Recycling Old Antibiotics with Ionic Liquids
Abstract
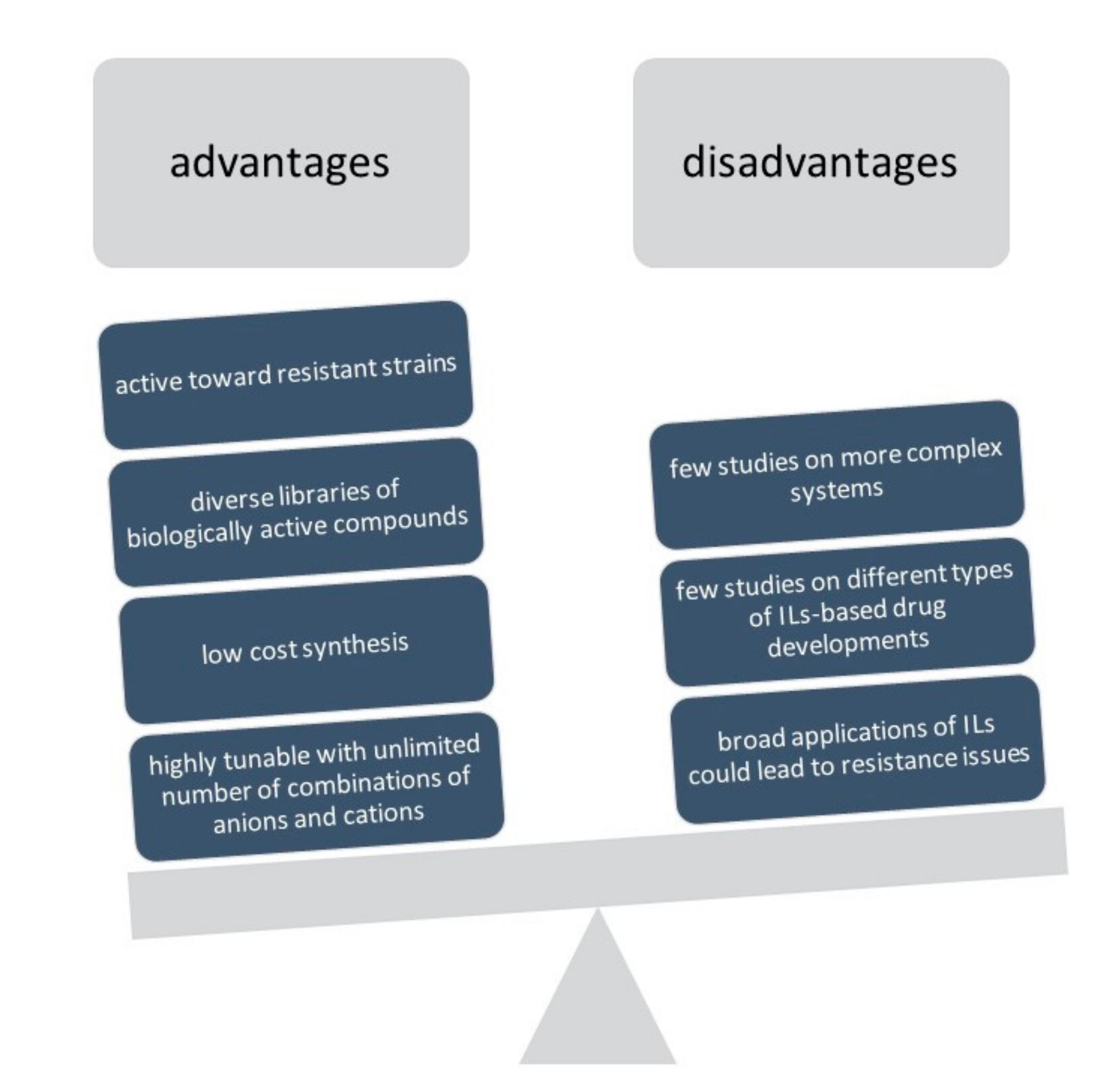
:1. Introduction
2. Ionic Liquids and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
2.1. Ionic Liquids
2.2. Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Applications of Ionic Liquids
2.3. Structure–Activity Relationships of Bioactive Ionic Liquids
2.4. ILs as Antimicrobial Agents
ILs Active Against Resistant Microorganisms
2.5. Poly(ionic Liquids)
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleming, A. On the Antibacterial Action of Cultures of A Penicillium, With Special Reference to Their Use in the Isolation of B. Influenzae. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1929, 10, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryskier, A. Antimicrobial Agents: Antibacterials and Antifungals; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cloutier, M.J. Antibiotics—Mechanisms of Action and the Acquisition of Resistance—When Magic Bullets Lose Their Magic. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 1995, 59, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, G.A.; Raoult, D.; Dubourg, G. Antibiotic discovery: History, methods and perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sener, B.; Koseoglu, O.; Gur, D.; Bryskier, A. Mechanisms of macrolide resistance in clinical pneumococcal isolates in a university hospital, Ankara, Turkey. J. Chemother. 2005, 17, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C. Molecular mechanisms that confer antibacterial drug resistance. Nature 2000, 406, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C. Where will new antibiotics come from? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonovics, J.; Abbate, J.L.; Baker, C.H.; Daley, D.; Hood, M.E.; Jenkins, C.E.; Johnson, L.J.; Murray, J.J.; Panjeti, V.; Rudolf, V.H.W.; et al. Evolution by any other name: Antibiotic resistance and avoidance of the E-word. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajdacs, M. The Continuing Threat of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nathan, C. Resisting antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.-J.; Legido-Quigley, H.; Hsu, L.Y. Antimicrobial Resistance in One Health. In Global Health Security; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 209–229. [Google Scholar]
- Baquero, F.; Martinez, J.-L.; Canton, R. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos de Opitz, C.L.; Sass, P. Tackling antimicrobial resistance by exploring new mechanisms of antibiotic action. Future Med. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.; Ashley, E.A.; Celhay, O.J.; Douangnouvong, A.; Hamers, R.L.; Ling, C.L.; Lubell, Y.; Miliya, T.; Roberts, T.; Soputhy, C.; et al. ACORN (A Clinically-Oriented Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network): A pilot protocol for case based antimicrobial resistance surveillance. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa Varona, O.; Chaintarli, K.; Muller-Pebody, B.; Anjum, M.F.; Eckmanns, T.; Norström, M.; Boone, I.; Tenhagen, B.-A. Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance and Drug Usage in the Human and Livestock Sector and Foodborne Antimicrobial Resistance in Six European Countries; Robert Koch Institute: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Roope, L.S.J.; Smith, R.D.; Pouwels, K.B.; Buchanan, J.; Abel, L.; Eibich, P.; Butler, C.C.; Tan, P.S.; Walker, A.S.; Robotham, J.V.; et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance: What economics can contribute. Science 2019, 364, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Paul, M.; Huttner, A. New and improved? A review of novel antibiotics for Gram-positive bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Kelley, S.P.