Abstract
Antibacterial microcapsules were prepared using chitosan as the shell material and Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extract as the core material. The optimal preparation process for the microcapsules of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extract were determined via orthogonal and single-factor experiments as follows: the mass ratio of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts and chitosan (MT:MC) was 3.0:1, the pH value of microencapsulation was 7, and the reaction temperature was 50 °C. The MT:MC increased, the glossiness of the coatings increased and then decreased, the color difference and roughness of the coatings showed an increasing trend, the transmittance of the coatings decreased, the grade of citric acid resistance decreased, the resistance to ethanol and detergents of the coatings increased, and the fracture elongation of the coating increased and then fell. As the MT:MC of microcapsules increased, the antibacterial rates of the coating against Escherichia coli increased first, then decreased, and lastly increased. The trend of the coating against Staphylococcus aureus first increased and then decreased. When the microcapsule MT:MC was 3.0:1, the performance of the coating was better, and the antibacterial rates against the two bacteria were 67.14% and 68.39%, respectively. Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts endow waterborne coatings with antibacterial properties, expanding the application range of waterborne coatings.
1. Introduction
With the improvement of the economy and living standards, health and hygiene issues have received increasing attention from people [1]. However, the pollution caused by microorganisms in the environment where people live is extremely severe [2]. The use of antibacterial materials is the simplest and most effective way to achieve a pollution-free environment [3,4,5]. On the premise of not changing the original adhesion of the coating, an ideal antibacterial coating should meet the characteristics of low cost, low toxicity, high antibacterial efficiency, broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, and antibacterial persistence [6,7,8]. The antibacterial agents added to antibacterial coatings are mainly divided into three types: natural antibacterial agents [9], organic antibacterial agents [10], and inorganic antibacterial agents [11]. Natural antibacterial agents are non-toxic, have a wide range of sources, and have significant antibacterial effects, but their stability is poor [12,13]. Natural antibacterial agents are prepared into microcapsules to improve their stability and corrosion resistance [14]. These antibacterial microcapsules are added to waterborne coatings to endow them with antibacterial properties, which is of great practical significance for improving the service life of coatings, enriching the functions of waterborne coatings, and protecting substrates [15,16,17].
With the proposal of the “dual carbon” goal, while developing antibacterial and antiviral coatings, the toxicological properties of coatings have also been given attention [18]. The production concept of green, non-toxic, and sustainable development is advocated [19,20,21]. Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts belong to the Rutaceae family, and its parts have extremely high medicinal value [22]. The chemical components of its anhydrous ethanol extract have good antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli [23]. He et al. isolated resveratrol from the Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam and tested it against Gram-positive bacteria, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and broad-spectrum antibiotics β- Lactamase Staphylococcus aureus with it having strong antibacterial activity, and the minimum inhibitory concentration against all three bacteria was 0.156 mg/mL [24]. Duraipandiyan et al. [25] used hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, methanol and water extracts of Toddalia asiatica leaves and isolated the compound Flindersine to test against bacteria and fungi. They found that ethyl acetate extract showed promising antibacterial and antifungal activity and the isolated compound Flindersine showed moderate activity against bacteria and fungi. The existing commercial antibacterial products mainly include antibacterial additives such as Miao Kangbao, Biocote, and SteriTouchden, as well as antibacterial coatings such as SilverSan, InterponAM, and Nippon Cleansing 120 bamboo charcoal antibacterial [26]. The main reason why antibacterial coatings can exert antibacterial effects is that special antibacterial agents are added to the coating formula, which can have a sustained antibacterial ability after coating is completed [27]. Chitosan was selected as the shell material and Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts were selected as the core material for the preparation of microcapsules. They are both natural products that are environmentally friendly. At the same time, microcapsule technology was used to overcome the weakness of the poor stability of natural antibacterial agents. The shell material chitosan also has antibacterial properties, and it was synergized with the core material antibacterial agent, effectively improving the antibacterial performance against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. This coating had more significant sustainable properties compared to other similar technologies on the market due to its more certain composition, ease of addition, mixing and dispersion, and stable mixing.
Chitosan was selected as the shell material and Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts was selected as the core material for the preparation of microcapsules. A three factor, two level orthogonal experiment was designed to explore the optimal preparation process of microcapsules by analyzing factors such as yield, encapsulation rate, microstructure, and chemical composition. On this basis, a single-factor experiment was conducted. The obtained single-factor microcapsules were added to the waterborne topcoat at the same content to prepare an antibacterial coating, and the effect of the mass ratio of chitosan and Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts on the antibacterial coating was investigated. In this study, Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts were prepared into microcapsules and added to the coating. This not only improved the poor stability of natural antibacterial agents, but also enhanced the antibacterial efficacy of the coating, reduced environmental pollution, and maintained the stability of the substrate itself, expanding the application range of waterborne coatings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Table 1 shows the list of experimental materials. The Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam Leaves were from Lingshan County, Qinzhou City, Guangxi Province, China. The leaves were placed in a 40 °C oven (Shanghai Jinghong Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and dried to a constant weight. They were ground into powder using a crusher (Zhejiang Fengli Crushing Equipment Co., Ltd., Shengzhou, China). The coating was a waterborne acrylic topcoat (Jiangsu Haitian Technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China). A 50 mm × 50 mm × 10 mm sized silicone mold was selected to prepare the coating. The size of the glass substrate (Jiangsu Huaou Glass Co., Ltd., Yancheng, China) was 25 mm × 75 mm × 10 mm.

Table 1.
List of experimental materials.
2.2. Preparation Method and Experimental Design of Microcapsules
2.2.1. Preparation Method of Microcapsules
First, 0.20 g of acetic acid was diluted in 19.8 g of deionized water in a beaker (Ningbo Pulai Experimental Instrument Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China) and a 1% concentration acetic acid solution was prepared. A 0.20 g of chitosan powder was weighed and added to the acetic acid solution and then a magnetic stirrer (Yancheng Xieying Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Yancheng, China) was added. The beaker was placed in a water bath pot (Gongyi Yuhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Gongyi, China) with a set speed of 600 rpm and a temperature of 60 °C until the chitosan powder was completely dissolved to form a chitosan shell material solution. The leaf powder was mixed with anhydrous ethanol in a mass ratio of 1:15 in the beaker, and the beaker was sealed with cling film. The concentration of blade powder was 6.25%. The beaker was placed in the water bath pot for extraction for 70 min with a set speed of 600 rpm and a temperature of 60 °C. The extracted mixture was put into a centrifuge (Shanghai Luxiangyi Centrifuge Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and centrifuged for 7 min at a speed of 7000 rpm. The mixture was filtered using a vacuum pump (Ningbo Aifake Vacuum Technology Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China) combined with a Buchner funnel (Wuhan Dingsheng Zhongtian Experimental Instrument Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) to obtain the filtrate. The obtained filtrate was subjected to rotary evaporation and dried to obtain a solid extract, sealed, and then stored in a cool and dark place for future use [28]. Tween-80 and X-100 were weighed to prepare an emulsifier solution with a mass fraction of about 3.0%. The solution was added dropwise to the Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts. The speed of the water bath pot was set to 600 rpm and the temperature was 50 °C. The solution was placed in the water bath pot for 45 min. The prepolymer solution was sucked up by a dropper and added to the core material lotion drop by drop. The core material (0.20 g) and shell material (0.40–0.80 g) solution were fully mixed for 1 h. The concentration range of the core material was 0.25–0.45%, and the concentration range of the shell material was 0.89–1.01%. The 0.5 mol/mL NaOH solution was added to adjust the pH value of the solution to around 7. The TPP solution with a concentration of 5.0% was added; then, the beaker was placed in the water bath for the crosslinking reaction and microencapsulated for 3 h. The speed of the water bath was set to 600 rpm and the temperature was 60 °C. The obtained solution was cooled at room temperature. The high-speed centrifuge speed was set to 7000 rpm, and the resulting product was centrifuged for 10 min. The upper clear liquid was poured out, and the solid product was placed in a freeze-drying machine (Ningbo Xinzhi Freeze Drying Equipment Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China) for 24 h before being taken out and ground. The final product obtained was a powdered microcapsule [29].
2.2.2. Orthogonal and Single-Factor Experimental Design of Microcapsules
According to the preliminary experimental results, the main influencing factors in the preparation process of chitosan-coated Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extract microcapsules included MT:MC, the pH value of the solution during the crosslinking reaction, and the reaction temperature. An orthogonal experiment was designed to investigate the effects of MT:MC, the pH value of the solution during the crosslinking reaction, and the reaction temperature on the preparation of microcapsules. A single-factor experiment was designed to investigate the effect of MT:MC on the preparation of microcapsules, based on the optimal preparation parameters obtained by combining the yield and encapsulation rate of the orthogonal experiments. Table 2 shows the material table for the orthogonal experiments. Table 3 shows the material table for single-factor experiments.

Table 2.
Orthogonal test bill of materials.

Table 3.
Single-factor test bill of materials.
2.3. Preparation Method of the Coating
The prepared microcapsules were added to the waterborne topcoat with a mass fraction of 5% and mixed evenly to obtain 1.0 g of topcoat coating. The obtained topcoat coating was evenly applied in the silicone mold, leveled, and dried at room temperature. The coating was dried in the oven at a set temperature of 55 °C for 30 min.
2.4. Testing and Characterization
2.4.1. Performance Characterization of Microcapsules
- (1)
- Coverage rate (C): The microcapsules were soaked in ethanol for 24 h and then filtered and dried. The formula given calculates the coverage rate, quantifying the extent of the shell material covering the microcapsule surface (1). M1 is the weight of microcapsules, M2 is the weight of the filter paper, and M3 is the weight of the total mass of the dried filter paper and shell material.
- (2)
- Yield rate (Y): The total mass, M1, includes all materials. After drying, the microcapsule powder mass is M2. The yield rate calculation is shown in the Formula (2).
- (3)
- Microscopic morphology and chemical composition: Microcapsule morphology was observed via a Zeiss optical microscope (OM, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Tescan, Brno, the Czech Republic) was employed to scrutinize the microcapsule and coating microstructures. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Brucker AG, Karlsruhe, Germany) was used to determine the chemical composition of both the microcapsules and the coatings.
