The Effects of Ti Additions and Deposition Parameters on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel-Nitride Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Film Composition Analysis
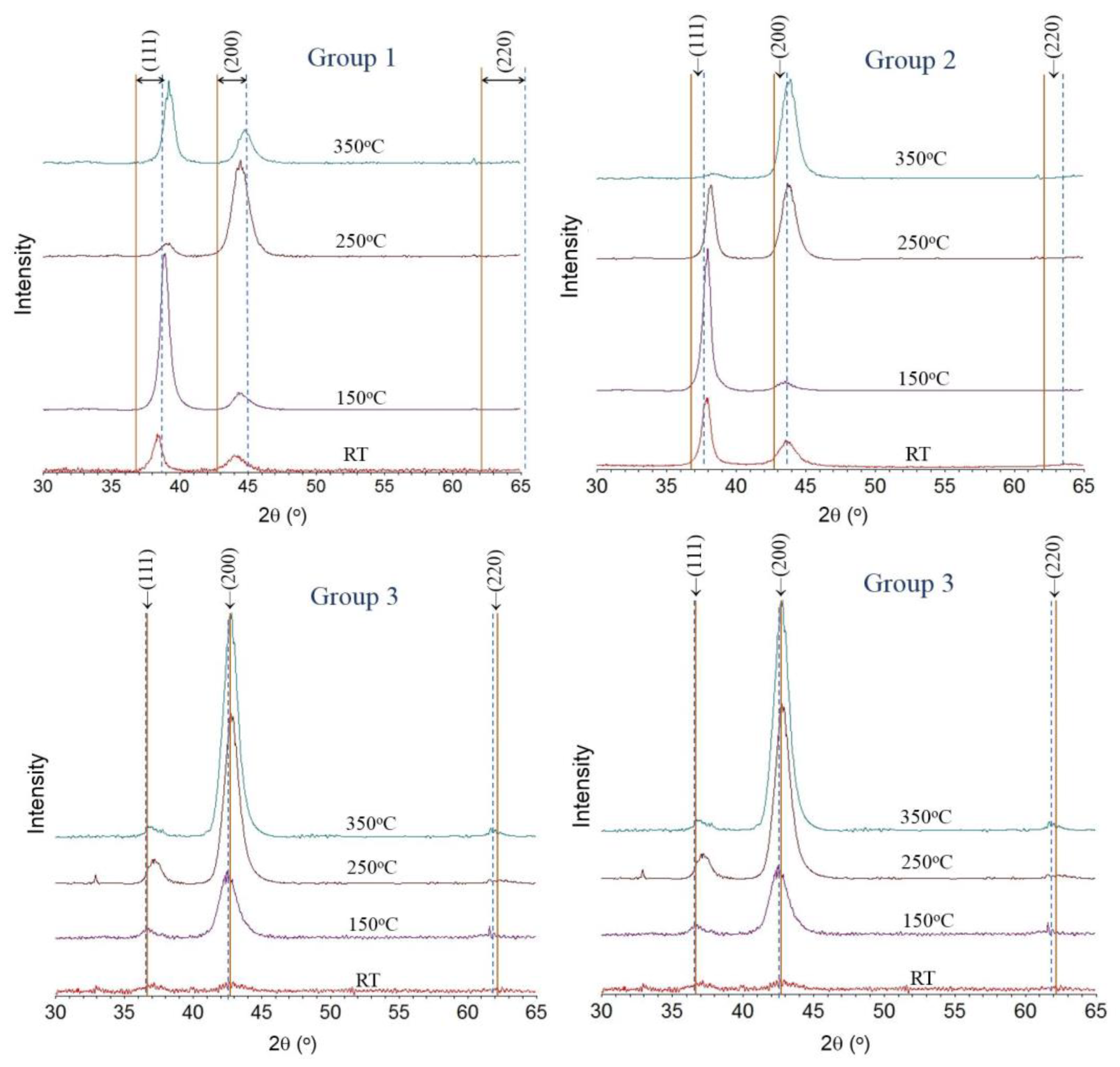
3.2. Crystal Structure
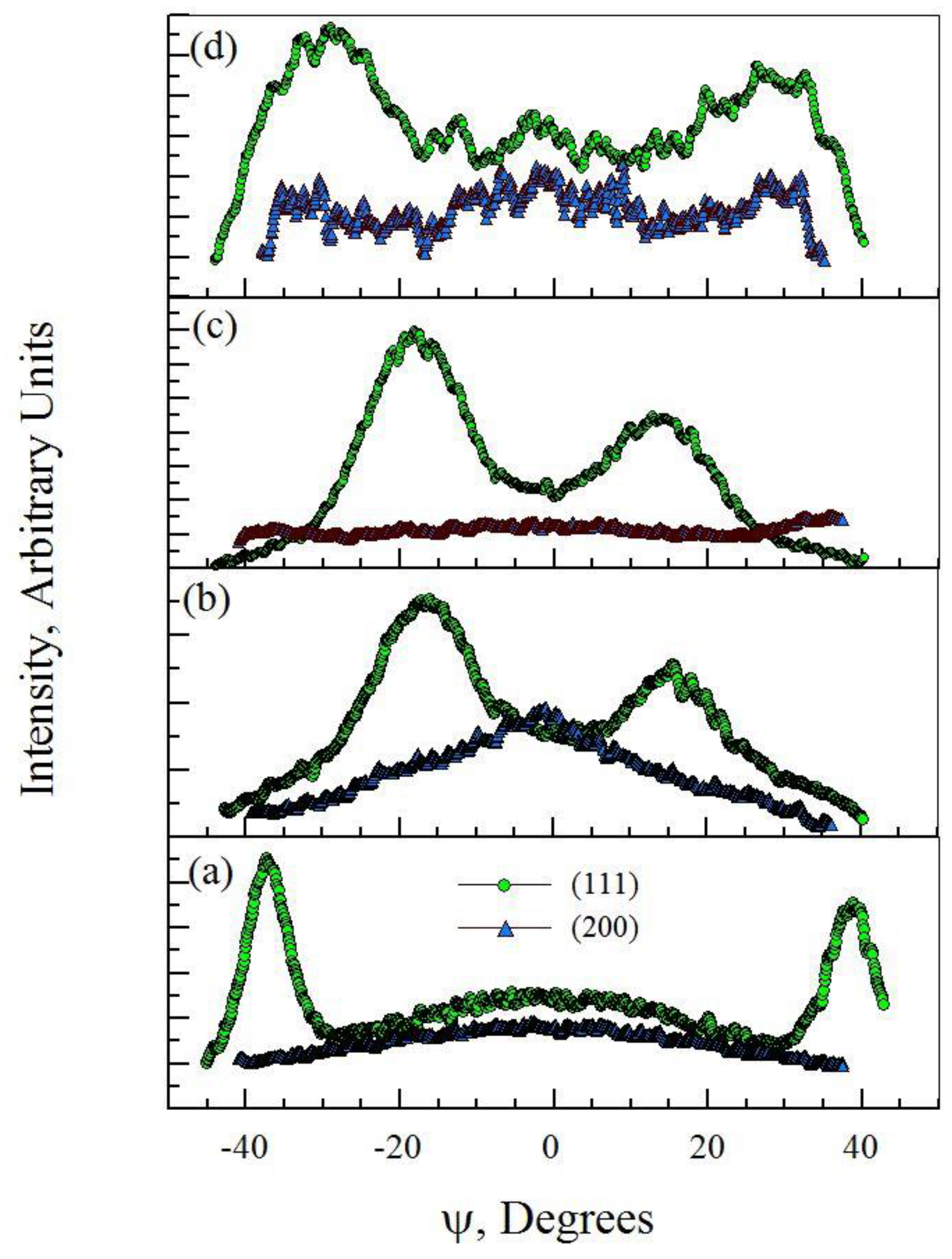
3.3. Film Microstructure
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The effects Ti additions to stainless steel nitride films, up to a concentration of 12 at.% were examined and did not reveal the formation of any new, additional phases. All films had a nominally fcc-based structure with varying degrees of lattice distortion. Within this composition range, TiN appears to form a solid solution with stainless steel-nitride; however, the possibilities of Ti clustering on the metal sublattice or short-range ordering of N atoms cannot be discounted based on the observations made in this work.
