3.1. PEO Treatments
Titanium dioxide formation in an alkaline solution may be the result of two concomitant reactions,
with O
2− and OH
− coming from water spitting and basicity present at the oxide–electrolyte interface. Those reactions contribute to the formation of a progressively thicker barrier, causing, beyond a certain threshold, anodic breakdown to occur. This extensively contributes to the retention, according to complex plasma and electrochemical reactions, of Si-containing species, such as SiO
2.
The addition of organic molecules can significantly affect the kinetics of the above equations, resulting in peculiar features investigated in the following paragraphs.
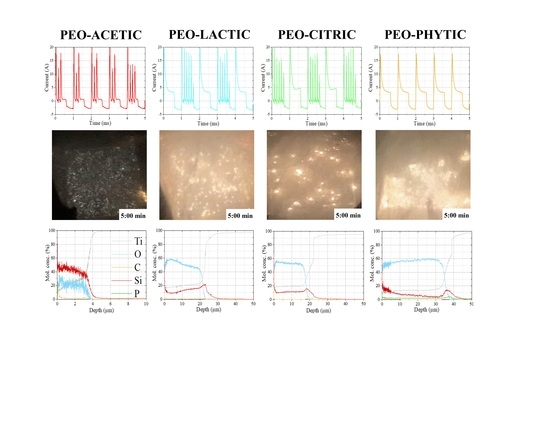
For this reason, voltage (
V)–time curves are presented in
Figure 2 for all PEO treatments. It was possible to see that the use of different organic additives had a strong influence when sparks started to manifest over the electrode surface (~50 V, in present conditions). In particular, abrupt
V oscillations were observed when acetic acid (
Figure 2a) was added to the alkaline bath, with peaks reaching ~170 V. The opposite holds true in case of phytic acid (
Figure 2d), with a
V trend very well reproduced, showing almost the absence of strong
V surges, confirming the presence of less destructive discharges responsible to induce strong variations of the impedance of the electrochemical cell.
To obtain a deeper insight regarding PEO regime evolution and possible differences among the different solutions tested, current (
I)–time plots were collected at 300 s of treatment and are shown in
Figure 3 at the millisecond time scale. According to previous
V features, apart from an initial capacitive
I peak, arising from the charging of the electrical double layer (EDL), only phytic acid (
Figure 3d) presented a smooth decay until the
I plateau (responsible for oxide growth) was reached and maintained for the entire duration of the anodic half-part of the duty (60%).
Therefore, the absence of
I surges is an indication of the higher ionic contribution with respect to the electronic one required to sustain the multitude of sparks. Similarities were instead observed in
Figure 3b,c confirming the close trend highlighted in
Figure 2b,c, where an intermediate behavior between phytic and acetic acids (the latter probably showing a lower level of ionic current) was established. Interestingly, the trend seemed to correlate not only with the acidity constant of the organic additives used in the present analysis and corresponding to ~1.5 for phytic, ~3.13 for citric, ~3.86 for lactic and ~4.76 for acetic acids [
28,
29] but also and more importantly with the molecular weight of the organic acids considered to be fully deprotonated in such a high-pH environment.
The integration of the anodic and cathodic
I contributions and their ratio
are very informative to account for the plasma regime present over the electrode. In fact, values > 1 are indicative of “soft plasma” [
30,
31] control, where the higher amount of cathodic
I transmitted to the sample favors the suppression of intense discharges responsible for oxide destruction and loss of protectiveness. However, the
R values collected in
Table 2 are far from indicative of the occurrence of such phenomenon where a higher amount of transmitted anodic charge was always verified. Two
R values were collected in case of PEO-LA and PEO-CI, compatibly with the two different
I behaviors observed. A higher amount of anodic
I was transmitted when no peak was present, with values tending to the one observed for phytic acid (0.31).
3.2. Oxide Morphology and Composition
The samples’ bulk structure was investigated according to XRD with diffractograms collected in
Figure 4.