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Chemistry: Develop ionic liquid drugs. Nature 2015, 528, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Comeau, A.M.; Tetart, F.; Trojet, S.N.; Prere, M.F.; Krisch, H.M. Phage-Antibiotic Synergy (PAS): β-Lactam and Quinolone Antibiotics Stimulate Virulent Phage Growth. PLoS ONE 2007, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, W.N.; Concepcion-Acevedo, J.; Park, T.; Andleeb, S.; Bull, J.J.; Levin, B.R. Synergy and Order Effects of Antibiotics and Phages in Killing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jo, Y.; Hwang, Y.J.; Hong, H.W.; Hong, S.S.; Park, K.; Myung, H. Phage-Antibiotic Synergy via Delayed Lysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messali, M.; Aouad, M.R.; El-Sayed, W.S.; Ali, A.A.S.; Ben Hadda, T.; Hammouti, B. New Eco-Friendly 1-Alkyl-3-(4-phenoxybutyl) Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids Derivatives: A Green Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial Activity and POM Analyses. Molecules 2014, 19, 11741–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoimenovski, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Bica, K.; Rogers, R.D. Crystalline vs. Ionic Liquid Salt Forms of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: A Position Paper. Pharmaceut. Res. 2010, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Ionic liquids: A brief history. Biophys. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angell, C.A.; Ansari, Y.; Zhao, Z.F. Ionic Liquids: Past, present and future. Faraday Discuss. 2012, 154, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids—From molten salts to neoteric. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.R.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Teixeira, C.; Prudencio, C.; Gomes, P.; Ferraz, R. Ionic Liquids for Topical Delivery in Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 7520–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P.; Prudêncio, C. Chapter 16. Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids. In Ionic Liquid Devices; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 404–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z. Ionic Liquids as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Chemmedchem 2011, 6, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, W.L.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids then and now: From solvents to materials to active pharmaceutical ingredients. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 2007, 80, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological Activity of Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Pharmaceutics and Medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrucho, I.M.; Branco, L.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Ionic Liquids in Pharmaceutical Applications. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Bento, C.M.; Pena, A.C.; Figueiredo, L.M.; Prudencio, C.; Aguiar, L.; Silva, T.; Ferraz, R.; Gomes, M.S.; Teixeira, C.; et al. Cinnamic Acid Conjugates in the Rescuing and Repurposing of Classical Antimalarial Drugs. Molecules 2020, 25, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, S.; Santos, M.M.; Ferraz, R.; Prudencio, C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Branco, L.C. A Novel Approach for Bisphosphonates: Ionic Liquids and Organic Salts from Zoledronic Acid. Chemmedchem 2019, 14, 1767–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Cerqueira, M.J.; Prudencio, C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P.; Ferraz, R. Antiproliferative Organic Salts Derived from Betulinic Acid: Disclosure of an Ionic Liquid Selective Against Lung and Liver Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5682–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, R.; Silva, D.; Dias, A.R.; Dias, V.; Santos, M.M.; Pinheiro, L.