Structure-Property Relationships in Suspension HVOF Nano-TiO2 Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Suspension Preparation
2.2. Spray Process
2.3. Coating Characterisation
3. Results
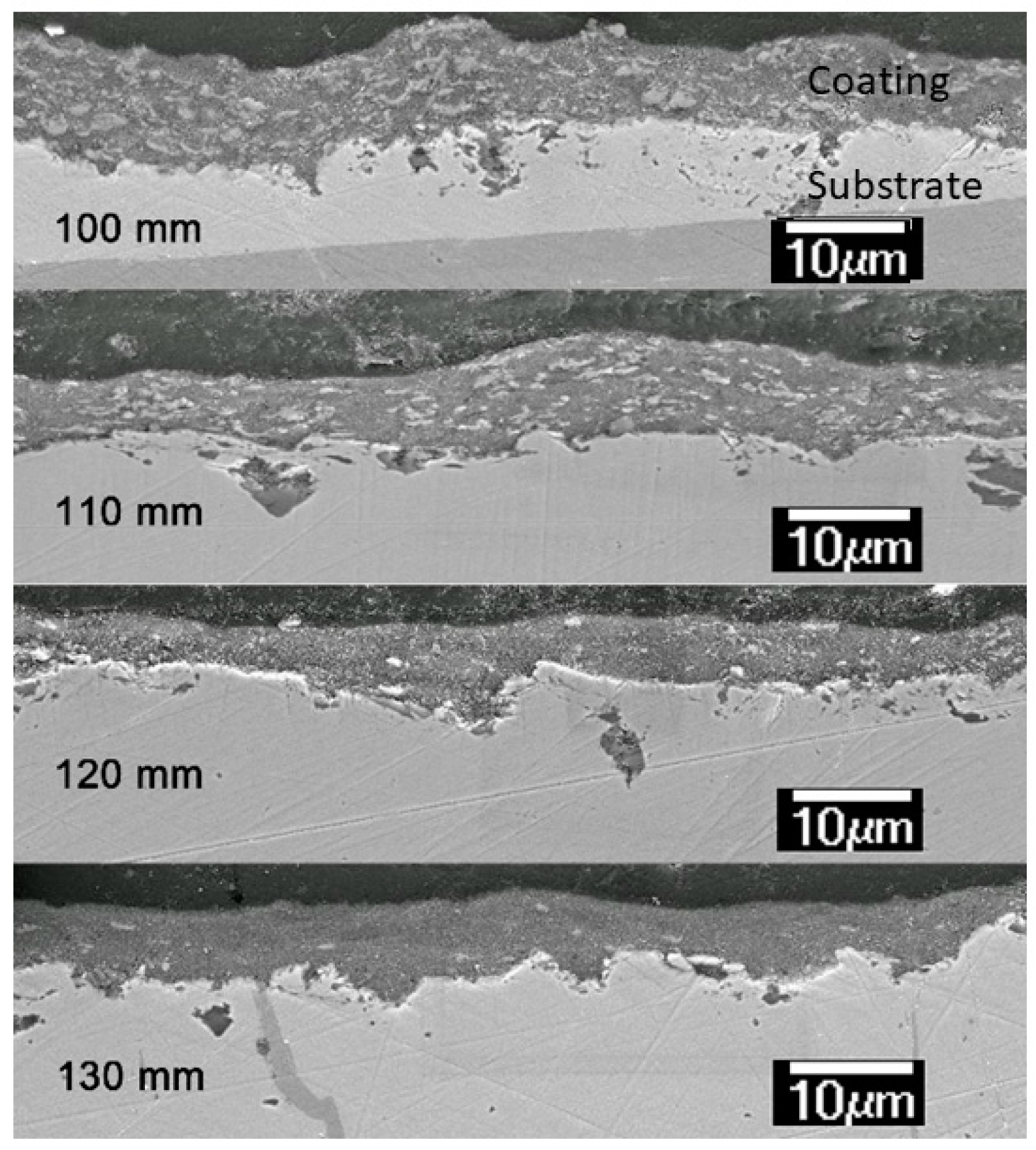
