Electro-Coloring Mechanism of Aluminum Anodic Oxides in Tin-Based Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
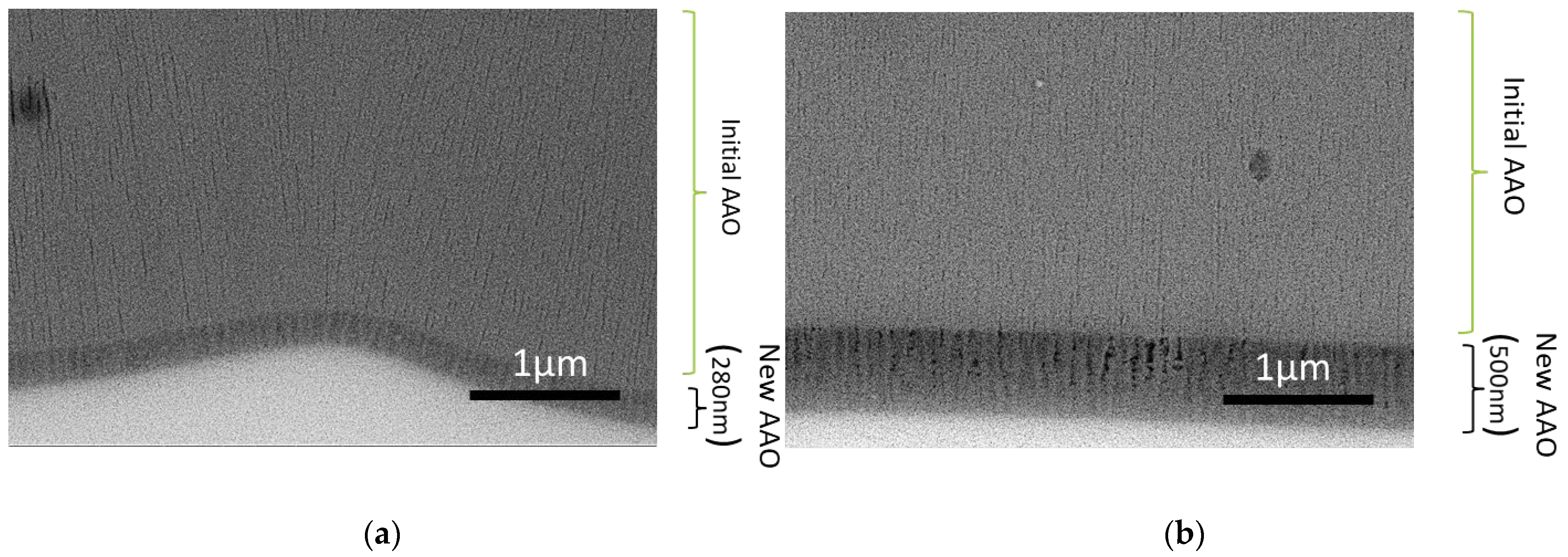
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Free-Standing AAO Layers
2.2. Electrochemical Investigation Methodology for the Determination of the Coloring Mechanism of AAO in Sn-Based E-Coloring Solutions
2.2.1. Preparation of AAO Films for E-Coloring
2.2.2. CV-Controlled E-Coloring Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
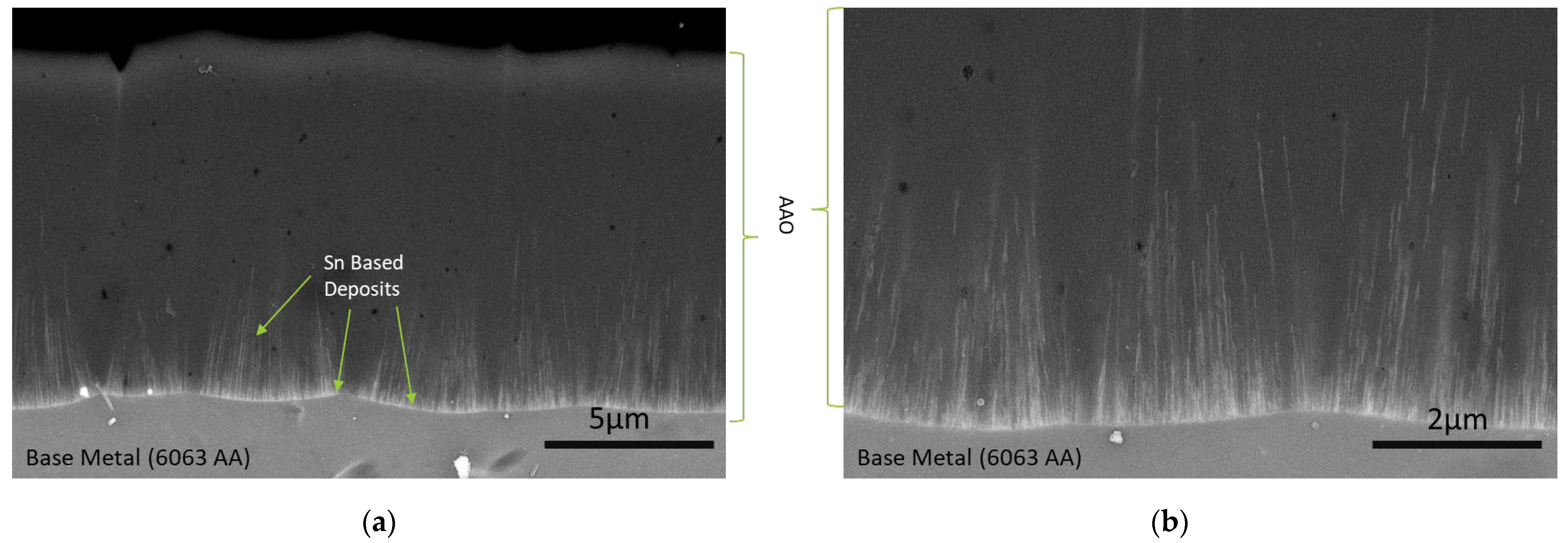
3.1. Chemical Characterization of Tin Deposits in Free-Standing AAO Films
3.2. Electrochemical Analysis of E-Coloring Process with High-Scan-Rate CV
