Applications of Oxide Coatings in Photovoltaic Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The absorber is responsible for absorption and conversion of incident photons to charge carriers;
- Electrodes are necessary to convey the photo-generated carriers to an external load;
- Antireflection coatings (ARCs) are applied to PV cells to ensure a gradual increase of the refractive index as incident photons traverse from air through to the absorber so as to reduce the backward reflection losses;
- Back reflectors are used to prevent energy waste when the absorber is too thin to absorb all the incident photons in one pass;
- Buffers and/or barriers are used to prevent irregularities at interfaces from affecting PV cell performance. These may be defect states caused by lattice mismatch, too large energy band offsets or diffusion of contaminants into the absorber, among others.
2. Ideal Material Characteristics for Various Functions in PV Cells
2.1. Appropriate Opto-Electronic Properties

2.2. Suitability for Manufacturing
2.3. Toxicity and Environmental Benignity
2.4. Environmental and Chemical Stability
3. Survey of Oxides with Proven or Potential Application in PV Cells
 and
and  corresponding to oxides, peroxides and super oxides. Typically, an oxide is formed when a metal/metalloid donates two electrons to the 2p orbital of the oxygen atom such that the oxygen orbitals form the valence band of the resulting oxide. Since this review is confined to solid state photovoltaic devices, only solid oxides are considered. The type of oxide formed depends to a large extent on the position of the bonding cation in the periodic table (see Figure 2).
corresponding to oxides, peroxides and super oxides. Typically, an oxide is formed when a metal/metalloid donates two electrons to the 2p orbital of the oxygen atom such that the oxygen orbitals form the valence band of the resulting oxide. Since this review is confined to solid state photovoltaic devices, only solid oxides are considered. The type of oxide formed depends to a large extent on the position of the bonding cation in the periodic table (see Figure 2).
3.1. Refractory Metal Oxides
3.2. Oxides of Ferrous Metals
3.3. Oxides of Precious Metals
3.4. Oxides of Fusible Metals
3.5. Semi-Metal Oxides
3.6. Multinary Oxides
4. Typical Methods of Growing Oxide Coatings for Solar Cells
5. Oxides in Contemporary Photovoltaic Cell Technologies
5.1. Crystalline Silicon PV Cells
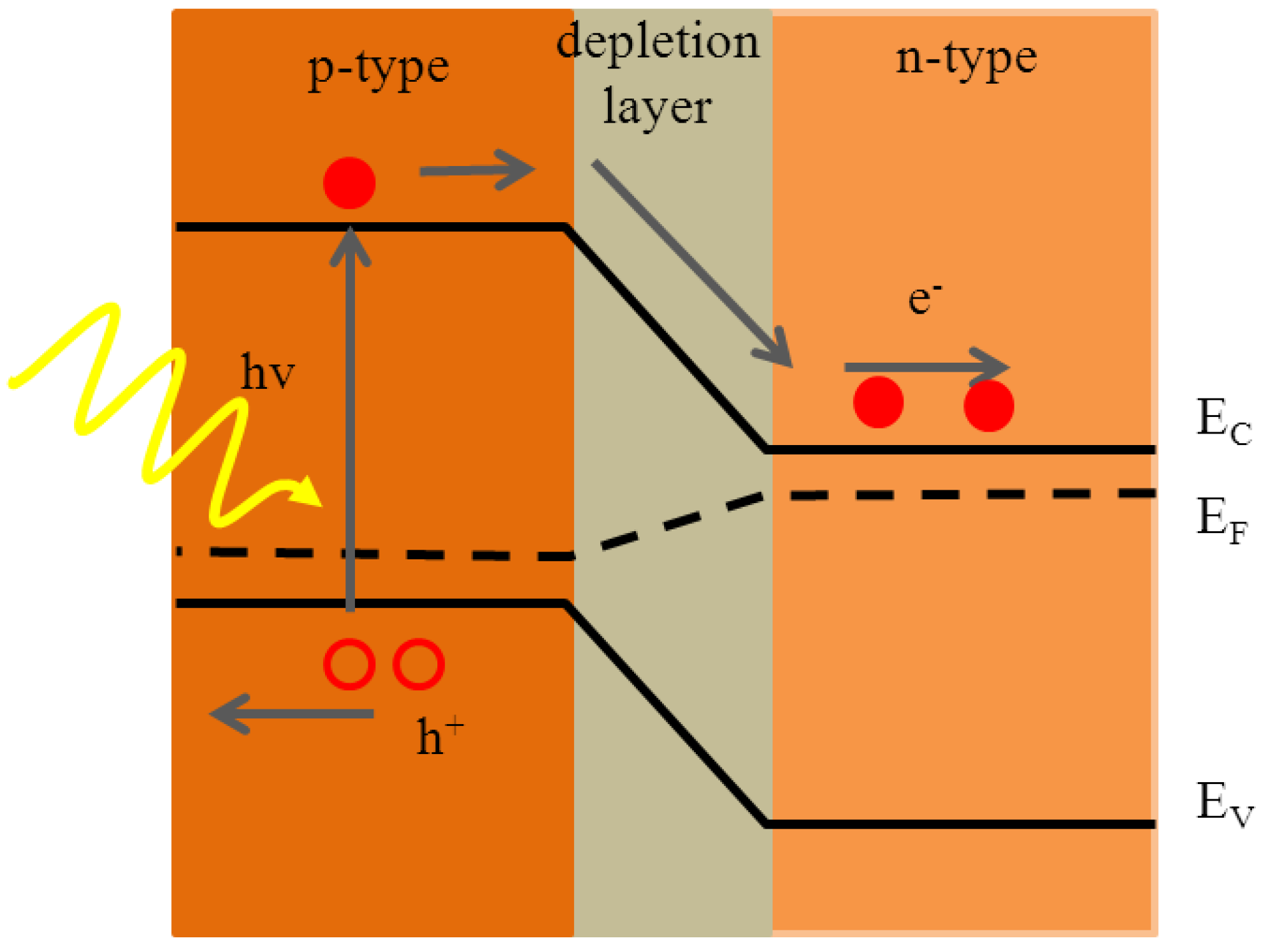
