Wear and Friction Characteristics of 65Mn Steel for Spike-Tooth Harrow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
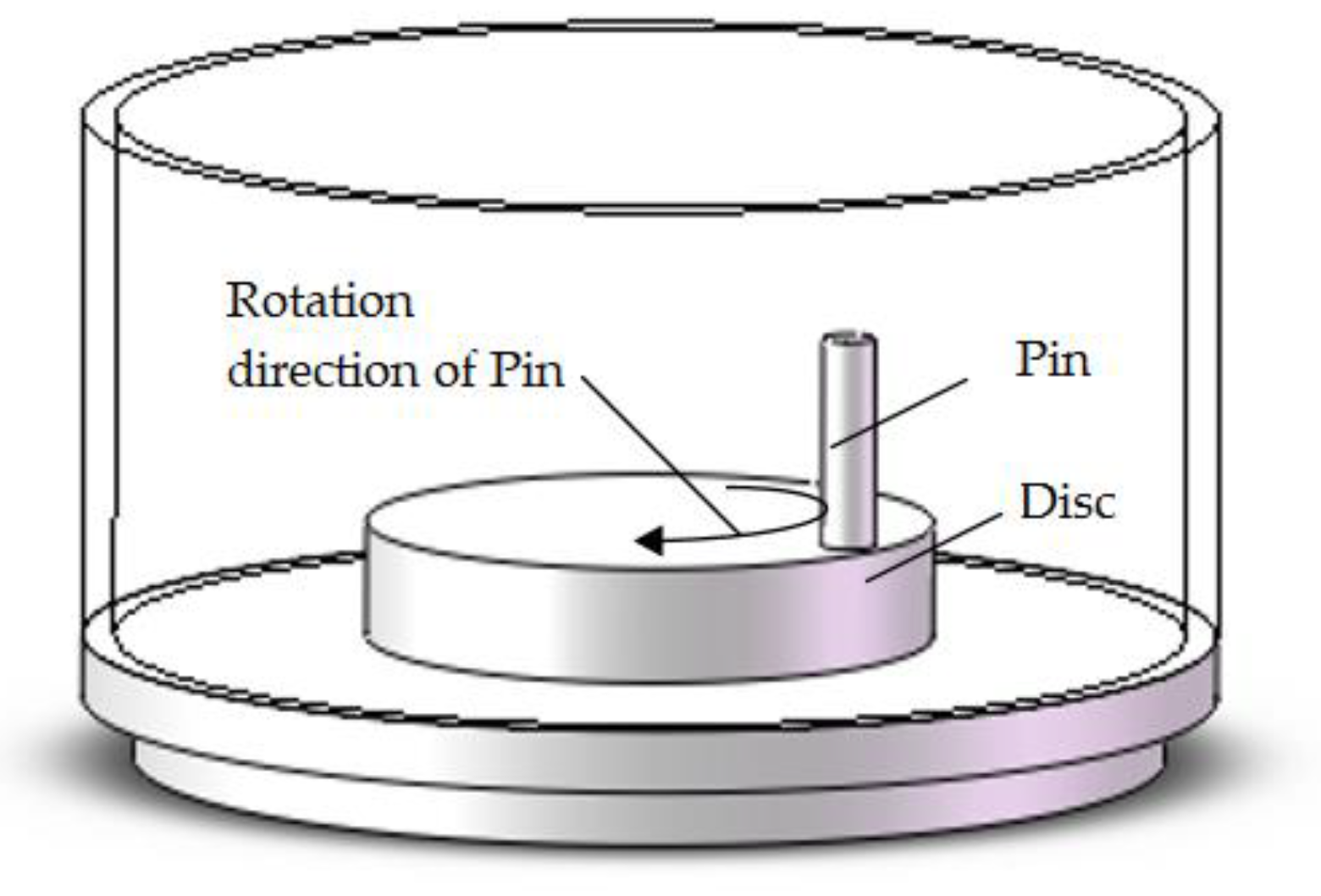
2. Experimental Set-Up
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wear Loss and Friction Coefficient
3.1.1. Effect of Load
3.1.2. Effect of Speed
3.1.3. Effect of Moisture and Soil
3.2. Wear Surface and Damage Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noorhosseini, S.A.; Damalas, C.A. Environmental Impact of Peanut Production under Different Levels of Nitrogen Fertilization. Agriculture 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carneiro, A.P.; Rodríguez, O.; Macedo, E.A. Dissolution and fractionation of nut shells in ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 227, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.S.; Carminati, J.A.; Silva, I.C.R.N.; Silva, D.L.; Bernardi, A.O.; Copetti, M.V. Salmonella, Escherichia coli and Enterobacteriaceae in the peanut supply chain: From farm to table. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.C. Study on Key Technologies of Half-feed Peanut Combine Harvester. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xu, Z.R. Application Situation and Progress Analysis of Peanuts Piecewise Harvest Machine. Agric. Mech. Res. 2012, 34, 234–237. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, M.; Zhao, B.Q.; Gao, L.X. Categories and Characteristics of Peanut Harvesting Machinery. Agric. Sci. Technol. Equip. 2013, 10, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.H.; Yang, R.B.; Shang, S.Q. Design of 4SHWZ- 1800 Self- propelled and Segmented Peanut Harvester. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2014, 36, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhichao, H.; Baoliang, P.; Wenqing, Y.; Hai’ou, W.; Lijia, T.; Lianglong, H. Design of 4LH2 type half-feed and self-propelled peanut combine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T. Design and Experiment Study on the Spring-finger Type of Peanut Pickup Device. Ph.D. Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, C.F.; Lin, W.S. The processing and fracture analysis on transmission shafts of a peanut harvester. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 201, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Río López, B.; García Diez, A.; Mier Buenhombre, J.L.; Camba Fabal, C.; Filgueira Vizoso, A. Microstructural Analysis and Tribology Behavior of a Medium-Mn Steel with Mo. Metals 2018, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.L.; Cao, Z.X.; Wang, C.; Huang, C.X. Effect of volume fraction and mechanical stability of austenite on ductility of medium Mn steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 11, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Wang, H.H.; Luo, Q.; Li, L.; Sun, C.; Misra, R.D.K. Correlation between microstructure and impact toughness of weld heat-affected zone in 5 wt.