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. Mechanical Properties
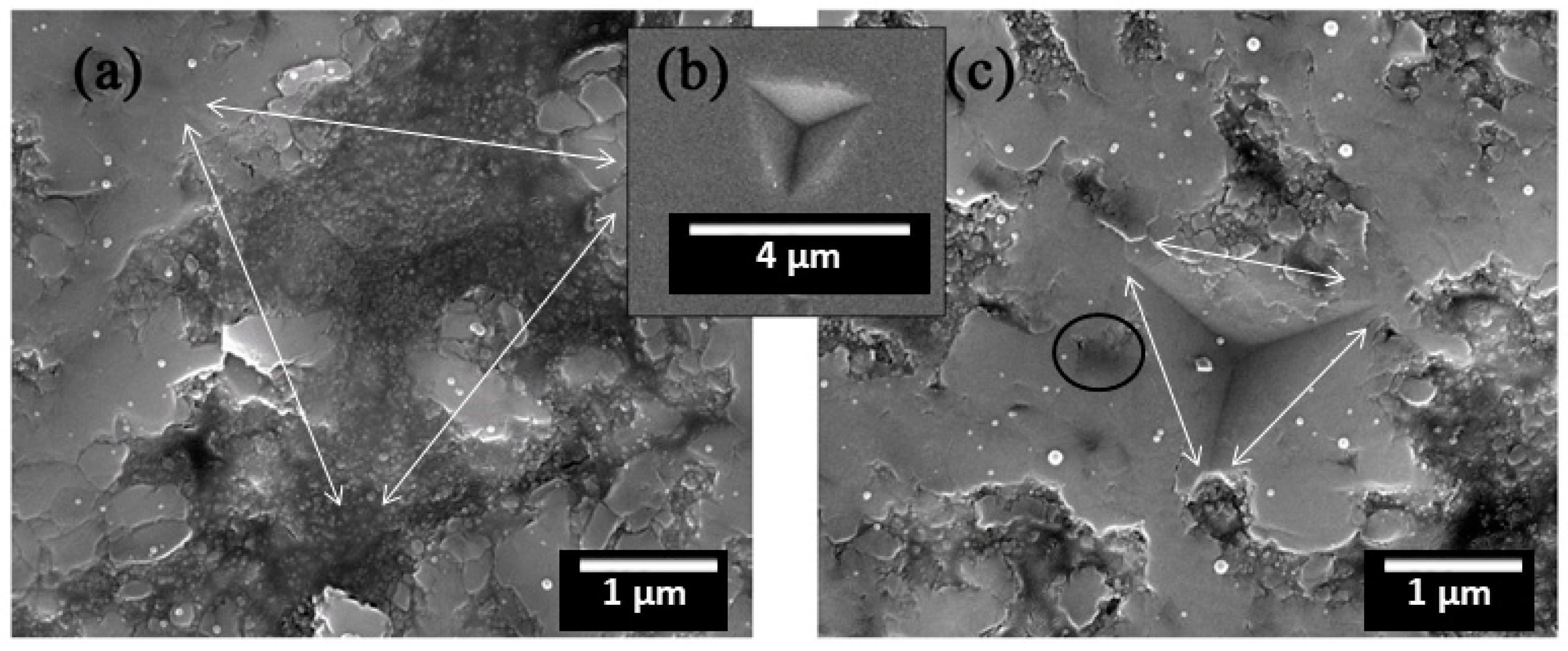
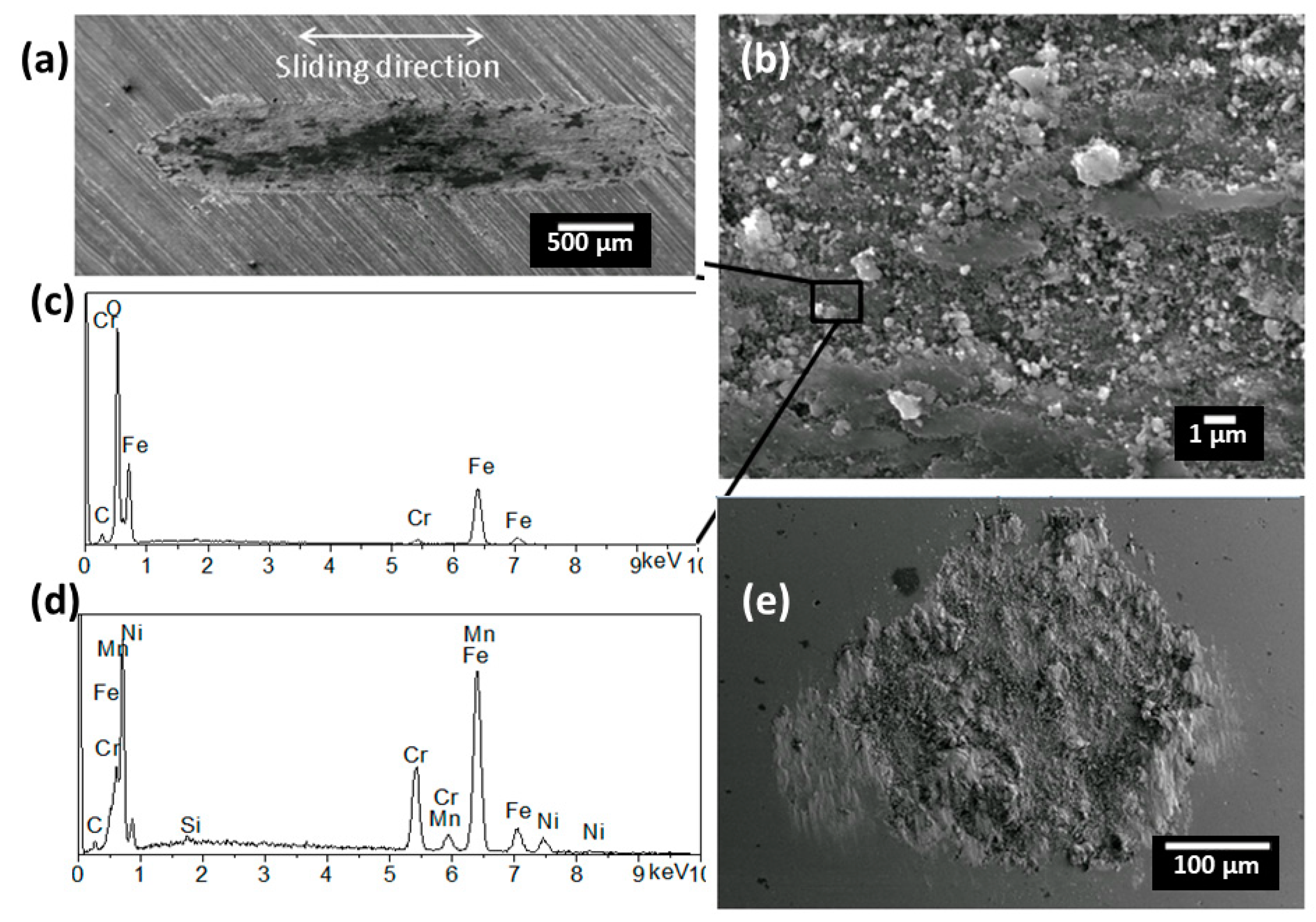
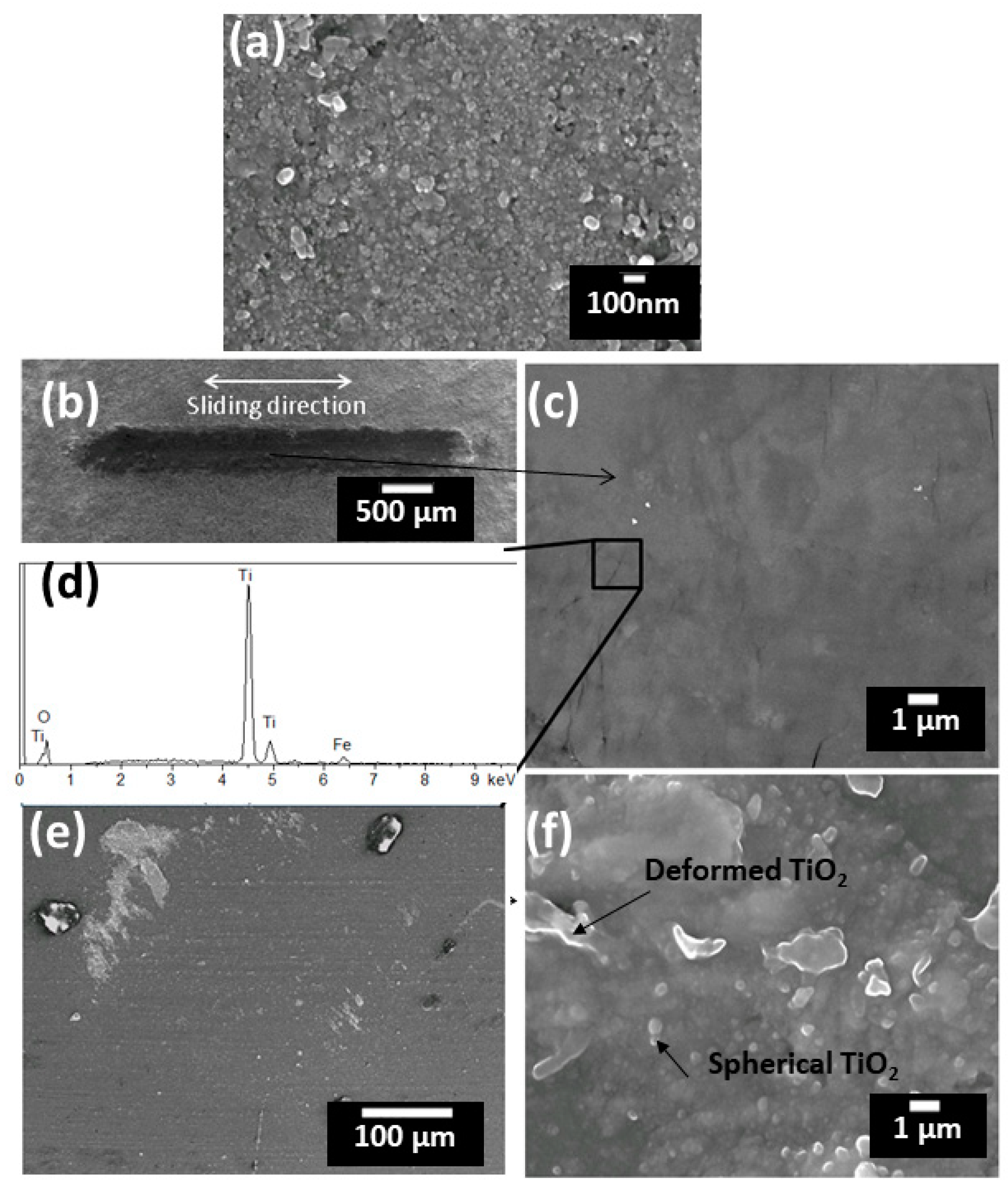
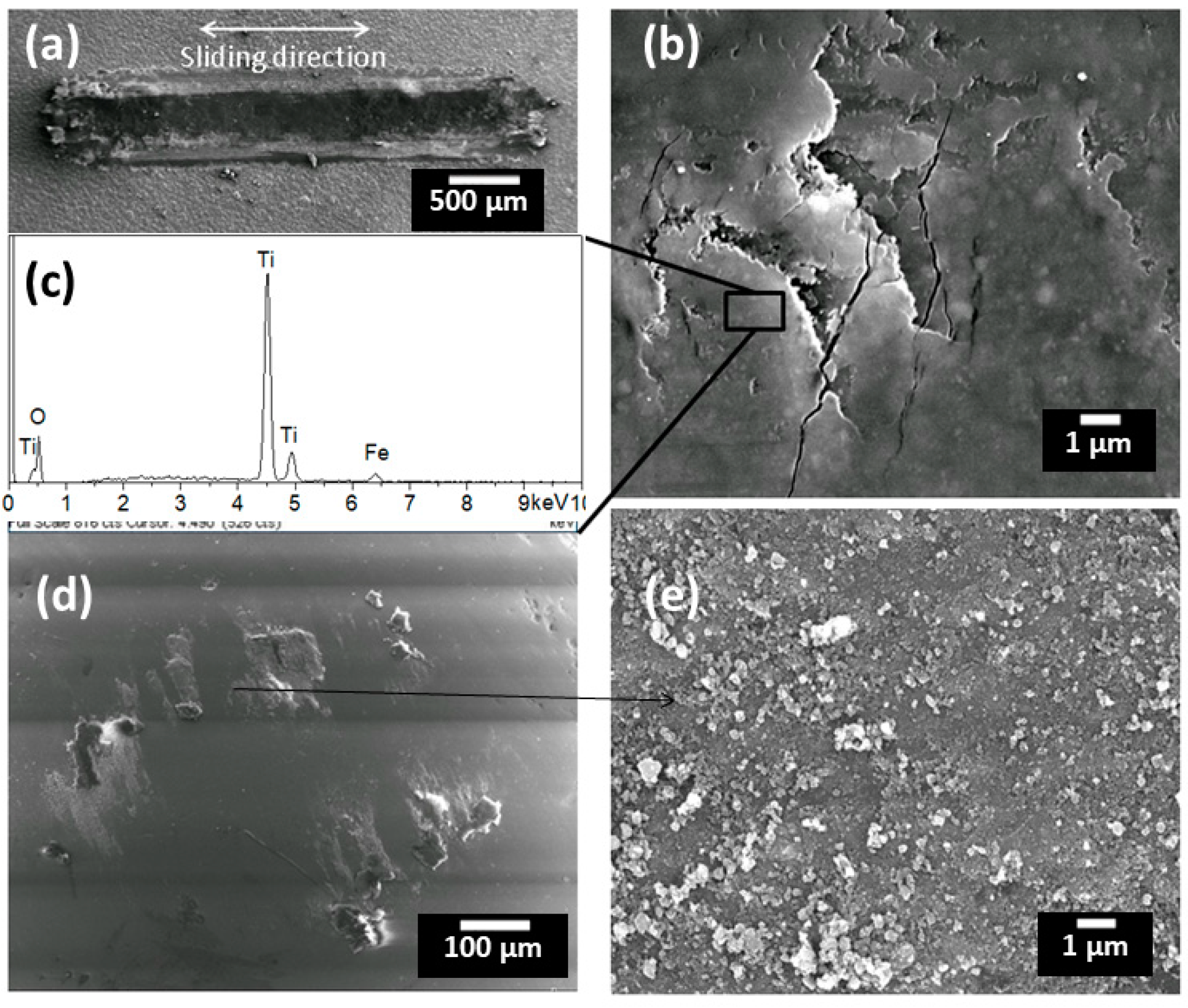
3.3. Friction and Wear Behaviour
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Increasing extents of feedstock melting corresponded to increased rutile contents in the coatings, which led to an increase in overall hardness with a reduced plasticity.
