Flexible P(VDF-TrFE) Shared Bottom Electrode Sensor Array Assisted with Machine Learning for Motion Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
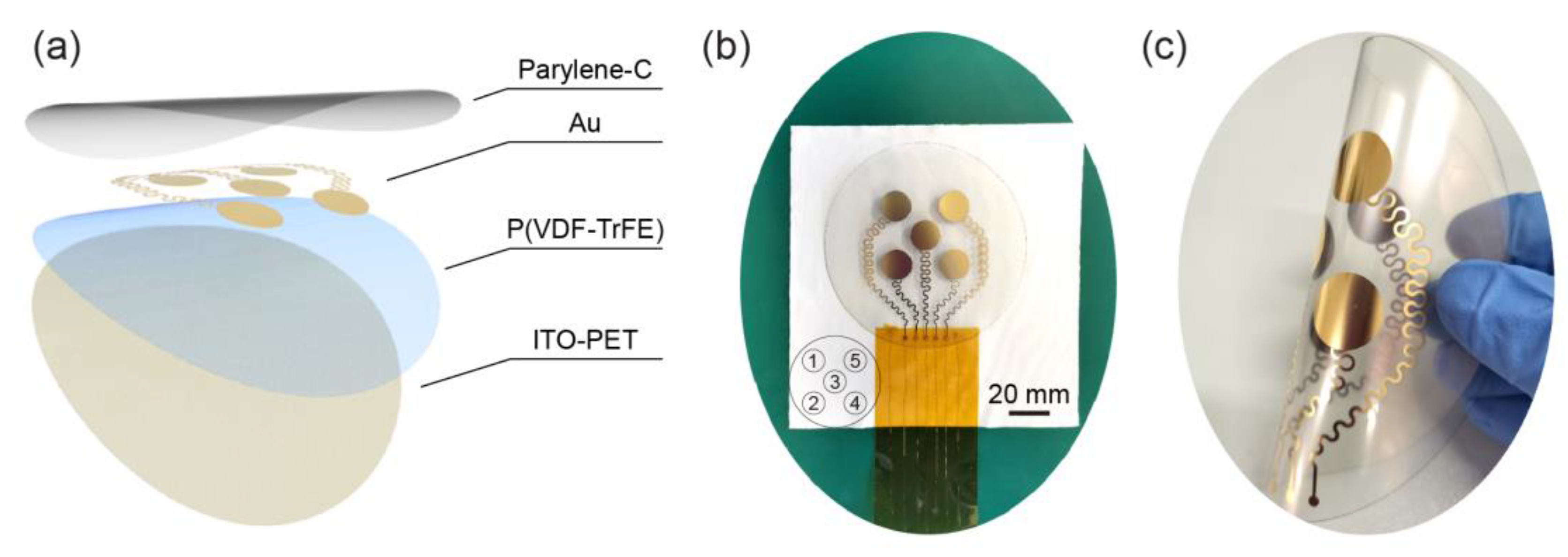
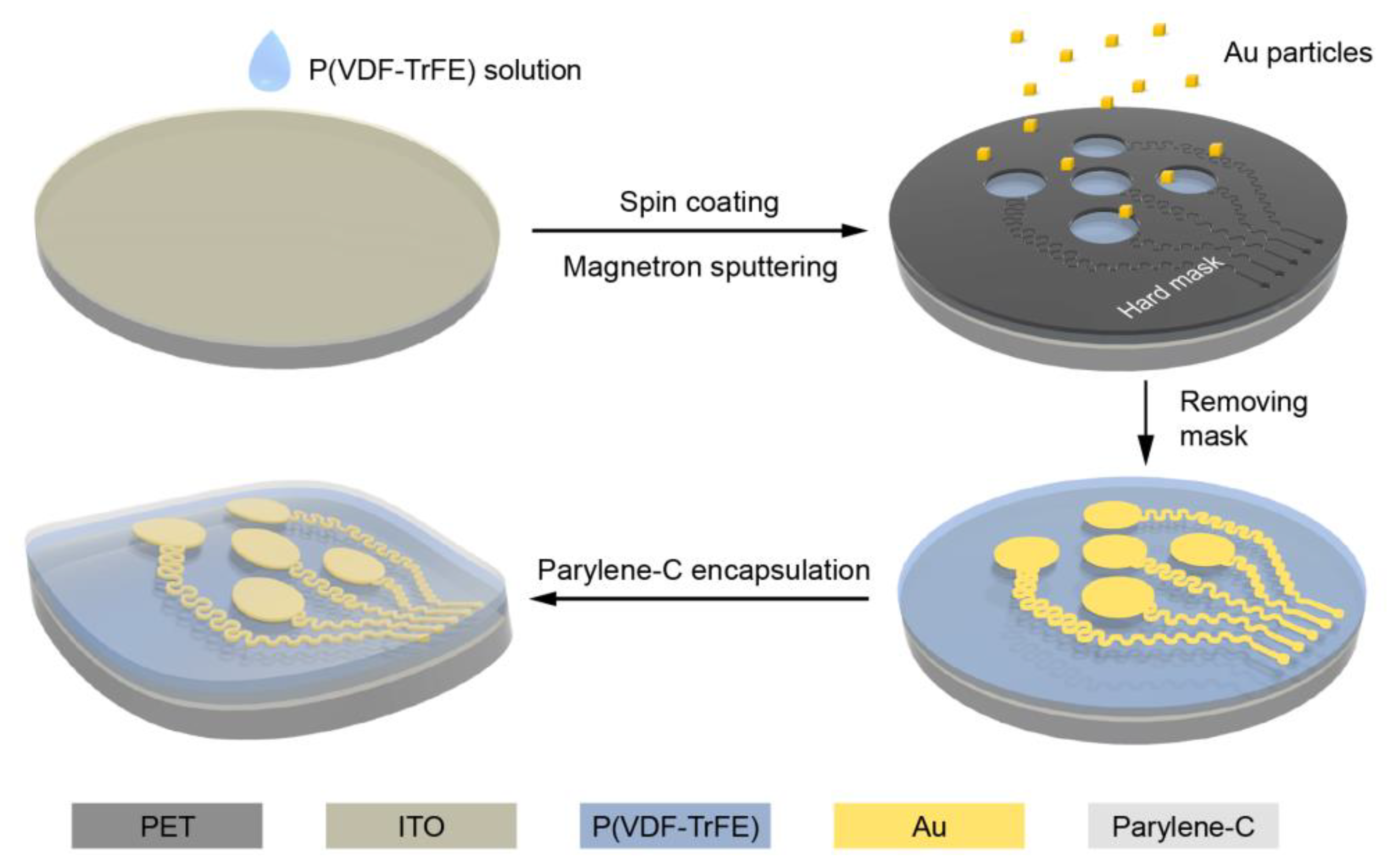
2. Fabrication of the Piezoelectric Sensor Array
3. Results and Discussions
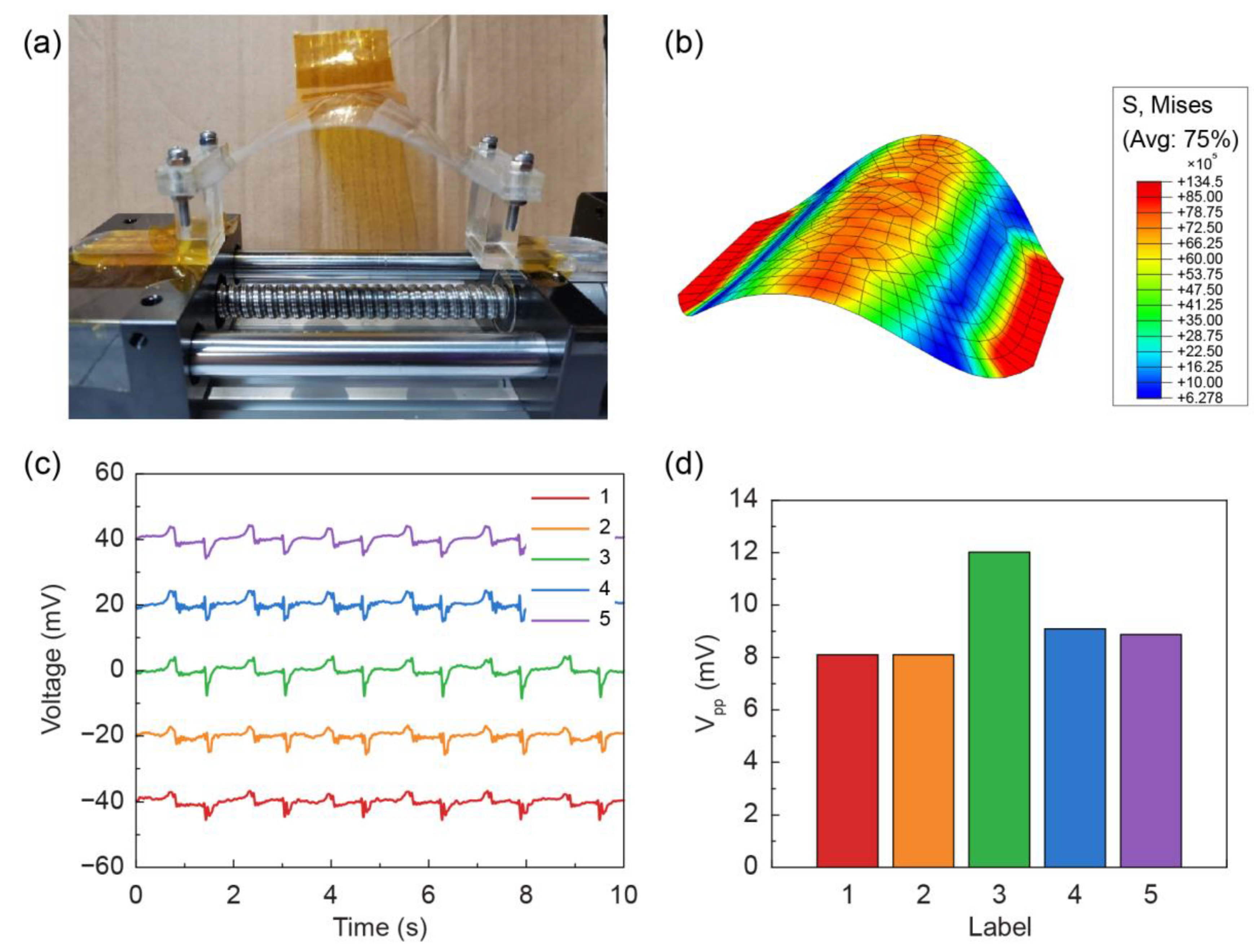
3.1. Characterization of the Piezoelectric Sensor Array
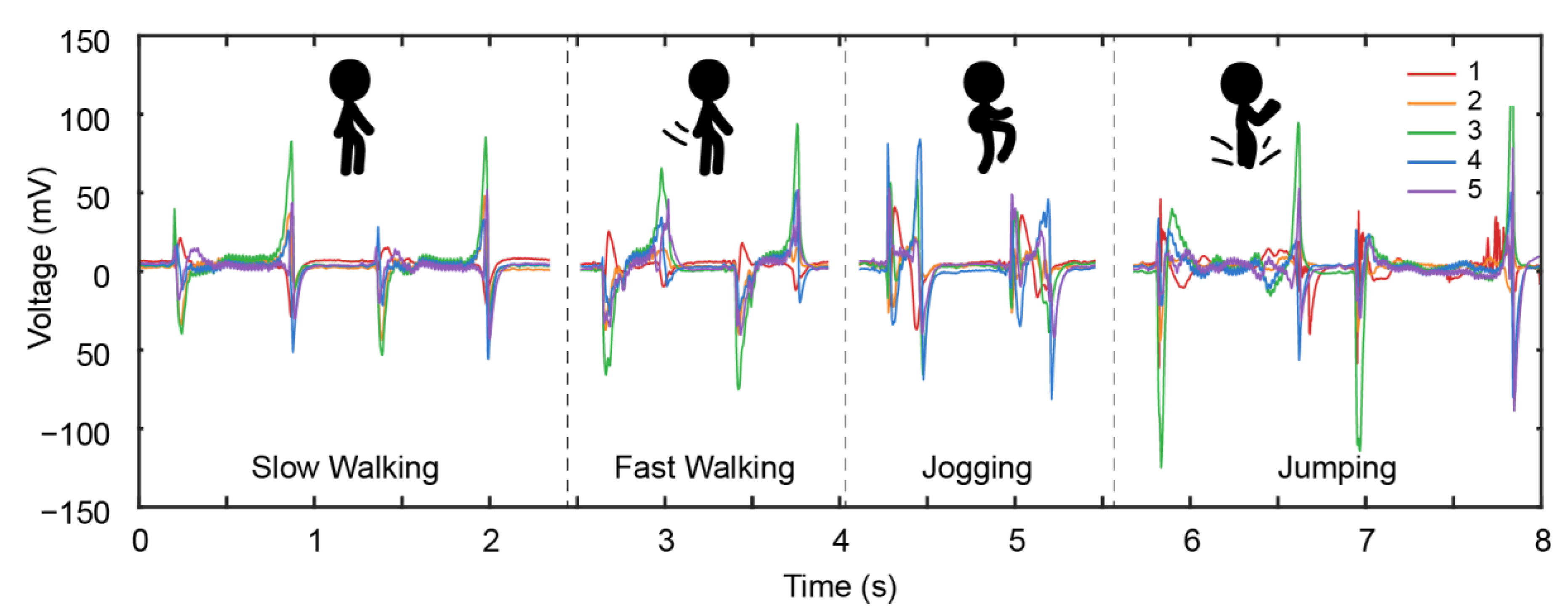
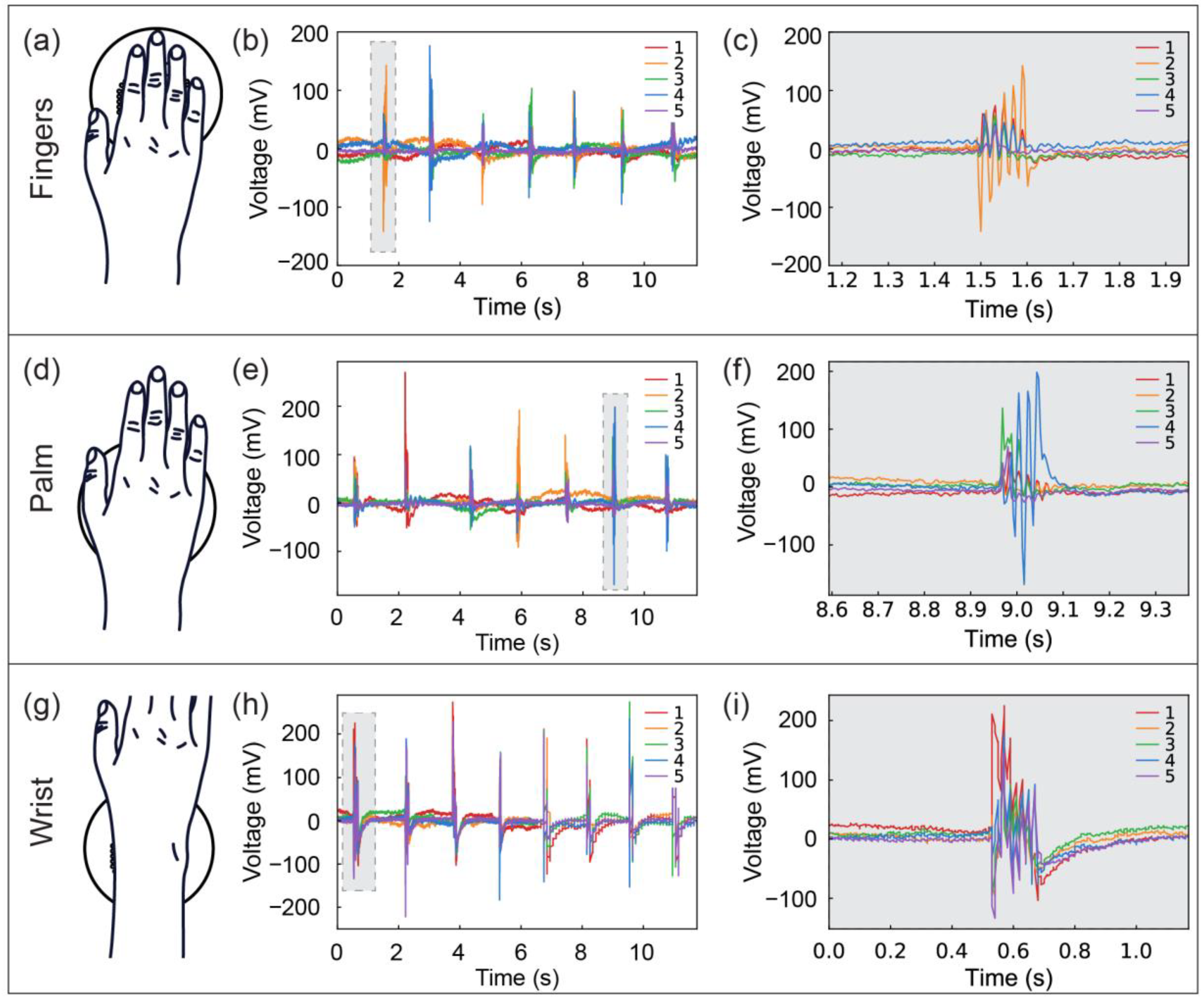
3.2. Activity Monitoring
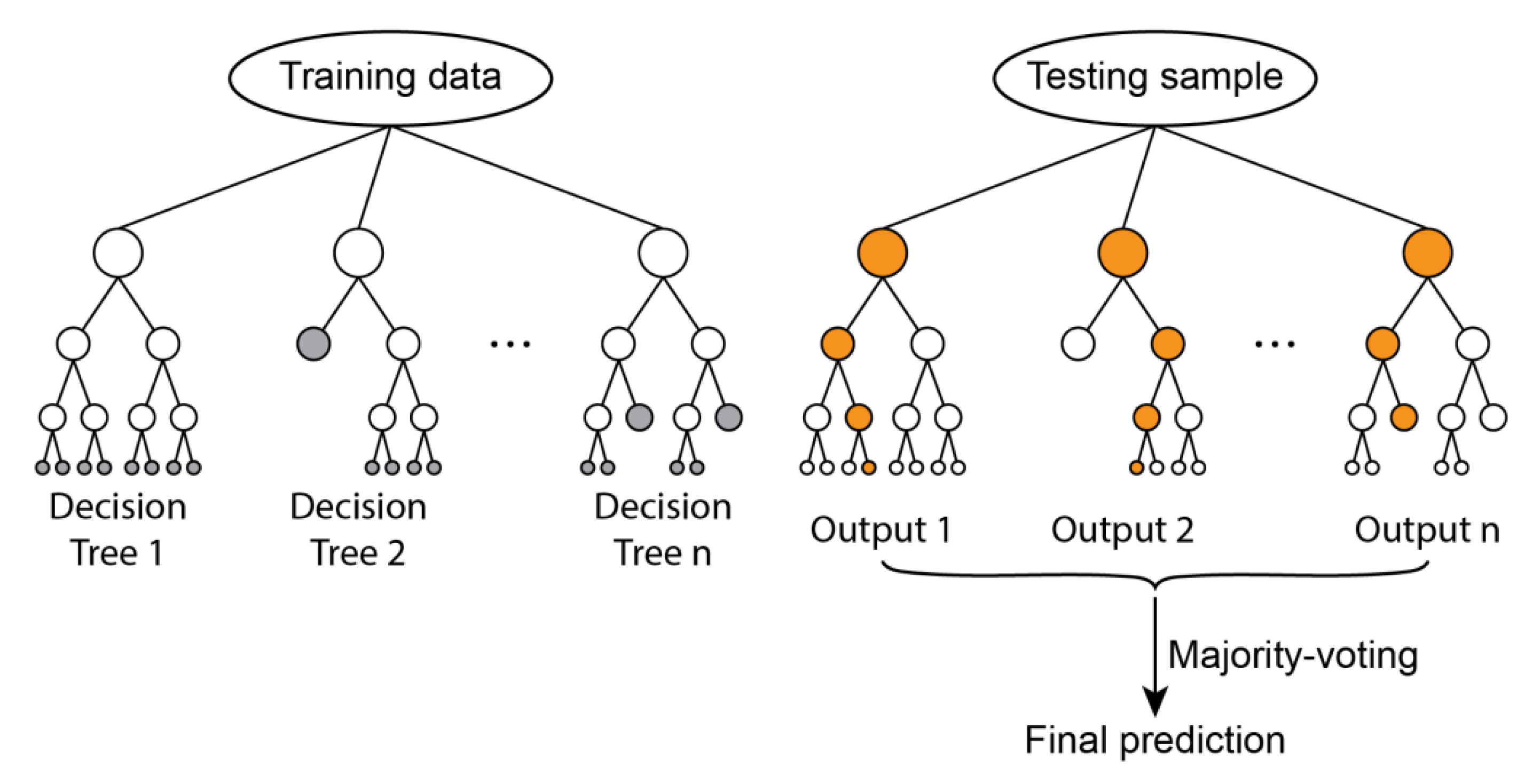
3.3. Tactile Recognition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jafarifarmand, A.; Badamchizadeh, M.A.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Nazari, M.A.; Tazehkand, B.M. A new self-regulated neuro-fuzzy framework for classification of EEG signals in motor imagery BCI. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 26, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.-K.; Fu, L.; Liu, L.; Lee, D.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Meng, Y. Human identification with electrocardiogram. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2018, 12, 798–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, S.R.A.; Hamid, T.; Mahmood, R.; Alam, M.A.; Rafi, T.; Haque, M.Z.U.; Munir, M.W. Wireless brain computer interface for smart home and medical system. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 106, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; An, N.; Tian, H.; Wang, C.; Han, T.; Wang, L.; Lu, B. High-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators with imprinted P (VDF-TrFE)/BaTiO3 nanocomposite micropillars for self-powered flexible sensors. Small 2017, 13, 1604245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shao, J.; An, N.