Influence of Prevailing Wind Direction on Sapping Quantity of Rammed Earth Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Methods
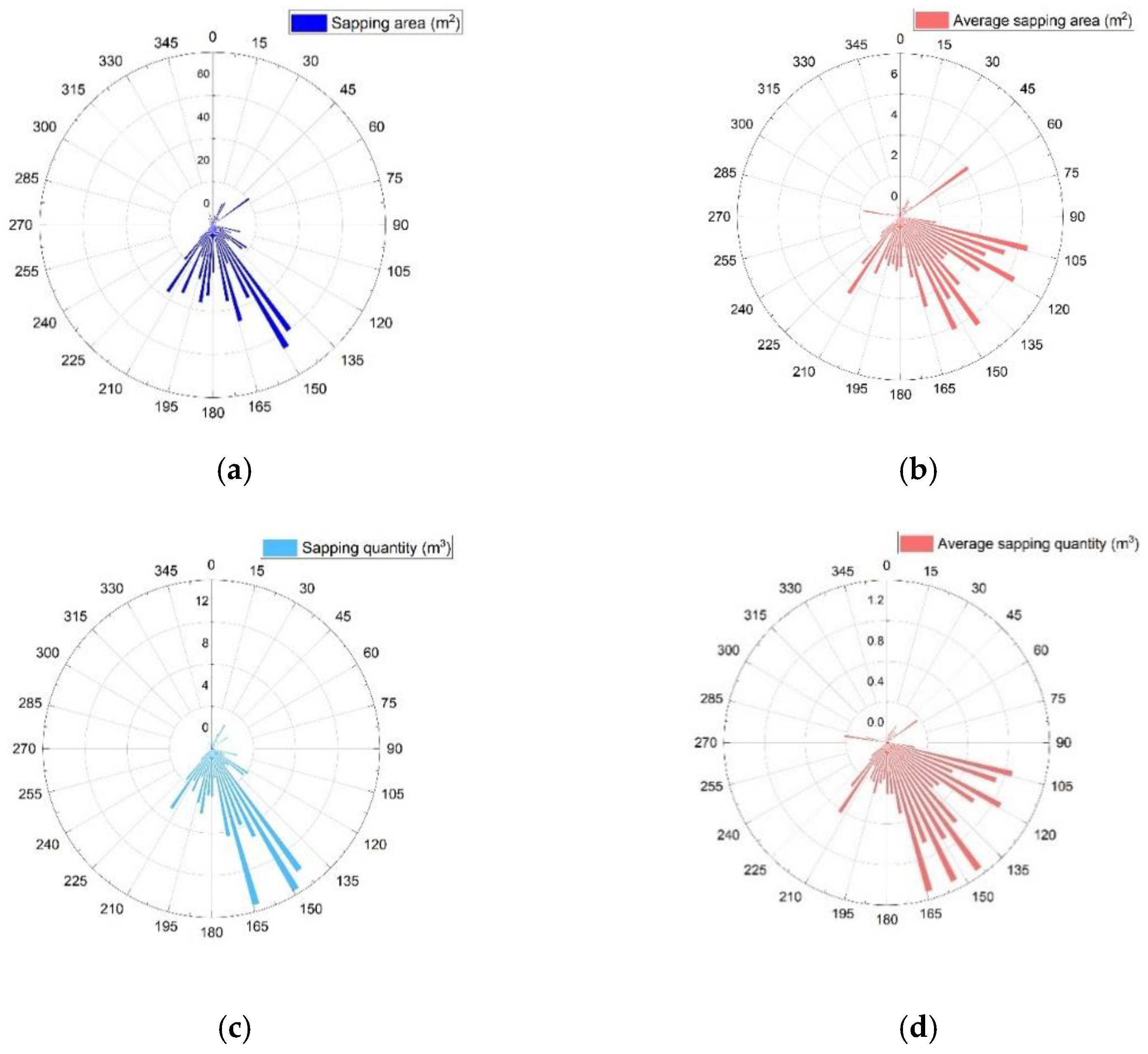
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Sapping quantity at windward of the Wall is nearly 10 times of leeward, which is a solid proof of influence of wind direction.
- Huge difference in sapping quantity of windward could be observed for the Wall with various azimuth and highest sapping quantity could be found at windward of the Wall with an angle of 30° to prevailing wind direction.
