Preparation and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-W-CF Composite Coating on P110 Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Electrodes
2.3. Preparation of Ni-W-CF Coating
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
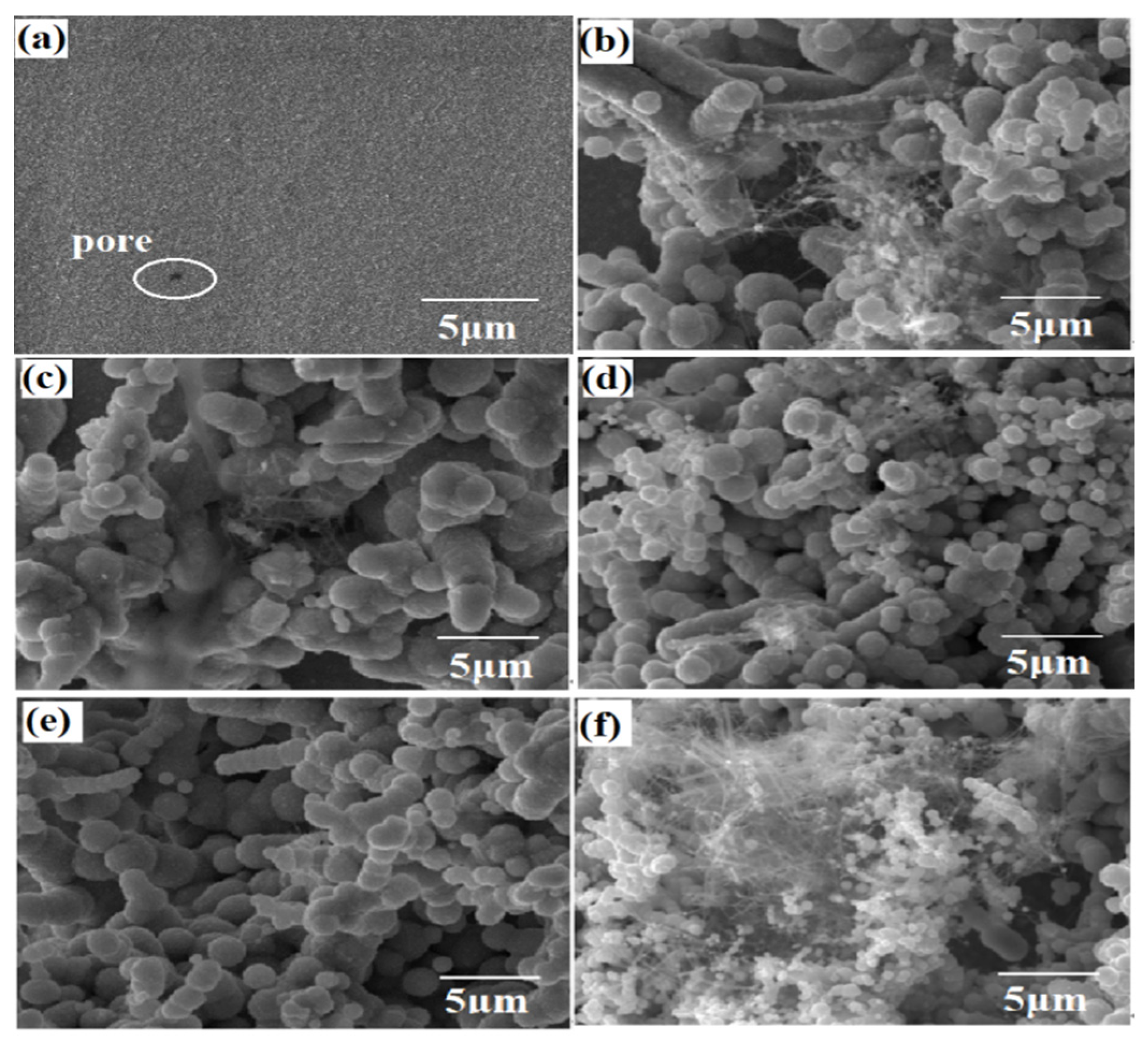
3.1. Microstructure of Coatings with Different CF Content
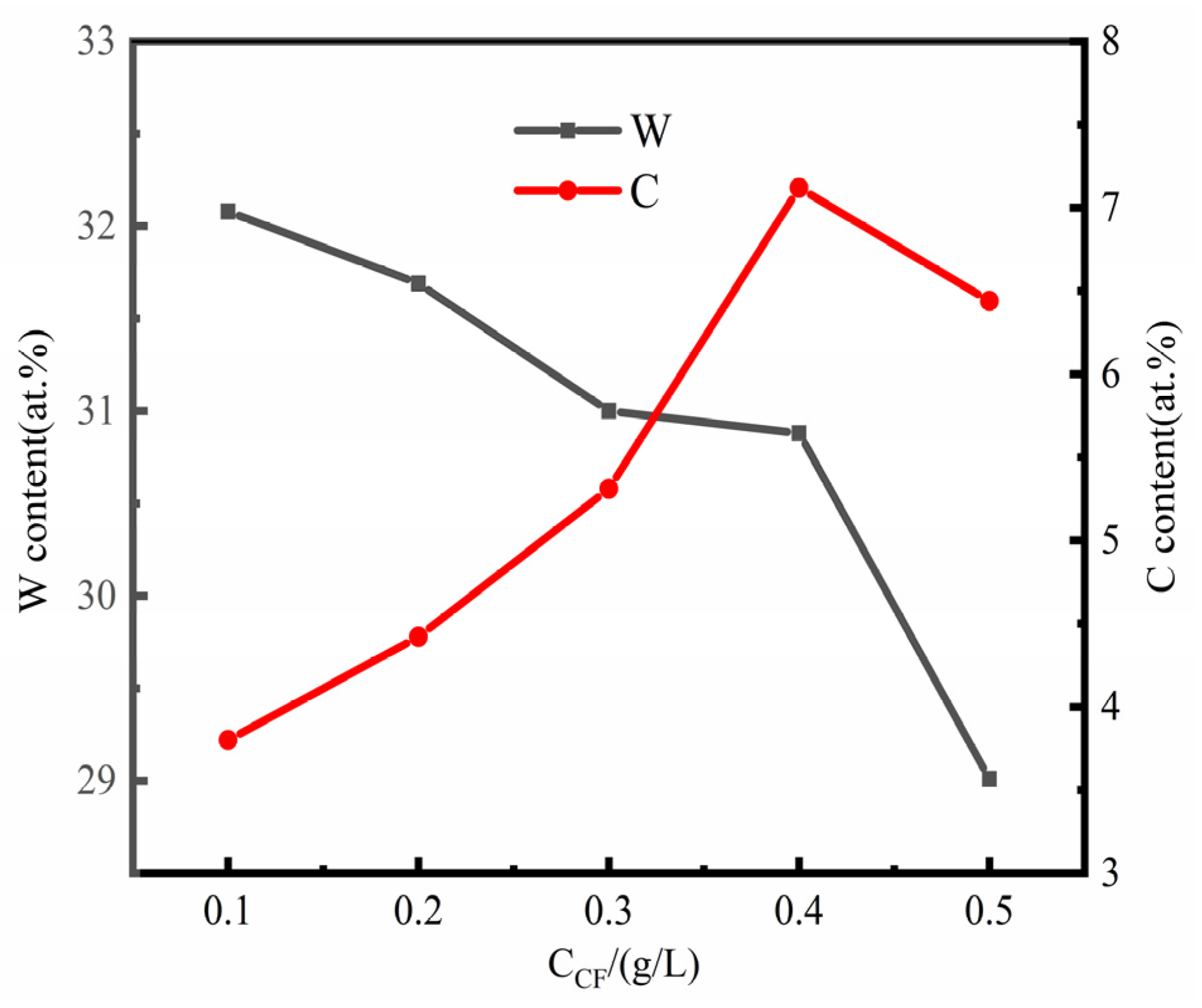
3.2. Effect of CF Concentration on Tungsten and Carbon Contents in Composite Coatings
3.3. Surface Roughness Analysis of Coating with Different CF Content
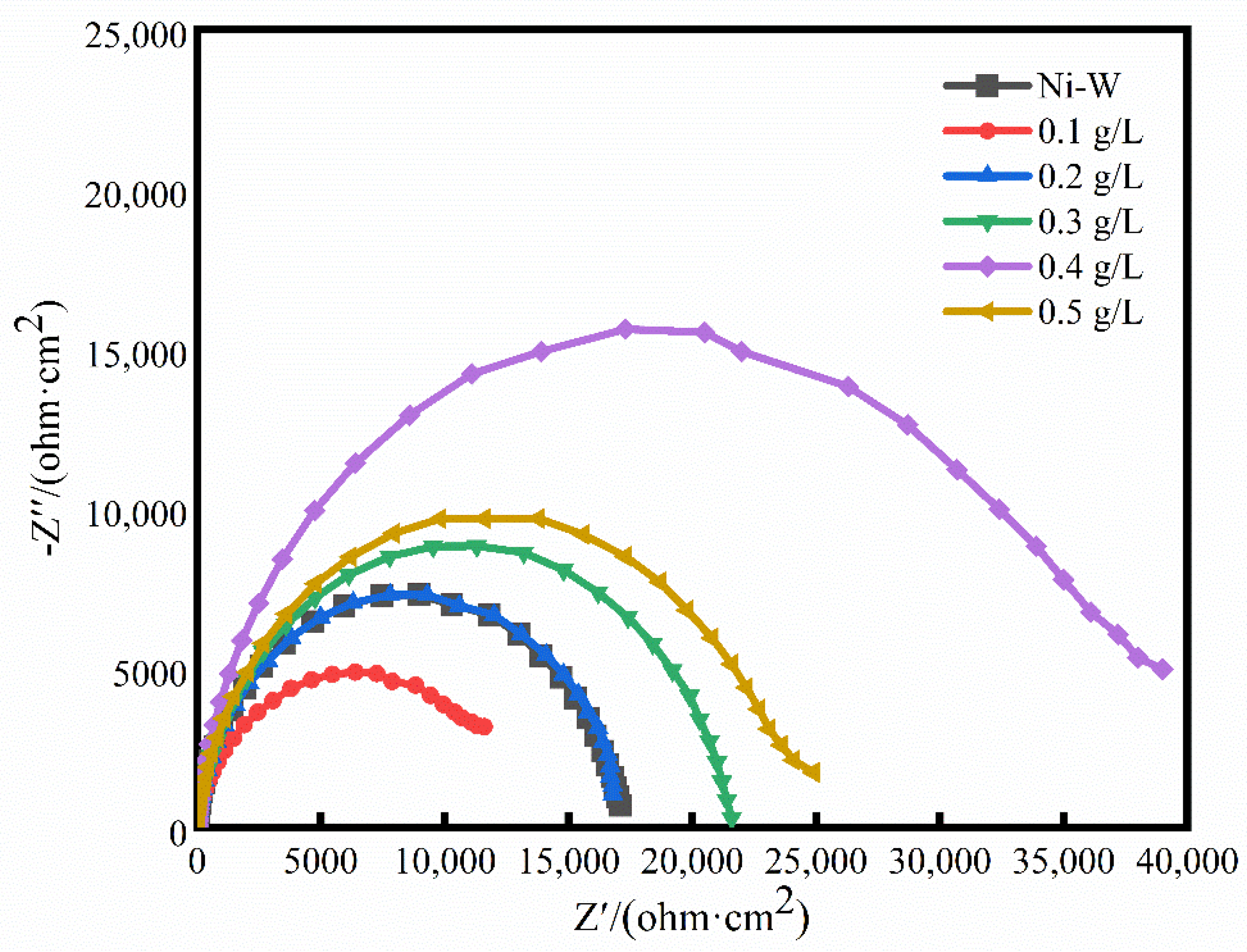
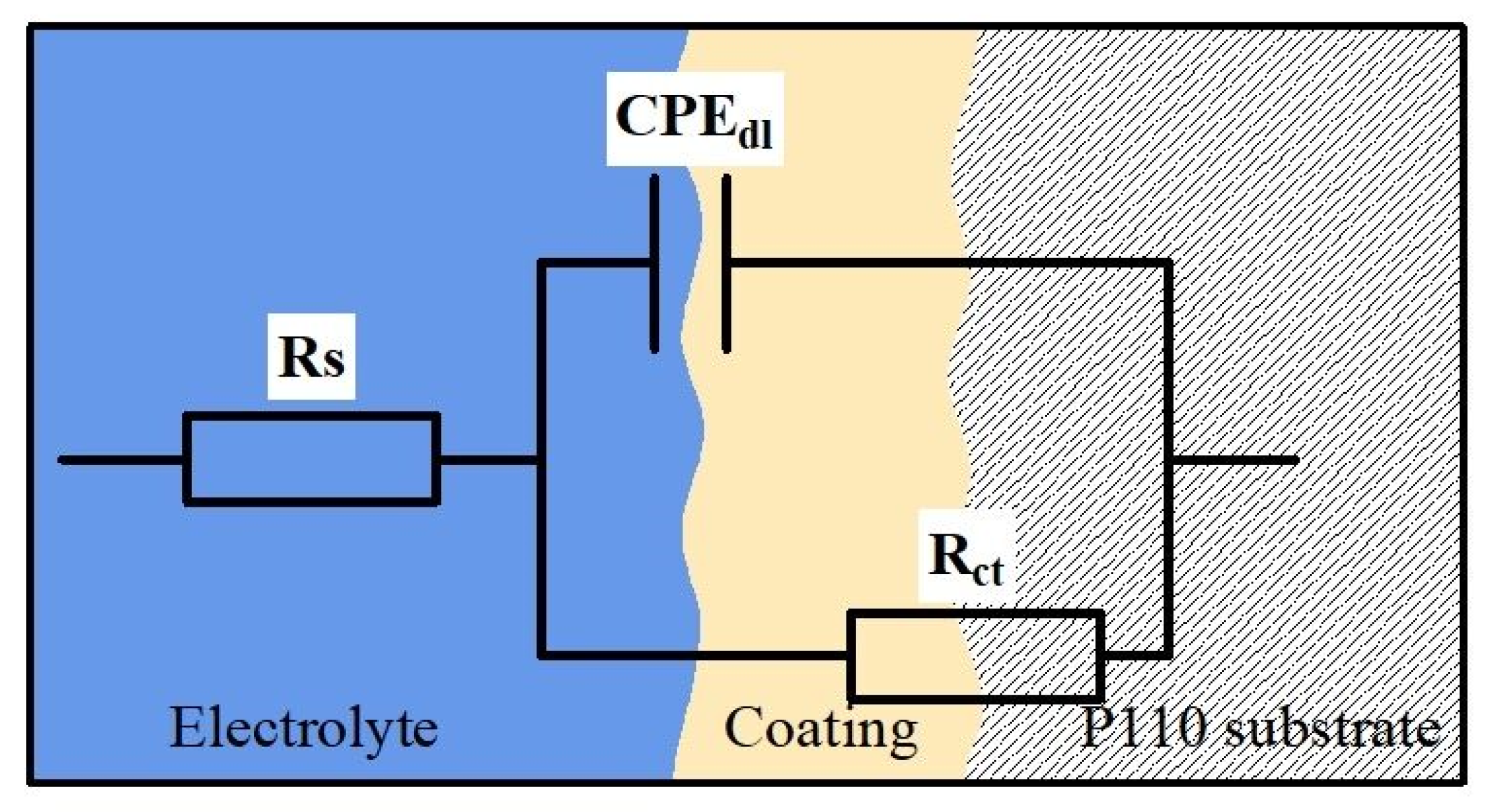
3.4. Corrosion Resistance of Coatings with Different CF Content
3.5. Formation and Corrosion Mechanism of Ni-W-CF Coating
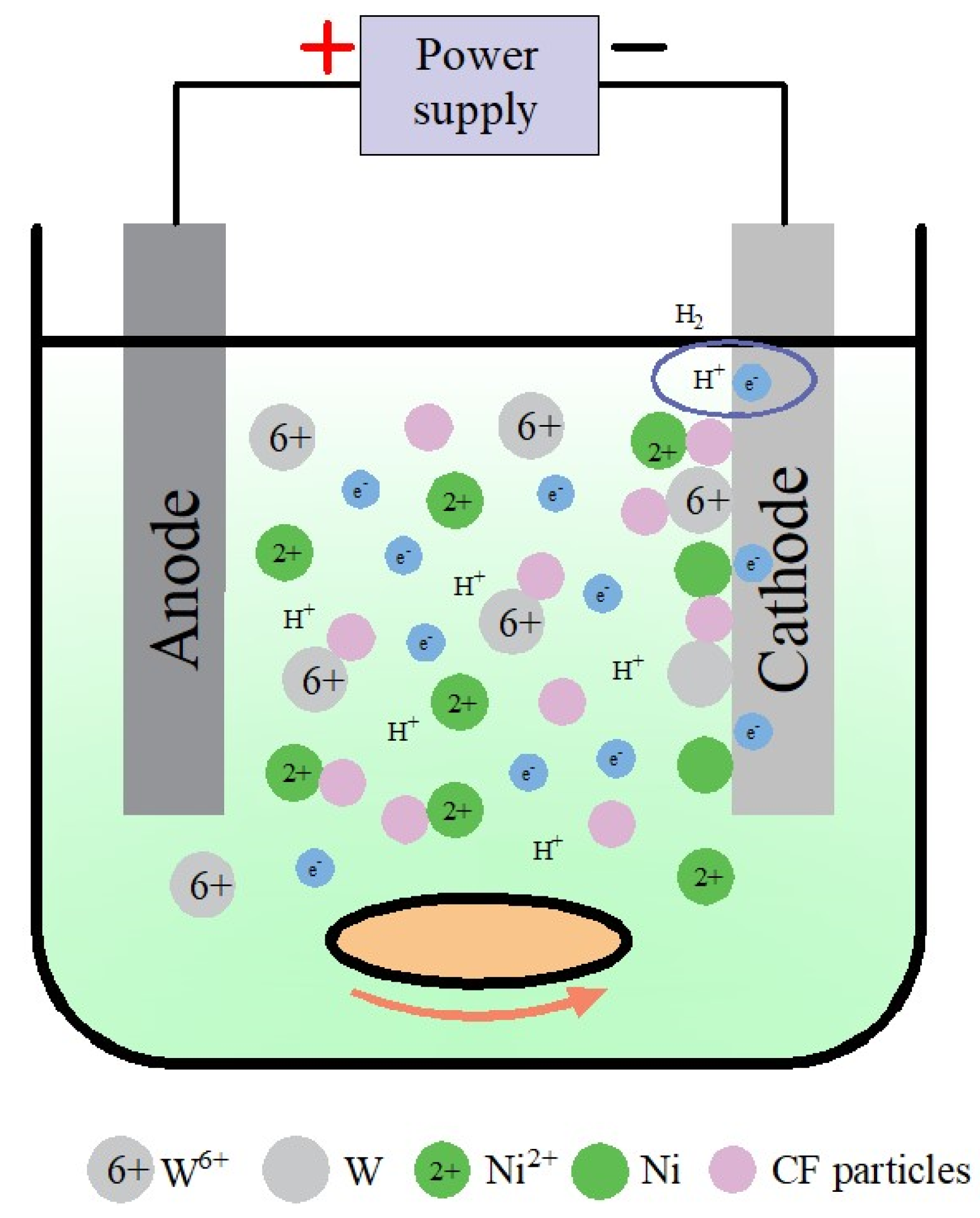
3.5.1. Formation Process of Ni-W-CF Coating
- (a)
- Ion migration: When CF particles are added to the plating solution, anionic surfactants (e.g., SDS in the plating solution in this study) adsorb around the CF particles, forming a negative surface charge, and Ni2+ may adsorb on the surface of the CF particles, resulting in the formation of a Stern layer [39]. At a high potential gradient, the Stern layer attracts negative tungsten citrate, and Ni2+ generates CF particle @Ni/W ion cloud structure on the outer surface of the CF particle. When the current is energized, Ni2+, (W6+) Citrate, CF and the CF particle @Ni/W ion cloud migrate to the cathode by electrophoresis under the action of electric field or convection.
- (b)
- Weak adsorption: The CF particles wrapped by the Ni/W ion cloud are loosely adsorbed on the cathode surface by the diffusion layer under the action of electric field force, and the adsorption is physical and reversible.
- (c)