2.4.2. Color Difference Testing of the Coating
In the light of GB/T 11186.3-1989 [30], a SEGT-J colorimeter (Zhuhai Tianchuang Instrument Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China) was utilized to assess and record the chromaticity of the coating. The color difference (ΔE) between the microcapsule-containing coating and the pure coating was determined using Formula (3), taking into account ΔL (brightness variation), Δa (red–green difference), and Δb (yellow–blue difference).
2.4.3. Glossiness, Transmittance, and Light Loss Testing of the Coating
In GB/T 4893.6-2013 [31], a glossmeter (Shenzhen Linshang Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) was used to test and record the glossiness values of the coating at three incidence angles of 20°, 60°, and 85°, with the unit being GU.
A UV spectrophotometer (Beijing Puxi General Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) was employed to determine and analyze the transmittance of the coating across the visible light spectrum, ranging from 380 to 780 nm.
The light loss incurred by the coating was subsequently quantified using Formula (4), where GL denotes the light loss rate, G0 represents the glossiness of the coating in its unmodified state (without microcapsules), and G1 signifies the glossiness after the incorporation of microcapsules.
2.4.4. Roughness and Tensile Testing of the Coating
The roughness value was tested and recorded using a JB-4C roughness tester (Cangzhou Oupu Testing Instrument Co., Ltd., Cangzhou, China).
Silicone molds were used for curing and demolding of the coatings. A universal mechanical testing machine (Instron, Boston, MA, USA) was used to conduct tensile tests on the coatings. The fracture elongation of the coating, calculated using Formula (5), quantifies the elongation (e) at the fracture point, taking into account the original length (L1) and the length at fracture (L), providing a measure of the coating’s tensile properties.
2.4.5. Cold Liquid Resistance
According to GB/T 4893.1-2021 [32], a citric acid solution with a mass fraction of 10%, undescended ethanol with a volume fraction of 96%, and a cleaning agent prepared with deionized water were chosen as the experimental liquids. Damage to the surface was inspected under specified lighting conditions. The test results were evaluated using numerical levels.
2.4.6. Antibacterial Properties of the Coating
Adhering to GB/T 21866-2008 [33], the testing protocol was meticulously executed. Escherichia coli (ATCC25922) and Staphylococcus aureus (ACTT6538) were selected for antibacterial testing. An agar plate medium was prepared by accurately weighing 24 g of agar medium into 1000 mL of distilled water, followed by sterilization. The slant-preserved bacterial strains were then inoculated onto the agar plates and incubated in a constant temperature and humidity incubator (Shanghai Zhetu Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 38 °C for 18–20 h. The 9 g of nutrient broth and 500 mL of distilled water were weighed to prepare the nutrient broth culture medium. The polyethylene film was soaked in 70.0% ethanol solution for 30 min, washed with eluent, dried, and set aside for later use. Fresh bacteria from the agar medium were transferred into this broth using an inoculation ring. The sterilized nutrient broth culture medium was sequentially diluted in a ten-fold increase to form a 1:1000 bacterial suspension. Approximately 0.5 mL of this bacterial suspension was then dispensed onto both the test coating and the control group surfaces. A sterilized plastic film was applied to each specimen’s surface using sterilized tweezers, and the specimens were placed in sterilized culture dishes before being transferred to a constant temperature and humidity incubator set at 38 °C and RH > 90% for 24 h of cultivation. Following the incubation period, the samples were removed, and 20 mL of eluent was added. The samples were thoroughly rinsed by clamping the thin film with tweezers and repeatedly flushing it. The rinse solution was then inoculated into nutrient agar culture medium and re-incubated in the same incubator conditions for an additional 48 h. Finally, in accordance with GB/T 4789.2-2022 [34], the colony count in the culture medium was meticulously measured and recorded using a colony counter (Guansen Biotechnology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). After 48 h of cultivation, the actual number of colonies recovered from each sample was scaled up by a factor of 1000 for easier counting or standardization purposes. The formula utilized to calculate the antibacterial rate, as presented in Formula (6), designates R as the antibacterial rate, measured in percentage (%). In this formula, B represents the average number of colonies recovered from pure coating samples after 48 h, expressed in CFU/piece. Similarly, C denotes the average number of bacteria recovered from the antibacterial coating sample after the same duration, expressed in CFU/piece.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Microcapsule Preparation Results
3.1.1. Analysis of the Yield and Encapsulation Rate Results of the Microcapsules
Table 4 shows the analysis of the microcapsule yield results obtained from the orthogonal experiments. In the four groups of microcapsule samples in the orthogonal experiment, the difference in yield was very small, and the yield difference of the four samples fluctuated around 0.5%. From the range of results, the reaction temperature had the greatest impact on the yield of microcapsules. For the yield of microcapsules, the primary and secondary factors affecting their preparation process were C > A > B, and the optimal preparation process was A1, B2, and C2. Table 5 shows the analysis of variance results for yield. The variance results for the three factors were the same as the range results, and none of the three influencing factors were significant.

Table 4.
Analysis of the yield of the microcapsules during the orthogonal test.

Table 5.
Variance analysis table of yield results.
Table 6 shows the analysis of the microcapsule encapsulation rates obtained from the orthogonal experiments. The coverage rate is an important factor used to evaluate the encapsulation effect of microcapsules and affects their antibacterial properties. Sample 3# had the highest encapsulation rate of 29.71%. The minimum coverage rate was sample 2#, and the coverage rate result was 20.20%. Based on their range results, the primary and secondary levels of three factors were A > B > C. The factor A (MT:MC) had the greatest impact on the encapsulation rate of microcapsules. Based on the variance results in Table 7, the optimal preparation process was A2, B1, and C2. The optimal preparation process parameters for the microcapsules were MT:MC of 3.0:1, a microencapsulation pH value of 7, and a reaction temperature of 50 °C.

Table 6.
Analysis on the results of the orthogonal test of the microcapsule coverage rate.

Table 7.
Analysis of variance table for coverage rate.
A single-factor experiment was designed and conducted based on the optimal preparation parameters obtained from the yield and coverage rate of orthogonal experiments. Using MT:MC, which had a relatively large influencing factor, as the experimental variable, the pH value of the solution during fixed microencapsulation was 7, and the reaction temperature was 50 °C (determined based on the results of coverage rate) for single-factor testing. Table 8 shows the yield and coverage rate results of the single-factor experimental microcapsules. The highest yield of sample 5# was 30.58%, while the lowest yield of sample 9# was 22.97%. The yield of the microcapsules decreased with the increase in MT:MC. This is because, under the premise of maintaining the quality of the shell material, as the quality of the Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts increase, there will be an excess of core material that is not covered. Sample 7# had the highest coverage rate of 37.74%, while Sample 5# had the lowest coverage rate of 28.73%. The coverage rate of microcapsules showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase in MT:MC. This is because as the quality of the core material increases, the concentration of emulsifiers remains unchanged. When the core material is excessive, the emulsification effect on the core material is poor and not fully emulsified, resulting in a decrease in the coverage rate of the microcapsules.

Table 8.
The yield and coating rate of the microcapsules were tested via a single-factor experiment.
3.1.2. Microscopic Morphology Analysis of the Microcapsules
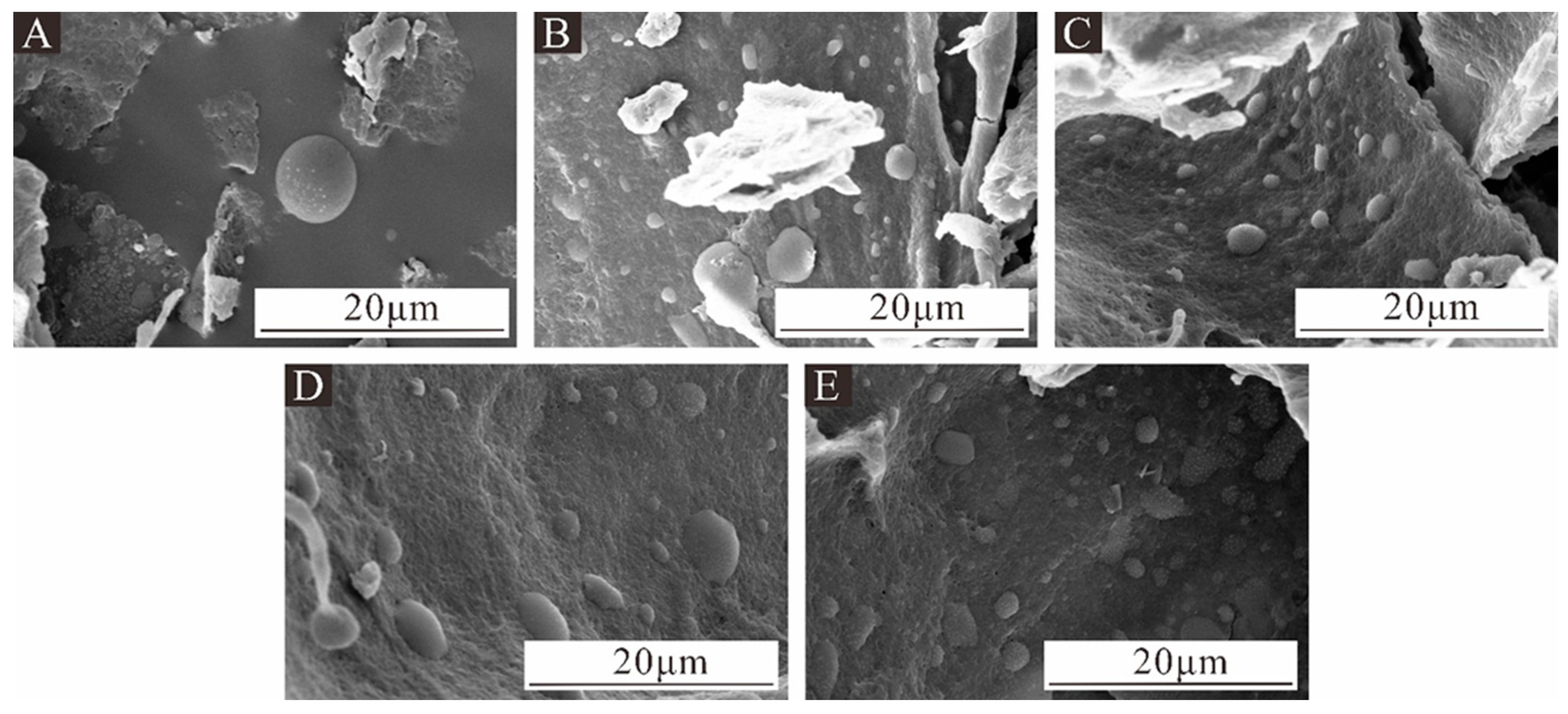
Figure 1 shows the SEM images of five microcapsule samples prepared in a single-factor experiment. When MT:MC was 2.0:1, there were fewer successfully prepared mi-crocapsules and more irregular aggregates present. When MT:MC was 2.5:1, many spherical microcapsules of different sizes were observed, but there were still many ir-regular aggregates present. When MT:MC was 3.0:1, the prepared microcapsules exhibited adhesion and uneven size. When MT:MC was 3.5:1 and 4.0:1, there were many mi-crocapsule microspheres, but the microcapsules exhibited uneven dispersion and local adhesion. This is because the core material content is too high and not completely emulsified and dispersed, resulting in an increase in the viscosity of the core material emulsion. During the process of microencapsulation, the core material will be present between the encapsulated microcapsules, leading to the formation of adhesion between them, and resulting in a slightly sticky and rough texture of the formed microcapsule powder [35].
