Polysialic Acid Modified Liposomes for Improving Pharmacokinetics and Overcoming Accelerated Blood Clearance Phenomenon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Synthesis of PSA-BS18
2.4. Preparation of Liposomes
2.5. Characterization of Liposomes
2.5.1. Particle Size, PDI and Zeta Potential
2.5.2. Morphology of Liposomes
2.5.3. Determination of the Encapsulation Efficiency
2.6. Determination of the Fixed Aqueous Layer Thickness (FALT)
2.7. Pharmacokinetics of Liposomes in Wistar Rats
2.7.1. Pharmacokinetics of Liposomes after Single Injection
2.7.2. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Liposomes after Repeated Injections
2.8. Pharmacokinetics of Liposomes in Beagle Dogs
2.9. Quantification of IgM
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
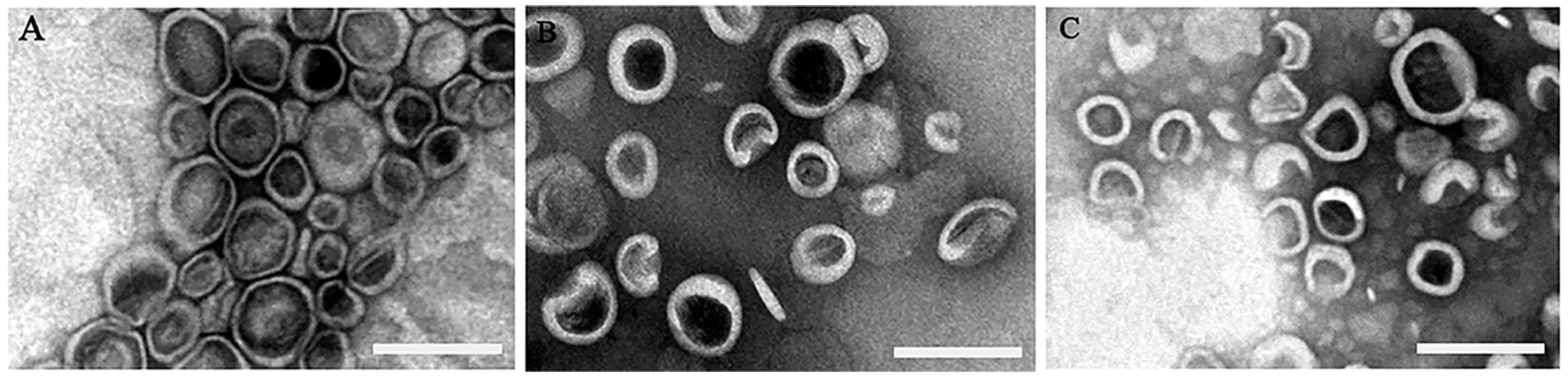
3.1. The Characteristics of the Prepared Liposomes
3.2. The Comparison of FALT around Liposomes
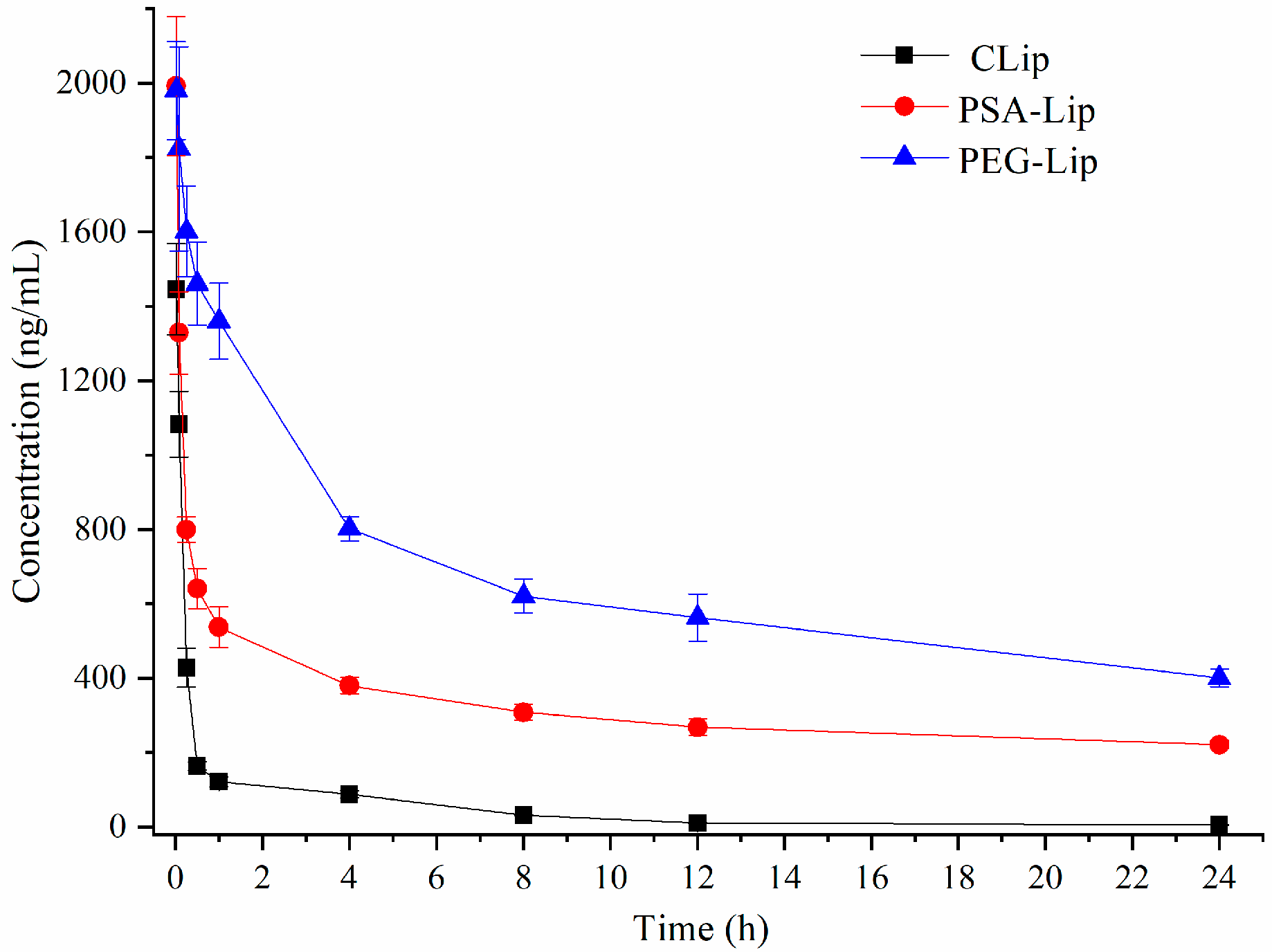
3.3. Pharmacokinetics of Liposomes after Single Injection in Wistar Rats
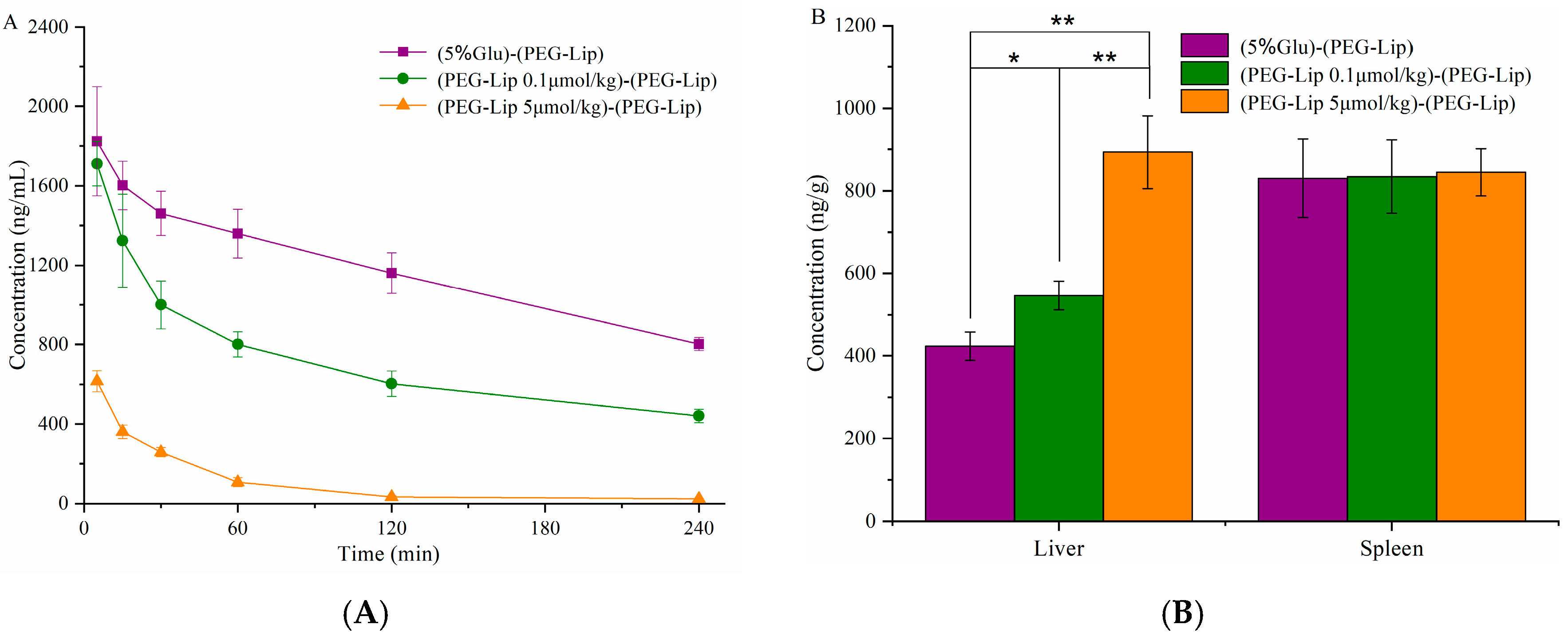
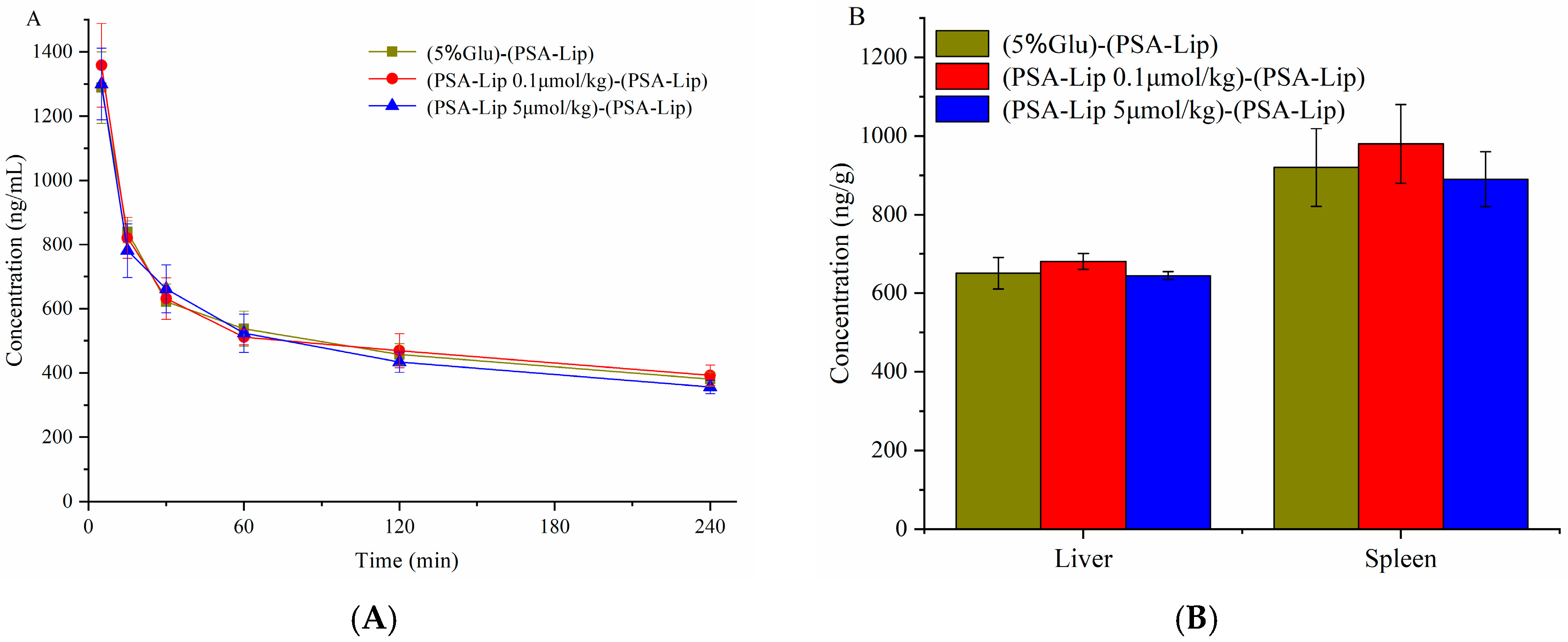
3.4. Pharmacokinetics and Bio-Distribution of Various Liposomes after the Repeated Injections in Wistar Rats
3.5. Pharmacokinetics of Various Liposomes after the Injections in Beagle Dogs
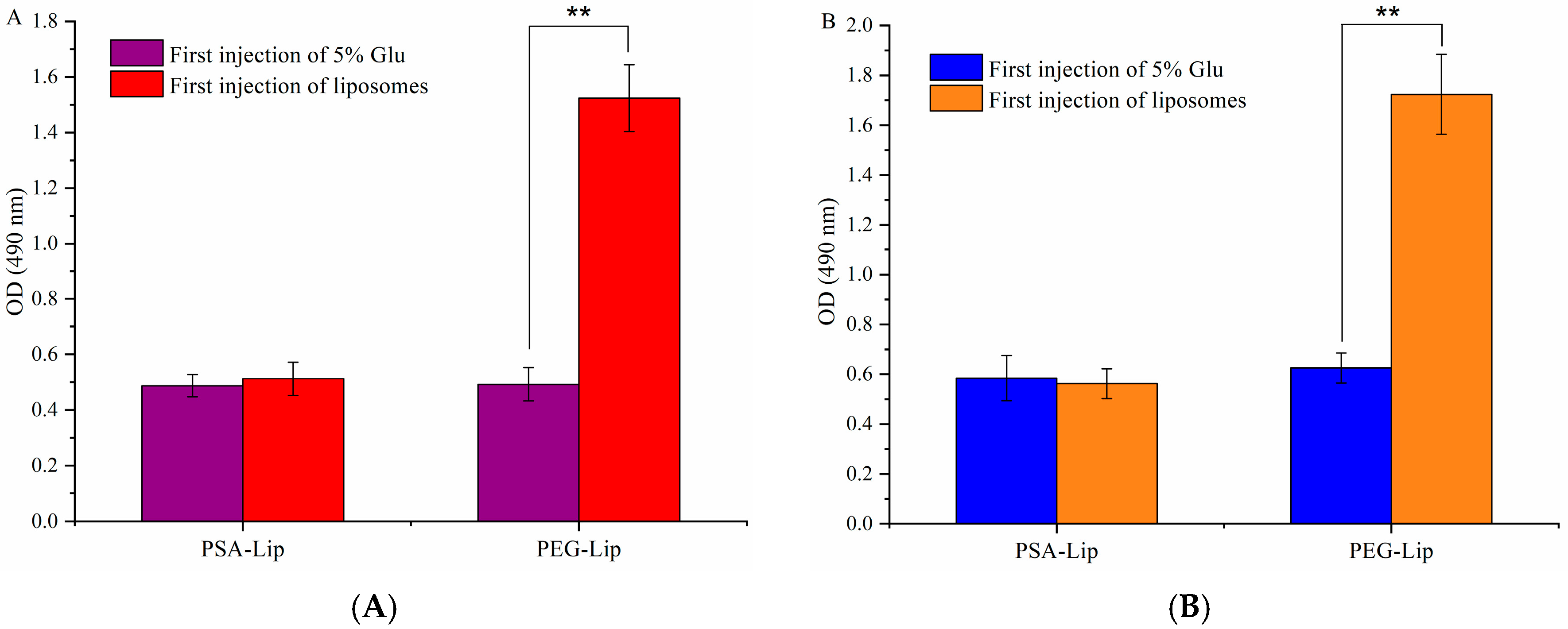
3.6. Determination of the Production of Anti-PEG (PSA) IgM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howard, M.D.; Jay, M.; Dziublal, T.D.; Lu, X. PEGylation of nanocarrier drug delivery systems: State of the art. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2008, 4, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Khan, S.; Imran, M.; Sohail, M.; Shah, S.W.A.; de Matas, M. PEGylation: A promising strategy to overcome challenges to cancer-targeted nanomedicines: A review of challenges to clinical transition and promising resolution. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Hansen, C.; Martin, F.; Redemann, C.; Yau-Young, A. Liposomes containing synthetic lipid derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) show prolonged circulation half-lives in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1066, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlerken, L.E.; Vyas, T.K.; Amiji, M.M. Poly(ethylene glycol)-modified nanocarriers for tumor-targeted and intracellular delivery. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: Pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Cho, H.-J.; Yoon, H.Y.; Yoon, I.-S.; Ko, S.-H.; Shim, J.-S.; Cho, J.-H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Hyaluronic acid derivative-coated nanohybrid liposomes for cancer imaging and drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellens, H.; Bentz, J.; Szoka, F.C. PH-induced destabilization of phosphatidylethanolamine-containing liposomes: Role of bilayer contact. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Harashima, H.; Kiwada, H. Liposome clearance. Biosci. Rep. 2002, 22, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.; Kumar, D.; Meenan, B.J.; Dixon, D. Polyethylene glycol functionalized gold nanoparticles: The influence of capping density on stability in various media. Gold Bull 2011, 44, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishburn, C.S. The pharmacology of PEGylation: Balancing PD with PK to generate novel therapeutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4167–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Lila, A.S.; Kiwada, H.; Ishida, T. The accelerated blood clearance (ABC) phenomenon: Clinical challenge and approaches to manage. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, E.T.M.; Laverman, P.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Storm, G.; Scherphof, G.L.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Corstens, F.H.M.; Boerman, O.C. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Shimizu, T.; Alaaeldin, E.; Hussein, A.; Sarhan, H.A.; Szebeni, J.; Ishida, T. PEGylated liposomes: Immunological responses. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Ichihara, M.; Hyodo, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Ishihara, H. Influence of dose and animal species on accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, G.T.; Mészáros, T.; Vashegyi, I.; Fülöp, T.; Örfi, E.; Dézsi, L.; Rosivall, L.; Bavli, Y.; Urbanics, R.; Mollnes, T.E.; et al. Pseudo-anaphylaxis to polyethylene glycol (PEG)-coated liposomes: Roles of anti-PEG IgM and complement activation in a porcine model of human infusion reactions. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9315–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Ichihara, M.; Sadzuka, Y.; Kiwada, H. Effect of the physicochemical properties of initially injected liposomes on the clearance of subsequently injected PEGylated liposomes in mice. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Harada, M.; Wang, X.Y.; Ichihara, M.; Irimura, K.; Kiwada, H. Accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated liposomes following preceding liposome injection: Effects of lipid dose and PEG surface-density and chain length of the first-dose liposomes. J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriadis, G.; Fernandes, A.; Mital, M.; McCormack, B. Polysialic acids: Potential in improving the stability and pharmacokinetics of proteins and other therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 1964–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.I.; Gregoriadis, G. The effect of polysialylation on the immunogenicity and antigenicity of asparaginase: Implication in its pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 217, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, J.Z.; Rougon, G. Cell biology of polysialic acid. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1997, 7, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Major, D.; Rutishauser, U. Role of charge and hydration in effects of polysialic acid on molecular interactions on and between cell membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23039–23044. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muhlenhoff, M.; Eckhardt, M.; Gerardy-Schahn, R. Polysialic acid: Three-dimensional structure, biosynthesis and function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1998, 8, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Simpson, S.D.; Gulati, S.; McQuillen, D.P.; Pangburn, M.K.; Rice, P.A. A novel sialic acid binding site on factor H mediates serum resistance of sialylated Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, J.; Simard, D.; Gilbert, M.; Lovering, A.L.; Wakarchuk, W.W.; Tanner, M.E.; Strynadka, N.C.J. Structural and mechanistic analysis of sialic acid synthase NeuB from Neisseria meningitidis in complex with Mn2+, phosphoenolpyruvate, and N-acetylmannosaminitol. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3555–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.A.; Wardwell, P.R. Polysialic acid: Overcoming the hurdles of drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.M.; Feng, R.; Chen, J.P.; Duan, L.