- According to sapping level of various parts of the Wall, pertinence of traditional and mature conservation measures, would improve, which could avoid further deterioration due to inadequate conservation or waste of conservation cost because of excessive conservation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Preservation of earthen heritage sites on the Silk Road, northwest China from the impact of the environment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.M.; Chen, W.W.; Cui, K.; Zhang, K.W. Study on Damage Assessment of Earthen Sites of the Ming Great Wall in Qinghai Province Based on Fuzzy-AHP and AHP-TOPSIS. Int. J. Archi. Herit. 2019, 14, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.M.; Chen, W.W.; Cui, K.; Guo, Z.Q.; Wu, G.P.; Ren, X.F. An exploration of the military defense system of the Ming Great Wall in Qinghai Province from the perspective of castle-based military settlements. Archaeol. Anthrop. Sci. 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, J.K.; Dai, P.F. Consolidation effect of composite materials on earthen sites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, A.; D’Ayala, D.; Sequeira, L. Assessment of wind-driven rain impact, related surface erosion and surface strength reduction of historic building materials. Build. Environ. 2012, 57, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.W.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, H.W.; Guo, Z.Q. Feasibility of protecting earthen sites by infiltration of modified polyvinyl alcohol. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Wang, X.D.; Sun, M.L.; Chen, W.W.; Guo, Q.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Conservation of Jiaohe ancient earthen site in China. J. Rock. Mech. Geotech. 2011, 3, 270–281. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, T.; Chen, W.W.; Du, Y.M.; Li, W.J.; Su, N. Snowfall-related deterioration behavior of the Ming Great Wall in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, W.M.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.G.; Ye, B. Desiccation of NaCl-contaminated soil of earthen heritages in the Site of Yar City, northwest China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Wang, T.R.; Wang, X.D.; Guo, Q.L. Laboratory experimental study of infrared imaging technology detecting the conservation effect of ancient earthen sites (Jiaohe Ruins) in China. Eng. Geol. 2012, 125, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yin, B.T.; Peng, X.Q.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhang, L. Wind-rain erosion of Fujian Tulou Hakka Earth Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qu, L.J.; He, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Gu, H. The Great Wall of China: A physical barrier to gene flow? Heredity 2003, 90, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Guan, X.P.; Chen, W.W.; Chen, M.M.; Han, W.F. Effects of salinized deterioration and aeolian ullage on soils in undercutting areas of earthern ruins in arid regions (II). J. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 39, 1777–1784. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bui, Q.B.; Morel, J.C.; Reddy, B.V.; Ghayad, W. Durability of rammed earth walls exposed for 20 years to natural weathering. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Skidmore, E.; Hasi, E.; Wagner, L.; Tatarko, J. Dune sand transport as influenced by wind directions, speed and frequencies in the Ordos Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2005, 67, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Drag distributions of non-uniform buildings from surface pressure measurements in wind tunnel. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, J.K.; Van Boxel, J.H.; Sterk, G. Wind forces and related saltation transport. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Mohotti, D.; Chauhan, K. Experimental and numerical study on mean pressure distributions around an isolated gable roof building with and without openings. Build. Environ. 2018, 132, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.M.; Chen, W.W.; Cui, K.; Zhang, J.K.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.Y. Damage assessment of earthen sites of the Ming Great Wall in Qinghai Province: A comparison between Support Vector Machine (SVM) and BP Neural Network. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2020, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, M.J. A map of the great wall of China. Imago. Mundi 1956, 13, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.G. The Zhuang minority in the Ming era. Ming. Stud. 2013, 1989, 15–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.K.; Long, Y.; Zuan, X. The Annals of Xining Wei, 1st ed.; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 1993; pp. 27–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.H. Qinghai Economic History, 1st ed.; Qinghai Peoples’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 1998; pp. 235–247. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.S.; Li, L.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, E.Z.; Li, Z.X. Deterioration mechanisms of building materials of Jiaohe ruins in China. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Pei, Q.Q.; Guo, Q.L.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhao, J.Z. Stress mechanism for the rammed layer interfaces of earthen heritage sites with different treatments. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 39, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Viles, H. A controlled field experiment to investigate the deterioration of earthen heritage by wind and rain. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X. Records of Xining; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 1993. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. The New Annals of Xining Fu; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 2016; pp. 47–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Yan, L.; Cao, Y.C. Research on the great wall and military settlements of Xining Wei in Ming Dynasty. Archit. J. 2012, S1-07, 30–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://m.news.cctv.com/2021/10/05/ARTIE03citWOtA4QJFwqs4b2211005.shtml (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Chen, W.W.; Su, N.; Yang, G. Effect of wind field on sapping quantity of earthen architecture ruins along the ridge in semi-humid area. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 37, 1807–1813. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.nmic.cn/data/cdcdetail/dataCode/B.0011.0001C.html (accessed on 25 March 2014).