It was possible to see that all the samples presented both amorphous and crystalline characters with anatase, rutile and low quartz as the main crystal structures. Acetic acid (
Figure 3a) promoted a lower coating growth, compared with other solutions, as the Ti metal intensities were substantially higher. Nonetheless, the presence of both TiO
2 polymorphs, i.e., anatase and rutile, was detected. On the other hand, if the electrolytic bath was enriched with lactic (
Figure 4b) or citric (
Figure 4c) acid, rutile was the main phase composing the coating. Moreover, some intensities related to low quartz appeared, confirming a partial transition of amorphous silica to the crystalline form. PEO carried out in phytic acid induced the largest amount of amorphous SiO
2 formation according to the broad feature observed in
Figure 4d in the 2θ range ~28 ÷ 35°. It is not clear if the lower anatase and rutile reflections were related to a lower overall amount or to a sort of encapsulation effect [
32], caused by the SiO
2 layer that, generally, disposes in the top portion of the oxide coatings [
33,
34], thus altering the intensities of the peaks indicative of the underlying phases. Rietveld XRD quantification allowed us to estimate the relative amount of the crystalline phases present in the samples. The results are collected in
Table 3.
It is possible to notice how the quantity of low quartz scaled with the
I trend previously observed. In fact, phytic acid presenting a relatively smooth
I distribution (see
Figure 4d) did not allow crystalline SiO
2 to stabilize; however, this was enhanced when current surges manifested.
After encapsulation, in epoxy resin, and cutting by metal shearing, sample cross-sections were analyzed by SEM-EDS and the results are highlighted in
Figure 5. In agreement with previous observations, advanced by looking at Ti XRD reflections, PEO-AC determined the lower oxide growth (~4.5 µm), while, when using phytic acid as organic additive, a coating of ~32.5 µm developed. Similar
I trends resulted in comparable thicknesses for the samples PEO-LA (~19.35 µm) and PEO-CI (~19.53 µm). Morphology was greatly affected by the type of additive used in the electrolytic bath; in fact, when using acetic acid, a coating mainly constituted by agglomerated particles resulted. Two layers composed PEO-LA, PEO-CI and PEO-PH (see
Figure 5g,m,s), namely, one in contact with the metal with similar features to PEO-AC and one thick upper region with evidence of densification occurred by the plasma generated during the process. PEO-PH, in particular, appeared quite friable, as part of the coating was often detached during the encapsulation procedure in the epoxy resin.
This was confirmed by looking at the coating weights collected in
Section 3.3, where, despite the larger thickness, PEO-PH presented a lower weight gain than both PEO-LA and PEO-CI. The coating growth rates were evaluated, presenting 0.84 µm·min
−1 for PEO-AC, 3.63 µm·min
−1 for PEO-LA, 3.66 µm·min
−1 for PEO-CI and 6.09 µm·min
−1 for PEO-PH. These results suggest an important influence of the additive used on the kinetics of growth of the coatings; this aspect is deepened in
Section 4.
The EDS analysis over oxide cross-sections allowed us to discern the presence of both elements belonging to the electrolyte (such as Si, Na, O and C, plus P for PEO-PH) and to the substrate (Ti). In particular, Si was found to be very abundant for all the oxides apart from PEO-PH where accumulation in the form of agglomerates resulted. In addition, Na and C were present inside the coating, mainly disposing in the upper oxide portion, sign that these cations were mainly incorporated inside the material during the plasma event. This is particularly true for PEO-AC and PEO-PH, demonstrating a higher C retention even in the deepest region of the coating. The addition of phytic acid, instead, permitted P to accumulate inside the coating, disposing, in particular, at the oxide bottom.
The SEM-EDS analysis confined to the samples’ surfaces (
Figure 6) allowed us to distinguish different morphologies depending on the organic additive used.
In particular, when using acetic acid, a porous surface, common [
35] to PEO treatments performed in low pH environments [
3,
7], developed with pore diameters of ~0.98 ± 0.3 µm. The pores’ number was substantially reduced when using lactic (
Figure 6 and
Figure 7) and citric (
Figure 6m, even if their size was markedly increased (~4.64 ± 2.1 µm for PEO-LA and ~18.5 ± 3.4 µm for PEO-CI). Moreover, when using lactic acid, acicular deposits formed over the surface, demonstrating a homogeneous elemental composition with respect to the background. Apart from the sample PEO-AC, large cracks cut the sample surfaces departing from the holes left by discharges, a result compatible with the stress release generated by the abrupt cooling of the melted oxide. A very different morphology was observed when dealing with phytic acid, characterized by roundly shaped agglomerates, sometimes crossed by pores (diameter of ~4.34 ± 1.1 µm) as a result of a spark event.
