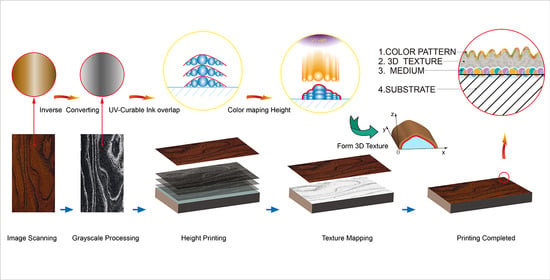
Digital 3D Wood Texture: UV-Curable Inkjet Printing on Board Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. UV-Curable Inks and Printer
2.2. Digital Image Design
2.3. Printing Substrate
2.4. Mapping Printing
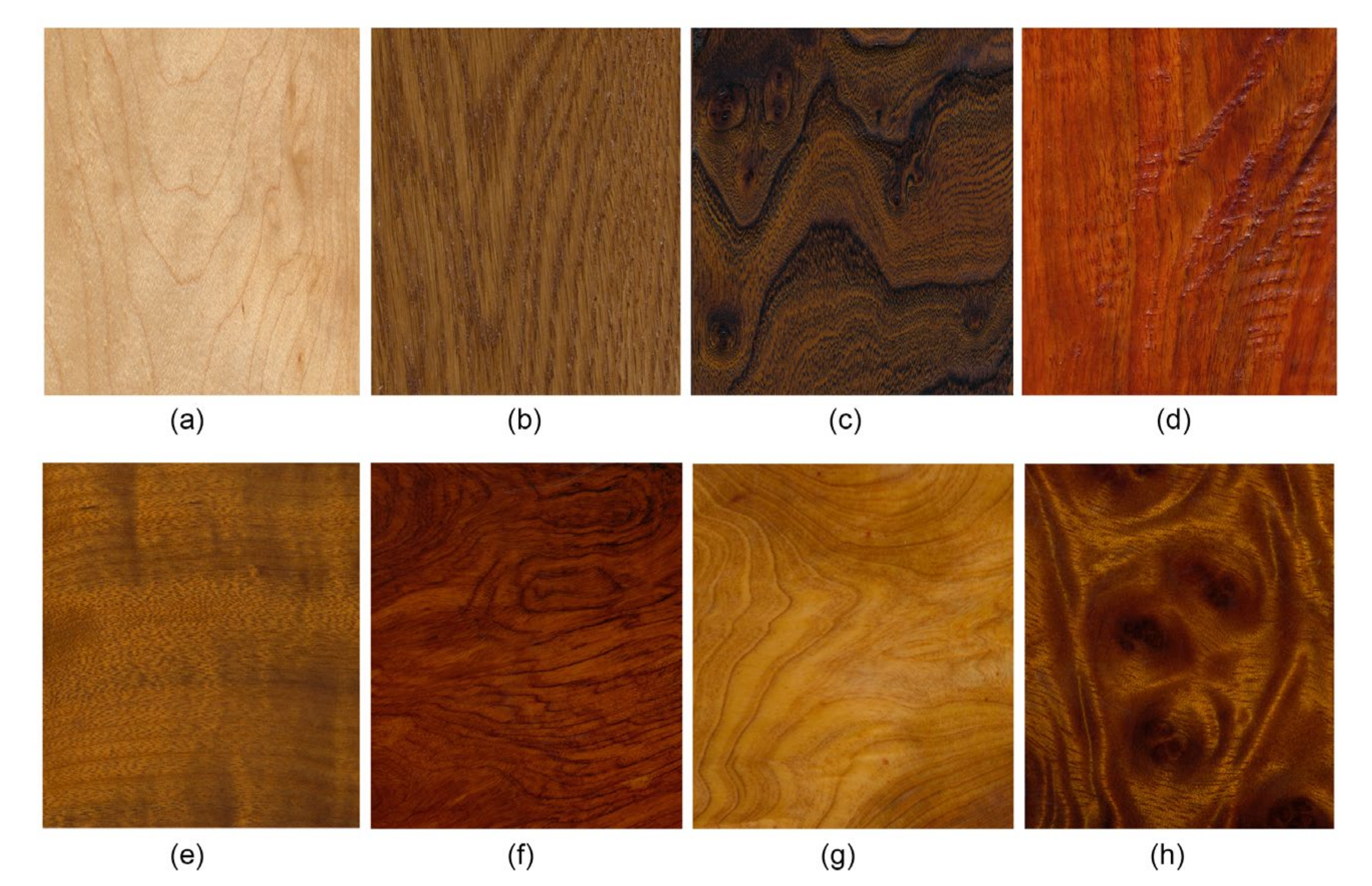
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manuel, A.; Leonhart, R.; Broman, O.; Becker, G. Consumers’ perceptions and preference profiles for wood surfaces tested with pairwise comparison in Germany. Ann. For. Sci. 2015, 72, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badila, M.; Dolezel-Horwath, E.; Zikulnig-Rusch, E.M.; Schmidt, T.; Kandelbauer, A. Evaluation of the compatibility between low pressure melamine (LPM) film printing substrates and inkjet inks. Holz Roh Werkst. 2012, 70, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stute, F.; Mici, J.; Chamberlain, L.; Lipson, H. Digital wood: 3D internal color texture mapping. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 5, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.C.; Mantysalo, M.; Niklaus, F. Inkjet Printing, Laser-Based Micromachining and Micro 3D Printing Technologies for MEMS. In Handbook of Silicon Based MEMS Materials and Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 550–564. [Google Scholar]
- Fiedor, P.; Ortyl, J. A new approach to micromachining: High-precision and innovative additive manufacturing solutions based on photopolymerization technology. Materials 2020, 13, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Haverinen, H.M.; Dhagat, P.; Jabbour, G.E. Inkjet printing-process and its applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakeim, O.A.; Arafa, A.A.; Zahran, M.K.; Abdou, L.A.W. Characterisation and application of pigmented UV-curable inkjet inks. Pigment. Resin Technol. 2018, 47, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, I.M.; Martin, G.D. Inkjet Technology for Digital Fabrication; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, E.; Woolliams, P.; Clarke, B.; Gregory, A.; Greedy, S.; Smartt, C.; Wildman, R.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Hague, R.; Dickens, P.; et al. 3D inkjet-printed UV-curable inks for multi-functional electromagnetic applications. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Langenscheidt, A. Curing behavior of a UV-curable inkjet ink: Distinction between surface-cure and deep-cure performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gans, B.B.-J.; Duineveld, P.C.; Schubert, U.S. Inkjet printing of polymers: State of the art and future developments. Adv. Mater. 2010, 16, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Akashi, M. Rapid fabrication of polylactide stereocomplex using layer-by-layer deposition by inkjet printing. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 5589–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pei, X.; Song, P.; Sun, H.; Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X. Porous bioceramics produced by inkjet 3D printing: Effect of printing ink formulation on the ceramic macro and micro porous architectures control. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 155, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Coskun, A.F.; England, G.; Cho, S.; Butt, H.; Hurwitz, J.; Kolle, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Hart, A.J.; Folch, A.; et al. Nanoart: Art on the nanoscale and beyond (Adv. Mater. 9/2016). Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1724–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.; Tasdelen, M.A.; Laun, J.; Junkers, T.; Yagci, Y.; Matyjaszewski, K. Photomediated controlled radical polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 73–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoath, S.D. Fundamentals of Inkjet Printing: The Science of Inkjet And Droplets; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Matyjaszewski, K.; Davis, T.P. Handbook of Radical Polymerization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, M.; Shibasaki, R.; Zhao, H.; Manandhar, D. Development of digital surface model and feature extraction by integrating laser scanner and CCD sensor. Proceedings of the KSRS Conference. The Korean Society of Remote Sensing. 