current protocols for the treatment of peri-implantitis. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2019, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelis, S.E.; Gindri, I.M.; Valderrama, P.; Wilson, T.G., Jr.; Huang, J.; Rodrigues, D.C. Effects of decontamination solutions on the surface of titanium: Investigation of surface morphology, composition, and roughness. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-López del Amo, F.; Yu, S.H.; Wang, H.L. Non-surgical therapy for peri-implant diseases: A systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2016, 7, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I.; Maguire, R. Re-osseointegration on previously contaminated surfaces: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20 (Suppl. 4), 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, H.L.; Norton, M.; Korostoff, J.; Ko, K.I.; Fiorellini, J.P. Surgical alternatives for treating peri-implantitis. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2018, 38, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Layton, D.M.; Roccuzzo, A.; Heitz-Mayfield, L.J. Clinical outcomes of peri-implantitis treatment and supportive care: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 16), 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, F.; Keeve, P.L.; Ramanauskaite, A.; Schwarz, F.; Koo, K.T.; Sculean, A.; Romanos, G. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis—Consensus report of working group 4. Int. Dent. J. 2019, 69 (Suppl. 2), 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E.; Mombelli, A.; Faddy, M.; Lang, N.P. Anti-infective surgical therapy of peri-implantitis. A 12-month prospective clinical study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Máximo, M.B.; de Mendonça, A.C.; Renata Santos, V.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M.; Duarte, P.M. Short-term clinical and microbiological evaluations of peri-implant diseases before and after mechanical anti-infective therapies. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallström, H.; Persson, G.R.; Lindgren, S.; Renvert, S. Open flap debridement of peri-implantitis with or without adjunctive systemic antibiotics: A randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, E.; Ghisolfi, M.; Murgolo, N.; Chiapasco, M.; Lops, D.; Vogel, G. Therapy of peri-implantitis with resective surgery. A 3-year clinical trial on rough screw-shaped oral implants. Part I: Clinical outcome. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, G.; Turri, A. Outcome of surgical treatment of peri- implantitis: Results from a 2-year prospective clinical study in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Wennström, J.L.; Lindhe, J. Long-term outcome of surgical treatment of peri- implantitis. A 2–11-year retrospective study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcuac, O.; Derks, J.; Abrahamsson, I.; Wennström, J.L.; Petzold, M.; Berglundh, T. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: 3-year results from a randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chaar, E.; Almogahwi, M.; Abdalkader, K.; Alshehri, A.; Cruz, S.; Ricci, J. Decontamination of the infected implant surface: A scanning electron microscope study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulos, A.; Bertl, K.; Eren, S.; Gotfredsen, K. Mechanical and biological complications after implantoplasty-A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravidà, A.; Siqueira, R.; Saleh, I.; Saleh, M.H.A.; Giannobile, A.; Wang, H.-L. Lack of clinical benefit of implantoplasty to improve implant survival rate. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Gaudioso, L.; Lungo, M.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical therapy of single peri-implantitis intrabony defects, by means of deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Roos-Jansåker, A.M.; Persson, G.R. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis lesions with or without the use of a bone substitute-a randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Bonino, F.; Bonino, L.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical therapy of peri-implantitis lesions by means of bovine-derived xenograft: Comparative results of a prospective study on two different implant surfaces. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoury, F.; Buchmann, R. Surgical therapy of peri-implant disease: A 3-year follow-up study of cases treated with 3 different techniques of bone regeneration. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froum, S.J.; Froum, S.H.; Rosen, P.S. Successful management of peri-implantitis with a regenerative approach: A consecutive series of 51 treated implants with 3- to 7.5-year follow-up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2012, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, P.; Constantinides, C. Resolution of a peri-implantitis defect using sterile saline for implant surface detoxification: A case report with clinical re-entry. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2015, 5, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Pittoni, D.; Roccuzzo, A.; Charrier, L.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis intrabony lesions by means of deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen: 7-year-results. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, F.; Hamlet, S.; Ivanovski, S. Regenerative surgical therapy for peri-implantitis using deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen, enamel matrix derivative and Doxycycline-A prospective 3-year cohort study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Signorini, L.; Pistilli, R.; Patini, R.; Pistilli, V.; Pesce, P. A prospective case series on surgical treatment of circumferential and semi-circumferential defects due to peri-implantitis. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33 (Suppl. 1), e072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emanuel, N.; Machtei, E.E.; Reichart, M.; Shapira, L. D-PLEX500: A local biodegradable prolonged release doxycycline-formulated bone graft for the treatment for peri-implantitis. A randomized controlled clinical study. Quintessence Int. 2020, 51, 546–553. [Google Scholar]
- Lagervall, M.; Jansson, L.E. Treatment outcome in patients with peri-implantitis in a periodontal clinic: A retrospective study. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E.; Mombelli, A.; Loup, P.J.; Heitz, F.; Kruger, E.; Lang, N.P. Supportive peri-implant therapy following anti-infective surgical peri-implantitis treatment: 5-year survival and success. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Peri-Implant Health | Peri-Implant Mucositis | Peri-Implantitis (with Records) | Peri-Implantitis (No Records) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual signs of inflammation | - | + | + | + |
| BOP with/without suppuration | - | + | + | + |
| Increased PD vs. previous visit | - | - | + | ≥6 mm |
| Increased RBL from initial remodeling | - | - | + initial bone remodeling should not be ≥2 mm | ≥3 mm apical to the most coronal part of the intraosseous implant portion |
| Local Antibiotics | Systemic Antibiotics | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-surgical debridement | Inconclusive results | Inconclusive results |
| Open Flap Debridement | No evidence | No benefit |
| Apically-Positioned Flap | No evidence | No benefit |
| Guided Bone Regeneration | Encouraging short-term results | Recommended |
| Method of Decontamination | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Curettes | • Good debris removal | • Significant implant surface alteration |
| Titanium Curettes | • Good debris removal | • Minimal implant surface alteration |
| Plastic Curettes | • No implant surface alteration | • Ineffective debris removal • Fragile |
| Ultrasonic with Dedicated Tip | • Excellent debris removal | • Minimal implant surface alteration |
| Ultrasonic without Dedicated Tip | • Total debris removal | • Significant implant surface alteration |
| Titanium Brushes | • Excellent debris removal | • Significant implant surface alteration • Fragile |
| Air-abrasive Devices | • Excellent debris removal • Minimal implant surface alteration | • Soft tissue damage with inappropriate use |
| Lasers | • Excellent bacterial decontamination | • Dose-dependent efficacy |
| Chlorhexidine | • None | • No adjunctive effects |
| Chemical Agents (H2O2, H3PO4, EDTA, etc.) | • Controversial | • Morphologic agents and corrosion with pH < 3 |
| Systemic Antibiotics | • Limited evidence | |
| Local Antibiotics | • Limited evidence | |
| Photodynamic antimicrobial | • Limited evidence | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kormas, I.; Pedercini, C.; Pedercini, A.; Raptopoulos, M.; Alassy, H.; Wolff, L.F. Peri-Implant Diseases: Diagnosis, Clinical, Histological, Microbiological Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110835
Kormas I, Pedercini C, Pedercini A, Raptopoulos M, Alassy H, Wolff LF. Peri-Implant Diseases: Diagnosis, Clinical, Histological, Microbiological Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. A Narrative Review. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(11):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110835
Chicago/Turabian StyleKormas, Ioannis, Chantal Pedercini, Alessandro Pedercini, Michail Raptopoulos, Hatem Alassy, and Larry F. Wolff. 2020. "Peri-Implant Diseases: Diagnosis, Clinical, Histological, Microbiological Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. A Narrative Review" Antibiotics 9, no. 11: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110835
APA StyleKormas, I., Pedercini, C., Pedercini, A., Raptopoulos, M., Alassy, H., & Wolff, L. F. (2020). Peri-Implant Diseases: Diagnosis, Clinical, Histological, Microbiological Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. A Narrative Review. Antibiotics, 9(11), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110835