The presence of these hollow protuberances is indicative of the condensation of a molten oxide with high viscosity and presence of abundant gas evolution exerting high pressure responsible for this hemispherical shape formation [
36]. Irrespectively of the organic additive used, Ti, O, Si, Na and C were always present over the electrode surfaces. Ti in particular seemed to concentrate, in the case of PEO-LA, around the central hole highlighted in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7, while it seemed rather homogeneously distributed over the surface for all the other samples. Similar results manifested when looking at the Si, O and Na signals for PEO-LA, PEO-CI and PEO-PH, indicating that those elements actively participated in the discharge process. It is difficult to draw similar observations for the sample PEO-AC, as the relatively homogeneous morphology did not allow us to separate relevant features from EDS inspection. Interestingly, a relatively high C signal was detected in
Figure 6l,r in the case of PEO-LA and PEO-CI near the hole boundaries.
For the elemental quantifications purpose, a GD-OES analysis was performed and the results are displayed in
Figure 7, with element quantities expressed as molar concentrations (%).
The thickness values seemed to well agree with the data extracted via SEM, confirming PEO-AC to be the thinner oxide and the addition of phytic to favor the growth of the thickest coating. Looking at the molar concentration of the elements present in the sample PEO-AC (
Figure 7a) permitted us to speculate the synthesis of structures different from TiO
2 and SiO
2, such as titanium silicide. However, as the former phase was not detected by the previous XRD analysis, it should be assumed the formation of an amorphous structure if present. In the case of PEO-LA and PEO-CI, similar elemental profiles were observed to agree with the previous
I trend and XRD analysis, highlighting TiO
2 polymorphs, amorphous SiO
2 and low quartz as the main phases. Interestingly, both PEO-CI and PEO-PH presented a smoother transition of Ti in correspondence of the oxide–metal interface, probably according to the formation of low valence oxide phases localized in the oxide region immediately in contact with the metallic substrate [
37]. Apart from the sample PEO-AC, a Si peak denoted accumulation in correspondence of the metal–oxide interfacial region. C content was relatively low in all cases apart from the sample PEO-AC, correlating with previous EDS observations, while the presence of P for the sample PEO-PH was confirmed and enhanced at the coating bottom.
Light emitted during the electrochemical process was analyzed according to in situ OES and collected in the form of spectra as in
Figure 8.
The main elements participating in the optical emission events were labeled according to the NIST database [
38]. Generally, the most intense lines belonged to Ti, O, C and Si species. Interestingly, in case of PEO-AC, where a less developed spectrum agrees with a lower plasma intensity, Ti I (594.175 nm) was the most intense line, as opposed to other conditions facing Ti II (590.163 nm) as the species responsible for the most relevant optical transition. Apart from PEO-AC, all the treatments produced the transition line Ti IV (at 624.774 nm) related to the Ti
3+ species. In addition, neutral carbon (C I) was always detected, while C
2+ (C III at 540.836 nm) contribution was registered only when using phytic acid. The same result can be highlighted for Na II, O II and O IV, while O III was present in all treatments apart from PEO-AC.
3.3. Electrochemical Tests
Corrosion resistance was tested in free corrosion conditions in sulfuric acid. Weight losses were then converted into corrosion rates, collected in
Table 4, by subtracting the weight of the coating introduced during PEO; this allowed us to limit the analysis to substrate dissolution only.
Despite the lower thickness, acetic acid addition allowed all the other materials to be outperformed by almost one order of magnitude, resulting in a corrosion performance even better than the one registered by Ti grade 7 (C.R. ~0.21 mm·year
−1) [
39] immersed in the same solution. The corrosion rates presented significant scattering. This can be attributed to the presence of weak spots localized at the samples’ edges determined by the establishment of long-lasting plasma as the result of electric field amplification.
To further investigate the response of the PEO oxides, EIS tests were carried out in the previous solution and the results are plotted in
Figure 9 in the form of Nyquist and Bode representations.
Imaginary impedance versus frequency provides a rich source of information of the system under investigation. In fact, being the latter quantity independent of solution resistance, it is possible to extract the characteristic frequency of the process occurring over the electrode surface simply by reading the value in correspondence of the -Z″ peak. The presence of one peak is indicative of a single activation-energy-controlled corrosion reaction and the low relaxation frequency allows us to speculate a reaction controlled by diffusion of charged species inside the porosity of the oxide. As the E
corr was always anodic with respect to the conduction band of the material (estimated ~ −0.2 V/SSC
sat. in present conditions), no oxide reduction was expected to occur during the EIS tests. Higher impedance values were observed in the cases of PEO-PH and PEO-AC, presenting larger semicircle diameters and a lower characteristic frequency, sign that diffusion phenomena occurred in a slower time scale with respect to other samples. Since the slopes of the -Z″ significantly differed from +1 and −1, indicating the presence of distributed processes, a constant phase element was used instead of the capacitor in the Randles circuit (R
s-R
ct//CPE) fitting Z spectra, where R
s and R
ct are indicative of solution and charge transfer resistance. The results are collected in
Table 5.
