Abstract
A series of methacrylic copolymers bearing thiazolium cationic groups and catechol moieties were evaluated as antibacterial coatings on a variety of materials including aluminum and plastics such as polycarbonate, poly(methyl methacrylate), and silicone rubber. The thermal properties of the copolymers were first studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The cationic copolymers were thermally stable up to 200 °C and presented glass transition temperatures values well above 100 °C; thus, an acceptable thermal behavior for typical biomedical applications. The cationic copolymers with variable content of the adhesive anchoring N-(3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl) methacrylamide (DOMA) units were coated onto the metal and polymeric substrates by drop casting and the adhesive properties of the obtained coatings were further evaluated as a function of DOMA content and substrate. Optical profilometry, attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectra, and antimicrobial studies reveal that the coatings adhere stronger to metal substrates than to the polymeric substrates. The copolymers with higher content of DOMA, 24 mol.%, resist solvent erosion treatment when coated onto all substrates and exhibit antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive S. aureus bacteria after this erosion treatment. In contrast, copolymers with low content, 9 mol.% of DOMA, only remain attached onto the aluminum metal substrate after solvent treatment, while on polymeric substrates the coatings are almost removed and do not show any efficacy against S. aureus bacteria.
1. Introduction
Mussel inspired catechol containing polymers have attracted special interest in many research areas in recent years. The amino acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine (L-DOPA), found in the adhesive proteins secreted by mussels, contributes to the adhesion capacity on a variety of materials under wet conditions [1,2] and has stimulated research in the development of catechol based compounds for enhancing adhesion properties [3,4], almost being considered as a universal anchoring group. Many catechol-based polymeric materials have been developed in recent years for surface modification applications and the design of coatings with multiple applications [5]. Of all these strategies, catechol-containing vinyl monomers offer great versatility as they allow the preparation of synthetic polymers with catechol moieties on their side chains by simple radical polymerization. For instance, N-(3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl) methacrylamide (DOMA) has been widely employed to prepare a variety of alkyl methacrylate-based copolymers by random copolymerization with other functional monomers for applications as diverse as glue [6], oil repellent coatings [7], anticorrosion coatings [8], DNA immobilization [9], antifouling [10], and antibacterial coatings [11,12]. By this method, systematic tailoring of copolymer composition can be easily afforded to modulate their properties, including their adhesive capacity. Herein, we study a family of cationic methacrylate-based copolymers containing randomly distributed DOMA units as antibacterial coatings. The copolymers were composed of N-(3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl) methacrylamide (DOMA) and 2-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethyl methacrylate (MTA), in which the thiazole groups of MTA units were further quaternized with methyl and butyl iodide to lead to cationic thiazolium moieties [11]. The cationic copolymers exhibited significant antibacterial activity and strong adhesion onto glass substrates. In the current work, these copolymers were examined as antibacterial coatings onto substrates typically used in biomedical applications, such as aluminum, and plastics such as polycarbonate, poly(methyl methacrylate), and silicone.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
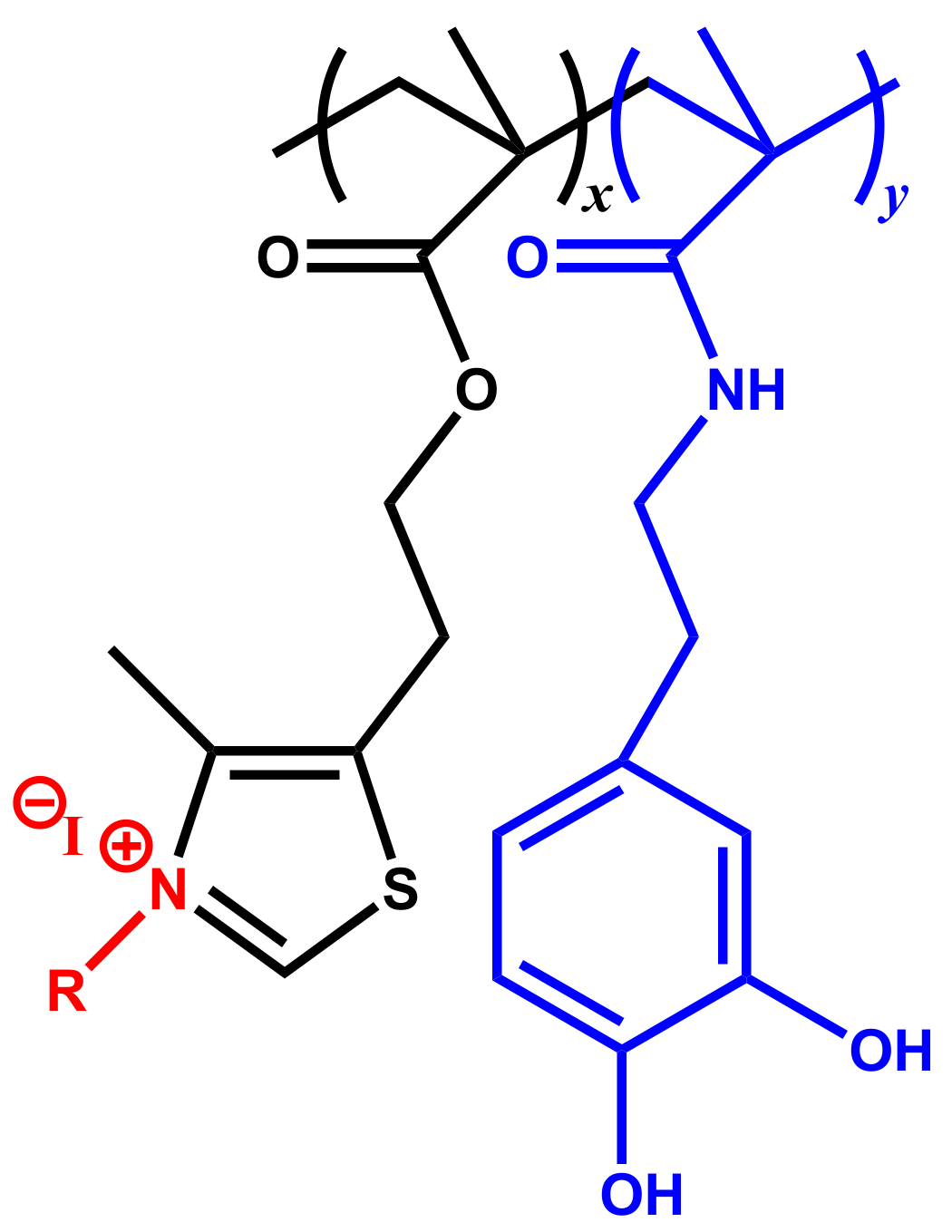
The statistical copolymers composed of 2-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethyl methacrylate (MTA) and N-(3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl) methacrylamide (DOMA), named as P(DOMAx-co-MTAy), were synthesized by conventional free radical polymerization according to a previous work [11]. From these copolymers, the corresponding cationic samples were obtained by quaternization reaction with methyl and butyl iodide, leading to P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M and P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)B copolymers, respectively [11] (Figure 1). The substrates polycarbonate (PC) and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) were obtained from LagoPlast® (Madrid, Spain), whereas aluminum metallic substrate (Al) and silicone rubber were purchased from RS component (Madrid, Spain).