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.C. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Ionic Liquids and Organic Salts Based on Penicillin G and Amoxicillin hydrolysate Derivatives against Resistant Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bystrzanowska, M.; Pena-Pereira, F.; Marcinkowski, L.; Tobiszewski, M. How green are ionic liquids?—A multicriteria decision analysis approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Fundamental importance of ionic interactions in the liquid phase: A review of recent studies of ionic liquids in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. J. Mol. Liquids 2018, 272, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, P.; Garcia-Verdugo, E.; Luis, S.V.; Pucheault, M.; Vaultier, M. (Bio) Catalytic Continuous Flow Processes in scCO(2) and/or ILs: Towards Sustainable (Bio) Catalytic Synthetic Platforms. Curr. Organ. Synth. 2011, 8, 810–823. [Google Scholar]
- Agatemor, C.; Ibsen, K.N.; Tanner, E.E.L.; Mitragotri, S. Ionic liquids for addressing unmet needs in healthcare. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2018, 3, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvim, H.G.O.; Bataglion, G.A.; Ramos, L.M.; de Oliveira, A.L.; de Oliveira, H.C.B.; Eberlin, M.N.; de Macedo, J.L.; da Silva, W.A.; Neto, B.A.D. Task-specific ionic liquid incorporating anionic heteropolyacid-catalyzed Hantzsch and Mannich multicomponent reactions. Ionic liquid effect probed by ESI-MS(/MS). Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 3306–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giernoth, R. Task-Specific Ionic Liquids. Angewandte Chemi. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2834–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.Y.; Mukherjee, A.; Muller, P.; Rogers, R.D.; Myerson, A.S. Exploring the role of ionic liquids to tune the polymorphic outcome of organic compounds. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freemantle, M. Designer solvents—Ionic liquids may boost clean technology development. Chem. Eng. News 1998, 76, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmiah, S.; Srinivasadesikan, V.; Tseng, M.-C.; Chu, Y.-H. On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2009, 14, 3780–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miskiewicz, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Szymczak, M.; Bartus, K.; Kowalczyk, P. The Use of Liquids Ionic Fluids as Pharmaceutically Active Substances Helpful in Combating Nosocomial Infections Induced by Klebsiella Pneumoniae New Delhi Strain, Acinetobacter Baumannii and Enterococcus Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hough, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Pernak, J.; Grisel, J.E.; Carliss, R.D.; Soutullo, M.D.; et al. The third evolution of ionic liquids: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. N. J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deetlefs, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Shara, M. Predicting physical properties of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; p. 776.