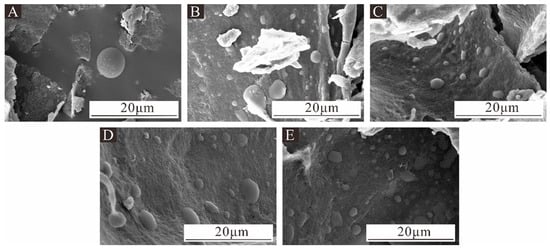
Figure 1.
SEM images of microcapsules under the single-factor test: (A) Sample 5#, (B) Sample 6#, (C) Sample 7#, (D) Sample 8#, and (E) Sample 9#.
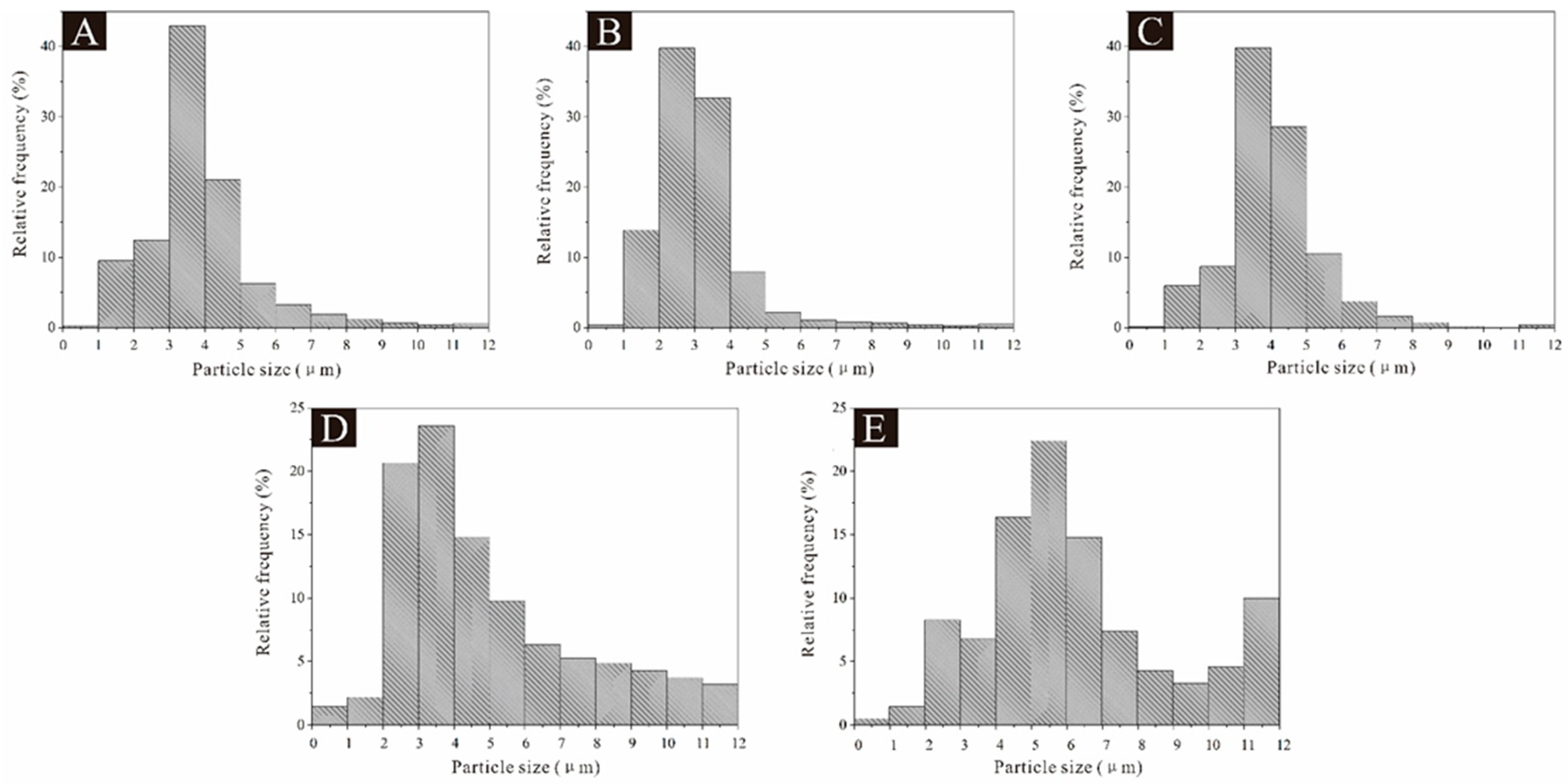
As shown in Figure 2, the particle size of the 5# microcapsule sample was widely distributed between 3.0 μm and 5.0 μm. The particle size of the 6# microcapsule sample was concentrated between 2.0 μm and 4.0 μm. The particle size of 7# microcapsules was mainly distributed in 3.0–5.0 μm. The particle size of 8# microcapsules was concentrated between 2.0 μm and 7.0 μm. The particle size distribution of microcapsules was relatively uniform compared to the first four groups of samples, with a distribution between 2.0 μm and 12.0 μm. The particle size distribution of microcapsule samples 8# and 9# was relatively uniform.
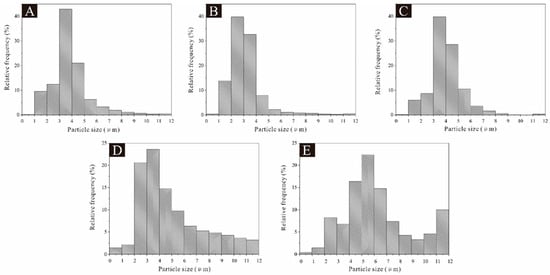
Figure 2.
Particle size distribution: (A) 5#, (B) 6#, (C) 7#, (D) 8#, and (E) 9#.
3.1.3. Chemical Composition Analysis of the Microcapsules
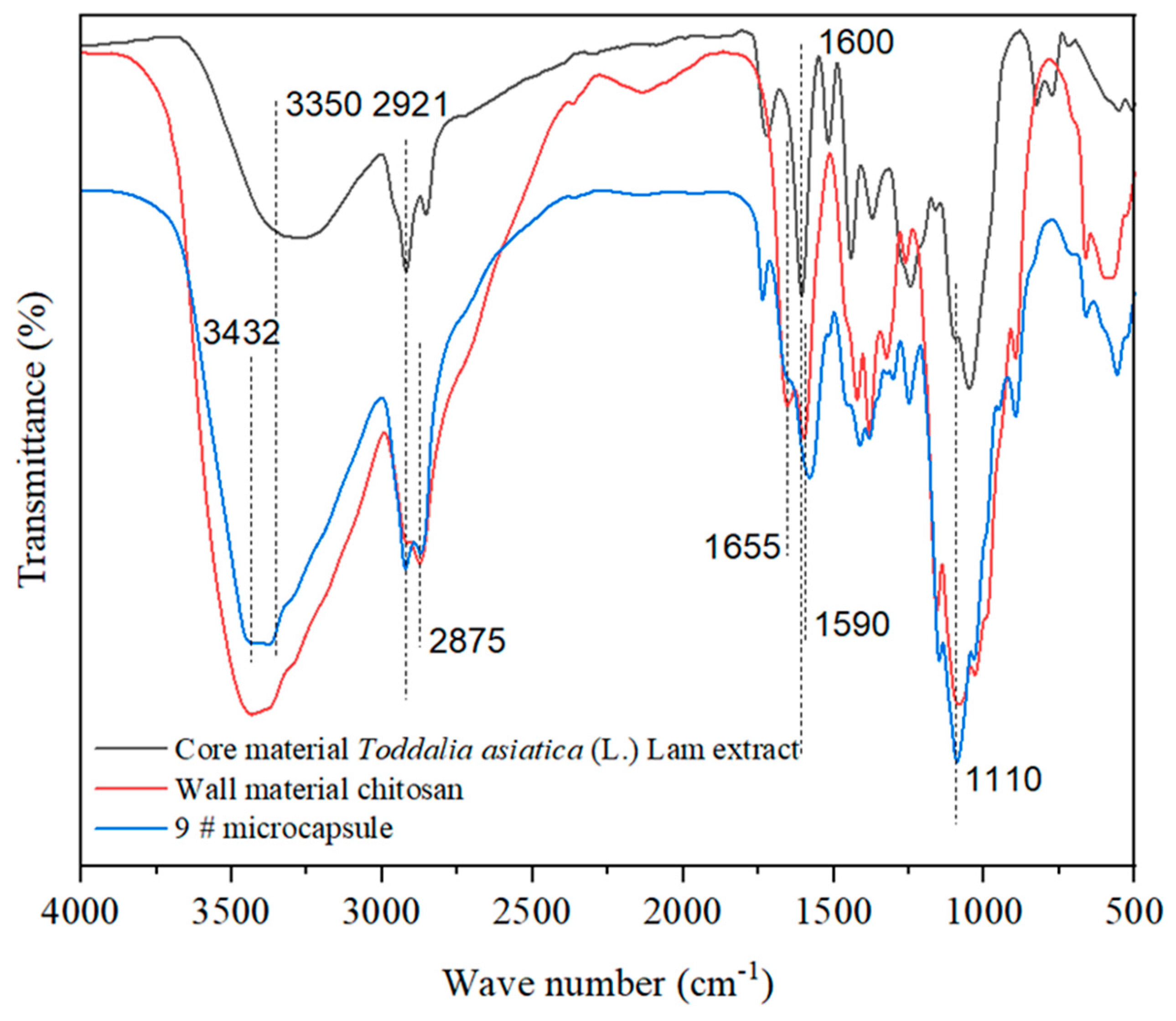
As shown in Figure 3, the absorption peak at 3350 cm−1 was the stretching vibration peak of C–O in the core material. The characteristic peak at 1655 cm−1 was the stretching absorption peak of C=O in chitosan. The characteristic peak at 1590 cm−1 was the deformation vibration peak of –NH2 in chitosan [36]. The two stretching vibration absorption peaks generated at 2921 cm−1 and 2875 cm−1 were the absorption peaks of C–H in chitosan, and the absorption peak of –OH in chitosan was at 3432 cm−1, indicating the presence of shell material chitosan in the microcapsules [37]. The absorption peaks at 1600 cm−1 and 1110 cm−1 were characteristic peaks of C=N and C–O in coumarin compounds in the core material, which are positioned on the absorption curve of the microcapsules, proving the presence of the core material Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extract in the microcapsules as well. The above proves that microcapsules had been successfully prepared.