- Available online: http://www.gov.cn/govweb/gzdt/2007-02/13/content_525933.htm (accessed on 13 February 2007).
- Ren, X. Resources’ Investigation Report of Ming Great Wall in Qinghai Province; Cultural Relics Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 58–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Kang, L. Statistical characteristics of wind erosion events in the erosion area of Northern China. Catena 2018, 167, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.Q.; He, B.J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.X.; Darko, A.; Zhao, Z.Q. Sensitivity analysis of wind pressure coefficients on CAARC standard tall buildings in CFD simulations. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 16, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.J.; Cheng, G.D.; Zhang, K.C.; Wang, J.C.; Zu, R.P.; Fang, H.Y. An experimental study of the mechanisms of freeze/thaw and wind erosion of ancient adobe buildings in northwest China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2007, 66, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yan, G.S.; Pei, Q.Q. Durability of ancient earthen architecture under wind erosion in the Milan Ancient City along the Silk Road of China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 163, 3230–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Li, L.; Li, G.M.; Pei, X.J. Failure modes classification and failure mechanism research of ancient city wall. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Zhao, X.Z.; Zhu, M.J.; Chen, W.W.; Han, W.F. Effects of salinized deterioration and aeolian ullage on soils in undercutting area of earthen ruins in arid region (III): Capillary process. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 5, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Richards, J.; Viles, H.; Guo, Q.L. The importance of wind as a driver of earthen heritage deterioration in dryland environments. Geomorphology 2020, 369, 107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Du, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wu, G.P.; Yu, L. An evaluation system for the development of scaling off at earthen sites in arid areas in NW China. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.X.; Wang, X.D.; Chen, W.W.; Sun, M.L.; Guo, Q.L.; Zhang, J.K.; He, F.G.; Yang, S.L. Specifications of Investigation for Preservation Engineering of Earthen Sites; Cultural Relics Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- ICOMOS China. Principles for the Conservation of Heritage Sites in China (Billingual); ICOMOS China: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 76–78. Available online: http://openarchive.icomos.org/id/eprint/1650/ (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Wang, X.D. Philosophy and Practice of Conservation of Earthen Architecture Sites: A Case Study of the Jiaohe Ancient Site in Xinjiang; The Peoples Press of Gansu: Lanzhou, China, 2010; pp. 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]






| Number | Leeward | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orientation (°) | Overall Length of Wall (m) | Area (m2) | Volume (m3) | 20 m Mean-Area (m2) | Mean-Depth (m) | 20 m Mean-Volume (m3) | |
| 1 | 275–279 | 15.89 | 1.46 | 0.33 | 1.83 | 0.23 | 0.42 |
| 2 | 280–284 | 40.07 | 1.37 | 0.41 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 0.21 |
| 3 | 285–289 | 19.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 290–294 | 39.59 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 295–299 | 19.93 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 300–304 | 80.98 | 1.23 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
| 7 | 305–309 | 120.21 | 1.78 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| 8 | 310–314 | 71.29 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 315–319 | 40.14 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
| 10 | 320–324 | 182.64 | 1.86 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| 11 | 325–329 | 281.14 | 3.53 | 0.70 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 12 | 330–334 | 117.83 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.03 |
| 13 | 335–339 | 148.27 | 1.20 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.02 |
| 14 | 340–344 | 201.11 | 5.70 | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.06 |