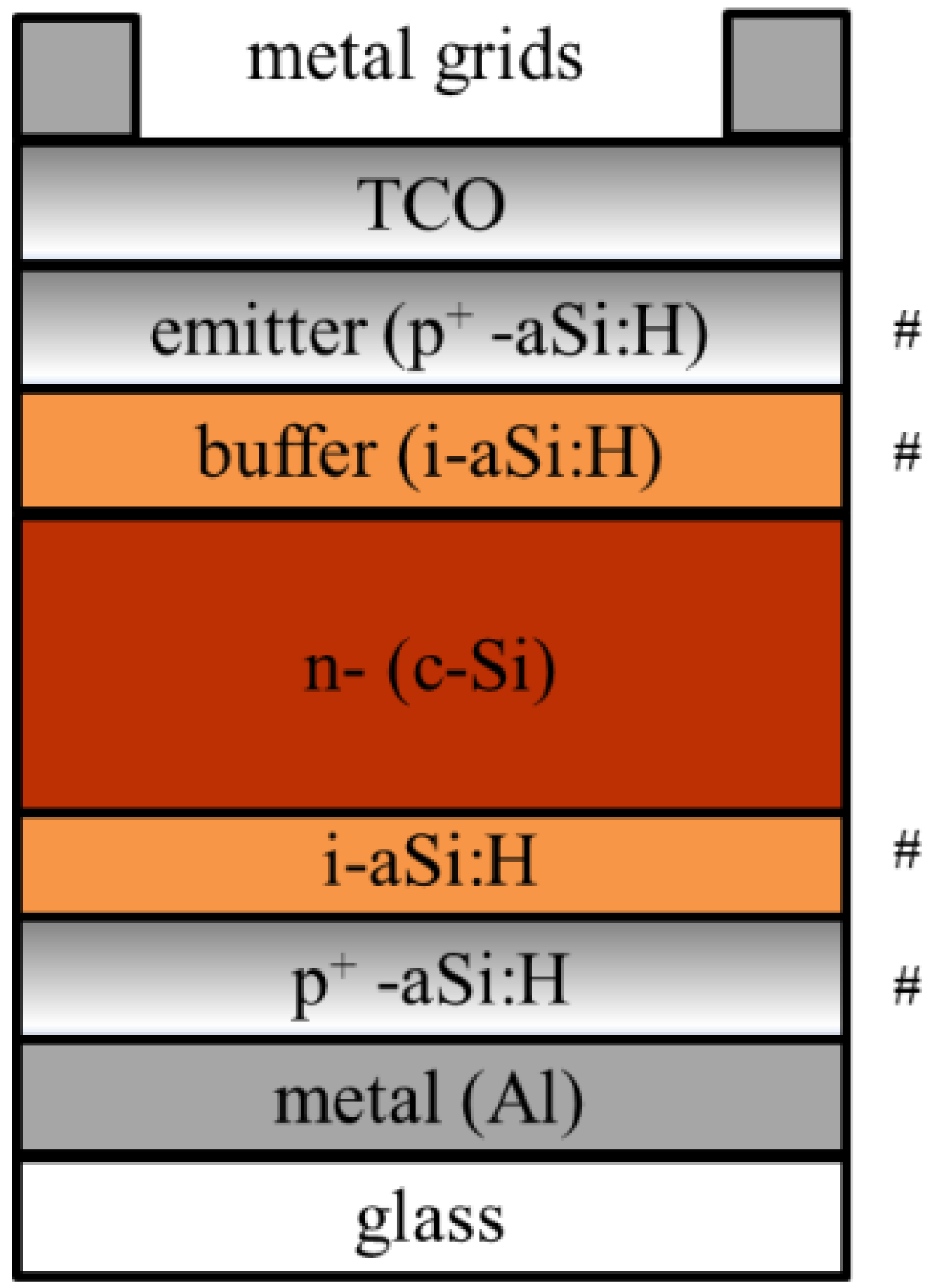
5.2. Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film PV Cells on Glass
5.3. Ternary Compound Semiconductor PV Cells

5.4. PIN Solar Cells

5.5. Dye sensitized Solar Cells

5.6. Organic Photovoltaic Cells

5.7. Concentrator Photovoltaic Devices
6. Emergent PV Concepts Benefiting from the Use of Oxides
6.1. Semi-Transparent PV Cells
6.2. Bifacial PV Cells
6.3. Mechanically Stacked PV Cells
6.4. Oxide Nanosized Materials for PV
6.5. Photonic Crystals for PV
6.6. Photovoltaic Integrated Devices for Stand-Alone Functionality

6.7. Luminescent Spectral Converters
6.8. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic PV Cells
6.9. Extremely Thin Absorber ETA Solar Cells
6.10. Perovskite Absorber PV Cells
6.11. “New” Single Cation Oxides for PV
6.12. Ferro Electric Photovoltaics
6.13. All Oxide PV
6.14. Quantum Effect Photovoltaic Devices
7. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torrance, J.B.; Lacorre, P.; Asavaroengchai, C.; Metzger, R.M. Why are some oxides metallic, while most are insulating? Physica C 1991, 182, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, K.; Major, S.; Pandya, D. Transparent conductors—A status review. Thin Solid Films 1983, 102, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Fang, X.; Liao, M.; Xu, X.; Zeng, H.; Yoshio, B.; Golberg, D. A comprehensive review of one-dimensional metal-oxide nanostructure photodetectors. Sensors 2009, 9, 6504–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. High dielectric constant gate oxides for metal oxide Si transistors. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 327–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellings, P.; Bouwmeester, H. Ion and mixed conducting oxides as catalysts. Catal. Today 1992, 12, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, A.; Mizokawa, T.; Morikawa, K.; Fujimori, A.; Barman, S.; Maiti, K.; Sarma, D.; Tokura, Y.; Onoda, M. Electronic structure of early 3d-transition-metal oxides by analysis of the 2p core-level photoemission spectra. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Record Solar Cell with 44.7% Efficiency. Press Release 2013; Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme ISE: Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, 23 September 2013. Available online: http://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/en/press-and-media/press-releases/presseinformationen-2013/world-record-solar-cell-with-44.7-efficiency (accessed on 17 March 2014).