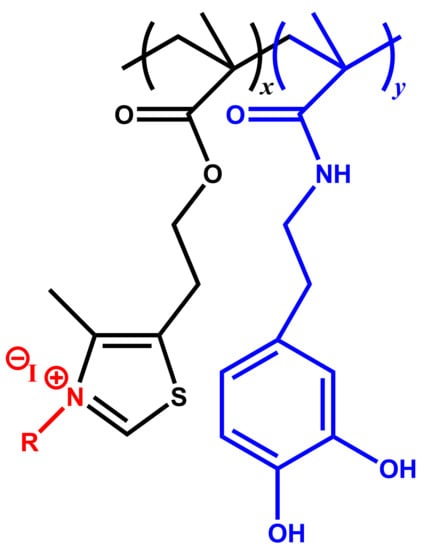
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of quaternized copolymers P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)R.
For microbiological assay, sodium chloride aqueous solution (NaCl, 0.9%, BioXtra, suitable for cell cultures) and phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Columbia agar plates with 5% sheep blood were purchased from BioMérieux (Madrid, Spain). The strain of Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus, ATCC 29213) was obtained from OxoidTM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.2. Film Formation and Adhesive Properties Tests
Films were formed onto different substrates of 1 cm × 1 cm, polycarbonate (PC), poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), silicone rubber, and aluminum metallic substrate (Al), all previously washed with ethanol and dried. The films were obtained by drop casting from 50 µL of polymer solution in distilled water (2 mg/mL), and then were subsequently dried in an oven at 60 °C overnight. Solvent erosion experiments were carried out to study the adhesion of the copolymers on polymeric and metallic substrates. For these experiments, distilled water was used as a solvent. The films were immersed in water for 3 days and then washed with fresh water.
2.3. Characterization
The copolymers P(DOMAx-co-MTAy), P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M, and P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)B were thermally characterized by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The measurements were conducted on a TA Q2000 instrument (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) under dry nitrogen (50 cm3·min−1). The samples were equilibrated at 0 °C and heated to 200 °C at 10 °C/min, then rapidly cooled to 0 °C and again heated to 200 °C at 10 °C/min. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of copolymers was performed on a TA Instruments (TGA Q500, TA instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) at a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1 from 40 to 800 °C, under nitrogen atmosphere. The instrument was calibrated both for temperature and weight by standard methods.
The surface topography of the prepared films was analyzed by optical profilometry using a Zeta-20 optical profiler (Zeta Instruments, San Jose, CA, USA) with a 100× optical objective and 13 nm of vertical resolution. Infrared (IR) spectra were recorded on a Spectrum Two instrument (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA) with the universal Attenuance Total Reflectance (ATR) sampling accessory module and reflectance bands were given in wavenumbers (cm−1).
2.4. Antimicrobial Test
Antimicrobial activity of the prepared coatings was determined following the E2149-13a standard method of the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) [13] against S. aureus (ATCC 29213) bacteria. Each coated substrate was placed in a sterile falcon tube and then 10 mL of the bacterial suspension (106 CFU/mL) were added. Falcon tubes with only the inoculum and substrates Al, PC, PMMA, and Silicone were also prepared as control experiments. The samples were shaken at room temperature at 150 rpm for 24 h. Bacterial concentrations at time 0 and after 24 h were calculated by the plate count method.
3. Results and Discussion
Several copolymers with different chemical compositions were tested as antimicrobial coating. The MTA and DOMA copolymers were previously prepared using different feed ratios (monomer molar ratio MTA/DOMA = 90/10, 80/20, 70/30). The content of DOMA in the copolymer was limited to 30 mol.% of DOMA, as it is reported to be an optimal composition because a higher content does not enhance the adhesive properties [11,14,15]. The obtained copolymer compositions are given in Table 1. Then, the copolymers were successfully quaternized to obtain cationic copolymers with antimicrobial properties [11].

Table 1.
Compositions and thermal parameters of the synthesized copolymers, glass transition temperature (Tg), decomposition temperatures at 10% weight loss (Td10), temperatures of the maximum rate of weight loss for each step (Tdmax1, Tdmax2, and Tdmax3) and weight loss for each step (wt.%1, wt.%2, wt.%3).