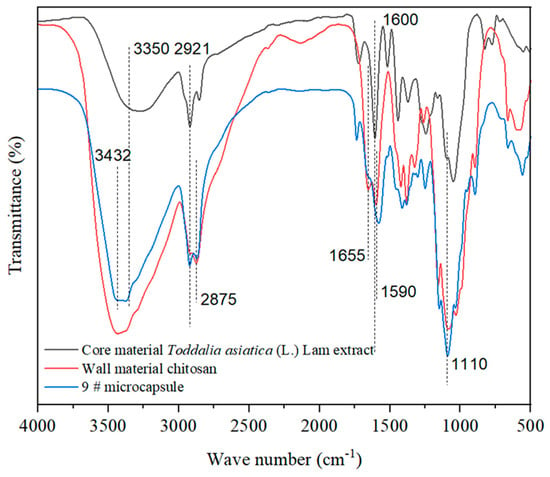
Figure 3.
Infrared spectra of core materials, shell materials, and microcapsules.
3.2. Microscopic Morphology and Chemical Composition Analysis of the Coating
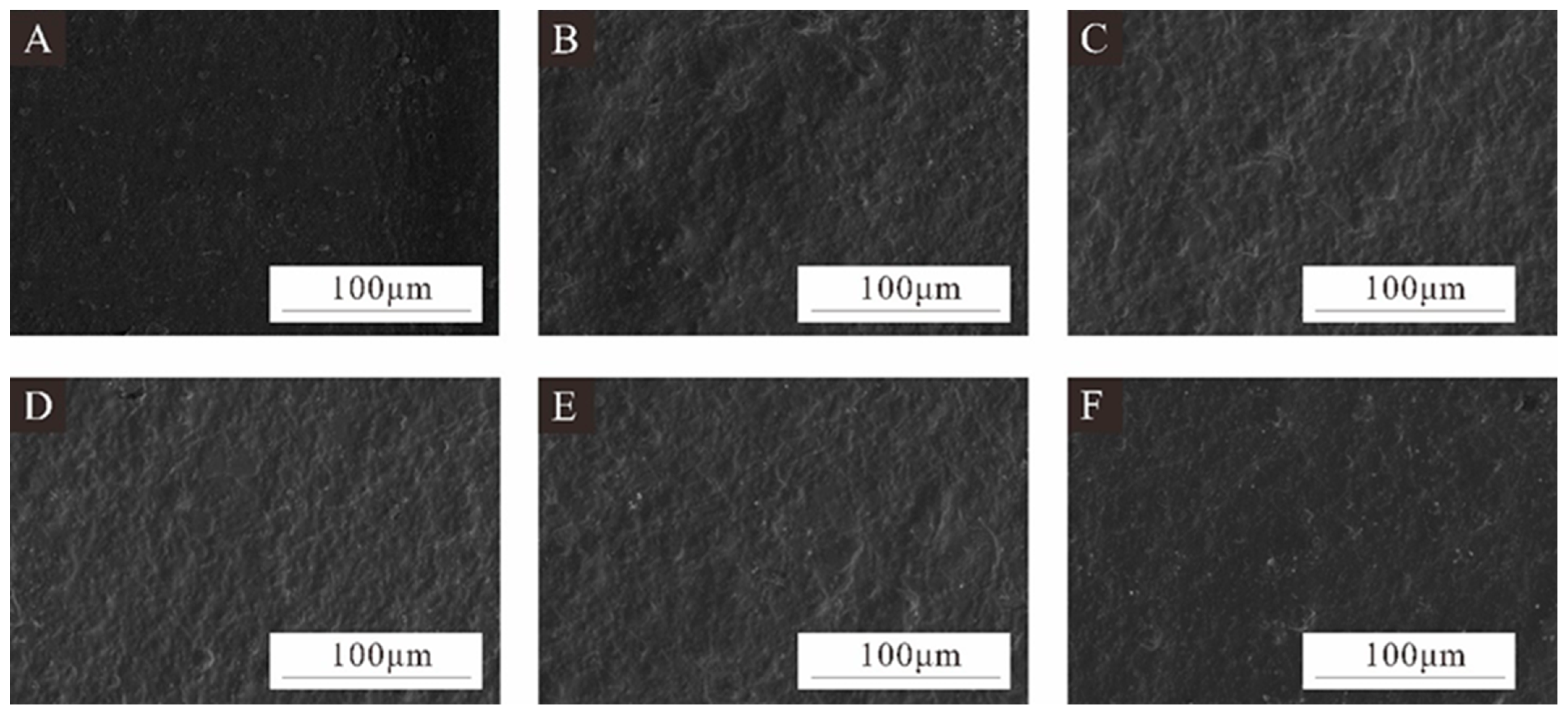
Figure 4 shows SEM images of the coating prepared using microcapsules with different MT:MC at a 5.0% additive content. When the microcapsule content in the coating was 0%, the surface was relatively flat and smooth. The surface of the antibacterial coating with the addition of 5.0% microcapsules becomes rough, with many protrusions. The surface of the antibacterial coating with samples 5# and 6# added was rougher because there are more irregular aggregates in these two microcapsules, resulting in poor surface smoothness of the prepared coating. The coating of samples 7#, 8#, and 9# had slightly lower roughness compared to the antibacterial coatings of samples 5# and 6#. However, due to the uneven dispersion and local adhesion of these three microcapsule samples, the surface of the prepared coatings was rougher and more uneven than that of the pure coating.
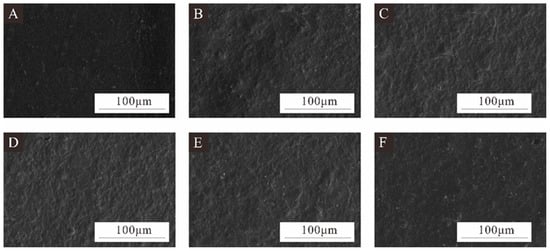
Figure 4.
SEM images of coatings prepared by adding 5.0% microcapsules with different MT:MC: (A) coating without microcapsules, (B) coating with microcapsules 5#, (C) coating with microcapsules 6#, (D) coating with microcapsules 7#, (E) coating with microcapsules 8#, and (F) coating with microcapsules 9#.
