Experimental Investigation to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Solar PV Panels Using Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanomaterial
Abstract
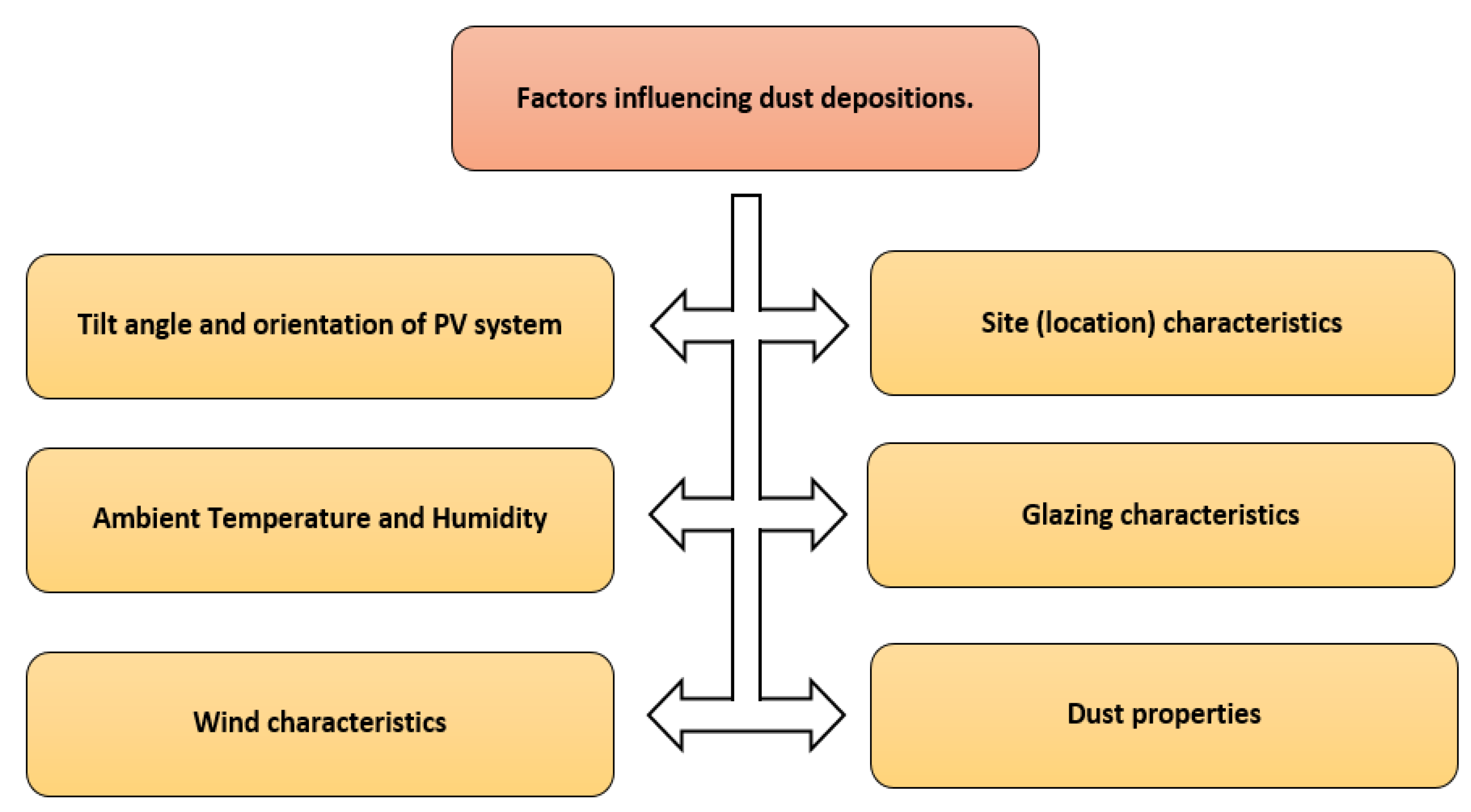
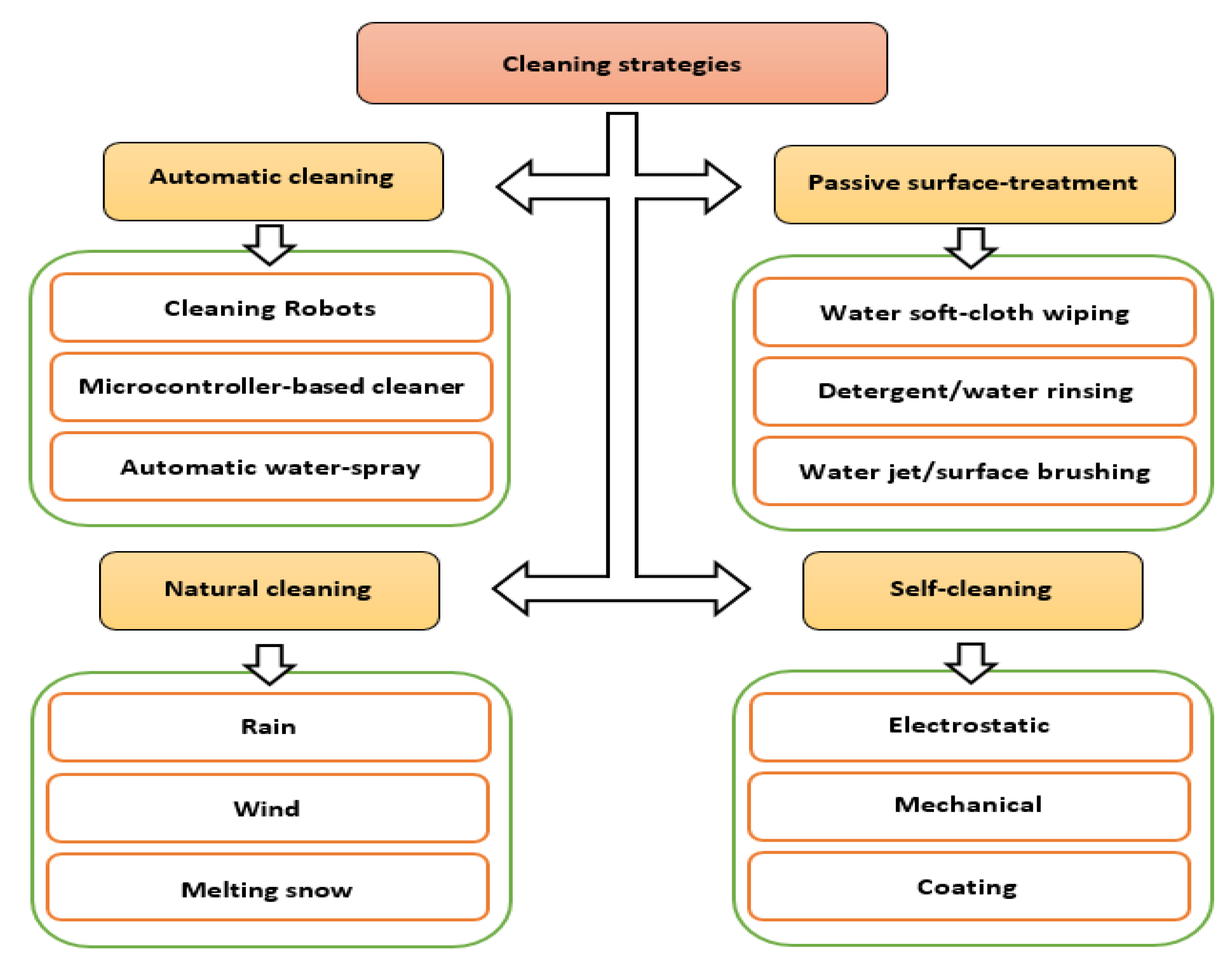
1. Introduction
- Improving experimentally the overall efficiency of solar PV panels by coating them with hydrophobic SiO2 nanomaterial to reduce the dust composition on the PV panels.
- Estimating the parameters of a PV panel, the optimal five parameters of a single diode model, which is a non-linear optimization problem, by using an accurate mathematic model, a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm and experimental data of I-V characteristics of PV panel.
- Experimental measurement of the output power of the PV panels for 45 days, measured every hour per day.
- Also, the anti-static and anti-reflection effects of coating solar PV panel with hydrophobic SiO2 nanomaterial were investigated experimentally.
