Does the Nano Character and Type of Nano Silver Coating Affect Its Influence on Calcareous Soil Enzymes Activity?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
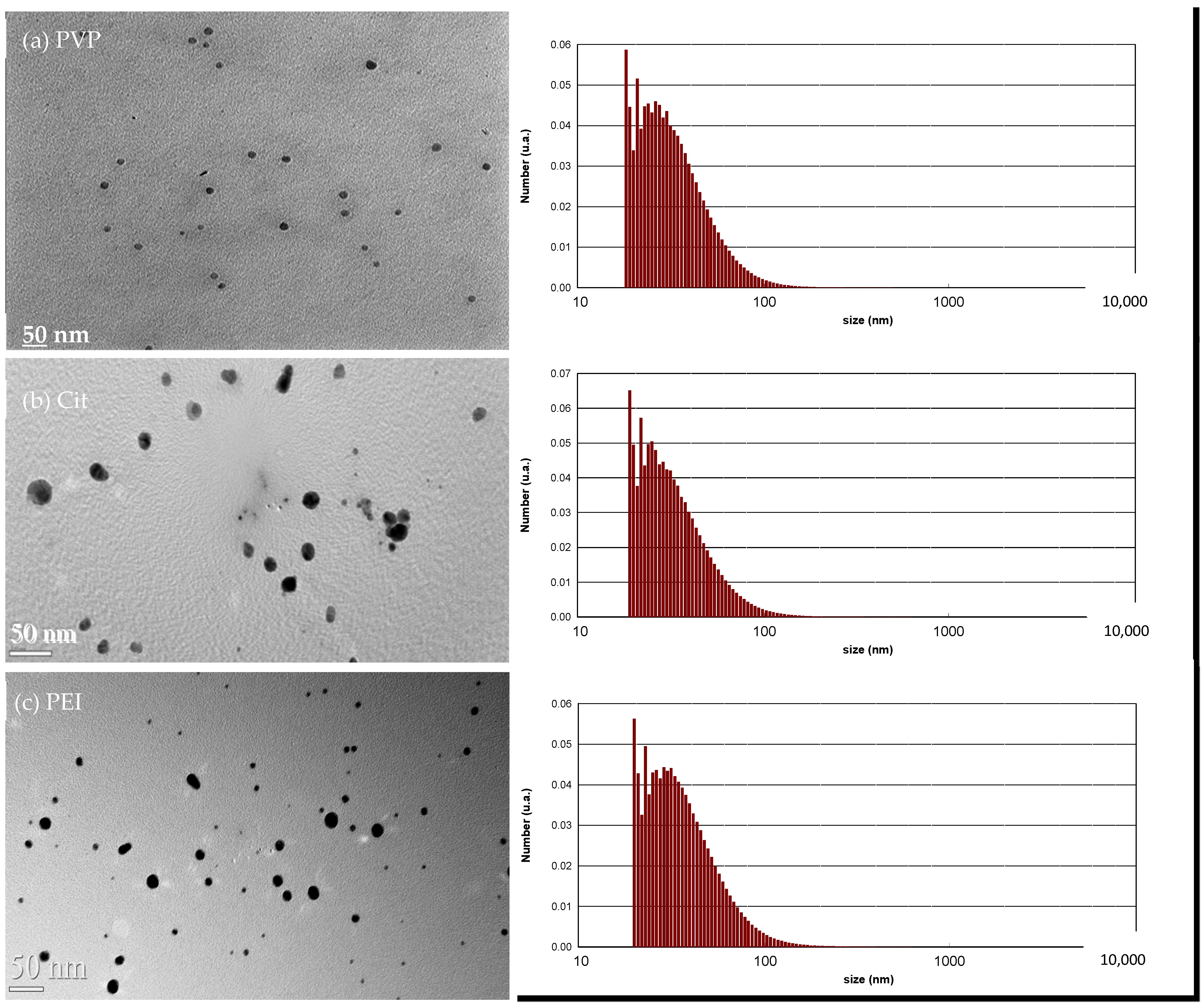
2.1. Characterization of AgNPs
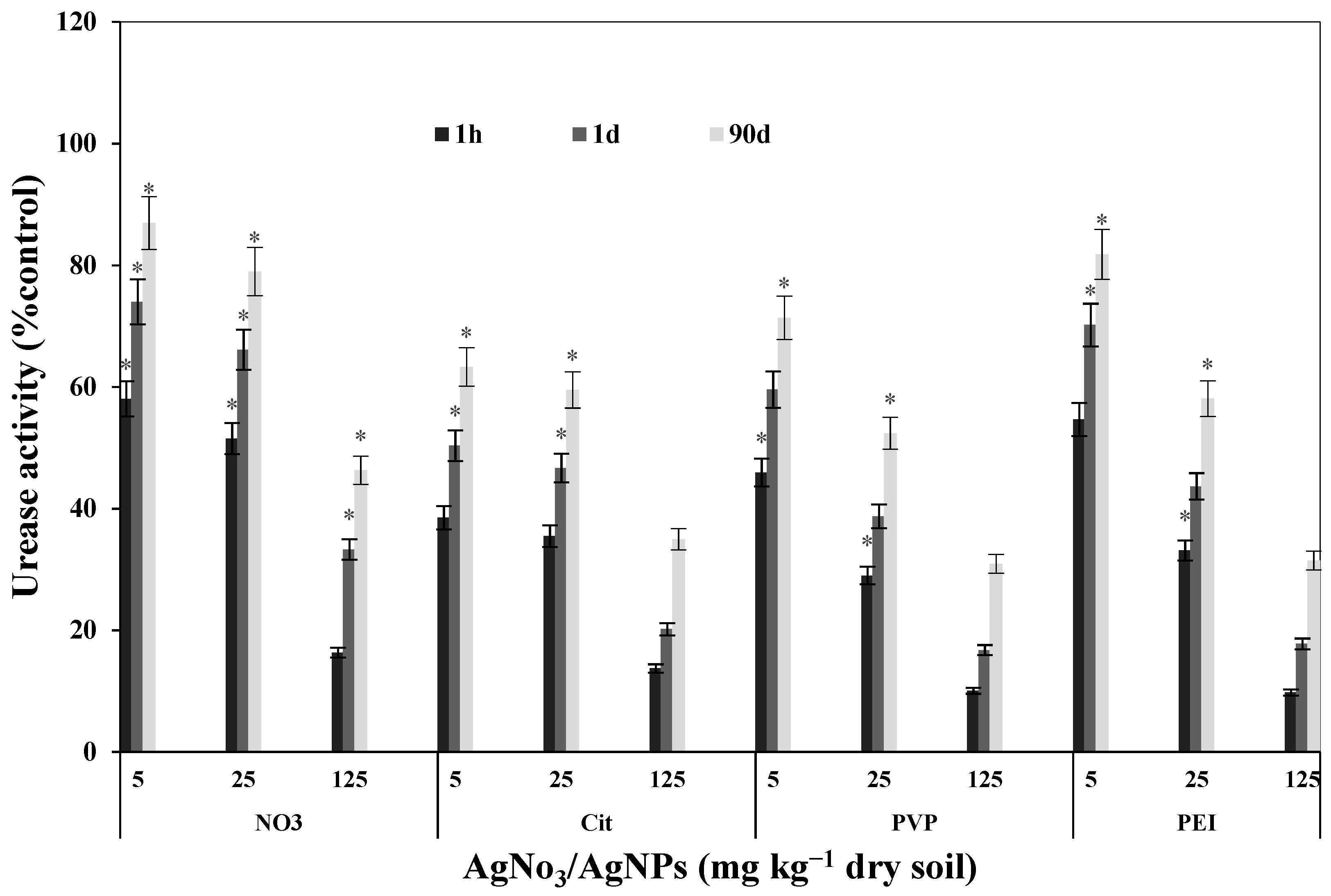
2.2. Urease Activity
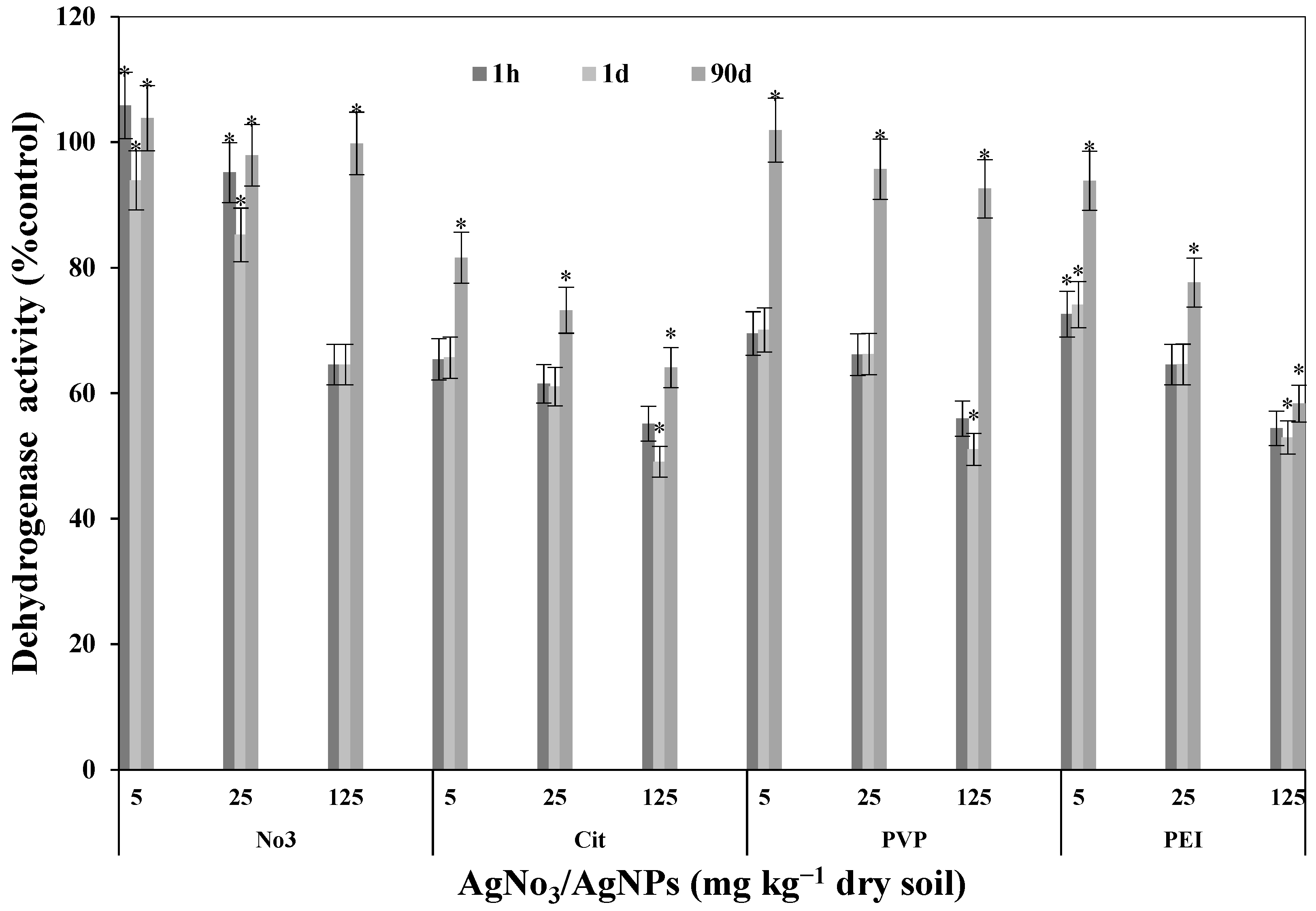
2.3. Dehydrogenase Activity
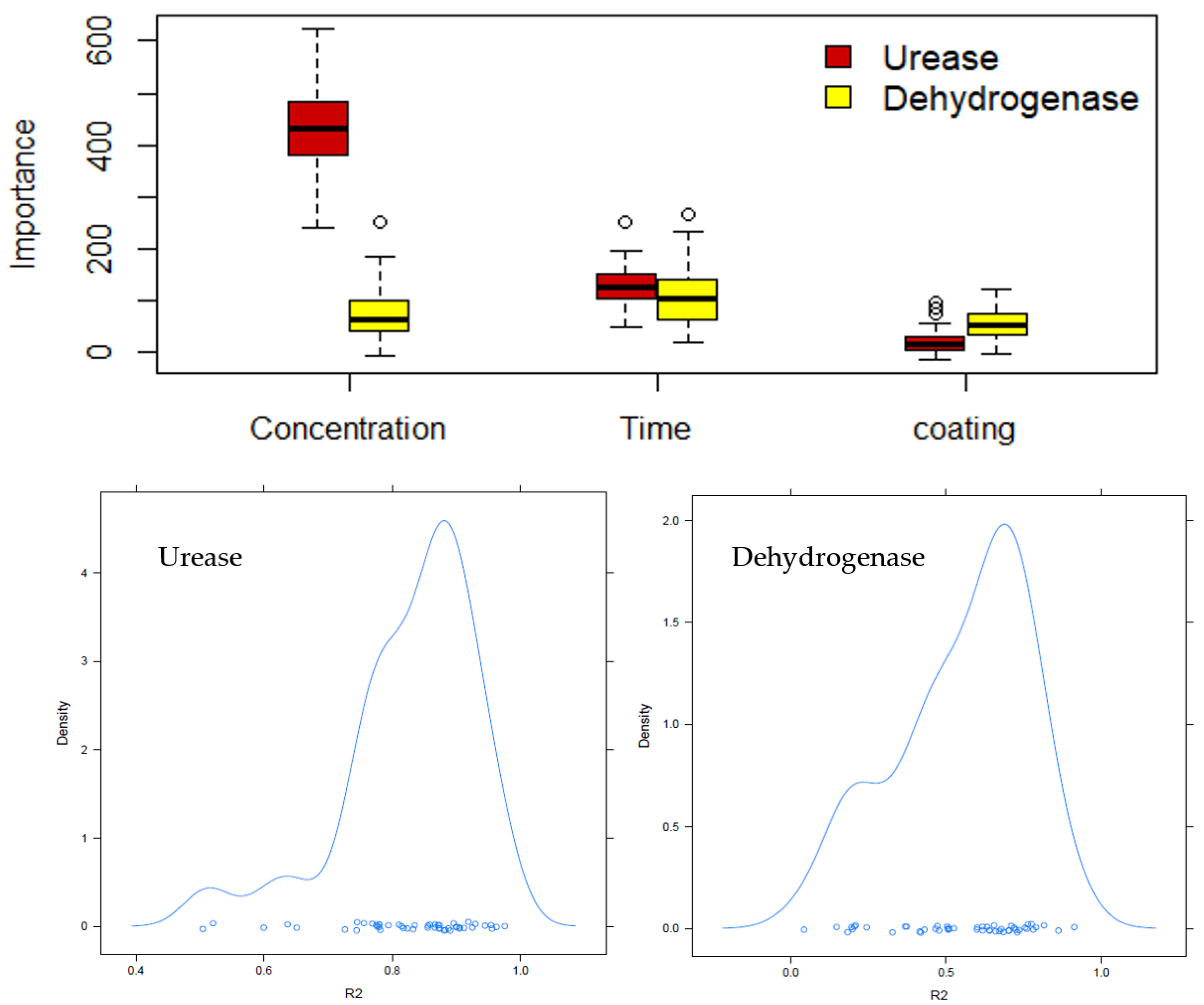
2.4. Random Forest
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Samples
3.2. Characterization of AgNPs
3.3. Urease Activity
3.4. Dehydrogenase Activity
3.5. Random Forest
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sotiriou, B.G.A.; Sannomiya, T.; Teleki, A.; Krumeich, F.; Vörös, J.; Pratsinis, S.E. Non-Toxic Dry-Coated Nanosilver for Plasmonic Biosensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 4250–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawoud, T.M.; Yassin, M.A.; El-Samawaty, A.R.M.; Elgorban, A.M. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Nigrospora Oryzae Showed Antifungal Activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Nuñez, N.V.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. Mode of Antiviral Action of Silver Nanoparticles against HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrent, L.; Iglesias, M.; Hidalgo, M.; Marguí, E. Analytical Capabilities of Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry for Silver Nanoparticles Determination in Soil Adsorption Studies. Spectrochim. Acta-Part B At. Spectrosc. 2016, 126, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braakhuis, H.M.; Cassee, F.R.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; De La Fonteyne, L.J.J.; Oomen, A.G.; Krystek, P.; De Jong, W.H.; Van Loveren, H.; Park, M.V.D.Z. Identification of the Appropriate Dose Metric for Pulmonary Inflammation of Silver Nanoparticles in an Inhalation Toxicity Study. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grün, A.L.; Manz, W.; Kohl, Y.L.; Meier, F.; Straskraba, S.; Jost, C.; Drexel, R.; Emmerling, C. Impact of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNP) on Soil Microbial Community Depending on Functionalization, Concentration, Exposure Time, and Soil Texture. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro, E.; Piccapietra, F.; Wagner, B.; Wagner, B.; Marconi, F.; Marconi, F.; Kaegi, R.; Kaegi, R.; Odzak, N.; Odzak, N. Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles To. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho, P.S.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; Lofts, S.; Svendsen, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Soil: Fate, Behavior, and Effects on Soil Invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlich, K.; Klawonn, T.; Terytze, K.; Hund-Rinke, K. Hazard Assessment of a Silver Nanoparticle in Soil Applied via Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2013, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourdineaud, J.-P.; Štambuk, A.; Šrut, M.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Ivanković, D.; Lisjak, D.; Sauerborn Klobučar, R.; Dragun, Z.; Bačić, N.; Klobučar, G.I. V Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Effects to the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida–the Importance of Tissue over Soil Concentrations. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatpour, S.; Shirvani, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Nourbakhsh, F.; Bazarganipour, M. Dose–Response Effects of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Nitrate on Microbial and Enzyme Activities in Calcareous Soils. Geoderma 2017, 285, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.J.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Z.G.; Fu, S.L. Enzyme Activities of Urban Soils under Different Land Use in the Shenzhen City, China. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, C.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.-S.; Yan, C.-N.; Liu, J.-L.; Jiang, Y.-D. Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Soil Enzyme Activity of Different Wetland Plant Soil Systems. Soil Sediment Contam. 