Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Membranes with Special Wettability for Oil–Water Separation: A Review
Abstract
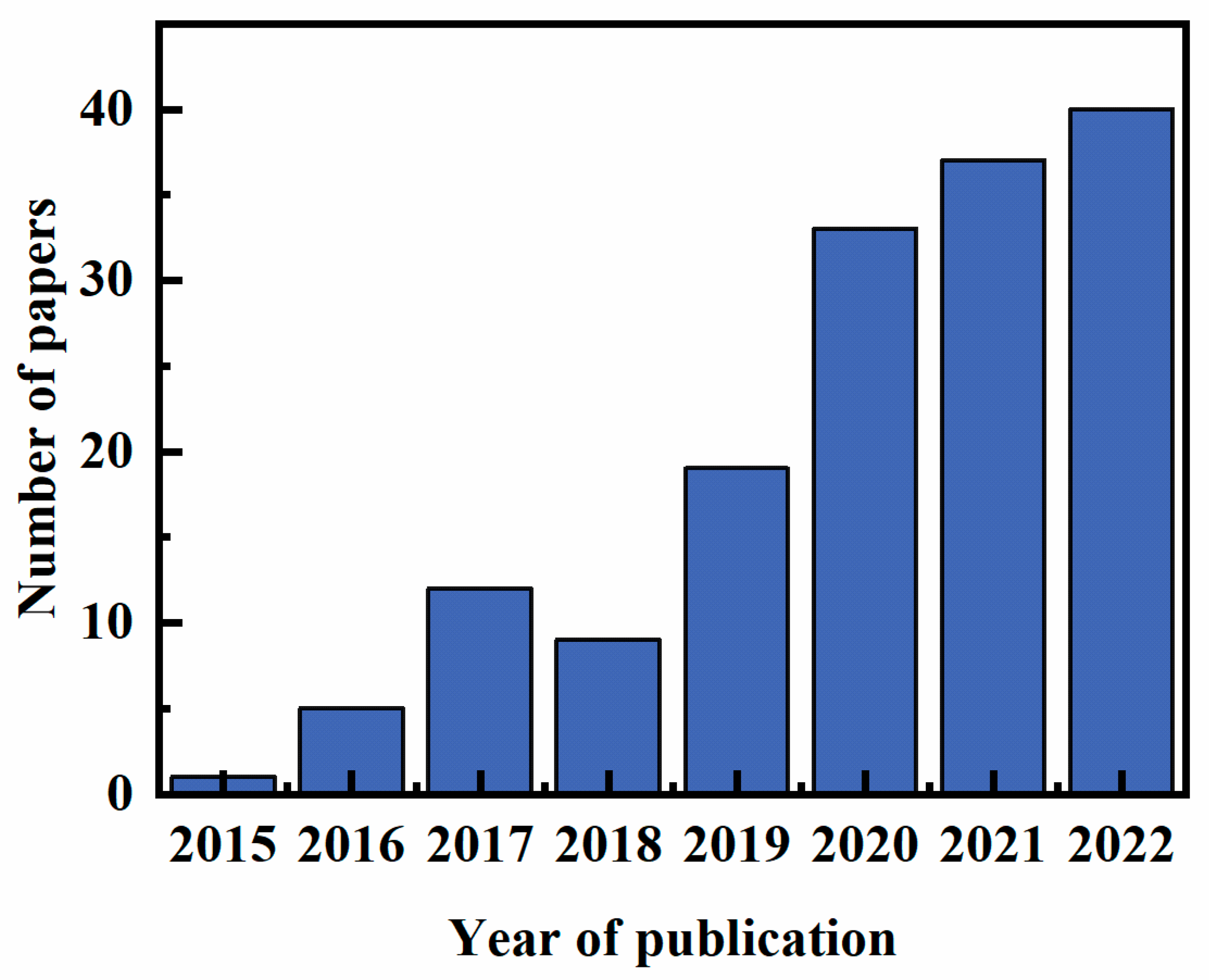
:1. Introduction
2. The Mechanism of Oil–Water Separation
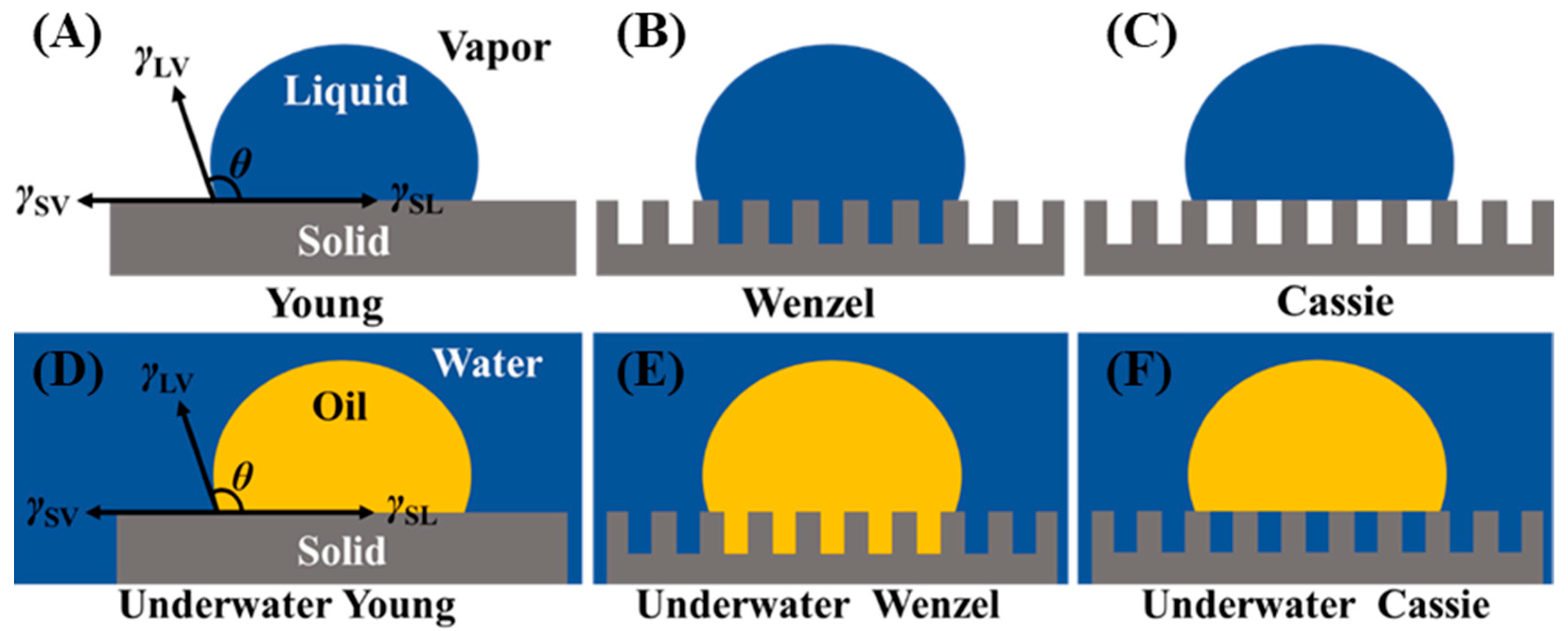
2.1. Basic Theory of Wettability
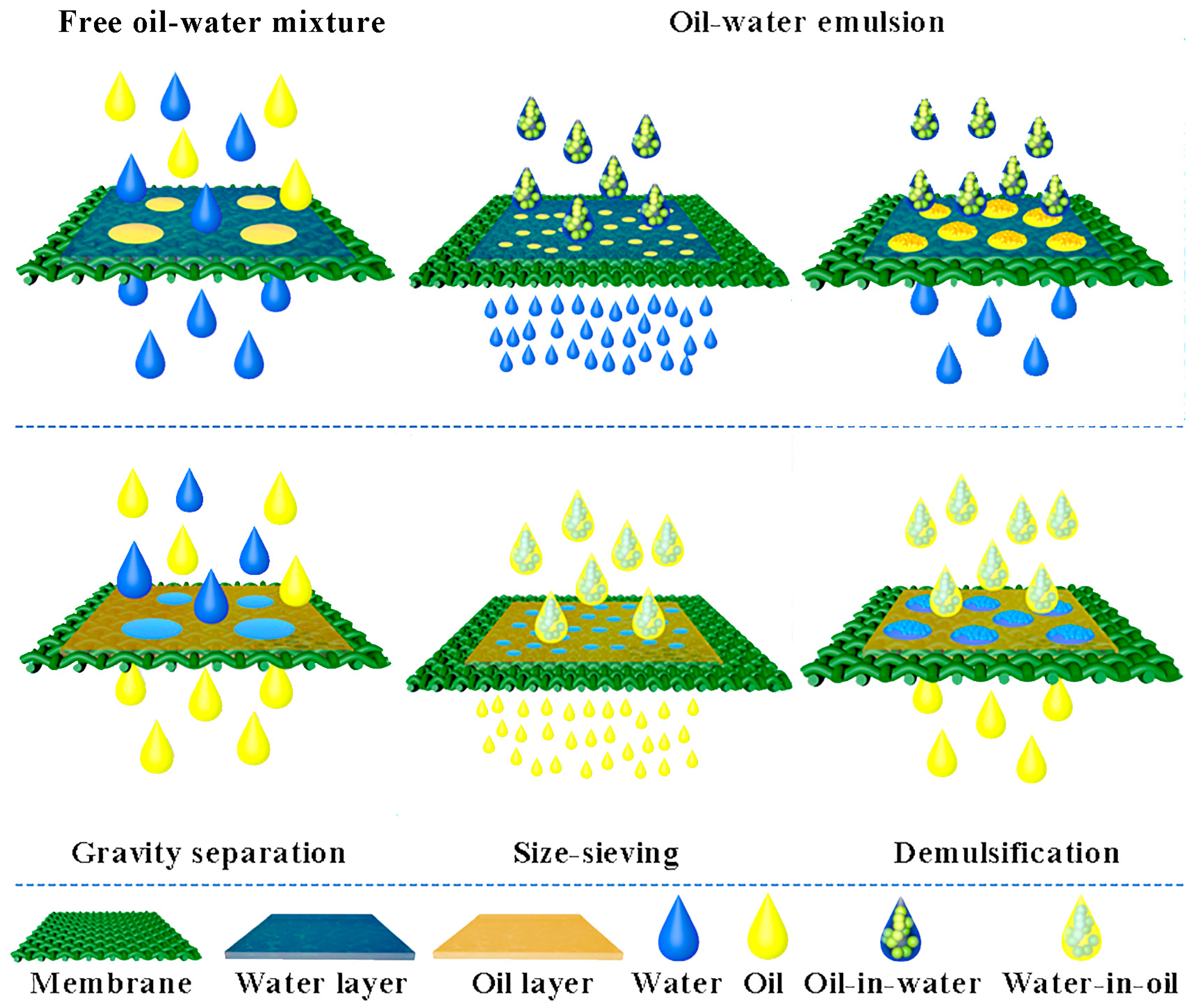
2.2. Separation of Free Oil–Water Mixture
2.3. Separation of Oil–Water Emulsion
3. Methods to Prepare MOFs-Based Materials for Oil–Water Separation
3.1. In Situ Growth Method
3.1.1. Substrate Pre-Modification Method
3.1.2. Precursor Sacrifice Method
3.1.3. Crystal Seed Growth
3.2. Deposition Method
3.2.1. Direct Deposition
3.2.2. Electrochemical Deposition
3.2.3. Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly
3.2.4. Filtration Deposition
3.2.5. Spin-Coating
3.3. Blending Membrane Method
3.3.1. Electrospinning
3.3.2. Phase Inversion
4. The Classification of MOFs Used for Oil–Water Separation
4.1. ZIF Series
4.2. UiO Series
4.3. MIL Series
4.4. Other MOFs
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beyer, J.; Trannum, H.C.; Bakke, T.; Hodson, P.V.; Collier, T.K. Environmental effects of the deepwater horizon oil spill: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.I.; Olaniran, A.O. Treatment of industrial oily wastewater by advanced technologies: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.B.; Oleinik, P.H.; Leal, T.F.; Marques, W.C.; Nicolodi, J.L.; Lopes, B. Integrated environmental vulnerability to oil spills in sensitive areas. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murawski, S.A.; Kilborn, J.P.; Bejarano, A.C.; Chagaris, D.; Donaldson, D.; Hernandez, F.J.; MacDonald, T.C.; Newton, C.; Peebles, E.; Robinson, K.L. A synthesis of deepwater horizon impacts on coastal and nearshore living marine resources. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 594862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, B.A.; Lim, A.; Intawong, C.; Rheanpumikankit, S.; Suksri, S.; Ingviya, T. Haematological, renal, and hepatic function changes among Rayong oil spill clean-up workers: A longitudinal study. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2022, 95, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingviya, T.; Intawong, C.; Abubaker, S.; Strickland, P.T. Exposure assessment of rayong oil spill cleanup workers. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padikkal, S.; Sumam, K.S.; Sajikumar, N. Sustainability indicators of water sharing compacts. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 2027–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.Z.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.N.; Feng, L. Superwetting porous materials for wastewater treatment: From immiscible oil/water mixture to emulsion separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, I.F.; Varanasi, K.K. Separating nanoscale emulsions: Progress and challenges to date. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 36, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putatunda, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sen, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. A review on the application of different treatment processes for emulsified oily wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhasel, K.; Kchaou, M.; Alquraish, M.; Munusamy, Y.; Jeng, Y.T. Oily wastewater treatment: Overview of conventional and modern methods, challenges, and future opportunities. Water 2021, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkin, D.S.; Nedwed, T.J. Effectiveness of mechanical recovery for large offshore oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Sun, Y.H.; Guo, Z.G.; Liu, W.M. Janus membranes with asymmetric wettability applied in oil/water emulsion separations. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2000253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.H.; Shi, S.Q.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.Z. Design, development, and outlook of superwettability membranes in oil/water emulsions separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitao, T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Kitagawa, S.; Wang, B.; Uemura, T. Hybridization of MOFs and polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3108–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Liu, X.L.; Demir, N.K.; Chen, J.P.; Li, K. Applications of water stable metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5107–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, U.; Jee, S.; Rao, P.C.; Shin, J.; Ko, C.; Yoon, M.; Park, K.S.; Choi, K.M. Recent advances in process engineering and upcoming applications of metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 426, 213544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, N.; Yuvaraj, P.; Fathima, N.N. Fabrication of non-fluorinated superhydrophobic and flame retardant porous material for efficient oil/water separation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 286, 126190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borazjani, A.R.; Akhlaghi, B.; Abbasi, M.; Osfouri, S. Investigation of petroleum products dehydration using natural zeolite and activated carbon. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, Y.S.; Zhang, D.; Guan, Y.H.; Bao, M.T.; Wang, Z.N. A super-hydrophobic and antibiofouling membrane constructed from carbon sphere-welded MnO2 nanowires for ultra-fast separation of emulsion. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, R.M.; Kuriya, G.; Kurkuri, M.D.; Kigga, M. MOF based engineered materials in water remediation: Recent trends. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sharma, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Hydrophobic metal-organic frameworks: Potential toward emerging applications. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 050701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, A.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. Metal-organic frameworks: A new generation potential material for aqueous environmental remediation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 140, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydaghdari, M.; Saboor, F.H.; Babapoor, A.; Karve, V.V.; Asgari, M. Recent Advances in MOF-Based Adsorbents for Dye Removal from the Aquatic Environment. Energies 2022, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Singh, A.; Trivedi, M.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J.Q. Metal organic frameworks as efficient adsorbents for drugs from wastewater. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, D.Q.C.; Liao, D.H.; Qin, T.R.; Prakash, O.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J.Q. A new 3D 8-connected Cd(II) MOF as a potent photocatalyst for oxytetracycline antibiotic degradation. CrystEngComm 2022, 24, 6933–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.T.; Zou, J.F.; Han, Y.T.; Liao, Z.H.; Lu, P.F.