3.2.1. Determination of the Suitability of Potential and Scan Rate Limits for E-Coloring
3.2.2. CV Experiments Conducted on AAO in Tin-Ion-Free and Tin-Ion-Containing Electrolytes
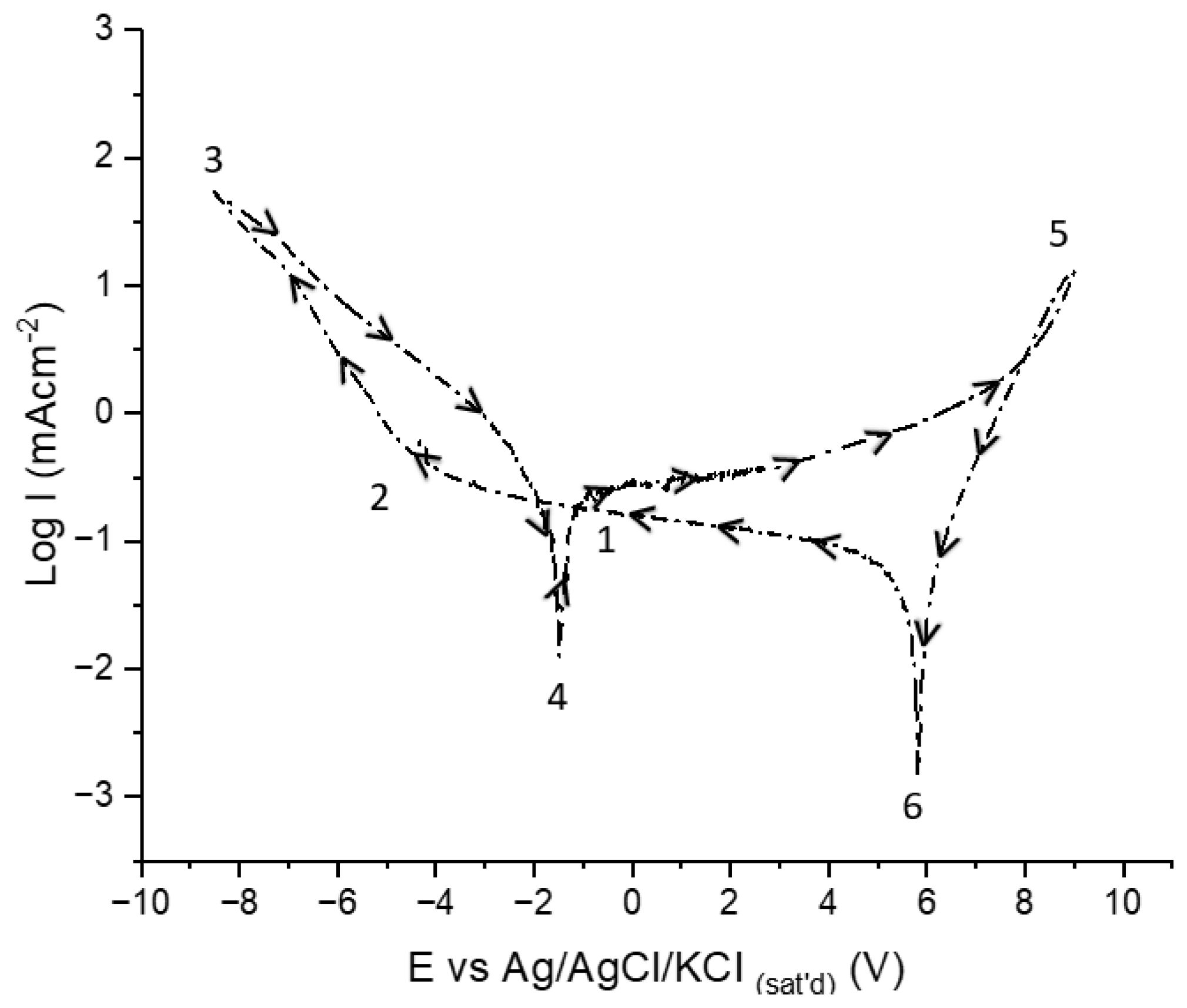
Explanation of Critical Potentials Observed during CV of AAO in Tin-Ion-Free Electrolytes
- At point 2 after cathodic breakdown until point 4:
- At point 4 for until point 5.
- At point 4, Al metal is not protected at pore bottoms; thus, corrosion starts at the mixed potential of the anodic (Reaction 5) and cathodic (Reaction 6) half-cell reactions in aluminate-rich pore bottom electrolytes. This is followed by passivation of Al (Reaction 7).