- Jansen, K.; Delahoy, A. A laboratory technique for the evaluation of electrochemical transparent conductive oxide delamination from glass substrates. Thin Solid Films 2003, 423, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, F. Materials Handbook: A Consise Desktop Reference, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.J.; Wei, S.H.; Al-Jassim, M.M.; Yan, Y. Prediction of the chemical trends of oxygen vacancy levels in binary metal oxides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 142109:1–142109:3. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, L. The thermodynamic properties of the oxides and their vaporisation processes. Chem. Rev. 1953, 52, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahi, R.; Taga, Y.; Mannstadt, W.; Freeman, A.J. Electronic and optical properties of anatase TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 7459–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R. Chemical vapour deposition of coatings on glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1997, 218, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitosugi, T.; Yamada, N.; Nakao, S.; Hirose, Y.; Hasegawa, T.H. Properties of TiO-based transparent conducting oxides. Phys. Stat. Solidi A 2010, 7, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Das, C.; Lambertz, A.; Huepkes, J.; Reetz, W.; Finger, F. A constructive combination of antireflection and intermediate-reflector layers for a-Si/µc-Si thin film solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Murakami, T.N.; Comte, P.; Liska, P.; Graetzel, C.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Graetzel, M. Fabrication of thin film dye sensitized solar cells with solar to electric power conversion efficiency over 10%. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 4613–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Manders, J.R.; Tsang, S.W.; So, F. Metal oxides for interface engineering in polymer solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24202–24212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Baik, S.J.; Im, J.S.; Fang, L.; Jeon, J.W.; Lima, K.S. Towards a high efficiency amorphous silicon solar cell using molybdenum oxide as a window layer instead of conventional p-type amorphous silicon carbide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. High dielectric constant oxides. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 28, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Baik, S.J.; Lim, K.S.; Yoo, S.H.; Seo, M.S.; Kang, S.J.; Seo, J.W. Tungsten oxide as a buffer layer inserted at the SnO2/p-a-SiC interface of pin-type amorphous silicon based solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 193501:1–193501:4. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, B.K.; Polity, A.; Reppin, D.; Becker, M.; Hering, P.; Klar, P.J.; Sander, T.; Reindl, C.; Benz, J.; Eickhoff, M.; et al. Binary copper oxide semiconductors: From materials towards devices. Phys. Stat. Solidi B 2012, 249, 1487–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C. Review of preparation and optoelectronic characteristics of Cu2O-based solar cells with nanostructure. Mater. Sci. Semincond. Process. 2013, 16, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Miyata, T.; Nishi, Y. Efficiency improvement of Cu2O-based heterojunction solar cells fabricated using thermally oxidized copper sheets. Thin Solid Films 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, A.; Poeppelmeier, K.; Mason, T.; Chang, R.; Marks, T. Chemical and thin film strategies for new transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 2000, 25, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kawazoe, H.; Yasukawa, M.; Hyodo, H.; Kurita, M.; Yanagi, H.; Hosono, H. P-type electrical conduction in transparent thin films of CuAlO2. Nature 1997, 389, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawazoe, H.; Yanagi, H.; Ueda, K.; Hosono, H. Transparent p-type conducting oxides: Design and fabrication of p-n heterojunctions. MRS Bull. 2000, 25, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ögzur, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.; Dogan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Walle, C. Hydrogen as a cause of doping in zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, H.; Jia, H.; Kondo, M. Impact of front and rear texture of thin film micro-crystalline silicon solar cells on their ligh trapping properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 044505:1–044505:5. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, S.; Feitknecht, L.; Schlüchter, R.; Kroll, U.; Vallat-Sauvain, E.; Shah, A. Rough ZnO layers by LP-CVD process and their effect in improving performance of amorphous and microcrystalline silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karazhanov, S.Z.; Ravindran, P.; Vajeeston, P.; Ulyashin, A.; Finstad, T.; Fjellvåg, H. Phase stability, electronic structure and optical properties of indium oxide polytypes. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 075129:1–075129:13. [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness, C.; Stagarescu, C.B.; Ryan, P.J.; Downes, J.E.; Fu, D.; Smith, K.E.; Egdell, R.G. Influence of shallow core-level hybridization on the electronic structure of post-transition-metal oxides studied using soft X-ray emission and absorption. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 165104:1–165104:10. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Ashida, T.; Oka, N.; Shigesato, Y. Carrier density dependence of optical band gap and work function in Sn-doped In2O3 films. Appl. Phys. Express 2010, 3, 061101:1–061101:3. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.C.; Goodenough, J.B. Xray photoemission spectroscopy studies of Sn-doped indium oxide films. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar]
- Orita, M.; Ohta, H.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Deep-ultra-violet transparent conductive beta-Ga2O3 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 4166–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikokhatnyi, O.I.; Kumta, P.N. Ab-initio study of fluorine-doped tin dioxide: A prospective catalyst support for water electrolysis. Physica B 2011, 406, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Maeda, H.; Hosono, H.; Kawazoe, H. Band-gap widewide of CdO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 6174–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calnan, S.; Tiwari, A. High mobility transparent conducting oxides for thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droessler, L.; Assender, H.E.; Watt, A.A.R. Thermally deposited lead oxides for thin film photovoltaics. Mater. Lett. 2012, 71, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinu, L.; Poitras, D. Plasma deposition of optical films and coatings: A review. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2000, 18, 2619–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Arnell, R. Magnetron sputtering: A review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 2000, 56, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, G.; Delabie, A.; Vitanov, P.; Alexieva, Z.; Dekkers, H.; De Wolf, S.; Beaucarne, G. Very low surface recombination velocities on p-type silicon wafers passivated with a dielectric with fixed negative charge. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 3438–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoex, B.; Gielis, J.J.H.; van de Sanden, M.C.M.; Kessels, W.M.M. On the c-Si surface passivation mechanism by the negative-charge dielectric Al2O3. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliskin, W.A. Comparison of properties of dielectric films deposited by various methods. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1977, 14, 1064–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuhashi, M.; Gotoh, Y.; Adachi, K. Texture morphology of SnO2:F films and cell reflectance. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 27, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.S.; Burton, S.; Pan, P. The variation of physical properties of plasma-deposited silicon nitride and oxynitride with their compositions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1984, 131, 2348–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammler, D.; Harder, B.; Hrabe, N.; McDonald, N.; Gonzalez, G.; Penake, D.; Mason, T. Subsolidus phase relations and transparent conductors in the cadmium-indium-tin oxide system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammler, D.; Mason, T.; Young, D.; Coutts, T.; Ko, D.; Poeppelmeier, K.; Williamson, D. Comparison of thin film and bulk forms of the transparent oxide solution Cd1+xIn2–2xSnxO4. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 5979–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.; Da Silva, J.L.; Wei, S.H. Multi-component Transparent Conducting Oxides: Progress in Materials Modelling. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 334210:1–334210:12. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, H.; Lin, W.; Kyaw, A.; Jin, Y.; Jin, K.; Sun, X.; Wu, T. Tunable photovoltaic effect and solar cell performance of self-doped perovskite SrTiO3. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 042131:1–042131:9. [Google Scholar]
