Electrochemical Oxidation of Pb II Using Carbon Electrodes Doped with Nanocellulose-FeOx
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
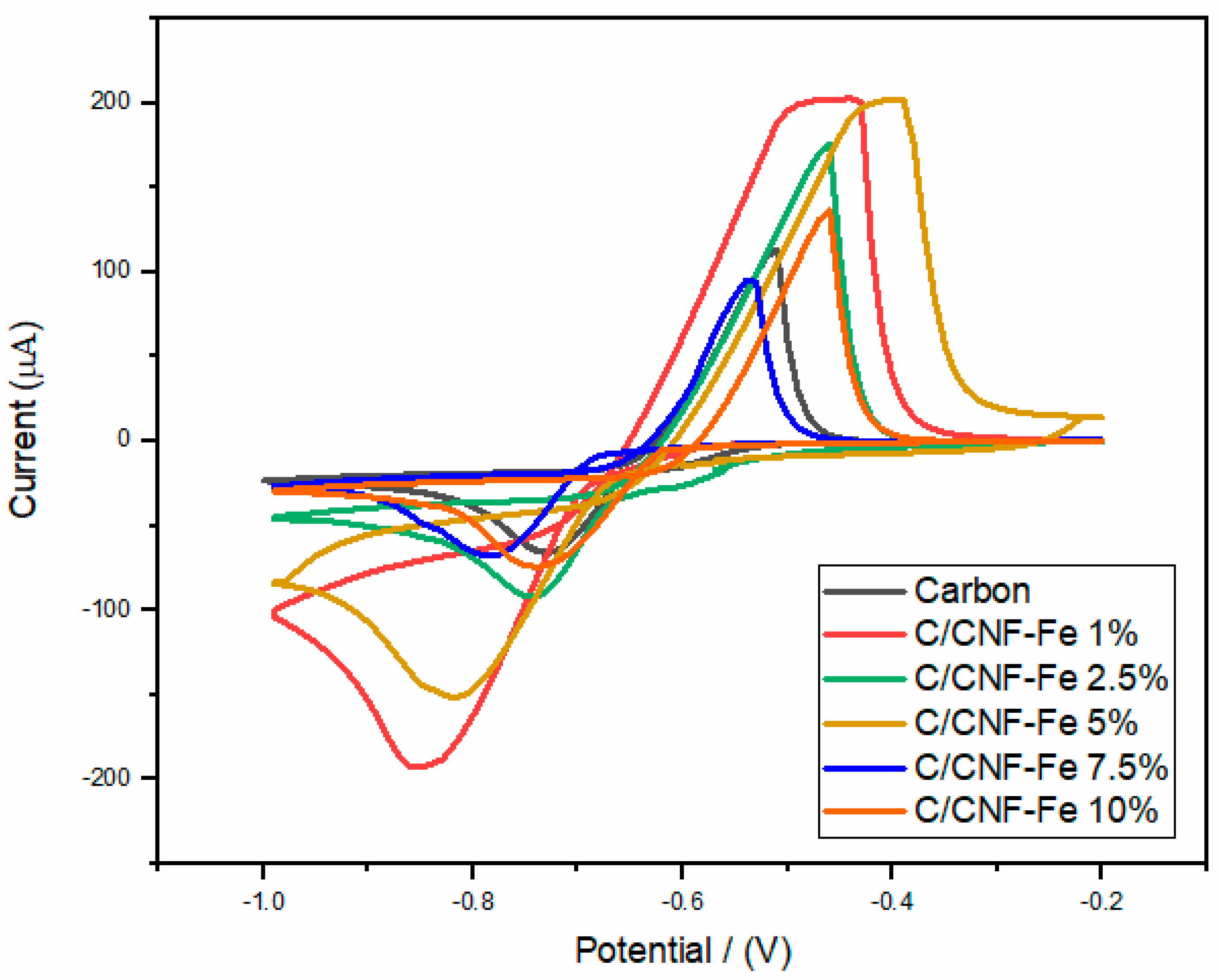
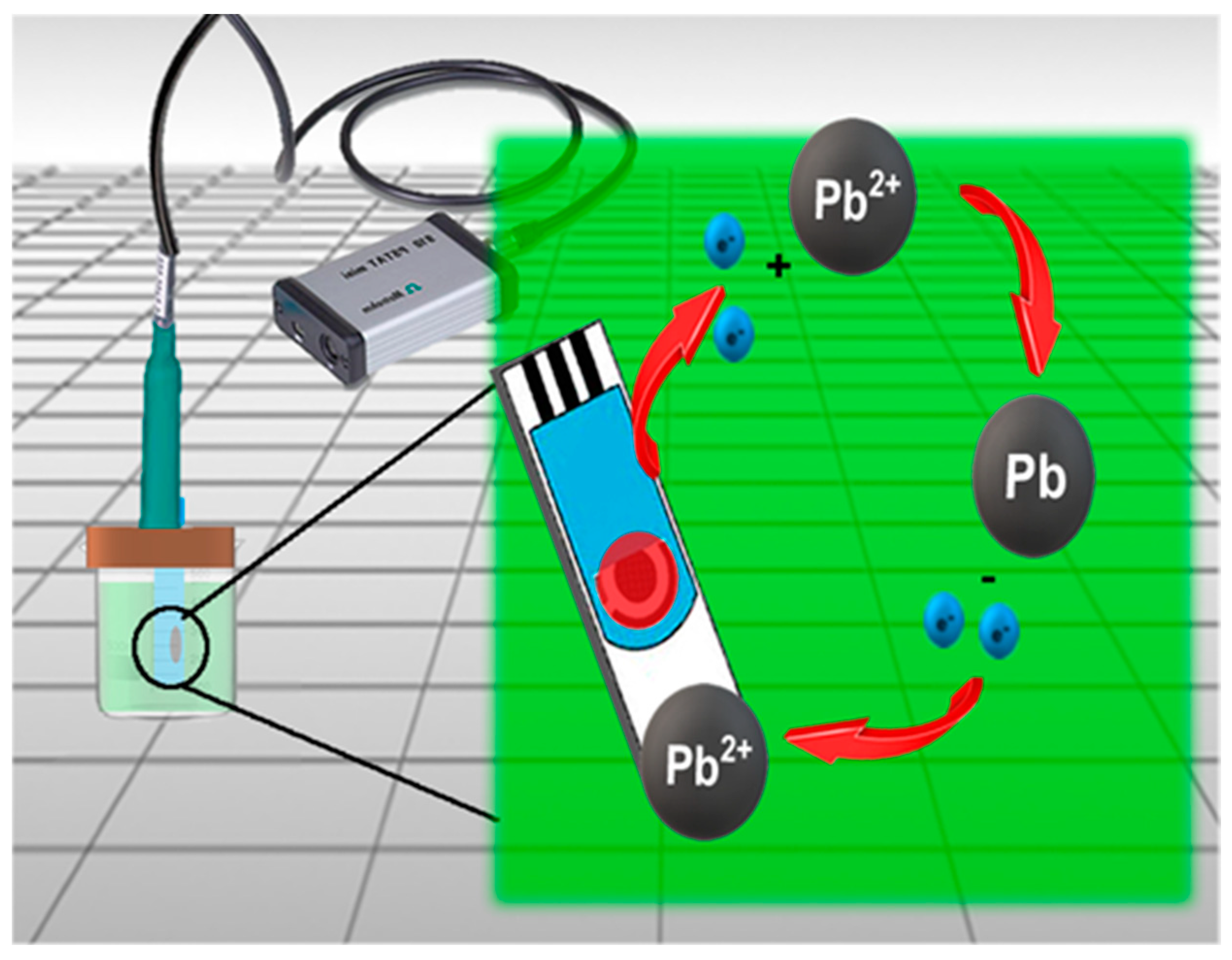
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, Y.S.; Risbud SRabolt, J.F.; Stroeve, P. Synthesis and characterization of nanometer-size Fe3O5 and γ-Fe2O3 particles. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 2209–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobson, J. Gene therapy progress and prospects: Magnetic nanoparticle-based gene delivery. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudgne, S.; Peterson, C.; Vessely, C.; Koda, J.; Stevens, S.; Catterall, L. Adsorption and desorption of chemotherapeutic drugs from a magnetically carrier (MTC). J. Control. Release 2001, 74, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appenzeller, T. The Man Who Dared to Think Small. Science 1991, 254, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine appli-cation. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Gao, J.; Wu, G.; Liu, P.; Guo, W.; Zhou, H.; Ge, J.; Hu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Amorphous Metal Oxide Nanosheets Featuring Reversible Structure Transformations as Sodium-Ion Battery Anodes. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Q. Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy matel biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 2003, 37, 43311–44330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y. Enhanced removal of Hg(II) from acidic aqueous solution using thiol-functionalized biomass. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Chen, B.; Qin, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, J. Facile Ultrasonic Synthesis of CoO Quantum Dot/Graphene Nanosheet Composites with High Lithium Storage Capacity. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, C.; Xie, M.; Sun, H.; Hu, T.; Lu, F.; Scott, S.M.; George, S.M.; Lian, J. Synthesis of ZnO quantum dot/graphene nanocomposites by atomic layer deposition with high lithium storage capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7319–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-S.; Zhou, G.; Yin, L.-C.; Ren, W.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.-M. Graphene/metal oxide composite electrode materials for energy storage. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongruang, S. Bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum strains from agricultural waste products. In Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals, Proceedings of the ABAB Symposium (Part A: Enzyme Engineering and Biotechnology), Denver, CO, USA, 29 April–2 May 2007; Adney, W.S., McMilland, J.D., Mielenz, J., Klasson, K.T., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraj, S.H.; Gupta, S.G. Production of bacterial cellulose from Enterobacter amnigenus GH-1 isolated from rotten apple. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, C.G.C.; Thomas, H.; Andreas, K.; Beatriz, M.C.A.; Uzziel, P.B.E.; María, Z.A. Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Thypha domingensis Named Southern Cattail Using a Batch Reactor. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Z.; Zhu, H.; Gillette, E.; Han, X.; Rubloff, G.W.; Hu, L.; Lee, S.B. Natural Cellulose Fiber as Substrate for Supercapacitor. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6037–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tammela, P.; Strømme, M.; Nyholm, L. Cellulose-based Supercapacitors: Material and Performance Considerations. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, D.-W.; Li, F.; Du, J.; Cheng, H.-M. Graphene-Cellulose Paper Flexible Supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Shao, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Peng, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, F. Cellulose nanofiber-graphene all solid-state flexible supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Feng, T.; Yao, Q.; Xie, J.; Xia, H. Fe2O3Nanoneedles on Ultrafine Nickel Nanotube Arrays as Efficient Anode for High-Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Fu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Tao, X.; Zhi, C.; Hu, H. A high-performance fiber-shaped PEDOT@MnO2//C@Fe3O4 asymmetric supercapacitor for wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14877–14883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Ton, Y. Advanced Ti-Doped Fe2O3@PEDOT Core/Shell Anode for High-Energy Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1402176. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Isogai, A. Cellulose Nanofibers Prepared by TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation of Native Cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Tan, S.; Gao, J.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of Ag nanoparticles on the nanocellulose and their antibacterial study. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 100, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Guerrero, C.F.; Gray, D.G. Chiral nematic phase formation by aqueous suspensions of cellulose nanocrystals prepared by oxidation with ammonium persulfate. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2567–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macclesh del Pino, L.A.; Morales, A.B.; Castro, C.F.; Leon, U. In situ synthesis of Ag/AgCl nanoparticles in a Cellulose nanofibers matrix via in situ: A conductive paper. Cellulose 2021, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorova, I.; Botto, R.E.; Arisz, P.W.; Boon, J.J. Cellulose char structure: A combine analytical Py-GC-MS, FTIR and NMR study. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 262, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.S. Methylcellulose synthesis from corn cobs study of the effect of solvent 421 conditions on product properties by thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 809. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Cheng, J.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Hyun, J. Elecromagnetic nanocomposite of bacterial cellulose using magnetite nanoclusters and polyaniline. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Liu, T. Characterization of nanoparticles by scattering techniques. J. Nanoparticles Res. 2000, 2, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, A.N.; Panaitescu, D.M.; Spataru, D.D.; Radovici, C.; Trusca, R.; Somoghi, R. Preparation and characterization of PVA composites with cellulose nanofibers obtained by ultrasonication. BioResources 2011, 6, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, C.; Chauve, G.; Le Berre, J.-F.; Methot, M.; O’Connor, B.; Bouchard, J. Critical discussion of light scattering and mi-croscopy techniques for CNC particle sizing. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2014, 29, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, C.; Saini, A.; Maji, P.K. Energy efficient facile extraction process of cellulose nanofibers and their dimensional characterization using their dimensional characterization using light. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucrsch, A.; Littke, W.; Lang, P.; Burchard, W. Static and dynamic light scattering on solutions of precrystalline be-ta-galactosidase. J. Cryst. Growth 1991, 110, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Liu, A.-H.; Liu, G.-Y.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Zhong, X.-B.; Ma, X.-Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.-Y. Fe3O4–pyrolytic graphite oxide composite as an anode material for lithium secondary batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Jiang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Microemulsion-mediated hydrothermal growth of pagoda-like Fe3O4 microstructures and their application in a lithium–air battery. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8843–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lu, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, T.; Du, P.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Wen, J.; Miller, D.J.; Miller, J.T.; et al. Synthesis of Porous Carbon Supported Palladium Nanoparticle Catalysts by Atomic Layer Deposition: Application for Rechargeable Lithium–O2 Battery. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Deng, S.; Fan, H.M.; Mhaisalkar, S.; Tan, H.R.; Tok, E.S.; Loh, K.P.; Chin, W.S.; Sow, C.H. α-Fe2O3 nanotubes-reduced graphene oxide composites as synergistic electrochemical capacitor materials. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2958–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, I.J.; Sotiropoulos, S. Electrodeposition of Ni from a high internal phase emulsion (HIPE) template. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liao, Y.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lu, X. Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in cellulose nanofibre/graphite carbon hybrid aerogels as advanced negative electrodes for flexible asymmetric supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17378–17388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Kandasamy, G.; Upadhyay, R.K.; Bhattacharya, G.; Banerjee, D.; Maity, D.; Deshusses, M.A.; Roy, S.S. Terephthalic acid capped iron oxide nanoparticles for sensitive electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions in water. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 788, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, V.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Preparation of high surface area nickel electrodeposit using a liquid crystal template technique. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Yu, L.; Ma, W.; Geng, B.; Zhang, X. Flexible superior electrode architectures based on three-dimensional porous spinous α-Fe2O3 with a high performance as a supercapacitor. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 9581–9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhayati, E.; Juang, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, C.-C. Effects of dynamic polarization on boron-doped NCD properties and on its performance for electrochemical-analysis of Pb (II), Cu (II) and Hg (II) in aqueous solution via direct LSV. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-F.; Zhao, L.-J.; Jiang, T.-J.; Li, S.-S.; Yang, M.; Huang, X.-J. Sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions using amino-functionalized carbon microspheres. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 760, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Filho, L.C.S.; Janegitz, B.C.; Fatibelilo-Filho, O.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Banks, C.E. Inexpensive and disposable copper mini-sensor modified with bismuth for lead and cadmium determination using square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghill, K.E.; Xiao, L.; Wildgoose, G.G.; Compton, R.G. Electroanalytical Determination of Cadmium(II) and Lead(II) Using an Antimony Nanoparticle Modified Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Calabuig, A.; Guerrero, D.; Serrano, N.; del Valle, M. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Heavy Metals by Use of Crown Ether-modified Electrodes and Chemometrics. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
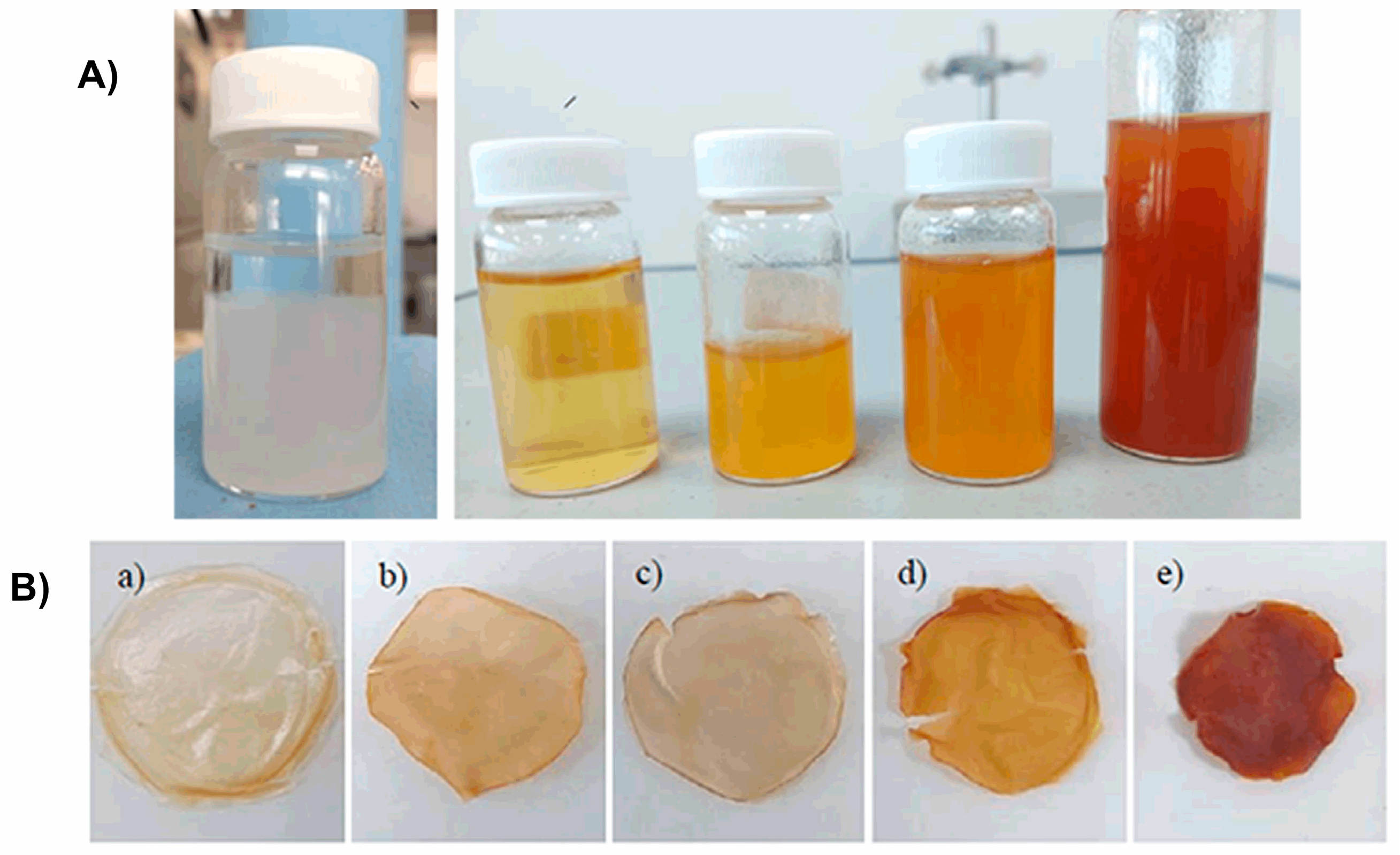
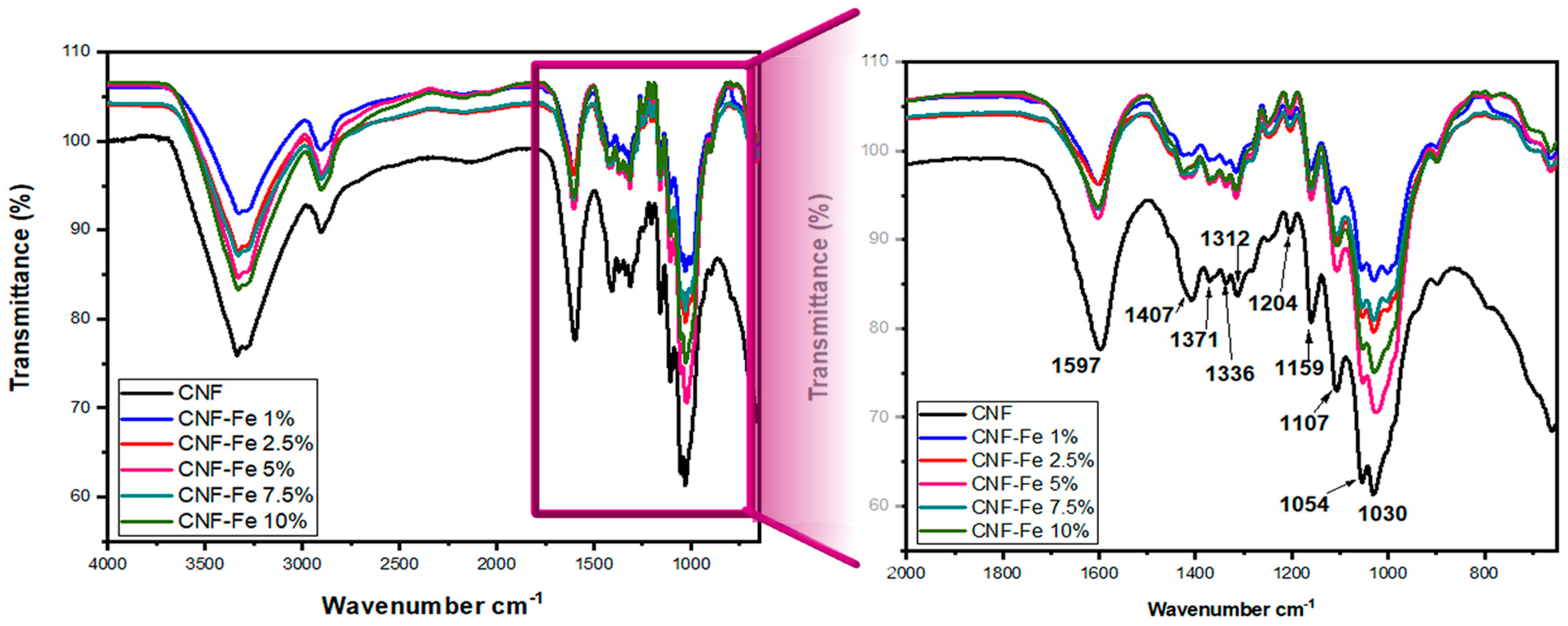
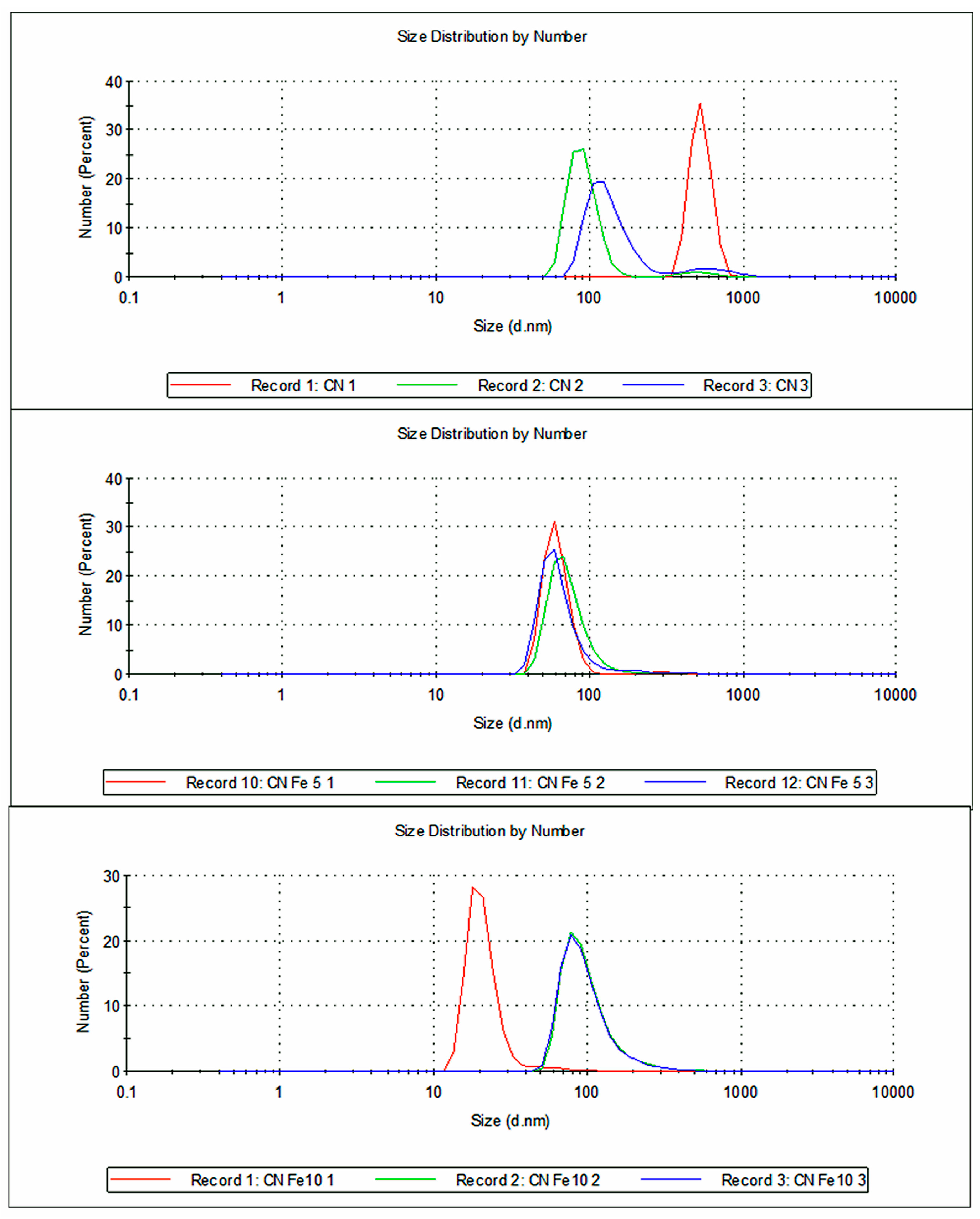
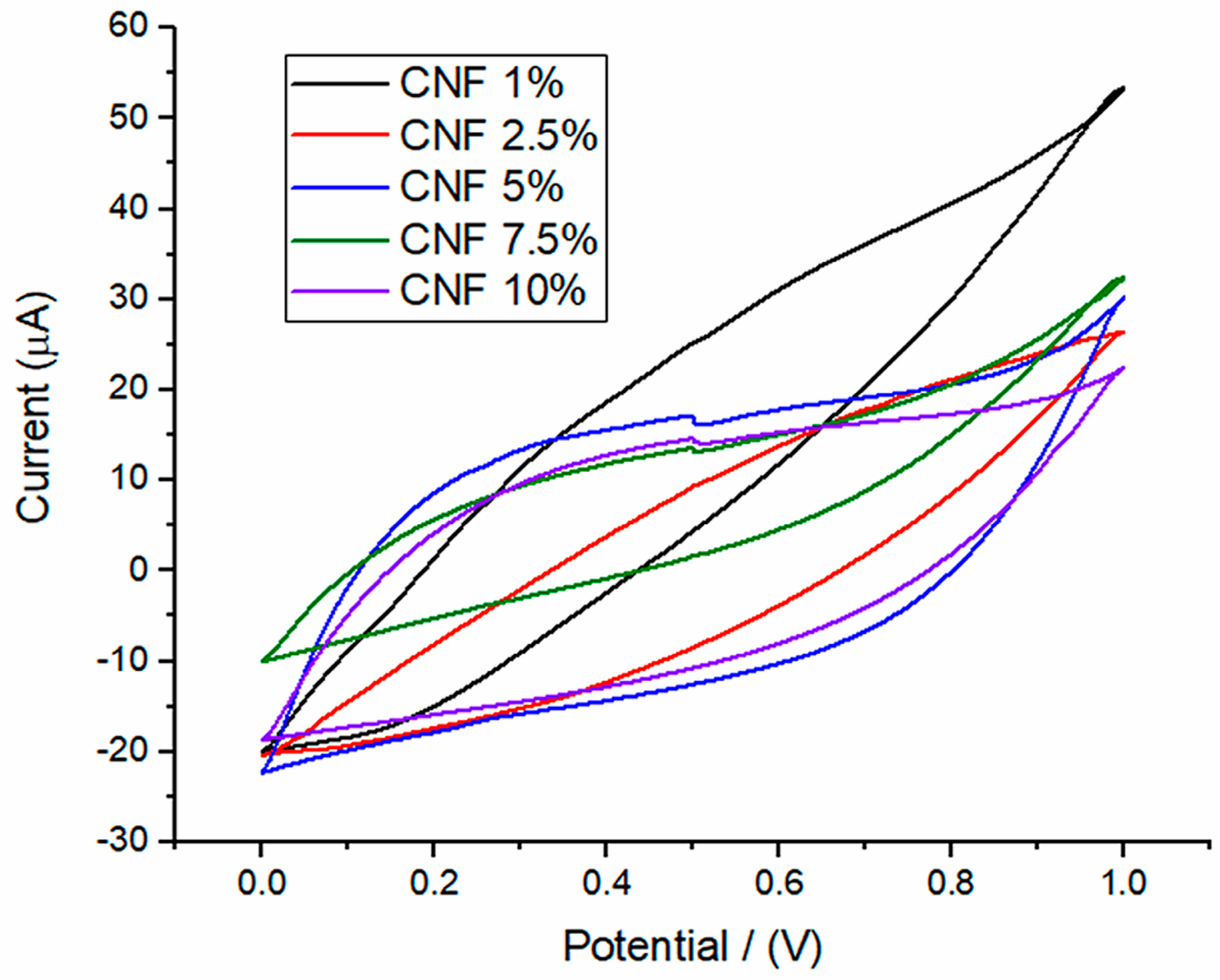
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 3336 | O-H Stretching vibration | Zhang X. et al. [25] |
| 2905 | CH-Stretching vibration | Zhang X. et al. [25] |
| 1579 | C=O Streching vibration | Castro-Guerrero et al. [26] |
| 1407 | CH2- Pyranose ring Vibration | Pastorova, I. [28] |
| 1202 | C-O-C Streching | Rai, K. [29] |
| Electrode Material | Ion | Concentration (μM) | LOD (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond (BD-NCD) | Pb(II) | 1–22.5 | 1.399 | [45] |
| Amino-Carbon microsphere (NH2-CMS) | Pb(II) | 0.5–1.2 | 0.05 | [46] |
| Copper mini-sensor modified with bismuth | Pb(II) Cd(II) | 1.3–13 | 0.8 | [47] |