2017, 26, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviozzi, A.; Levi-Minzi, R.; Cardelli, R.; Riffaldi, R. A Comparison of Soil Quality in Adjacent Cultivated, Forest and Native Grassland Soils. Plant Soil 2001, 233, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Dick, R.P. Soil Enzyme Activity: A Brief History and Biochemistry as a Basis for Appropriate Interpretations and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandick, A.K.; Dick, R.P. Field Management Effects on Soil Enzyme Activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.M.; Oleksyszyn, M. Enzyme Activities and Carbon Dioxide Flux in a Sonoran Desert Urban Ecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Xue, Y.; Eivazi, F.; Afrasiabi, Z. Size, Concentration, Coating, and Exposure Time Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on the Activities of Selected Soil Enzymes. Geoderma 2021, 381, 114682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, S.M.; Tilton, R.D.; Lowry, G. V Critical Review: Impacts of Macromolecular Coatings on Critical Physicochemical Processes Controlling Environmental Fate of Nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 283–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.R.; Batley, G.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Croteau, M.; Handy, R.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Judy, J.D.; Schirmer, K. Nanomaterials in the Environment: Behavior, Fate, Bioavailability, and Effects—an Updated Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2029–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, L.P.; Chatterjee, A.; Acharya, K.; De, P.; Das, M. Enzyme Responsive Nucleotide Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles with Effective Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activity. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1538–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E. The Role of Surface Charge in Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Medical Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowry, G.V.; Gregory, K.B.; Apte, S.C.; Lead, J.R. Transformations of Nanomaterials in the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6893–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saei, A.A.; Yazdani, M.; Lohse, S.E.; Bakhtiary, Z.; Serpooshan, V.; Ghavami, M.; Asadian, M.; Mashaghi, S.; Dreaden, E.C.; Mashaghi, A. Nanoparticle Surface Functionality Dictates Cellular and Systemic Toxicity. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 6578–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Harper, B.J.; Harper, S.L. Differential Dissolution and Toxicity of Surface Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles in Small-Scale Microcosms: Impacts of Community Complexity. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotze, E.M.; Phenrat, T.; Lowry, G.V. Nanoparticle Aggregation: Challenges to Understanding Transport and Reactivity in the Environment. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gitipour, A.; Thiel, S.W.; Scheckel, K.G.; Tolaymat, T. Anaerobic Toxicity of Cationic Silver Nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, Y.; Hunting, E.R.; Wouters, M.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijver, M.G. Silver Nanoparticles, Ions, and Shape Governing Soil Microbial Functional Diversity: Nano Shapes Micro. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grün, A.-L.; Scheid, P.; Hauröder, B.; Emmerling, C.; Manz, W. Assessment of the Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on the Relevant Soil Protozoan Genus Acanthamoeba. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2017, 180, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, A.-L.; Straskraba, S.; Schulz, S.; Schloter, M.; Emmerling, C. Long-Term Effects of Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles on Microbial Biomass, Enzyme Activity, and Functional Genes Involved in the Nitrogen Cycle of Loamy Soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 69, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; LWW: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1954; Volume 78, ISBN 0038-075X. [Google Scholar]
- Loeppert, R.H.; Suarez, D.L. Carbonate and Gypsum. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3. Chemical Methods; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 437–474. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of the Degtjareff Method for Determining Soil Organic Matter, and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bache, B.W. The Measurement of Cation Exchange Capacity of Soils. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1976, 27, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A. Water Retention: Laboratory Methods. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods; American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; Volume 5, pp. 635–662. [Google Scholar]
- Keeney, D.R.; Nelson, D.W. Nitrogen Inorganic Forms. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Agronomy Monograph 9, Part 2; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; Volume 643. [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Assay of Urease Activity in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, A. The Determination of the Dehydrogenase Activity in Soil by Means of TTC (Triphenyltetrazolium). Soil Biol. 1966, 6, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Jośko, I.; Oleszczuk, P.; Futa, B. The Effect of Inorganic Nanoparticles (ZnO, Cr2O3, CuO and Ni) and Their Bulk Counterparts on Enzyme Activities in Different Soils. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.J. Evidence for the Inhibitory Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on the Activities of Soil Exoenzymes. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakin, A.; Garzetti, D.; Bouabe, H.; Sprague, L.D. Chapter 73—Yersinia Enterocolitica. In Molecular Medical Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Tang, Y.-W., Sussman, M., Liu, D., Poxton, I., Schwartzman, J.B.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 1319–1344. ISBN 978-0-12-397169-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, H.A.H. Ureolytic Microorganisms and Soil Fertility: A Review. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 2565–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, J.F.; Kistiakowsky, G.B.; Kridl, A.G. Inhibition of Urease by Silver Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuvel, S.; Subramanian, B.; Ponnuraj, K. Conformational Change Results in Loss of Enzymatic Activity of Jack Bean Urease on Its Interaction with Silver Nanoparticle. Protein J. 2015, 34, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, L.B.; Zhang, Z.Y. Adsorption