Abstract
Nanobiotechnology has offered great attention in drug delivery and the development of various medicines used to treat microorganism infections. The present investigation deals with antimycobacterial activity, in-vitro hemolysis assay, and antioxidant activity of nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiO NPs). NiO NPs, with controlled size and shape, prepared by a simple and inexpensive successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method was scanned using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) digital images for surface morphology confirmation. Spherical irregular island-type NPs of about 24 nm diameter are obtained. The X-ray diffraction pattern demonstrates the synthesis of polycrystalline and cubic in phase NiO NPs. The Raman spectrum has revealed the presence of two vibration bands cantered at 550 and 1095 cm−1 for one photon longitudinal optical, and two longitudinal optical modes, respectively. The as-prepared NiO NPs endow 10 µg/mL against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis, MTCC-300) and 10 µg/mL against Mycobacterium phlei (M. phlei, MTCC-1723) inhibitory concentrations. The hemolytic activity of NiO NPs has also been explored. The antioxidant result demonstrates 63.44% for NiO NPs over 88.23% for standard, i.e., di(phenyl)-(2, 4, 6-trinitrophenyl) viminoazaniun antioxidant. Taken together, NiO NPs act as a potential candidate against mycobacteria.
1. Introduction
The flexible ability of material science and nanotechnology to arrange nanostructures of controlled size and shape is likely to lead to the expansion of new drugs [1]. Thereby, the synthesis of novel nanoparticles (NPs) of metal oxides/chalcogenides/halides etc., has received a huge attention on account of their inimitable physical, chemical, and efficient biological properties [2,3,4]. The physicochemical properties of NPs can be tuned through dropping or varying sizes, mostly when the manipulations are done at the atomic level. This enables us to use nano-sized metals and metal oxides of zinc, silver, copper, nickel, gold, cobalt, iron titanium and iron, etc., in biomedical applications. The bactericidal activity of these materials is mainly depending on their concentration in the growth/synthesis medium [5]. It is recognized that the NPs of metals and metal oxides adduce sufficient potential in the context of combating bacteria. Versatile nickel oxide (NiO) has been envisaged in gas sensing [6], photovoltaic [7], catalysis activity [8], light-emitting diode [9], and supercapacitor [10], etc., applications. Several chemical and physical methods, including magnetron sputtering [11], wet chemical bath deposition [12], electrochemical deposition [13], and sol-gel [14], etc., are being considered for the synthesis of NiO nanomaterials with various phase structures and surface morphologies. Moreover, NiO possesses outstanding bio-medical properties, and its non-hazardous nature has engrossed investigations on other plausible nano-bio-technology device applications [15]. All the above-reported synthesis processes are either complicated, time-consuming, costly, or tedious, with a large number of hazardous byproducts toxic byproducts. The SILAR chemical synthesis method has received remarkable attention due to its simplicity, inexpensive, high loading rate, and uniqueness in synthesizing nanostructures of controlled shapes/sizes [16].
Patients who are infected with multidrug-resistant (MDR) tuberculosis, are practically incurable by standard first-line treatment. Moreover, lengthily drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is also a big challenge to global tuberculosis control organization. Both issues posed a serious health threat for human health. M. tuberculosis is a gram-positive microorganism, Ref. [17] and M. phlei belongs to the mycobacteriaceae and saprophytic species. It is ubiquitous and existing in soil, dust, and water [18]. Among the most common oxides, NiO can be useful in an antibacterial and anticancer agent. Recently, NiO NPs have attracted increasing attention owing to the potential capacity to penetrate several human and animal cell systems [19]. Mariam et al. used Ni and NiO NPs to study the cytotoxic effect against human colon adenocarcinoma (HT-29) cells [20]. Ada et al., investigated the cytotoxicity and apoptotic effects of NiO NPs on the human cervix [21]. Ramasami et al., investigated antimicrobial activity against the two bacterial (Bacillus cereus and Klebsiella aerogenes) strains and one fungal (Candida albicas) treated with NiO NPs [22]. Talebian et al., reported antibacterial activity against two common foodborne pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli using NiO NPs [23]. Umaralikhan et al., performed antibacterial studies against a set of (gram-positive) Staphylococcus aureus and (gram-negative) Escherichia coli bacterial strains where 60 °C temperature treated NiO NPs possessed higher antibacterial effect as compared to the room-temperature treated NiO NPs [24]. Research on an antibacterial activity using mesoporous NiO NPs as antimycobacterial agent is still at the initial stage.
In the present study, we present on the synthesis of NiO NPs using a simple, eco-friendly, and cost-effective SILAR chemical method. Furthermore, the antimycobacterial activity of NiO NPs was assessed and their potential application in two mycobacterial species viz., M. tuberculosis and M. phlei. was also tested. The hemolysis assay was performed to examine the biocompatibility of NiO NPs as a potential candidate. The hemolytic activities of NiO NPs as compared to Rifampicin were measured at various concentrations. The hemolytic activity was depending upon the material concentration used. The as-synthesized NiO NPs have endowed lesser toxicity to RBCs as well as to other body parts. The antioxidant activity was examined by free radical scavenging assay with different concentrations of NiO NPs using the 1,1-diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All the chemicals and reagents were analytical grade used as received. Nickel (II) chloride hexahydrate (99.9%, NiCl2·6H2O), and ammonia solution (28–30%, NH4OH) were used to synthesizing NiO NPs. The ultrasonically cleaned glass substrate was used as a supporting medium for the forming of nickel hydroxide by the SILAR method.