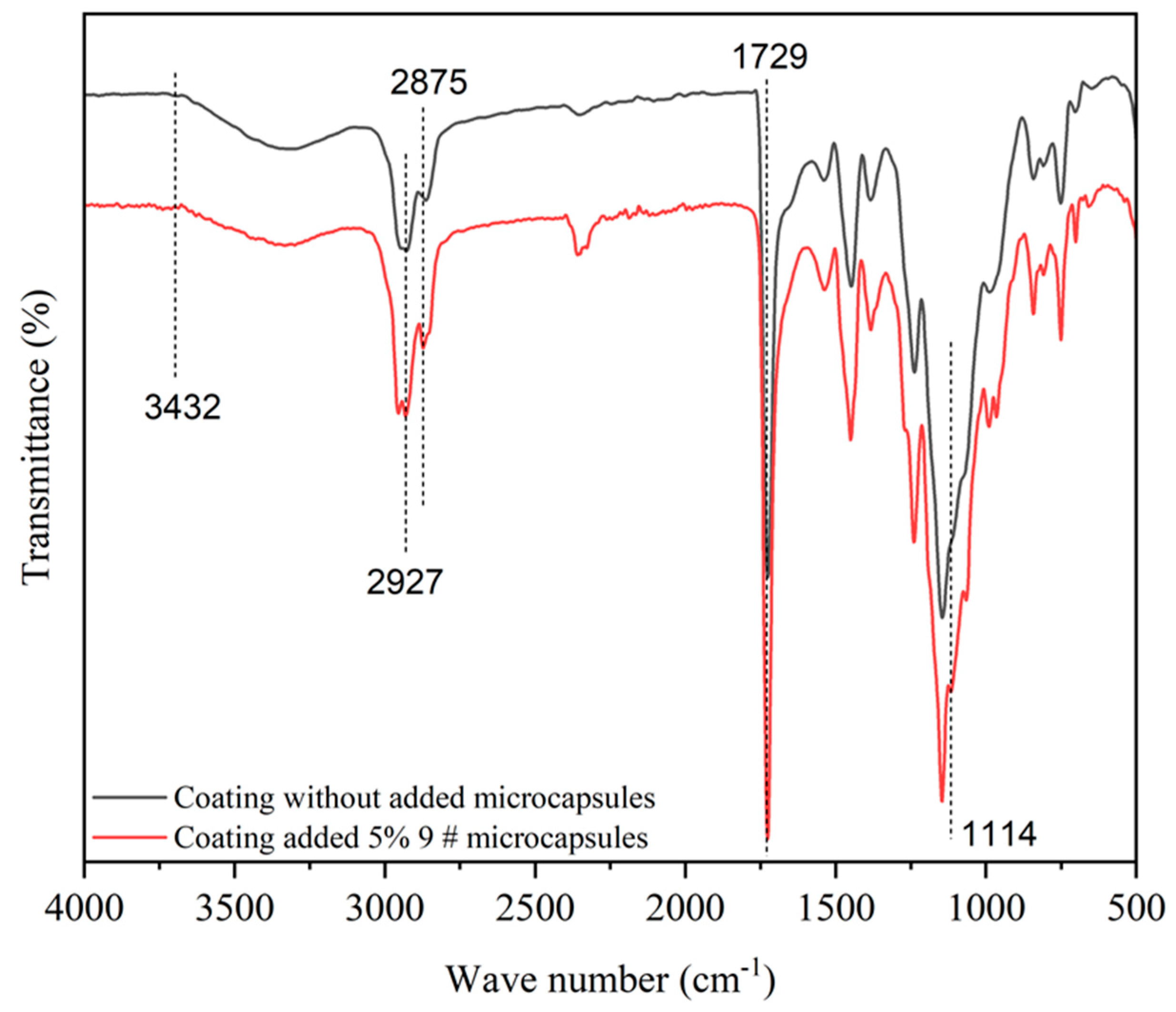
As shown in Figure 5, the absorption peak at 1729 cm−1 was the absorption peak of C=O in waterborne coatings [38]. There were the stretching vibration peaks of N–H and O–H at 3425 cm−1 and the two stretching vibration absorption peaks of C–H in shell material chitosan appeared at 2921 cm−1 and 2875 cm−1, respectively [39]. The characteristic peak appearing at 1114 cm−1 was the absorption peak of C–O in the microcapsule core material. This proved that after adding the prepared microcapsules to the waterborne topcoat, the shell and core components belonging to the microcapsules still existed, and there was no chemical reaction between the microcapsules and the waterborne topcoat.
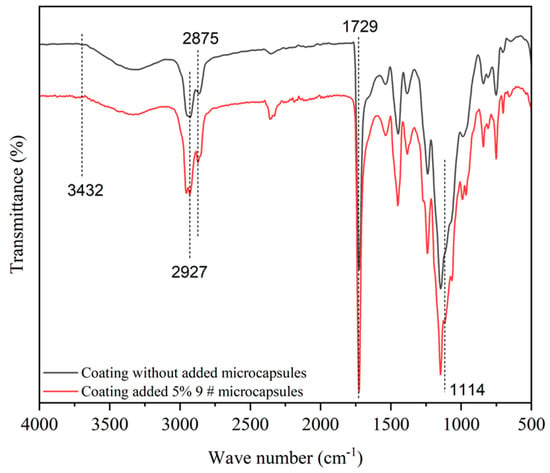
Figure 5.
Infrared spectra of the coating.
3.3. Influence of Different MT:MC of Microcapsules on the Optical Properties of the Coatings
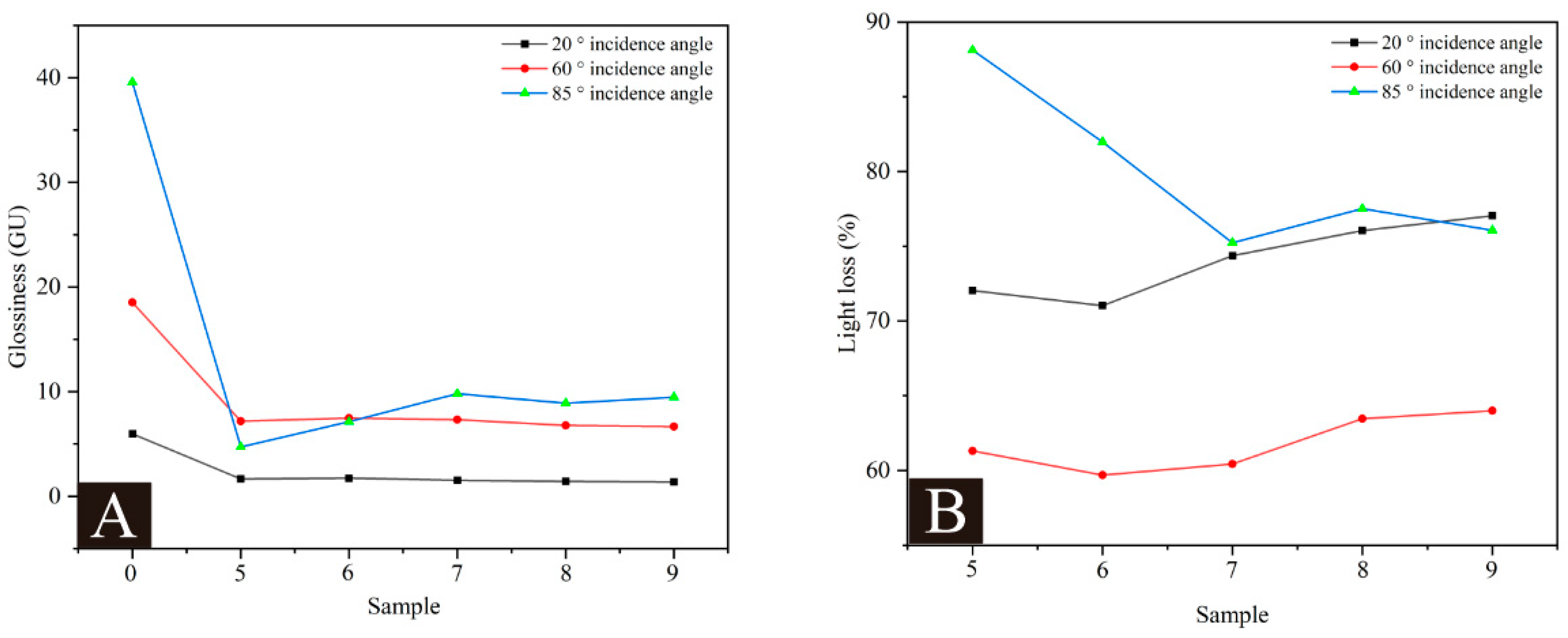
Glossiness is an important indicator for the surface coating of wooden products. Table 9 shows the effect of microcapsules with different MT:MC on the glossiness and light loss of coatings. 0# represents the glossiness value of the coating without microcapsules added. Figure 6A shows the changes in the surface glossiness and light loss of the coating measured at three incident angles. Compared with the coating without microcapsules, the addition of microcapsules greatly reduced the glossiness of the coating itself. The difference in glossiness between coatings varied relatively little at an incidence angle of 60°. As the MT:MC increased, the glossiness showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. The maximum value reached 7.47 GU when the MT:MC was 2.5:1, followed by 7.33 GU; at this time, the MT:MC was 3.0:1. As shown in Figure 6B, as the MT:MC increased, the light loss of the coating showed a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. The light loss of the coating at a 60° incidence angle reached the minimum value of 59.69% when the MT:MC was 2.5:1, followed by 60.44%; at this time, the MT:MC was 3.0:1. This is because the prepared microcapsule powder is relatively sticky and rough. Adding it to the waterborne coating for curing reduces the smoothness of the coating, thereby reducing the surface light reflection performance of the coating [40,41]. When the added microcapsules MT:MC was 2.5:1 and 3.0:1, the glossiness and light loss of the coating were relatively excellent, and the coating performance was better.

Table 9.
Effect of microcapsules with different MT:MC on the glossiness of the coatings.
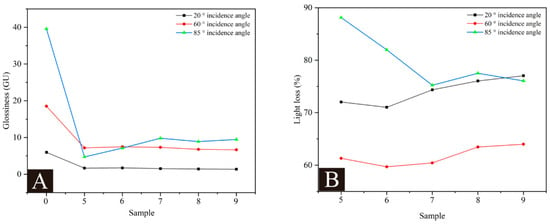
Figure 6.
Effect of MT:MC of microcapsules on (A) the glossiness and (B) light loss of the coating.