- Reduction and strong adsorption of Ni and W: Ni2+ and (W6+) Citrate adsorbed on the cathode surface and the metal ions wrapped around the CF surface obtain electrons and are reduced to Ni and W metal atoms, which will form a strong adsorption force due to the continuously enhanced electrostatic gravitational force. The adsorption is irreversible.
- (d)
- Co-deposition: CF particles adsorbed on the electrodeposited surface are gradually wrapped by the reduced Ni and W atoms, to achieve co-deposition. With the extension of deposition time, the thickness of the coating gradually increases, forming a Ni-W-CF composite coating with a certain thickness.
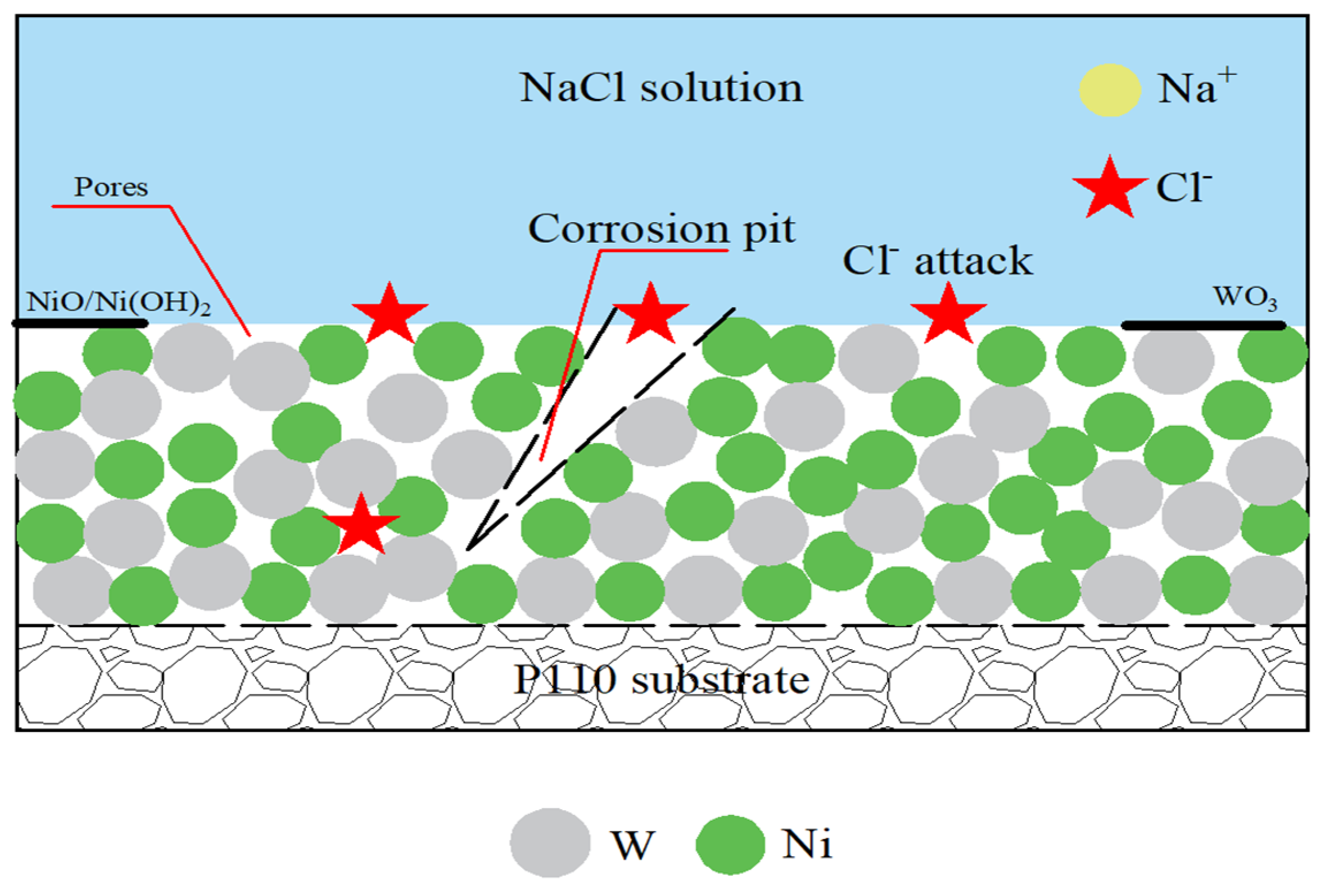
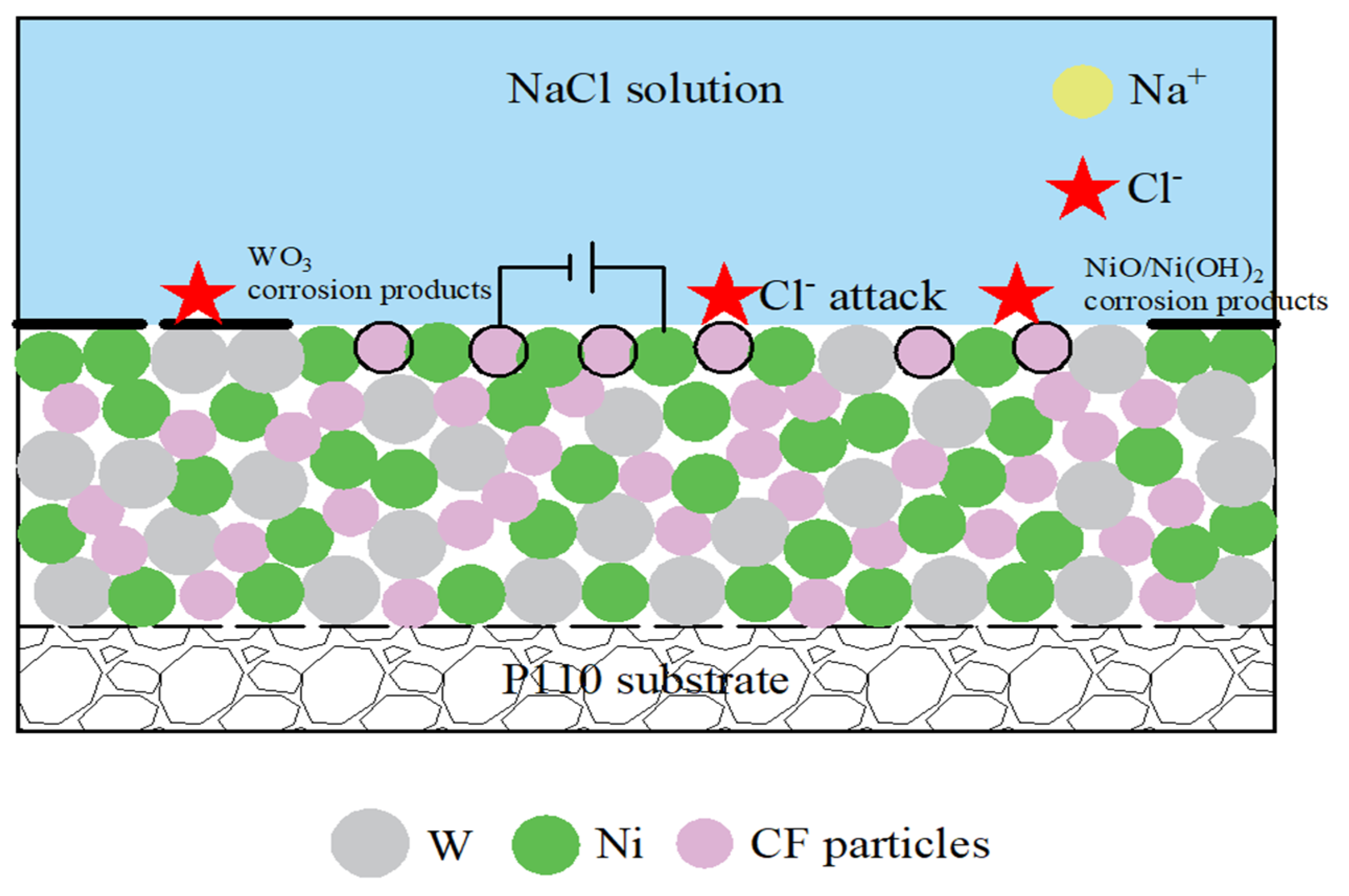
3.5.2. Corrosion Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.-L.; Ouyang, Y.; Xie, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.; Dai, W.; Wu, L. Nickel interlayer enables indirect corrosion protection of magnesium alloy by photoelectrochemical cathodic protection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 558, 149840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Cheng, G.; Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yan, D. Silicon nitride modified enamel coatings enable high thermal shock and corrosion resistances for steel protection. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofuyekpone, O.D.; Utu, O.G.; Onyekpe, B.O.; Adediran, A.A.; Oki, M. Evaluation of protection performances of Stylosanthes gracilis extract against 304L corrosion in H2SO4 solution. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2020, 2, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tang, A.; Pan, F. Fabrication and characterization of Mg-M layered double hydroxide films on anodized magnesium alloy AZ31. