Reinforcement of Environmental DNA Based Methods (Sensu Stricto) in Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation: A Review
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
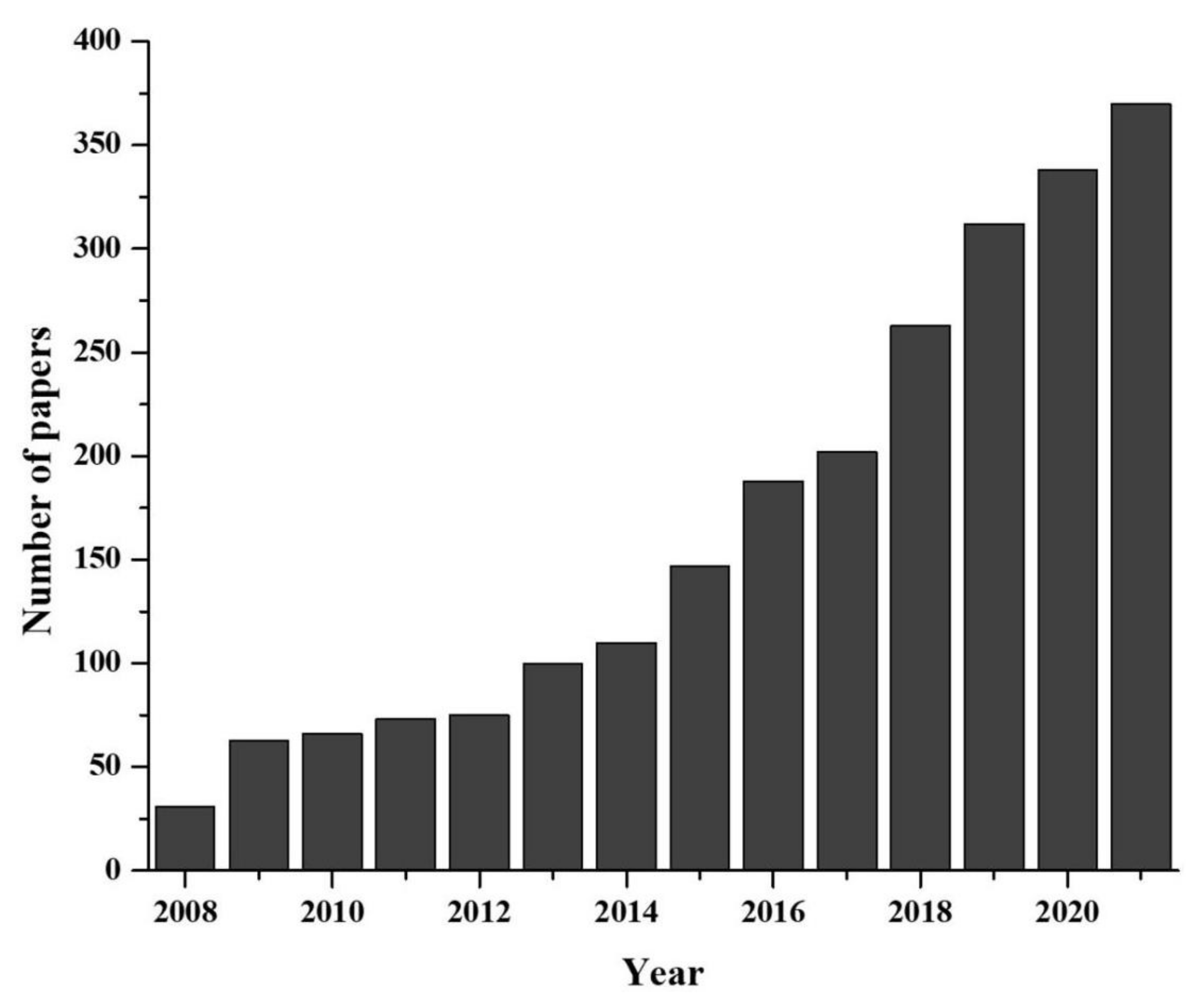
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Sampling and Laboratory Protocol for eDNA
2.1. Collection and Accumulation of eDNA Samples
2.1.1. Aquatic Environment
2.1.2. Terrestrial Environment
2.1.3. Extraction of eDNA from Other Organisms without Isolating Target Taxa
2.2. Preservation of Samples in eDNA Technique
2.3. The eDNA Analysis in Laboratory
3. Precautions in eDNA Study
3.1. Precautions in Field
3.2. Precautions in Laboratory
4. Application of eDNA in Conservation Biology
4.1. Early Detection of Invasive Species
4.2. Species Detection for Conservation
4.3. Biodiversity Monitoring at the Community Level
5. Current Research Focus
6. Recommendation of eDNA Study and Future Perspective
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arneth, A.; Shin, Y.-J.; Leadley, P.; Rondinini, C.; Bukvareva, E.; Kolb, M.; Midgley, G.F.; Oberdorff, T.; Palomo, I.; Saito, O. Post-2020 biodiversity targets need to embrace climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30882–30891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titeux, N.; Brotons, L.; Settele, J. IPBES Promotes Integration of Multiple Threats to Biodiversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 969–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Palacios, C.; Wiens, J.J. Recent responses to climate change reveal the drivers of species extinction and survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4211–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiner, K.; Fronhofer, E.A.; Mächler, E.; Walser, J.-C.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA reveals that rivers are conveyer belts of biodiversity information. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berry, T.E.; Saunders, B.J.; Coghlan, M.L.; Stat, M.; Jarman, S.; Richardson, A.; Davies, C.H.; Berry, O.; Harvey, E.S.; Bunce, M. Marine environmental DNA biomonitoring reveals seasonal patterns in biodiversity and identifies ecosystem responses to anomalous climatic events. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogram, A.; Sayler, G.S.; Barkay, T. The extraction and purification of microbial DNA from sediments. J. Microbiol. Methods 1987, 7, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-unseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Pilliod, D.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L. Molecular Detection of Vertebrates in Stream Water: A Demonstration Using Rocky Mountain Tailed Frogs and Idaho Giant Salamanders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Duparc, A.; Pellier-Cuit, S.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C. Persistence of Environmental DNA in Freshwater Ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Miquel, C.; Taberlet, P.; Bellemain, E.; Miaud, C. Improved detection of an alien invasive species through environmental DNA barcoding: The example of the American bullfrogLithobates catesbeianus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Møller, P.R.; Rasmussen, M.; Willerslev, E. Detection of a Diverse Marine Fish Fauna Using Environmental DNA from Seawater Samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Wiuf, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Orlando, L.; Willerslev, E. Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 21, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Doi, H.; Kawabata, Z. Estimation of Fish Biomass Using Environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deiner, K.; Walser, J.-C.; Mächler, E.; Altermatt, F. Choice of capture and extraction methods affect detection of freshwater biodiversity from environmental DNA. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, J.; Apothéloz-Perret-Gentil, L.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA: What’s behind the term? Clarifying the terminology and recommendations for its future use in biomonitoring. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 4258–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Morissette, O.; Bean, C.W.; Manu, S.; Banerjee, P.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Beng, K.C.; Alter, S.E.; Roger, F.; Holman, L.E. Trade-offs between reducing complex terminology and producing accurate interpretations from environmental DNA: Comment on “Environmental DNA: What’s behind the term?” by Pawlowski et al., (2020). Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 4601–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: Opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Stewart, K.A.; Clemente-Carvalho, R.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Gong, C.; Ma, L.; Zhao, J.; Lougheed, S.C. Comparing fish prey diversity for a critically endangered aquatic mammal in a reserve and the wild using eDNA metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muha, T.P.; Skukan, R.; Borrell, Y.J.; Rico, J.M.; Garcia de Leaniz, C.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Consuegra, S. Contrasting seasonal and spatial distribution of native and invasive Codium seaweed revealed by targeting species-specific eDNA. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 8567–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Mächler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, D.M.; De Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banchi, E.; Ametrano, C.G.; Tordoni, E.; Stanković, D.; Ongaro, S.; Tretiach, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Muggia, L.; Verardo, P.; Tassan, F.; et al. Environmental DNA assessment of airborne plant and fungal seasonal diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Peng, Y.; Fang, W.; Altermatt, F.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. Application of Environmental DNA Metabarcoding for Predicting Anthropogenic Pollution in Rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11708–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fossøy, F.; Brandsegg, H.; Sivertsgård, R.; Pettersen, O.; Sandercock, B.K.; Solem, Ø.; Hindar, K.; Mo, T.A. Monitoring presence and abundance of two gyrodactylid ectoparasites and their salmonid hosts using environmental DNA. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Brown, A.D.; Daum, M.N.; De La Garza, K.A.; Driskill, J.; Garrett, K.; Goldstein, M.S.; Luk, A.; Maguire, J.I.; Moke, R.; et al. Detection of the Amphibian Pathogens Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) and Ranavirus in West Texas, USA, Using Environmental DNA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiner, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Bernatchez, L. The future of biodiversity monitoring and conservation utilizing environmental DNA. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, S.; Fossøy, F.; Larsen, B.M.; Brandsegg, H.; Sivertsgård, R.; Karlsson, S. Downstream transport and seasonal variation in freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) eDNA concentration. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.A.; Biessy, L.; Latchford, J.L.; Zaiko, A.; von Ammon, U.; Audrezet, F.; Cristescu, M.E.; Pochon, X. Release and degradation of environmental DNA and RNA in a marine system. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 704, 135314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, Y.; Kusakabe, A.; Tsuchida, K.; Tsuzuku, Y.; Okada, S.; Kitamura, T.; Tomita, S.; Mukai, T.; Tagami, M.; Takagi, M.; et al. Discovery of an unrecorded population of Yamato salamander (Hynobius vandenburghi) by GIS and eDNA analysis. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweiss, K.E.; Lehman, R.N.; Drymon, J.M.; Phillips, N.M. Development of highly sensitive environmental DNA methods for the detection of Bull Sharks, Carcharhinus leucas (Müller and Henle, 1839), using Droplet Digital™ PCR. Environ. DNA 2019, 2, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, S.; Takahara, T.; Doi, H.; Shibata, N.; Yamanaka, H. The detection of aquatic macroorganisms using environmental DNA analysis—A review of methods for collection, extraction, and detection. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, C.R.; Uy, K.L.; Everhart, R.C. Fish environmental DNA is more concentrated in aquatic sediments than surface water. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, M.E.; Oyler-McCance, S.; Dorazio, R.M.; Fike, J.A.; Smith, B.; Hunter, C.T.; Reed, R.N.; Hart, K.M. Environmental DNA (eDNA) Sampling Improves Occurrence and Detection Estimates of Invasive Burmese Pythons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Z.; Hänfling, B.