% manganese steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Effects of Boronizing Treatment on Corrosion Resistance of 65Mn Steel in two Acid Mediums. Phys. Procedia 2013, 50, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, C.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Xu, J.Y.; Song, X.C.; Zhao, Y.F. Microstructures and properties of electrical discharge strengthened layers on 65Mn steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Qiao, Y.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y. Effects of Salt Bath Nitrocarburizing on Wear Resistance of 65Mn Spring Steel. Surf. Technol. 2017, 46, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ucgul, M.; Fielke, J.M.; Saunders, C. Three-dimensional discrete element modelling (DEM) of tillage: Accounting for soil cohesion and adhesion. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 129, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sosa, M.; Olofsson, U. A pin-on-disc study of the tribology characteristics of sintered versus standard steel gear materials. Wear 2015, 340–341, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godino, L.; Pombo, I.; Sanchez, J.A.; Izquierdo, B. An original tribometer to analyze the behavior of abrasive grains in the grinding process. Metals 2018, 8, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Variable | Values |
|---|---|
| Load (N) | 2, 5, 8 |
| Rotating speed (r/min) | 300, 450, 600 |
| Soil types | sandy soil, loam |
| Soil moisture | 0, 10%, 20% |
| Revolutions | 12,250 |
| Temperature (°C) | 20–28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Z.; Du, C.; Chen, Q.; Niu, T.; Wang, N.; Song, W. Wear and Friction Characteristics of 65Mn Steel for Spike-Tooth Harrow. Coatings 2021, 11, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030319
Lu Z, Du C, Chen Q, Niu T, Wang N, Song W. Wear and Friction Characteristics of 65Mn Steel for Spike-Tooth Harrow. Coatings. 2021; 11(3):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030319
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Zhiguo, Chuanyu Du, Qingcai Chen, Tianying Niu, Na Wang, and Wanli Song. 2021. "Wear and Friction Characteristics of 65Mn Steel for Spike-Tooth Harrow" Coatings 11, no. 3: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030319
APA StyleLu, Z., Du, C., Chen, Q., Niu, T., Wang, N., & Song, W. (2021). Wear and Friction Characteristics of 65Mn Steel for Spike-Tooth Harrow. Coatings, 11(3), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030319