- At Point 5:
- At Point 6:
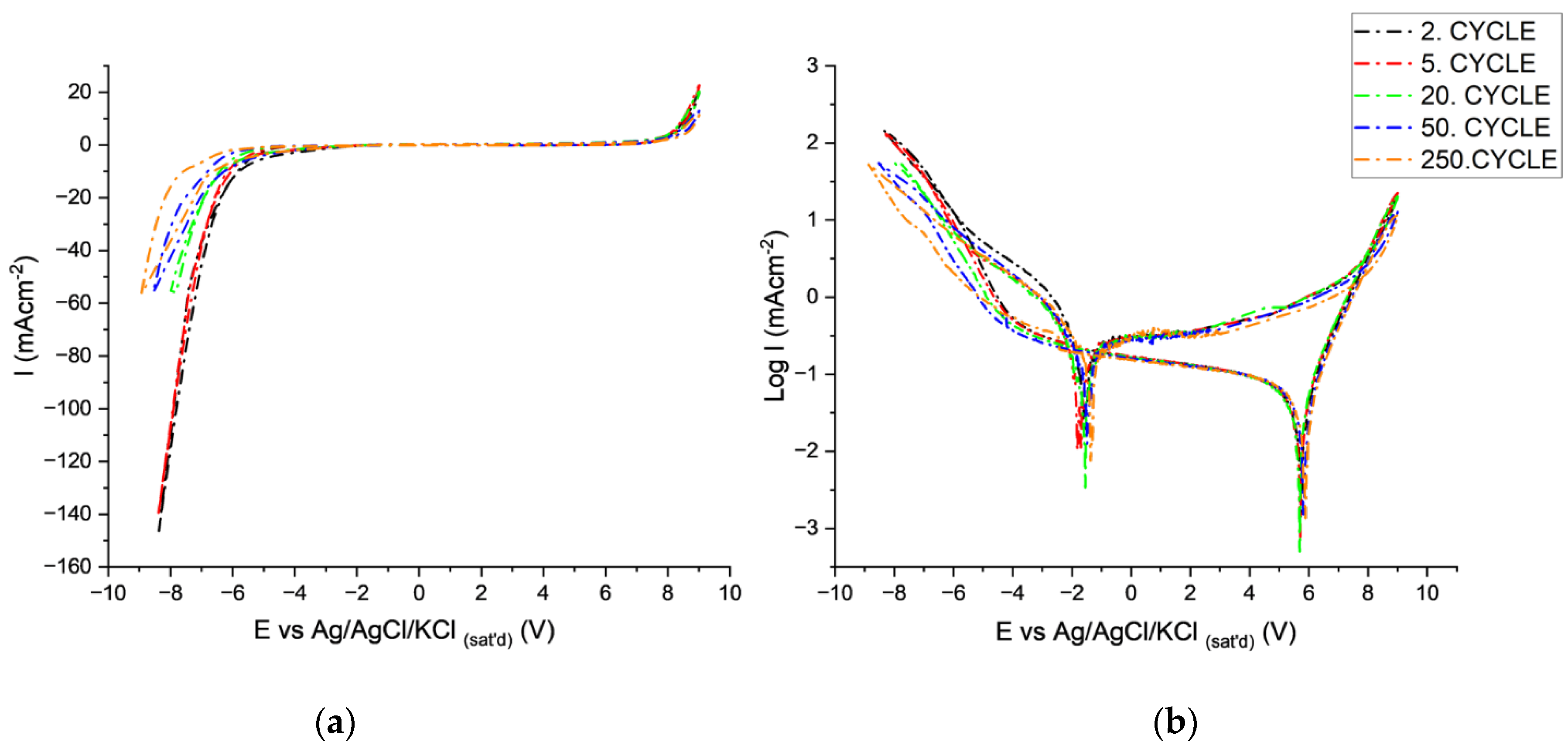
Variation in CV Behavior with Cycling in Tin-Ion-Free Electrolytes
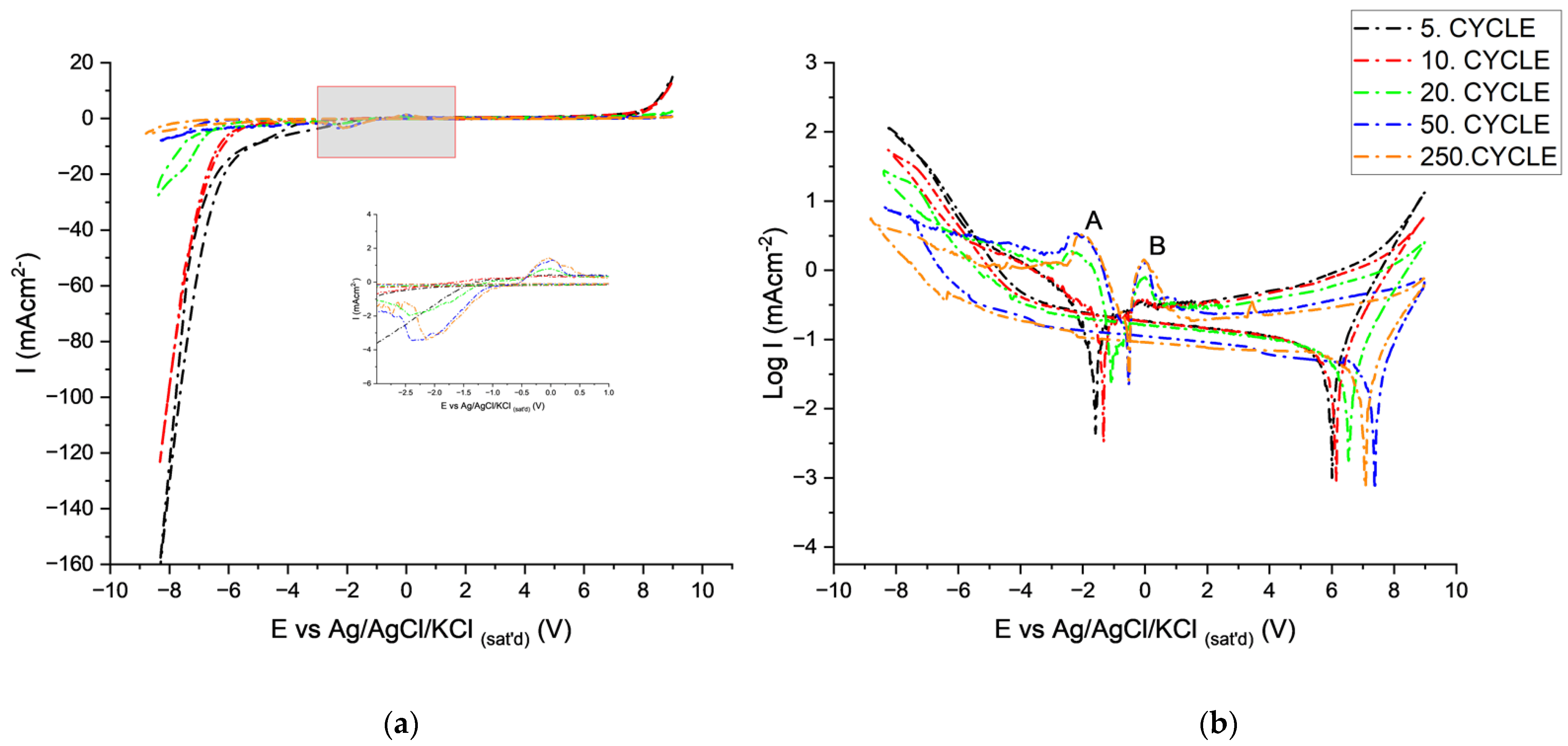
CV Behavior of AAO in Tin-Ion-Containing Electrolytes
- At point 2 after cathodic breakdown until point A, rates of reaction 1 and 2 decreased because of the high over potential of HER on tin oxides. The rates of chemical dissolution of the AAO layer (reaction 3) and Al (reaction 4) at the pore bottom also decreased due to limited alkalinization.