- The film structure was further evaluated by determination of the c/a ratio based on the (111)/(200) peak positions. Values of c/a > 1 were observed for most films, which can be associated with the formation of the S-phase. The effect of Ti was to increase the incorporation of N into the lattice, resulting in lower lattice distortion.
- Films with higher titanium levels (generally >10 at.%) showed higher film densities, reduced surface roughness and a reduction in the coarse, faceted grain structure that is characteristic of stainless steel-nitride coatings.
- The hardness of the films with higher Ti and N levels (group 3 and 4 in Table 1) was significantly higher than stainless steel nitride films or plasma-nitrided stainless steel surfaces previously reported in the literature. However, the effects of deposition parameters (temperature, bias) were less notable, as all films at the highest Ti compositions (groups 3 and 4) showed hardness levels between 18–23 GPa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.L.; Bell, T. Structure and corrosion resistance of plasma nitrided stainless steels. Surf. Eng. 1985, 1, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Samandi, M.; Shedden, B.A.; Smith, D.I.; Collins, G.A.; Hutchings, R.; Tendys, J. Microstructure, corrosion, and tribological behaviour of plasma immersion ion-implanted austenitic stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1993, 59, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menthe, E.; Rie, K.T.; Schultze, J.W.; Simson, S. Structure and properties of plasma-nitrided stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 412, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.L.; Davis, J.A.; Wilber, P.J.; Vajo, J.J.; Wei, R.; Matossian, J.N. Relative roles of ion energy, ion flux, sample temperature in low-energy nitrogen ion implantation of Fe-Cr-Ni stainless steel. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. B 1997, 127–128, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mändl, S.; Günzel, R.; Richter, E.; Möller, W. Nitriding of austenitic stainless steels using plasma immersion ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 372, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blawert, C.; Mordike, B.L. Nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation for surface treatment and wear protection of austenitic stainless steel X6CrNiTi1810. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 116–119, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Larisch, B.; Brusky, U.; Spies, H.-J. Plasma nitriding of stainless steels at low temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 116–119, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, E.; Günzel, R.; Parasacandola, S.; Telbizova, T.; Kruse, O.; Möller, W. Nitriding of stainless steel and aluminum alloys by plasma immersion ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 128–129, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mändl, S.; Günzel, R.; Richter, E.; Möller, W.; Rauschenbach, B. Annealing behavior of nitrogen implanted stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 128–129, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Marchev, K.; Cooper, C.V.; Meletis, E.I. Intensified plasma-assisted nitriding of AISI 316L stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 160, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratushka, S.N.; Tyurin, Y.N.; Kolisnichenko, O.V.; Mikhalev, A.D.; Tkachenko, R.Y.; Makhmudov, N.A.; Pshik, A.V.; Denisenko, R.; Yakushchenko, I.V. Structure and tribological characteristics of steel under melting by plasma flow and simultaneous Mo and W alloying. J. Frict. Wear 2012, 33, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrebnyak, A.D.; Bratushka, S.N.; Il’yashenko, M.V.; Makhmudov, N.A.; Kolisnichenko, O.V.; Tyurin, Y.N.; Uglov, V.V.; Pshik, A.V.; Kaverin, M.V. Tribological and physical-mechanical properties of protective coatings from Ni-Cr-B-Si-Fe/WC-Co-Cr before and after fission with a plasma jet. J. Frict. Wear 2011, 32, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchev, K.; Hidalgo, R.; Landis, M.; Vallerio, R.; Cooper, C.V.; Giessen, B.C. The metastable m phase layer on ion-nitrided austenitic stainless steels Part 2: Crystal structure ad observation of its two-directional orientation anisotropy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 112, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Marchev, K.; Landis, M.; Vallerio, R.; Cooper, C.V.; Giessen, B.C. The m phase layer on ion-nitrided austenitic stainless steels III: An epitaxial relationship between the m Phase and the γ parent phase and a review of structural identification of this phase. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 116–119, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewell, M.P.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Priest, J.M.; Short, K.T.; Collins, G.A. The nature of expanded austenite. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 131, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewell, M.P.; Priest, J.M. Higher-order diffractometry of expanded austenite using synchrotron radiation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, T.; Somers, M.A.J. On the crystallographic structure of the S-phase. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Kahn, H.; Dalton, J.C.; Michal, G.M.; Ernst, F.; Heuer, A.H. Orientation dependence of nitrogen supersaturation in austenitic stainless steel during low-temperature gas nitriding. Acta Mater. 2014, 79, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, B.K.; Stahl, K.; Christiansen, T.L.; Oddershede, J.; Winther, G.; Somers, M.A.J. On the elusive structure of expanded austenite. Scr. Mater. 2017, 131, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.J.; Yu, G.P.; Huang, J.H. Mechanical properties of TiN thin film coatings on 304 stainless steel substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 149, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, A.; Leroy, C.; Michel, H.; Frantz, C. Properties of sputtered stainless-steel coatings and structural analogy with low temperature plasma nitride layers of austenitic steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1991, A140, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourjot, A.; Foos, M.; Frantz, C. Basic properties of sputtered 310 stainless steel-nitrogen coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1990, 43–44, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedden, B.A.; Kaul, F.N.; Samandi, M.; Window, B. The role of energetic neutrals in reactive magnetron sputtering of nitrogen-doped austenitic stainless steel coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 97, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwagne, G.; Hody, H.; Colaux, J. Structural and quantitative analysis of stainless steel coatings deposited by DC-magnetron sputtering in a reactive atmosphere. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 383, 174–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappaganthu, S.R.; Sun, Y. Formation of an MN-type cubic nitride phase in reactively sputtered stainless steel-nitrogen films. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 267, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappaganthu, S.R.; Sun, Y. Influence of sputter deposition conditions on phase evolution in nitrogen-doped stainless steel films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 59, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, J.; Fryska, S.; Suszko, T. The influence of temperature and nitrogen pressure on S-phase coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2013, 90, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alresheedi, F.I.; Krzanowski, J.E. Structure and morphology of stainless steel coatings sputter-deposited in a nitrogen/argon atmosphere. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 314, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benia, H.M.; Guemmaz, M.; Schmerber, G.; Mosser, A.; Parlebas, J.-C. Investigations on non-stoichiometric zirconium nitrides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 200, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.S.; Harper, J.M.; Cuomo, J.J.; Smith, D.A. Alignment of thin films by glancing angle ion bombardment during deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1985, 47, 932–933. [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C.; Hultman, L. Microstructural design of hard coatings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 1032–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, T.; Somers, M.A.J. Controlled dissolution of colossal quantities of nitrogen in stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37A, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratz, L.B. Thermodynamic Properties of Carbides, Nitrides and Other Selected Substances; Bulletin 696; U.S. Dept. of the Interior: Albany, OR, USA, 1994.