2.2. Formulation of NiO NPs
Briefly, one cycle for the synthesis of nickel hydroxide on substrate surface was a combination of two half-cycles; the first half cycle was an immersion of vertical plunging of the cleaned glass substrate into the freshly prepared 0.1 M NiCl2·6H2O as a source of nickel wherein ammonia solution was added for pH ≈ 12, so that nickel species (Ni2+) can adsorb on the glass substrate. When the ammonia solution was added into the nickel chloride solution, the ionic product of nickel hydroxide exceeds the solubility product and the solution can be changed into turbid which is associated to the formation of nickel hydroxide. We believed that, at higher pH, solution attains super-saturation thereby, ions find considerably high energy and fast rate of reaction by losing OH− ions [25],
with an excess amount of ammonia solution, Ni2+ ion forms a complex structure with coordination number four as shown in the following reaction:
In the second half, the same glass substrate was engrossed in hot water containing about 90 °C temperature as a source of OH– ions for 20 s to form a nickel hydroxide (Ni(OH)2) film layer. When the glass substrate was immersed into the above solution, the force of attraction between nickel complex ions and substrate leads to adsorb on the substrate surface eventually by forming an adherent film of Ni(OH)2 as follows:
In this way, one SILAR cycle of nickel hydroxide was completed. This process was repeated thirty times to get a consistent, well-adherent, and fairly thick film of nickel hydroxide. After completion of the reaction, a greenish precipitate of nickel hydroxide was formed on a glass substrate, which was air calcinated at 300 °C for 2 h in a local home-made muffle furnace for obtaining black-colored phase pure NiO NPs film. NiO NPs were scratched from the glass substrate by means of through the knife of well and clean edge and powder of NiO NPs so obtained was employed for physical and biogenic measurements.
2.3. Characterization Techniques
The surface morphology of the NiO NPs was confirmed with FE-SEM (Nova 200, FEI, Waltham, MA, USA) digital images. The HR-TEM image was recorded using an FEI TECNAI G2 20 STWIN instrument. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrum was used to investigate the crystal phase (XRD-6000, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) operating at 40 kV and 60 mA. The presence of Ni and O surface elements was identified through energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis. The phase purity was confirmed by the Raman microscopy (Renishaw, Gloucestershire, UK) and the laser beam of λ = 532 nm was focused using a lens to produce a spot on the surface of NiO NPs. Moreover, the surface area and pore-size distribution studies were performed on Belsorp II, BET, Japan Inc. instruments.
2.4. Antimycobacterial Activity
The mycobacterium strains; M. tuberculosis and M. phlei were procured from Gene Bank Institute of Microbial Technology, Chandigarh, India. These organisms were grown on the Lowenstein Jensen medium. The sensitivity strain of M. tuberculosis and M. phlei were calculated towards the as-synthesized NiO NPs by applying agar cup diffusion methods. A sterile cork borer, having a diameter of 7 mm, was used to bore holes into seeding plates containing solidified nutrient agar. The as-synthesized NiO NPs (1 mg/mL) were prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), diluted further to make a concentration range of 2–50 µg/mL, and added to the well to evaluate the antimicrobial study. The samples were incorporated into a well-labeled seeding plate through a sterile pipette. The test was carried out using two parallel experimental conditions and their experiments were kept in the refrigerator for pre-diffusion of samples and incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. The growth inhibition activity of the test organism was shown after 48 h incubation, and the diameter of the inhibition zone was measured. The antimycobacterial activity of standard Rifampicin anti-tuberculosis (TB) drug was also measured simultaneously for comparison. The growth inhibition activity test was performed in Microwell 96-Well Sterile microplates (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) by dispensing into 200 µL comprising 100 µL of standardized suspension of M. tuberculosis and M. phlei (1 × 1006 cells/mL) and 100 µL of different NiO NPs concentrations incubated up to 48 h at 37 °C. The inhibitory effect of NiO NPs on the formation of mycobacteria growth was monitored. The minimum inhibitory concentration of Rifampicin was also measured for comparative study. The minimum inhibitory concentration was defined at a minimum concentration of the samples which, in fact, inhibited the growth of test microorganisms.