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Xu, C.; Ding, Y. Self-powered flexible pressure sensors with vertically well-aligned piezoelectric nanowire arrays for monitoring vital signs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 11806–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaraj, W.; Dahiya, R. Fingerprint-Enhanced Capacitive-Piezoelectric Flexible Sensing Skin to Discriminate Static and Dynamic Tactile Stimuli. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Wang, C.; Dong, L.; Yu, R.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Z.L.; Pan, C. Flexible and controllable piezo-phototronic pressure mapping sensor matrix by ZnO NW/p-polymer LED array. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2884–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Gao, S.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, H. Highly Morphology-Controllable and Highly Sensitive Capacitive Tactile Sensor Based on Epidermis-Dermis-Inspired Interlocked Asymmetric-Nanocone Arrays for Detection of Tiny Pressure. Small 2020, 16, 1904774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.; Jo, E.; Kim, J. Multi-Layered, Hierarchical Fabric-Based Tactile Sensors with High Sensitivity and Linearity in Ultrawide Pressure Range. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Cui, D.; Shi, Y.; Dong, M.; Liu, C.; Ding, T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y. An overview of lead-free piezoelectric materials and devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12446–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ge, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Cretu, E.; Li, X. Novel tactile sensor technology and smart tactile sensing systems: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Mandal, D. Synergistically enhanced piezoelectric output in highly aligned 1D polymer nanofibers integrated all-fiber nanogenerator for wearable nano-tactile sensor. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.H.; Wong, Y.-D.; Su, Y.-M. Piezoelectric cement sensor and impedance analysis for concrete health monitoring. In Proceedings of the Nondestructive Characterization and Monitoring of Advanced Materials, Aerospace, Civil Infrastructure, and Transportation XIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; p. 109710Y. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Xu, Q.; Gu, L.; Ma, F.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Single crystalline lead zirconate titanate (PZT) nano/micro-wire based self-powered UV sensor. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yi, Z.; Tang, G.; Liu, J. A gullwing-structured piezoelectric rotational energy harvester for low frequency energy scavenging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Xie, F.; Tian, Y.; Li, N.; Dong, X.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Qu, D. A Battery-and Leadless Heart-Worn Pacemaker Strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 2000477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yi, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xie, F.; Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Shao, X.; Li, Y. Direct powering a real cardiac pacemaker by natural energy of a heartbeat. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Unno, K.; Makino, E.; Ito, Y.; Shimada, S. Characterization of sputtered ZnO thin film as sensor and actuator for diamond AFM probe. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2002, 102, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.Q.; Luo, J.; Du, X.; Flewitt, A.; Li, Y.; Markx, G.; Walton, A.; Milne, W. Recent developments on ZnO films for acoustic wave based bio-sensing and microfluidic applications: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 143, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; He, P.; Yang, B.; Yi, Z.; Lu, L.; Liu, J. A flexible piezoelectric strain sensor array with laser-patterned serpentine interconnects. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8463–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. Conjuncted Pyro-Piezoelectric Effect for Self-Powered Simultaneous Temperature and Pressure Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tu, S.; Fu, R.; Li, J.; Hu, F.; Yan, B.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S. Flexible Piezoelectric Pressure Tactile Sensor Based on Electrospun BaTiO3/Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Nanocomposite Membrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33989–33998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullapalli, H.; Vemuru, V.S.; Kumar, A.; Botello-Mendez, A.; Vajtai, R.; Terrones, M.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Ajayan, P.M. Flexible piezoelectric ZnO–paper nanocomposite strain sensor. Small 2010, 6, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Deng, W.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, D.; Yan, C.; He, X.; Yang, T.; Jin, L.; Chu, X.; Zhang, H. Rich lamellar crystal baklava-structured PZT/PVDF piezoelectric sensor toward individual table tennis training. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Wu, D. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator made of poly (vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene)(PVDF-TrFE) thin film. Nano Energy 2014, 7, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yang, B.