High-Temperature Erosion of SiC-NiCrAlY/Cr3C2-NiCr Coating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
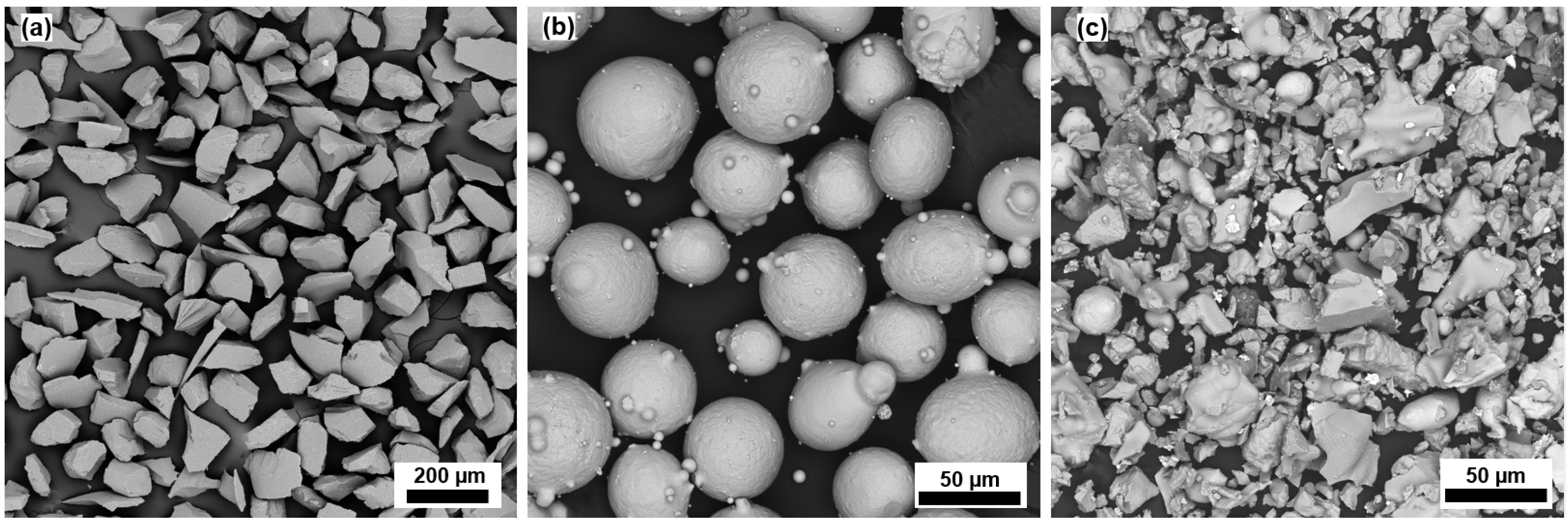