2.5. Hemolytic Assays
The outside cell study (hemolytic assay) activity of chemically synthesized NiO NPs was tested through blood cells. The blood sample was taken and stored in tubes containing ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) as an anti-coagulant. The blood sample was centrifuged at 634× g at 20 °C on centrifuge (Heraeus Megafuge 40, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) for 10 min. After centrifugation, the sample was washed three times with phosphate buffer saline (PBS). Also, PBS has added additionally to the pellet to give way a 10% (v/v) erythrocytes/PBS suspension. The pellet was further diluted to 10-fold with phosphate buffer. The as-prepared suspension (100 µL) was taken into the Eppendorf tube and added to different concentrations of the test sample (100 µL) in the sillar buffer. The tubes containing samples were incubated at room-temperature for 1 h and further centrifuged for 10 min. Finally, supernatant (150 µL) was taken and transferred to a microtiter plate to evaluate the absorbance wavelength at 450 nm. The Triton-X 100 (1% v/v) was used as a total hemolytic agent (positive control). The total hemolysis in percentage was calculated using Equation (5) as follows:
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
The antioxidant activity of NiO NPs was confirmed using the DPPH method, as reported previously [26]. For this as-prepared stock solution (1 mg/mL) was diluted to various concentrations i.e., 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 µg/mL in methanol. Separately DPPH solution (0.3 mM) was prepared and 1 mL was added to 3 mL of NiO NPs solution. The tube was kept aside at room-temperature for 30 min for the completion of the reaction process. The L-ascorbic acid was the standard that has antioxidant properties due to the presence of the ester group which produces the substrates by protecting double bonds and scavenging oxygen [27]. It has lowered the oxidation state of numerous metals. The absorbance of each sample was observed at 517 nm wavelength using an ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer (S) (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The scavenging activity (%) was measured using the equation as follows:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure, Morphology, and Porosity Measurements
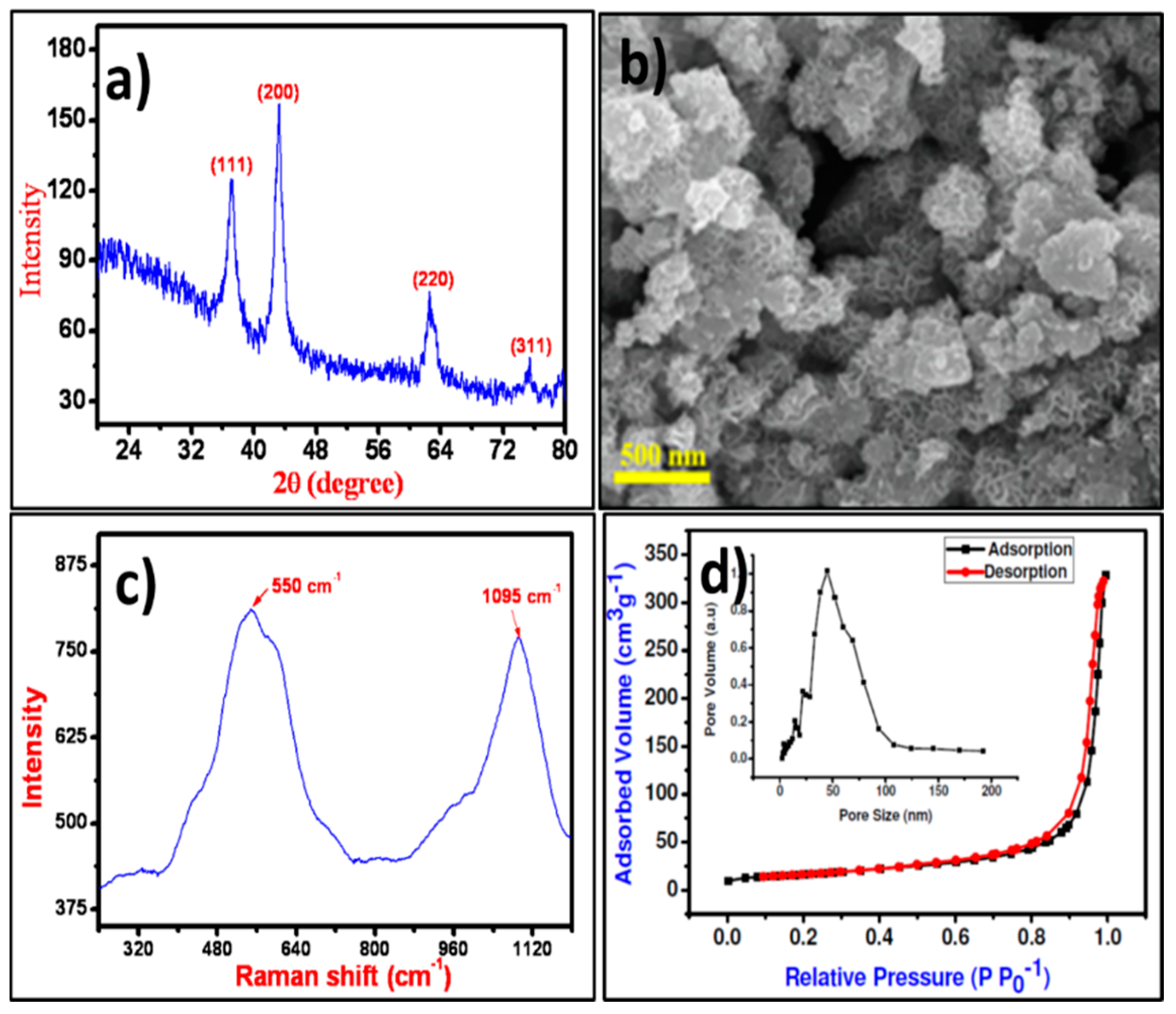
The crystal structure and phase of the NiO NPs were confirmed from the XRD pattern presented in Figure 1a wherein, the characteristic the XRD peaks of the NiO at 37.28°, 43.31°, 62.54°, and 75.46° for (111), (200), (220), and (311) planes, respectively were noted. The obtained XRD pattern was polycrystalline in nature, and all optimized peaks were exactly matched with JCPDS file no. 47-1049 for the cubic phase of NiO [28]. The average crystallite size estimated from full-width half maxima of X-ray diffraction peak using the Debye-Scherrer equation for (111) peak was about 38 nm [29]. The surface appearance of NiO was analyzed by FE-SEM images as displayed in Figure 1b. The surface of the FE-SEM image demonstrated irregular islands. Each island was composed of several different-shaped NPs. These islands were well-separated from one another with air-voids, loosely connected and piled up over one another that made it difficult to measure their exact dimensions. Raman shift spectrum of NiO NPs as displayed in Figure 1c demonstrated two vibration bands centered at 550 and 1095 cm−1, which are attributed to the one phonon longitudinal optical and two longitudinal optical modes of Ni-O oscillation, respectively [30]. The surface area of NiO NPs evaluated by N2 adsorption-desorption hysteresis curves as shown in Figure 1d confirmed 57.84 m2·g−1 surface area. Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) method was used to estimate the 50.56 nm pore-size of NiO NPs. Such higher surface area with more active sites will be useful for easy processing which may enhance the interaction between the surface of NiO NPs and cell walls of microorganisms for higher inhibition [31].
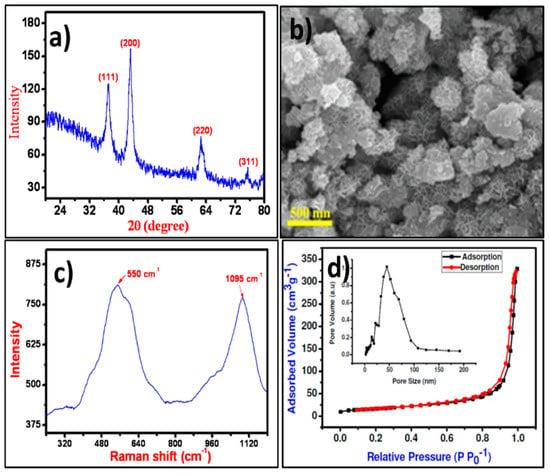
Figure 1.
(a) XRD pattern, (b) FE‒SEM image, (c) Raman spectrum, and (d) N2 adsorption‒desorption plots (with pore‒size distribution as inset) of NiO NPs.