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Liu, J.Q.; Peng, Y.Q. Recent advances in Al(iii)/In(iii)-based MOFs for the detection of pollutants. N. J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19577–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Pan, A.; Liu, J.Q.; Liu, X.X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, C.Y.; Fu, G.N.; Peng, C.Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Wan, X.C. Hierarchical camellia-like metal-organic frameworks via a bimetal competitive coordination combined with alkaline-assisted strategy for boosting selective fluoride removal from brick tea. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 642, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, X.C.; Ren, G.N.; Zhao, X.C.; Pu, X.P.; Li, W.Z. Facile synthesis of superhydrophobic ZIF-8/bismuth oxybromide photocatalyst aerogel for oil/water separation and hazardous pollutant degradation. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Samavati, A.; Nordin, N.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Malek, N. Enhanced performance and antibacterial properties of amine-functionalized ZIF-8-decorated GO for ultrafiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, M.; Bilal, M.; Sajid, M.; Nawaz, M.S.; Ihsanullah, I. MOF-based membranes for oil/water separation: Status, challenges, and prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.N.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired superspreading surface: From essential mechanism to application. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.J. Bio-inspired superwettable materials: An interview with Lei Jiang. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, P.M.; Naebe, M.; Wang, X.G.; Kandasubramanian, B. Nano-fluoro dispersion functionalized superhydrophobic degummed & waste silk fabric for sustained recovery of petroleum oils & organic solvents from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.N.; Han, M.; Guan, L.; Han, L.; Hemraj, A.; Tam, K.C. Sustainable superhydrophobic surface with tunable nanoscale hydrophilicity for water harvesting applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Z.; Li, H.Q.; Lai, X.J.; Huang, W.; Lin, Z.Y.; Zeng, X.R. Superwettable Janus nylon membrane for multifunctional emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 642, 119995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Weng, D.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.D. Separation mechanism and construction of surfaces with special wettability for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11006–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.N.; Chen, Z.X.; He, A.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Xu, Z.K. Janus membranes with controllable asymmetric configurations for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 7907–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Sun, W.; Chen, J.; Dai, C.L.; Yan, B.; Zeng, H.B. Bio-inspired membrane with adaptable wettability for smart oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Lu, Q.Y. Porous clusters of metal-organic framework coated stainless steel mesh for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.X.; Zhao, X.T.; Jia, N.; Cheng, L.J.; Liu, L.F.; Gao, C.J. Superwetting oil/water separation membrane constructed from in situ assembled metal-phenolic networks and metal-organic frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10000–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.C.; Li, Y.J.; Nian, P.; Liu, H.O.; Qiu, J.S.; Zhang, X.F. Fabrication of oriented metal-organic framework nanosheet membrane coated stainless steel meshes for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.D.; Zhao, F.X.; Peng, T.P.; Liu, H.; Xie, L.; Jiang, C.W. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic metal meshes with microhierarchical structure via in situ self-assembly metal-organic framework for efficient oil-water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 402, 126344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ma, Q.; Jin, Z.W.; Nian, P.; Wang, Z. Switchable superlyophobic zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 film-coated stainless-steel meshes for selective oil-water emulsion separation with high flux. N. J. Chem. 2020, 44, 13534–13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Li, S.P.; Yao, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Z.G.; Chai, C.P. Preparation and characterization of polypropylene non-woven fabric/ZIF-8 composite film for efficient oil/water separation. Polym. Test 2021, 100, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Huang, W.; Guo, Z.P.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wu, F.; Huang, J.J.; Yang, H.J.; Zhou, Y.S.; Xu, W.L.; Gu, S.J. Robust fluorine-free colorful superhydrophobic PDMS/NH2-MIL-125(Ti)@cotton fabrics for improved ultraviolet resistance and efficient oil-water separation. Cellulose 2019, 26, 9335–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.Z.; Cheng, J.; Yan, Y.Y.; Xu, S.P.; Zhou, C.L. Ultrafast preparation of hydrophobic ZIF-67/copper mesh via electrodeposition and hydrophobization for oil/water separation and dyes adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wei, W.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.H.; Zheng, C.B.; Zhang, Y.F.; Deng, P.Y. Continuous ultrathin UiO-66-NH2 coatings on a polymeric substrate synthesized by a layer-by-layer method: A kind of promising membrane for oil-water separation. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6658–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Yu, Z.X.; Zeng, H.J.; Feng, X.F.; Liu, Y.C.; Cao, K.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Long, R.X. Using a simple method to prepare UiO-66-NH2/chitosan composite membranes for oil-water separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Shangkum, G.Y.; Chammingkwan, P.; Taniike, T. Surface wettability switching of a zeolitic imidazolate framework-deposited membrane for selective efficient oil/water emulsion separation. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 614, 126204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Mu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.T. Inverse desert beetle-like ZIF-8/PAN composite nanofibrous membrane for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Yuan, D.; Geng, Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.Z.; Xie, Y.Z.; Wang, L.M.; Ning, X.; Ming, J.F. MOF-embedded bifunctional composite nanofiber membranes with a tunable hierarchical structure for high-efficiency PM0.3 purification and oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 39831–39843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.Y.; Xie, A.T.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.G.; Pan, J.M. Fabrication of multi-functional imprinted composite membrane for selective tetracycline and oil-in-water emulsion separation. Compos. Commun. 2021, 28, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, G.R.; Cui, M.B. Hydrophilic modification and anti-fouling properties of PVDF ultrafiltration membrane via blending of nano-particle MIL-101 MOFs. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2021, 16, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B. Metal-organic framework membranes: Production, modification, and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 100, 21–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.N.; Chen, G.Q.; Zheng, X.L.; Dai, M.; Peng, C.S. Metal-organic framework membranes: Recent development in the synthesis strategies and their application in oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.Y.; Guan, J.; Zhang, C.M.; Yuan, P.C.; Liu, L.N.; Afzal, M.Z.; Wang, S.G.; Sun, X.F. Photoinduced superwetting membranes for separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.M.; Li, J.H.; Ma, L.L.; Pang, Y.J.; Liu, L.L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, L.; Qu, M.N. High-flux oil-water separation with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity ZIF-67@Cu(OH)(2) nanowire membrane. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 3140–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, Y.X.; Dai, L.H.; Xu, F.; Qu, K.; Xu, Z. Anchoring metal organic frameworks on nanofibers via etching-assisted strategy: Toward water-in-oil emulsion separation membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, H.; Kallem, P.; Otyepkova, E.; Geyer, F.; Schneemann, A.; Ranc, V.; Banat, F.; Zboril, R.; Otyepka, M.; Fischer, R.A.; et al. Two-dimensional MOF-based liquid marbles: Surface energy calculations and efficient oil-water separation using a ZIF-9-III@PVDF membrane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 23651–23659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.H.; Chen, D.Y.; Li, N.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Li, H.; He, J.H.; Lu, J.M. Superhydrophobic metal-organic framework membrane with self-repairing for high-efficiency oil/water emulsion separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhu, H.M.; Zhang, B.Q. Facial fabrication of superhydrophobic ZIF-7 coatings with fast self-healing ability for ultra-efficient emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, P.Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, C.L.; Tan, L.X.; Wang, L. ZIF-L(Co) coated stainless steel meshes with superwettability for efficient multiphase liquid separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Lewis, A.; Chen, Z.P.; Fan, X.F.; Radacsi, N.; Semiao, A.J.C.; Wang, H.T.; Huang, Y. Smart ZIF-L mesh films with switchable superwettability synthesized via a rapid energy-saving process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.M.; Su, Q.; Lin, Q.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Long, S.R.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J. Multifunctional oxidized poly (arylene sulfide sulfone)/UiO-66 nanofibrous membrane with efficient adsorption/separation ability in harsh environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, M.Y.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Xu, Z.H.; Gan, D.; Huang, Z.; Ma, L.L.; Yang, B.; Zhou, Y. Robust superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic membrane optimized by Cu doping modified metal-organic frameworks for oil-water separation and water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
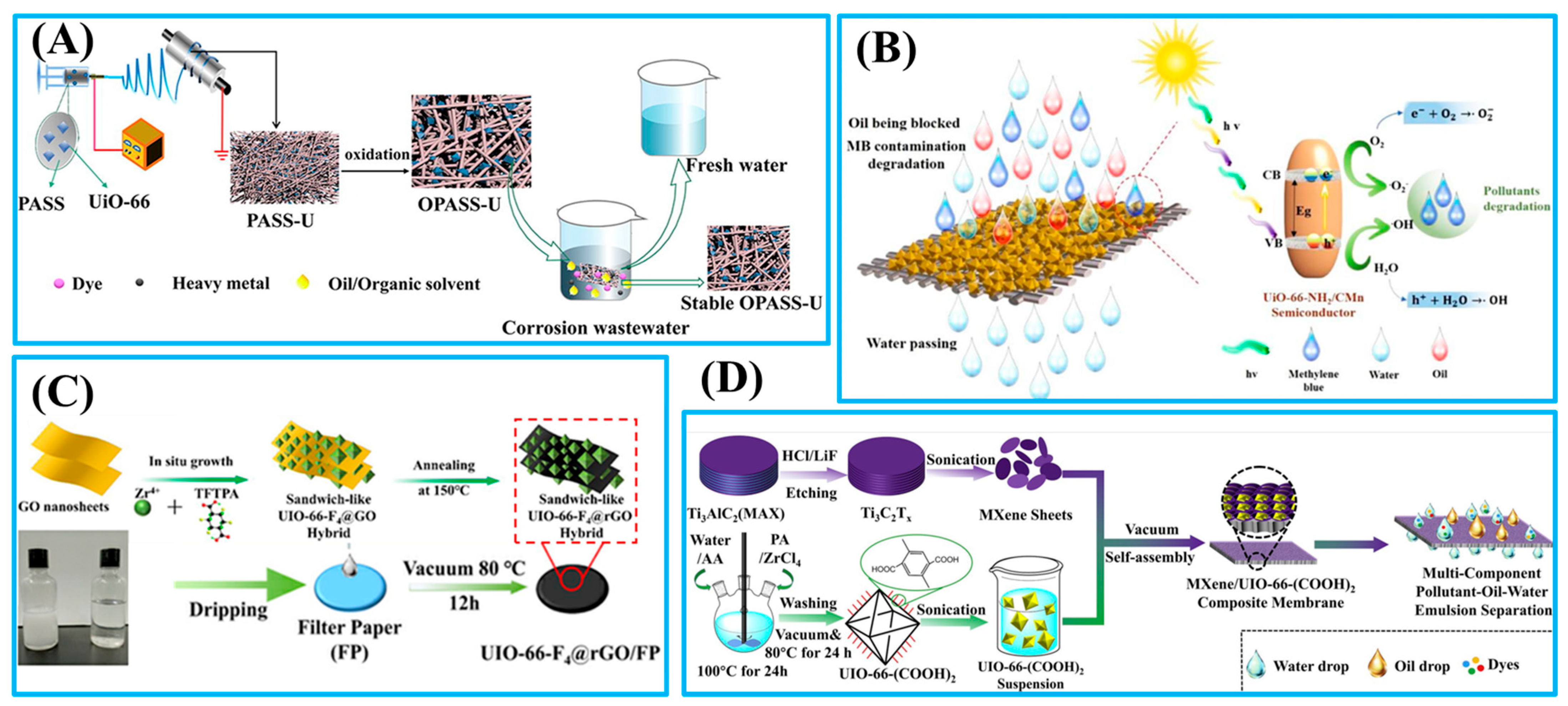