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, J. Electrospinning core-sheath piezoelectric microfibers for self-powered stitchable sensor. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ding, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Flexible PVDF based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dario, P.; De Rossi, D. Tactile sensors and the gripping challenge: Increasing the performance of sensors over a wide range of force is a first step toward robotry that can hold and manipulate objects as humans do. IEEE Spectr. 1985, 22, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H. A robot attached the soft sensor using PVDF film for objects discrimination. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2018, 192, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-H.; Wang, M.-S.; Yu, Y.-C.; Mu, C.-L.; Lu, K.-F.; Lin, C.-T. Flexible tactile sensor for the grasping control of robot fingers. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Intelligent Systems, Tainan, Taiwan, 31 May–2 June 2013; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, H.J.; Chung, G.S.; Kim, K.K.; Park, K.S. A smart health monitoring chair for nonintrusive measurement of biological signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 16, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, K.; Garain, S.; Henkel, K.; Schmeißer, D.; Mandal, D. Self-Powered Human-Health Monitoring through Aligned PVDF Nanofibers Interfaced Skin-Interactive Piezoelectric Sensor. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 862–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peters, J. Bioinspired tactile sensor for surface roughness discrimination. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 255, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, İ.M.; Akça, E. Design of a piezoelectric based tactile sensor with bio-inspired micro/nano-pillars. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Tang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, B.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Insole Plantar Pressure Mapping System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, J.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, S. Scalable Imprinting of Flexible Multiplexed Sensor Arrays with Distributed Piezoelectricity-Enhanced Micropillars for Dynamic Tactile Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 2000046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W. A flexible field-limited ordered ZnO nanorod-based self-powered tactile sensor array for electronic skin. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16302–16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Okada, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Togashi, K.; Zymelka, D.; Takamatsu, S.; Itoh, T. Ultra-thin piezoelectric strain sensor array integrated on flexible printed circuit for structural health monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.H.; Hong, S.K.; Wang, H.S.; Han, J.H.; Pham, T.X.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Yoo, C.D.; Lee, K.J. Flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensors and machine learning for speech processing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 1904020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Haptic-feedback smart glove as a creative human-machine interface (HMI) for virtual/augmented reality applications. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; He, T.; Lee, C. Technologies toward next generation human machine interfaces: From machine learning enhanced tactile sensing to neuromorphic sensory systems. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 031305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Sun, Z.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Shan, X.; Salam, B.; Lee, C. Deep learning enabled smart mats as a scalable floor monitoring system. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, R.; Goldsmith, P. A Wrist-Worn Piezoelectric Sensor Array for Gesture Input. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2018, 38, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Lukowicz, P.; Troster, G. Textile pressure sensor for muscle activity and motion detection. In Proceedings of the 2006 10th IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Montreux, Switzerland, 11–14 October 2006; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Shi, C.; Ren, H. A High-Sensitivity Tactile Sensor Array Based on Fiber Bragg Grating Sensing for Tissue Palpation in Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.-B.; Wu, X.-M.; Han, X.-C.; Chen, J.-Y. Studies on strain sensing properties of PVDF piezoelectric films. In Proceedings of the 2017 Symposium on Piezoelectricity, Acoustic Waves, and Device Applications (SPAWDA), Chengdu, China, 27–30 October 2017; pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Proc. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2017, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, A.; Bansho, Y.; Noda, K.; Iwata, H.; Sugano, S. Tactile object recognition using deep learning and dropout. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.U.; Bai, S. Intention detection for dexterous human arm motion with FSR sensor bands. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2017 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Vienna, Austria, 6–9 March 2017; pp. 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.; Sturm, J.; Stachniss, C.; Reisert, M.; Burkhardt, H.; Burgard, W. Object identification with tactile sensors using bag-of-features. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]

| Metric | MIN–MAX Ratio | STD Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| This work | 11.3% | 4.6% |
| Li et al. [45] | 65.2% | 27.2% |
| Tian et al. [20] | 91.0% | 31.9% |
| Category | Finger | Palm | Wrist | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Array | 93.3% | 96.6% | 96.6% | 95.5% |
| Single sensor | 80.0% | 83.3% | 90.0% | 84.4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, W.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Flexible P(VDF-TrFE) Shared Bottom Electrode Sensor Array Assisted with Machine Learning for Motion Detection. Coatings 2020, 10, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111094
Ding W, Lu L, Chen Y, Liu J, Yang B. Flexible P(VDF-TrFE) Shared Bottom Electrode Sensor Array Assisted with Machine Learning for Motion Detection. Coatings. 2020; 10(11):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111094
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Wenqing, Lijun Lu, Yu Chen, Jingquan Liu, and Bin Yang. 2020. "Flexible P(VDF-TrFE) Shared Bottom Electrode Sensor Array Assisted with Machine Learning for Motion Detection" Coatings 10, no. 11: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111094
APA StyleDing, W., Lu, L., Chen, Y., Liu, J., & Yang, B. (2020). Flexible P(VDF-TrFE) Shared Bottom Electrode Sensor Array Assisted with Machine Learning for Motion Detection. Coatings, 10(11), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111094