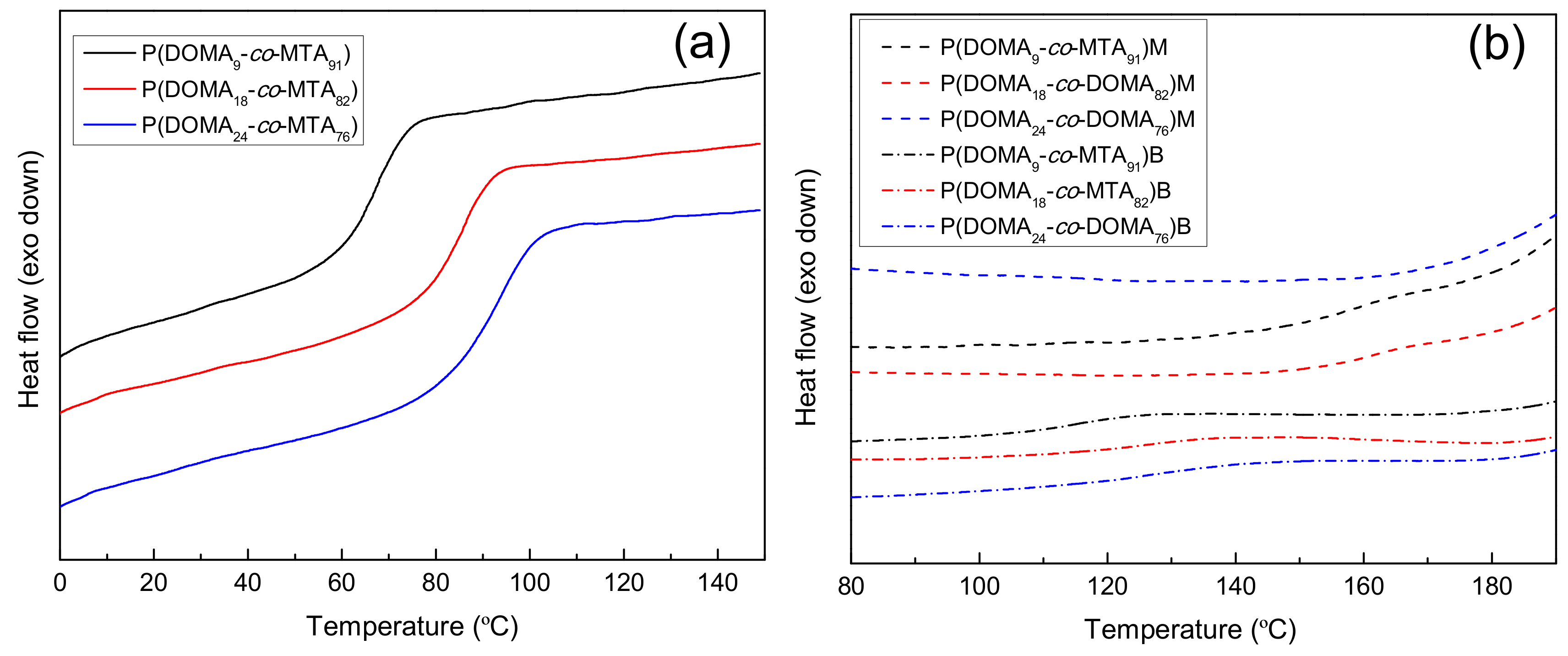
Initially, the thermal properties of the obtained copolymers were studied as they are of great importance for the applicability of these antimicrobial coatings. Polymeric films serving as coatings for materials in biomedical applications should meet severe property requirements, including thermal stability, as they should resist processes such as autoclaving. All the copolymers were first analyzed by DSC and the glass transition temperatures, Tg, determined on the second heating scan are given in Table 1 and represented in Figure 2. It is clearly observed in the unquaternized series, P(DOMAx-co-MTAy), that the Tg value of the copolymers gradually shifts to higher temperature as the content of DOMA increases in the copolymer. The incorporation of relatively bulky catechol units in the copolymer reduces the chain mobility [6]. Upon quaternization, the Tg of the corresponding copolymers further increases, either with methyl or butyl iodide. This significant variation in the glass transition temperature is in concordance with previous studies [16,17] and is more relevant in the copolymers quaternized with methyl iodide. In fact, in the copolymer with the highest content of DOMA, P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M, the Tg is not appreciated in the temperature range studied. Further temperature increase seems to provoke the degradation of the polymer before the glass transition temperature occurs. The introduction of ionic charges upon quaternization gives additional interactions between the polymer segments and hinders the relaxation of the chains. In contrast, increasing the length of the quaternizing agent exerts a plasticization effect, and the Tg of butylated copolymers decreases with respect to the methylated copolymers.
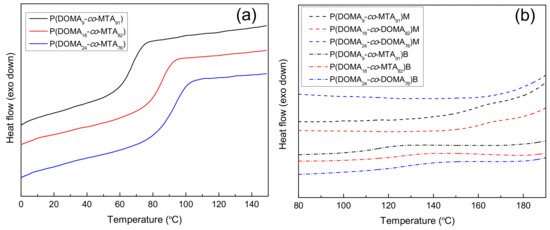
Figure 2.
DSC curves of (a) P(DOMAx-co-MTAy) copolymers and (b) P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M and P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)B cationic copolymers.
