The Effects of the Finishing Polish Process on the Tribological Properties of Boride Surfaces of AISI 4140 Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surface Preparation Process
2.2. Surface Characterization
2.3. Tribological Characterization
3. Results
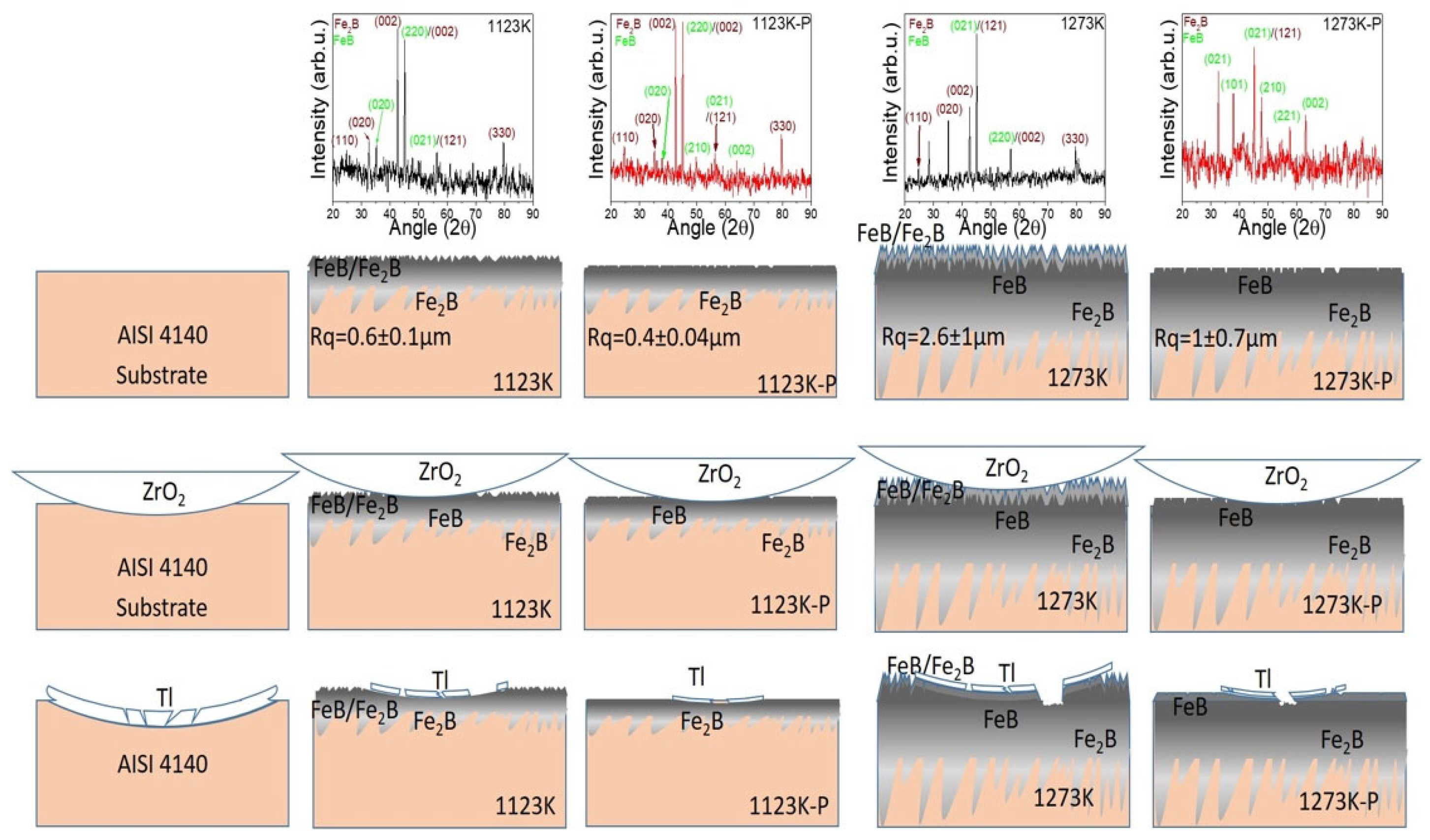
3.1. Surface Characterization