2. Mathematical Model of the PV Panel
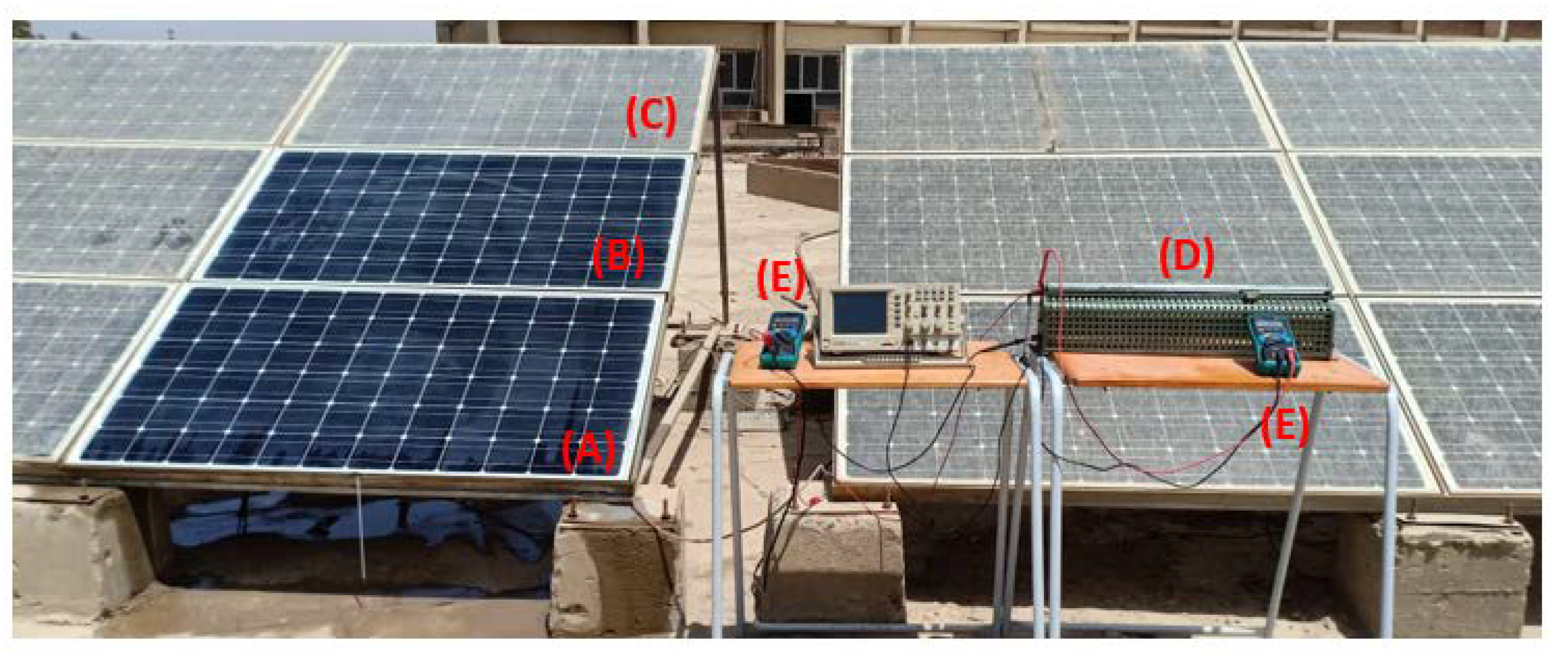
3. Experimental Set-Up
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
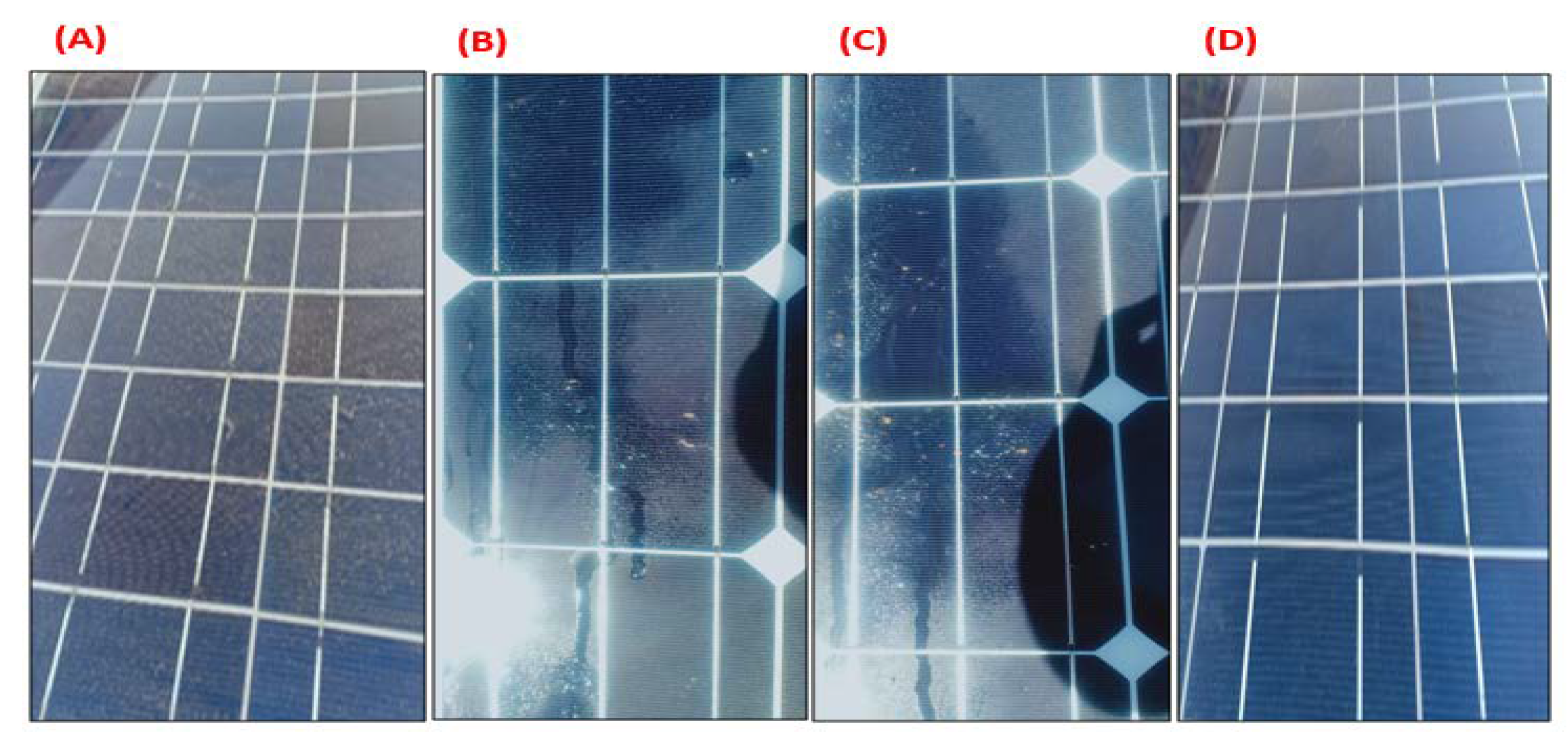
- The output power, which indicates the overall efficiency of the solar PV system, was increased by 15% more than the dusty panels and 5% more than the uncoated panels which were cleaned manually every day.
- The anti-static effect was improved due to the water droplets spreading away and producing a thin layer with less resistance for photons. The small water droplets joined and ran easily off the surface of the panel. The flow of the water on the surface caused dust to fall, unlike the other non-coated panel, on which the flow of water produced a mud layer on the surface of the panel.
- Due to the anti-reflection effect, the temperature of the panels was reduced by about 10% compared to the dusty panel and 5% compared to the manual cleaning panel without the coating.
