Chronic Variable Stress Induces Hepatic Fe(II) Deposition by Up-Regulating ZIP14 Expression via miR-181 Family Pathway in Rats
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of Chronic Variable Stress
2.3. Measurement of Plasma Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.5. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation and Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes
2.6. Determination of Feed and Liver Iron Content
2.7. Measurement of Hepatic Fe(II) Concentration
2.8. RNA Isolation and mRNA Quantification
2.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
2.10. Prediction of miRNA Targeting ZIP14
2.11. Quantification of miRNA with Real-Time PCR
2.12. Cell Culture and Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
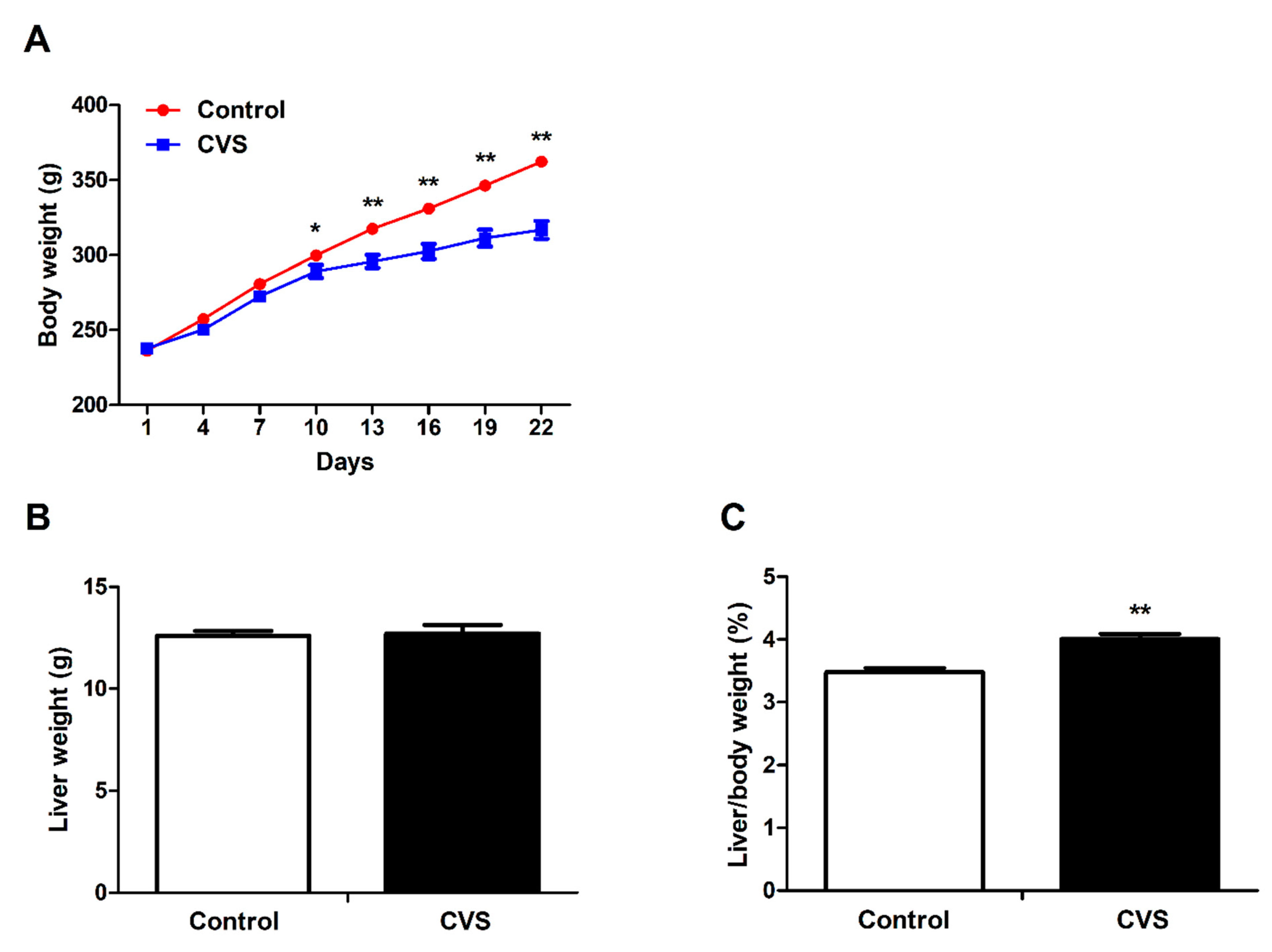