- Assmann, E.; Blaha, P.; Laskowski, R.; Held, K.; Okamoto, S.; Sangiovanni, G. Oxide heterostructures for efficent solar cells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 078701:1–078701:5. [Google Scholar]
- Grinberg, I.; West, D.V.; Torres, M.; Gou, G.; Stein, D.M.; Wu, L.; Chen, G.; Gallo, E.M.; Akbashev, A.R.; Davies, P.K.; Spanier, J.E.; Rappe, A.M. Perovskite oxides for visible-light-absorbing ferroelectric and photovoltaic materials. Nature 2013, 503, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Takagi, A.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Room temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 2004, 432, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Nomura, K.; Yanagi, H.; Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. Photovoltaic properties of n-type amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O and p-type single crystal Si heterojunction solar cells: Effects of Ga content. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 3808–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, H. Ionic amorphous oxide semiconductors: Material design, carrier transport and device application. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.C.; Aspinall, H.C.; Chalker, P.R. Chemical vapour deposition of metal oxides for microelectronics applications. In Chemical Vapour Deposition: Precursors; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2009; pp. 357–412. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, S.; Nyberg, T. Fundamental understanding and modeling of reactive sputtering processes. Thin Solid Films 2005, 476, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarelli, R.M.; Ginley, D.S.; O’Hayre, R. Solution processing of transparent conductors: From flask to film. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40, 5406–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, H.; Deguire, M.R. Recent progress in the synthesis of oxide films from liquid solutions. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 117, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, A.T.G.; Kamath, V.P. Electrochemical synthesis of metal oxides and hydroxides. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, M.; Niinisto, J. Atomic layer deposition. In Chemical Vapour Deposition: Precursors; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2009; pp. 158–206. [Google Scholar]
- Stirn, R.J.; Yeh, Y.C.M. A 15% efficient antireflection-coated metal-oxide-semiconductor solar cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1975, 27, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Blakers, A.W.; Shi, J.; Keller, E.M.; Wenham, S. High-efficiency silicon solar cells. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1984, 31, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberle, A.G. Surface passivation of c-Si solar Cells: A review. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2000, 8, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielke, D.; Petermann, J.; Werner, F.; Veith, B.; Brendel, R.; Schmidt, J. 21.7% Efficient PERC Solar Cells with AlOx Tunneling Layer. In Proceedings of 26th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, Hamburg, Germany, 5–6 September 2011; pp. 1115–1119.
- Sopori, B. Silicon nitride processing for control of optical and electronic properties of silicon solar cells. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 32, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Book, F.; Wiedenmann, T.; Schubert, G.; Plagwitz, H.; Hahn, G. Influence of the front surface passivation quality on large area n-type silicon solar cells with Al alloyed rear emitter. Energy Procedia 2011, 8, 487–492. [Google Scholar]
- Frosch, C.J.; Derick, L. Surface Protection and Selective Masking during Diffusion in Silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1957, 104, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueranantasun, A.; Richards, B.; Honsberg, C.; Cotter, J.E. Titanium dioxide film as a phosphorus diffusion barrier in silicon solar cells. In Proceedings of 3rd World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, 2003, Osaka, Japan, 11–18 May 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1411–1414.
- Tanaka, M.; Taguchi, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Sawada, T.; Tsuda, S.; Nakano, S.; Hanafusa, H.; Kuwano, Y. Development of new a-Si/c-Si heterojunction solar cells: ACJ-HIT (Artificially Constructed Junction-Heterojunction with Intrinsic Thin-Layer). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 31, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, M.; Yano, A.; Tohoda, S.; Matsuyama, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Nishiwaki, T.; Fujita, K.; Maruyama, E. 24.7% Record efficiency HIT solar cell on thin silicon wafer. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2014, 4, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, C.; Sritharathikhun, J.; Yamada, A.; Konagai, M. Fabrication of heterojunction solar cells by using microcrystalline hydrogenated silicon oxide film as an emitter. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Aeberhard, U.; Smirnov, V.; Hollaender, B.; Finger, F.; Rau, U. Wide Gap Microcrystalline Silicon Oxide Emitter for a-SiOx:H/c-Si Heterojunction Solar Cells. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.; Wong, J.; Aberle, A.G. Heterojunction silicon wafer solar cells using amorphous silicon suboxides for interface passivation. Energy Procedia 2012, 15, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatshoar, B.; Shahrjerdi, D.; Hopstaken, M.; Fogel, K.; Sadana, D.K. High-efficiency heterojunction solar cells on crystalline germanium substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Ruske, F.; Sontheimer, T.; Gorka, B.; Bloeck, U.; Gall, S.; Rech, B. Microstructure and photovoltaic performance of polycrystalline silicon thin films on temperature stable ZnO:Al layers. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 084506:1–084506:7. [Google Scholar]
- Amkreutz, D.; Müller, J.; Schmidt, M.; Hänel, T.; Schulze, T. Electron-beam crystallized large grained silicon solar cell on glass substrate. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2011, 19, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nast, O.; Wenham, S.R. Elucidation of the layer exchange mechanism in the formation of polycrystalline silicon by aluminum-induced crystallization. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, J.; Evans, R.; Schubert, U.; Eggleston, B.D.; Ong, D.; Kim, K.; Huang, J.; Kunz, O.; Keevers, M.; Egan, R.; et al. Thin-film polycrystalline silicon solar cells formed by diode laser crystallisation. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2013, 21, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.; Hariskos, D.; Lotter, E.; Paetel, S.; Wuerz, R.; Menner, R.; Wischmann, W.; Powalla, M. New world record efficiency for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells beyond 20%. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2011, 19, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Emery, K.; Hishikawa, Y.; Warta, W.; Dunlop, E. Solar cell efficiency tables (version 42). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2013, 21, 827–837. [Google Scholar]
- Minemoto, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Satoh, T.; Negami, T.; Takakura, H.; Hamakawa, Y. Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells with controlled conduction band offset of window/Cu(In,Ga)Se2. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 8327–8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatzel, T.; Steigert, H.; Klenk, R.; Lux-Steiner, M.; Niesen, T.; Visbeck, S. Zn1−xMgxO as a window layer in completely Cd-free Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 based thin film Solar cells. In Proceedings of Technical Digest of the 14th International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference (PVSEC-14), Bangkok, Thailand, 26–30 January 2004; p. 707.