- The overall efficiency of the solar PV panels increased due to their ability to remove dust without using any energy source or human aid.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández-Cerero, D.; Fernández-Montes, A.; Jakóbik, A. Limiting global warming by improving data-centre software. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 44048–44062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Alghassab, M.; Ziedan, H.A. An optimal sizing of stand-alone hybrid PV-fuel cell-battery to desalinate seawater at saudi NEOM city. Processes 2020, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, V.S.; Darvekar, S.K. Solar Photovoltaic panels cleaning methods: A Review. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018, 118, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, K.; Gronfula, M.G.; Ziedan, H.A. Novel soft-switching integrated boost DC-DC converter for PV power system. Energies 2020, 13, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafiq, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Adzman, N.N.; Abd Rahim, N. Advances in approaches and methods for self-cleaning of solar photovoltaic panels. Solar Energy 2018, 162, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziedan, H.A.; Elbaset, A.A.; Mourad, A.N. Optimization of PV/wind power system case study: supplying large industry load in Egypt. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2020, 15, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljev, P.; Borodinas, S.; Bareikis, R.; Struckas, A. Ultrasonic system for solar panel cleaning. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 200, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, M.; Ahmed, A.; Ziedan, H.; Sayed, K.; Amery, M.; Swify, M. A Solar-wind Hybrid Power System for Irrigation Toshka Area. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (AEECT), Amman, Jordan, 6–8 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamaase, K.; Ramasesane, T.; Zibani, I.; Matlotse, E.; Motshidisi, K. Automated dust detection and cleaning system of PV module. IOSR J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2017, 12, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.S.; Bahaj, A.B.S.; Blunden, L.S.; Wu, Y. Dust removal from solar PV modules by automated cleaning systems. Energies 2019, 12, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Housani, M.; Bicer, Y.; Koç, M. Assessment of various dry photovoltaic cleaning techniques and frequencies on the power output of CdTe-type modules in dusty environments. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, L.; Sakhrieh, A.; Aboushi, A.; Hamdan, A.; Abdelhafez, E.; Hamdan, M. Optimized cleaning and cooling for photovoltaic modules based on the output performance. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, S.; Sayigh, A.; Ip, K. Dust effect on flat surfaces—A review paper. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Fareed, S.; Khan, U.A.; Khan, S.; Farooq, M.U.; Saher, S. Development of Anti-Reflective and Self-Cleaning SiO2 Nanoparticles Coatings for Photovoltaic Panels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Swat, Pakistan, 7–9 February 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Peng, C. Fabrication of transparent superhydrophobic glass with fibered-silica network. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 407, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Yang, L.; Liao, R. Novel, stable and durable superhydrophobic film on glass prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Mater. Lett. 2017, 199, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Feng, J.; Yao, Y.; Ma, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, X. Fabrication of recyclable and durable superhydrophobic materials with wear/corrosion-resistance properties from kaolin and polyvinylchloride. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Men, X.; Zhu, X.; Ge, B.; Chu, F.; Zhang, Z. One-step spraying to fabricate nonfluorinated superhydrophobic coatings with high transparency. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. Superhydrophobic and anti-icing properties at overcooled temperature of a fluorinated hybrid surface prepared via a sol-gel process. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4540–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, G.; Li, M.; Mao, L. A study on superhydrophobic coating in anti-icing of glass/porcelain insulator. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, D.A.; Polizos, G.; Smith, D.B.; Lee, D.F.; Rajic, S.; Datskos, P.G.; Hunter, S.R. Spray-on anti-soiling coatings that exhibit high transparency and mechanical durability. In Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C3I) Technologies for Homeland Security and Homeland Defense XIII, Proc. of SPIE 9074; Carapezza Edward, M., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, F. A novel superhydrophobic hybrid nanocomposite material prepared by surface-initiated AGET ATRP and its anti-icing properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9390–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Karunakaran, R.G.; Guo, J.; Yang, S. Transparent, superhydrophobic surfaces from one-step spin coating of hydrophobic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mammen, L.; Butt, H.-J.; Vollmer, D. Candle soot as a template for a transparent robust superamphiphobic coating. Science 2012, 335, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Song, Y. Super-hydrophobic surfaces to condensed microdroplets at temperatures below the freezing point retard ice/frost formation. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3993–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, J. A facile layer-by-layer deposition process for the fabrication of highly transparent superhydrophobic coatings. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2730–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.F.; Wang, J.N.; Smith, I.H.; Sanderson, K.D. Superhydrophobic and transparent coatings based on removable polymeric spheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.Y.; Phang, I.Y.; Vancso, G.J.; Huskens, J.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Stable and transparent superhydrophobic nanoparticle films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3260–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.; Cannavale, A.; De Marco, L.; Arico, A.S.; Cingolani, R.; Gigli, G. Durable superhydrophobic and antireflective surfaces by trimethylsilanized silica nanoparticles-based sol–gel processing. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6357–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, L.; Wu, X.; Dai, W.; Qiu, Y. Fabrication and anti-frosting performance of super hydrophobic coating based on modified nano-sized calcium carbonate and ordinary polyacrylate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 8818–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Surface Roughness and Contact Angle. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1949, 53, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, D.; Babu, T.S.; Allam, D.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Eteiba, M.B. Fractional chaotic ensemble particle swarm optimizer for identifying the single, double, and three diode photovoltaic models’ parameters. Energy 2020, 195, 116979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.N.; Rezk, H.; Al-Dahifallah, M.; Sergeant, P. Hybrid photovoltaic-thermoelectric generator powered synchronous reluctance motor for pumping applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146979–146988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percenta Nanotechnology. Available online: https://percenta-nanoproducts.com/ (accessed on 9 May 2020).