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Hu, Y.W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, T.Y.; Deng, Y.H.; Song, Y.Z. Development of a nattokinase-polysialic acid complex for advanced tumor treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 145, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Hu, L.; Peng, B.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Deng, Y. Polysialic acid-polyethylene glycol conjugate-modified liposomes as a targeted drug delivery system for epirubicin to enhance anticancer efficiency. Drug Deliv. Transl Res. 2018, 8, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, M.; Hu, L.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; et al. Targeted delivery of pixantrone to neutrophils by poly(sialic acid)-p-octadecylamine conjugate modified liposomes with improved antitumor activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Hu, L.; Peng, B.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y. Polysialic acid-modifying liposomes for efficient delivery of epirubicin, in-vitro characterization and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, H.; Gutman, D.; Cohen-Sela, E.; Haber, E.; Elmalak, O.; Koroukhov, N.; Danenberg, H.D.; Golomb, G. Preparation of alendronate liposomes for enhanced stability and bioactivity: In vitro and in vivo characterization. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.R.; Zhang, N.; Silvers, A.L.; Forstner, M.B.; Bader, R.A. Synthesis and evaluation of cyclosporine A-loaded polysialic acid–polycaprolactone micelles for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 51, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadzuka, Y.; Nakade, A.; Hirama, R.; Miyagishima, A.; Nozawa, Y.; Hirota, S.; Sonobe, T. Effects of mixed polyethyleneglycol modification on fixed aqueous layer thickness and antitumor activity of doxorubicin containing liposome. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 238, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Miyagishima, A.; Sadzuka, Y.; Nozawa, Y.; Mochizuki, Y.; Ohshima, H.; Hirota, S. Determination of the thickness of the fixed aqueous layer around polyethyleneglycol-coated liposomes. J. Drug Target. 1995, 3, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, F.; Arif, I.; Botting, R.; Fante, C.; Quintieri, L.; Clementi, C.; Schiavon, O.; Pasut, G. Polysialic acid as a drug carrier: Evaluation of a new polysialic acid-epirubicin conjugate and its comparison against established drug carriers. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Hreczuk-Hirst, D.H.; McCormack, B.; Mital, M.; Epenetos, A.; Laing, P.; Gregoriadis, G. Polysialylated insulin: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1622, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, Y. Repeated injections of PEGylated liposomal topotecan induces accelerated blood clearance phenomenon in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; She, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y. Accelerated drug release and clearance of PEGylated epirubicin liposomes following repeated injections: A new challenge for sequential low-dose chemotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1257. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, X.; Sui, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; She, Z.; Deng, Y. A noticeable phenomenon: Thiol terminal PEG enhances the immunogenicity of PEGylated emulsions injected intravenously or subcutaneously into rats. Eur. J. Pharm. BioPharm. 2013, 85, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, K.Q.; Deng, Y.H.; Chen, D.W. Effects of cleavable PEG-cholesterol derivatives on the accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated liposomes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4757–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Tang, W.; She, Z.; Deng, Y. A frustrating problem: Accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated solid lipid nanoparticles following subcutaneous injection in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. BioPharm. 2012, 81, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Takeda, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Kimoto, A.; Kobayashi, C.; Takasaki, N.; Yuki, K.; Tanaka, K.-I.; Takenaga, M.; Igarashi, R.; et al. Accelerated blood clearance phenomenon upon repeated injection of PEG-modified PLA-nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, M.; Ma, Y.; Zang, G.; She, Z.; Deng, Y. Repeated injection of PEGylated solid lipid nanoparticles induces accelerated blood clearance in mice and beagles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2891. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Ichihara, M.; Hyodo, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H.; Ishihara, H.; Kikuchi, H. Accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated liposomes containing doxorubicin upon repeated administration to dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Ichihara, M.; Wang, X.; Yamamoto, K.; Kimura, J.; Majima, E.; Kiwada, H. Injection of PEGylated liposomes in rats elicits PEG-specific IgM, which is responsible for rapid elimination of a second dose of PEGylated liposomes. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H. Anti-PEG IgM elicited by injection of liposomes is involved in the enhanced blood clearance of a subsequent dose of PEGylated liposomes. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Lifely, M.R.; Esdaile, J. Immunity and protection of mice against Neisseria meningitidis group B by vaccination, using polysaccharide complexed with outer membrane proteins: A comparison with purified B polysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 1985, 47, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, T. Membrane oligo- and polysialic acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Kitajima, K. Disialic, oligosialic and polysialic acids: Distribution, functions and related disease. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, X.; Su, Y.; Pei, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiao, J.; Huang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Accelerated blood clearance phenomenon upon cross-administration of PEGylated nanocarriers in beagle dogs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3533–3545. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiong, Y.; Ding, J.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Deng, Y. Effects of stability of PEGylated micelles on the accelerated blood clearance phenomenon. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chu, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiao, J.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; et al. Accelerated blood clearance of nanoemulsions modified with PEG-cholesterol and PEG-phospholipid derivatives in rats: The effect of PEG-lipid linkages and PEG molecular Weights. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | First Injection (Blank Liposomes) | Second Injection (DiR Labeled Liposomes) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 5%Glu | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| B | 5%Glu | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| C | PSA-Lip (0.1 μmol phospholipid/kg) | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| D | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| E | PEG-Lip (0.1 μmol phospholipid/kg) | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| F | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| Group | First Injection (Blank Liposomes) | Second Injection (DiR Labeled Liposomes) |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 5%Glu | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| Ⅱ | 5%Glu | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| Ⅲ | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) | PSA-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| Ⅳ | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) | PEG-Lip (5 μmol phospholipid/kg) |
| Formulation | Particle Size (nm) | Polydispersity | Zeta Potential (mV) | EE (%) | FALT (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clip | 128.4 ± 3.4 | 0.154 ± 0.012 | −12.1 ± 3.0 | 95.2 ± 1.6 | 0.28 ± 0.04 |
| PSA-Lip | 125.6 ± 8.3 | 0.164 ± 0.021 | −18.6 ± 5.1 | 96.3 ± 1.4 | 0.83 ± 0.05 |
| PEG-Lip | 111.3 ± 5.6 | 0.132 ± 0.011 | −16.7 ± 2.6 | 96.1 ± 2.3 | 2.61 ± 0.08 |
| Parameter | CLip | PSA-Lip | PEG-Lip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (μg·L−1) | 1146.3 ± 233.2 | 1992.3 ±125.6 | 1996.3 ± 114.3 |
| AUC (0-t) (μg·L−1·h) | 2223.3 ±125.6 | 7213.8 ± 100.27 | 15781.4 ± 336.28 |
| MRT (0-t)(h) | 5.12 ± 1.01 | 9.23 ± 0.46 | 12.32 ± 0.65 |
| CLz (L·kg−1·h−1) | 0.512 ± 0.141 | 0.085 ± 0.008 | 0.017 ± 0.004 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y. Polysialic Acid Modified Liposomes for Improving Pharmacokinetics and Overcoming Accelerated Blood Clearance Phenomenon. Coatings 2020, 10, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090834
Han X, Zhang T, Liu M, Song Y, Liu X, Deng Y. Polysialic Acid Modified Liposomes for Improving Pharmacokinetics and Overcoming Accelerated Blood Clearance Phenomenon. Coatings. 2020; 10(9):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090834
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xi, Ting Zhang, Mengyang Liu, Yanzhi Song, Xinrong Liu, and Yihui Deng. 2020. "Polysialic Acid Modified Liposomes for Improving Pharmacokinetics and Overcoming Accelerated Blood Clearance Phenomenon" Coatings 10, no. 9: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090834
APA StyleHan, X., Zhang, T., Liu, M., Song, Y., Liu, X., & Deng, Y. (2020). Polysialic Acid Modified Liposomes for Improving Pharmacokinetics and Overcoming Accelerated Blood Clearance Phenomenon. Coatings, 10(9), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090834