- The as-sprayed surface roughness did not seem play an important role for tribological performance of the developed coatings when their Ra varied between 0.53 and 1.18 µm.
- The coating composed of most agglomerate particles (12% melted particles) had the lowest coefficient of friction, whereas the coating composed of mostly melted particles (81% melted particles) presented the highest coefficient of friction. Results also indicate that a higher fraction of agglomerated particles (proportional to anatase content) were beneficial to the formation of tribo-film at sliding surfaces.
- Wear resistance of the coatings were proven to be not rational to their hardness. The coating with mostly agglomerate particles (12% melted splats) had the lowest wear rate and the coating with moderate melted particles (51%) had the worst performance against wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toma, F.-L.; Potthoff, A.; Berger, L.-M.; Leyens, C. Demands, potentials, and economic aspects of thermal spraying with suspensions: A critical review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.S.; Marple, B.R. Thermal spray coatings engineered from nanostructured ceramic agglomerated powders for structural, thermal barrier and biomedical applications: A review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2007, 16, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchais, P.; Montavon, G.; Lima, R.S.; Marple, B.R. Engineering a new class of thermal spray nano-based microstructures from agglomerated nanostructured particles, suspensions and solutions: An invited review. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, R.; Rauch, A.; Rauch, J. Introduction to high velocity suspension flame spraying (HVSFS). J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2008, 17, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Sil, A.; Jayaganthan, R. A study on sliding and erosive wear behaviour of atmospheric plasma sprayed conventional and nanostructured alumina coatings. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Liao, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Normand, B.; Ji, V.; Ding, C.X.; Coddet, C. Improvement in wear resistance of plasma sprayed yttria stabilized zirconia coating using nanostructured powder. Tribol. Int. 2004, 37, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Hwang, B.; Song, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, N. Correlation of microstructure and wear resistance of Al2O3-TiO2 coatings plasma sprayed with nanopowders. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.S.; Moreau, C.; Marple, B.R. HVOF-sprayed coatings engineered from mixtures of nanostructured and submicron Al2O3-TiO2 powders: An enhanced wear performance. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2007, 16, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, C. Tribological properties of nanostructured zirconia coatings deposited by plasma spraying. Wear 2002, 253, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.P.; Ahn, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.J. Microstructure and wear resistance of nanostructured Al2O3–8wt.% TiO2 coatings plasma-sprayed with nanopowders. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.H.; Gell, M.; Sohn, Y.H.; Goberman, D.; Shaw, L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Xiao, T.D.; Wang, Y.; Strutt, P. Fabrication and evaluation of plasma sprayed nanostructured alumina–titania coatings with superior properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 301, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Goberman, D.; Shaw, L.; Gell, M. Indentation fracture behavior of plasma-sprayed nanostructured Al2O3–13wt.%TiO2 coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 346, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darut, G.; Ageorges, H.; Denoirjean, A.; Fauchais, P. Tribological performances of YSZ composite coatings manufactured by suspension plasma spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 217, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Robinson, B.W.; de Villiers-Lovelock, H.; Wood, R.J.K.; Wang, S.C. Wettability of hierarchically-textured ceramic coatings produced by suspension HVOF spraying. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13864–13873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F. Suspension HVOF Sprayed Coatings for Specialised Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Toma, F.L.; Sokolov, D.; Bertrand, G.; Klein, D.; Coddet, C.; Meunier, C. Comparison of the photocatalytic behavior of TiO2 coatings elaborated by different thermal spraying processes. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2006, 15, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgese, L.; Gelfi, M.; Bontempi, E.; Goudeau, P.; Geandier, G.; Thiaudiere, D.; Depero, L.E. Young modulus and Poisson ratio measurements of TiO2 thin films deposited with Atomic Layer Deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G133-05 Standard Test Method for Linearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Mandzy, N.; Grulke, E.; Druffel, T. Breakage of TiO2 agglomerates in electrostatically stabilized aqueous dispersions. Powder Technol. 2005, 160, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joud, J.C.; Houmard, M.; Berthomé, G. Surface charges of oxides and wettability: Application to TiO2–SiO2 composite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 287, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, R.; Shoja-Razavi, R.; Mozafarinia, R.; Jamali, H. Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of plasma-sprayed nanostructured and conventional yttria stabilized zirconia thermal barrier coatings. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 8805–8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannier, E.; Darut, G.; Sanchez, E.; Denoirjean, A.; Bordes, M.C.; Salvador, M.D.; Rayon, E.; Ageorges, H. Microstructure and photocatalytic activity of suspension plasma sprayed TiO2 coatings on steel and glass substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozerski, S.; Łatka, L.; Pawlowski, L.; Cernuschi, F.; Petit, F.; Pierlot, C.; Podlesak, H.; Laval, J.P. Preliminary study on suspension plasma sprayed ZrO2 + 0.8wt.% Y2O3 coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, K. Hardness Testing: Principles and Applications; ASM International: Geauga County, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rayón, E.; Bonache, V.; Salvador, M.D.; Bannier, E.; Sánchez, E.; Denoirjean, A.; Ageorges, H. Nanoindentation study of the mechanical and damage behaviour of suspension plasma sprayed TiO2 coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ctibor, P.; Neufuss, K.; Chraska, P. Microstructure and abrasion resistance of plasma sprayed titania coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2006, 15, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, S.C.; Wood, R.J.K.; Zekonyte, J.; Luo, Q.; Walsh, F.C. Hardness of porous nanocrystalline Co-Ni electrodeposits. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, L. The Science and Engineering of Plasma-Sprayed Coatings; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, S.H.; Lin, C.K.; Berndt, C.C. Elastic response of thermal spray deposits under indentation tests. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 2093–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolelli, G.; Cannillo, V.; Gadow, R.; Killinger, A.; Lusvarghi, L.; Rauch, J. Properties of high velocity suspension flame sprayed (HVSFS) TiO2 coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Tang, B.; Li, X.Y. Microstructure and wear resistance of N-doped TiO2 coatings grown on stainless steel by plasma surface alloying technology. J. Iron. Steel. Res. Int. 2011, 18, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, R.; Pawlowski, L.; Roudet, F.; Kozerski, S.; Petit, F. Characterization of mechanical properties of suspension plasma sprayed TiO2 coatings using scratch test. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.S.; Marple, B.R. Superior performance of high-velocity oxyfuel-sprayed nanostructured TiO2 in comparison to air plasma-sprayed conventional Al2O3-13TiO2. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2005, 14, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prchlik, L.; Sampath, S. Effect of the microstructure of thermally sprayed coatings on friction and wear response under lubricated and dry sliding conditions. Wear 2007, 262, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hawthorne, H.M. The damage mechanisms of several plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings in controlled scratching. Wear 1999, 233–235, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Ang, A.S.M.; Pala, Z.; Shaw, E.C.; Hussain, T. Suspension High Velocity Oxy-Fuel (SHVOF)-sprayed alumina coatings: Microstructure, nanoindentation and wear. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2016, 25, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
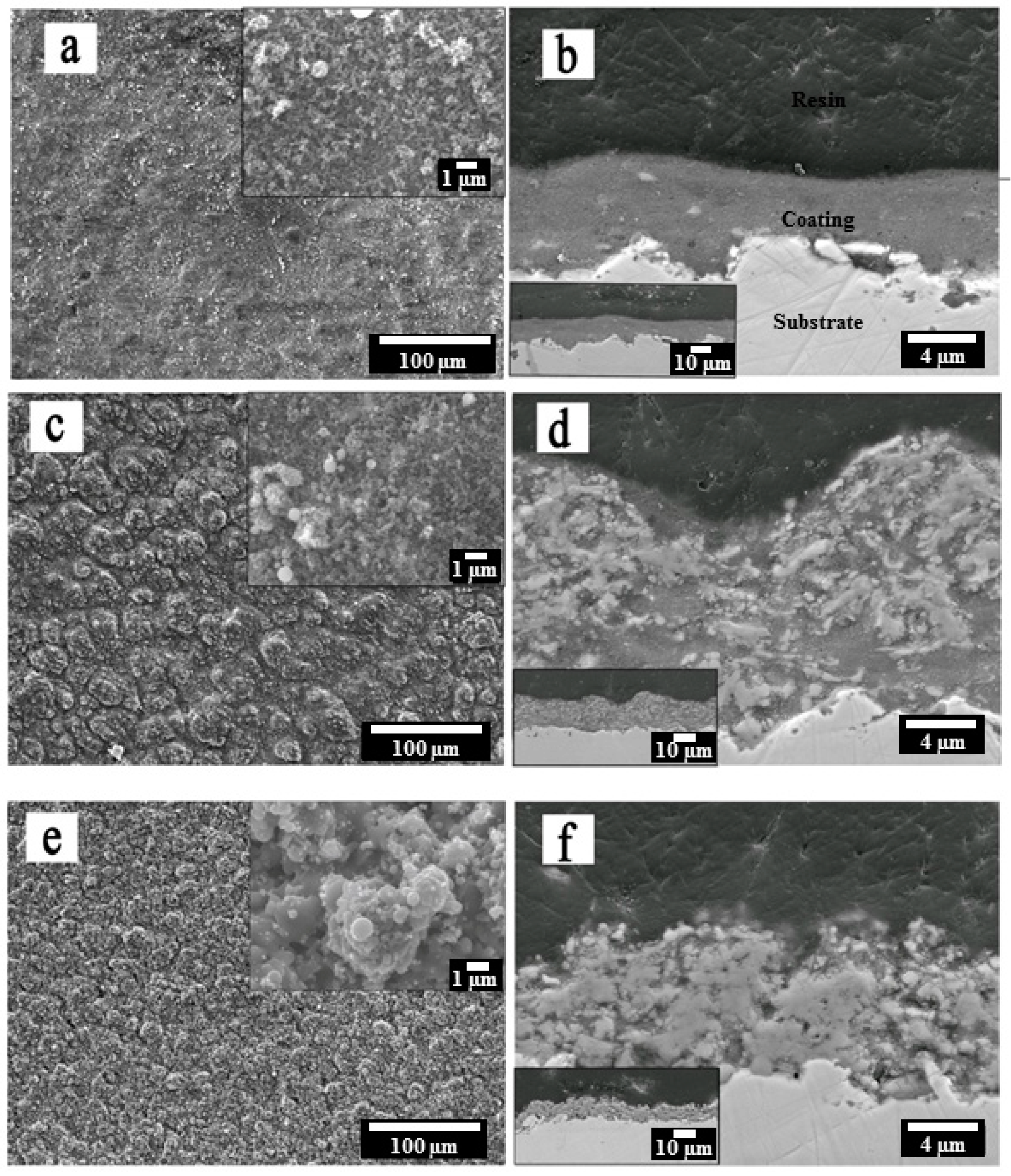
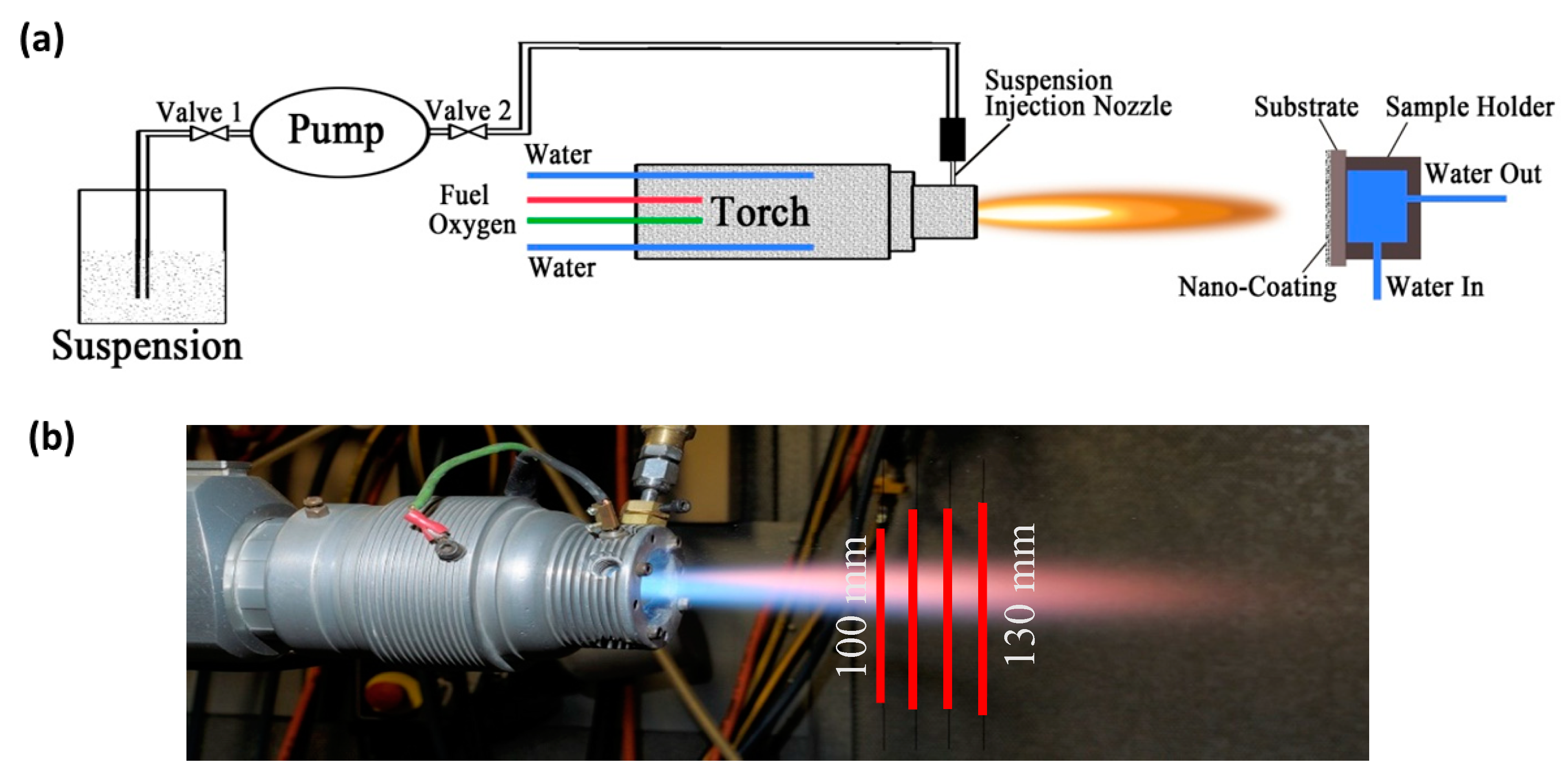
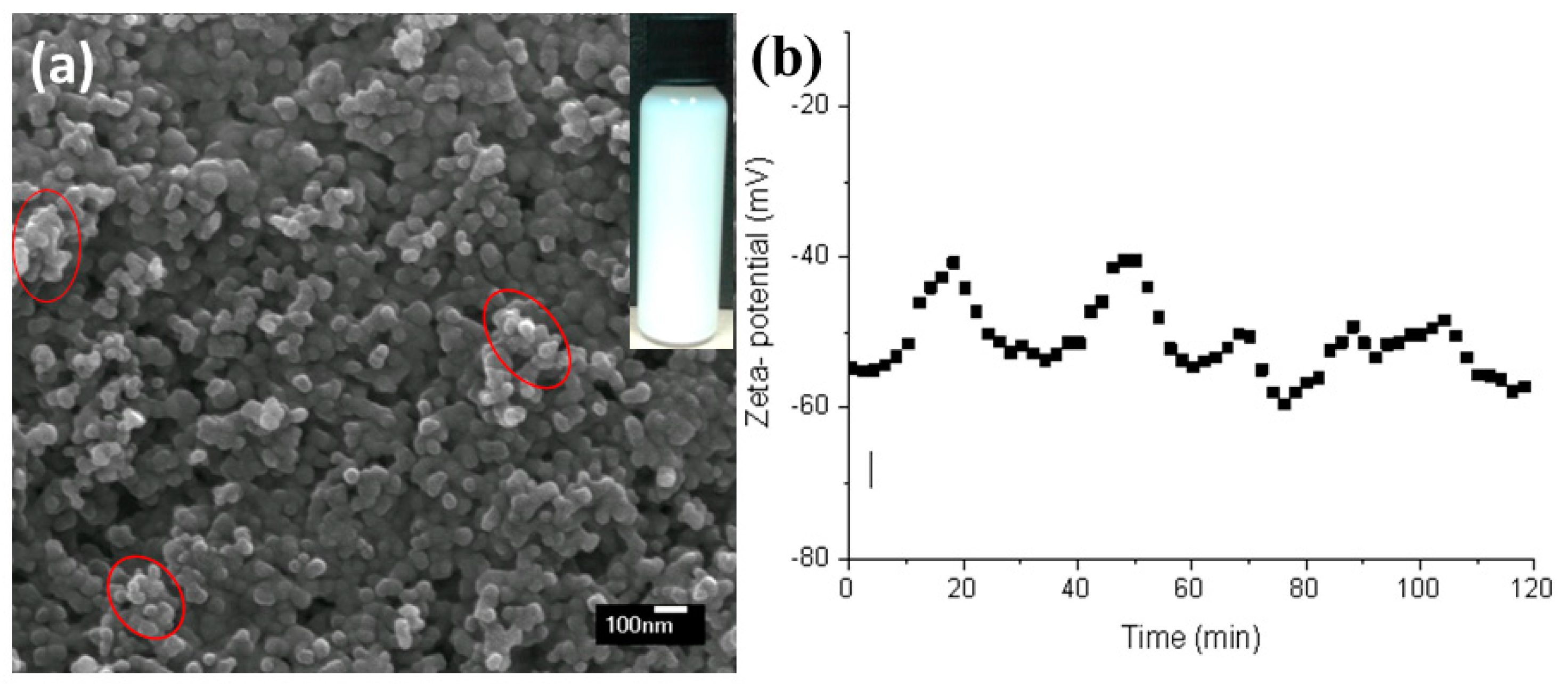


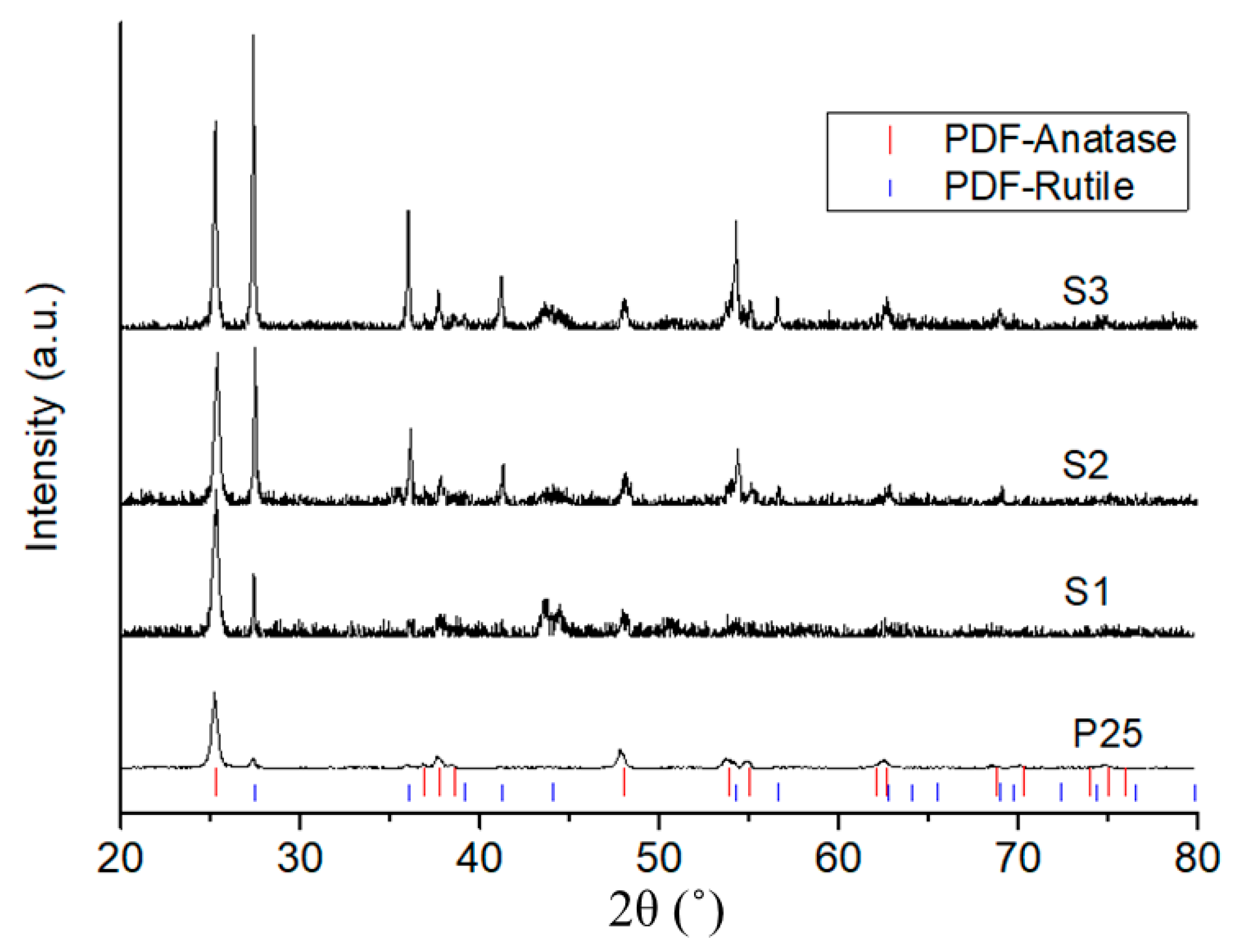
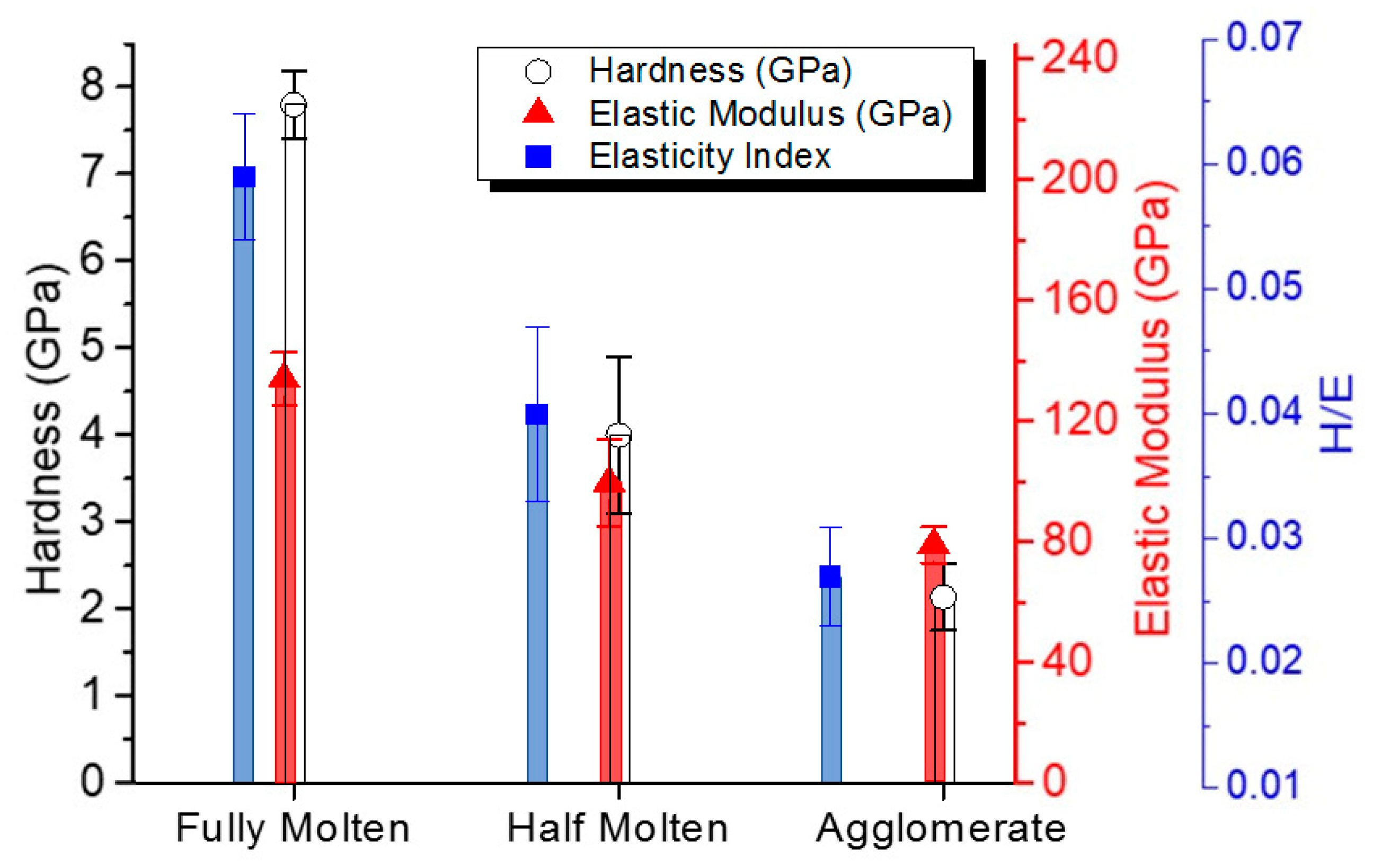


| Label | Suspension Feed Rate, mL/min | Solvent, v/v | Spray Distance, mm | Fuel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 20 | H2O:isopropanol = 9:1 | 130 | Propylene |
| S2 | 20 | H2O:isopropanol = 10:0 | 100 | Hydrogen |
| S3 | 20 | H2O:isopropanol = 9:1 | 150 | Hydrogen |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Pass spacing, mm | 2 |