- Holbrey, J.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 1999, 1, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. Green solvents for the future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, E.B.; Culver, S.L.; Fox, P.A.; Goode, R.D.; Ntai, I.; Tickell, M.D.; Traylor, R.K.; Hoffman, N.W.; Davis, J.H. Sweet success: Ionic liquids derived from non-nutritive sweeteners. Chem. Commun. 2004, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, L.Y.; Pashirova, T.N.; Doktorovova, S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, S.B.; Souto, E.B. Cationic Surfactants: Self-Assembly, Structure-Activity Correlation and Their Biological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, A.R.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Ferraz, R.; Prudêncio, C. Anti-cancer potential of Ionic Liquids. ChemMedChem 2016, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, M.; Piszora, M.; Caicedo, N.; Jungnickel, C.; Stolte, S. Toxicity of ionic liquid cations and anions towards activated sewage sludge organisms from different sources—Consequences for biodegradation testing and wastewater treatment plant operation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Smiglak, M.; Griffin, S.T.; Hough, W.L.; Wilson, T.B.; Pernak, A.; Zabielska-Matejuk, J.; Fojutowski, A.; Kita, K.; Rogers, R.D. Long alkyl chain quaternary ammonium-based ionic liquids and potential applications. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder-Kubis, J.; Tomczuk, K. The effect of the cationic structures of chiral ionic liquids on their antimicrobial activities. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 4190–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, J.; Wisniewska, A.; Kulig-Adamiak, A.; Lewicka, L.; Cieniecka-Roslonkiewicz, A.; Kita, K.; Fojutowski, A.; Nawrot, J.; Materna, K.; Pernak, J. Long-Alkyl-Chain Quaternary Ammonium Lactate Based Ionic Liquids. Chemistry Eur. J. 2008, 14, 9305–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, O.F.; Castro, R.; Gutierrez, M.; Valenzuela, D.G.; Santos, L.; Ramirez, D.; Guzman, L. Novel Alkylimidazolium Ionic Liquids as an Antibacterial Alternative to Pathogens of the Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Molecules 2018, 23, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forero-Doria, O.; Araya-Maturana, R.; Barrientos-Retamal, A.; Morales-Quintana, L.; Guzman, L. N-alkylimidazolium Salts Functionalized with p-Coumaric and Cinnamic Acid: A Study of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effects. Molecules 2019, 24, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallakpour, S.; Dinari, M. Ionic liquids as green solvents: Progress and prospects. In Green Solvents II; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Sintra, T.E.; Neves, C.; Shimizu, K.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Goncalves, F.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Freire, M.G.; Santos, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The effect of the cation alkyl chain branching on mutual solubilities with water and toxicities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19952–19963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, W.; Becherini, S.; D’Andrea, F.; Lupetti, A.; Chiappe, C.; Guazzelli, L. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial activity of different types of ionic liquids. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demberelnyamba, D.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, S.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.J.; Yoo, I.D. Synthesis and antimicrobial properties of imidazolium and pyrrolidinonium salts. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.M.; Layland, N.J.; Page, M.I.; Martin, F.; Oferrall, R.M. Thiazolidine ring-opening in penicillin derivatives. 2. Enamine formation. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1991, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araujo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; da Ponte, M.N.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z. Development of novel ionic liquids based on ampicillin. Medchemcomm 2012, 3, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.R.; Hobden, J.A.; Warner, I.M. Recycling Antibiotics into GUMBOS: A New Combination Strategy to Combat Multi-Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Molecules 2015, 20, 6466–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.R.; Li, M.; El-Zahab, B.; Janes, M.E.; Hayes, D.; Warner, I.M. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of β-Lactam Antibiotic-Based Imidazolium- and Pyridinium-Type Ionic Liquids. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, K.; Yoshizawa, M.; Ohno, H. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids from 20 Natural Amino Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2398–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Araujo, J.M.M.; Alves, F.; Matos, C.; Ferraz, R.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; et al. Evaluation of solubility and partition properties of ampicillin-based ionic liquids. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2013, 456, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florindo, C.; Costa, A.; Matos, C.; Nunes, S.L.; Matias, A.N.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Novel organic salts based on fluoroquinolone drugs: Synthesis, bioavailability and toxicological profiles. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2014, 469, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Noronha, J.; Murtinheira, F.; Nogueira, F.; Machado, M.; Prudencio, M.; Parapini, S.; D’Alessandro, S.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, A.; et al. Primaquine-based ionic liquids as a novel class of antimalarial hits. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56134–56138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Pinheiro, M.; Gomes, A.; Teixeira, C.; Prudencio, C.; Reis, S.; Gomes, P. Effects of novel triple-stage antimalarial ionic liquids on lipid membrane models. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4190–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, B.; Teixeira, C.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Prudencio, M.; Gomes, P. Primacins, N-cinnamoyl-primaquine conjugates, with improved liver-stage antimalarial activity. Medchemcomm 2012, 3, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vale, N.; Moreira, R.; Gomes, P. Primaquine revisited six decades after its discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gilmore, B.F. The antimicrobial potential of ionic liquids: A source of chemical diversity for infection and biofilm control. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blesic, M.; Marques, M.H.; Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Lopes, A. Self-aggregation of ionic liquids: Micelle formation in aqueous solution. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Skrzypezak, A.; Lota, G.; Frackowiak, E. Synthesis and properties of trigeminal tricationic ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luczak, J.; Hupka, J.; Thoming, J.; Jungnickel, C. Self-organization of imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2008, 329, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, B.F. Antimicrobial Ionic Liquids; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.Y.; Ou, G.N.; Zhou, C.Y.; Wang, M.H.; Chen, S.Y. Antimicrobial Ionic Liquids with Fumarate Anion. J. Chem. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; El-Harbawi, M.; Noaman, Y.A.; Bustam, M.A.B.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Affandi, N.A.; Hefter, G.; Yin, C.Y. Synthesis and anti-microbial activity of hydroxylammonium ionic liquids. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walkiewicz, F.; Materna, K.; Kropacz, A.; Michalczyk, A.; Gwiazdowski, R.; Praczyk, T.; Pernak, J. Multifunctional long-alkyl-chain quaternary ammonium azolate based ionic liquids. N. J. Chem. 2010, 34, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.G.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Alviano, D.S.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Toxicity of ionic liquids toward microorganisms interesting to the food industry. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37157–37163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, F.; Lautard, C.; Garzino, F.; Giorgio, S.; Raimundo, J.M.; Bolla, J.M.; Camplo, M. Antibacterial activities of fluorescent nano assembled triphenylamine phosphonium ionic liquids. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3770–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Wathier, M.; Zegans, M.E.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; Kowalski, R.; Grinstaff, M.W. Diphosphonium Ionic Liquids as Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Agents. Cornea 2012, 31, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hough-Troutman, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Griffin, S.; Reichert, W.M.; Mirska, I.; Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Adamska, T.; Nawrot, J.; Stasiewicz, M.; Rogers, R.D.; et al. Ionic liquids with dual biological function: Sweet and anti-microbial, hydrophobic quaternary ammonium-based salts. N. J. Chem. 2009, 33, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, J.; Wiśniewska, A.; Kulig-Adamiak, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Praczyk, T.; Michalczyk, A.; Walkiewicz, F.; Materna, K.; Pernak, J. Mandelate and prolinate ionic liquids: Synthesis, characterization, catalytic and biological activity. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 1325–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nie, Y. Toxicity and antimicrobial activities of ionic liquids with halogen anion. J. Environ. Protect. 2011, 2, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, R.; Teixeira, V.; Rodrigues, D.; Fernandes, R.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.C. Antibacterial activity of Ionic Liquids based on ampicillin against resistant bacteria. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4301–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mester, P.; Jehle, A.K.; Leeb, C.; Kalb, R.; Grunert, T.; Rossmanith, P. FTIR metabolomic fingerprint reveals different modes of action exerted by active pharmaceutical ingredient based ionic liquids (API-ILs) on Salmonella typhimurium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32220–32227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K.; Bera, S.; Singh, M.; Mondal, D. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, and Biological Importance of Pyrimidinium Ionic Liquids. Chemistryselect 2019, 4, 6888–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Nizamov, I.S.; Salikhov, R.Z.; Sabirzyanova, L.R.; Vorobev, V.V.; Burganova, T.I.; Shaidoullina, M.M.; Batyeva, E.S.; Cherkasov, R.A.; Abdullin, T.I. Synthesis and characterization of pyridoxine, nicotine and nicotinamide salts of dithiophosphoric acids as antibacterial agents against resistant wound infection. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, A.N.; Ozturk, I.; Tuncel, A.; Ocakoglu, K.; Colak, S.G.; Hosgor-Limoncu, M.; Yurt, F. Synthesis of new water-soluble ionic liquids and their antibacterial profile against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Heliyon 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araque, P.; Herrera, A.; Montano, D.; Yepes, A.; Garcia, E.; Sepulveda, J.; Torijano, S.; Cardona, G.W. Antimicrobial activity and in silico study of methylimidazolium-furanchalcone hybrids and 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium salts. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64, 4547–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neves, Y.F.; Eloi, A.C.L.; de Freitas, H.M.M.; Soares, E.G.O.; Rivillo, D.; da Silva, V.D.; Schrekker, H.S.; Badel, J.L. Imidazolium salts as alternative compounds to control diseases caused by plant pathogenic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović-Šanta, S.; Kojic, V.; Atlagic, K.; Tot, A.; Vranes, M.; Gadzuric, S.; Karaman, M. Anticancer and antimicrobial properties of imidazolium based ionic liquids with salicylate anion. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2020, 85, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, R.; Tokuda, M.; Suzuki, T.; Minami, H. Preparation of Poly(ionic liquid) Hollow Particles with Switchable Permeability. Langmuir 2016, 32, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernandez-Garcia, M. Poly(ionic liquid)s as antimicrobial materials. Eur. Polymer J. 2018, 105, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Kong, L.L.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.P. Antibacterial activities of N-alkyl imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid) nanoparticles. Polymer Chem. 2019, 10, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Q.; Xu, Q.M.; Guo, J.N.; Qin, J.; Mao, H.L.; Wang, B.; Yan, F. Structure-Antibacterial Activity Relationships of Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Monomers, Poly(ionic liquids) and Poly(ionic liquid) Membranes: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.T.; Lobo, L.; Oliveira, I.S.; Gomes, J.; Teixeira, C.; Nogueira, F.; Marques, E.F.; Ferraz, R.; Gomes, P. Building on Surface-Active Ionic Liquids for the Rescuing of the Antimalarial Drug Chloroquine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.; Ferraz, R.; Prudencio, C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Costa-Rodrigues, J. Differential effects of antiepileptic drugs on human bone cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19691–19701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuvada, S.; Nangia, A. Polymorphism in an API ionic liquid: Ethambutol dibenzoate trimorphs. Crystengcomm 2012, 14, 7840–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Malhotra Sanjay, V. Ionic Liquids as Pharmaceutical Salts: A Historical Perspective. In Ionic Liquid Applications: Pharmaceuticals, Therapeutics, and Biotechnology; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D. Are Myths and Preconceptions Preventing Us from Applying Ionic Liquid Forms of Antiviral Medicines to the Current Health Crisis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ILs with Antimicrobial Activity | Microorganisms | Authors and Year of Publication | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cation | Anion | ||
| didecyldimethylammonium, benzalkonium | lactate | Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus mutans, Enterococcus faecium, Moraxella catarrhalis, Escherichia coli, Serratia marcescens, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis | Cybulski, 2008 [58] |
| didecyldimethylammonium, benzalkonium, cetylpyridinium, 3-hydroxy-1-octyloxymethylpyridinium | saccharinate, acesulfamate | Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecium, Escherichia coli, Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae | Hough-Troutman 2009 * [88] |
| didecyldimethylammonium, benzalkonium, domiphen | mandelate, prolinates | Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecium, Serratia marcescens, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonasaeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis | Cybulski, 2011 [89] |