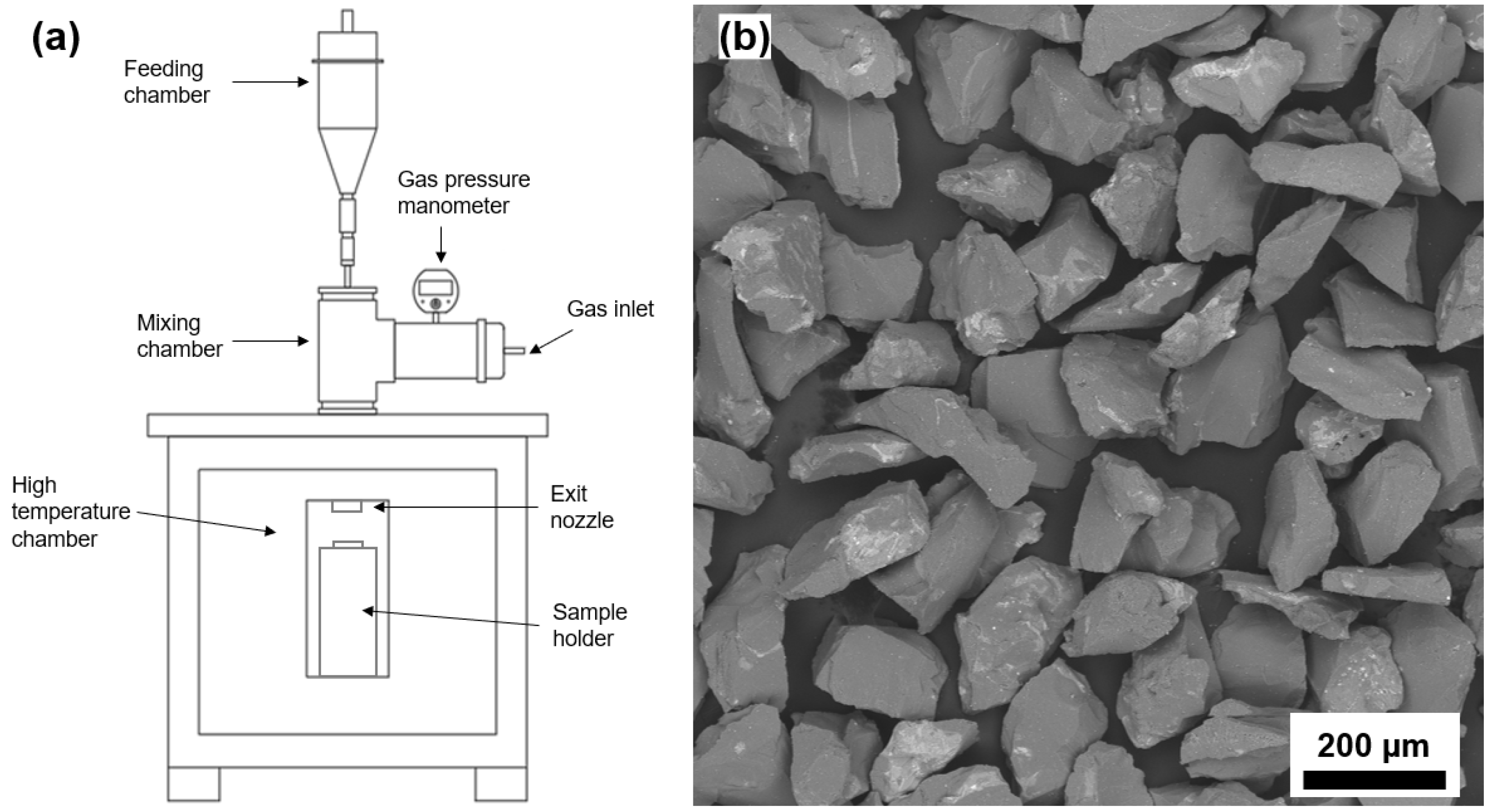
2.1. Synthesis and Coatings Deposition
2.2. Coatings’ Characterization
2.3. High-Temperature Erosion Wear Test