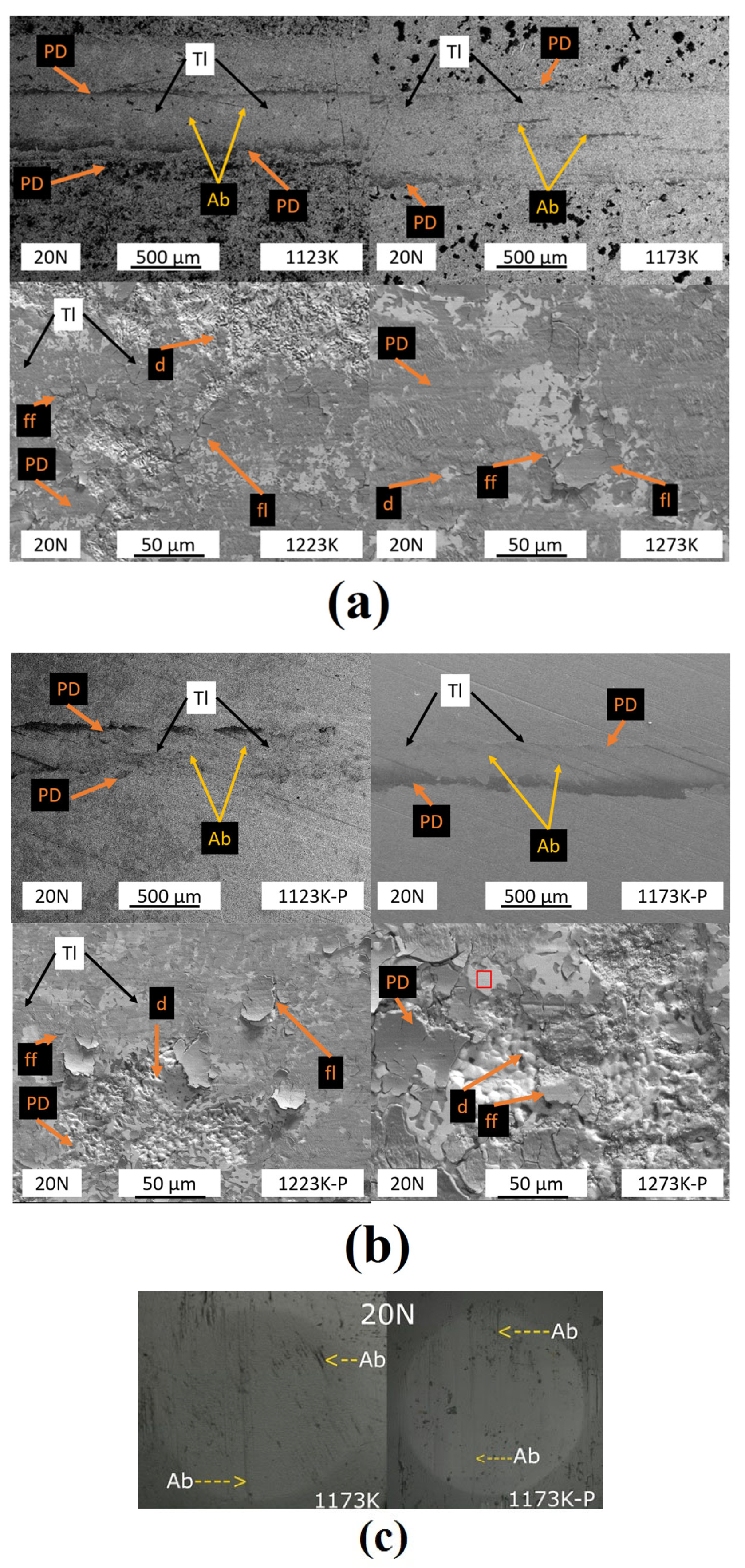
3.1.1. Morphology
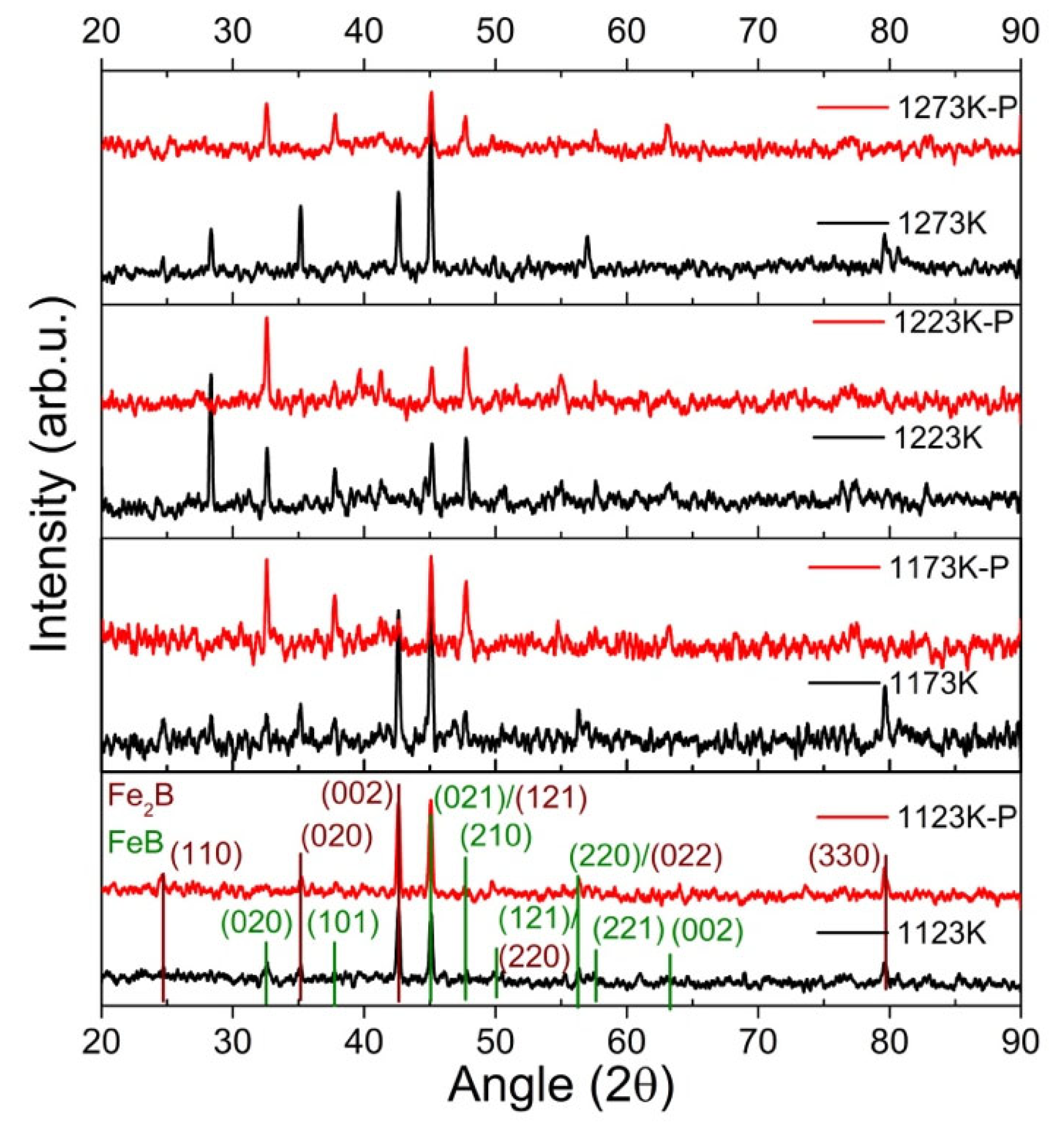
3.1.2. Crystalline Structure
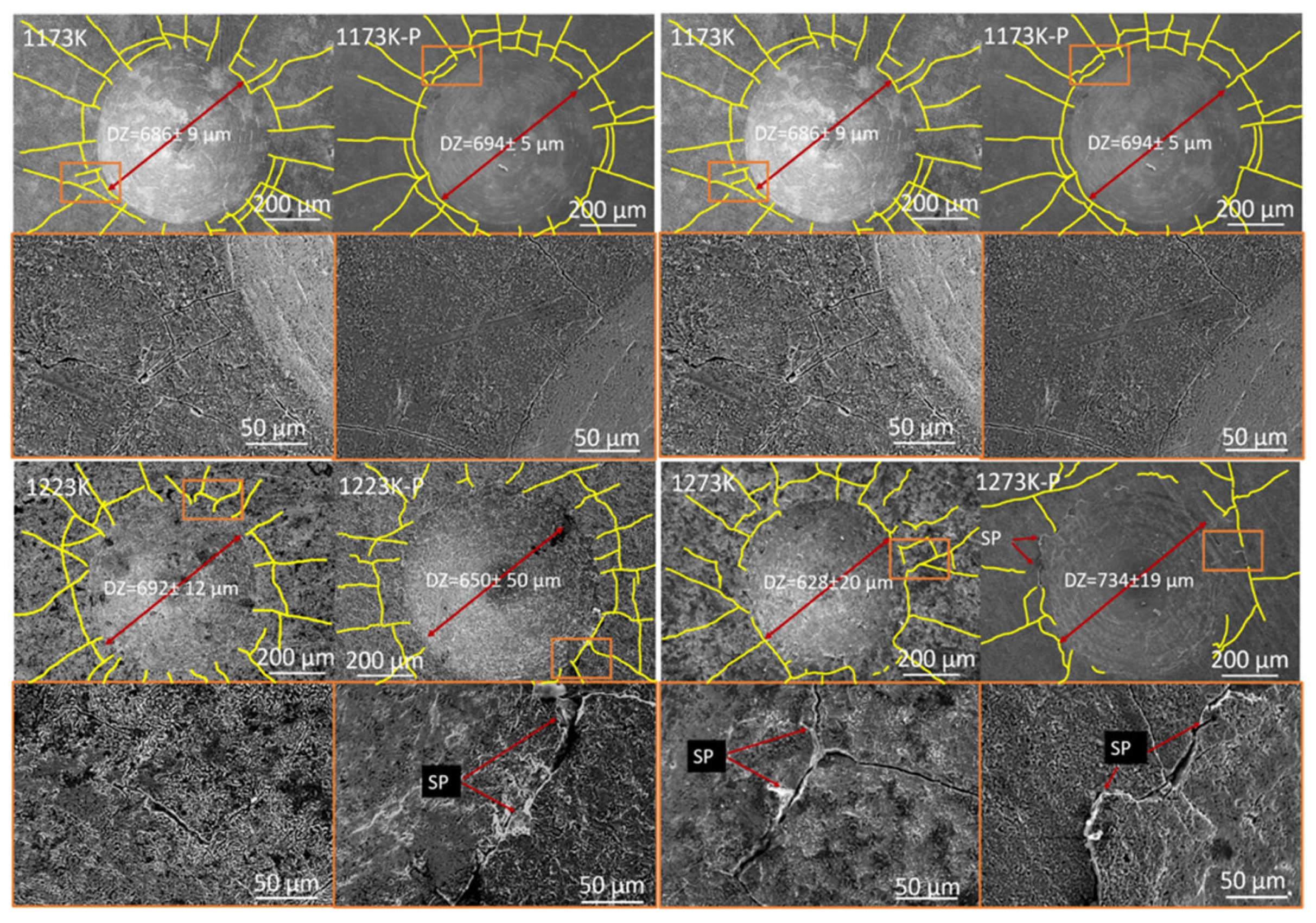
