The Influence of Alumina Airborne-Particle Abrasion on the Properties of Zirconia-Based Dental Ceramics (3Y-TZP)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. The Vickers Hardness Evaluation of 3Y-TZP
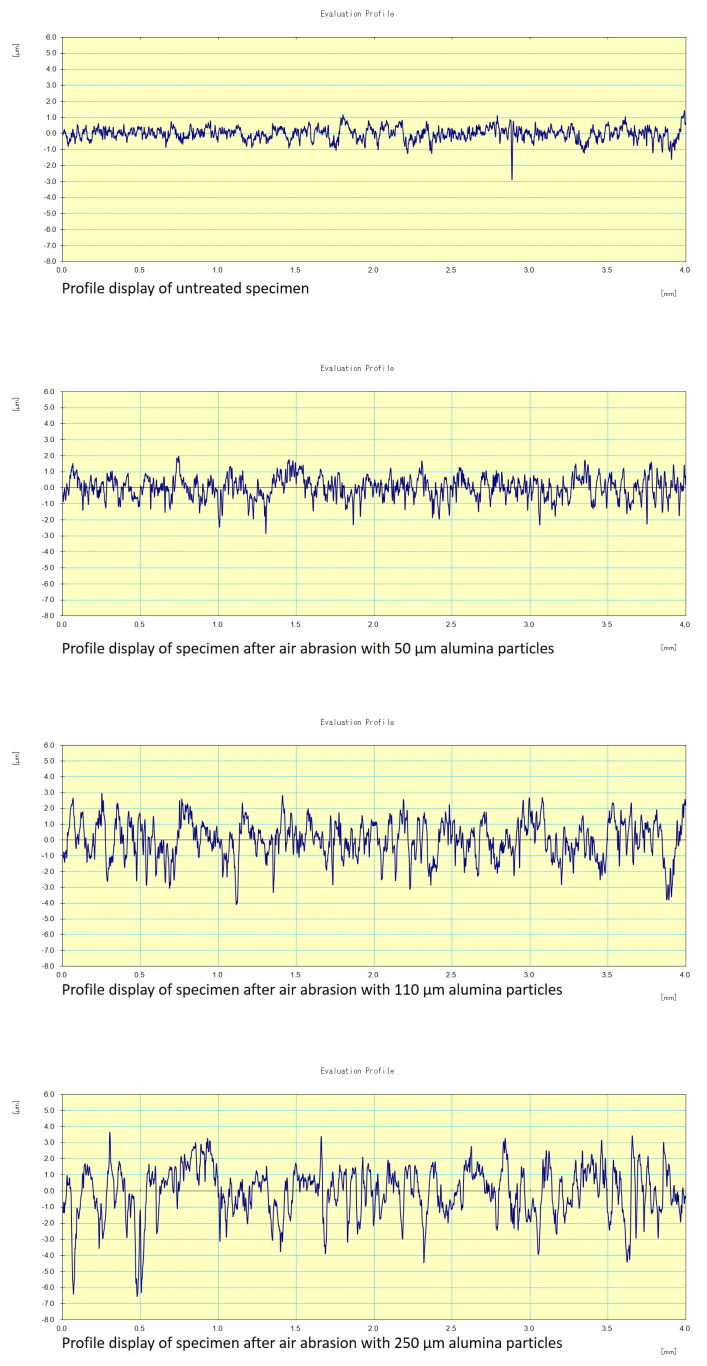
2.3. The Zirconia Roughness Evaluation
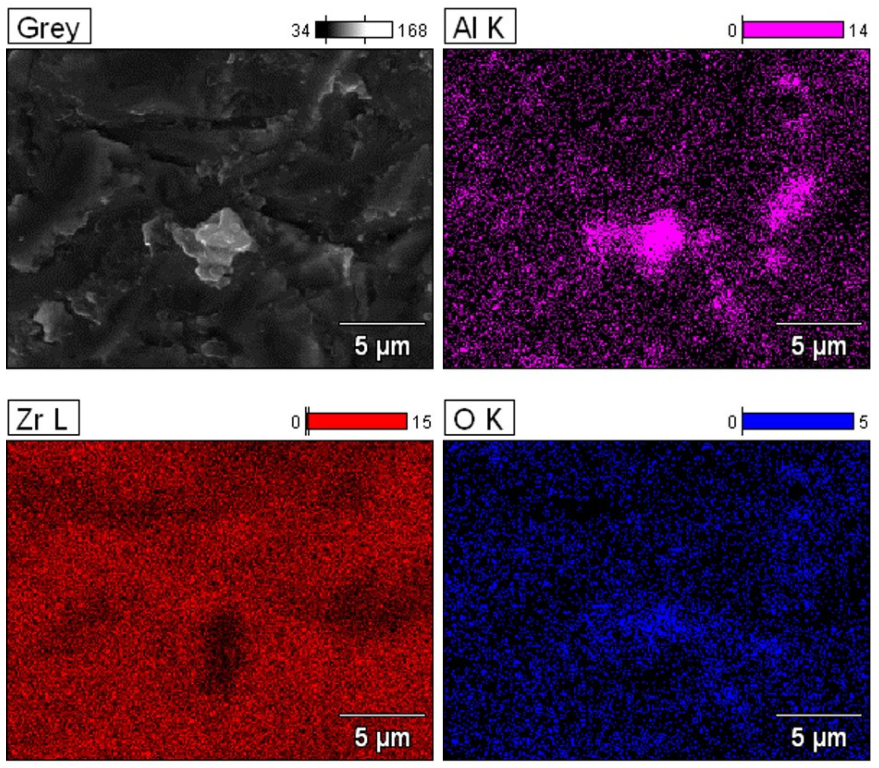
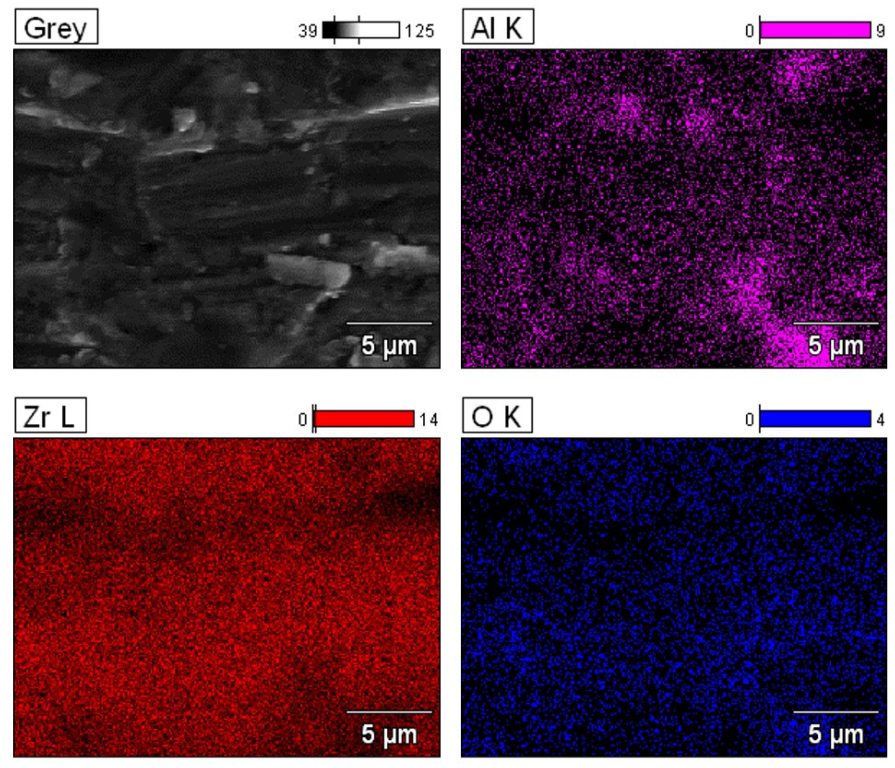
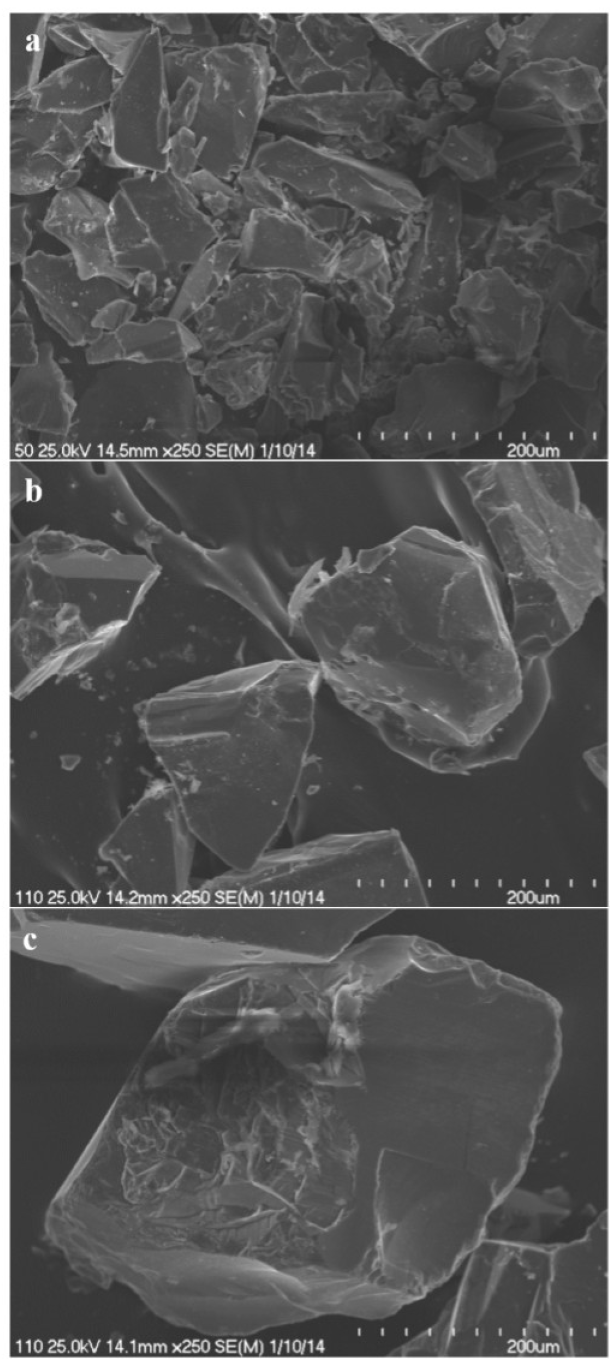
2.4. SEM–EDS Microanalysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
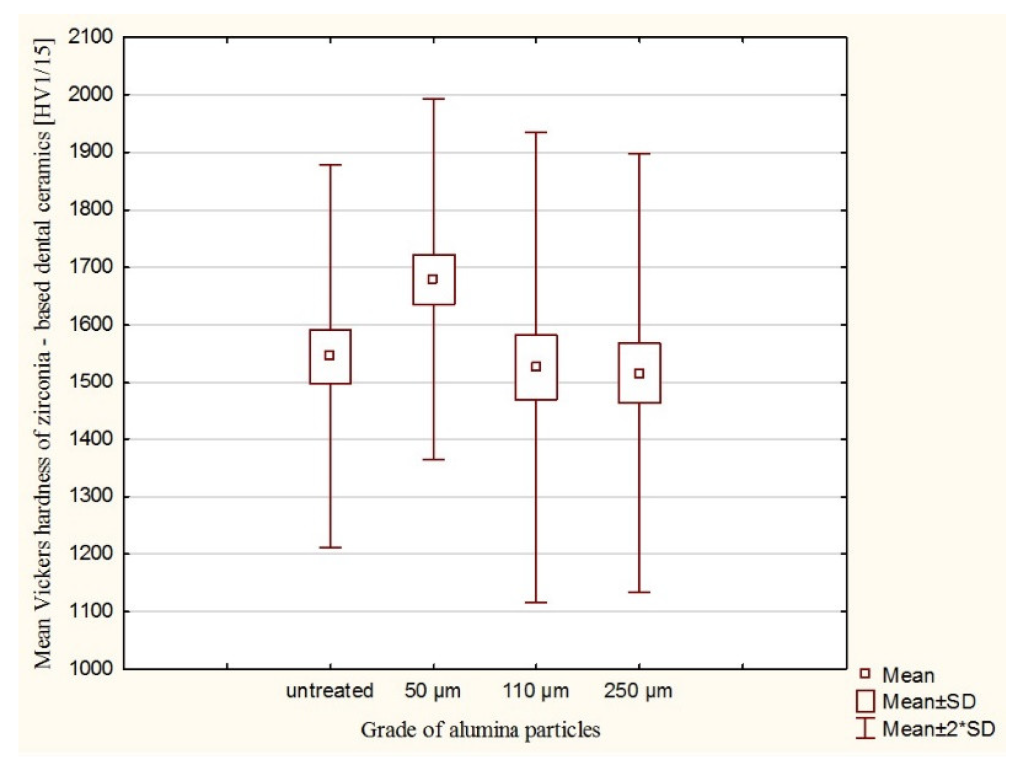
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gamborena, I.; Blatz, M.B. A clinical guidelines to predictable esthetics with zirconium oxide ceramic restorations. Quintessence Dent. Technol. 2006, 29, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Potiket, N.; Chiche, G.; Finger, I.M. In vitro fracture strength of teeth restored with different all-ceramic crown systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, C.; Vult von Steyern, P.; Sunzel, B.; Nilner, K. Allceramic two- to five-unit implant-supported reconstructions. A randomized, prospective clinical trial. Swed. Dent. J. 2006, 30, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Covacci, V.; Bruzzese, N.; Maccauro, G.; Andreassi, C.; Ricci, G.A.; Piconi, C.; Marmo, E.; Burger, W.; Cittadini, A. In vitro evaluation of the mutagenic and carcinogenic power of high purity zirconia ceramic. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piconi, C.; Maccauro, G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, R.L.; Powers, J.M. Craig’s Restorative Dental Materials; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 253–285. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Al Kheraif, A.A.; Jamaluddin, S.; Elsharawy, M.; Divakar, D.D. Recent Trends in Surface Treatment Methods for Bonding Composite Cement to Zirconia: A Review. J. Adhes. Dent. 2017, 19, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blatz, M.B.; Phark, J.-H.; Ozer, F.; Mante, F.K.; Saleh, N.; Bergler, M.; Sadan, A. In vitro comparative bond strength of contemporary self-adhesive resin cements to zirconium oxide ceramic with and without air-particle abrasion. Clin. Oral Investig. 2010, 14, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatz, M.B.; Sadan, A.; Martin, J.; Lang, B. In vitro evaluation of shear bond strengths of resin to densely sintered high-purity zirconium-oxide ceramic after long-term storage and thermal cycling. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Tsuo, Y.; Atsuta, M. Bonding of dual-cured resin cement to zirconia ceramic using phosphate acid estermonomer and zirconate coupler. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 77B, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatz, M.B.; Chiche, G.; Holst, S.; Sadan, A. Influence of surface treatment and simulated aging on bond strengths of luting agents to zirconia. Quintessence Int. 2007, 38, 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Łagodzińska, P.; Bociong, K.; Sokołowski, J.; Dejak, B. Comparative study of the shear bond strength of zirconia-based dental ceramics to resin cements after chemo-mechanical surface modification. J. Stoma 2019, 72, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.L.; Castillo-Oyague, R.; Lynch, C.D.; Montero, J.; Albaladejo, A. Influence of sandblasting granulometry and resin cement composition on microtensile bond strength to zirconia ceramic for dental prosthetic framework. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phark, J.-H.; Duarte, S.; Blatz, M.; Sadan, A. An in vitro evaluation of the long-term resin bond to a new densely sintered high-purity zirconium-oxide ceramic surface. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 101, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.; Ha, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Effect of sandblasting and various metal primers on the shear bond strength of resin cement to Y-TZP ceramic. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Barloi, A.; Kern, M. Influence of air–abrasion on zirconia ceramic bonding using an adhesive composite resin. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuo, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Atsuta, M. Effects of alumina-blasting and adhesive primers on bonding between resin luting agent and zirconia ceramics. Dent. Mater. J. 2006, 25, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaas, A.C.; Yang, B.; Kern, M. Panavia F 2.0 bonding to contaminated zirconia ceramic after different cleaning procedures. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmac, T.; Oblak, C.; Jevnikar, P.; Funduk, N.; Marion, L. Strength and reliability of surface treated Y-TZP dental ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2000, 53, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmac, T.; Oblak, C.; Jevnikar, P.; Funduk, N.; Marion, L. The effect of Surface grinding and sandblasting on flexural strength and reliability of 3Y-TZP zirconia ceramic. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotic, J.; Jevnikar, P.; Kocjan, A. Ageing kinetics and strength of airborne- particle abraded 3Y-TZP ceramics. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzato, M.; Quach, L.; Albakry, M.; Swain, M.V. Influence of surface and heat treatments on the flexural strength of Y-TZP dental ceramic. J. Dent. 2005, 33, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintapalli, R.K.; Marro, F.G.; Jimenez-Pique, E.; Anglada, M. Phase transformation and subsurface damage in 3Y-TZP after sandblasting. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lawn, B.R.; Rekow, E.D.; Thompson, V.P. Effect of sandblasting on the long term performance of dental ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 71B, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallmann, L.; Ulmer, P.; Reusser, E.; Hammerle, C.F. Surface characterization of dental Y-TZP ceramic after air abrasion treatment. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Yamadad, K.; Pezzotti, G.; Nawa, M.; Ban, S. Mechanical properties of dental zirconia ceramics changed with sandblasting and heat treatment. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śmielak, B.; Klimek, L. Effect of air abrasion on the number of particles embedded in Zirconia. Materials 2018, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvie, R.C.; Hannink, R.H.; Pascoe, R.T. Ceramic steel? Nature 1975, 258, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lughi, V.; Sergo, V. Low temperature degradation–aging- of zirconia: A critical review of the relevant aspects in dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swab, J.J. Low temperature degradation of Y-TZP materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 6706–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokoshi, M.; Vanmeensel, K.; Zhang, F.; De Munck, J.; Eliades, G.; Minakuchi, S.; Naert, I.; Meerbeek, B.; Vleugels, J. Aging resistance of surface–treated dental zirconia. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K.; Ahn, B. Effect of Al2O3 Sandblasting Particle Size on the Surface Topography and Residual Compressive Stresses of Three Different Dental Zirconia Grades. Materials 2021, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, C.; Tucci, A.; Esposito, L.; Scotti, R. Microstructural changes produced by abrading y-TZP in presintered and sintered conditions. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallmann, L.; Ulmer, P.; Reusser, E.; Hammerle, C.F. Effect of blasting pressure, abrasive particle size and grade on phase transformation and morphological change of dental zirconia surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 4293–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkamhaeng, K.; Dawson, D.V.; Holloway, J.A.; Denry, I. Effect of Surface Modification on In-Depth Transformations and Flexural Strength of Zirconia Ceramics. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e364–e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K.; Yoo, K.-W.; Kim, S.-J.; Jung, C.-H. Phase Transformations and Subsurface Changes in Three Dental Zirconia Grades after Sandblasting with Various Al2O3 Particle Sizes. Materials 2021, 14, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishido, S.; Inagaki, R.; Kanno, T.; Svanborg, P.; Barkarmo, S.; Ortengren, U.; Nakamura, K. Residual stress associated with crystalline phase transformation of 3–6 mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics induced by mechanical surface treatments. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 146, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintapalli, R.K.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Marro, F.G.; Anglada, M. Effect of sandblasting and residual stress on strength of zirconia for restorative dentistry applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 29, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoca, S.; Yilmaz, H. Influence of surface treatments on surface roughness, phase transformation, and biaxial flexural strength of 3Y-TZP ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91B, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, L.; Ulmer, P.; Wille, S.; Polomskyi, O.; Kobel, S.; Trottenberg, T.; Bornholdt, S.; Haase, F.; Kersten, H.; Kern, M. Effect of surface treatments on the properties and morphological change of dental zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łagodzińska, P.; Dejak, B.; Krasowski, M.; Konieczny, B. The Influence of Alumina Airborne-Particle Abrasion with Various Sizes of Alumina Particles on the Phase Transformation and Fracture Resistance of Zirconia-Based Dental Ceramics. Materials 2023, 16, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xing, Y.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Gui, X. Effect of roughness on wettability and floatability: Based on wetting film drainage between bubbles and solid surfaces. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xia, W.; Peng, Y.; Xi, G. Dynamic pore wetting and its effects on porous particle flotation: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, R.; Kheur, M.; Kheur, S. Effect of simulated chairside grinding procedures using commercially available abrasive agents on the surface properties of zirconia. J. Indian. Prosthodont. Soc. 2017, 17, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traini, T.; Gherlone, E.; Parabita, S.F.; Caputi, S.; Piattelli, A. Fracture toughness and hardness of a Y_TZP dental ceramic after mechanical surface treatments. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maerten, A.; Zaslansky, P.; Mochales, C.; Traykova, T.; Mueller, W.D.; Fratzl, P.; Fleck, C. Characterizing the transformation near indents and cracks in clinically used dental yttria-stabilized zirconium oxide constructs. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subasi, M.G.; Inan, O. Evaluation of the topographical surface changes and roughness of zirconia after different surface treatments. Lasers Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergeröder, C.; Wille, S.; Kern, M. Comparison of Testing Designs for Flexural Strength of 3Y-TZP and 5Y-PSZ Considering Different Surface Treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Technical Data of 3Y-TZP | ||
|---|---|---|
| Unit | Value | |
| Bending strength (4-point) | MPa | >1200 |
| E-module | GPa | >200 |
| Grain size | µm | ≤0.6 |
| Density | g/cm3 | ≥6.07 |
| Open porosity | % | 0 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (WAK) (25–500 °C) | 1/K | 10.0 ± 0.5 × 10−6 |
| Chemical solubility | µg/cm2 | <5 |
| Radioactivity | Bq/g | 0.0156 |
| Chemical Composition of 3Y-TZP | |
|---|---|
| Oxide | Mass Percentage |
| ZrO2 + HfO2 +Y2O3 | >99.0 |
| Y2O3 | 4.5–5.6 |
| HfO2 | <5 |
| Al2O3 | <0.5 |
| Other oxides | <0.5 |
| Surface Roughness Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Ra | Roughness average: arithmetic mean deviation of the roughness profile; the arithmetic mean value of the absolute deviations of the profile from the mean line. This value is related to abrasive wear. |
| Rq | RMS roughness: root-mean-square deviation of the profile. |
| Rz | Average maximum height of the profile: roughness profile height according to 10 points: this is the mean of the height of the five highest profile points above the mean line, reduced by the height of the five lowest profile points. |