3. Results and Discussion
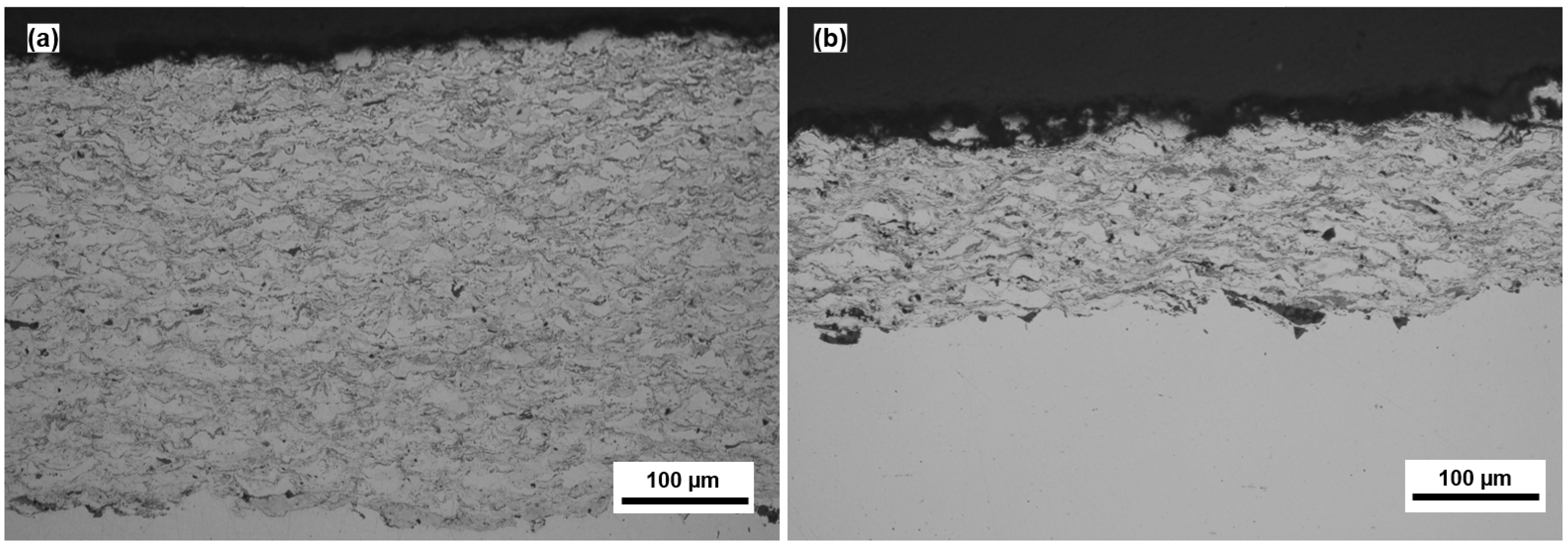
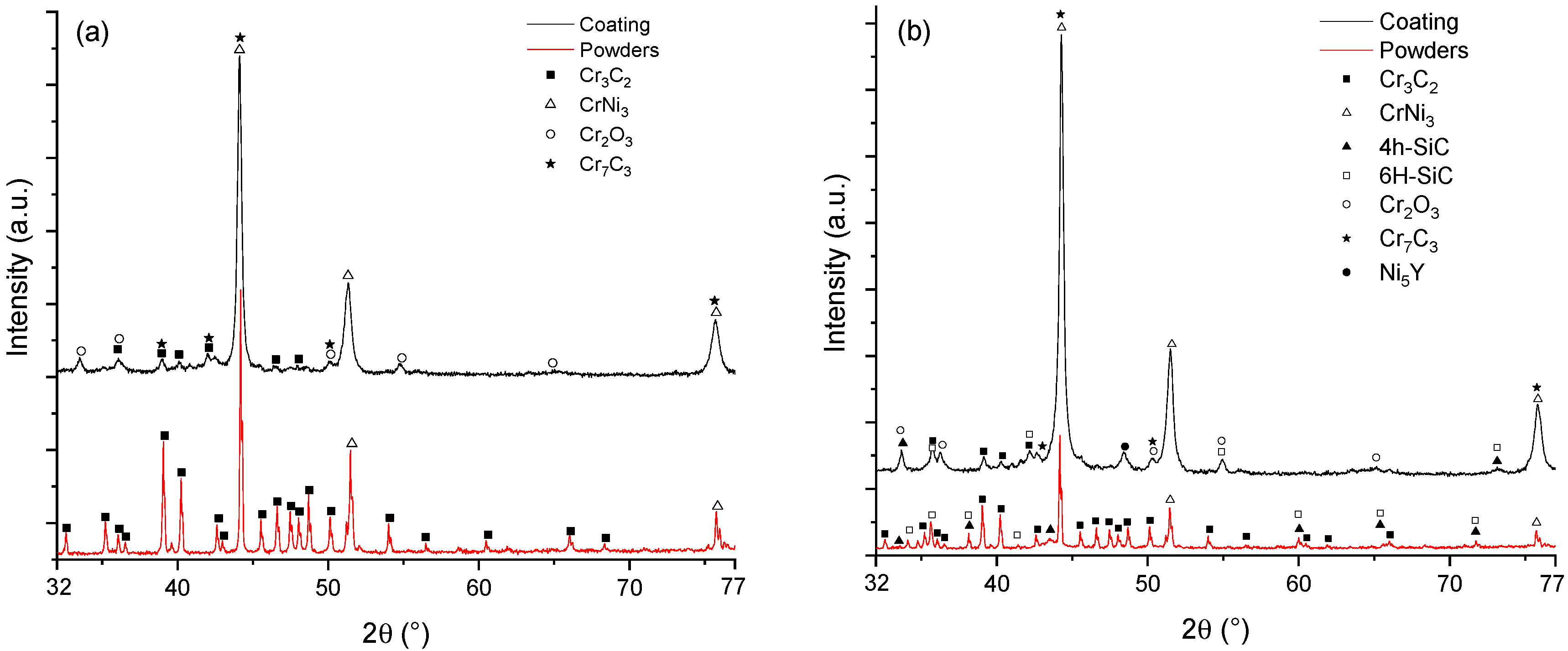
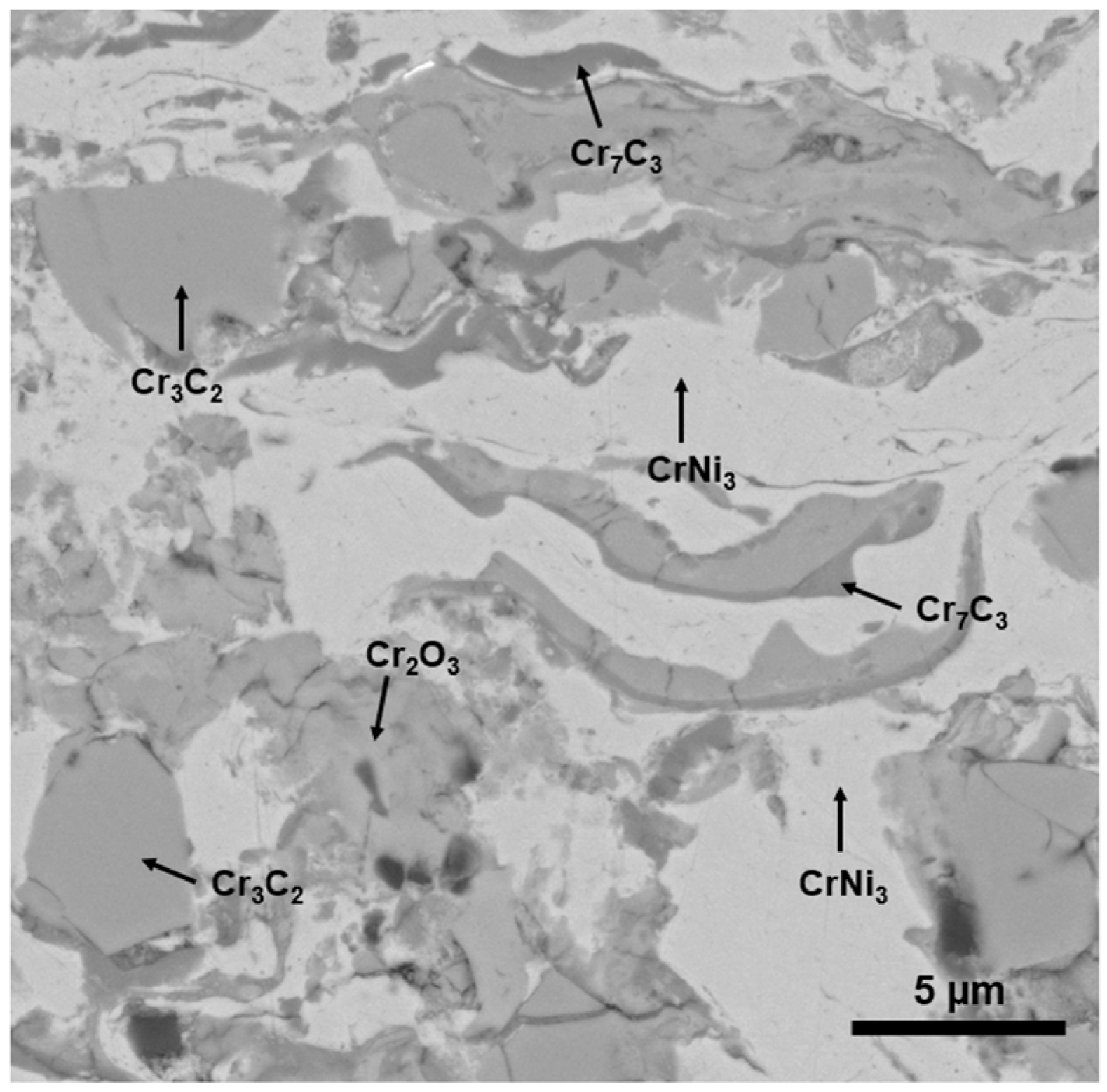