| 15 | 345–349 | 237.95 | 2.76 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| 16 | 350–354 | 110.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 17 | 355–359 | 175.75 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 18 | 0–4 | 240.01 | 1.30 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.02 |
| 19 | 5–9 | 305.06 | 1.36 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.02 |
| 20 | 10–14 | 205.91 | 5.24 | 0.92 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.09 |
| 21 | 15–19 | 145.07 | 3.88 | 0.66 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.09 |
| 22 | 20–24 | 222.46 | 10.69 | 1.56 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
| 23 | 25–29 | 270.38 | 11.76 | 2.57 | 0.87 | 0.22 | 0.19 |
| 24 | 30–34 | 162.36 | 3.84 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.15 | 0.07 |
| 25 | 35–39 | 140.03 | 4.43 | 0.91 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.13 |
| 26 | 40–44 | 119.51 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.02 |
| 27 | 45–49 | 40.11 | 1.56 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.17 | 0.13 |
| 28 | 50–54 | 101.51 | 20.79 | 1.88 | 4.10 | 0.09 | 0.37 |
| 29 | 55–59 | 80.56 | 1.12 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.04 |
| 30 | 60–64 | 40.01 | 0.75 | 0.14 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.07 |
| Windward | |||||||
| 1 | 95–99 | 16.21 | 1.44 | 0.23 | 1.78 | 0.16 | 0.29 |
| 2 | 100–104 | 40.25 | 12.94 | 2.56 | 6.43 | 0.20 | 1.27 |
| 3 | 105–109 | 19.34 | 5.23 | 1.10 | 5.41 | 0.21 | 1.14 |
| 4 | 110–114 | 40.54 | 9.26 | 1.43 | 4.57 | 0.16 | 0.71 |
| 5 | 115–119 | 20.36 | 6.49 | 1.30 | 6.37 | 0.20 | 1.27 |
| 6 | 120–124 | 80.99 | 18.96 | 4.16 | 4.68 | 0.22 | 1.03 |
| 7 | 125–129 | 119.82 | 17.54 | 3.94 | 2.93 | 0.23 | 0.66 |
| 8 | 130–134 | 71.81 | 10.60 | 2.26 | 2.95 | 0.21 | 0.63 |
| 9 | 135–139 | 39.34 | 8.61 | 2.03 | 4.38 | 0.24 | 1.03 |
| 10 | 140–144 | 184.66 | 60.12 | 14.20 | 6.51 | 0.24 | 1.54 |
| 11 | 145–149 | 282.94 | 66.09 | 15.57 | 4.67 | 0.24 | 1.10 |
| 12 | 150–154 | 122.39 | 37.45 | 9.24 | 6.12 | 0.25 | 1.51 |
| 13 | 155–159 | 146.93 | 19.00 | 7.72 | 2.59 | 0.41 | 1.05 |
| 14 | 160–164 | 202.17 | 46.27 | 15.36 | 4.58 | 0.33 | 1.52 |
| 15 | 165–169 | 237.42 | 35.88 | 8.43 | 3.02 | 0.24 | 0.71 |
| 16 | 170–174 | 108.78 | 7.92 | 2.74 | 1.46 | 0.34 | 0.50 |
| 17 | 175–179 | 179.70 | 22.09 | 4.55 | 2.46 | 0.21 | 0.51 |
| 18 | 180–184 | 247.48 | 32.91 | 4.43 | 2.66 | 0.14 | 0.36 |
| 19 | 185–189 | 307.79 | 36.28 | 6.20 | 2.36 | 0.17 | 0.40 |
| 20 | 190–194 | 206.71 | 25.72 | 5.28 | 2.49 | 0.21 | 0.51 |
| 21 | 195–199 | 142.64 | 15.69 | 2.88 | 2.20 | 0.18 | 0.40 |
| 22 | 200–204 | 226.22 | 34.36 | 4.39 | 3.04 | 0.13 | 0.39 |
| 23 | 205–209 | 270.25 | 11.39 | 3.45 | 0.84 | 0.31 | 0.26 |
| 24 | 210–214 | 164.81 | 37.22 | 6.82 | 4.52 | 0.18 | 0.83 |
| 25 | 215–219 | 138.72 | 20.44 | 3.80 | 2.95 | 0.19 | 0.55 |
| 26 | 220–224 | 122.02 | 8.58 | 1.47 | 1.41 | 0.17 | 0.24 |
| 27 | 225–229 | 39.57 | 2.38 | 0.39 | 1.20 | 0.17 | 0.20 |
| 28 | 230–234 | 105.18 | 1.46 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
| 29 | 235–239 | 80.81 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.03 |
| 30 | 240–244 | 39.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, N.; Yang, B.; Chen, W.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Influence of Prevailing Wind Direction on Sapping Quantity of Rammed Earth Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty. Coatings 2022, 12, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12050707
Su N, Yang B, Chen W, Xu L, Li Y. Influence of Prevailing Wind Direction on Sapping Quantity of Rammed Earth Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty. Coatings. 2022; 12(5):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12050707
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Na, Bo Yang, Wenwu Chen, Linrong Xu, and Yongwei Li. 2022. "Influence of Prevailing Wind Direction on Sapping Quantity of Rammed Earth Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty" Coatings 12, no. 5: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12050707
APA StyleSu, N., Yang, B., Chen, W., Xu, L., & Li, Y. (2022). Influence of Prevailing Wind Direction on Sapping Quantity of Rammed Earth Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty. Coatings, 12(5), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12050707