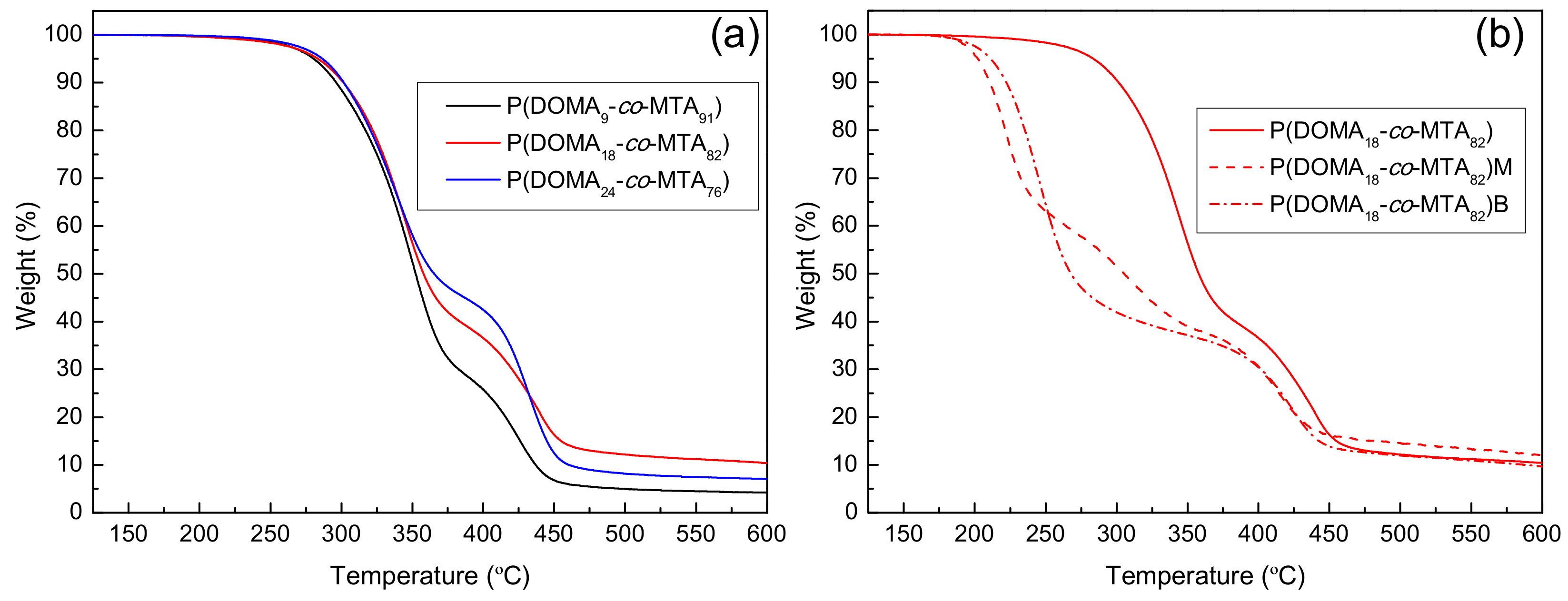
The thermal stability of the copolymers was further analyzed by TGA under inert atmosphere. All the unquaternized P(DOMAx-co-MTAy) copolymers were thermally stable until relative high temperatures, with decomposition temperatures at 10% weight loss (Td10) of around 280 °C (see Table 1). This decomposition temperature slightly increases with the content of DOMA units in the copolymer. Therefore, the incorporation of DOMA in the polymer structures, in addition to increasing the Tg of the coatings, seems to enhance the thermal stability, as previously observed [8]. Two main degradation stages are clearly visible in the copolymers, in which the weight loss in the first step increases with the content of MTA in the copolymers (Figure 3a). This fact suggests that this stage could be mainly associated with the degradation of the MTA units. On the other hand, a drastic change is appreciated in the thermal behavior of the quaternized samples; both the methylated and butylated copolymers exhibit a reduced thermal stability in comparison with the unquaternized counterparts (see Figure 3b). This decrease in the stability of polymers upon quaternization process has been reported in other studies and was attributed to diverse factors, including loss of hydrogen bonds, presence of ionic charge, and incorporation of alkyl groups susceptible for degradation [17,18,19,20]. Table 1 summarizes the Td10 and the temperatures of the maximum rate of weight loss for each step (Tdmax1, Tdmax2, and Tdmax3). In general, the degradation temperatures significantly decreased in the cationic copolymers, in particular the Td10 and Tdmax values of the first degradation stage. As shown before, this step is more related with the MTA units, which are the components modified by the quaternization reaction, providing thiazolium groups [17].
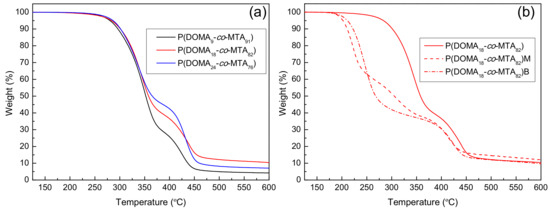
Figure 3.
TGA analysis of (a) unquaternized P(DOMAx-co-MTAy) copolymers and (b) influence of the quaternization of P(DOMA18-co-MTA82) on the thermogravimetric behavior.
In the case of cationic copolymers quaternized with methyl iodide, P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M, the degradation occurs in three stages, while two stages appear for the butylated copolymers [17]. In addition, the Td10 and Tdmax values improve in the copolymers quaternized with butyl iodide [21]. Therefore, the quaternization with a longer alkyl agent seems to stabilize the macromolecular structure of the cationic copolymers.
Although the incorporation of cationic charge into the macromolecular structure of the copolymer reduces the thermal stability, the obtained cationic copolymers still exhibit an acceptable thermal stability for biomedical applications.
Once the synthesized copolymers were thermally characterized, we explored the ability of these copolymers to form adherent coatings on different substrates. The copolymers were deposited by drop casting from water solution on a variety of substrates. The thickness of the obtained films was measured by optical profilometry at different points, with values of 2.3 ± 0.3 µm on PC, 2.2 ± 0.2 µm on silicone, 0.6 ± 0.1 µm on PMMA, and 1.3 ± 0.1 µm on Al. Then, to evaluate the adhesive capacity of dopamine moieties of the prepared coatings, the films were subsequently exposed to water immersion (which is a good solvent for the copolymers) for 3 days. For comparative purposes, PMTA homopolymers, quaternized with either methyl or butyl iodide, PMTAM and PMTAB, respectively, were also used as control experiments. After the water treatment, the resulting surfaces were visually analyzed by optical profilometry.