| Authors | Year | Nano-Coating Materials | Water CA/SA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alam et al. [14] | 2019 | SiO2 | 168.5/2 |
| Zhang et al. [15] | 2017 | Hybrid soot/SiO2 | 166/1 |
| Yuan et al. [16] | 2017 | Al2O3-ZnO | 168.9/1 |
| Qu et al. [17] | 2017 | Kaolin/PVC | 155/5 |
| Li et al. [18] | 2016 | PTMS-SiO2 | 158.5 |
| Tang et al. [19] | 2015 | HFTES | 166/4 |
| Li et al. [20] | 2014 | SiO2 | 163.6/1.4 |
| Schaeffer et al. [21] | 2014 | Functionalized-SiO2 | 160/2.5 |
| Zhan et al. [22] | 2014 | SiO2-P(BA-Co-EFOA) | 170.3/3 |
| Xu et al. [23] | 2012 | F-SiO2 | 150/5 |
| Deng et al. [24] | 2012 | Hybrid carbon/SiO2 | 165 ± 1/1 |
| He et al. [25] | 2011 | ZnO-FAS | 165.8/1 |
| Li et al. [26] | 2009 | SiO2 | 157/1 |
| Xu et al. [27] | 2009 | PS/FAS | 160/0 |
| Ling et al. [28] | 2009 | SiO2-APTS | 162.3 ± 1/4 ± 1 |
| Manca et al. [29] | 2009 | TMS-SiO2 | 168/3 |
| Wang et al. [30] | 2007 | CaCO3-polyacrylate | 155/2 |
| Module Type | ESP-160 PPW |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power Pmax (W) | 160 |
| Maximum Voltage Vmax (V) | 12 |
| Maximum current Imax (A) | 13.3 |
| Module Efficiency (%) | 15.4 |
| Parameter | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short circuit current (A) | 1 | 10 | 5.53 |
| Diode saturation current (A) | 1 × 10−8 | 1 × 10−4 | 8.86 × 10−7 |
| Ideality factor n | 0.1 | 3 | 0.69 |
| Series resistance (Ω) | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.21 |
| Shunt resistance (Ω) | 10 | 1000 | 76.58 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alamri, H.R.; Rezk, H.; Abd-Elbary, H.; Ziedan, H.A.; Elnozahy, A. Experimental Investigation to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Solar PV Panels Using Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanomaterial. Coatings 2020, 10, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050503
Alamri HR, Rezk H, Abd-Elbary H, Ziedan HA, Elnozahy A. Experimental Investigation to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Solar PV Panels Using Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanomaterial. Coatings. 2020; 10(5):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050503
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlamri, Hatem R., Hegazy Rezk, Heba Abd-Elbary, Hamdy A. Ziedan, and Ahmed Elnozahy. 2020. "Experimental Investigation to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Solar PV Panels Using Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanomaterial" Coatings 10, no. 5: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050503
APA StyleAlamri, H. R., Rezk, H., Abd-Elbary, H., Ziedan, H. A., & Elnozahy, A. (2020). Experimental Investigation to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Solar PV Panels Using Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanomaterial. Coatings, 10(5), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050503