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 431, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, L.M.; Taryba, M.G.; Carmezim, M.J.; Montemor, M.F. Self-healing ceria-modified coating for corrosion protection of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2018, 142, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Liang, W.; Huang, G.; Jiang, B.; Atrens, A.; Pan, F. Superhydrophobic coatings for corrosion protection of magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 52, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, A.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, H.; Long, Y.; Li, L.; Atrens, A.; Pan, F. In-situ grown super- or hydrophobic Mg-Al layered double hydroxides films on the anodized magnesium alloy to improve corrosion properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 366, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, L.; Tang, A.; Ma, Y.; Song, G.-L.; Zheng, D.; Jiang, B.; Atrens, A.; Pan, F. Active corrosion protection by a smart coating based on a MgAl-layered double hydroxide on a cerium-modified plasma electrolytic oxidation coating on Mg alloy AZ31. Corros. Sci. 2018, 139, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, C.; Yan, W.; Tu, J.; Ding, X. Fabrication and corrosion property of conversion films on magnesium alloy from deep eutectic solvent. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, J.; Kašiarová, M.; Dobročka, E.; Zemanova, M. Corrosion and tribological properties of nanocrystalline pulse electrodeposited Ni–W alloy coatings. Trans. IMF 2017, 95, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.-H.; Sheu, H.-H.; Ger, M.