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Fan, J.; Li, J. Methodology of fish eDNA and its applications in ecology and environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 755, 142622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantera, I.; Cilleros, K.; Valentini, A.; Cerdan, A.; Dejean, T.; Iribar, A.; Taberlet, P.; Vigouroux, R.; Brosse, S. Optimizing environmental DNA sampling effort for fish inventories in tropical streams and rivers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Eble, J.E.; Gaither, M.R. A practical guide to sample preservation and pre-PCR processing of aquatic environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 20, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, C.D.; Dunthorn, M.; Anslan, S.; De Lima, V.X.; Tedersoo, L.; Nilsson, R.H.; Antonelli, A. Advancing biodiversity assessments with environmental DNA: Long-read technologies help reveal the drivers of Amazonian fungal diversity. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 7509–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Sigsgaard, E.E. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of wild flowers reveals diverse communities of terrestrial arthropods. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mariani, S.; Baillie, C.; Colosimo, G.; Riesgo, A. Sponges as natural environmental DNA samplers. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R401–R402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratsch, R.; Kingsbury, B.A.; Jordan, M.A. Exploration of Environmental DNA (eDNA) to Detect Kirtland’s Snake (Clonophis kirtlandii). Animals 2020, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogarten, J.F.; Hoffmann, C.; Arandjelovic, M.; Sachse, A.; Merkel, K.; Dieguez, P.; Agbor, A.; Angedakin, S.; Brazzola, G.; Jones, S. Fly-derived DNA and camera traps are complementary tools for assessing mammalian biodiversity. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drummond, A.J.; Newcomb, R.D.; Buckley, T.R.; Xie, D.; Dopheide, A.; Potter, B.C.; Heled, J.; Ross, H.A.; Tooman, L.; Grosser, S.; et al. Evaluating a multigene environmental DNA approach for biodiversity assessment. GigaScience 2015, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jørgensen, L.V.G.; Nielsen, J.W.; Villadsen, M.K.; Vismann, B.; Dalvin, S.; Mathiessen, H.; Madsen, L.; Kania, P.W.; Buchmann, K. A non-lethal method for detection of Bonamia ostreae in flat oyster (Ostrea edulis) using environmental DNA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wineland, S.M.; Arrick, R.F.; Welch, S.M.; Pauley, T.K.; Mosher, J.J.; Apodaca, J.J.; Olszack, M.; Holmes, J.N.; Waldron, J.L. Environmental DNA improves Eastern Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis alleganiensis) detection over conventional sampling methods. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, M.; O’Grady, J.; Ball, B.; Carlsson, J.; De Eyto, E.; McGinnity, P.; Jennings, E.; Regan, F.; Parle-McDermott, A. The application of CRISPR-Cas for single species identification from environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, Q.; Su, X.; Zhou, L.; Tang, M.; Fu, R.; Li, J.; Huang, Q. Ultra-deep sequencing enables high-fidelity recovery of biodiversity for bulk arthropod samples without PCR amplification. GigaScience 2013, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, R.; Oliveira, I.D.B.; Dias, P.D.A.; Bidinotto, A.B.; Telles, M.P.D.C. BarcodingGO: A problem-based approach to teach concepts related to environmental-DNA and bioinformatics. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2020, 49, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, J.A.; Mahon, A.R. From molecules to management: Adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushio, M.; Murata, K.; Sado, T.; Nishiumi, I.; Takeshita, M.; Iwasaki, W.; Miya, M. Demonstration of the potential of environmental DNA as a tool for the detection of avian species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobin, P.C. Managing invasive species. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shabani, F.; Ahmadi, M.; Kumar, L.; Solhjouy-Fard, S.; Tehrany, M.S.; Shabani, F.; Kalantar, B.; Esmaeili, A. Invasive weed species’ threats to global biodiversity: Future scenarios of changes in the number of invasive species in a changing climate. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaggio, A.J.; Engeman, R.M.; Hopken, M.W.; Humphrey, J.S.; Keacher, K.L.; Bruce, W.E.; Avery, M.L. Detecting an elusive invasive species: A diagnostic PCR to detect B urmese python in F lorida waters and an assessment of persistence of environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2014, 14, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, L.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Budny, M.L.; Mahon, A.R. The use of environmental DNA in invasive species surveillance of the Great Lakes commercial bait trade. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 29, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, E.L.; Economou, C.K.; Faulkes, C.G.; Gilbert, J.D.; Bennett, F.; Drinkwater, R.; Littlefair, J.E. eDNAir: Proof of concept that animal DNA can be collected from air sampling. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglès d’Auriac, M.B.; Strand, D.A.; Mjelde, M.; Demars, B.O.; Thaulow, J. Detection of an invasive aquatic plant in natural water bodies using environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, J.; Valentini, A.; Dejean, T.; Montarsi, F.; Taberlet, P.; Glaizot, O.; Fumagalli, L. Detection of Invasive Mosquito Vectors Using Environmental DNA (eDNA) from Water Samples. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.P.; Barnes, M.A.; Hwang, C.-T.; Mahon, A.R.; Feder, J.L.; Ruggiero, S.T.; Tanner, C.E.; Lodge, D.M. Rapid Invasive Species Detection by Combining Environmental DNA with Light Transmission Spectroscopy. Conserv. Lett. 2013, 6, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.R.; Renshaw, M.A.; Gantz, C.A.; Umek, J.; Chandra, S.; Lodge, D.M.; Egan, S.P. Environmental DNA (eDNA) detects the invasive crayfishes Orconectes rusticus and Pacifastacus leniusculus in large lakes of North America. Hydrobiologia 2017, 800, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsström, T.; Vasemägi, A. Can environmental DNA (eDNA) be used for detection and monitoring of introduced crab species in the Baltic Sea? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mächler, E.; Deiner, K.; Steinmann, P.; Altermatt, F. Utility of environmental DNA for monitoring rare and indicator macroinvertebrate species. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, A.A.; Barberán, A.; Bertone, M.A.; Menninger, H.L.; Dunn, R.; Fierer, N. The diversity of arthropods in homes across the United States as determined by environmental DNA analyses. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 6214–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clusa, L.; Ardura, A.; Fernández, S.F.; Roca, A.A.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. An extremely sensitive nested PCR-RFLP mitochondrial marker for detection and identification of salmonids in eDNA from water samples. PeerJ 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robson, H.L.A.; Noble, T.H.; Saunders, R.; Robson, S.; Burrows, D.W.; Jerry, D. Fine-tuning for the tropics: Application of eDNA technology for invasive fish detection in tropical freshwater ecosystems. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carim, K.J.; Dysthe, J.C.; McLellan, H.; Young, M.K.; McKelvey, K.S.; Schwartz, M.K. Using environmental DNA sampling to monitor the invasion of nonnative Esox lucius (northern pike) in the Columbia River basin, USA. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchii, K.; Doi, H.; Minamoto, T. A novel environmental DNA approach to quantify the cryptic invasion of non-native genotypes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 16, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Jane, S.F.; Lowe, W.H.; Whiteley, A.R.; Schwartz, M. Robust Detection of Rare Species Using Environmental DNA: The Importance of Primer Specificity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Ammon, U.; Wood, S.A.; Laroche, O.; Zaiko, A.; Lavery, S.D.; Inglis, G.J.; Pochon, X. Linking Environmental DNA and RNA for Improved Detection of the Marine Invasive Fanworm Sabella spallanzanii. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Kim, D.; Yoon, T.J.; Shin, S. Early detection of marine invasive species, Bugula neritina (Bryozoa: Cheilostomatida), using species-specific primers and environmental DNA analysis in Korea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauger, A.N.; Hollis-Etter, K.M.; Etter, D.R.; Roloff, G.J.; Mahon, A.R. Use of environmental DNA (eDNA) in streams to detect feral swine (Sus scrofa). PeerJ 2020, 8, e8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miralles, L.; Dopico, E.; Devloo-Delva, F.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Controlling populations of invasive pygmy mussel (Xenostrobus securis) through citizen science and environmental DNA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Engle, C.; Salach, P.; Fakher, U.; Stedtfeld, T.; Dreelin, E.; Stevenson, R.J.; Latimore, J.; Hashsham, S.A. Isothermal amplification of environmental DNA (eDNA) for direct field-based monitoring and laboratory confirmation of Dreissena sp. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, N.; Stepien, C.A. Invasion genetics from eDNA and thousands of larvae: A targeted metabarcoding assay that distinguishes species and population variation of zebra and quagga mussels. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3515–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymus, K.; Marshall, N.; Stepien, C.A. Environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding assays to detect invasive invertebrate species in the Great Lakes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miralles, L.; Parrondo, M.; de Rojas, A.H.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Borrell, Y.J. Development and validation of eDNA markers for the detection of Crepidula fornicata in environmental samples. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardura, A.; Zaiko, A.; Martinez, J.L.; Samulioviene, A.; Semenova, A.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. eDNA and specific primers for early detection of invasive species–A case study on the bivalve Rangia cuneata, currently spreading in Europe. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 112, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davy, C.M.; Kidd, A.G.; Wilson, C. Development and Validation of Environmental DNA (eDNA) Markers for Detection of Freshwater Turtles. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simpfendorfer, C.; Kyne, P.; Noble, T.; Goldsbury, J.; Basiita, R.K.; Lindsay, R.; Shields, A.; Perry, C. Jerry Environmental DNA detects Critically Endangered largetooth sawfish in the wild. Endanger. Species Res. 2016, 30, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huerlimann, R.; Cooper, M.K.; Edmunds, R.C.; Villacorta-Rath, C.; Le Port, A.; Robson, H.L.A.; Strugnell, J.M.; Burrows, D.; Jerry, D.R. Enhancing tropical conservation and ecology research with aquatic environmental DNA methods: An introduction for non-environmental DNA specialists. Anim. Conserv. 2020, 23, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, L.R.; Handley, L.L.; Hahn, C.; Boonham, N.; Rees, H.C.; Gough, K.C.; Lewis, E.; Adams, I.P.; Brotherton, P.; Phillips, S.; et al. Needle in a haystack? A comparison of eDNA metabarcoding and targeted qPCR for detection of the great crested newt (Triturus cristatus). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 6330–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Löfgren, A.; Hjerne, O.; Nordén, S.; Saetre, P. Environmental DNA (eDNA) detects the pool frog (Pelophylax lessonae) at times when traditional monitoring methods are insensitive. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, N.; Yasumiba, K.; Takahara, T. Efficacy of environmental DNA to detect and quantify stream tadpoles of Odorrana splendida. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katano, I.; Harada, K.; Doi, H.; Souma, R.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA method for estimating salamander distribution in headwater streams, and a comparison of water sampling methods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spear, S.F.; Groves, J.D.; Williams, L.A.; Waits, L. Using environmental DNA methods to improve detectability in a hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis) monitoring program. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresdal, J.D.; Farrell, A.D.; Goldberg, C.S. Environmental DNA Detection of the Golden Tree Frog (Phytotriades auratus) in Bromeliads. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osathanunkul, M. eDNA-based monitoring of parasitic plant (Sapria himalayana). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S.H.; Niemiller, K.D.K.; Dooley, K.E.; Nix, J.; Niemiller, M.L. Using environmental DNA methods to survey for rare groundwater fauna: Detection of an endangered endemic cave crayfish in northern Alabama. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troth, C.R.; Burian, A.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Bulling, M.; Nightingale, J.; Mauvisseau, C.; Sweet, M.J. Development and application of eDNA-based tools for the conservation of white-clawed crayfish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowart, D.; Breedveld, K.G.H.; Ellis, M.J.; Hull, J.M.; Larson, E.R. Environmental DNA (eDNA) applications for the conservation of imperiled crayfish (Decapoda: Astacidea) through monitoring of invasive species barriers and relocated populations. J. Crustac. Biol. 2018, 38, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltz, K.; Lyle, J.; Ovenden, J.; Morgan, J.A.T.; Moreno, D.A.; Semmens, J. Application of environmental DNA to detect an endangered marine skate species in the wild. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Sugatani, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Imamura, A. Environmental DNA analysis as a non-invasive quantitative tool for reproductive migration of a threatened endemic fish in rivers. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 11964–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Kume, G.; Gotou, M.; Kono, T.; Fujii, T.; Inui, R.; Kurita, Y. Using environmental DNA analyses to assess the occurrence and abundance of the endangered amphidromous fish Plecoglossus altivelis ryukyuensis. Biodivers. Data J. 2020, 8, e39679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laramie, M.B.; Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S. Characterizing the distribution of an endangered salmonid using environmental DNA analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yatsuyanagi, T.; Ishida, R.; Sakata, M.K.; Kanbe, T.; Mizumoto, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kamada, S.; Namba, S.; Nii, H.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA monitoring for short-term reproductive migration of endemic anadromous species, Shishamo smelt (Spirinchus lanceolatus). Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Carl, H.; Møller, P.R.; Thomsen, P.F. Monitoring the near-extinct European weather loach in Denmark based on environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brys, R.; Halfmaerten, D.; Neyrinck, S.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Auwerx, J.; Sweet, M.; Mergeay, J. Reliable eDNA detection and quantification of the European weather loach (Misgurnus fossilis). J. Fish Biol. 2020, 98, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, P.S.; Schumer, G.; Blankenship, S.; Campbell, E. Detection of Adult Green Sturgeon Using Environmental DNA Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhel, J.B.; Marques, V.; Fernández, A.P.; Borrero-Pérez, G.H.; Martinezguerra, M.M.; Valentini, A.; Dejean, T.; Manel, S.; Loiseau, N.; Velez, L. Detection of the elusive Dwarf sperm whale (Kogia sima) using environmental DNA at Malpelo island (Eastern Pacific, Colombia). Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Katano, I.; Sakata, Y.; Souma, R.; Kosuge, T.; Nagano, M.; Ikeda, K.; Yano, K.; Tojo, K. Detection of an endangered aquatic heteropteran using environmental DNA in a wetland ecosystem. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, K.; Ma, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J. Using environmental DNA to assess population-wide spatiotemporal reserve use. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, T.; Schingen, M.; Windisch, H.S.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Ziegler, T.; Fink, P. Monitoring a loss: Detection of the semi-aquatic crocodile lizard (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) in inaccessible habitats via environmental DNA. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienert, F.; De Danieli, S.; Miquel, C.; Coissac, E.; Poillot, C.; Brun, J.-J.; Taberlet, P. Tracking earthworm communities from soil DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleton, M.; Rees, G.N.; Watson, G.; Campbell, C.; Nielsen, D. Environmental DNA reveals landscape mosaic of wetland plant communities. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 19, e00689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynggaard, C.; Nielsen, M.; Santos-Bay, L.; Gastauer, M.; Oliveira, G.; Bohmann, K. Vertebrate diversity revealed by metabarcoding of bulk arthropod samples from tropical forests. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, R.E.; Fonseca, D.M.; Gable, S.; Kyle, K.E.; Hamilton, G.C.; Nielsen, A.L.; Lockwood, J.L. Moving eDNA surveys onto land: Strategies for active eDNA aggregation to detect invasive forest insects. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Stewart, K.A.; Antognazza, C.M.; Bunholi, I.V.; Deiner, K.; Barnes, M.A.; Saha, S.; Verdier, H.; Doi, H.; Maity, J.P. Plant-animal interactions in the era of environmental DNA (eDNA)—A review. Authorea Prepr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.R.; Kéry, M.; Ursenbacher, S.; Hyman, O.J.; Collins, J.P. Site occupancy models in the analysis of environmental DNA presence/absence surveys: A case study of an emerging amphibian pathogen. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. Assessment of fish communities using environmental DNA: Effect of spatial sampling design in lentic systems of different sizes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 20, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heyde, M.; Bunce, M.; Wardell-Johnson, G.; Fernandes, K.; White, N.E.; Nevill, P. Testing multiple substrates for terrestrial biodiversity monitoring using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals primary chemical contaminants in freshwater sediments from different land-use types. Chemosphere 2016, 172, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, N.A.; Djurhuus, A.; Closek, C.; Hepner, M.; Olesin, E.; Visser, L.; Kelble, C.; Hubbard, K.; Breitbart, M. Assessing eukaryotic biodiversity in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary through environmental DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeDuc, N.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Howland, K.L.; Archambault, P.; Sevellec, M.; Normandeau, E.; Dispas, A.; Winkler, G.; McKindsey, C.W.; Simard, N.; et al. Comparing eDNA metabarcoding and species collection for documenting Arctic metazoan biodiversity. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Møller, P.R.; Sigsgaard, E.E.; Knudsen, S.; Jorgensen, O.A.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA from Seawater Samples Correlate with Trawl Catches of Subarctic, Deepwater Fishes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Sato, Y.; Sado, T.; Araki, H.; Kondoh, M.; Minamoto, T.; Miya, M. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ushio, M.; Fukuda, H.; Inoue, T.; Makoto, K.; Kishida, O.; Sato, K.; Murata, K.; Nikaido, M.; Sado, T.; Sato, Y.; et al. Environmental DNA enables detection of terrestrial mammals from forest pond water. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, e63–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, N.T.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Chaganti, S.R. Environmental (e)RNA advances the reliability of eDNA by predicting its age. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, K.J.; Sethi, S.A.; Lodge, D.M.; Andrés, J. Nuclear eDNA estimates population allele frequencies and abundance in experimental mesocosms and field samples. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, E.L. Molecular detection of trophic interactions: Emerging trends, distinct advantages, significant considerations and conservation applications. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andújar, C.; Arribas, P.; Gray, C.; Bruce, C.; Woodward, G.; Yu, D.W.; Vogler, A.P. Metabarcoding of freshwater invertebrates to detect the effects of a pesticide spill. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 27, 146–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choo, L.Q.; Vogler, A.P.; Crampton-Platt, A. Shotgun mitogenomics across body size classes in a local assemblage of tropical Diptera: Phylogeny, species diversity and mitochondrial abundance spectrum. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5086–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, O.; Jarman, S.; Bissett, A.; Hope, M.; Paeper, C.; Bessey, C.; Schwartz, M.K.; Hale, J.; Bunce, M. Making environmental DNA (eDNA) biodiversity records globally accessible. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Taxonomic Group | Environment | Species and Target Region | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphibian | Pond | Lithobates catesbeianusCyt-b | [8] |
| Angiosperms | River, Lake & Stream | Elodea canadensis trnL | [56] |
| Arthropod | Freshwater sources | Aedes albopictus ITS; Ae. j. japonicusCOI, Ae. KoreicusCOI | [57] |
| Lake | Eriocheir sinensis, Carcinus maenusCOI | [58] | |
| Orconectes rusticus; Pacifastacus leniusculusCOI | [59] | ||
| Seawater | Rhithropanopeus harrisiiCOI | [60] | |
| River and Lake | Crangonyx pseudogracilisCOI | [61] | |
| Dust sample | Community COI | [62] | |
| Fish | Aquarium, River & Reservoirs | Oncorhynchus mykiss, Salmo salar, Salmo trutta, Salvelinus fontinalis, and Salvelinus namaycush16s | [63] |
| Fresh water tank | Oreochromis mossambicus16s | [64] | |
| River, Lake & Creek | Esox luciusCOI, Cyt-b | [65] | |
| Pond | Lepomis macrochirusCyt-b | [15] | |
| River & Reservoirs | Cyprinus carpioSNPs | [66] | |
| River & Lake | Hypophthalmichthys nobilis, H. molitrixMDL | [9,54] | |
| Streams | Salvelinus fontinalisCyt-b | [67] | |
| Invertebrate | Seawater | Sabella spallanzaniiCOI | [68] |
| Bugula neritinaCOI | [69] | ||
| Mammal | Streams & Creek | Sus scrofa MDL | [70] |