3.2. Crystallite Size Analysis
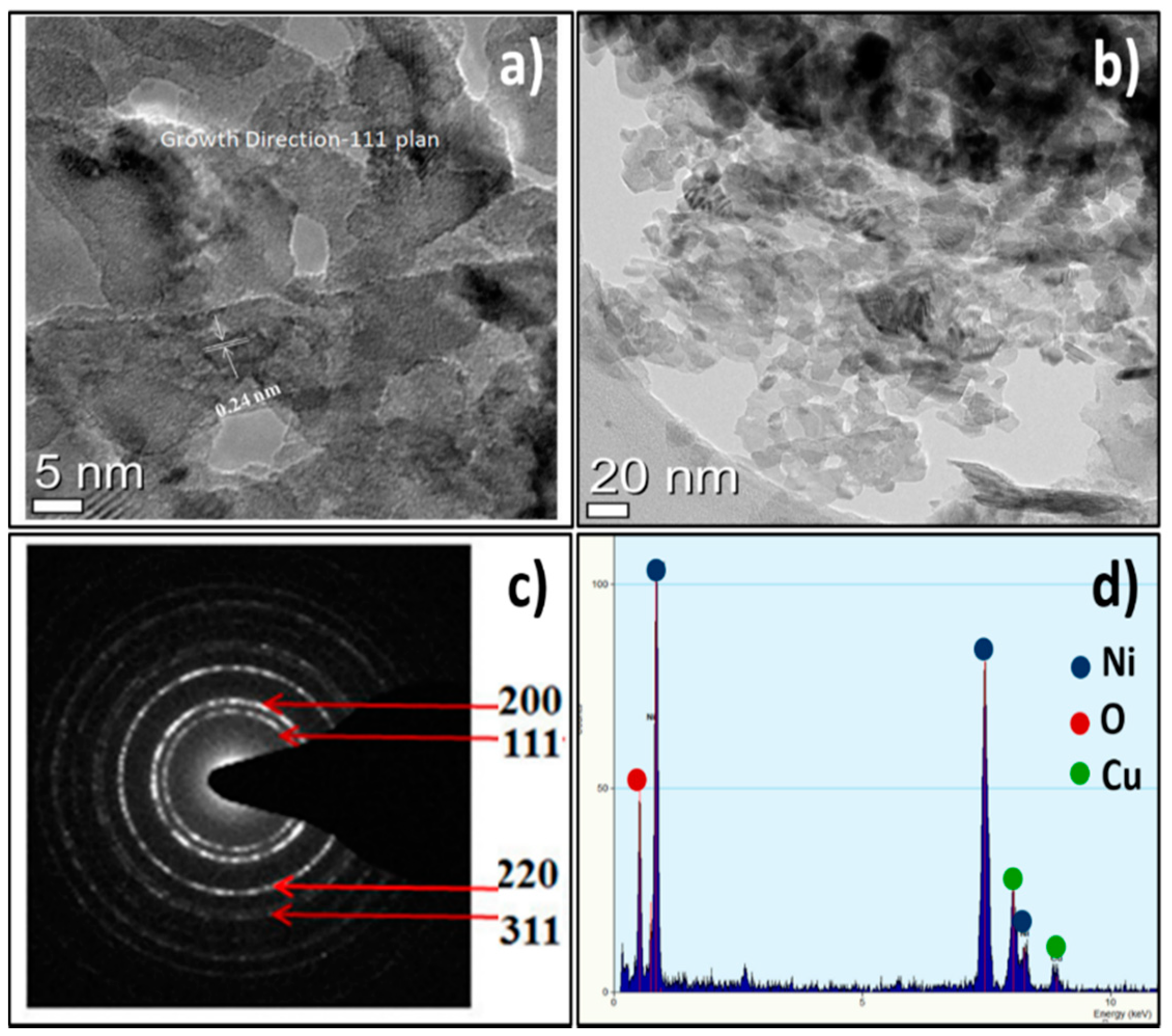
The HR-TEM image of the as-prepared NiO NPs displayed fine and regular lattice fringe spacing’s over the high-resolution scanned area (Figure 2a,b). The distance between the adjacent lattice spacing was measured from the HR-TEM analysis was 0.24 nm, well-indexed with the d-spacing of the (111) crystallographic plane of NiO, and was consistent with X-ray diffraction results [32]. The sharp continuous rings for (111), (200), (220), and (311) diffractions were observed in the selected area energy diffraction (SAED) pattern which were in accord to the polycrystalline nature of the NiO NPs (Figure 2c) [33]. The HR-TEM appended EDX analysis confirmed the existence of uniformly distributed both Ni and O elements, confirming the formation of NiO. The Cu peaks were additionally showed up because of the copper grid substrate utilized while scanning (Figure 2d).
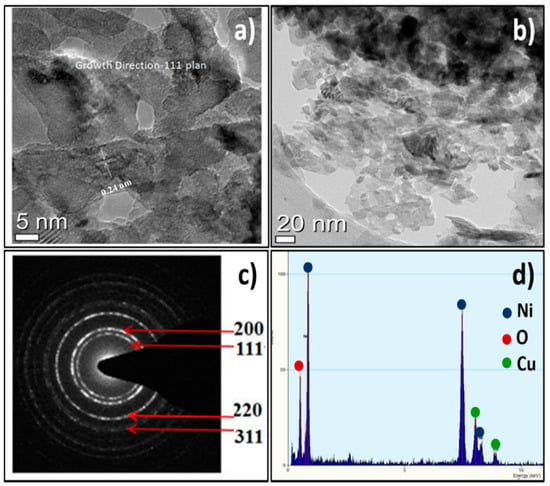
Figure 2.
(a,b) HR-TEM, (c) SAED, and (d) EDX of NiO NPs.