| Rsk | Skewness: a measure of the asymmetry of the profile to the mean line; a negative value indicates that a greater percentage of the profile is below the mean line, while a positive value indicates that more of the profile is above the line. |
| Rsm | Mean spacing of profile irregularities: the mean width of the profile elements; the mean value of the roughness intervals. |
| Rt | Maximum height of the roughness profile: the vertical distance measured between the highest and the lowest points of the profile. |
| Vo | Retention volume: the area in a roughness profile measured between the ratio curve and the one-hundred-percent material line below the core roughness. |
| Researched Groups (Size of Alumina Particles Used For Air Abrasion) | Surface Roughness Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra (µm) | Rq (µm) | Rz (µm) | Rsk | Rsm (µm) | Rt (µm) | Vo (μm3/μm2) | |
| Untreated | 0.286 | 0.383 | 3.053 | 0.218 | 161.300 | 5.133 | 0.003 |
| 50 µm | 0.668 | 0.838 | 5.106 | −0.001 | 132.233 | 6.400 | 0.006 |
| 110 µm | 0.909 | 1.139 | 6.989 | −0.233 | 116.833 | 8.264 | 0.007 |
| 250 µm | 1.501 | 1.882 | 13.773 | −0.131 | 304.300 | 13.773 | 0.010 |
| P | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0987 | 0.0572 | 0.0188 | 0.0156 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łagodzińska, P.; Dejak, B.; Konieczny, B. The Influence of Alumina Airborne-Particle Abrasion on the Properties of Zirconia-Based Dental Ceramics (3Y-TZP). Coatings 2023, 13, 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13101691
Łagodzińska P, Dejak B, Konieczny B. The Influence of Alumina Airborne-Particle Abrasion on the Properties of Zirconia-Based Dental Ceramics (3Y-TZP). Coatings. 2023; 13(10):1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13101691
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁagodzińska, Paulina, Beata Dejak, and Bartłomiej Konieczny. 2023. "The Influence of Alumina Airborne-Particle Abrasion on the Properties of Zirconia-Based Dental Ceramics (3Y-TZP)" Coatings 13, no. 10: 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13101691
APA StyleŁagodzińska, P., Dejak, B., & Konieczny, B. (2023). The Influence of Alumina Airborne-Particle Abrasion on the Properties of Zirconia-Based Dental Ceramics (3Y-TZP). Coatings, 13(10), 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13101691