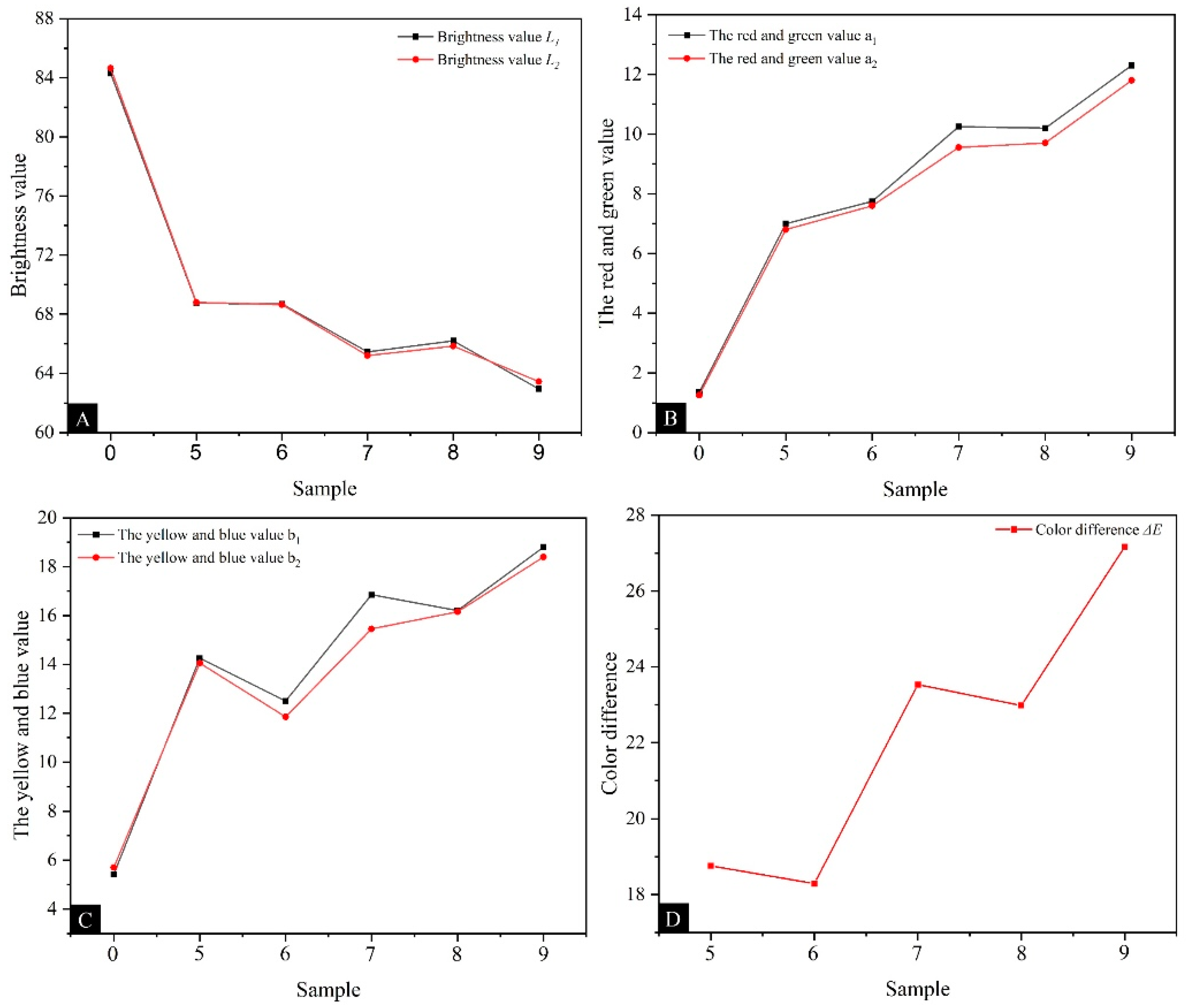
Table 10 shows the changes in chromaticity and the color difference values of coatings with different MT:MC. As shown in Figure 7A, the brightness value of the coating showed a fluctuating downward trend with the increase in MT:MC. The addition of microcapsules reduced the reflection ability of the coating to light, thereby reducing the brightness value of the coating. Figure 7B,C show an overall upward trend in the red green and yellow blue values of the coating. This is because the microcapsules are brown in color, and as the core material amount increases, the color of the microcapsules gradually darkens, resulting in an increase in the red–green and yellow–blue values of the coating. As shown in Figure 7D, the color difference value of the coating generally showed an upward trend with the increase in MT:MC. When the MT:MC was 2.5:1, the minimum color difference value was 18.29. When the MT:MC was 4.0:1, the maximum color difference value was 27.17. This is because microcapsules themselves are relatively rough and have a strong sense of particle size. After adding the coating, there were uneven dispersion, local agglomeration, and other phenomena, which increased the color difference of the coating and affected its aesthetics [42,43].

Table 10.
Effect of microcapsules with different MT:MC on the chromaticity and color difference of the coating.
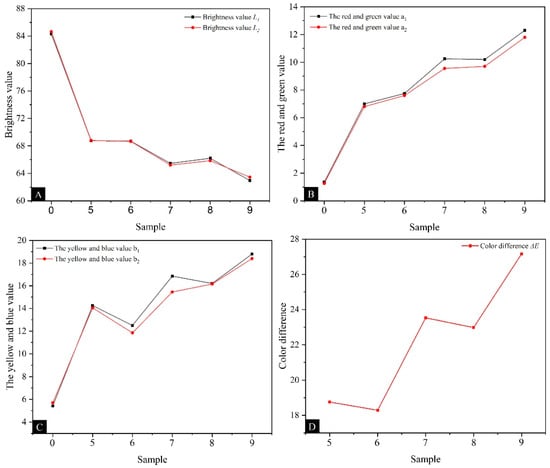
Figure 7.
The effects of microcapsules with different MT:MC on the chromaticity value and color difference of the coating: (A) L value, (B) a value, (C) b value, and (D) ΔE.
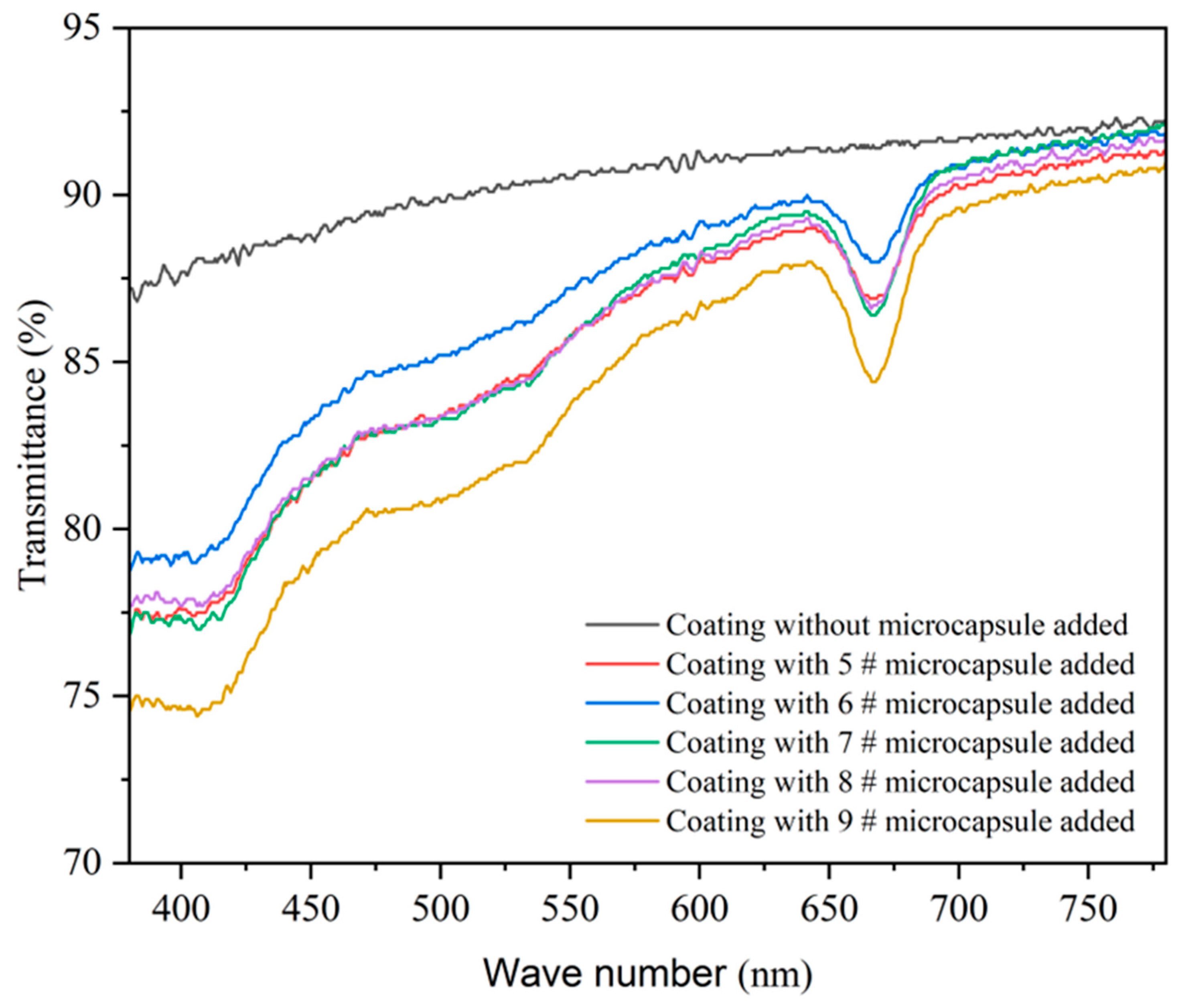
Figure 8 shows the variation trend of transmittance of coatings prepared using microcapsules with different MT:MC. Compared with the coating without microcapsules, the overall transmittance of the coating-added microcapsules was lower. As the MT:MC continues to increase, the overall transmittance of the prepared coating in the visible light band shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. Table 11 shows the transmittance of waterborne coatings containing different MT:MC microcapsules in the visible light band. When the added microcapsule MT:MC was 2.5:1 (sample 6#) and 3.0:1 (sample 7#), the transparency of the coating was relatively excellent, with corresponding visible light transmittance of 87.05% and 86.00%, respectively. When adding MT:MC at 4.0:1 (sample 9#), the light transmittance of the coating was poor, corresponding to a visible light transmittance of 84.08%. Due to the increasing aggregation phenomenon of microcapsules, the surface roughness of the prepared coating is enhanced, which reduces the transmission and reflection of incident light, enhances the scattering phenomenon of light, and thus reduces the transmittance of the coating. When the MT:MC was 4.0:1, the minimum transmittance appeared. Because the coating containing the 9# microcapsule has a darker color, this reduces the penetration ability of light and the transmittance of the coating.