3.3. Antimycobacterial Activity
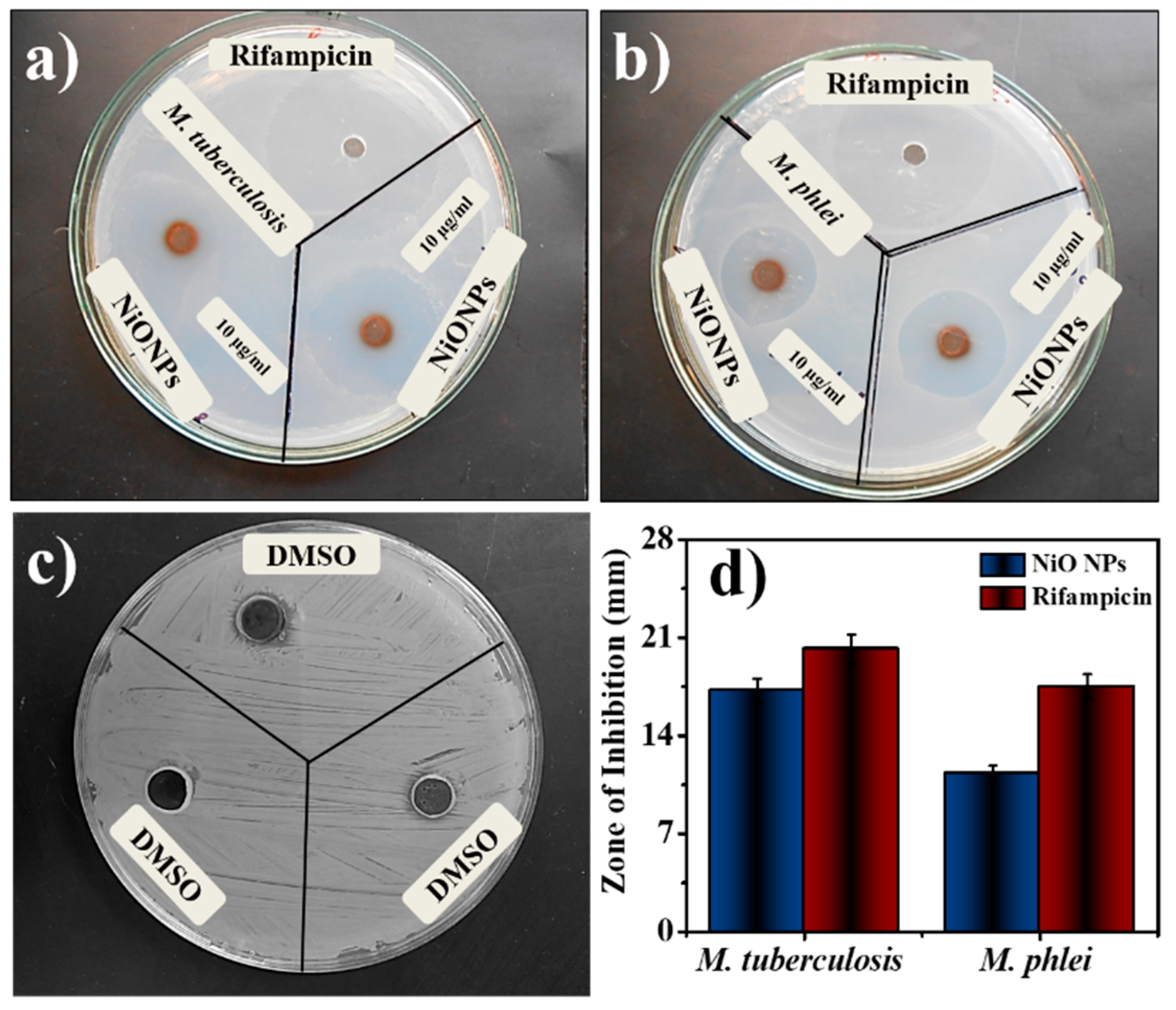
Table 1 summarized the antimycobacterial activities of NiO NPs, where the sensitivity of mycobacterial strains was tested. NiO NPs demonstrate minimum inhibitory concentration at 1.11 ± 0.10 for M. tuberculosis and 1.31 ± 0.06 for M. phlei. Based on several research reports, two mechanisms of action for antimycobacterial activity were proposed [34]. The increased review of system (ROS) level was achieved in the interaction between metallic NPs and the bacteria. As the NPs are attached to the bacterial surfaces, they can accumulate, either in the cytoplasm to disrupt the cellular function or by disorganizing the membrane [2,35]. The maximum activity was achieved at a concentration of 10 µg/mL NiO NPs against M. tuberculosis and 10 µg/mL against M. phlei from the tested concentration. The smaller size and higher surface area of NiO NPs could produce a good activity against the tested organisms. The mycobacterial growth decreased at the tested NPs concentration. The bacterial growth slowed down and prohibited the growth of microorganisms. The better activity was achieved by the NiO NPs by inhibiting the growth of an organism and with the enhancement of the membrane permeability, leading to disruption of the membrane [36]. Rifampicin is a very powerful anti-TB drug, which acts by inhibiting the early stage also to decrease the percentage of persistent TB cases [37]. This result was in comparison with the standard Rifampicin (10 µg/mL) against both the organisms depicted high activity. The zone of inhibition of tested NiO NPs showed comparable results with standard Rifampicin (Figure 3a–c). Figure 3d exhibited the zone of inhibition of common solvent DMSO, which was used to prepare all the specimens to check the antimycobacterial activity. Individual result was the mean of three independent experiments and minimum inhibitory activity was calculated using micro dilution assay.

Table 1.
Minimum inhibitory concentration activity of NiO NPs against M. tuberculosis and M. phlei.
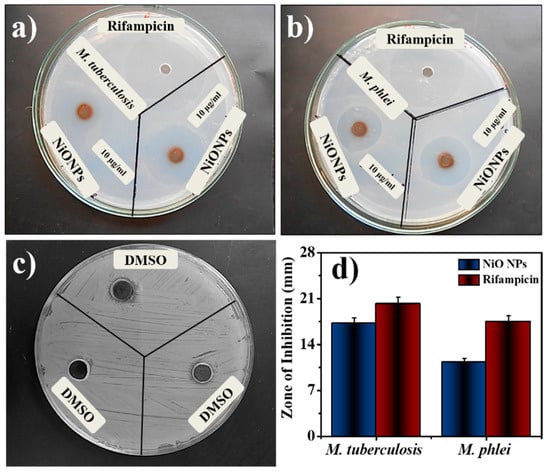
Figure 3.
Antimycobacterial activity by using agar plates (a) M. tuberculosis, (b) M. phlei, (c) DMSO, and (d) comparative bar graph.