- Oddershede, J.; Christiansen, T.L.; Stahl, K.; Somers, M.A.J. EXAFS investigation of low temperature nitride stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 5358–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hones, P.; Sanjines, R.; Levy, F. Characterization of sputter-deposited chromium nitride thin films for hard coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 94–95, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Andritschky, M.; Pischow, K.; Wang, Z. Microstructure of CrN coatings produced by PVD techniques. Thin Solid Films 1999, 355–356, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, W.; Neidhardt, J.; Willmann, H.; Sartory, B.; Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C. Thermal decomposition routes of CrN hard coatings synthesized by reactive arc evaporation and magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayal, A.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, A.; Ganesan, V.; Behera, L.; Singh, S.; Basu, S. Study of magnetic iron nitride thin films deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 275, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.H.; Tay, B.K.; Lau, S.P.; Sun, X.W.; Li, S.; Sun, C.Q. Structural and magnetic properties of iron-nitride thin films deposited using a filtered cathodic vacuum arc. Thin Solid Films 2005, 478, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gupta, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Misra, P.; Kukreja, L.M. Study of iron nitride thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. J Alloys Compd. 2001, 326, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, G.J.W.R.; Sikkens, M. Structure of reactively sputtered nickel nitride films. Thin Solid Films 1983, 105, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, N.; Bogdanov, Ž.; Goncić, B.; Štrbac, S.; Rakočević, Z. Reactively sputtered Ni, Ni(N) and Ni3N films: Structural, electrical and magnetic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4027–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J. Introduction to instrumented indentation testing. Exp. Tech. 2009, 33, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidelli, M.; Sebastiani, M.; Collet, C.; Guillemet, R. Determination of the elastic moduli and residual stresses of freestanding Au-TiW bilayer thin films by nanoindentation. Mater. Des. 2016, 106, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidelli, M.; Sebastiani, M.; Johanns, K.E.; Pharr, G.M. Effects of indenter angle on the micro-scale fracture toughness measurement by pillar splitting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 12, 5731–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Temperature °C | Iron at.% | Chromium at.% | Nickel at.% | Oxygen at.% | Nitrogen at.% | Titanium at.% | N/ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Fe + Ni + Cr + Ti) | |||||||
| Group 1: −100 V Bias, SS: 150 W, Ti: 150 W | |||||||
| 25 | 35.6 | 9.3 | 4.4 | 10.2 | 35.3 | 5.2 | 0.65 |
| 150 | 40.3 | 8.9 | 4.4 | 12.5 | 30.4 | 3.5 | 0.53 |
| 250 | 37.9 | 9.6 | 4.3 | 8.5 | 34.8 | 4.8 | 0.61 |
| 350 | 42.0 | 11.5 | 5.0 | 3.7 | 34.8 | 3.0 | 0.57 |
| Group 2: −100 V Bias, SS: 100 W, Ti: 100 W (*) | |||||||
| 25 | 27.7 | 8.3 | 6.1 | 4.8 | 45.2 | 8.0 | 0.90 |
| 250 | 28.4 | 6.9 | 4.5 | 11.3 | 41.5 | 7.4 | 0.88 |
| Group 3: −100 V Bias, SS: 50 W, Ti: 150 W | |||||||
| 25 | 23.7 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 2.7 | 50.3 | 11.2 | 1.07 |
| 150 | 23.0 | 7.2 | 4.3 | 3.0 | 52.2 | 10.4 | 1.16 |
| 250 | 22.4 | 6.2 | 5.9 | 4.5 | 46.5 | 14.6 | 0.95 |
| 350 | 19.2 | 6.8 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 51.6 | 12.9 | 1.17 |
| Group 4: −140 V Bias, SS: 50 W, Ti: 150 W | |||||||
| 25 | 23.0 | 6.2 | 5.1 | 4.3 | 50.3 | 11.1 | 1.11 |
| 150 | 24.1 | 7.5 | 4.8 | 1.5 | 51.7 | 10.5 | 1.10 |
| 250 | 21.8 | 6.4 | 4.6 | 3.2 | 52.9 | 11.1 | 1.20 |
| 350 | 20.1 | 7.7 | 4.6 | 4.0 | 50.6 | 13.0 | 1.12 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alresheedi, F.I.; Krzanowski, J.E. The Effects of Ti Additions and Deposition Parameters on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel-Nitride Thin Films. Coatings 2019, 9, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050329
Alresheedi FI, Krzanowski JE. The Effects of Ti Additions and Deposition Parameters on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel-Nitride Thin Films. Coatings. 2019; 9(5):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050329
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlresheedi, Faisal I., and James E. Krzanowski. 2019. "The Effects of Ti Additions and Deposition Parameters on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel-Nitride Thin Films" Coatings 9, no. 5: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050329
APA StyleAlresheedi, F. I., & Krzanowski, J. E. (2019). The Effects of Ti Additions and Deposition Parameters on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel-Nitride Thin Films. Coatings, 9(5), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050329