| Torch linear velocity, mm/s | 600 |
| Torch cooling system | Water cooling |
| Combustion chamber length, mm | 135 |
| Profile of suspension nozzle, mm | 0.3/orifice |
| Number of passes | 15 |
| Flame condition 1 | – |
| Propylene flow rate, slpm | 80.5 |
| Oxygen flow rate, slpm | 280.0 |
| Flame condition 2 | – |
| Hydrogen flow rate, slpm | 788.0 |
| Oxygen flow rate, slpm | 264.0 |
| Samples | Hardness Hv, GPa | Surface Roughness Ra, µm | Wear Rate, ×10−7 mm3/Nm | Coefficient of Friction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304SS | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 0.56 ± 0.14 | 5.13 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
| S1 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 0.35 ± 0.02 |
| S2 | 4.0 ± 0.9 | 1.18 ± 0.18 | 5.13 ± 0.13 | 0.48 ± 0.04 |
| S3 | 7.8 ± 0.4 | 0.96 ± 0.17 | 1.77 ± 0.05 | 0.62 ± 0.03 |
| Spray Distance | CR, % | Surface Roughness, μm | Coefficient of Friction | Specific Wear Rate, ×10−7 mm3/(N m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mm | 58 | 0.72 ± 0.10 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 2.47 ± 0.07 |
| 110 mm | 53 | 0.44 ± 0.15 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 2.01 ± 0.09 |
| 120 mm | 45 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.64 ± 0.07 |
| 130 mm | 41 | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.02 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Robinson, B.W.; Lovelock, H.L.d.V.; Wood, R.J.K. Structure-Property Relationships in Suspension HVOF Nano-TiO2 Coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080504
Zhang F, Wang S, Robinson BW, Lovelock HLdV, Wood RJK. Structure-Property Relationships in Suspension HVOF Nano-TiO2 Coatings. Coatings. 2019; 9(8):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080504
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Feifei, Shuncai Wang, Ben W. Robinson, Heidi L. de Villiers Lovelock, and Robert J.K. Wood. 2019. "Structure-Property Relationships in Suspension HVOF Nano-TiO2 Coatings" Coatings 9, no. 8: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080504
APA StyleZhang, F., Wang, S., Robinson, B. W., Lovelock, H. L. d. V., & Wood, R. J. K. (2019). Structure-Property Relationships in Suspension HVOF Nano-TiO2 Coatings. Coatings, 9(8), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080504