3.2. Adhesion Test
3.3. Tribological Results
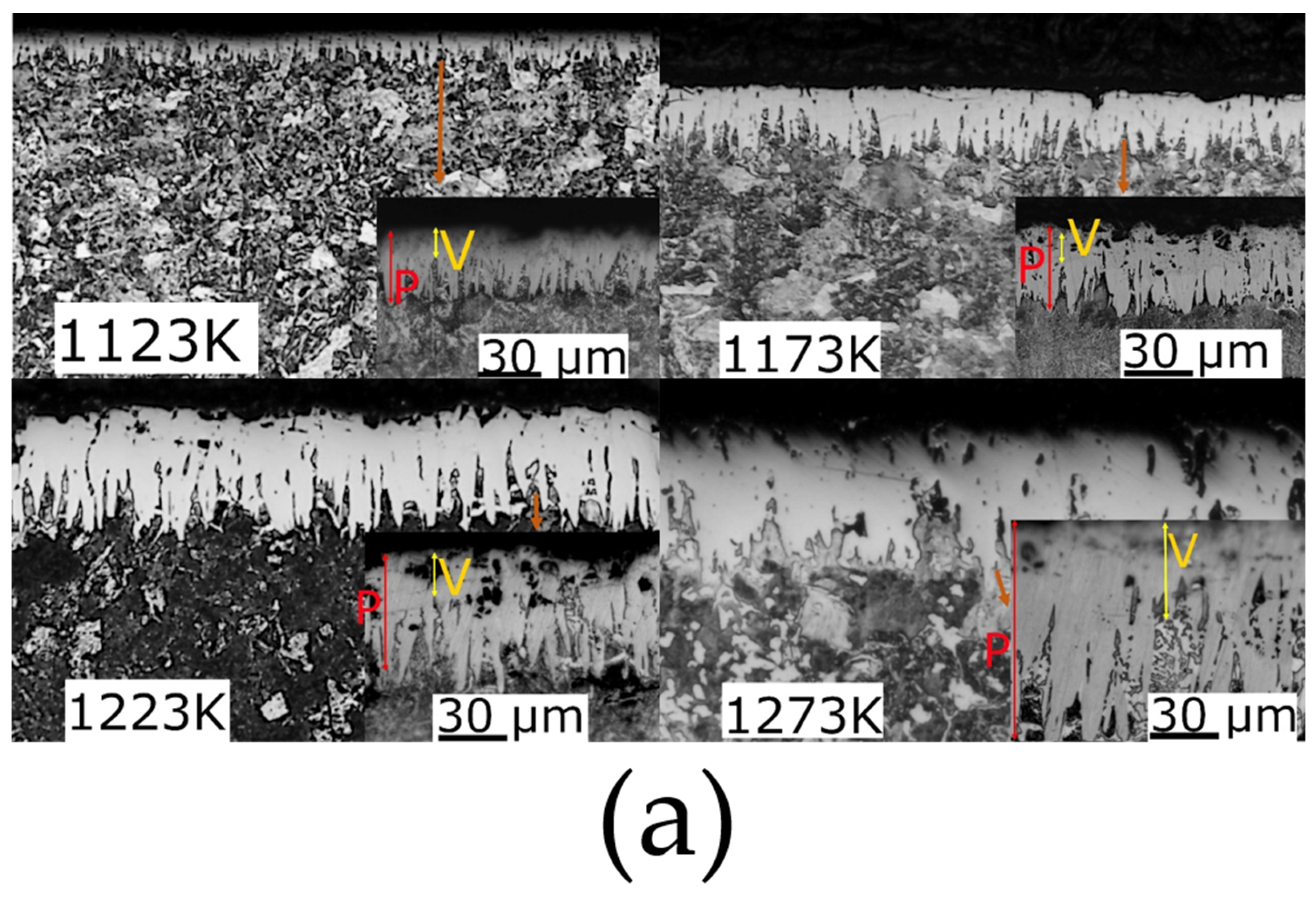
3.3.1. Wear
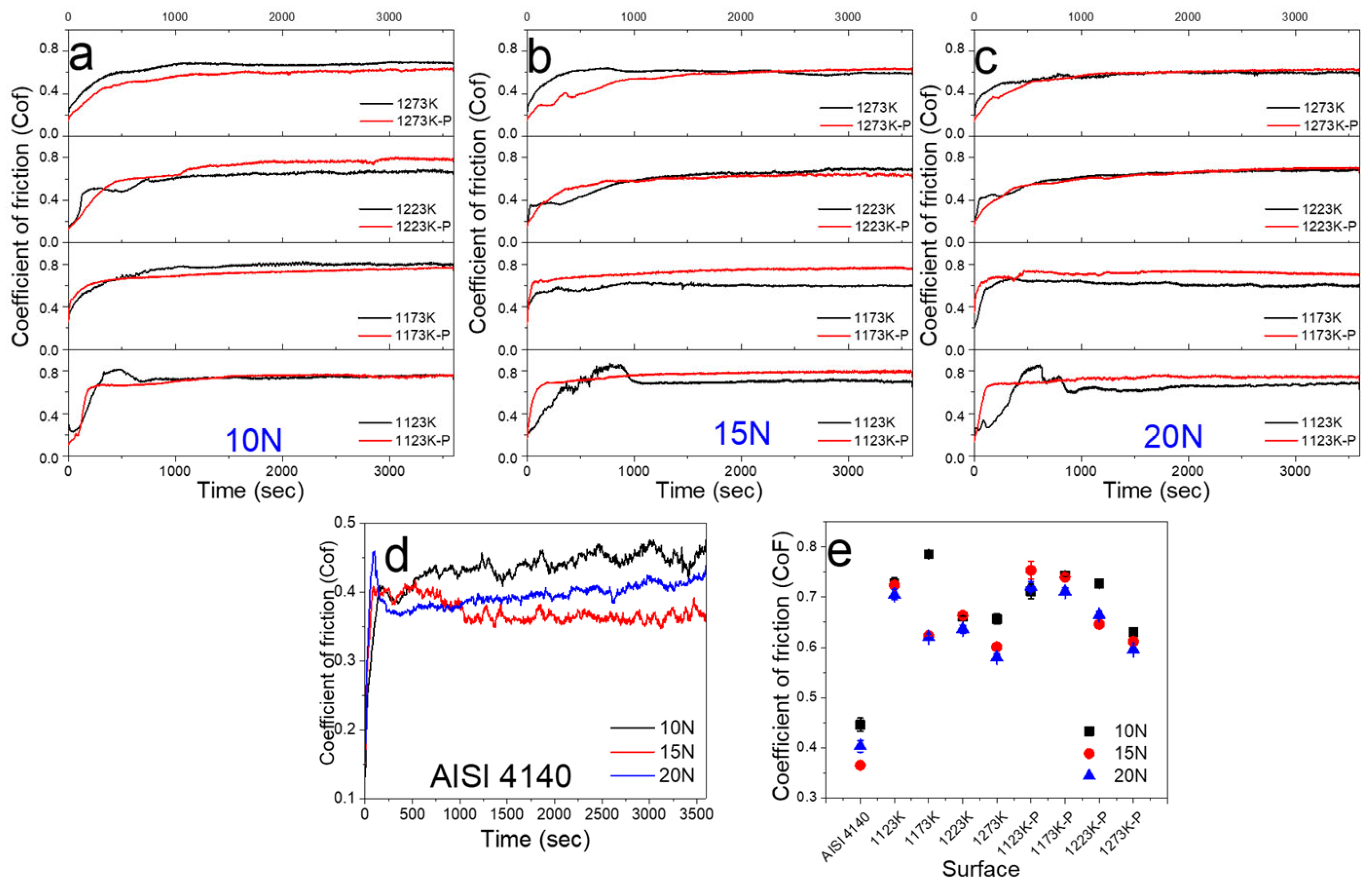
3.3.2. Coefficient of Friction (Cof)