- At Point A:
- At Point B:
- Primary, secondary passivation of metallic tin and dehydration of anodic oxide occurs [59].
- At point 5:
- Reactions 8 and 9 take place at a lower rate compared to tin-free electrolytes because of the presence of tin oxides at the pore bottom.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sulka, G.D. Introduction to Anodization of Metals. In Nanostructured Anodic Metal Oxides: Synthesis and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–34. ISBN 9780128167069. [Google Scholar]
- Nahum, E.Z.; Lugovskoy, A.; Lugovskoy, S.; Sobolev, A. Synthesis of Titanium Oxide Nanotubes Loaded with Hydroxyapatite. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, K.; Schmuki, P. Anodic Formation of Self-Organized Cobalt Oxide Nanoporous Layers. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheasby, P.G.; Pinner, R. Anodizing of aluminum. In The Surface Treatment and Finishing of Aluminum and Its Alloys; Finishing Publications Ltd.: Warrington, UK, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 330–420. [Google Scholar]
- Schwirn, K.; Lee, W.; Hillebrand, R.; Steinhart, M.; Nielsch, K.; Gösele, U. Self-Ordered Anodic Aluminum Oxide Formed by H2SO4 Hard Anodization. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Tang, Y.; Ouyang, M. Self-Ordered, Controlled Structure Nanoporous Membranes Using Constant Current Anodization. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4624–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulka, G.D.; Parkoła, K.G. Temperature Influence on Well-Ordered Nanopore Structures Grown by Anodization of Aluminium in Sulphuric Acid. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.E.; Wood, G.C. Anodic Films on Aluminium. In Treatise on Material Science and Technology; Scully, J.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 23, pp. 205–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, J.W.; Downie, T.C.; Goulding, C.W. Anodic Oxide Films On Aluminum. Chem. Rev. 1969, 69, 365–405+393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Jani, A.M.; Losic, D.; Voelcker, N.H. Nanoporous Anodic Aluminium Oxide: Advances in Surface Engineering and Emerging Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 636–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari Nezhad, M.; Kolahi, A.; KazemZad, M.; Saiedifar, M. Electrolytic Coloring of Anodized Aluminum by Copper. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 829, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Liang, C.H.; Wang, H. Structure and Distribution of Electrodeposits on Anodic Aluminium Films by Electrolytic Colouring in Zinc Sulphate Solution. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2007, 85, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, A.S.; Thompson, G.E.; Wood, G.C. Investigation of the electrolytic Coloring of Porous Anodic Films on Aluminum using Electron Microscopy. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 1975, 53, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, N.M.; Mo, G.H.; Ignatiev, A. Development of an Al203-Co Selective Absorber For Solar Collectors. Thin Solid Films 1989, 172, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzer, S.S.; Kadirgan, F.; Sohmen, H.M.S.; Wetherilt, A.J.; Tureture, I.E. Spectroscopic Characterization of Al O-Ni Selective Absorbers for Solar Collectors. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1998, 52, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimizad, A.; Raeissi, K.; Ashrafizadeh, F. Characterization of Aluminum Anodized Layers Modified in Sulfuric and Phosphoric Acid Baths and Their Effect on Conventional Electrolytic Coloring. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2438–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graeve, I.; Laha, P.; Goossens, V.; Furneaux, R.; Verwimp, D.; Stijns, E.; Terryn, H. Colour Simulation and Prediction of Complex Nano-Structured Metal Oxide Films. Test Case: Analysis and Modeling of Electro Coloured Anodized Aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4349–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, S.; Fernandez, A.M. Electrolytic Nickel Impregnation of Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide Films Using AC Voltage as Solar Selective Absorber. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheasby, P.G.; Pinner, R. Anodizing in Architecture. In The Surface Treatment and Finishing of Aluminum and Its Alloys; Finishing Publications Ltd.: Warrington, UK, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 700–740. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-F.; Hebert, K.R. Change Produced by Cathodic Polarization in the Electrical Conduction Behavior of 419 Surface Films on Aluminum Electrochemical Systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Jagminas, A.; Lichušina, S.; Kurtinaitiene, M.; Selskis, A. Concentration Effect of the Solutions for Alumina Template AC Filling by Metal Arrays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 211, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, J.; Bonino, J.-P.; Bes, R.S. Nickel Pigmented Anodized Aluminium as Solar Selective Absorbers. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goad, D.G.W.; Moskovits, M. Colloidal Metal in Aluminum-Oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 1978, 49, 2929–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangaraki-Kaplanoglou, I.; Theohari, S.; Dimogerontakis, T.; Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Wang, Y.M.; Kuo, H.H.; Kia, S. An Investigation of Electrolytic Coloring Process of Anodized Aluminum Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2749–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akolkar, R.; Wang, Y.M.; Kuo, H.H. Kinetics of the Electrolytic Coloring Process on Anodized Aluminum. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2007, 37, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.L.; Raub, C.J.; Muramaki, T. The State of Tin in Tin-Anodized Aluminum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1978, 125, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanová, M.; Chovancová, M.; Krivošík, P. A New Approach to Nickel Electrolytic Colouring of Anodised Aluminium. Chem. Pap. 2009, 63, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffei, M.F.; Abd El-Rehim, S.S.; Shaaban, N.A.; Huisen, H.S. Electrolytic Coloring of Anodic Aluminum for Selective Solar Absorbing Films: Use of Additives Promoting Color Depth and Rate. Renew. Energy 2001, 23, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagminas, A.; Niaura, G.; Kuzmarskyte, J.; Butkiene, R. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Effect for Copper Oxygenous Compounds Array within the Alumina Template Pores Synthesized by AC Deposition from Cu(II) Acetate Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 225, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchama, L.; Azzouz, N.; Boukmouche, N.; Chopart, J.P.; Daltin, A.L.; Bouznit, Y. Enhancing Aluminum Corrosion Resistance by Two-Step Anodizing Process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Shen, W.Z. Improved Two-Step Anodization Technique for Ordered Porous Anodic Aluminum Membranes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 655, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zähr, J.; Oswald, S.; Türpe, M.; Ullrich, H.J.; Füssel, U. Characterisation of Oxide and Hydroxide Layers on Technical Aluminum Materials Using XPS. Proc. Vac. 2012, 86, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Skariah, B. Spray Deposited Mg-Doped SnO2 Thin Film LPG Sensor: XPS and EDX Analysis in Relation to Deposition Temperature and Doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 625, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Smart, R.C.; Skinner, W.M.; Gerson, A.R. XPS of Sulphide Mineral Surfaces: Metal-Deficient, Polysulphides, Defects and Elemental Sulphur. Surf. Interface Anal. 1999, 28, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K.; Goldoni, A.; Larciprete, R.; Lizzit, S. A Fast XPS Study of Sulphate Promoted Propene 447 Decomposition over Pt{1 1 1}. Surf. Sci. 2002, 553, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, S. X -Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in Analysis of Surfaces Update Based on the Original Article by Steffen Oswald. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry 2000; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nisancioglu, K.; Holtan, H. Cathodic Polarization of Commercially Pure Aluminium. Corros. Sci. 1979, 19, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, B.C.; Nelson, G.C.; Zavadil, K.R.; Barbour, J.C.; Wall, F.D.; Sullivan, J.P.; Windisch, C.F.; Engelhardt, M.H.; Baer, D.R. Hydration of Passive Oxide Films on Aluminum. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 4705–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Hebert, K.R. Participation of Aluminum Hydride in the Anodic Dissolution of Aluminum in Alkaline Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, C189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Lee, D.N. Assessment of Proton Transport in Amorphous Aluminum Oxide by Cathodic Polarization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassel, A.W.; Lohrengel, M.M. Initial Stages of Cathodic Breakdown of Thin Anodic Aluminium Oxide Films. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco Owens, A.; Veys-Renaux, D.; Rocca, E. Reverse Scan Polarization of Anodic Aluminum Oxide until 505 Detachment in Sulfuric Acid: Mechanisms and Morphologies. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 435, 141361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Klasky, M.; Letellier, B.C. The Aluminum Chemistry and Corrosion in Alkaline Solutions. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 384, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.E.; Wood, G.C. The Effect of Alternating Voltage on Aluminum Electrodes. Corros. Sci. 1978, 18, 721–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Hebert, K.R. Factors Controlling the Time Evolution of the Corrosion Potential of Aluminum in Alkaline Solutions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching-Feng, L.; Porter, M.D.; Hebert, K.R. Surface Films Produced by Cathodic Polarization of Aluminum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, C.; Chu, L.; Lai, W.; Chiang, A.S.; Fang, W. Implementation of a New Capacitive Touch Sensor Using the Nanoporous Anodic Aluminum Oxide (Np-AAO) Structure. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3409–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsal, L.F.; Vojkuvka, L.; Formentin, P.; Pallarés, J.; Ferré-Borrull, J. Fabrication and Optical Characterization of Nanoporous Alumina Films Annealed at Different Temperatures. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, F.; Paolini, G. A Study of AC Anodizing of Aluminium in Sulphuric Acid Solutions. Trans. IMF 1964, 42, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, H.; Okano, H.; Wada, K.; Inoue, S. Fabrication of Alumina Films with Laminated Structures by Ac Anodization. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 014209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, H.; Okano, H.; Wada, K.; Inoue, S.; Byun, I. Synthesis of Laminated Alumina Films by AC Oxidation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D240–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kape, J.M. Further Development in the AC Anodizing of Aluminum in Sulfuric Acid Electrolytes. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 1985, 63, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, V.; John, S.; Shenoi, B.A. Influence of Addition Agents for A.C: Anodizing in Sulphuric Acid Electrolytes. Surf. Technol. 1983, 19, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, S.I.; Moon, S.M. Corrosion Mechanism of Pure Aluminium in Aqueous Alkaline Solution. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.M.; Tribollet, B.; Sutter, E.M.M. New Insights into the Cathodic Dissolution of Aluminium Using Electrochemical Methods. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 216, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, R.L.; De Oliveira, G.M.; Barbosa, L.L.; Pallone, E.M.J.A.; Carlos, I.A. Study of an Alkaline Bath for Tin Deposition in the Presence of Sorbitol and Physical and Morphological Characterization of Tin Film. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2006, 36, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaśniewski, D.; Grdeń, M. Electrochemical Behaviour of Tin in Alkaline Electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 61, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, I.A.; Darwish, S.; Khalil, M.W.; Galal, A. Potentiodynamic and Cyclic Voltametric Studies on the Passivity of Tin in Neutral Phosphate Buffer. Materwiss Werksttech 1985, 16, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, V.; López Teijelo, M. Oxide/Hydroxide Films on Tin. II: Characterization of the Anodic Growth in Alkaline Solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 613, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, S.D.; Norman, H. Anodic passivation of tin in slightly alkaline solutions. Electrochim. Acta 1980, 25, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunold, R.; Broli, A. Anodic And Cathodic Behaviour of Tin In Acidic Sulphate Solutions. Corros. Sci. 1973, 13, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyil, C.; Akdas, G.; Afsin, P.; Ürgen, M. Freestanding SnO2 Films Produced with Anodic Polarization in Acidic Media Containing Colloidal Tin Hydroxides. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 221, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, D.; Avcı, B.; Ürgen, M. Electrocatalytic Performance of Interconnected Self-Standing Tin Nanowire Network Produced by AAO Template Method for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. ChemElectroChem 2023, 10, e202300196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraska, L.; Gawlak, K.; Wiercigroch, E.; Malek, K.; Kozieł, M.; Andrzejczuk, M.; Marzec, M.M.; Jarosz, M.; Brzózka, A.; Sulka, G.D. The Effect of Anodizing Potential and Annealing Conditions on the Morphology, Composition and Photoelectrochemical Activity of Porous Anodic Tin Oxide Films. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 319, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraska, L.; Gawlak, K.; Gurgul, M.; Dziurka, M.; Nowak, M.; Gilek, D.; Sulka, G.D. Influence of Anodizing Conditions on Generation of Internal Cracks in Anodic Porous Tin Oxide Films Grown in NaOH Electrolyte. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
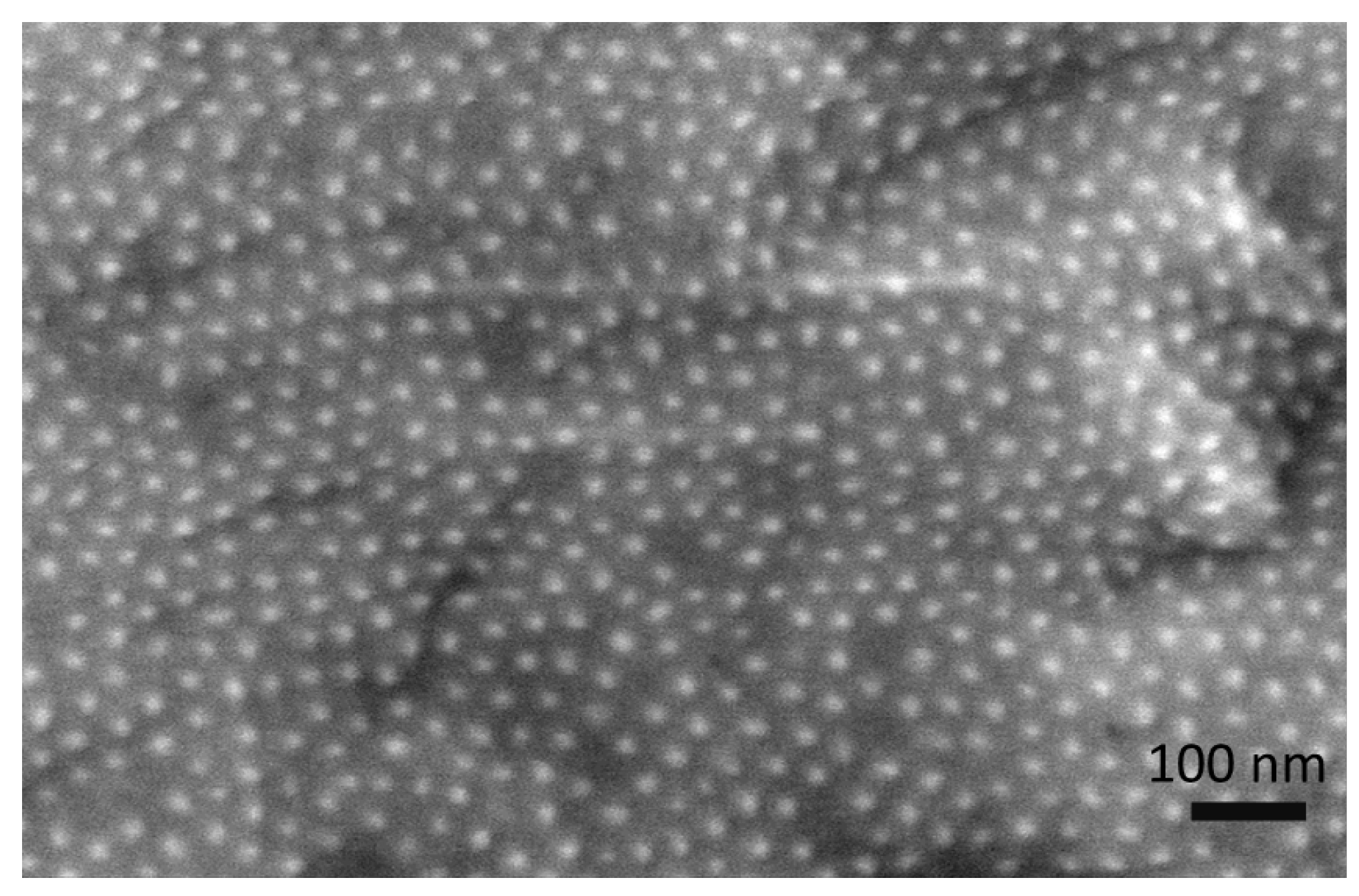
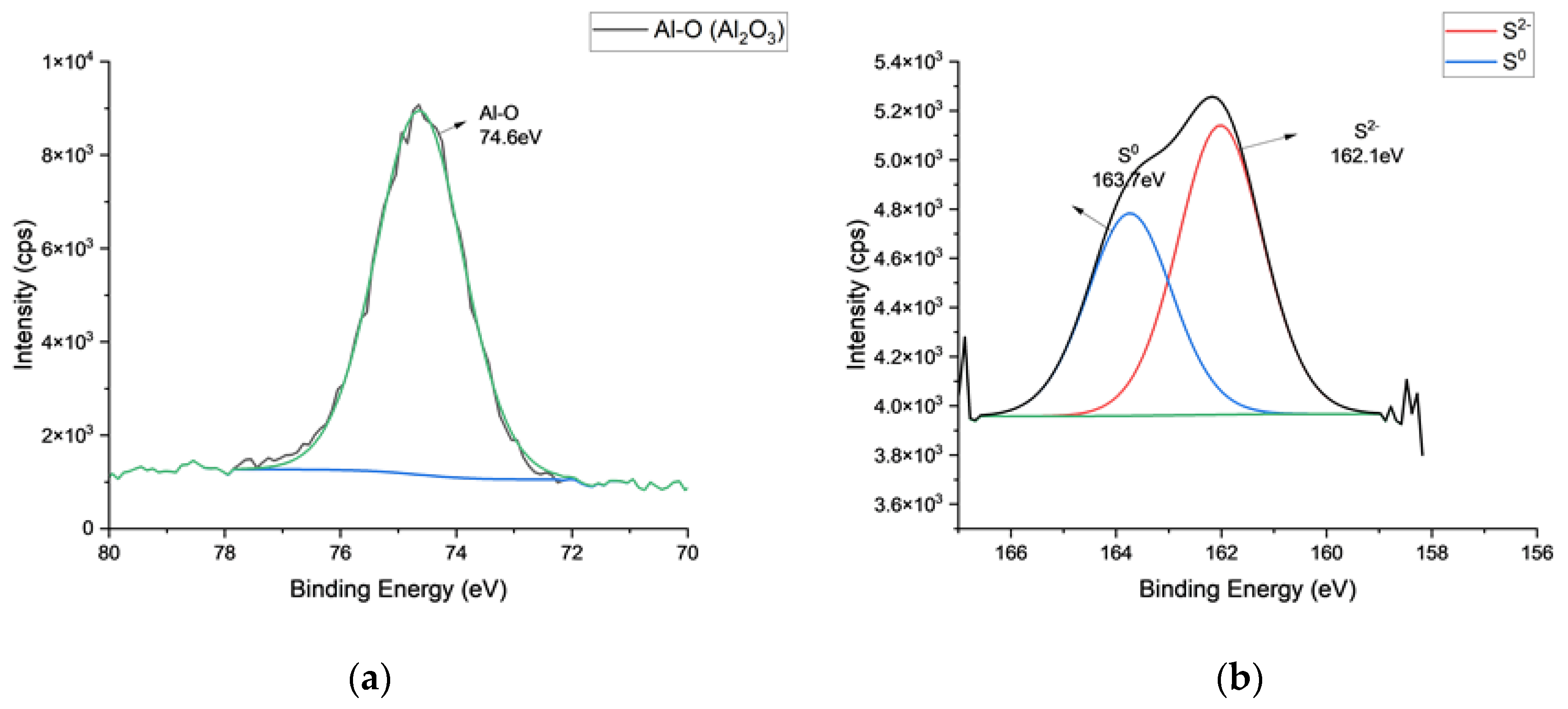
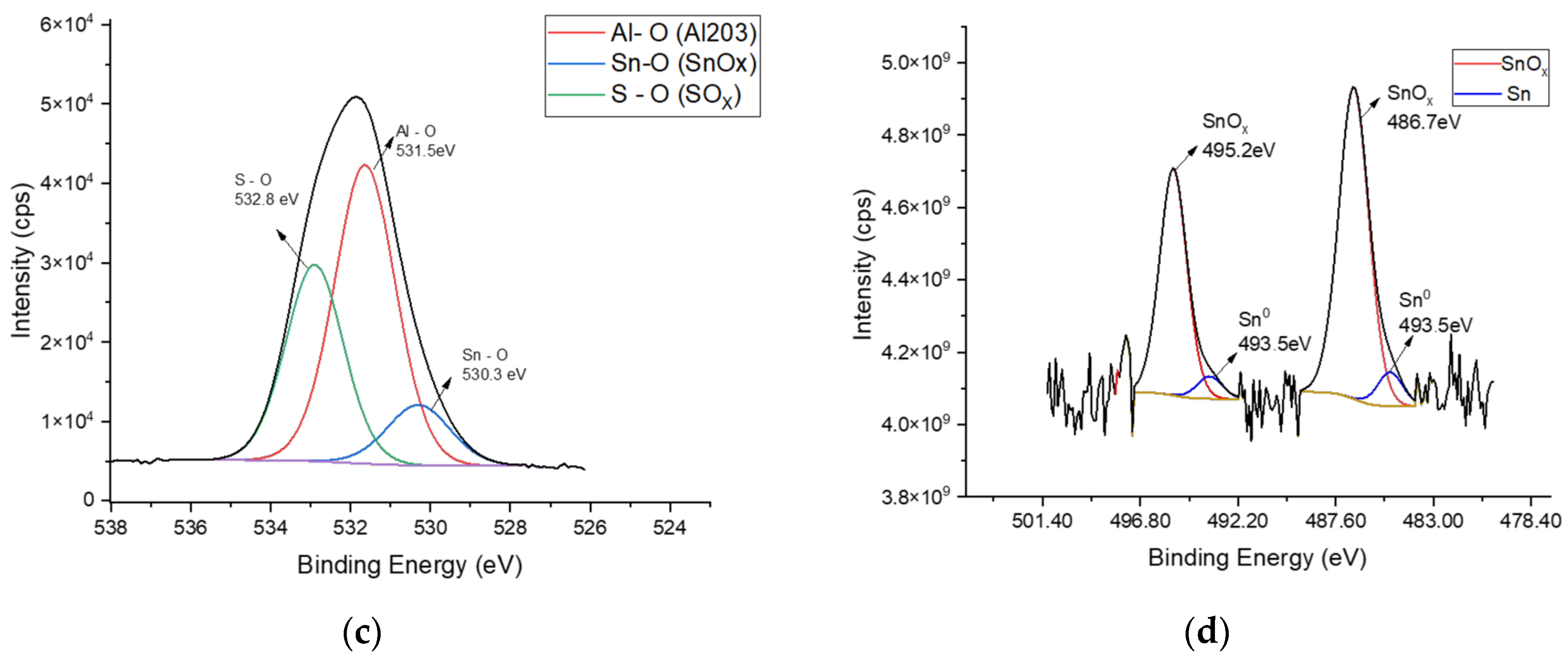
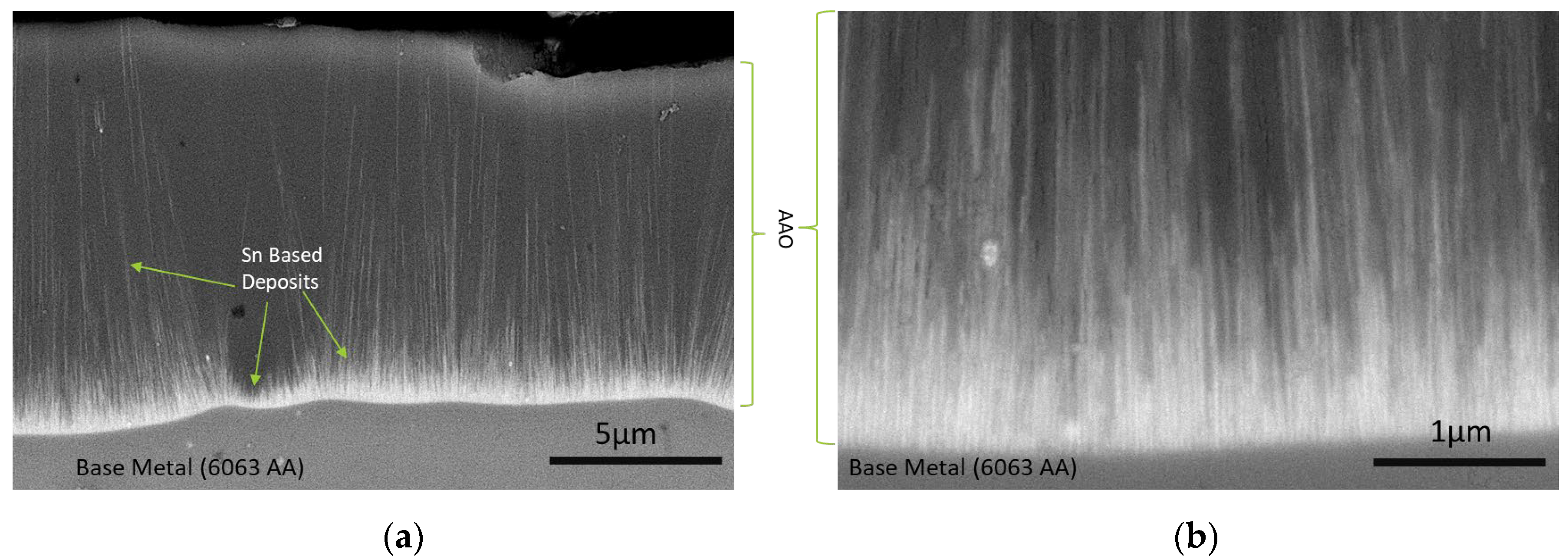
| Alloying Element | Si | Fe | Cu | Mg | Cr | Zn | Mn | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 0.41 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.51 | <0.10 | <10 | <10 | Balance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afsin, P.; Akyil, C.; Kazmanlı, K.; Ürgen, M. Electro-Coloring Mechanism of Aluminum Anodic Oxides in Tin-Based Electrolytes. Coatings 2024, 14, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050616
Afsin P, Akyil C, Kazmanlı K, Ürgen M. Electro-Coloring Mechanism of Aluminum Anodic Oxides in Tin-Based Electrolytes. Coatings. 2024; 14(5):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050616
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfsin, Pinar, Can Akyil, Kürşat Kazmanlı, and Mustafa Ürgen. 2024. "Electro-Coloring Mechanism of Aluminum Anodic Oxides in Tin-Based Electrolytes" Coatings 14, no. 5: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050616
APA StyleAfsin, P., Akyil, C., Kazmanlı, K., & Ürgen, M. (2024). Electro-Coloring Mechanism of Aluminum Anodic Oxides in Tin-Based Electrolytes. Coatings, 14(5), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050616