3.1. Coating Characterization
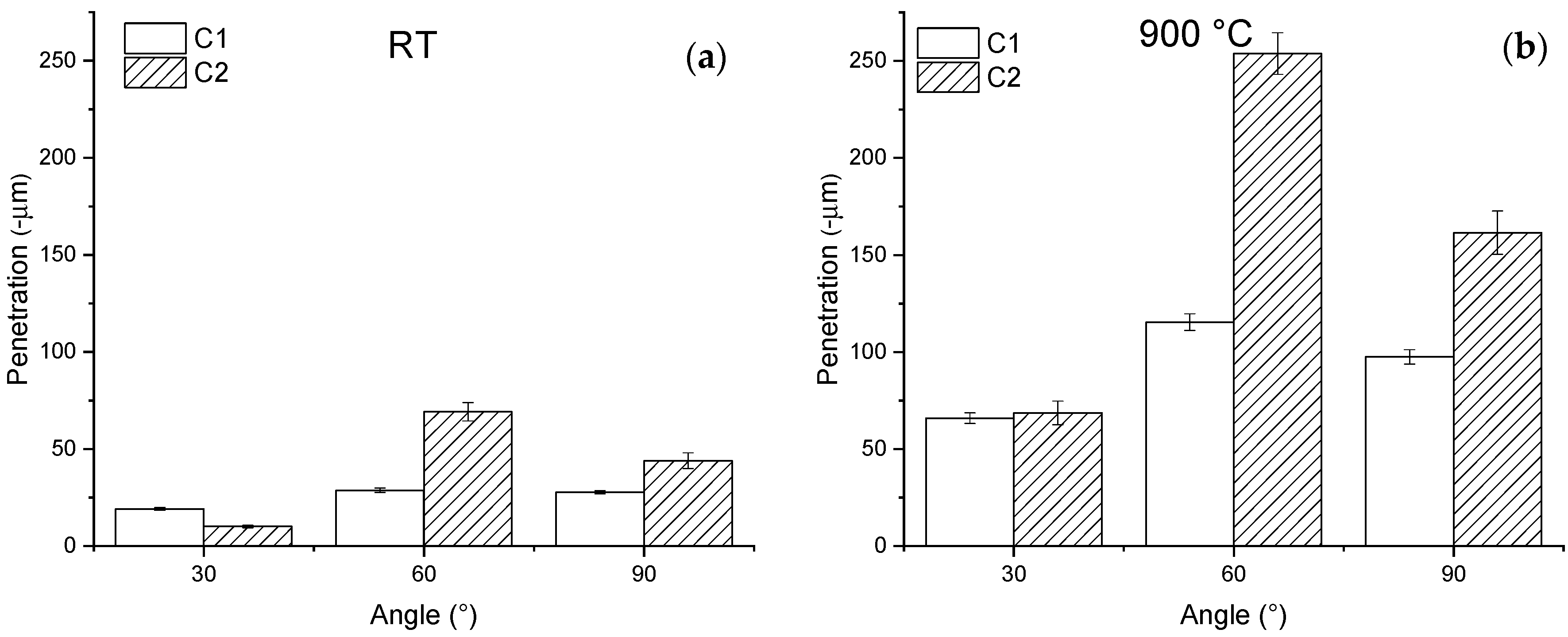
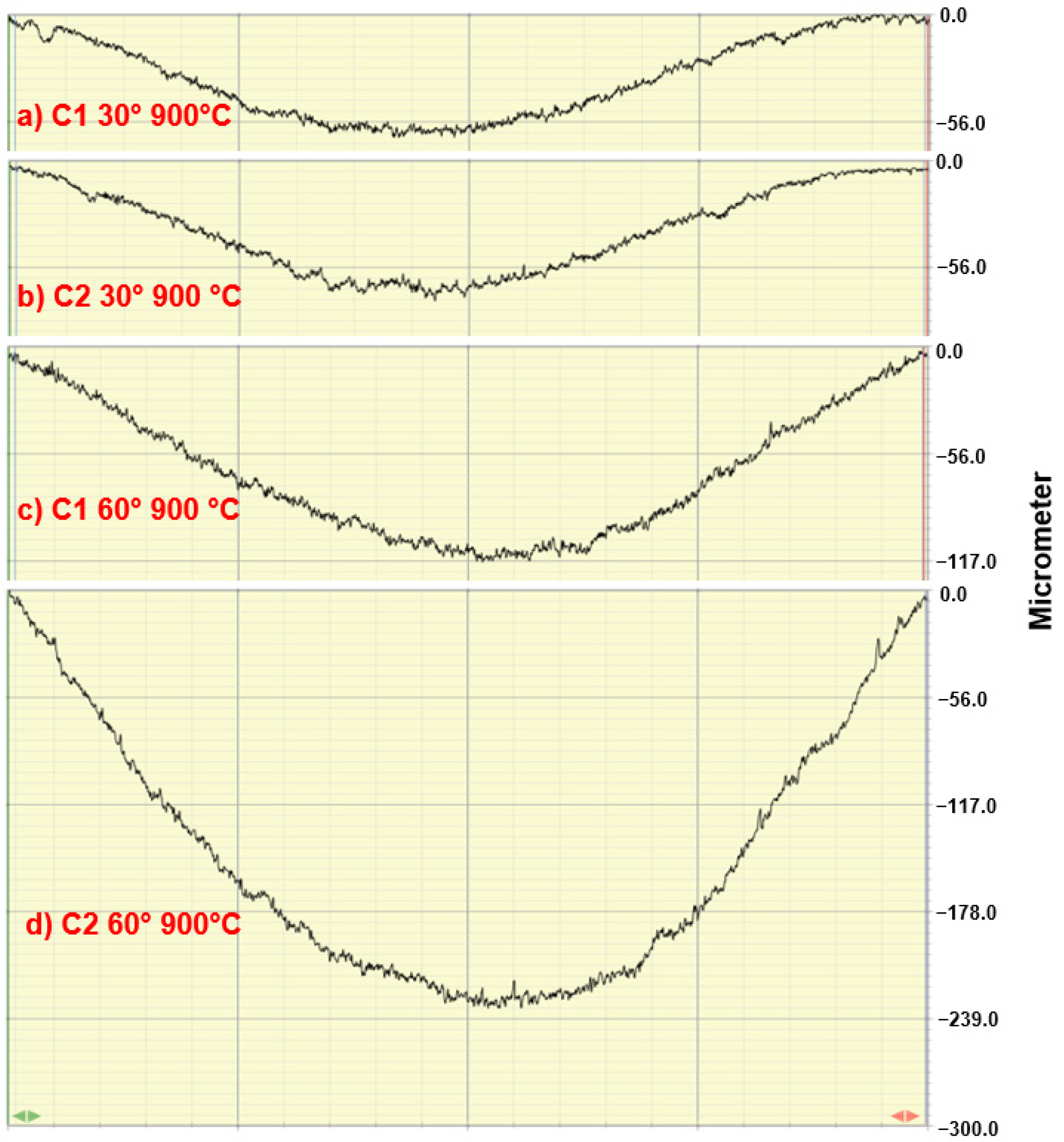
3.2. Erosion Tests
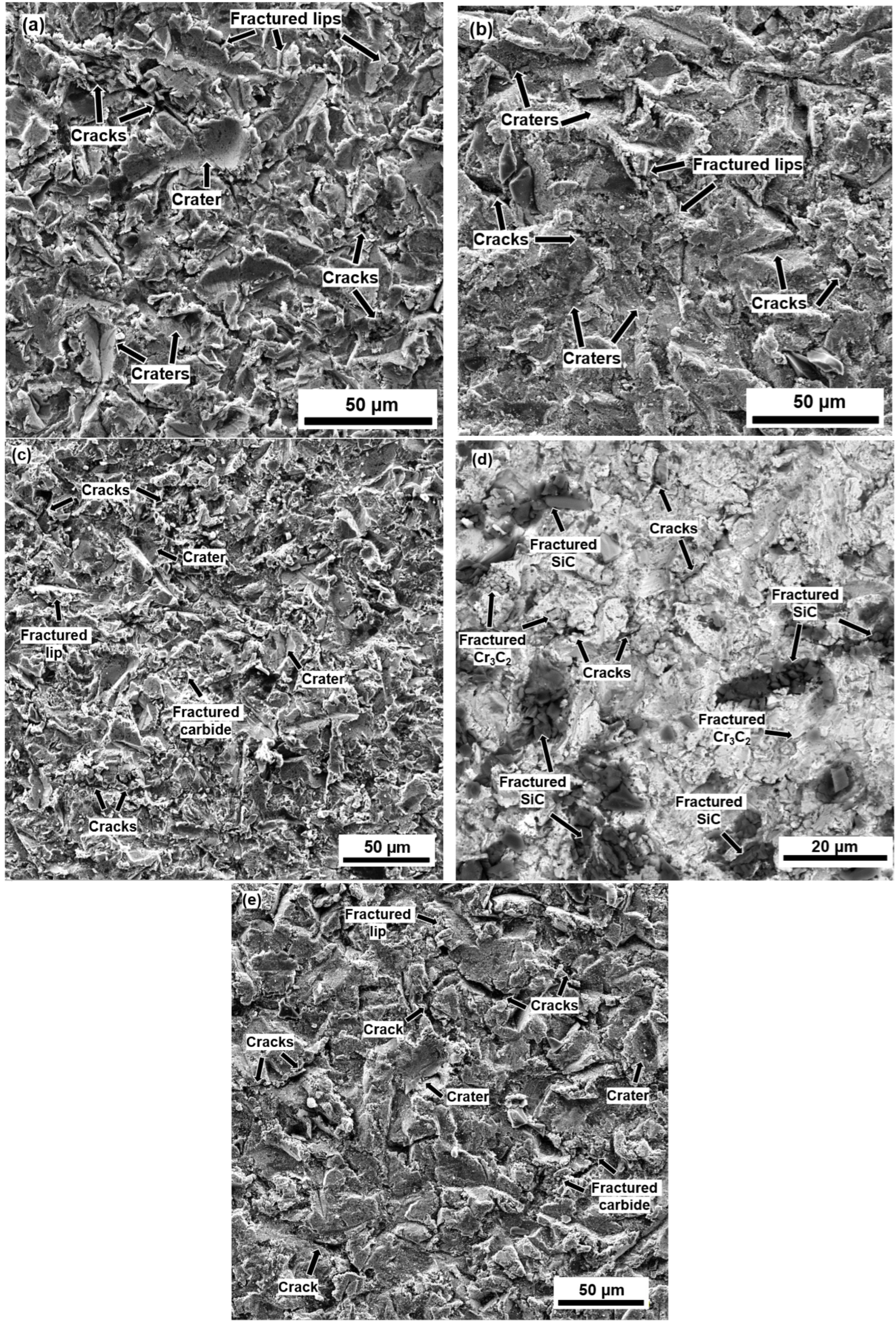