- Zhan, Y.Q.; He, S.J.; Hu, J.X.; Zhao, S.M.; Zeng, G.Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, G.Y.; Sengupta, A. Robust super-hydrophobic/super-oleophilic sandwich-like UIO-66-F4@rGO composites for efficient and multitasking oil/water separation applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Zhan, Y.Q.; Hu, J.X.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhao, S.M.; Feng, Q.Y.; Yang, W. Chemically stable two-dimensional MXene@UIO-66-(COOH)2 composite lamellar membrane for multi-component pollutant-oil-water emulsion separation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 197, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; He, Y.; Luo, P.Y.; Ma, L.; Li, S.S.; Nie, Y.L.; Zhong, F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, L. Photocatalytic GO/M88A “interceptor plate” assembled nanofibrous membrane with photo-Fenton self-cleaning performance for oil/water emulsion separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
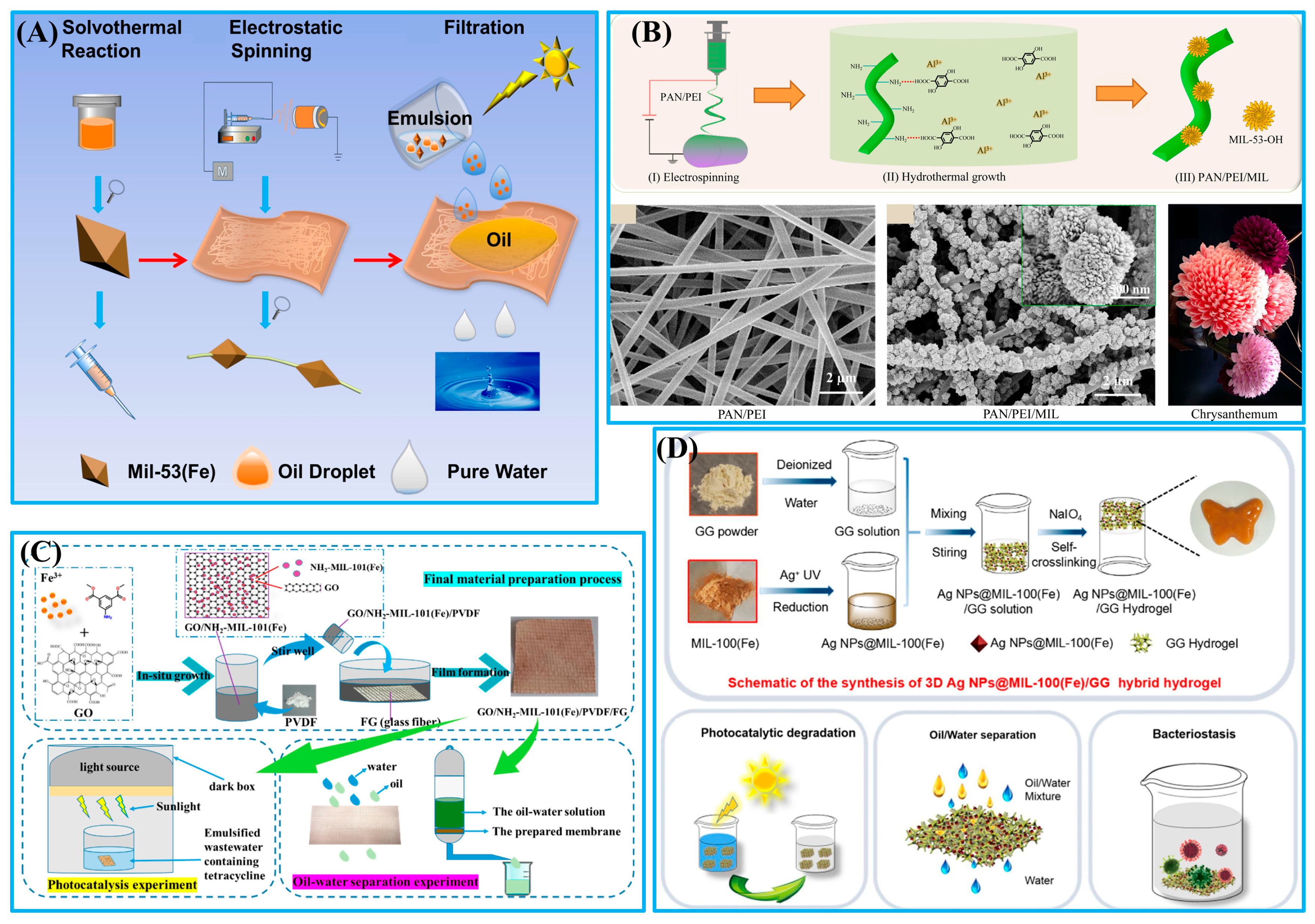
- Xiang, X.; Chen, D.Y.; Li, N.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Li, H.; He, J.H.; Lu, J.M. Mil-53(Fe)-loaded polyacrylonitrile membrane with superamphiphilicity and double hydrophobicity for effective emulsion separation and photocatalytic dye degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 119910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Yu, Z.X.; Liu, Y.C.; Li, X.Y.; Long, R.X.; Wang, P.Q.; Wang, J. NH2-MIL-125@PAA composite membrane for separation of oil/water emulsions and dyes. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.; Chao, M.; Xue, J.W.; Sun, D.F.; Xia, F.J.; Xue, Q.Z. Dual-functional membrane decorated with flower-like metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient removal of insoluble emulsified oils and soluble dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.W.; Han, X.F.; Xu, Z.Q. A robust PVDF-assisted composite membrane for tetracycline degradation in emulsion and oil-water separation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Liu, C.R.; Meng, X.; Gao, K.; Lu, W.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Dai, L.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, C.Y.; Wang, W.L.; et al. Facile synthesis of Ag NPs@ MIL-100(Fe)/guar gum hybrid hydrogel as a versatile photocatalyst for wastewater remediation: Photocatalytic degradation, water/oil separation and bacterial inactivation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Fu, M.; Yang, J.C.; Zhong, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhou, Y. Surface charge regulation of MIL-100(Fe) by anion exchange for demulsifying the cationic surfactant-stabilized O/W emulsion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 49964–49973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, Y.D.; Yu, F.Y.; Zhang, H.M. In-situ construction of MOFs-based superhydrophobic/superoleophilic coating on filter paper with self-cleaning and antibacterial activity for efficient oil/water separation. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, M.Y.; Gan, D.; Wang, M.R.; Zeng, H.J.; Liao, M.Q.; Chen, J.; Tu, W.W.; Niu, W. Ultrahigh flux of graphene oxide membrane modified with orientated growth of MOFs for rejection of dyes and oil-water separation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.J.; Xu, M.J.; Gao, J.M.; Zong, Y.Q.; Wang, M.X.; Ma, S.S. Multifunctional porphyrinic Zr-MOF composite membrane for high-performance oil-in-water separation and organic dye adsorption/ photocatalysis. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, J.T.; Wu, J.L.; Jiang, X.L.; Xu, M. Preparation of underwater superoleophobic polyimide mesh for oil/water separation via a simple Ce/Cu-MOF in-situ growth strategy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahringer, A.; Hennemann, M.; Clark, T.; Bein, T.; Medina, D.D. Energy efficient ultrahigh flux separation of oily pollutants from water with superhydrophilic nanoscale metal-organic framework architectures. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2021, 60, 5519–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaid, M.; Alsadun, N.; Shekhah, O.; Almahfoodh, S.; Zhou, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Eddaoudi, M. Deployment of superhydrophilic and super-antifouling Cr-soc-MOF-1-based membrane for ultrafast separation of stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 31067–31076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Li, N.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Li, H.; He, J.H.; Lu, J.M. Modified-MOF-808-loaded polyacrylonitrile membrane for highly efficient, simultaneous emulsion separation and heavy metal ion removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39227–39235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Y.; Bian, H.Z.; Dai, M.; Liu, X.; Peng, C.S. Underwater superoleophobic HKUST-1/PDA@SM membrane with excellent stability and anti-fouling performance for oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 678, 121655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Ding, S.L.; Wu, J.; Guo, Z.G. Underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophilic copper benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate (HKUST-1) mesh for self-cleaning and on-demand emulsion separation. Langmuir 2023, 39, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material | Preparation Method | Liquids of Separation | O/W Volume Ratio | Separation Efficiency (%) | Permeation Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8/GO | LBL | Toluene in water | - | - | 110 ± 6 | [58] |
| ZIF-67@Cu(OH)2 | In-suit growth | Oil–water mixture | 1:1 | 99 | 23,854 | [59] |
| ZIF-71/PVDF-HFP | Electrospinning and in-suit growth | Water-in-oil emulsions | 99:1 | >99 | 6577.68 | [60] |
| ZIF-9-III@PVDF | Phase inversion | Water-in-oil emulsions | 99:1 | 99.8 | 14.3 | [61] |
| ZIF-90 | Solvothermal method | Water-in-oil emulsions | - | 99.98 | 1260 | [62] |
| CPE-ZIF-7-coated SSM | Hydrothermal growth and dip-coating | Water-in-oil emulsion | 9:1 | 99.9 | 1056 | [63] |
| ZIF-8/PAN | Coprecipitation and electrospinning | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:50 | 99.92 | 2514 | [52] |
| ZIF-L(Co)@SSM | One-pot method | Polar/nonpolar liquids | 1:1 | >96 | - | [64] |
| ZIF-L(Zn)@SSM | Pre-seeding and secondary growth | Oil–water mixture | - | 99.98 | 1.24 × 105 | [65] |
| Material | Preparation Method | Liquids of Separation | O/W Volume Ratio | Separation Efficiency (%) | Permeation Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Other Functions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPASS/UiO-66 | Electrospinning | Water-in-oil emulsions | 40:1 | 98.44 | 636 | Adsorption of dyes (10 mg/L)and heavy metal ions (4 mg/L) | [66] |
| SSM/UiO-66-NH2/CMn | Hydrothermal | Oil–water mixtures | 1:1 | >99 | - | Degradation of dyes (10mg/L) | [67] |
| UiO-66-F4@rGO | Dip-coating | Water-in-oil emulsions | - | 99.73 | 990.45 | - | [68] |
| MXene@UiO-66-(COOH)2 | Vacuum-assisted self-assembly | Toluene-in-water emulsion | - | 99.54 | 498.91 | - | [69] |
| Material | Preparation Method | Liquids of Separation | O/W Volume Ratio | Separation Efficiency (%) | Permeation Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Other Functions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPAN@GO/M88A | Hydrothermal | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:100 | >99 | 920–7083(20–100 kpa) | Photo-Fenton self-cleaning properties | [70] |