- Platzer-Björkman, C.; Törndahl, T.; Abou-Ras, D.; Malmström, J.; Kessler, J.; Stolt, L. Zn(O,S) buffer layers by atomic layer deposition in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 based thin film solar cells: Band alignment and sulfur gradient. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 044506:1–044506:10. [Google Scholar]
- Braunger, D.; Hariskos, D.; Walter, T.; Schock, H. An 11.4% efficient polycrystalline thin film solar cell based on CuInS2 with a Cd-free buffer layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1996, 40, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ae, L.; Kieven, D.; Chen, J.; Klenk, R.; Rissom, T.; Tang, Y.; Lux-Steiner, M.C. ZnO nanorod arrays as an antireflective coating for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2010, 18, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Törndahl, T.; Platzer-Björkman, C.; Kessler, J.; Edoff, M. Atomic layer deposition of Zn1−xMgxO buffer layers for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2007, 15, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, F.; Rudmann, D. Technological aspects of flexible CIGS solar cells and modules. Solar Energy 2004, 77, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gledhill, S.; Zykov, A.; Allsop, N.; Rissom, T.; Schniebs, J.; Kaufmann, C.A.; Lux-Steiner, M.; Fischer, C.H. Spray pyrolysis of barrier layers for flexible thin film solar cells on steel. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcia, P.; McLean, R.; Hegedus, S. Encapsulation of Cu(InGa)Se2 solar cells with Al2O3 thin film moisture barrier grown by atomic layer deposition. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 2375–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, S.; Hommoto, H.; Kido, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamada, A.; Niki, S. Efficiency enhancement of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells fabricated on flexible polymide substrates using alkali-silicate glass thin layers. Appl. Phys. Express 2008, 1, 092303:1–092303:3. [Google Scholar]
- Gloeckler, M.; Sankin, I.; Zhao, Z. CdTe solar cells at the threshold to 20% efficiency. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2013, 3, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Keane, J.; Dhere, R.; DeHart, C.; Duda, A.; Gessert, T.; Asher, S.; Levi, D.; Sheldon, P. 16.5%-Efficient CdS/CdTe Polycrystalline Thin Film Solar Cell. In Proceedings of 17th European Photovoltaics Solar Energy Conference, Munich, Germany, 22–26 October 2001; pp. 995–1000.
- Ferekides, C.; Balasubramanian, U.; Manazza, R.; Viswanathan, V.; Zhao, H.; Morel, D. CdTe thin film solar cells: device and technology issues. Solar Energy 2004, 77, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, T.K.; Tang, J.; Bag, S.; Gunawam, O.; Gokmen, T.; Zhu, Y.; Mitzi, D.B. Beyond 11% Efficiency: Characteristics of State-of-the-Art Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Kluth, O.; Wieder, S.; Siekmann, H.; Schoepe, G.; Reetz, W.; Vetterl, O.; Lundszien, D.; Lambertz, A.; Finger, F.; et al. Development of highly effcient thin film silicon solar cells on texture-etched zinc oxide-coated glass substrates. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Kawai, H.; Okamoto, H.; Hamakawa, Y. Improvement in the efficiency of amorphous silicon solar cells utilising the optical confinement effect by means of a TiO2/Ag/SUS back surface reflector. Solar Cells 1984, 11, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Guha, S. Study of back reflectors for amorphous silicon alloy solar cell application. J.Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluth, O.; Losio, P.; Bakehe, S.; Caglar, O.; Goldbach, H.; Keller, M.; Benagli, S.; Meier, J. Up-scaling of high throughput a-Si solar cell design on ZnO to 1.4 M² modules. In Proceedings of 24th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 21–25 September 2009.
- Daube, C.; Schmidt, U.; Severin, D.; Kurthen, C.; Goergens, C.; Ahmed, K.; Vermeir, I.; Kuhr, N.; Klein, S.; Straub, A.; et al. Advanced large area TCO production line for economic manufacturing of high efficiency a-Si/µc-Si based thin film modules. In Proceedings of 25th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition / 5th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, Valencia, Spain, September 2010; pp. 2771–2774.
- Klein, S.; Wieder, S.; Buschbaum, S.; Schwanitz, K.; Stolley, T.; Severin, D.; Obermeyer, P.; Kress, M.; Sommer, E.; Marschner, T.; et al. Large area thin film solar modules with 10% efficiency for mass production. In Proceddings of 25th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition / 5th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, Valencia, Spain, September 2010; pp. 2708–2712.