| Mollusca | Estuaries | Xenostrobus securisCOI | [71] |
| River, Lake & Stream | Dreissena polymorpha, D. bugensis, D. rostriformis Limnoperna fortuneCOI; Dreissena sp. 18s | [58,72,73] | |
| Lakes | Community 16s | [74] | |
| Seawater | Crepidula fornicataCOI | [75] | |
| Rangia cuneata16s | [76] | ||
| Reptile | Freshwater | Python bivittatusCyt-b, ND4 | [34,53] |
| Pond | Trachemys scriptaCOI | [77] |
| Taxonomic Group | Environment | Species, Conservation Status, Detection Method, Target Region | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphibian | Pond | Triturus cristatusLC, qP, Cyt-b | [80] |
| Pool | Pelophylax lessonaeLC, qP, Cyt-b | [81] | |
| Stream | Odorrana splendidaEN, qP, Cyt-b | [82] | |
| Onychodactylus japonicusLC, qP, 12s | [83] | ||
| Drainage | Cryptobranchus alleganiensisNT, qP, Cyt-b | [84] | |
| Stream | Cryptobranchus alleganiensis alleganiensisNT, qP, Cyt-b | [45] | |
| Hynobius vandenburghiEN, qP, Cyt-b,12s | [30] | ||
| Bromeliads’ water | Phytotriades auratusEN, qP, Cyt-b | [85] | |
| Angiosperm | Rhizospheric soil/Flora | Sapria himalayanaEN, qP, ITS | [86] |
| Arthropod | Caves/springs (Water) | Cambarus speleocoopiEN, qP, COI | [87] |
| River/pond | Austropotamobius pallipesEN, qP, COI | [88] | |
| River/Lake/Spring Creek | Pacifastacus fortisCR, qP, COI | [89] | |
| River/lake | Baetis buceratusVU, cP, COI | [61] | |
| Harbor | Zearaja maugeanaEN, qP, ND4 | [90] | |
| River/lake | Opsariichthys uncirostris uncirostrisTh, qP, MDL | [91] | |
| River | Pristis pristisCR, cP, COI | [78] | |
| Plecoglossus altivelis ryukyuensisEN, qP, ND4 | [92] | ||
| Oncorhynchus tshawytschaEN, qP, COI | [93] | ||
| Fish | River | Spirinchus lanceolatusTh, qP, Cyt-b | [94] |
| River/lake | Hypophthalmichthys nobilisDD Hypophthalmichthys molitrixNT, cP, MDL | [9] | |
| Strems | Salvelinus confluentusVU, qP, Cyt-b | [67] | |
| Wetland | Misgurnus fossilisLC, qP, Cyt-b, COI | [95,96] | |
| Acipenser medirostrisNT, qP, COI | [97] | ||
| Sea | Kogia simaDD, MB, 12s | [98] | |
| Heteropterans | Streams/wetland | Nepa hoffmanniEN, qP, 16s | [99] |
| Mammals | Lake | Neophocaena asiaeorientalisEN, MB, 16s, Cyt-b | [20,100] |
| Reptile | Streams | Shinisaurus crocodilurusEN, qP, Cyt-b | [101] |
| Taxonomic Group | Environment and Target Region | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Arthropod | Dust sample COI | [62] |
| Wild flower COI, 16s | [39] | |
| Bird | Water from Zoo cages 12s | [50] |
| Eukaryote | Soil, scat, plant material & arthropods COI, 12s | [109] |
| Freshwater sediments 18s | [110] | |
| Freshwater COI | [5] | |
| Seawater COI, 18s | [111,112] | |
| Fish | Seawater 12s | [113,114] |
| Fungi | Soil and organic litter COI, ITS, 18s | [38] |
| Mammal | Forest pond water 12s | [115] |
| Fly derived DNA 16s | [42] | |
| Mollusc | Lake 16s | [74] |
| Plant and fungi | Air ITS | [23] |
| Plant | Wetland 18s, trnL | [103] |
| Vertebrate | Bulk Arthropod 12s, 16s | [104] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banerjee, P.; Dey, G.; Antognazza, C.M.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Chan, M.W.Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chao, H.-C.; Lu, C.-M.; et al. Reinforcement of Environmental DNA Based Methods (Sensu Stricto) in Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation: A Review. Biology 2021, 10, 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121223
Banerjee P, Dey G, Antognazza CM, Sharma RK, Maity JP, Chan MWY, Huang Y-H, Lin P-Y, Chao H-C, Lu C-M, et al. Reinforcement of Environmental DNA Based Methods (Sensu Stricto) in Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation: A Review. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121223
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanerjee, Pritam, Gobinda Dey, Caterina M. Antognazza, Raju Kumar Sharma, Jyoti Prakash Maity, Michael W. Y. Chan, Yi-Hsun Huang, Pin-Yun Lin, Hung-Chun Chao, Chung-Ming Lu, and et al. 2021. "Reinforcement of Environmental DNA Based Methods (Sensu Stricto) in Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation: A Review" Biology 10, no. 12: 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121223
APA StyleBanerjee, P., Dey, G., Antognazza, C. M., Sharma, R. K., Maity, J. P., Chan, M. W. Y., Huang, Y.-H., Lin, P.-Y., Chao, H.-C., Lu, C.-M., & Chen, C.-Y. (2021). Reinforcement of Environmental DNA Based Methods (Sensu Stricto) in Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation: A Review. Biology, 10(12), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121223