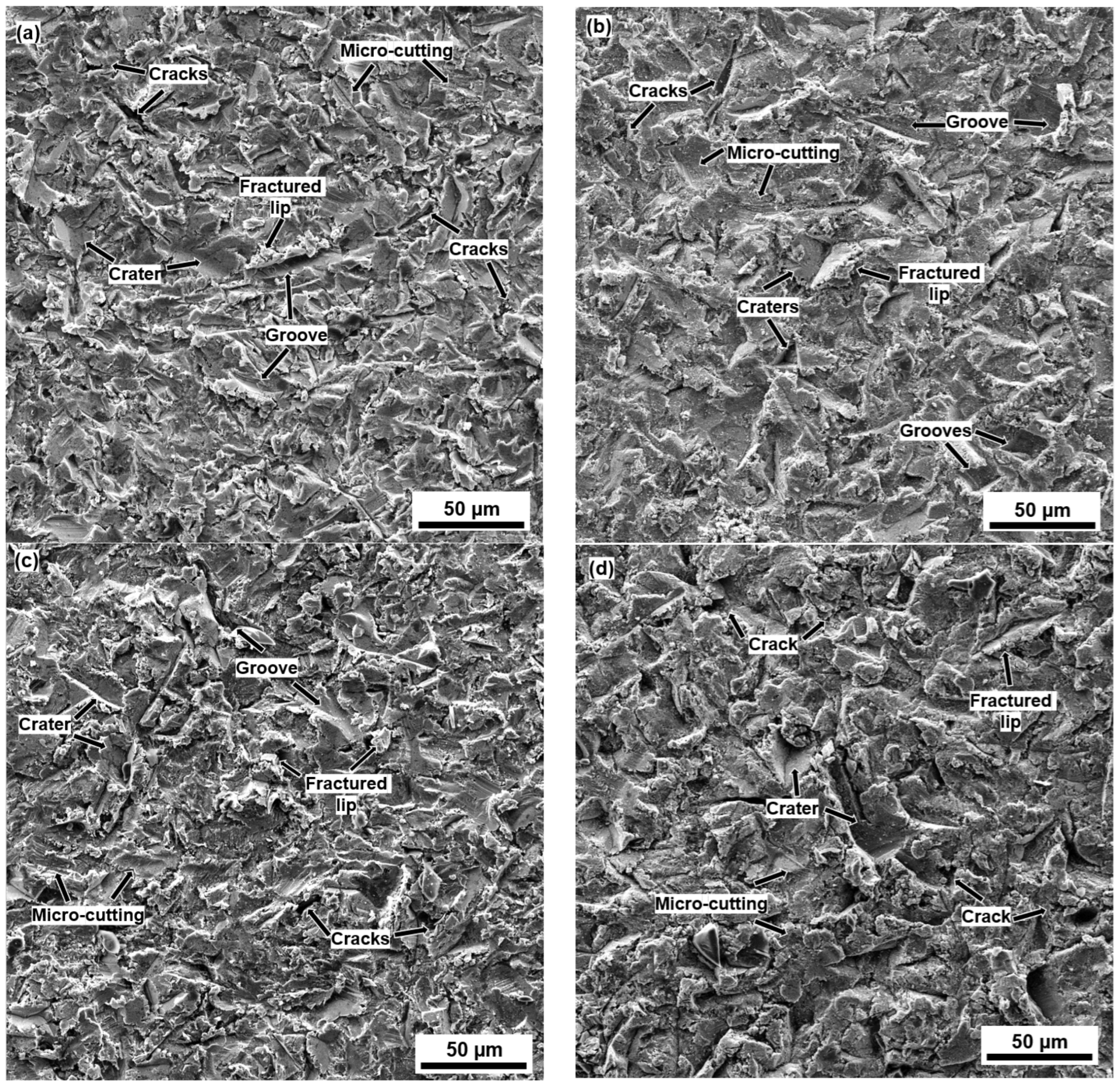
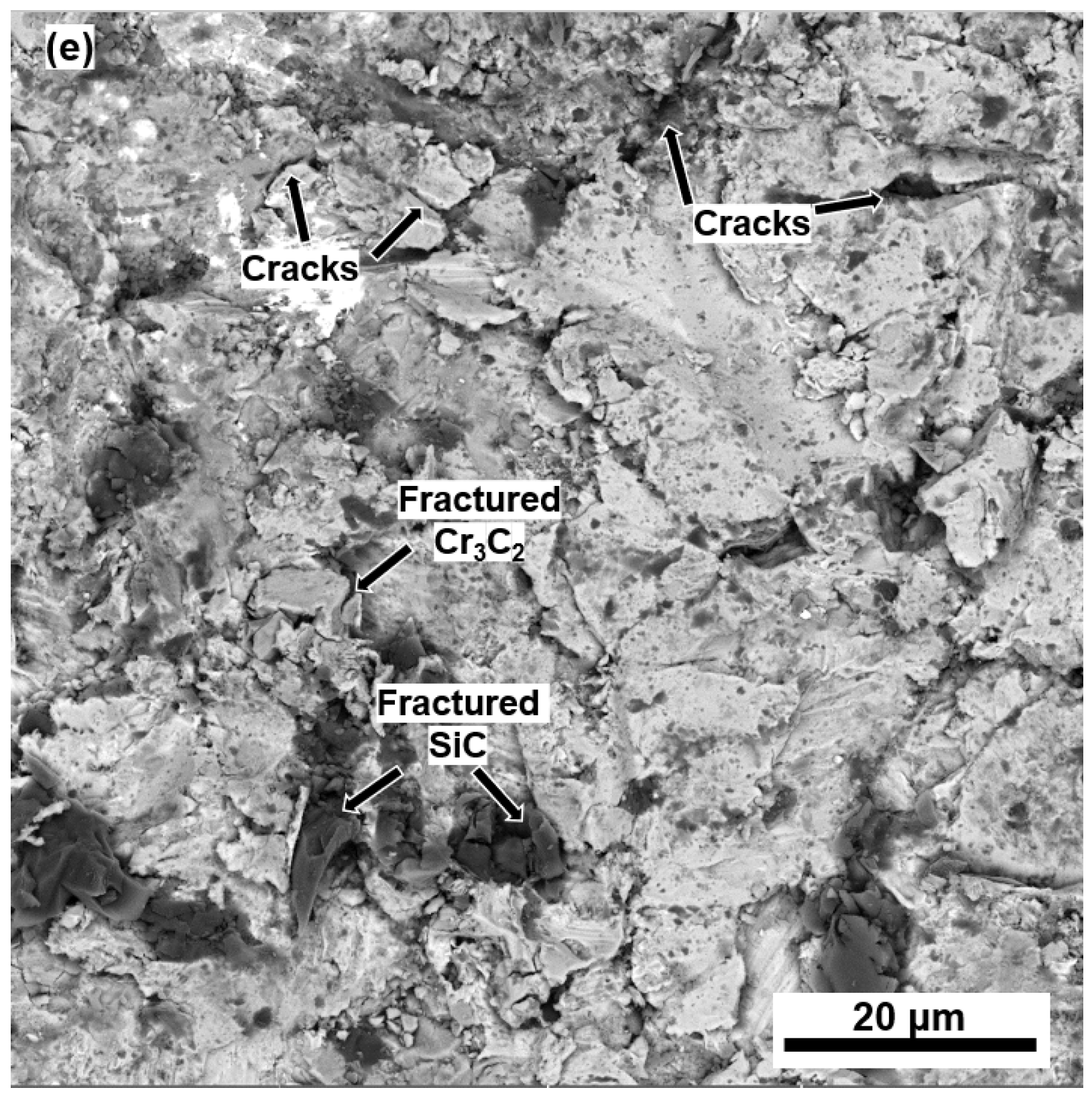
3.3. Erosion Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
- The SiC added to the C2 specimen was successfully stabilized, increasing the microhardness by 11% compared with the C1 coating but decreasing its KIC by 62.2%.