- Fujibayashi, T.; Matsui, T.; Kondo, M. Improvement in quantum efficiency of thin film Si solar cells due to the suppression of optical reflectance at transparent conducting oxide/Si interface by TiO2/ZnO antireflection coating. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat-Sauvain, E.; Bailat, J.; Meier, J.; Niquille, X.; Kroll, U.; Shah, A. Influence of the substrate’s surface morphology and chemical nature on the nucleation and growth of microcrystalline silicon. Thin Solid Films 2005, 485, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnon, G.; Parascandolo, G.; Hänni, S.; Stuckelberger, M.; Charri‘ere, M.; Despeisse, M.; Meillaud, F.; Ballif, C. Silicon oxide buffer layer at the p-i interface in amorphous and microcrystalline silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells A 2014, 120, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Barua, A.K. Development of high quality p-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon oxide film and its use in improving the performance of single junction amorphous silicon solar cells. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertz, A.; Finger, F.; Holländer, B.; Rath, J.; Schropp, R. Boron-doped hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon oxide (µc-SiOx:H) for application in thin-film silicon solar cells. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 1962–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuony, P.; Alexander, D.; Perez-Wurfl, I.; Despeisse, M.; Bugnon, G.; Boccard, M.; Söderström, T.; Hessler-Wyser, A.; Hébert, C.; Ballif, C. Silicon filaments in silicon oxide for next-generation photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirner, S.; Gabriel, O.; Stannowski, B.; Rech, B.; Schlatmann, R. The growth of microcrystalline silicon oxide thin films studied by in situ plasma diagnostics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 051906:1–051906:4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Chung, J.W.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Heo, Y.; Lee, H.M. Remarkable progress in thin-film silicon solar cells using high-efficiency triple-junction technology. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 119, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenni, S.; Bugnon, G.; Parascandolo, G.; Boccard, M.; Escarre, J.; Despeisse, M.; Meillaud, F.; Ballif, C. High-efficiency microcrystalline silicon single-junction solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2013, 21, 821–826. [Google Scholar]
- Kirner, S.; Calnan, S.; Gabriel, O.; Neubert, S.; Zelt, M.; Stannowski, B.; Rech, B.; Schlatmann, R. An improved silicon-oxide-based intermediate-reflector for micromorph solar cells. Phys. Stat. Solidi C 2012, 9, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yue, G.; Sivec, L.; Yang, J.; Guha, S.; Jiang, C.S. Innovative dual function nc-SiOx:H layer leading to a 16% efficient multi-junction thin-film silicon solar cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 113512:1–113512:3. [Google Scholar]
- Schwanitz, K.; Klein, S.; Stolley, T.; Rohde, M.; Severin, D.; Trassl, R. Anti-reflective microcrystalline silicon oxide p-layer for thin-film silicon solar cells on ZnO. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 105, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despeisse, M.; Bugnon, G.; Feltrin, A.; Stueckelberger, M.; Cuony, P.; Meillaud, F.; Billet, A.; Ballif, C. Resistive interlayer for improved performance of thin film silicon solar cells on highly textured substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 073507:1–073507:3. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, D.; Dubail, S.; Anna Selvan, J.; Vaucher, N.P.; Platz, R.; Hof, C.; Kroll, U.; Meier, J.; Torres, P.; Keppner, H.; et al. The “micro-morph” solar cell: extending a-Si:H technology towards thin film crystalline silicon. In Proceedings of 25th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 May 1996; pp. 1053–1056.
- Buehlmann, P.; Bailat, J.; Domine, D.; Billet, A.; Meillaud, F.; Feltrin, A.; Ballif, C. In situ silicon oxide based intermediate reflector for thin-film silicon micromorph solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Schropp, R.E.I.; Chatham, H.; Hollingsworth, R.; Bhat, P.; Xi, J. Tunneling junction in amorphous silicon tandem solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1990, 56, 1871–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaucher, N.P.; Rech, B.; Fischer, D.; Dubail, S.; Goetz, M.; Keppner, H.; Wyrsch, N.; Beneking, C.; Hadjadj, O.; Shklover, V.; et al. Controlled nucleation of thin microcrystalline layers for the recombination junction in a-Si stacked cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1997, 49, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthisang, S.; Sriprapha, K.; Miyajima, S.; Yamada, A.; Konagai, M. Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Oxide Solar Cells Fabricated near the Phase Transition between Amorphous and Microcrocrystalline Structures. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriprapha, K.; Hongsingthong, A.; Krajangsang, T.; Inthisang, S.; Jaroensathainchok, S.; Limmanee, A.; Titiroongruang, W.; Sritharathikhun, J. Development of thin film a-SiO:H/a-Si:H double-junction solar cells and their temperature dependence. Thin Solid Films 2013, 546, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriprapha, K.; Piromjit, C.; Limmanee, A.; Sritharathikhun, J. Development of thin film amorphous silicon oxide/microcrystalline silicon double-junction solar cells and their temperature dependence. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, B.; Graetzel, M. A low-cost, high efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 1991, 353, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeeruddin, M.; Pechy, P.; Renouard, T.; Zakeeruddin, S.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Comte, P.; Liska, P.; Cevey, L.; Costa, E.; Shklover, V.; et al. Engineering of efficient panchromatic sensitizers for nanocrystalline TiO2 -based solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, P.; Docampo, P.; Johnston, M.B.; Snaith, H.J.; Herz, L.M. Electron mobility and injection dynamics in mesoporous ZnO, SnO2, and TiO2 films used in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5158–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, E.; Clifford, J.N.; Haque, S.A.; Lutz, T.; Durrant, J.R. Control of charge recombination dynamics in dye sensitized solar cells by the use of conformally deposited metal oxide blocking layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Masaki, N.; Jiang, K.; Yanagida, S. Sputtered Nb2O5 as a Novel Blocking Layer at Conducting Glass/TiO2 Interface in Dye-Sensitized Ionic Liquid Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 8092–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Han, H.; Tai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Chen, B.; Sebo, B.; et al. Enhancement in dye-sensitized solar cells based on MgO-coated TiO2 electrodes by reactive DC magnetron sputtering. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 215704:1–215704:6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.W. Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, R829–R858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odobel, F.; Le Pleux, L.; Pellegrin, Y.; Blart, E. New photovoltaic devices based on the sensitization of p-type semiconductors: challenges and opportunities. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattestad, A.; Mozer, A.J.; Fischer, M.K.R.; Cheng, Y.B.; Mishra, A.; Bauerle, P.; Bach, U. Highly efficient photocathodes for dye-sensitized tandem solar cells. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattestad, A.; Zhang, X.; Bach, U.; Cheng, Y.B. Dye-sensitized CuAlO2 photocathodes for tandem solar cell applications. J. Photon. Energy 2011, 1, 011103:1–011103:3. [Google Scholar]
- Burschka, J.; Pellet, N.; Moon, S.J.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Gao, P.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Graetzel, M. Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 2013, 499, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halls, J.J.M.; Walsh, C.A.; Greenham, N.; Marseglia, E.A.; Friend, R.; Moratti, S.C.; Holmes, A. Efficient photodiodes from interpenetrating polymer networks. Nature 1995, 376, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.W. Two-layer organic photovoltaic cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 48, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharber, M.; Mühlbacher, D.; Koppe, M.; Denk, P.; Waldrauf, C.; Heeger, A.; Brabec, C. Design Rules for Donors in Bulk-Heterojunction Solar Cells—Towards 10% Energy-Conversion Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.; Uddin, A. Organic—inorganic hybrid solar cells: A comparative review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 107, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrotriya, V.; Li, G.; Yao, Y.; Chu, C.W.; Yang, Y. Transition metal oxides as the buffer layer for polymer photovoltaic cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 073508:1–073508:3. [Google Scholar]
- Hau, S.K.; Yip, H.-L.; Baek, N.S.; Zou, J.; O’Malley, K.; Jen, A.K.-Y. Air stable inverted flexible polymer solar cells using zinc oxide nanoparticles as an electron selective layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 253301:1–253301:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, M.; Lu, Z.H. Thin-film metal oxides in organic semiconductor devices: their electronic structures, work functions and interfaces. NPG Asia Mater. 2013, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Chu, C.W.; Shrotriya, V.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y. Efficient inverted polymer solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Dou, L.; Yoshimura, K.; Kato, T.; Ohya, K.; Moriarty, T.; Emery, K.; Chen, C.C.; Gao, J.; Li, G.; et al. A polymer tandem solar cell with 10.6% power conversion efficiency. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1446:1–1446:10. [Google Scholar]
- Cotal, H.; Fetzer, C.; Boisvert, J.; Kinsey, G.; King, R.; Hebert, P.; Yoon, H.; Karam, N. III-V multijunction solar cells for concentrating photovoltaics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Sarmah, N.; Luo, X.; Reddy, K.; Mallick, T.K. Opportunities and challenges in micro- and nano-technologies for concentrating photovoltaic cooling: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2013, 20, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, G.M.; Kietzke, E.L.; Kietzke, T.; Tan, L.W.; Liew, P.K.; Zhu, F. Optical enhancement in semitransparent polymer photovoltaic cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 103505:1–103505:3. [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake, D.; Roberts, B.; Ku, P.C. Angular selective backreflector for semitransparent photovoltaics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 063302:1–063302:4. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.W.; Lee, D.J.; Yun, S.J. Semi-transparent amorphous silicon solar cells using a thin p-Si layer and a buffer layer. ECS Solid State Lett. 2013, 2, Q47–Q49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Tokado, T.; Ohmori, D.; Mise, T. Novel device structure for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells using Transparent conducting oxide back and front contacts. Solar Energy 2004, 77, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Kanda, Y.; Kijima, S.; Komiya, Y.; Ohmori, D.; Ishizaki, H.; Yamada, N. Bifacial CIGS thin film solar cells. In Proceedings of 20th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 6–10 June 2005; pp. 1739–1736.
- Ito, S.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Comte, P.; Liska, P.; Kuang, D.; Gratzel, M. Bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells based on an ionic liquid electrolyte. Nat. Photon. 2008, 2, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.N.; Khrypunov, G.; Kurdzesau, F.; Baetzner, D.; Romeo, A.; Zogg, H. CdTe solar cell in a novel configuration. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2003, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiwaki, S.; Siebentritt, S.; Walk, P.; Lux-Steiner, M.C. A stacked chalcopyrite thin-film tandem solar cell with 1.2 V open-circuit voltage. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2003, 11, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Liska, P.; Thampi, K.R.; Grätzel, M.; Brémaud, D.; Rudmann, D.; Upadhyaya, H.M.; Tiwari, A.N. Nanocrystalline dye-sensitized solar cell/copper indium gallium selenide thin-film tandem showing greater than 15% conversion efficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 203103:1–203103:3. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshidomi, S.; Hasumi, M.; Sameshima, T.; Makita, K.; Mastubara, K.; Kondo, M. Multi-Junction Solar Cells Fabricated with Conductive Transparent Adhesive. In Proceedings of 6th Thin Film Materials & Devices Meeting, Kyoto, Japan, 2–3 November 2009.