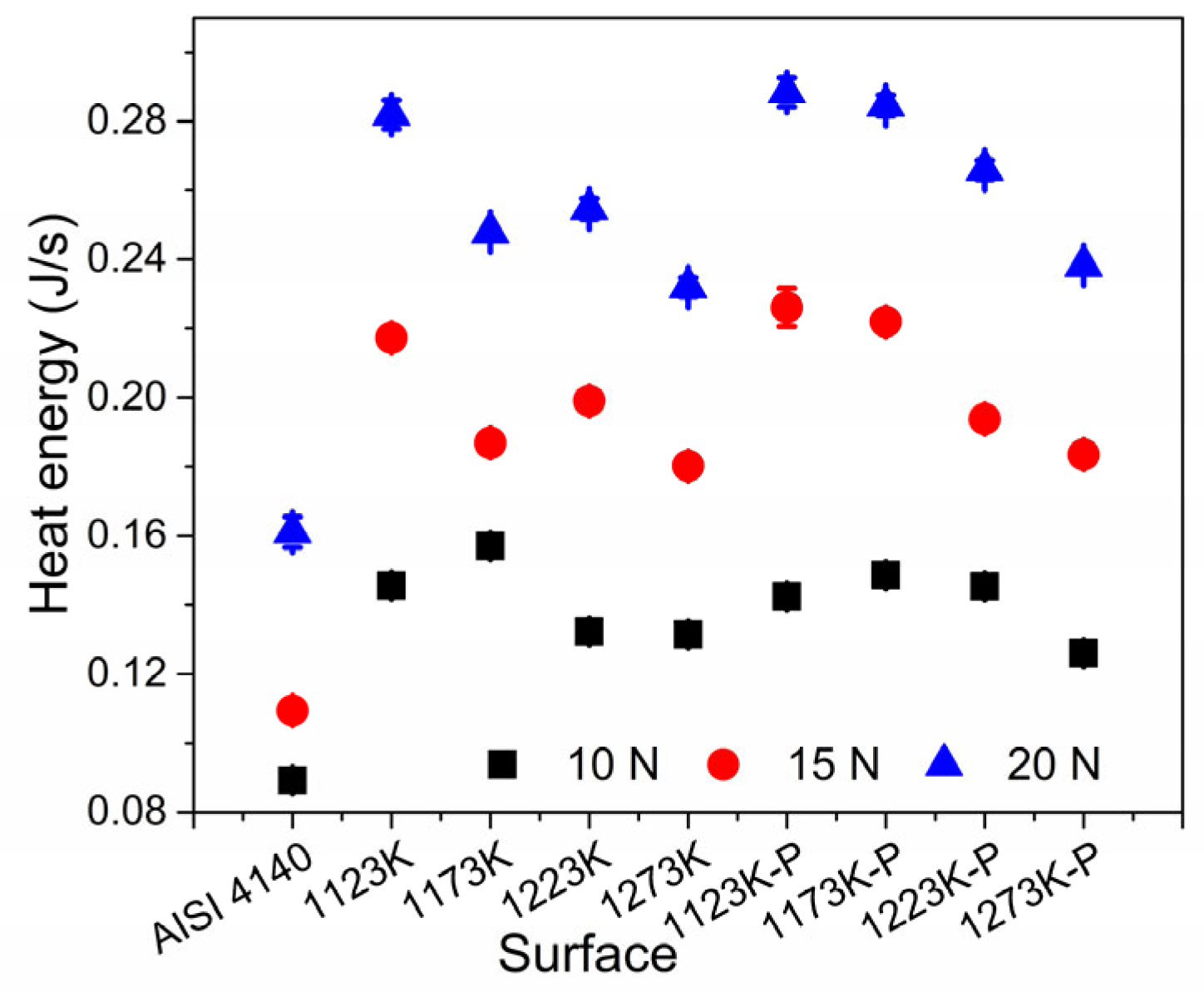
4. Discussion
- (1)
- The increment in the roughness value with the increment in the temperature treatment.