| Antimony Nanoparticle Modified Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode | Pb(II) Cd(II) | 0.2–2.41 | 0.12 | [48] |
| Terephthalic acid capped iron oxide nanoparticles | Pb(II) Cd(II) Hg(II) | 0.4–1.1 | 0.04 | [42] |
| Crown Ether-modified Electrodes | Pb(II) Cd(II) Hg(II) | 0.2–0.9 | 0.05 | [49] |
| Carbon electrode modified with CNF-Fe 5 % | Pb(II) | 0.2–1.2 | 0.23 | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez-Rojas, A.G.; Macclesh del Pino-Perez, L.A.; Castro-Guerrero, C.F.; Ramos-Galvan, C.E.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B. Electrochemical Oxidation of Pb II Using Carbon Electrodes Doped with Nanocellulose-FeOx. Fibers 2023, 11, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib11010008
Gomez-Rojas AG, Macclesh del Pino-Perez LA, Castro-Guerrero CF, Ramos-Galvan CE, Morales-Cepeda AB. Electrochemical Oxidation of Pb II Using Carbon Electrodes Doped with Nanocellulose-FeOx. Fibers. 2023; 11(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib11010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez-Rojas, Araceli G., Luis Alejandro Macclesh del Pino-Perez, Carlos Fernando Castro-Guerrero, Claudia Esmeralda Ramos-Galvan, and Ana Beatriz Morales-Cepeda. 2023. "Electrochemical Oxidation of Pb II Using Carbon Electrodes Doped with Nanocellulose-FeOx" Fibers 11, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib11010008
APA StyleGomez-Rojas, A. G., Macclesh del Pino-Perez, L. A., Castro-Guerrero, C. F., Ramos-Galvan, C. E., & Morales-Cepeda, A. B. (2023). Electrochemical Oxidation of Pb II Using Carbon Electrodes Doped with Nanocellulose-FeOx. Fibers, 11(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib11010008