of Cations onto the Surfaces of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 257, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, C.F.; Storey, S.; Clipson, N.; Doyle, E. Concentration-Dependent Responses of Soil Bacterial, Fungal and Nitrifying Communities to Silver Nano and Micron Particles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18693–18704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, W. Quantitative Assessment on Soil Enzyme Activities of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils with Various Soil Properties. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigginton, N.S.; De Titta, A.; Piccapietra, F.; Dobias, J.A.N.; Nesatyy, V.J.; Suter, M.J.F.; Bernier-Latmani, R. Binding of Silver Nanoparticles to Bacterial Proteins Depends on Surface Modifications and Inhibits Enzymatic Activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Quensen, J.; Mathieu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Pyrosequencing Reveals Higher Impact of Silver Nanoparticles than Ag+ on the Microbial Community Structure of Activated Sludge. Water Res. 2014, 48, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, P.; Mao, L.; Zhi, Y.; Shi, W. Assessment of Effects of Heavy Metals Combined Pollution on Soil Enzyme Activities and Microbial Community Structure: Modified Ecological Dose–Response Model and PCR-RAPD. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.N.; Allen, A.J.; MacCuspie, R.I.; Hackley, V.A. Dissolution, Agglomerate Morphology, and Stability Limits of Protein-Coated Silver Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 11442–11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of Silver Nanoparticle Release, Transformation and Toxicity: A Critical Review of Current Knowledge and Recommendations for Future Studies and Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 2295–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadishad, B.; Chahal, S.; Akbari, A.; Cianciarelli, V.; Azodi, M.; Ghoshal, S.; Tufenkji, N. Amendment of Agricultural Soil with Metal Nanoparticles: Effects on Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Community Composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1908–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadishad, B.; Chahal, S.; Cianciarelli, V.; Zhou, K.; Tufenkji, N. Effect of Gold Nanoparticles on Extracellular Nutrient-Cycling Enzyme Activity and Bacterial Community in Soil Slurries: Role of Nanoparticle Size and Surface Coating. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmatpour, S.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Shirvani, M.; Šimůnek, J. Transport of Silver Nanoparticles in Intact Columns of Calcareous Soils: The Role of Flow Conditions and Soil Texture. Geoderma 2018, 322, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makama, S.L. An In Vitro—In Vivo Integrated Approach for Hazard and Risk Assessment of Silver Nanoparticles for Soil Organisms; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9789462578432. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.97 |
| EC (dS·m−1) | 0.45 |
| CEC (cmolc·kg−1) | 8.5 |
| OC (%) | 0.58 |
| CaCO3 (%) | 17 |
| Sand (%) | 63 |
| Silt (%) | 13.3 |
| Clay (%) | 23.7 |
| Texture class | Sandy clay loam |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bazoobandi, A.; Fotovat, A.; Halajnia, A.; Philippe, A. Does the Nano Character and Type of Nano Silver Coating Affect Its Influence on Calcareous Soil Enzymes Activity? Coatings 2022, 12, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121968
Bazoobandi A, Fotovat A, Halajnia A, Philippe A. Does the Nano Character and Type of Nano Silver Coating Affect Its Influence on Calcareous Soil Enzymes Activity? Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121968
Chicago/Turabian StyleBazoobandi, Ahmad, Amir Fotovat, Akram Halajnia, and Allan Philippe. 2022. "Does the Nano Character and Type of Nano Silver Coating Affect Its Influence on Calcareous Soil Enzymes Activity?" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121968
APA StyleBazoobandi, A., Fotovat, A., Halajnia, A., & Philippe, A. (2022). Does the Nano Character and Type of Nano Silver Coating Affect Its Influence on Calcareous Soil Enzymes Activity? Coatings, 12(12), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121968