2003. Available online: https://www.koreascience.or.kr/article/CFKO200322941410192.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Elkhuizen, W.; Essers, T.; Song, Y.; Geraedts, J.; Weijkamp, C.; Dik, J.; Pont, S. Gloss, color, and topography scanning for reproducing a painting’s appearance using 3D printing. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2019, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.-W.; Yoon, R.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, Y.-D.; Lee, D.-H. Impacts of thresholds of gray value for cone-beam computed tomography 3D reconstruction on the accuracy of image matching with optical scan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, C.; Lefebvre, S.; Tarini, M. Rethinking texture mapping. Comput. Graph. Forum 2019, 38, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, C. Color Image to Grayscale Image Conversion. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Bali Island, Indonesia, 19–21 March 2010; Volume 2, pp. 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Baar, T.; Samadzadegan, S.; Urban, P.; Segovia, M.V.O. Interrelation between gloss and texture perception of 2.5D-printed surfaces. Electron. Imaging 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, T.; Samadzadegan, S.; Brettel, H.; Urban, P.; Segovia, M.V.O. Ortiz segovia, printing gloss effects in a 2.5D system. In Measuring, Modeling, and Reproducing Material Appearance; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; p. 90180M. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheveau, A. 3D Scanning Solution for Textured Object Using Photometric Stereo with Multiple Known Light Sources. In Archiving Conference; Society for Imaging Science and Technology: Springfield, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Matsuo, M.; Nakano, T. Determination of the change in appearance of lumber surfaces illuminated from various directions. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wu, Z.; Sang, R.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, M. Surface design of wood-based board to imitate wood texture using 3D printing technology. BioResources 2019, 14, 8196–8211. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, T.; Hiziroglu, S.; Kocapınar, M. Adhesion strength of cellulosic varnish coated wood species as function of their surface roughness. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gojzewski, H.; Guo, Z.; Grzelachowska, W.; Ridwan, M.; Hempenius, M.A.; Grijpma, D.W.; Vancso, G.J. Layer-by-layer printing of photopolymers in 3D: How weak is the interface? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8908–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, R.; Manley, A.J.; Wu, Z.; Feng, X. Digital 3D Wood Texture: UV-Curable Inkjet Printing on Board Surface. Coatings 2020, 10, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121144
Sang R, Manley AJ, Wu Z, Feng X. Digital 3D Wood Texture: UV-Curable Inkjet Printing on Board Surface. Coatings. 2020; 10(12):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121144
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Ruijuan, Adam John Manley, Zhihui Wu, and Xinhao Feng. 2020. "Digital 3D Wood Texture: UV-Curable Inkjet Printing on Board Surface" Coatings 10, no. 12: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121144
APA StyleSang, R., Manley, A. J., Wu, Z., & Feng, X. (2020). Digital 3D Wood Texture: UV-Curable Inkjet Printing on Board Surface. Coatings, 10(12), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121144