It is possible to see how PEO-LA and PEO-CI presented considerably lower Rct than the other samples. This could be related to the high degree of crystallinity reflected in the presence of the rutile and anatase domains observed via the XRD analysis. Conversely, PEO-AC and PEO-PH were found to be less crystalline, especially the latter, presenting a higher amorphous character probably favored by the presence of P. This was considered the reason why the substantial Rct reduction. However, even if, from an electrochemical point of view, PEO-PH demonstrated enhanced surface properties, the rough architecture permitted coating debonding to occur quite early, exposing the substrate to the aggressive solution and resulting in high corrosion rates. On the other hand, PEO-AC exhibited both high Rct and debonding resistance to long-time exposure in sulfuric acid at high temperature, indicative of better overall performances in low pH service. The exponent “n” of the constant phase element, used to approximate the capacitive behavior of the system, largely deviated from 1, compatibly with the high dispersion caused by inhomogeneities and surface roughness.
Cyclic voltammetry and Tafel analysis were performed on each PEO solution with the aim of investigating the electrochemical behavior of the metal far from E
corr. An anodic peak was detected for all the solutions tested, as illustrated in
Figure 10a. According to the absence of a cathodic current peak, this wave should correspond to a dissolution phenomenon [
40], as predicted by the Pourbaix diagram [
41], leading to the formation of titanates.
However, since, after the anodic wave,
i stabilized towards low anodic values, sudden repassivation with formation of TiO
2 was expected to happen. As the anodic current peak (
iaCV) was lower, ~0.004 A·cm
−2, in the case of PEO-AC, it was reasonable to assume the adsorption of acetates to control and limit both titanates’ formation and subsequent repassivation, compatibly with the huge anodic Tafel coefficient b
a ~3780 mV·decade
−1, collected in
Table 6, after Tafel analysis. Metal passivation was more efficient when using phytic and lactic acid. This can be demonstrated by the lower cathodic current plateau,
ic, observed at very cathodic potentials limiting the kinetics of water reduction. On the other hand, in the presence of acetic acid,
ic was substantially higher, sign that, after the anodic cycle, substrate passivation was less effective. Even if these results can be used to justify the overall lower oxide growth, they do not provide explanation for why acetic acid should favor the retention of such a high level of Si inside the material, leading to the speculation about the formation of titanium silicide-like phases. The justification of the latter finding deserves more in-depth studies and will be afforded in future papers.
The two vertical black dotted lines drawn in
Figure 10a (line 1 and line 2) are indicative of the potentials at which the two EIS tests were performed for all the solutions used during PEO, i.e., 0.5 V/SSCsat. (
Figure 11a) and 1.5 V/SSC
sat. (
Figure 11b), before and in correspondence of the anodic wave observed during the CV tests. It is possible to see that one-time constant was always present, compatibly with the electrode passivity held at low anodic potentials and reactivity shown at higher voltages.
The considerably higher impedances observed in the case of PEO-AC suggest the stronger tendency of acetates to limit charge transfer reactions at the electrode, while the contrary holds true in the case of phytic acid, favoring anodic reactions to occur. Things were different if performing EIS at 1.5 V/SSC
sat, where the markedly lower impedance values and the formation of capacitive arcs, intersecting the real impedance axis, demonstrated higher dissolution currents to flow. The negative imaginary impedance plotted in
Figure 11c is very informative about the time scale of the anodic dissolution process occurring over the electrode, with time constant inferable from the maximum of the -Z″ peak. This information, combined with the charge transfer resistance R
ct, extractable from the intersection of the arc in
Figure 11b with Z′, allows the capacitance
C of the system to be calculated as in Equation (6).
where
is the characteristic frequency of the dissolution process. The results are collected in
Table 7. After
C evaluation, the capacitor equation (Equation (7)) was used to extract the oxide film thickness
d, produced according to the anodic polarization, considering a dielectric constant
ε, for amorphous TiO
2, equal to 13.7 [
42], with
A corresponding to the geometric area of the sample and
to the permittivity of vacuum.
The thickness values are coherent with the trend highlighted from the SEM analysis of the PEO oxide cross-sections, confirming smaller molecules to be more effective in anodic reactions’ inhibition and consequent film growth.