- (2)
- The top layer presented a lower stress resistance due to its Fe2B phase content.
- (3)
- The increment in the coating thickness reduced the surface deformation during the sliding tests (see Figure 9).
- (4)
- The modification of the surface characteristics of the boride treatment with the increment in the temperature of the boride thermal treatment reduced the frictional stress (τfric), reducing the heat energy generated by the rubbing operations.
5. Conclusions
- The boride AISI 4140 surfaces at treatment temperatures of 1123, 1173, 1223, and 1273 K presented the FeB and Fe2B boride phases, with an incremental boride layer thickness and roughness with a sawtooth-like morphology.
- The finishing polish process reduced the roughness of the boride surfaces, obtaining an N7 surface quality classification for the 1273 K sample and removing a top layer formed by the Fe2B phase and residual material of the thermochemical treatment, revealing the FeB phase of the boride layers.
- Although the boride layer with and without the finishing process presented an acceptable adhesion characteristic, the number of fractures around the Rockwell C mark decreased with increments in the temperature of the thermochemical treatment, showing an increment in the absorption of energy before the layer fracture with increments in the thickness of the layer.
- The boride surfaces with and without the finishing polish process showed a similar wear track, with the formation of a tribolayer that protected the surfaces. However, the finishing polish process improves the stability of the tribological performance, showing a more constant reduction in the Cof value due to the revelation of the FeB phase and increments in the thickness of the boride layer by increments in the treatment temperature that reduce the boride surface deformation, production of heat energy, and adhesion forces between the Pin and the boride surfaces.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilal, M.M.; Yaqoob, K.; Zahid, M.H.; ul haq, E.; Tanveer, W.H.; Wadood, A.; Ahmed, B. Effect of austempering conditions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 4340 and AISI 4140 steels. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Silva, I.; Ortiz-Domínguez, M.; López-Perrusquia, N.; Meneses-Amador, A.; Escobar-Galindo, R.; Martinez-Trinidad, J. Characterization of AISI 4140 borided steels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 2372–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Ersozlu, I. Investigation of the mechanical properties and microstructure of friction welded joints between AISI 4140 and AISI 1050 steels. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, N.; Paul, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Machining of AISI 4140 steel under cryogenic cooling—Tool wear, surface roughness and dimensional deviation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 123, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, C.; Palombarini, G.; Carbucicchio, M. Mechanism of thermochemical growth of iron borides on iron. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Perrusquia, N.; de la Mora Ramírez, T.; Pérez Mendoza, G.J.; Olmos Domínguez, V.H.; Sánchez Huitron, D.; Doñu Ruiz, M.A. Experimental Study on Microalloyed Steel with Layers Subjected to Diesel. Coatings 2024, 14, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayalı, Y.; Yönetken, A. Investigation of wear behavior of borided materials produced by the powder metallurgy method in different compositions. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2021, 57, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Cortés, R.; Martínez-Trinidad, J.; Flores-Martínez, M.; Flores-Jiménez, M.; García-León, R. Sliding wear resistance of borided AISI 4140 steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 9101–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagkliveris, D.I.; Mavropoulos, A.; Triantafyllidis, G.K. Corrosion Behavior of Boronized and Borochromized AISI 4140 Steel After Acid Exposure Evaluated by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 8831–8845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litoria, A.K.; Joshi, A.A.; Joshi, M.D.; Dixit, G.; Singh, D.; Hosmani, S.S. Wear behaviour of boronized and duplex-treated AISI 4140 steel against DLC-coated boronized AISI 4140 disc. Surf. Eng. 2019, 35, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulutan, M.; Yildirim, M.M.; Çelik, O.N.; Buytoz, S. Tribological properties of borided AISI 4140 steel with the powder pack-boriding method. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 38, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Feng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zheng, S.; Peng, M.; Li, M.; Wu, Y. Growth kinetics and corrosion properties of pack-borided Ti-5Al-2.5Sn alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 473, 130003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Duan, Y.; Ma, L.; Zheng, S.; Li, M.; Peng, M.; He, Y.; Li, Y. Microstructure and oxidation behavior of BAl layers on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by REO-boriding and aluminizing at 700 °C, 800 °C, and 900 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 487, 131044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qu, D.; Duan, Y.; Peng, M. Microstructure and high-temperature oxidation behaviors of surface layer on TA2 pure titanium by boriding and aluminizing two-steps method. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 5646–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.-y.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.-y.; Duan, Y.-h.; Peng, M.-j. Corrosion and wear properties of TB2 titanium alloy borided by pack boriding with La2O3. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Duan, Y.; Bao, W.; Peng, M. Characterization and growth kinetics of boride layers on Ti-5Mo-5V-8Cr-3Al alloy by pack boriding with CeO2. Mater. Charact. 2020, 164, 110362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Bao, W.; Li, P.; Peng, M. Characteristics, wear and corrosion properties of borided pure titanium by pack boriding near α → β phase transition temperature. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 16380–16387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavas, B.; Goller, G. A novel approach to boriding of TZM by spark plasma sintering method. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 78, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Herrera, A.; Bermúdez-Rodríguez, G.; Hernández-Rodríguez, E.N.; Melendez-Lira, M.; Zapata-Torres, M. Boride coating on the surface of WC–Co-based cemented carbide. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 107, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, G.C.; Yener, T.; Ozcelik, G.; Ozkan, H. TiB-based coating formation on Ti6Al4V alloy. Mater. Test. 2024, 66, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girisken, I.; Çam, G. Characterization of microstructure and high-temperature wear behavior of pack-borided Co-based Haynes 25 superalloy. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 45, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.D.; Perrusquia, N.L.; Huerta, D.S.; San Miguel, C.T.; Calderón, G.U.; Moreno, E.C.; Suarez, J.C. Growth kinetics of boride coatings formed at the surface AISI M2 during dehydrated paste pack boriding. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 596, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, G.P.; Perrusquia, N.L.; Ruiz, M.D.; Melo-Máximo, L.; Velazquez, I.L. Characterization on AISI 316L Stainless Steel. Boriding Nitriding Boriding-Nitriding Micros Microana 2020, 26, 2432–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.Y.; Polycarpou, A.A.; Conry, T.F. Detailed surface roughness characterization of engineering surfaces undergoing tribological testing leading to scuffing. Wear 2003, 255, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, J.; Morris, N.; Leighton, M.; Rahmani, R.; Howell-Smith, S.; Wild, R.; Rahnejat, H. Asperity level tribological investigation of automotive bore material and coatings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 117, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Silva, I.; Balankin, A.; Sierra, A.; Lopez-Perrusquia, N.; Escobar-Galindo, R.; Morales-Matamoros, D. Characterization of rough interfaces obtained by boriding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2596–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VillaVelázquez-Mendoza, C.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, J.; Ibarra-Galván, V.; Hodgkins, R.; López-Valdivieso, A.; Serrato-Palacios, L.; Leal-Cruz, A.; Ibarra-Junquera, V. Effect of substrate roughness, time and temperature on the processing of iron boride coatings: Experimental and statistical approaches. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, S. Effects of boronizing process on the surface roughness and dimensions of AISI 1020, AISI 1040 and AISI 2714. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, A.; Aydin, S.; Koç, V.; Kanca, E.; Yildiz, M. Wear behavior of borided AISI D2 steel under linear reciprocating sliding conditions. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2019, 55, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Leyva, A.; Rosales-Lopez, J.; Šulhánek, P.; Olivares-Luna, M.; Mejía-Caballero, I.; Gogola, P.; Jurči, P.; Campos-Silva, I. The impact of post-treatments on the brittleness and wear resistance of borided 8% Cr steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Reyes, F.J.; Martínez-Trinidad, J.; Moreno-Pacheco, L.A.; Quintana-Hernández, O.; Wong-Ángel, W.; García-León, R.A. Effect of Layer Thickness on the Practical Adhesion of Borided Monel 400 Alloy. Coatings 2024, 14, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Perrusquia, N.; Doñu Ruiz, M.A.; García Bustos, E.D.; lores Martínez, M.; Urriolagoitia Calderón, G.M.; Torres San Miguel, C.R. Duplex surface treatment on microalloy steels by dehydrated paste pack boriding and pack carburizing. Mater. Lett. 2020, 280, 128573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santibañez, M.Y.; Quiñones-Galván, J.G.; López-Perrusquia, N.; Doñu-Ruiz, M.A.; García, E. Study of wear processes generated by cavitation phenomena produced by laser induced dielectric breakdown on borided and non-borided 316L stainless steel surfaces in bi-distilled water. Mater. Lett. 2023, 343, 134397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, L.L.; Pukasiewicz, A.G.M.; de Souza, G.B.; Soares, P.; Vidal, I.d.F.S.; Abrahão, R., Jr.; Torres, R.D. Microstructure Design of Powder-Pack Borided AISI 4140 Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 33, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Karataş, S. Effect of mechanical activation on jell boronizing treatment of the AISI 4140. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 275, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulutan, M.; Celik, O.N.; Gasan, H.; Er, U. Effect of different surface treatment methods on the friction and wear behavior of AISI 4140 steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, I. Mechanical properties and kinetics of borided AISI M50 bearing steel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5185–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamcı, M.; Nair, F.; Cerit, A.A. Microstructural and mechanical characterization of functionally graded Fe/Fe2B (Fe/B4C) materials fabricated by in-situ powder metallurgy method. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 18786–18799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Sanchez, E.; Rodriguez-Castro, G.; Meneses-Amador, A.; Bravo-Bárcenas, D.; Arzate-Vazquez, I.; Martinez-Gutierrez, H.; Romero-Romo, M.; Campos-Silva, I. Effect of the anisotropic growth on the fracture toughness measurements obtained in the Fe2B layer. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 237, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. Investigation on reactive sintering process of boron carbide ceramics by XRD. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Banthia, A.K. Low-temperature synthetic route for boron carbide. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milev, A.; Wilson, M.; Kannangara, G.K.; Tran, N. X-ray diffraction line profile analysis of nanocrystalline graphite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 111, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A. Crystallographic analysis of graphite by X-Ray diffraction. Coke Chem. 2017, 60, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.Y.; Rawn, C.J.; Jones, L.; Ow, H. Improved crystallographic data for graphite. Powder Diffr. 2003, 18, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Kurakevych, O.O.; Turkevich, V.Z.; Turkevich, D.V. Phase diagram of the B−B2O3 system at 5 GPa: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 6683–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hong, W.B.; Yan, X.J.; Chen, X.M. Preparation and microwave dielectric properties of B2O3 bulk. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2019, 16, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Rao, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Synthesis of porous boron-doped carbon nitride: Adsorption capacity and photo-regeneration properties. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkovska, I.; Homolová, V.; Petryshynets, I.; Csanádi, T. The influence of the third element on nano-mechanical properties of iron borides FeB and Fe2B formed in Fe-BX (X = C, Cr, Mn, V, W, Mn+ V) alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, B.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, A. One step reduction of Boric Acid to boron carbide nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 15331–15334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiage, M.; Tahara, N.; Yanase, I.; Kobayashi, H. Low-temperature synthesis of boron carbide powder from condensed boric acid–glycerin product. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1839–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergen, A.; Demirhan, M.; Bilen, M. Processing of boric acid from borax by a wet chemical method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2003, 14, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlaček, M.; Podgornik, B.; Vižintin, J. Influence of surface preparation on roughness parameters, friction and wear. Wear 2009, 266, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, K.; Liskiewicz, T.; Mathia, T. Surface morphology in engineering applications: Influence of roughness on sliding and wear in dry fretting. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalekian, M.; Kozeschnik, E.; Brantner, H.P.; Cerjak, H. Comparative analysis of heat generation in friction welding of steel bars. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, S.K.; Tian, P.; Tian, Y. Estimation of real contact area during sliding friction from interface temperature. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 065227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łępicka, M.; Tsybrii, Y.; Kiejko, D.; Golak, K. The effect of TiN and DLC anti-wear coatings on the tribofilm formation and frictional heat phenomena in coated metals vs. WC-Co. Materials 2021, 14, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torskaya, E.; Stepanov, F. Friction Reduction Due to Heating in the Sliding Contact of Smart Coating: Modeling of Mutual Effect. Lubricants 2022, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shipway, P.; Sun, W. The role of frictional power dissipation (as a function of frequency) and test temperature on contact temperature and the subsequent wear behaviour in a stainless steel contact in fretting. Wear 2015, 330, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H. The mechanism of oxidational wear. Wear 1995, 184, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniołek, K.; Kupka, M.; Barylski, A. Sliding wear resistance of oxide layers formed on a titanium surface during thermal oxidation. Wear 2016, 356, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynio, C.; Hattendorf, H.; Klöwer, J.; Eggeler, G. The evolution of tribolayers during high temperature sliding wear. Wear 2014, 315, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doñu Ruiz, M.A.; García Bustos, E.D.; de la Mora Ramirez, T.; Sánchez Huitron, D.; Cortes Suarez, V.J.; López Perrusquia, N. Characterization of Boride Coatings on AISI 8620 Steels without and with Hydrogen Permeation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6276742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, K.; Bigerelle, M.; Mathia, T.; Dubois, A.; Dubar, L. Dynamic evolution of interface roughness during friction and wear processes. Scanning J. Scanning Microsc. 2014, 36, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowska, A.; Bartkowski, D.; Swadźba, R.; Przestacki, D.; Miklaszewski, A. Microstructure, chemical composition, wear, and corrosion resistance of FeB–Fe2B–Fe3B surface layers produced on Vanadis-6 steel using CO2 laser. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morón, R.; Arellano-Ortiz, G.; Rodríguez-Castro, G.A.; Meneses-Amador, A.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Méndez-Méndez, J.V.; Campos-Silva, I. Wear performance under dry and lubricated conditions of post boriding heat treatment in 4140 steel. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 021702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment Temperature (K) | Morphology | Roughness (Rq) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak (μm) | Valley (μm) | Before FPP (μm) | After FPP (μm) | |
| 1123 | 40.6 ± 2.4 | 12.8 ± 3.2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.04 |
| 1173 | 48.2 ± 3 | 23.18 ± 4.2 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.08 |
| 1223 | 115.4 ± 3.5 | 87.9 ± 5 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.97 ± 0.03 |
| 1273 | 127.2 ± 7 | 80.2 ± 9 | 2.6 ± 1 | 1 ± 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Arcos, D.M.; López-Perrusquia, N.; Doñu-Ruiz, M.A.; Flores-Martínez, M.; Muhl Saunders, S.; Huitron, D.S.; García Bustos, E.D. The Effects of the Finishing Polish Process on the Tribological Properties of Boride Surfaces of AISI 4140 Steel. Coatings 2025, 15, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040474
Flores-Arcos DM, López-Perrusquia N, Doñu-Ruiz MA, Flores-Martínez M, Muhl Saunders S, Huitron DS, García Bustos ED. The Effects of the Finishing Polish Process on the Tribological Properties of Boride Surfaces of AISI 4140 Steel. Coatings. 2025; 15(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Arcos, Daniel Misael, Noé López-Perrusquia, Marco Antonio Doñu-Ruiz, Martin Flores-Martínez, Stephen Muhl Saunders, David Sánchez Huitron, and Ernesto David García Bustos. 2025. "The Effects of the Finishing Polish Process on the Tribological Properties of Boride Surfaces of AISI 4140 Steel" Coatings 15, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040474
APA StyleFlores-Arcos, D. M., López-Perrusquia, N., Doñu-Ruiz, M. A., Flores-Martínez, M., Muhl Saunders, S., Huitron, D. S., & García Bustos, E. D. (2025). The Effects of the Finishing Polish Process on the Tribological Properties of Boride Surfaces of AISI 4140 Steel. Coatings, 15(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040474