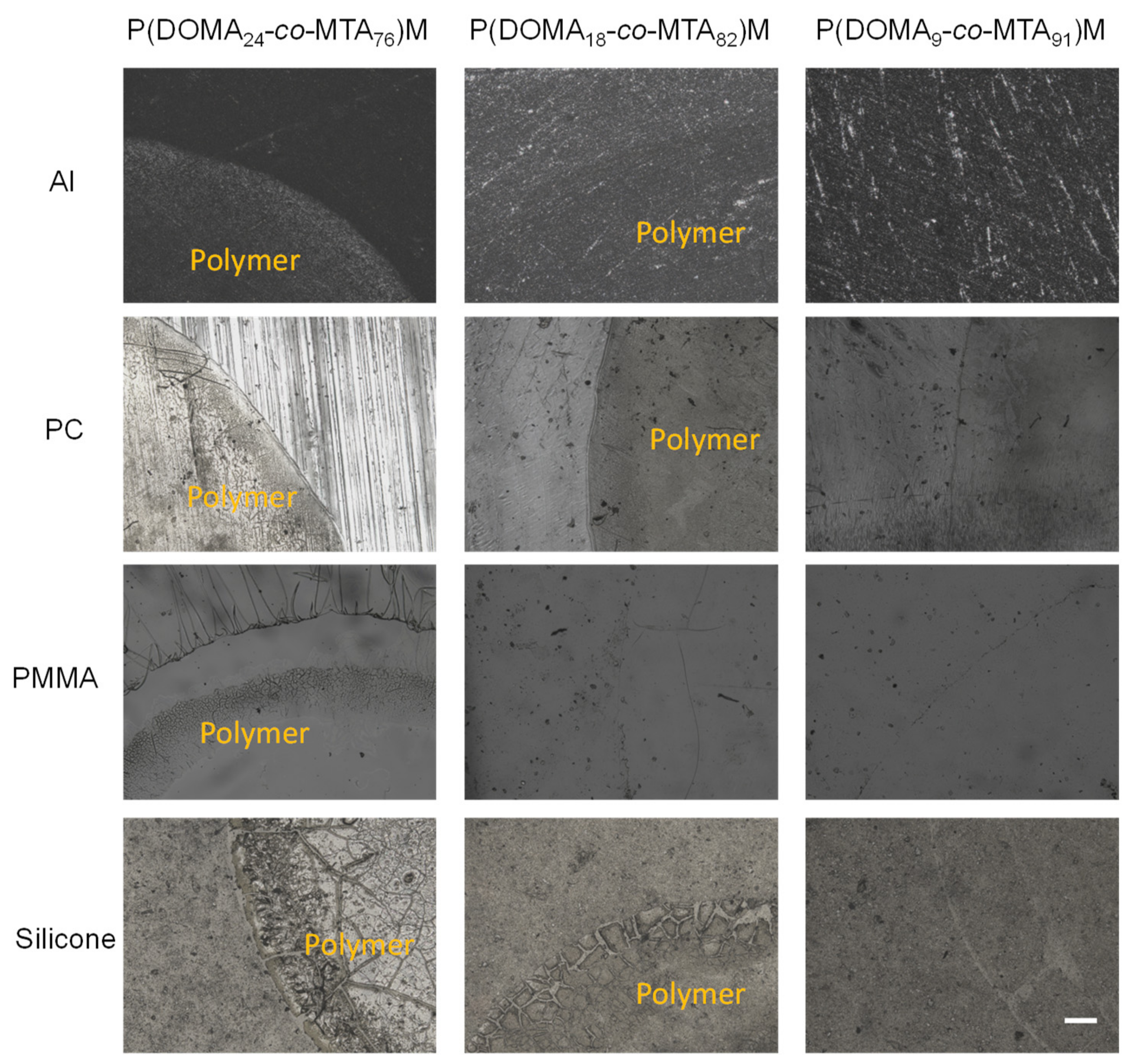
Figure 4 displays the optical images of P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M copolymers coated onto diverse substrates, including Al, PC, PMMA, and silicone. These images demonstrated the presence of coating adhered onto all tested surfaces for the copolymer composition with the highest content of DOMA, P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M. When the percentage of DOMA in the copolymer diminished, P(DOMA18-co-MTA82)M, the coating was rather visible, in particular on PMMA substrates, while the copolymer with the lowest content of DOMA, P(DOMA9-co-MTA91)M practically disappeared from all the tested substrates after water immersion treatment. Similar results were found for the cationic copolymers quaternized with butyl iodide, P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)B (Figure S1 of Supplementary Materials). Although the films seemed to be visible for the P(DOMA9-co-MTA91)B copolymer, the coating was considerably reduced. Concerning the coatings obtained from the homopolymers, PMTAM and PMTAB, without DOMA units, the polymers were completely removed from the substrates by water rinse. These findings prove the major role of DOMA in the adhesive properties of the polymeric coatings.
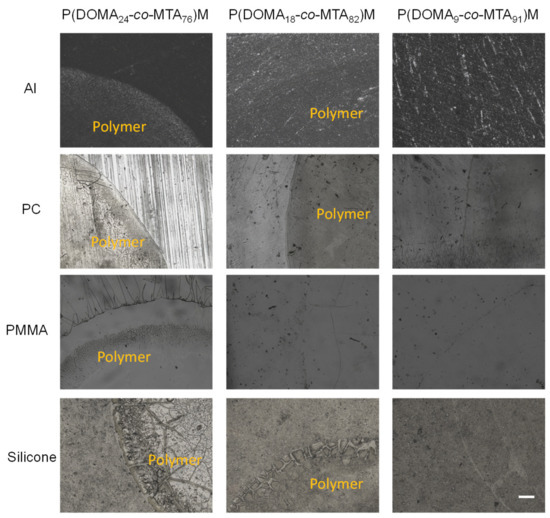
Figure 4.
Optical images of coatings made from P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M copolymers onto different substrates. Scale bar = 250 µm.