| 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium, alkylpyridinium | chloride, bromide | Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis | Yu, 2011 [90] |
| cetylpyridinium, 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-hexadecyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium | ampicillinate | Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecium | Cole, 2011 [69] |
| 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-hydroxy-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium, choline, tetraethylammonium, cetylpyridinium, trihexyltetradecylphosphonium. | ampicillinate | Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecali, Staphylococcus epidermidis | Ferraz, 2014 * [91] |
| chlorhexidine | ampicillinate, carbenicillinate, cephalothinate, oxacillinate | Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus faecalis, Bacillus cereus Enterococcus faecium | Cole, 2015 * [68] |
| 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium, trimethylalkylammonium, tributylmethylammonium, trioctylmethylammonium, tributylmethylphosphonium, trioctylmethylphosphonium, 1-ethyl-3-methylpiperidinium, 1-ethyl-1-methylmorpholinium, 1-butyl-3-methylpyrrolidinium | nalidixate | Salmonella species | Mester, 2016 * [92] |
| 3-cinnamyl-1-alkyl-imidazolium | chloride | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii | Doria, 2018 [59] |
| N-arylalkyl pyrimidinium, N-aryloxyalkylpyrimidinium | bromide, tetrafluoroborate, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide | Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus pumilis, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Goel, 2019 [93] |
| pyridoxinium O,O-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohex-1-yl], pyridoxinium O,O-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohex-1-yl], pyridoxinium O,O-di(2-isopropyl-5-methylphenyl. pyridoxinium O,O-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo [2.2.1]-hept-2-yl], nicotinium O,O- 2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohex-1-yl], nicotinium O,O-di(2-isopropyl-5-methylphenyl), nicotinium O,O-di[endo)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl, nicotinium O,O-di[2,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]-hept-3-yl], nicotinium O,O-dibutyl, Nicotinamide | dithiophosphate, | Pseudomonas aeroginosa Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermis | Dang, 2019 * [94] |
| 3-(3-propylimidazole)-1,8-naphthalene monoimide-1-dodecylimidazolium, 3-(3-propylimidazole)-1,8-naphthalene monoimide-1-hexacylimidazolium | bromide, bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonamide | Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonasaeruginosa Enterococcus faecali | Duman, 2019 [95] |
| N-cinnamoylimidazolium | bromide | Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonasaeruginosa | Forero-Doria, 2019 [60] |
| 3-methyl-1-alkylimidazolium, 3-methy-1-alkyllimidazolium-furanchalcone hybrid | bromide, tetrafluoroborate, hydroxide | Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus agalactiae, Bacillus subtilis | Arque, 2020 [96] |
| 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1,10-bis(methylimidazolium-1-yl) decane, 1-hexadecyl-2,3,4,5-tetram | chloride, bromide, n-hexadecyl, methanesulfonate | Dickeya chrysanthemi; Escherichia coli; Erwinia psidii; Pectobacterium carotovorum, Pseudomonas syringae, Xanthomonas axonopodis | Neves, 2020 [97] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, [2-(4-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl]-3-methylimidazolium, 1-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3-me-thylimidazolium, imidazolium | salicylate | Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis. Enterococcus faecalis, Proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Jovanović-Šanta, 2020 * [98] |
| Tetraethylammonium, trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium, cetylpyridinium, 1--ethyl--3--methylimidazolium, 3--(2--hydroxyethyl)--1--methylimidazolium, choline, | penicillin hydrolysate, amoxicillin hydrolysate | Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus | Ferraz, 2020 * [36] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prudêncio, C.; Vieira, M.; Van der Auweraer, S.; Ferraz, R. Recycling Old Antibiotics with Ionic Liquids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090578
Prudêncio C, Vieira M, Van der Auweraer S, Ferraz R. Recycling Old Antibiotics with Ionic Liquids. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(9):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090578
Chicago/Turabian StylePrudêncio, Cristina, Mónica Vieira, Seppe Van der Auweraer, and Ricardo Ferraz. 2020. "Recycling Old Antibiotics with Ionic Liquids" Antibiotics 9, no. 9: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090578
APA StylePrudêncio, C., Vieira, M., Van der Auweraer, S., & Ferraz, R. (2020). Recycling Old Antibiotics with Ionic Liquids. Antibiotics, 9(9), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090578