3.4. Hemolysis Assay
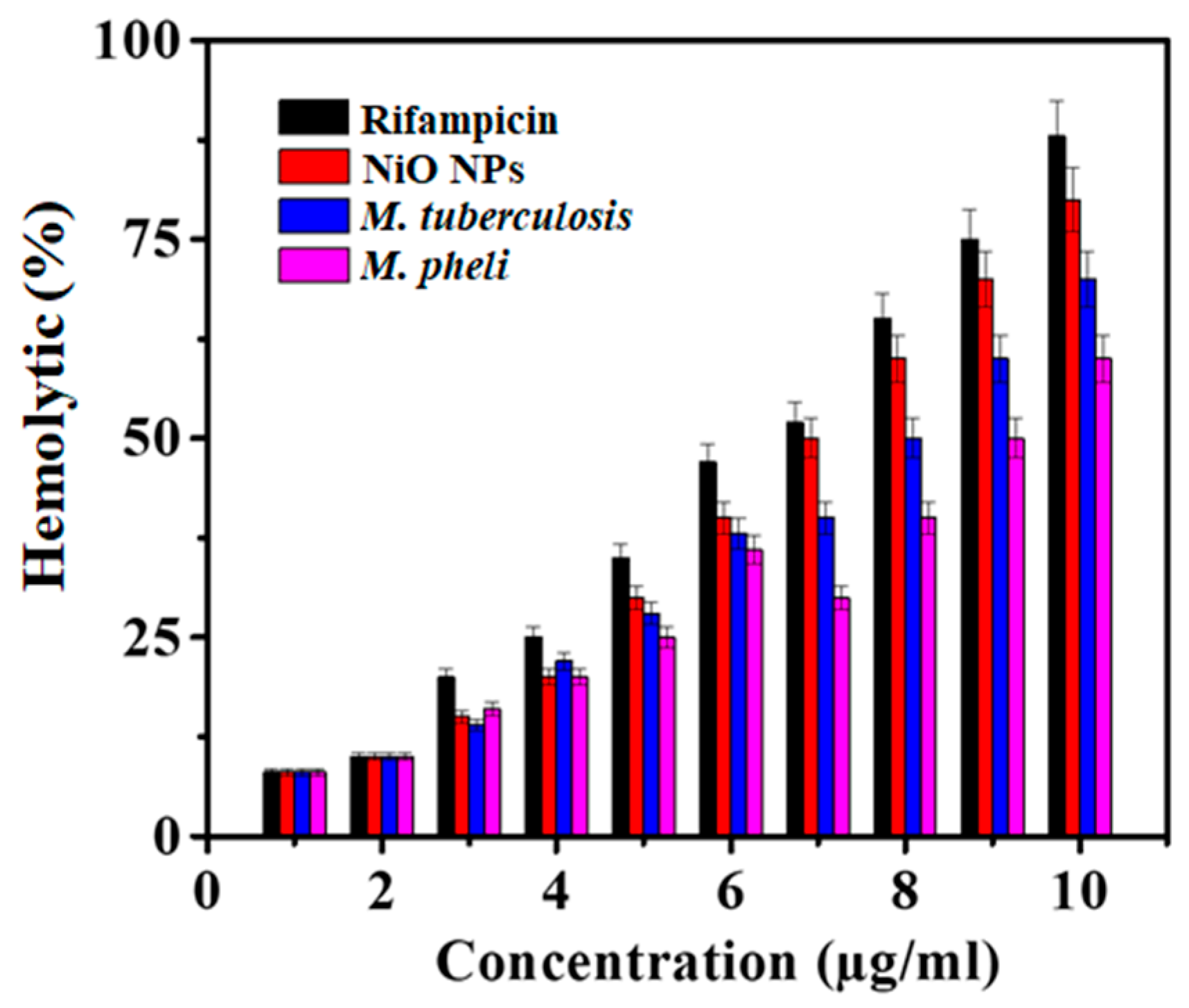
Hemolysis is typically related to the release of hemoglobin into the plasma due to the damage of the erythrocyte membrane. The in-vitro hemolytic assay is a conceivable screening tool for gauging in-vivo toxicity to host cells [38]. Here, the hemolysis activity was performed against NiO NPs where not any significant toxicity to erythrocytes was confirmed at the lowest growth inhibitory concentration (1–10 µg/mL various concentrations of NiO NPs). The hemolytic activity of the NiO NPs demonstrated lesser activity with respect to standard Rifampicin which was the function of the material concentration used. In the present study, as-synthesized NiO NPs endowed lesser toxicity to RBCs as well as to other body parts. Whereas, profound effects on dimorphism, adhesion, and biofilm formation by M. tuberculosis as well as M. phlei (Figure 4) were noted. There was a significant difference in the hemolysis was achieved with the tested NiO NPs than standard Rifampicin at 10 µg/mL.
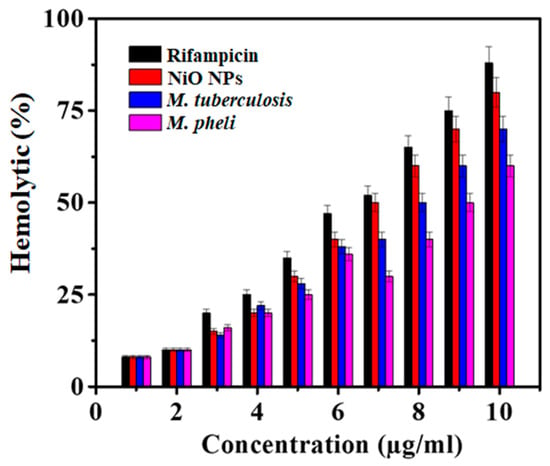
Figure 4.
Hemolytic activity of NiO NPs as compared to Rifampicin (Mean ± SD; n = 3).