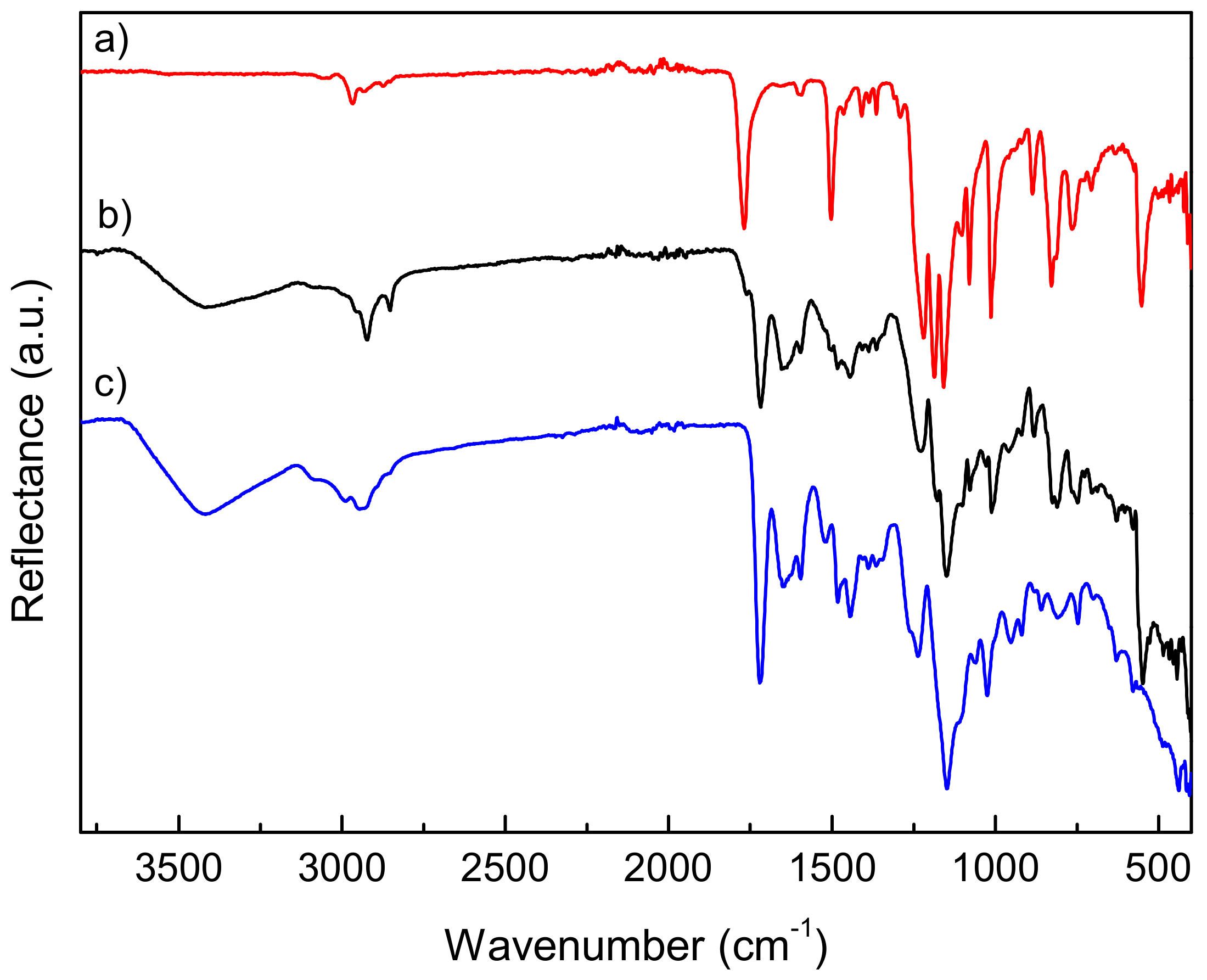
The coated surfaces were also analyzed after water treatment by ATR-FTIR analysis to further evaluate the permanence of the copolymer onto the substrates upon water washing treatment. Figure 5 shows as an example the spectrum of the film obtained from the copolymer P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M onto PC substrate, together with the spectra of both, PC substrate and P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M copolymer. Remarkably, representative signals of the copolymer were clearly identified in the spectrum of the coated surface at 1654 cm−1 (C=O, DOMA), 1723 cm−1 (C=O, MTA), 1590 cm−1 (C=N + thiazolium, MTA), and 1141 cm−1 (C–O, MTA) [12,22]. In addition, the signals attributed to PC substrate, such as at 1768 cm−1 (C=O, PC), were also appreciated, although their intensities were considerably reduced, due to the presence of the polymeric coating at the surface. ATR-FTIR spectra of the P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M coatings on the rest of tested substrates are shown in Figures S2–S4 of the Supplementary Materials. In all the substrates, signals corresponding to the copolymer were easily detected on the surfaces, proving the permanence of the coating after solvent treatment and, thus, its adhesion capacity. However, in the case of coatings prepared from copolymers with lower contents of DOMA, the signals assigned to them were rather detected and the spectra were dominated by the signals corresponding to the supports. This seems to indicate that these coatings with low contents of DOMA units were reduced or eliminated after the solvent treatment, as the theoretical depth penetration of ATR-FTIR is 2.01 µm (Diamond crystal, refractive index: 2.4 and angle of incidence: 45°).
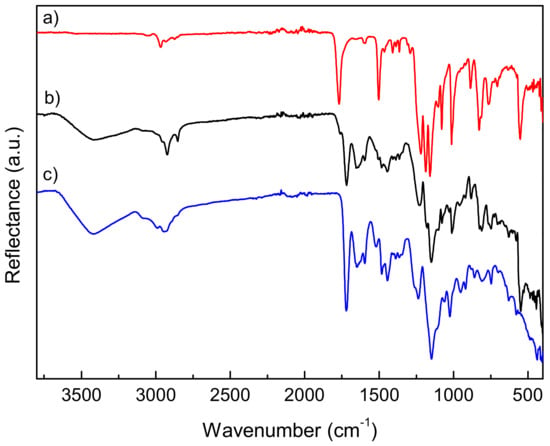
Figure 5.
ATR-FTIR spectra of (a) PC substrate, (b) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M coated on PC substrate, and (c) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M copolymer.