-D. Preparation and wear resistance of electrodeposited Ni-W/diamond composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 308, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Huan, Y.; Dong, J. Microstructural, surface and electrochemical properties of a novel Ni-B/Ni-W-BN duplex composite coating by co-electrodeposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, N.S.; Creus, J.; Feaugas, X.; Savall, C. Influence of metallurgical parameters on the electrochemical behavior of electrodeposited Ni and Ni-W nanocrystalline alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrillo, P.; Ribotta, S.; Gassa, L.; Benítez, G.; Salvarezza, R.; Vela, M. Phosphonic acid functionalization of nanostructured Ni-W coatings on steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Hu, A.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L. Electrodeposition and corrosion resistance of Ni-W-Al2O3 nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2017, 24, 1850015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyarzadeh, M.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Aghdam, A.S.R.; Torabinejad, V. Electrodeposition of Ni-W-Al2O3 nanocomposite coating with functionally graded microstructure. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 666, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Huan, Y. Preparation of Ni-W/SiC nanocomposite coatings by electrochemical deposition. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 702, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasekar, N.P.; Bathini, L.; Sundararajan, G. Tribological Behavior of Pulsed Electrodeposited Ni-W/SiC Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 5236–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sribalaji, M.; Wasekar, N.P.; Joshi, S.; Sundararajan, G.; Singh, R.; Keshri, A.K. Microstructural, phase