| MIL-53(Fe) | Solvothermal and electrospinning | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:100; 1:20; 1:10 | >90 | 380 | Dye degradation (100 ppm) | [71] |
| NH2-MIL-125@PAA | Hydrothermal and vacuum-assisted self-assembly process | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:100 | 99.5 | 500 | Dyes separation (20 ppm) | [72] |
| PAN/PEI/MIL | Electrospinning and hydrothermal | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:1 | >99 | 4000 | Dyes adsorption (10 ppm) | [73] |
| GO/NH2-MIL-101(Fe) | One-pot method | Gasoline–water mixtures | 1:1408 | - | 120 | Tetracycline degradation (100 mg/L) | [74] |
| Ag NPs@MIL-100(Fe)/GG | Blending and self-crosslinking | Oil–water mixtures | 1:1 | >97.82 | - | Photocatalytic performance (40 mg/L) | [75] |
| Material | Preparation Method | Liquids of Separation | O/W Volume Ratio | Separation Efficiency (%) | Permeation Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Other Functions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
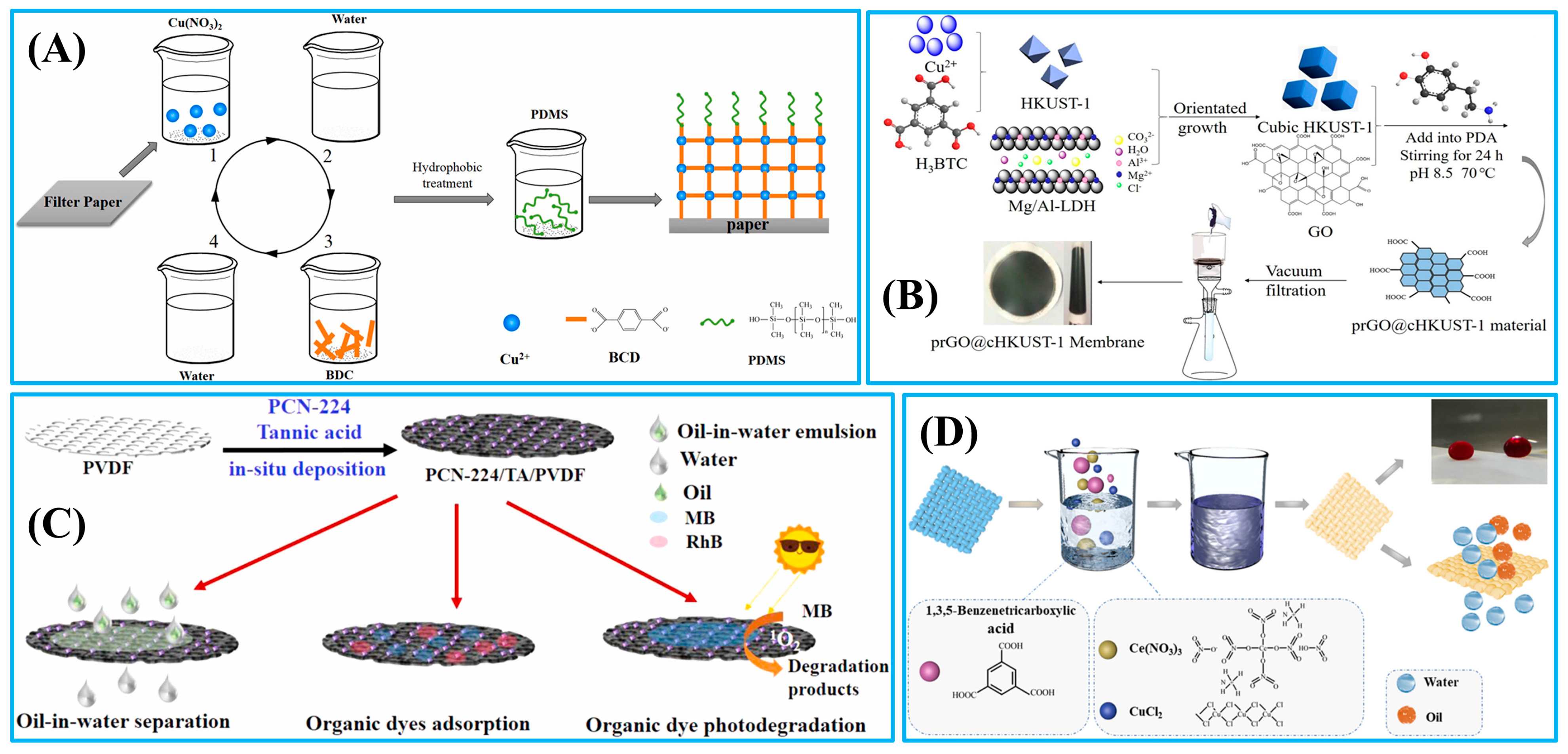
| PDMS/(Cu-MOFs)5@paper | LBL and in-suit growth | Oil–water mixtures | 1:1 | >98 | 55.8 | Antibacterial activity | [77] |
| prGO@cHKUST-1 | Hydrothermal | Oil–water emulsion | - | 99.6 | 28.6 | Dye adsorption (20 mg/L–100 mg/L) | [78] |
| PCN-224/TA/PVDF | In-suit deposition | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:99 | >99 | 1542 | Dye adsorption (10–50 ppm) | [79] |
| Ce/Cu-MOF | Dip-coating/in-suit growth | Oil–water mixtures | 1:4 | >98 | - | - | [80] |
| Co-CAT-1 | Vapor-assisted conversion | Oil–water mixtures | 1:1 | 99.98 | 8.4 × 105 | - | [81] |
| Cr-soc-MOF | Vacuum-assisted self-assembly method | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:100 | 98.7 | 7040.1 | - | [82] |
| MOF-808-EDTA | Solvothermal and electrospinning | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:10 | 99.97 | 379.3 | Heavy metal ions adsorption (Cu2+: 50 ppm) | [83] |
| HKUST-1/PDA@SM | Step-by-step deposition and hydrothermal synthesis | Oil-in-water emulsions | 1:9 | 95 | 200 | - | [84] |
| SSM@HKUST-1 | Electrochemical and in-suit growth method | Oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions | 1:100; 100:1 | 97.46; 99.63 | 569.7; 88.1 | - | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Tang, Q.; Lu, T.; Zhu, C.; Li, S.; Zhou, C.; Yang, H. Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Membranes with Special Wettability for Oil–Water Separation: A Review. Coatings 2023, 13, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13071241
Liu T, Tang Q, Lu T, Zhu C, Li S, Zhou C, Yang H. Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Membranes with Special Wettability for Oil–Water Separation: A Review. Coatings. 2023; 13(7):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13071241
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Teng, Qijin Tang, Tong Lu, Can Zhu, Shudi Li, Cailong Zhou, and Hao Yang. 2023. "Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Membranes with Special Wettability for Oil–Water Separation: A Review" Coatings 13, no. 7: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13071241
APA StyleLiu, T., Tang, Q., Lu, T., Zhu, C., Li, S., Zhou, C., & Yang, H. (2023). Metal–Organic Frameworks-Based Membranes with Special Wettability for Oil–Water Separation: A Review. Coatings, 13(7), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13071241