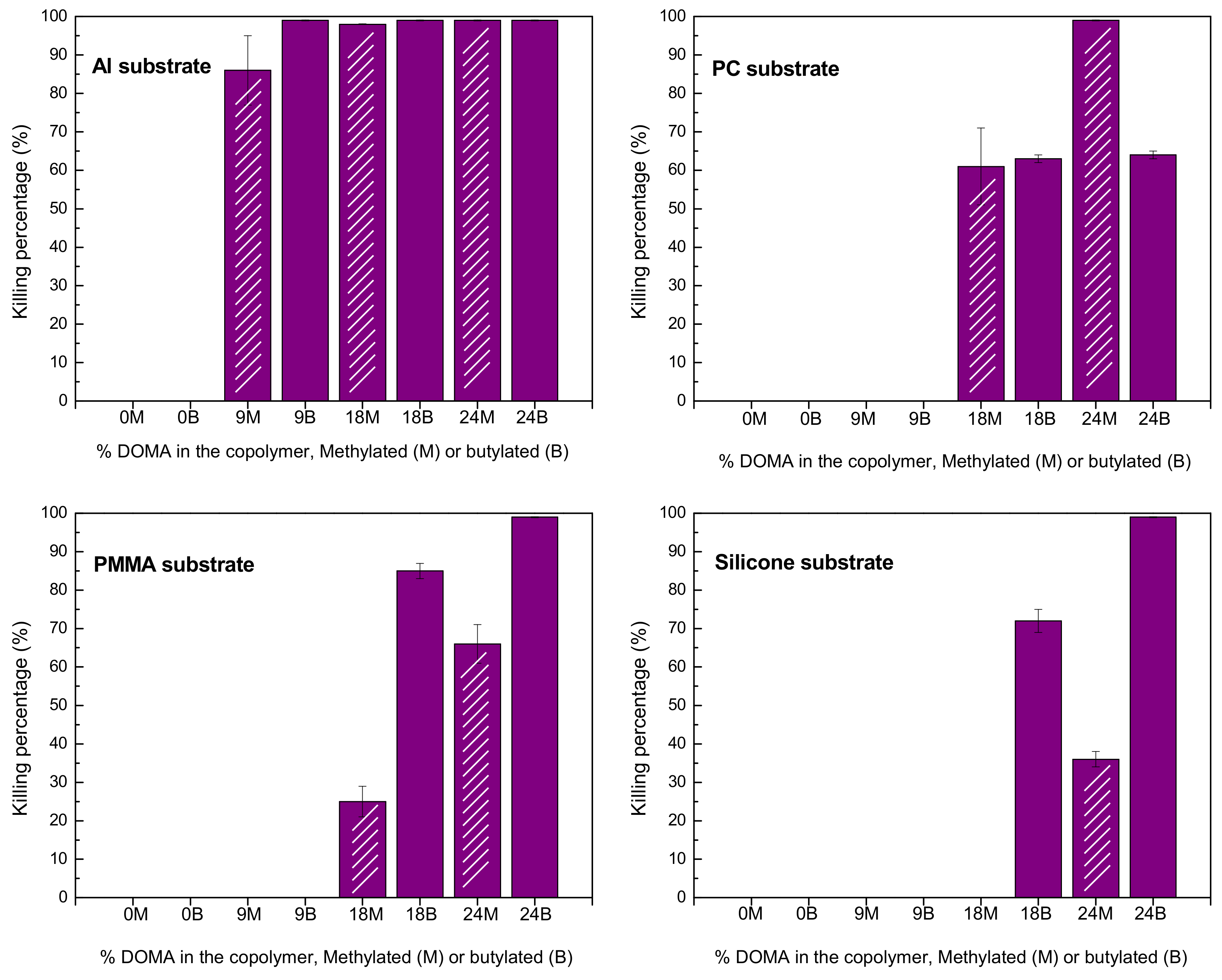
Then, the efficacy of these cationic coatings with adhesive anchors of dopamine to kill Gram-positive S. aureus upon contact was analyzed as a function of dopamine moieties content, alkylating agent, and substrate. The antimicrobial activity was evaluated by the E2149-13a standard method of the ASTM [13]. Before the test, films were immersed in distilled water for 3 h in order to remove the polymers non-strongly attached onto the substrates. PMMA, PC, silicone, and Al substrates were used as control. Figure 6 displays the antibacterial activity of all the coatings presented as the percentage of bacteria kill, which was calculated by the following equation:
where A is CFUs after contact with control substrates (PC, PMMA, Silicone or Al) and B is CFUs after contact with the polymer coated on the substrates.
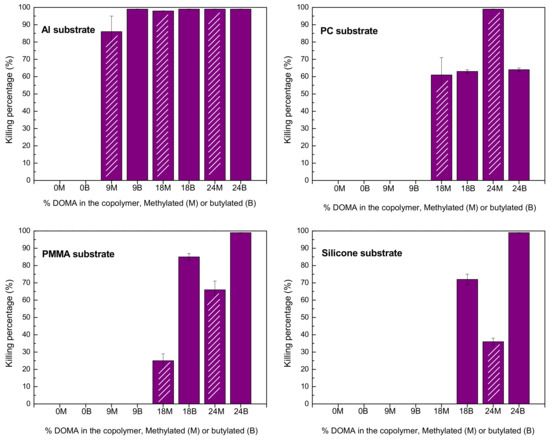
Figure 6.
Killing percentage for S. aureus of the coatings based on P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M and P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)B cationic copolymers on diverse substrates.
The results show that only coatings based on copolymers with a high percentage of DOMA exhibited significant antibacterial activity for all the substrates tested. However, when butylated and methylated copolymers with similar compositions were compared, no clear trend was appreciated, although methylated seemed to be weaker. Coatings obtained from the homopolymers PMTAM and PMTAB, with 100% of MTA units (0% of DOMA), did not show any activity in any of the substrates. Similarly, the cationic copolymers, either butylated or methylated, with only 9 mol.% of DOMA, were not able to inhibit bacterial growth when coated on polymeric substrates. This could be explained by the fact that such coatings with low content or without catechol units were not strongly adhered onto the surface, and were mostly removed in the previous solvent erosion treatment. Remarkably, the P(DOMA9-co-MTA91)M and P(DOMA9-co-MTA91)B coated onto aluminum substrate exerted antibacterial activity, pointing out that a low content of DOMA, 9 mol.%, might be enough to adhere onto a metallic aluminum substrate, while it is not sufficient to strongly attach onto polymeric substrate. Although catechol derivatives can attach to surfaces of a wide variety of materials, including metals, alloys, glass, inorganic oxides and polymers [3,4], the interactions with polymers seem to be weaker than with metals or other materials [6]. Catechol moieties exhibit multiple binding mechanisms depending on the chemistry of the surfaces, such as catechol-metal coordinate bonds, hydrogen bonds, and π−π interactions [4,23]. The attachment of catechol groups onto polymeric surfaces could be mainly due to hydrogen bonds, whereas coordinate bonds are implied in the adhesion on aluminum substrate. This can be the reason behind the results obtained in this study, copolymers with low content of DOMA are able to attach in a stronger manner onto aluminum substrate than onto polymeric substrates, retaining the antibacterial activity upon solvent erosion treatment.