- The better erosion resistance of C1 was attributed to its higher KIC.
- The addition of SiC particles combined with their low KIC promoted the nucleation and propagation of inter-splat cracking, detrimentally affecting their erosion resistance at both temperatures.
- At 900 °C, the erosion rate of both coatings increased, and the ductile behavior of both coatings also increased due to the increment in the metallic matrix ductility.
- The maximum penetration depth always occurred at a 60° impact angle due to a combination of low-impact-angle erosion mechanisms (micro-cutting and grooves), and normal-impact-angle erosion mechanisms (craters and cracks formation).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASTM G76-18; Standard Test Method for Conducting Erosion Tests by Solid Particle Impingement Using Gas Jets. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6.
- Kumar, P.; Sidhu, B.S. Characterization and High-Temperature Erosion Behaviour of HVOF Thermal Spray Cermet Coatings. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Z.; Fang, M.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Hu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.G.; Sun, H.R.; Huang, J.T.; Li, X.C. Solid Particle Impact Erosion of Alumina-Based Refractories at Elevated Temperatures. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surzhenkov, A.; Antonov, M.; Goljandin, D.; Kulu, P.; Viljus, M.; Traksmaa, R.; Mere, A. High-Temperature Erosion of Fe-Based Coatings Reinforced with Cermet Particles. Surf. Eng. 2016, 32, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.M. Application of Hardmetals as Thermal Spray Coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015, 49, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, J.K.N.; Satya Prasad, K.; Gopinath, K.; Venkataraman, B. Characterisation of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2-50(Ni20Cr) Coating and the Influence of Binder Properties on Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3975–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; James, B.; Hyland, M. High Temperature Erosion of Cr3C2-NiCr Thermal Spray Coatings-The Role of Phase Microstructure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.B.; Chandra, K.; Prakash, S. Characterisation and Erosion Behaviour of NiCrAlY Coating Produced by Plasma Spray Method on Two Different Ni-Based Superalloys. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Dong, L.; Li, L.; Meng, F. Erosion Behavior of Arc Sprayed FeTi/CrB MMC Coating at Elevated Temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 262, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulu, P.; Hussainova, I.; Veinthal, R. Solid Particle Erosion of Thermal Sprayed Coatings. In Proceedings of the Wear; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 258, pp. 488–496. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavendra Naik, K.; Kumar, R.K.; Saravanan, V.; Seetharamu, S.; Sampathkumaran, P. The Study of Cr3C2-25NiCr and 35WC-Co/65NiCrBSi-Based HVOF Coatings for High-Temperature Erosion Resistance Application. Tribol.-Mater. Surfaces Interfaces 2021, 16, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.M.; Liu, S.G.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.; Li, J. Effect of Al Content on High Temperature Erosion Properties of Arc-Sprayed FeMnCrAl/Cr3C2 Coatings. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Engl. Ed.) 2010, 20, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, J.R. Designing Oxidation-Resistant Coatings. JOM 2000, 52, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kuroda, S.; Murakami, H.; Katanoda, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Newman, S. Effects of Initial Oxidation on β Phase Depletion and Oxidation of CoNiCrAlY Bond Coatings Fabricated by Warm Spray and HVOF Processes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 221, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdelsztajn, L.; Tang, F.; Kim, G.E.; Provenzano, V.; Schoenung, J.M. Synthesis and Oxidation Behavior of Nanocrystalline MCrAIY Bond Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2005, 14, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Parco, M.; Lugscheider, E. Wear Behaviour of Al2O3 Dispersion Strengthened MCrAlY Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 184, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathapati, M.; Ramesh, M.R.; Doddamani, M. High Temperature Erosion Behavior of Plasma Sprayed NiCrAlY/WC-Co/Cenosphere Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 325, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithin, H.S.; Desai, V.; Ramesh, M.R. Elevated Temperature Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour of Carbide Reinforced CoCrAlY Composite Coatings. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 066529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Wilden, J.; Schinck, T.; Wank, A. Development of SiC-Composite Feedstock for HVOF Applications. In Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference, Essen, Germany, 4–6 March 2002; pp. 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, A.; Pala, Z.; Hussain, T. A Suspension High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Thermal Spray Manufacturing Route for Silicon Carbide–YAG Composite Coatings. Mater. Lett. 2020, 281, 128601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrabal, R.; Pardo, A.; Merino, M.C.; Mohedano, M.; Casajús, P.; Merino, S. Al/SiC Thermal Spray Coatings for Corrosion Protection of Mg–Al Alloys in Humid and Saline Environments. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarok, F.; Armada, S.; Fagoaga, I.; Espallargas, N. Thermally Sprayed SiC Coatings for Offshore Wind Turbine Bearing Applications. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tului, M.; Giambi, B.; Lionetti, S.; Pulci, G.; Sarasini, F.; Valente, T. Silicon Carbide Based Plasma Sprayed Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 207, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguro, K.; Ushida, T.; Hiraoka, T.; Esumi, K. Effects of Surfactants and Surface Treatment on Aqueous Dispersion of Silicon Carbide. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 60, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.C. Process for Dispersing Silicon Carbide Whiskers. U.S. Patent No. 4,956,316, 1990. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/es/detail.jsf?docId=US37885526&_cid=P22-LFVGRB-57515-1 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Guilemany, J.M.; Miguel, J.M.; Vizcaíno, S.; Lorenzana, C.; Delgado, J.; Sánchez, J. Role of Heat Treatments in the Improvement of the Sliding Wear Properties of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 157, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponton, C.B.; Rawlings, R.D. Vickers Indentation Fracture Toughness Test Part 1 Review of Literature and Formulation of Standardised Indentation Toughness Equations. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1989, 5, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, J.; Rodríguez, E.; González, M.A.; Cuenca, S.L.; Medina, A.; Vásquez, G.I. Erosion Behavior of 440C Stainless Steel Cryogenically Treated. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2020, 19, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, M.; Yung, D.L.; Goljandin, D.; Mikli, V.; Hussainova, I. Effect of Erodent Particle Impact Energy on Wear of Cemented Carbides. Wear 2017, 376–377, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Venkata Manoj Kumar, B.; Kim, Y.W. Effect of Impingement Angle and WC Content on High Temperature Erosion Behavior of SiC-WC Composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 68, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, M. Comparative Investigation on HVOF Sprayed Carbide-Based Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilemany, J.M.; Nutting, J.; Llorca-Isern, N. Characterisation of Cr3C2–Nicr Cermet Powder for High Velocity Oxyfuel Spraying. Powder Metall. 1994, 37, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussainova, I.; Antonov, M.; Jasiuk, I.; Du, X. Characterisation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cermets at Micro- and Nanoscales. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2011, 40, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonda, E.; Łatka, L.; Pakieła, W. Microstructure and Selected Properties of Cr3C2-Nicr Coatings Obtained by Hvof on Magnesium Alloy Substrates. Materials 2020, 13, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, N.; Sapate, S.G.; Jyoti Sahariah, B.; Bagde, P. Microstructural Characterization and Wear Behaviour of High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Sprayed Cr3C2-25NiCr Coating. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 17686–17693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Deng, C.; Zeng, K. High Temperature Wear Performance of HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo and Cr3C2-NiCr Hardmetal Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S. Development of High Carbide Dissolution/Low Carbon Loss Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings by Shrouded Plasma Spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 258, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Song, B.; Reddy, L.; Hussain, T. Preparation of MCrAlY–Al2O3 Composite Coatings with Enhanced Oxidation Resistance through a Novel Powder Manufacturing Process. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, A.L.; White, K.W. Microscale Fracture Mechanisms of a Cr3C2-NiCr HVOF Coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Lu, H.; Du, J.; Ran, X.; Zhang, X. Effect of NiCr Content on the Solid Particle Erosion Behavior of NiCr-Cr3C2 Coatings Deposited by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 381, 125144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, H.; Ran, X.; Qi, X. Comparison on Multi-Angle Erosion Behavior and Mechanism of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Sprayed by SPS and HVOF. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.A.; Rodríguez, E.; Mojardín, E.; Jiménez, O.; Guillen, H.; Ibarra, J. Study of the Erosive Wear Behaviour of Cryogenically and Tempered WC-CoCr Coating Deposited by HVOF. Wear 2017, 376–377, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, S. Solid Particle Erosion-Wear Behaviour of Cr3C2–NiCr Coating on Ni-Based Superalloy. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 168781401769458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J.; Zhang, S.J.; Li, C.X. High-Temperature Erosion of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coating and Mild Steel for Boiler Tubes. Proc. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2008, 17, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Spraying Parameters | C1 | C2 |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen flow | 707.92 L/min | 707.92 L/min |
| Kerosene flow | 333 mL/min | 333 mL/min |
| Spraying distance | 38.1 cm | 38.1 cm |
| Feed rate | 8.8 RPM | 12.12 RPM |
| Argon flux | 3.78 L/min | 11.8 L/min |
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Erodent | Angular Alumina |
| Particle size | 125–150 µm |
| Feed rate | 14.6 g/min |
| Test time | ~40 min |
| Particle velocity | 46.8 m/s |
| Impact angle | 30°, 60°, 90° |
| Inner diameter of the outlet nozzle | 1.5875 mm |
| Erodent load | 500 g |
| Impact distance | 69.85 mm |
| Air pressure | 34.5 kPa |
| Test temperatures | Room temperature (RT), 900 °C |
| Coating | Microhardness (HV0.5) | KIC (MPa m1/2) |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 641 ± 58 | 5.14 ± 0.27 |
| C2 | 711 ± 63 | 3.2 ± 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velez Barragan, E.E.; González Albarrán, M.A.; Rodríguez de Anda, E.; Vásquez Guillen, G.I.; de Jesús Ibarra Montalvo, J.; Díaz Guillén, J.C.; Chávez Aguilar, J.M. High-Temperature Erosion of SiC-NiCrAlY/Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. Coatings 2023, 13, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040720
Velez Barragan EE, González Albarrán MA, Rodríguez de Anda E, Vásquez Guillen GI, de Jesús Ibarra Montalvo J, Díaz Guillén JC, Chávez Aguilar JM. High-Temperature Erosion of SiC-NiCrAlY/Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. Coatings. 2023; 13(4):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040720
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelez Barragan, Eduardo Enrique, Marco Aurelio González Albarrán, Eduardo Rodríguez de Anda, Gabriel Israel Vásquez Guillen, José de Jesús Ibarra Montalvo, Juan Carlos Díaz Guillén, and Jorge Manuel Chávez Aguilar. 2023. "High-Temperature Erosion of SiC-NiCrAlY/Cr3C2-NiCr Coating" Coatings 13, no. 4: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040720
APA StyleVelez Barragan, E. E., González Albarrán, M. A., Rodríguez de Anda, E., Vásquez Guillen, G. I., de Jesús Ibarra Montalvo, J., Díaz Guillén, J. C., & Chávez Aguilar, J. M. (2023). High-Temperature Erosion of SiC-NiCrAlY/Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. Coatings, 13(4), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040720