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
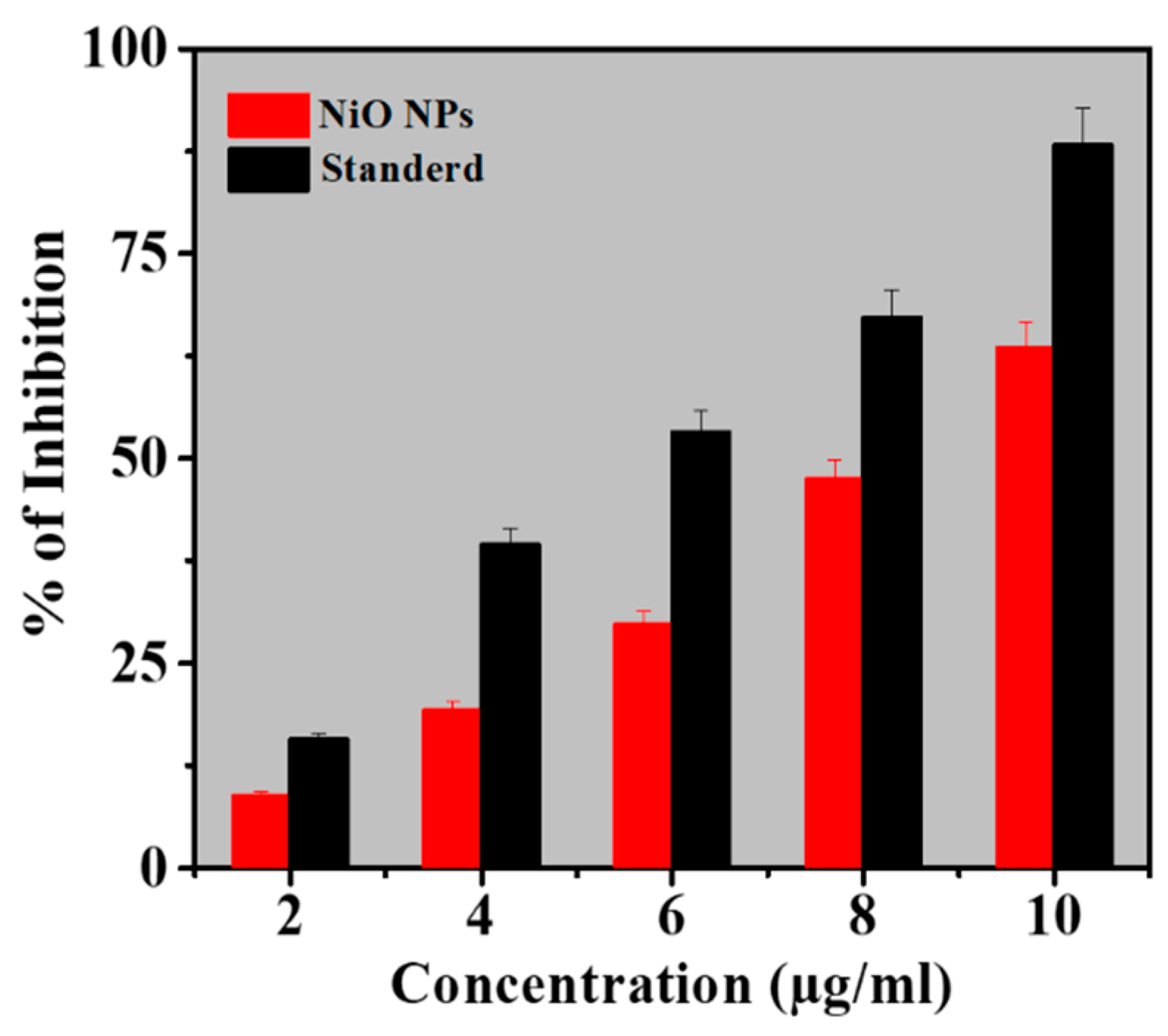
The antioxidant activity of as-synthesized NiO NPs was obtained by the DPPH method and the results were compared with the standard (ascorbic acid). DPPH method works on the principle of accepting hydrogen or electrons. The low IC50 indicates a strong DPPH scavenging activity whereas, the high IC50 gives poor DPPH scavenging activity [39]. Table 2 depicts the effect of different concentrations of NiO NPs on DPPH radical antioxidant activity where the as-synthesized NiO NPs were free radical scavengers. The DPPH activity of the NiO NPs and standard was found to be concentration-dependent. At concentrations of 2–10 µg/mL, NiO NPs demonstrated the scavenging activity of a scavenging activity ranging from 8.89% to 63.44%. The antioxidant activity was lower than that of standard ascorbic acid at the same concentration. However, for NiO NPs, the values of the percent inhibition recorded indicated an antioxidant activity potential of the NiO NPs (Figure 5)

Table 2.
Comparative antioxidant activity of NiO NPs and standard L-ascorbic acid (Mean ± SD; n = 3).
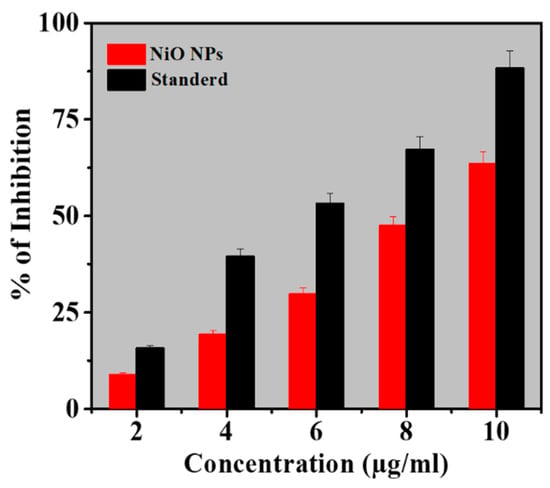
Figure 5.
Antioxidant activity of NiO NPs compared to L-ascorbic acid as standard (Mean ± SD; n = 3).
4. Conclusions
In summary, cubic NiO NPs, synthesized using the SILAR method, were envisaged in antimycobacterial, hemolysis and antioxidant activates. The surface morphology of NiO, confirmed from the FE-SEM and HR-TEM images was consisting of about 24 nm spherical irregular. The as-obtained NiO NPs, were polycrystalline, cubic in phase, and mesoporous in character. Raman spectrum identified two vibration bands centered at 550 and 1095 cm−1 for one photon longitudinal optical and two longitudinal optical modes, respectively. The surface chemical analysis confirmed a uniform distribution of Ni and O elements within the scanning surface area. The absence of any impurity peaks was suggesting the formation of phase pure and defect-free NiO. Excellent antimycobacterial, as well as antioxidant properties of NiO NPs were evidenced when used in biogenic applications. An antimycobacterial examination of both strains was performed against NiO NPs that showed greater antioxidant activity. Hemolytic assay study (cytotoxic study another name hemolytic assay) illustrated 99.9% inhibition in the growth of the cell, needed further optimization, for developing anti-TB agents in the future.