- Kelzenberg, M.D.; Boettcher, S.W.; Petykiewicz, J.A.; Turner-Evans, D.B.; Putnam, M.C.; Warren, E.L.; Spurgeon, J.M.; Briggs, R.M.; Lewis, N.S.; Atwater, H.A. Enhanced absorption and carrier collection in Si wire arrays for photovoltaic applications. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, J.; Walker, A.; van Ommering, K.; Aydil, E. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanowires and their integration into dye sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, S304–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uepping, J.; Bielawny, A.; Lee, S.; Knez, M.; Carius, R.; Wehrspohn, R.B. Electric transport in 3D photonic crystal intermediate reflectors for micromorph thin-film tandem solar cells. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.H.; Tumbleston, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Williams, S.; DeSimone, J.M.; Lopez, R.; Samulski, E.T. Photonic Crystal Geometry for Organic Solar Cells. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2742–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.G.; Woo, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, W. Rapid Fabrication of an inverse opal TiO2 photoelectrode for DSSC using a binary mixture of TiO2 nanoparticles and polymer microspheres. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3094–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.L.; Marsen, B.; Paluselli, D.; Rocheleau, R. Optimisation of hybrid photoelectrode for solar water splitting. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2005, 8, A247–A249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.G.; Warren, E.L.; Mckone, J.R.; Boettcher, S.W.; Mi, Q.; Santori, E.A.; Lewis, N.S. Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, F.F.; Han, L.; Smets, A.H.M.; Zeman, M.; Dam, B.; van de Krol, R. Efficient solar water splitting by enhanced charge separation in a bismuth vanadate-silicon tandem photoelectrode. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S.; Kato, N.; Kojima, S.; Imanishi, A.; Ogawa, S.; Yoshida, N.; Nonomura, S.; Nakato, Y. Efficient solar water splitting with a composite “n-Si/p-CuI/n-i-p a-Si/n-p GaP/RuO2” semiconductor electrode. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14575–14581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Tracy, C.E.; Pitts, J.R.; Gregg, B.A.; Branz, H.M. Stand-alone photovoltaic-powered electrochromic smart window. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetens, R.; Jelle, B.P.; Gustavsen, A. Properties, requirements and possibilities of smart windows for dynamic daylight and solar energy control in buildings: A state-of-the-art review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ende, B.M.; Aarts, L.; Meijerink, A. Lanthanide ions as spectral converters for solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 11081–11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupke, T.; Green, M.A.; Wuerfel, P. Improving solar cell efficiencies by up-conversion of sub-band-gap light. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4117–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, T.M. Improvement of conversion efficiency of silicon solar cells using up-conversion molybdate La2Mo2O9:Yb,R (R=Er, Ho) phosphors. J. Rare Earths 2011, 29, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupke, T.; Green, M.A.; Wurfel, P. Improving solar cell efficiencies by down-conversion of high-energy photons. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.B.; Lin, J.M.; Wu, J.H.; Lan, Z.; Li, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, F.G.; Huang, M.L.; Xiao, Y.M. Preparation of Gd2O3:Eu3+ downconversion luminsecent material and its application in dye-sensitized. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3114–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frindell, K.L.; Bartl, M.H.; Robinson, M.R.; Bazan, G.C.; Popitsch, A.; Stucky, G.D. Visible and near-IR luminescence via energy transfer in rare earth doped mesoporous titania thin films with nanocrystalline walls. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 172, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, H.; Saif, M.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M. Down-converting lanthanide doped TiO2 photoelectrodes for efficiency enhancement of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5792–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, K.; Pandit, B.; Liu, J.; Alphenaar, B.W. Charge transfer in rare earth oxide hybrid solar cells. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 592, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, K.; Belaidi, A.; Könenkamp, R. Solar cell with extremely thin absorber on highly structure surface. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2003, 18, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.M.; Teuscher, J.; Miyasaka, T.; Murakami, T.N.; Snaith, H.J. Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 2012, 338, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Johnston, M.B.; Snaith, H.J. Efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells by vapour deposition. Nature 2013, 501, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Feng, H.; Li, J. Graphene Oxide: Preparation, Functionalization, and Electrochemical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6027–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Tu, K.H.; Lin, C.C.; Chun-Wei, C.; Chhowalla, M. Solution-processable graphene oxide as an efficient hole transport layer in polymer solar cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3169–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, D.; Durstock, M.; Dai, L. Hole and electron extraction layers based on graphene oxide derivatives for high-performance bulk heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2228–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, Y.C.; Søndergaard, T.; Skovsen, E.; Gurevich, L.; Pedersen, K.; Garm, T.P. Pore size dependence of diffuse light scattering from anodised aluminium solar cell backback reflectors. Opt. Express 2013, 21, A84–A95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Sakhuja, M.; Danner, A.J.; Bhatia, C.S.; Yang, H. Large scale antireflective glass texturing using grid contacts in anodization methods. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 116, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, A.M.; von der Linde, D.; Negran, T.J. High-voltage bulk photovoltaic effect and the photorefractive process in LiNbO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1974, 25, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Seidel, J.; Byrnes, S.; Shafer, P.; Yang, C.H.; Rossell, M.; Yu, P.; Chu, Y.H.; Scott, J.; Ager, I.J.; et al. Above-bandgap voltages from ferroelectric photovoltaic devices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Solar energy: Ferroelectric photovoltaics. Nat. Photon. 2010, 4, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.; Fu, D.; Yang, S.Y.; Alarcon-Llado, E.; Wu, J.; Ramesh, R.; Ager, J.W., III. Efficient Photovoltaic Current Generation at Ferroelectric Domain Walls. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Wang, C.; Zheng, F.; Dong, W.; Fang, L.; Shen, M. High-Efficiency Ferroelectric-Film Solar Cells with an n-type Cu2O Cathode Buffer Layer. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehle, S.; Anderson, A.Y.; Barad, H.N.; Kupfer, B.; Bouhadana, Y.; Rosh-Hodesh, E.; Zaban, A. All-oxide photovoltaics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 3755–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, E.H. Infrared photovoltaics made by solution processing. Nature Photon. 2009, 3, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Koleilat, G.I.; Fischer, A.; Tang, J.; Debnath, R.; Levina, L.; Sargent, E.H. Enhanced open-circuit voltage in visible quantum dot photovoltaics by engineering of carrier-collecting electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3792–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.; Hoyer, P.; Weller, H. Quantum-sized PbS, CdS, Ag2S, Sb2S3 and Bi2S3 particles as sensitizers for various nanoporous wide band gap semi-conductors. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 3183–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Eda, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, W.; Chhowalla, M.; Milne, W.I.; Deng, W.Q. Incorporation of graphene in quantum dot sensitized solar cells based on ZnO nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6084–6086. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Uchaker, E.; Gao, R.; Qu, X.; Zhang, S.; Cao, G. Architectured ZnO photoelectrode for high efficiency quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3542–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, E.H. Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Nat. Photon. 2012, 6, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, A.H.; Thon, S.M.; Hoogland, S.; Voznyy, O.; Zhitomirsky, D.; Debnath, R.; Levina, L.; Rollny, L.R.; Carey, G.H.; Fischer, A.; et al. Hybrid passivated colloidal quantum dot solids. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkacs, D.; Chen, W.; Matheu, P.; Lim, S.; Yu, P.; Yu, E. Nanoparticle-induced light scattering for improved performance of quantum-well solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 091107:1–091107:3. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Calnan, S. Applications of Oxide Coatings in Photovoltaic Devices. Coatings 2014, 4, 162-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4010162
Calnan S. Applications of Oxide Coatings in Photovoltaic Devices. Coatings. 2014; 4(1):162-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4010162
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalnan, Sonya. 2014. "Applications of Oxide Coatings in Photovoltaic Devices" Coatings 4, no. 1: 162-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4010162
APA StyleCalnan, S. (2014). Applications of Oxide Coatings in Photovoltaic Devices. Coatings, 4(1), 162-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4010162