evolution and corrosion properties of silicon carbide reinforced pulse electrodeposited nickel-tungsten composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jia, W. Effect of current density and deposition time on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Ni-W/TiN nanocomposite coating. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 4870–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltowska-Lehman, E.; Indyka, P.; Bigos, A.; Szczerba, M.; Guspiel, J.; Koscielny, H.; Kot, M. Effect of current density on properties of Ni-W nanocomposite coatings reinforced with zirconia particles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 173, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, D.; Mei, T.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W. Fabrication and characterization of boron nitride reinforced Ni-W nanocomposite coating by electrodeposition. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 777, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, Y.; He, T.; Fan, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhan, Y. The influence of pulse plating parameters on microstructure and properties of Ni-W-Si3N4 nanocomposite coatings. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 18380–18392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W. Microstructural, surface and electrochemical properties of pulse electrodeposited Ni-W/Si3N4 nanocomposite coating. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 19907–19918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Ji, C. Synthesis and characterization of Ni-W/TiN nanocomposite coating with enhanced wear and corrosion resistance deposited by pulse electrodeposition. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 14015–14028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Murugadoss, V.; Kong, J.; He, Z.; Mai, X.; Shao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Angaiah, S.; et al. Overview of carbon nanostructures and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding. Carbon 2018, 140, 696–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; He, L.; Cheng, X.; Yang, X. Study on wear characteristics of carbon fiber at needle end in prefabricated composite weaving. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Gao, S.; Mäder, E.; Sharma, H.; Wei, L.Y.; Bijwe, J. Carbon fiber surfaces and composite interphases. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 102, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tudela, I.; Zhang, Y.; Pal, M.; Kerr, I.; Cobley, A. Ultrasound-assisted electrodeposition of thin nickel-based composite coatings with lubricant particles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Ji, V. Influence of Y2O3 nanoparticles on microstructures and properties of electrodeposited Ni-W-Y2O3 nanocrystalline coatings. Vacuum 2020, 181, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Su, Z.; Fan, Y.; He, Z. Fabrication of Ni-W-B4C composite coatings and evaluation of its micro–hardness and corrosion resistance properties. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9188–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Lu, X.; Zuo, Y.; Zhuang, N.; Chen, D. The effect of deformation on metastable pitting of 304 stainless steel in chloride contaminated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanlou, S.I.; Ahmadiyeh, S.; Yavari, R. Investigation of pulse electrodeposited Ni-Co/SiO2 nanocomposite coating. Surf. Eng. 2017, 33, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasekar, N.P.; Latha, S.M.; Ramakrishna, M.; Rao, D.; Sundararajan, G. Pulsed electrodeposition and mechanical properties of Ni-W/SiC nano-composite coatings. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyarzadeh, M.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Rouhaghdam, A.S.; Torabinejad, V. Electrochemical tailoring of ternary Ni-W-Co(Al2O3) nanocomposite using pulse reverse technique. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 705, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, Z.; Zare, H.R. A Comparative Study on the Effect of MWCNT as Reinforcement on the Corrosion Parameters of Different Ni-W/MWCNTs Nanocomposite Coatings in Various Corrosive Media. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, N. Kinetics of the Deposition of Inert Particles from Electrolytic Baths. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1972, 119, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, R. The electrical double layer: Recent experimental and theoretical developments. Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Mn | C | Si | Cr | Ti | Mo | V | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 1.71 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.012 | 0.012 |
| Sample | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (μA/cm2) | CR (mm/a) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-W | −0.254 | 0.43 | 0.0095 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.1g/L) | −0.361 | 0.56 | 0.2795 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.2 g/L) | −0.355 | 0.52 | 0.1254 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.3 g/L) | −0.239 | 0.29 | 0.0917 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.4 g/L) | −0.232 | 0.20 | 0.0060 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.5 g/L) | −0.246 | 0.26 | 0.0435 |
| Sample | Rs (Ω·cm2) | CPEdl (Ω·cm2) | n | Rct (Ω·cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-W | 1.5444 | 35 | 0.9 | 16,937.10 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.1g/L) | 5.3089 | 36 | 0.8 | 12,569 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.2 g/L) | 5.1535 | 34 | 0.8 | 17,091 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.3 g/L) | 6.0765 | 32 | 0.9 | 20,909 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.4 g/L) | 7.7608 | 29 | 0.9 | 37,219 |
| Ni-W-CF (0.5 g/L) | 6.5444 | 32 | 0.9 | 23,373 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liao, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L. Preparation and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-W-CF Composite Coating on P110 Steel. Coatings 2022, 12, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020231
Zhang Q, Feng Y, Chen Z, Liao W, Zhang S, Zhou J, Wu L. Preparation and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-W-CF Composite Coating on P110 Steel. Coatings. 2022; 12(2):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020231
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiuli, Yi Feng, Zhaoyang Chen, Wenzhi Liao, Shuo Zhang, Jun Zhou, and Lei Wu. 2022. "Preparation and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-W-CF Composite Coating on P110 Steel" Coatings 12, no. 2: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020231
APA StyleZhang, Q., Feng, Y., Chen, Z., Liao, W., Zhang, S., Zhou, J., & Wu, L. (2022). Preparation and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-W-CF Composite Coating on P110 Steel. Coatings, 12(2), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020231