Author Contributions
Data curation, J.R.K.; Formal analysis, A.S.K. and M.U.; Funding acquisition, A.M.A.; Investigation, A.S.K.; Methodology, J.R.K. and M.A.A.; Project administration, A.M.A.; Resources, R.S.M.; Supervision, A.N. and M.I.; Validation, M.U.; Visualization, R.S.M.; Writing–original draft, J.R.K.; Writing–review & editing, J.R.K. and R.S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia through IFKSURG-1435-010.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, “Ministry of Education” in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number IFKSURG-1435-010.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, R. Nanoparticle-based drugs and formulations: Current status and emerging applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Radhika, D.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Reddy, K.R.; Raghu, A.V. Nanostructured metal oxides and its hybrids for photocatalyticand biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 281, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mal, J.; Nancharaiahac, Y.V.; Hullebuschb, E.D.V.; Lensad, P.N.L. Metal chalcogenide quantum dots: Biotechnological synthesis and applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 41477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkir, M.; Yahia, I.S.; Ganesh, V.; Bitla, Y.; Ashraf, I.M.; Kaushik, A.; AlFaify, S. A facile synthesis of Au-nanoparticles decorated PbI2 single crystalline nanosheets for optoelectronic device applications. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokoena, T.P.; Swart, H.C.; Motaung, D.E. A review on recent progress of p-type nickel oxide based gas sensors: Future perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.; Yun, J.-H.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, E.H.; Park, H.-H. Excitonic metal oxide heterojunction (NiO/ZnO) solar cells for all-transparent module integration. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 170, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, N.; An, J.; Pang, H. Controllable synthesis of a mesoporous NiO/Ni nanorod as an excellent catalyst for urea electro-oxidation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Fang, Y.; Shen, H.; Du, Z. Solution-processed quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on NiO nanocrystals hole injection layer. Org. Electron. 2017, 44, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Ubaidullaha, M.; Ahmed, J.; Ahamad, T.; Ahmad, T.; Shaikh, S.F.; Naushad, M. Synthesis of NiOx@NPC composite for high-performance supercapacitor via Waste PET plastic-derived Ni-MOF. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Chen, R.-Z.; Sun, H. Optoelectronic properties of p-type NiO films deposited by direct current magnetron sputtering versus high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualela, S.; Lv, X.; Hu, Y.; Abd-Alla, M.D. NiO nanosheets grown on carbon cloth as mesoporous cathode for High-performance lithium-sulfur battery. Mater. Lett. 2020, 268, 127622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Girolamo, D.; Matteocci, F.; Piccinni, M.; Di Carlo, A.; Dini, D. Anodically electrodeposited NiO nanoflakes as hole selective contact in efficient air processed p-i-n perovskite solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 205, 110288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Lateef, H.M.; Khalaf, M.M.; Al-Omair, M.A.; Dao, V.-D.; Mohamed, I.M.A. Chemical synthesis of NiO nanostructure by surfactant-assisted sol–gel methodology for urea electrocatalytic oxidation. Mater. Lett. 2020, 276, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, J.P.; Paul, S.; Konwar, B.K.; Samdarshi, S.K. Nickel oxide nanoparticles: A novel antioxidant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 78, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, S.S.; Mane, R.S.; Chung, H.; Yoon, M.-Y.; Lokhande, C.D.; Han, S.-H. Use of successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method for amorphous titanium dioxide thin films growth. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, M.C.; Lépicier, P.; Morales, A.; Phillips, N.C. Mycobacterium phlei cell wall complex directly induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegl, P.V.; Feiner, C.M. Mycobacterium phlei infection of the foot: A Case Report. Foot Ankle Int. 1994, 15, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.; Zine, K.; Fahima, K.; Abdelfattah, E.; Sharifudin, S.M.; Duduku, K. NiO nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity mediated through ROS generation and impairing the antioxidant defense in the human lung epithelial cells (A549): Preventive effect of Pistacia lentiscus essential oil. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariam, A.; Kashif, M.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Bououdina, M.; Sankaracharyulu, M.; Jayachandran, M.; Hashim, U. Bio-synthesis of NiO and Ni nanoparticles and their characterization. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2014, 9, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Ada, K.; Turk, M.; Oguztuzun, S.; KILIÇ, M.; Demirel, M.; Tandogan, N.; Ersayar, E.; Öztürk, L. Cytotoxicity and apoptotic effects of nickel oxide nanoparticles in cultured HeLa cells. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2010, 48, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasami, A.K.; Reddy, M.V.; Balakrishna, G.R. Combustion synthesis and characterization of NiO nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 40, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian, N.; Doudi, M.; Kheiri, M. The anti-adherence and bactericidal activity of sol–gel derived nickel oxide nanostructure films: Solvent effect. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaralikhan, L.; Jaffar, M. Antibacterial and anticancer properties of NiO nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2016, 1, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mutkule, S.U.; Navale, S.T.; Jadhav, V.V.; Ambade, S.B.; Naushad, M.; Sagar, A.D.; Patil, V.B.; Stadler, F.J.; Mane, R.S. Solution-processed nickel oxide films and their liquefied petroleum gas sensing activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: Direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fuids and modifed version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cort, W.M. Antioxidant properties of ascorbic acid in foods. In Ascorbic Acid: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Uses; Seib, P.A., Tolbert, B.M., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; Volume 200, pp. 533–550. ISBN 9780841206328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xu, L.; Gui, Y.; Chen, W. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Hierarchical Ultrathin NiO Nanoflakes for High-Performance CH4 Sensing. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kemary, M.; Nagy, N.; El-Mehasseb, I. Nickel oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and spectral studies of interactions with glucose. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova-Ulmane, N.; Kuzmin, A.; Grabis, J.; Sildos, I.; Voronin, V.I.; Berger, I.F.; Kazantsev, V.A. Structural and magnetic properties of nickel oxide nanopowder. Solid State Phenom. 2011, 168, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.K.; Theriot, J.A. Surface Area to Volume Ratio: A natural variable for bacterial morphogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 815–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Ford, M.; Wang, G. Mesoporous NiO crystals with dominantly exposed {110} reactive facets for ultrafast lithium storage. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubaidullah, M.; Ahmed, J.; Ahamad, T.; Shaikh, S.F.; Alshehri, S.M.; Al-Enizi, A.M. Hydrothermal synthesis of novel nickel oxide@nitrogenous mesoporous carbon nanocomposite using costless smoked cigarette filter for high performance supercapacitor. Mater. Lett. 2020, 266, 127492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, V.; Sundaramahalingam, S.; Rajaram, R. Size-dependent antimycobacterial activity of titanium oxide nanoparticles against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4338–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.S.H.; Karthikeyan, C.; Ahamed, A.P.; Thajuddin, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ravi, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.; Paiva Abuçafy, M.; Berbel Manaia, E.; Junior, J.; Chiari-Andréo, B.; Pietro, R.; Chiavacci, L. Relationship between structure and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9395–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dookie, N.; Rambaran, S.; Padayatchi, N.; Mahomed, S.; Naidoo, K. Evolution of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A review on the molecular determinants of resistance and implications for personalized care. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Somma, S.; Cervellin, G. Hemolyzed specimens: A major challenge for emergency departments and clinical laboratories. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).