4. Conclusions
A family of cationic copolymers, P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)M and P(DOMAx-co-MTA9y)B, bearing variable content of DOMA adhesive units, and quaternized MTA as antibacterial components, were evaluated as antibacterial coatings over diverse substrates. The thermal properties of the copolymers demonstrated that, although the quaternization reaction to incorporate cationic charge on the macromolecular structures reduces their thermal stability, they are stable up to 200 °C. In addition, the quaternization reaction increases the glass transition temperature compared to the neutral counterpart. Related to the adhesive properties of the copolymers, the coatings adhered strongly for the copolymer composition with the highest content of DOMA, onto all the tested surfaces. However, when the percentage of DOMA in the copolymer diminished, the coating practically disappeared from polymeric substrates after solvent erosion treatment. These results suggested that the catechol groups interact in a weaker manner with polymeric substrates in comparison with an Al metal surface, and higher content of DOMA in the macromolecular structure is required for a strong adhesion of the coatings. The coatings that resist the solvent erosion treatment exhibit significant antibacterial activity against Gram-positive S. aureus. Then, the present study shows that the control of the copolymer composition enables the tune of the adhesive and antibacterial properties of these antibacterial coatings.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6412/9/11/733/s1, Figure S1: optical images of coatings made from P(DOMAx-co-MTAy)B copolymers onto different substrate. Scale bar = 250 µm, Figure S2: ATR-FTIR spectra of (a) PMMA substrate, (b) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M coated on PMMA substrate and c) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M copolymer, Figure S3: ATR-FTIR spectra of (a) silicone substrate, (b) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M coated on silicone substrate and (c) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M copolymer, and Figure S4: ATR-FTIR spectra of (a) Al substrate, (b) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M coated on Al substrate and (c) P(DOMA24-co-MTA76)M copolymer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F.-G. and A.M.-B.; Methodology, A.C.; Formal Analysis, A.C.; Investigation, C.E.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.M.-B.; Writing-Review and Editing, C.E., A.M.-B. and M.F.-G.; Visualization, M.F.-G.; Supervision, C.E. and A.M.B.; Project Administration, M.F.-G.; Funding Acquisition, M.F.-G.
Funding
This research was funded by the MINECO (Project MAT2016-78437-R), the Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI, Spain) and Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER, EU). C. Echeverria also acknowledges MINECO for her IJCI-2015-26432 contract.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Silverman, H.G.; Roberto, F.F. Understanding marine mussel adhesion. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H.; Tanzer, M.L. Polyphenolic substance of mytilus edulis: Novel adhesive containing L-dopa and hydroxyproline. Science 1981, 212, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Bioinspired catecholic chemistry for surface modification. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, E.; Falentin-Daudré, C.; Jérôme, C.; Lyskawa, J.; Fournier, D.; Woisel, P.; Detrembleur, C. Catechols as versatile platforms in polymer chemistry. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 236–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payra, D.; Fujii, Y.; Das, S.; Takaishi, J.; Naito, M. Rational design of a biomimetic glue with tunable strength and ductility. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F. Low surface energy surfaces from self-assembly of perfluoropolymer with sticky functional groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payra, D.; Naito, M.; Fujii, Y.; Yamada, N.L.; Hiromoto, S.; Singh, A. Bioinspired adhesive polymer coatings for efficient and versatile corrosion resistance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 15977–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, H.O.; Liu, Z.; Lau, K.H.; Lee, H.; Messersmith, P.B. Facile DNA immobilization on surfaces through a catecholamine polymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Xu, B.; Huang, X.; Zhuang, Q.; Lin, S. (PtBA-co-PPEGMEMA-co-PDOMA)-g-PPFA polymer brushes synthesized by sequential RAFT polymerization and ATRP. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiloeches, A.; Echeverría, C.; Cuervo-Rodríguez, R.; Plachà, D.; López-Fabal, F.; Fernández-García, M.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A. Adhesive antibacterial coatings based on copolymers bearing thiazolium cationic groups and catechol moieties as robust anchors. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jing, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Tan, Y. Diblock copolymer containing bioinspired borneol and dopamine moieties: Synthesis and antibacterial coating applications. Polymer 2017, 116, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM E2149-13a, Standard Test Method for Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Antimicrobial Agents under Dynamic Contact Conditions; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013; Available online: www.astm.org (accessed on 8 October 2019).
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, T.; Newland, B.; Duffy, P.; Annaidh, A.N.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D.; Wang, W. On-demand and negative-thermo-swelling tissue adhesive based on highly branched ambivalent PEG–catechol copolymers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6420–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos-Perez, C.R.; White, J.D.; Wilker, J.J. Polymer composition and substrate influences on the adhesive bonding of a biomimetic, cross-linking polymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9498–9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero, R.; Arbe, A.; Fernández-García, M.; López, D. Nanostructuration by self-assembly in N-alkyl thiazolium and triazolium side-chain polymethacrylates. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7180–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Bonilla, A.; Lopez, D.; Fernandez-Garcia, M. Providing antibacterial activity to poly (2-hydroxy ethyl methacrylate) by copolymerization with a methacrylic thiazolium derivative. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, R.S.; Kumbharkar, S.C.; Rewar, A.S.; Kharul, U.K. Polybenzimidazole based film forming polymeric ionic liquids: Synthesis and effects of cation–anion variation on their physical properties. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hess, A.R.; Jones, A.R.; Liu, X.; Barber, G.D.; Mallouk, T.E.; Allcock, H.R. Synthesis of new polyelectrolytes via backbone quaternization of poly (aryloxy- and alkoxyphosphazenes) and their small molecule counterparts. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbharkar, S.C.; Kharul, U.K. N-substitution of polybenzimidazoles: Synthesis and evaluation of physical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-Y.; Yi, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of N-alkylated polyamide-imides. Die Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1994, 222, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero, R.; López, D.; López-Fabal, F.; Gómez-Garcés, J.L.; Fernández-García, M. Antimicrobial polymethacrylates based on quaternized 1,3-thiazole and 1,2,3-triazole side-chain groups. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3449–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Messersmith, P.B.; Lee, H. Polydopamine surface chemistry: A decade of discovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7523–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).