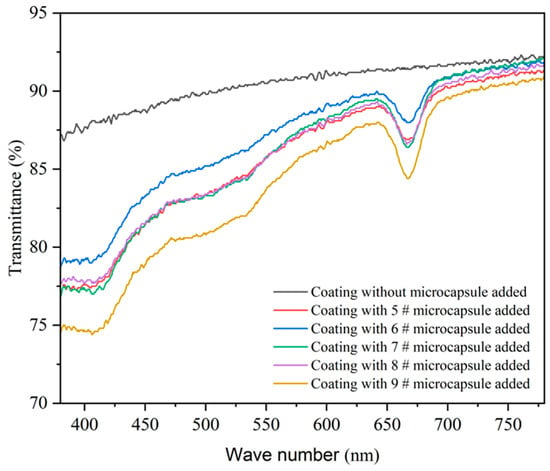
Figure 8.
Effect of the MT:MC of microcapsules on the transmittance of the coating.

Table 11.
Transmittance of coatings containing microcapsules with different MT:MC in the visible light band.
3.4. Influence of Different MT:MC of Microcapsules on the Cold Liquid Resistance of the Coatings
Table 12 shows the cold liquid resistance of coatings prepared from microcapsules with different MT:MC. The cold resistance levels of the coating without microcapsules to citric acid, ethanol, and cleaning agents were level 2, level 3, and level 4, respectively. After adding microcapsule samples to the coating, the citric acid resistance level of the coating decreased to level 3. Compared to the tested area, the color differences in the test area were seen from multiple directions. This is because chitosan can dissolve in weak acid solutions [44], and as the shell material of microcapsules, chitosan is affected by citric acid, thereby reducing the cold liquid resistance of the coating to citric acid. Compared with the coating without microcapsules added, the ethanol cold liquid resistance of the coating was improved. When adding microcapsules of samples 5# and 6#, the ethanol resistance level of the coating was level 2. When adding microcapsules of samples 7#, 8#, and 9#, the ethanol resistance level of the coating was level 1. The cleaning agent cold liquid resistance of the coating showed an upward trend with the increase in MT:MC. The cleaning agent resistance level of the added samples 5# and 6# microcapsule coating was raised to level 3, and the cleaning agent resistance level of the added samples 7#, 8#, and 9# microcapsule coating was raised to level 2. This is because the added microcapsules have a protective effect on the coating, thereby improving its performance. When the MT:MC of microcapsules added to the coating was 3.0:1, 3.5:1, and 4.0:1, the antibacterial coating prepared had excellent cold liquid resistance performance.

Table 12.
Cold-resistant liquid grade of coatings containing microcapsules with different MT:MC.
3.5. The Influence of Different MT:MC of Microcapsules on the Mechanical Properties of the Coatings
Table 13 shows the fracture elongation of the coating prepared by microcapsules with different MT:MC. The fracture elongation of the coating without microcapsules added was 24.77%. After adding microcapsules, the fracture elongation of the coating showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing and tended to stabilize. When adding the 7# microcapsule sample, the fracture elongation of the microcapsule coating reached its maximum value of 13.26%, at which point the microcapsule MT:MC was 3.0:1. The minimum fracture elongation of the coating was 7.24%, corresponding to the microcapsule MT:MC of 2.0:1. This is because the addition of microcapsules enhances the brittleness of the coating, thereby reducing its tensile resistance [45,46].

Table 13.
Effect of microcapsules with different MT:MC on the mechanical properties of the coatings.
From the changes in the roughness values of the coating shown in Table 13, compared with the coating without microcapsules, the addition of microcapsules increased the roughness of the coating. As the microcapsule MT:MC increased, the roughness showed a fluctuating trend of first increasing, then decreasing, and then increasing again. When sample 7# was added to the coating, the roughness reached a minimum value of 1.533 μm, corresponding to the microcapsule MT:MC of 3.0:1. When adding sample microcapsules 5# and 6#, the roughness was 2.426 μm and 2.764 μm, and the microcapsule MT:MC were 2.0:1 and 2.5:1, respectively. This is because the aggregation phenomenon of microcapsules in samples 5# and 6# is more severe, which can easily reduce the dispersibility of microcapsules in waterborne coatings, causing more protrusions in the coating.
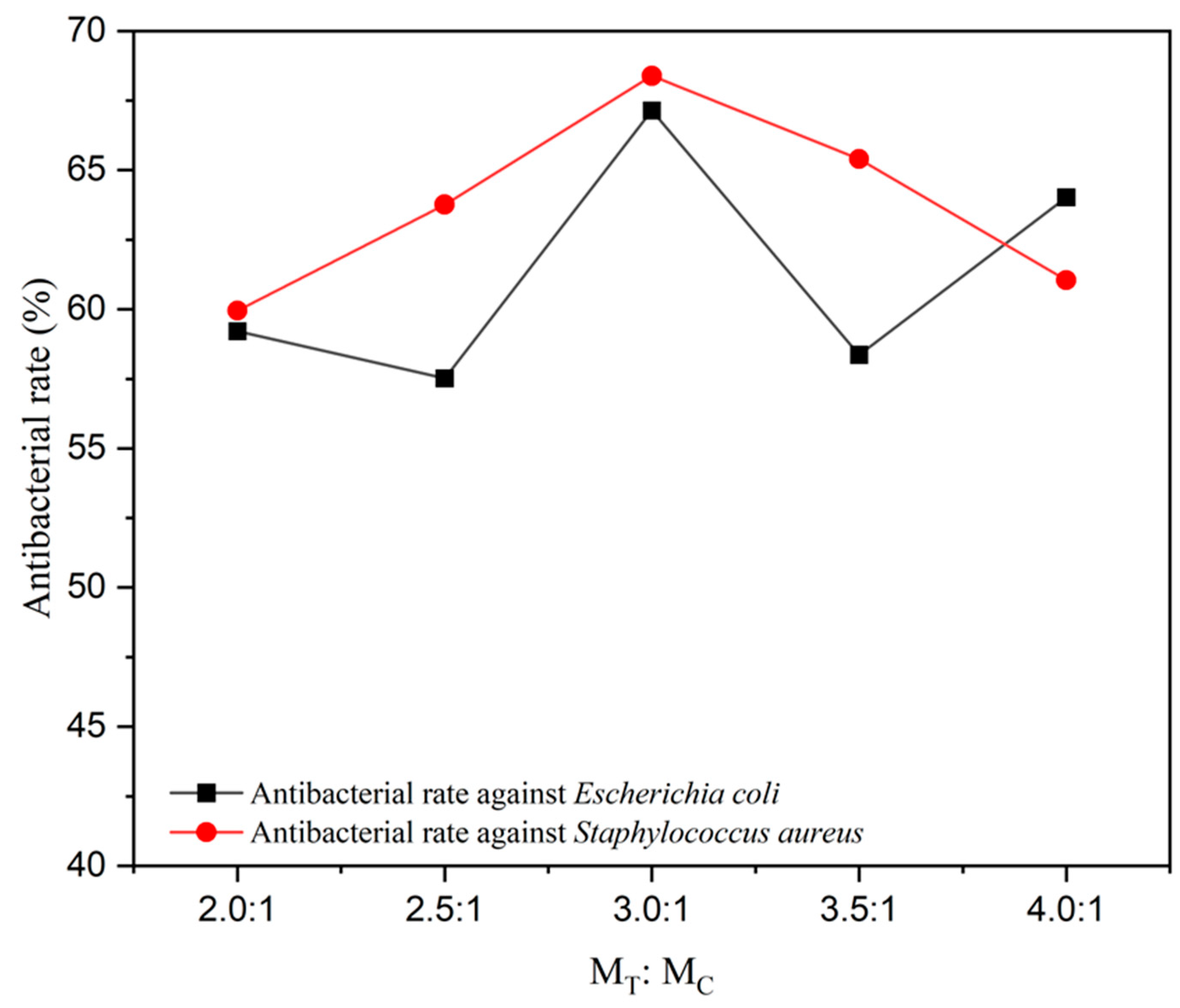
3.6. Effect of Microcapsules with Different MT:MC on the Antibacterial Performance of the Coatings
As shown in Table 14, compared to the colony recovery rate of the pure coating, the colony recovery rate of the coating with microcapsules added was significantly reduced. Figure 9 shows the trend of the antibacterial activity of microcapsules with different MT:MC against two types of bacteria in the coating. For Escherichia coli, as the microcapsule MT:MC increased, the antibacterial rate showed a trend of increasing, decreasing, and then increasing. When the added microcapsule MT:MC was 3.0:1, the antibacterial rate reached the maximum value of 67.14%. When the added microcapsule MT:MC was 2.5:1, the minimum antibacterial rate of the coating was 58.36%. This is because the coverage rate of microcapsules with MT:MC of 2.5:1 is lower, and the content of antibacterial agents in the core material is lower, so the antibacterial rate of the coating is lower. The antibacterial rate of the prepared coating against Staphylococcus aureus first increased and then decreased. When adding 7# microcapsules, the maximum antibacterial rate against Staphylococcus aureus was 68.39%, and the corresponding microcapsule MT:MC was 3.0:1. When the microcapsule MT:MC added to the coating was 2.0:1, the antibacterial rate reached the minimum value of 59.95%. This is because the core material content of microcapsules with MT:MC of 2.0:1 is relatively low, and the encapsulation rate of microcapsules is low. Therefore, there are fewer sustained-release antibacterial agents for the core material, and the antibacterial rate of the coating is lower. The antibacterial rate of the coating against Staphylococcus aureus was generally higher than that against Escherichia coli. This is because the effective antibacterial component coumarin compounds in the core material Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extract have better antibacterial effects on Staphylococcus aureus [47]. When the added microcapsule MT:MC was 3.0:1 (sample 7#), the antibacterial coating prepared had the highest antibacterial rates against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.

Table 14.
The average number of recovered colonies and antibacterial rate of the coating-added microcapsules with different MT:MC.
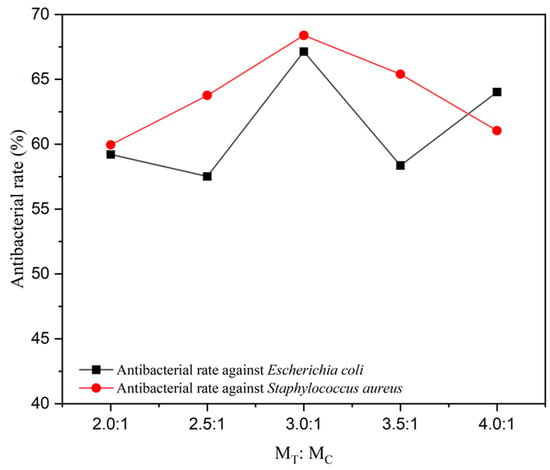
Figure 9.
Antibacterial rate of coatings containing microcapsules with different MT:MC.
4. Conclusions
The biggest influencing factor for preparing microcapsules was MT:MC. The optimal preparation process parameters for microcapsules were MT:MC of 3.0:1, a microencapsulation pH value of 7, and a reaction temperature of 50 °C. When the addition content was 5.0%, as the MT:MC of the added microcapsules increased, the glossiness showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. As the microcapsule MT:MC increased, the color difference value generally increased. The overall visible light transmittance increased and then decreased. The level of citric acid resistance of the coating decreased, while the level of ethanol and cleaning agent resistance increased, with the most significant improvement in cleaning agent resistance. The fracture elongation increased and then decreased, and the roughness value gradually increased. As the microcapsule MT:MC increased, the antibacterial rate against Escherichia coli increased, decreased, and then increased again. The antibacterial rate against Staphylococcus aureus increased and then decreased. When the microcapsule MT:MC was 3.0:1, the antibacterial rates of the coating against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus reached their maximum values, which were 67.14% and 68.39%, respectively. Based on the properties of the coating, the waterborne coating prepared with a microcapsule MT:MC of 3.0:1 exhibited excellent performance. The glossiness was 7.33 GU, the loss rate was 60.44%, the color difference ΔE was 23.53, the visible light transmittance was 86.00%, and the resistance to citric acid, ethanol, and cleaning agents was grade 3, grade 1, and grade 1, respectively. The fracture elongation was 13.26%, and the roughness was 1.533 μm. The antibacterial rates against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus were 67.14% and 68.39%, respectively. The preparation of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts into microcapsules can overcome the problems of the poor heat resistance, poor stability, and short shelf life of general natural antibacterial agents, while also endowing antibacterial agents with sustained-release properties. Compared to commonly used shell materials such as melamine resin and urea formaldehyde resin, chitosan is more environmentally friendly, the drugs used are non-toxic, the recycling of production waste is easier, and it is more environmentally friendly. Chitosan and Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extracts both have antibacterial properties, and their synergistic effect can effectively enhance the antibacterial performance of the coating. The results effectively improved the antibacterial rate of waterborne coatings, providing a new approach for the application of d Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam extract in waterborne coatings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology and writing—review and editing, Y.Z.; validation, resources, and data management, Y.W.; formal analysis, investigation, and supervision, X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was partly supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20201386).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, E.L.; Zhao, X.T.; Hu, J.L.; Wang, R.X.; Fu, S.; Qin, G.W. Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2569–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Fu, W.J.; Zhao, Y. Optimal design of the traditional Chinese wood furniture joint based on experimental and numerical method. Wood Res. 2024, 69, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Qin, M.; Xu, M.J.; Miao, F.Y.; Merzougui, C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Huang, D. The fabrication of antibacterial hydrogels for wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Kasal, A.; Erdil, Y.Z. The state of the art of biomechanics applied in ergonomic furniture design. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Li, G.W.; Cao, E.R.; Luo, J.L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, H.Y. Recent progress of antibacterial hydrogels in wound dressings. Mater. Today Biol. 2023, 19, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egghe, T.; Morent, R.; Hoogenboom, R.; De Geyter, N. Substrate-independent and widely applicable deposition of antibacterial coatings. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Xu, W.; Tan, Y. Multi-attribute hierarchical clustering for product family division of customized wooden doors. BioResources 2023, 18, 7889–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, R.J.; Yang, S.Q.; Fan, Z.X. Effects of MDF substrate surface coating process on UV inkjet print quality. Coatings 2023, 13, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.Y.; Xi, Y.W.; Weng, Y.X. Recent Advances in PLA-Based Antibacterial Food Packaging and Its Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, W. A review on recent trends of the antibacterial nonwovens air filter materials: Classification, fabrication, and application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.K.; Dai, R.; Chang, S.C.; Wei, Y.Q.; Zhang, B. Antibacterial mechanism of biogenic calcium oxide and antibacterial activity of calcium oxide/polypropylene composites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Gao, H.S.; Zhou, L.; Nie, Y. Screening Ionic Liquids by the COSMO-RS Method for the Preparation of Antibacterial Cellulose Fibers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 15525–15536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.W. Optimization of green extraction process of Cinnamomum camphora fruit dye and its performance by response surface methodology. BioResources 2023, 18, 4916–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Sun, Y.; Shen, L.M.; Han, J.L. Study on the process optimization of peanut coat pigment staining of poplar wood. Forests 2024, 15, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, R.J.; Yang, F.; Fan, Z.X. The effect of water-based primer pretreatment on the performance of water-based inkjet coatings on wood surfaces. Coatings 2023, 13, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.Q.; Zhou, Z.W.; Xu, R.; Dong, Y.T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, M.J. Effect of NaOH pretreatment on permeability and surface properties of three wood species. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 40362–40374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, J.P.; Kang, H.J.; Ke, Q. Synthesis of inorganic/organic hybrid-shell antibacterial polyurea microcapsules loaded with Ag/TiO2 nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 691, 133814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.G.; Wan, H. Comparative study on weathering durability properties of phenol formaldehyde resin modified sweetgum and southern pine specimens. Maderas. Cienc. Tecnol. 2022, 24, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Gu, Y.T.; Xu, W.; Lu, T.; Li, W.N.; Fan, H.B. Compressive properties of green velvet material used in mattress bedding. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.T.; Zhang, J.L. Fatigue performance of natural and synthetic rattan strips subjected to cyclic tensile loading. Forests 2022, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.T.; Zhang, J.L. Tensile Properties of Natural and Synthetic Rattan Strips Used as Furniture Woven Materials. Forests 2020, 11, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lei, K.; Ji, L.S. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. Mitochondrial DNA B 2021, 6, 1650–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Tian, P.; Feng, J.; Yang, N.A.; Yuan, L. A systematic review on traditional medicine Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam.: Chemistry and medicinal potential. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Wang, P.Q.; Wang, P.Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Kang, W.Y. Antibacterial mechanism of chelerythrine isolated from root of Toddalia asiatica (Linn) Lam. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraipandiyan, V.; Ignacimuthu, S. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of Flindersine isolated from the traditional medicinal plant, Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Gao, D.; Xu, W. Effect of paint process on the performance of modified poplar wood antique. Coating 2021, 11, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Fang, X.Y.; Han, J.T.; Wu, Z.H.; Zhang, J.L. Effect of coating thickness on sound absorption property of four wood species commonly used for piano soundboards. Wood Fiber Sci. 2020, 52, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.Y.; Xiao, X.H.; Li, G.K. Separation and purification of furanocoumarins from Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. using microwave-assisted extraction coupled with high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.Y.; Zhong, S.L.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X.J. Advances in chitosan-based microcapsules and their applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 11186.3-1989; Methods for Measuring the Color of Coatings—Part 3: Calculation of Color Difference. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- GB/T 4893.6-2013; Testing of Physical and Chemical Properties of Furniture Surface Paint Films—Part 6: Gloss Determination Method. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T 4893.1-2021; Test of Surface Coatings of Furniture—Part 1: Determination of Surface Resistance to Cold Liquids. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 21866-2008; Test Method and Effect for Antibacterial Capability of Paints Film. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 4789.2-2022; Microbiological Examination of Food Hygiene—Aerobic Plate Count. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Han, Y.; Yan, X.X.; Tao, Y. Effect of Number of Impregnations of Microberlinla sp. with Microcapsule Emulsion on the Performance of Self-Repairing Coatings on Wood Surfaces. Coatings 2022, 12, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, N.; Sargin, I.; Arslan, G.; Arslan, U.; Okudan, A. Ascorbic Acid Adsorption-Release Performance and Antibacterial Activity of Chitosanter (GMA-MA-NTBA) Polymer Microcapsules. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ni, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ma, R.J.; Jia, Z.H.; Chen, K.L. Fabrication of multiple protective fabric based on ZnO/chitosan composite microcapsules via thiol-ene click modification. Cellulose 2023, 30, 8023–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Yan, X.X.; Han, Y. Preparation of Melamine-Formaldehyde Resin/Rice Husk Powder Coated Epoxy Resin Microcapsules and Effects of Different Microcapsule Contents on the Properties of Waterborne Coatings on Tilia europaea Surface. Coatings 2022, 12, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, P.; Pedroso-Santana, S.; Kumar, Y.; Joly, N.; Martin, P.; Bocchetta, P. Ionotropic Gelation of Chitosan Flat Structures and Potential Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.C.; Xu, W. A fast method to prepare highly isotropic and optically adjustable transparent wood-based composites based on interface optimization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 218, 118898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Z.Y. Optical properties and lampshade design applications of PLA 3D printing materials. BioResources 2023, 18, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Gao, D.; Xu, W. Effect of polyurethane non-transparent coating process on paint film performance applied on modified poplar. Coating 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.C.; Xu, W. Toward interface optimization of transparent wood with wood color and texture by silane coupling agent. J. Mater. 2022, 57, 5825–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhuang, S.T. Chitosan-based materials: Preparation, modification and application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 131825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.G.; Chen, B.R.; Zhang, T.X. Experimental and numerical studies on mechanical behaviors of beech wood under compressive and tensile states. Wood Res. 2021, 66, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.G.; Liu, N. Numerical and Optimal Study on Bending Moment Capacity and Stiffness of Mortise-and-Tenon Joint for Wood Products. Forests 2020, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeki, N.M.; Mustafa, Y.F. Natural linear coumarin-heterocyclic conjugates: A review of their roles in phytotherapy. Fitoterapia 2024, 175, 105929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).