3.1. Body Weight, Liver Weight and Liver Indexes of Rats Exposed to Chronic Variable Stress
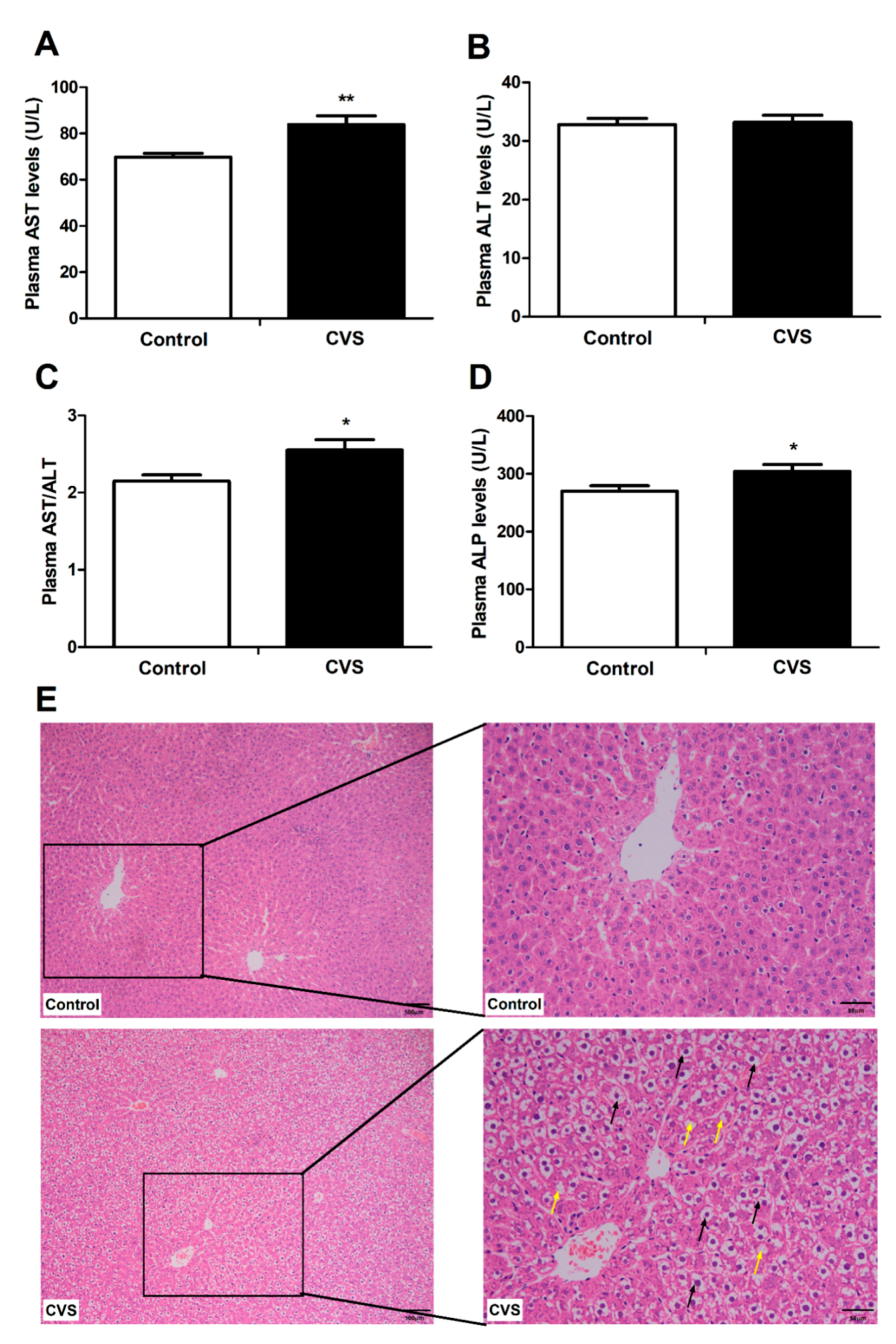
3.2. Indicators and Histomorphology Related to Liver Injury of Rats Exposed to Chronic Variable Stress
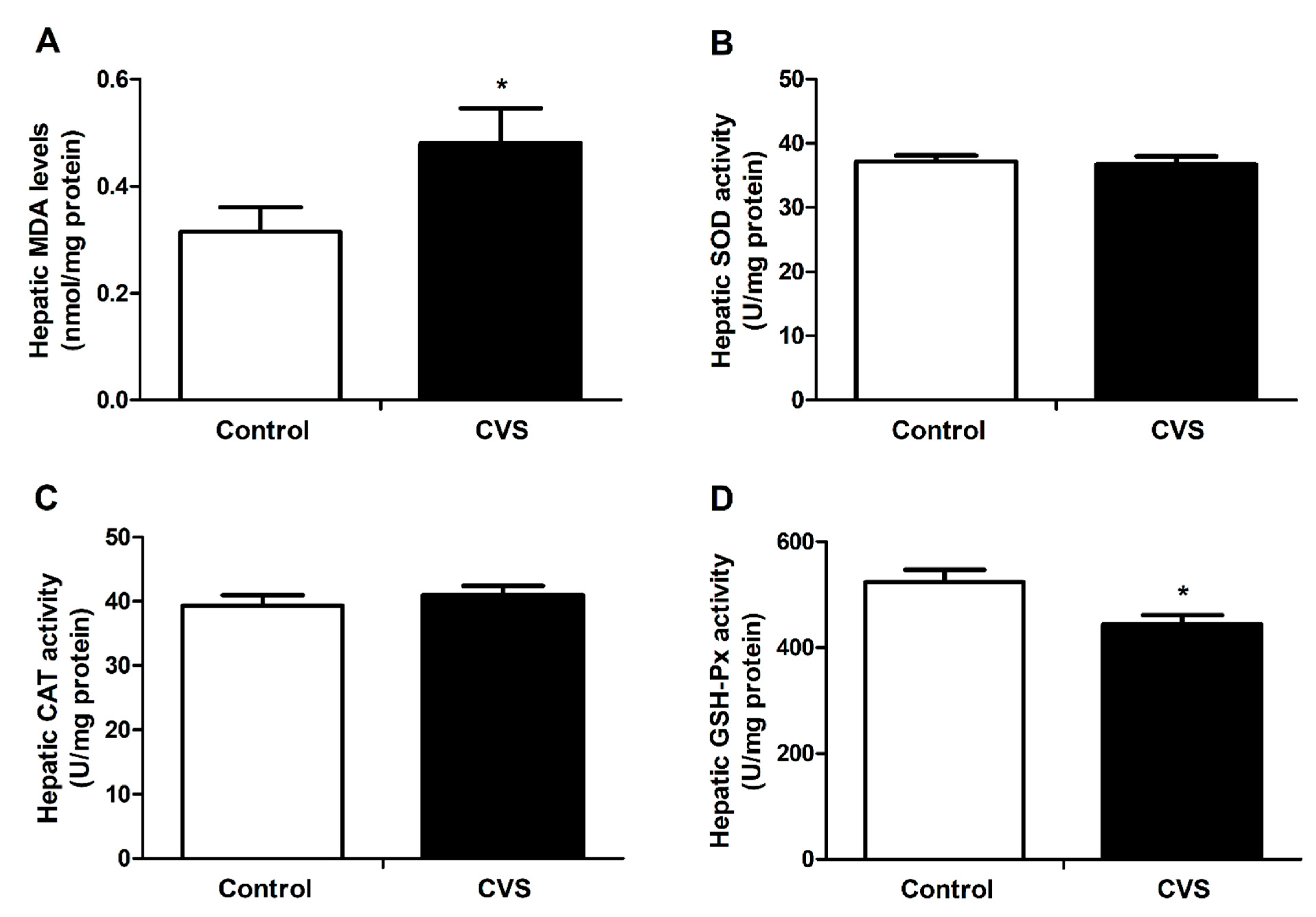
3.3. Hepatic Lipid Peroxidation and Activity of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Rats Exposed to Chronic Variable Stress
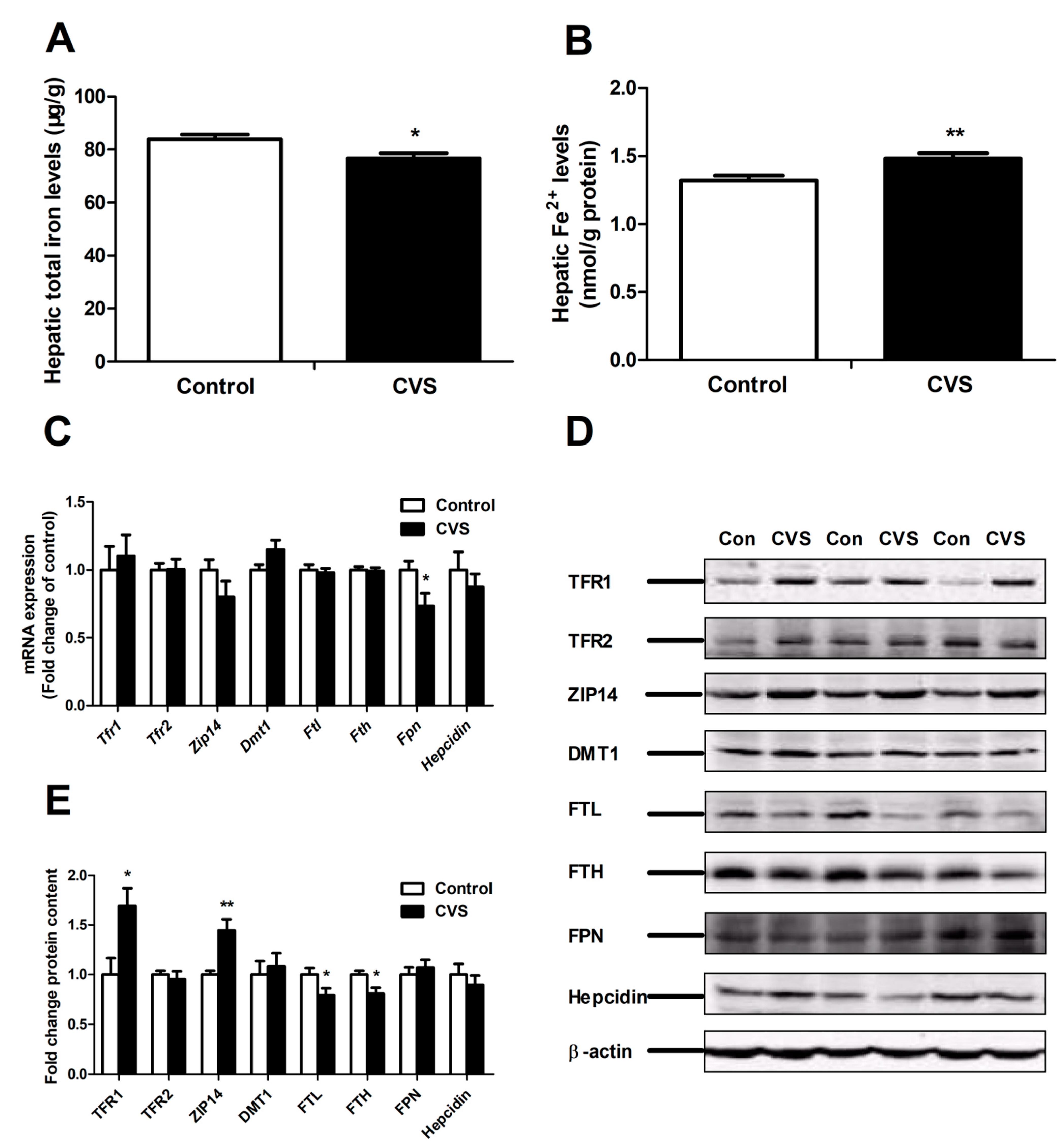
3.4. Levels of Hepatic Iron and Iron-Related Genes and Proteins in Rats Exposed to Chronic Variable Stress
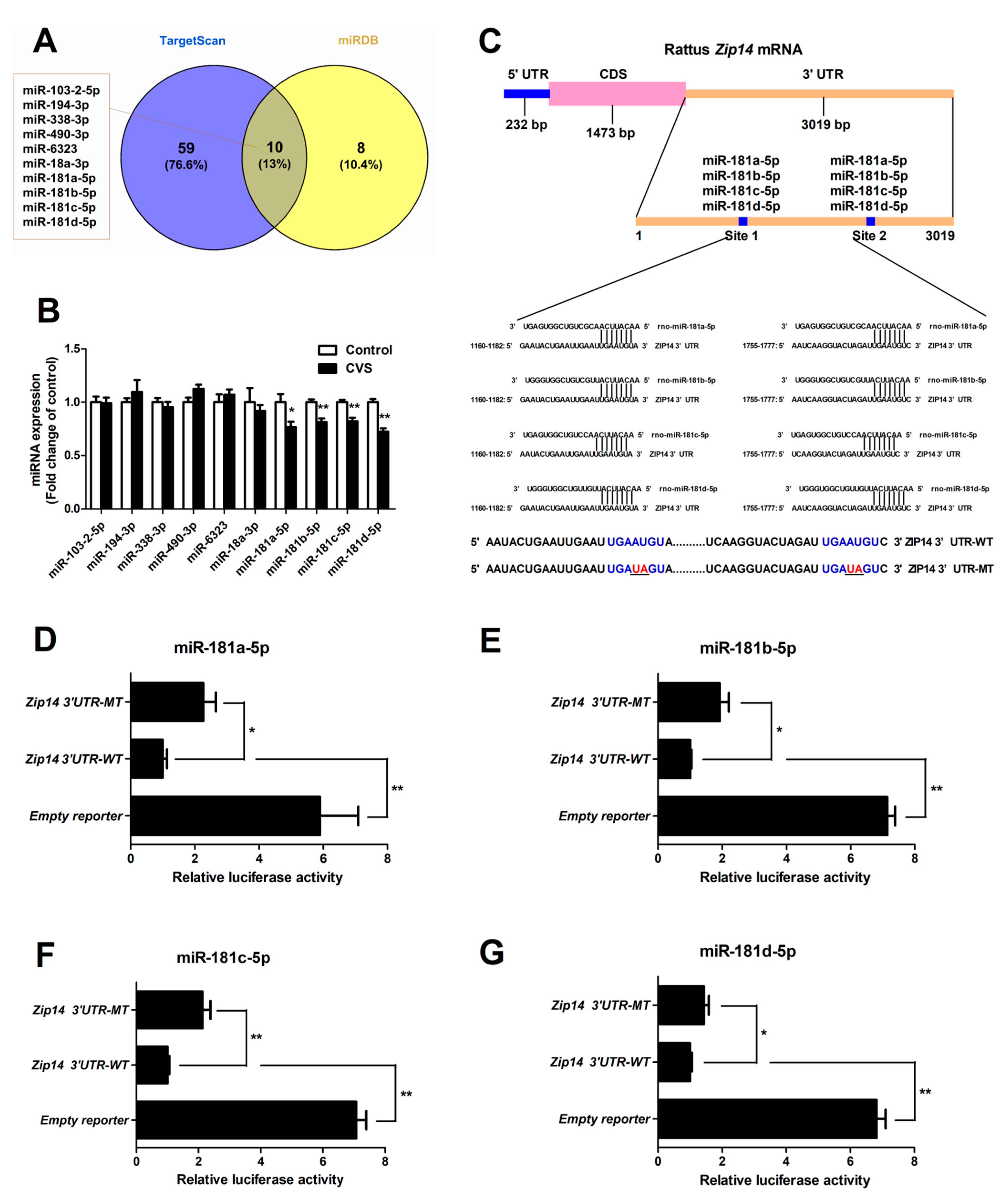
3.5. Hepatic Expression and Functional Validation of miRNAs Targeting Zip14
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crichton, R.R.; Wilmet, S.; Legssyer, R.; Ward, R.J. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of iron homeostasis and toxicity in mammalian cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2002, 91, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, P.T.; Heiskala, M.; Peterson, P.A.; Yang, Y. The roles of iron in health and disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 2001, 22, 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.E.; Caris-Veyrat, C.; Nowicki, M.; Bernard, J.P.; Morange, S.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Gleize, B.; Borel, P. The effect of an iron supplement on lycopene metabolism and absorption during digestion in healthy humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrangelo, A. Iron and the liver. Liver Int. 2016, 36 (Suppl. 1), 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Teng, X.; Zheng, H.; Shan, Z.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, H.; Fan, C.; Teng, W. Iron deficiency without anemia causes maternal hypothyroxinemia in pregnant rats. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delima, R.D.; Chua, A.C.; Tirnitz-Parker, J.E.; Gan, E.K.; Croft, K.D.; Graham, R.M.; Olynyk, J.K.; Trinder, D. Disruption of hemochromatosis protein and transferrin receptor 2 causes iron-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Taura, K.; Kodama, Y.; Schnabl, B.; Brenner, D.A. Hepatitis C virus-induced oxidative stress suppresses hepcidin expression through increased histone deacetylase activity. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawen, A.; Lane, D.J. Mammalian iron homeostasis in health and disease: Uptake, storage, transport, and molecular mechanisms of action. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 2473–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H. Transferrin and transferrin receptors update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, J.P.; Aydemir, F.; Nam, H.; Knutson, M.D.; Cousins, R.J. Zip14 (Slc39a14) mediates non-transferrin-bound iron uptake into cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13612–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkitkasemwong, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Coffey, R.; Zhang, W.; Chan, A.; Biel, T.; Kim, J.S.; Hojyo, S.; Fukada, T.; Knutson, M.D. SLC39A14 is required for the development of hepatocellular iron overload in murine models of hereditary hemochromatosis. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydemir, T.B.; Cousins, R.J. The multiple faces of the metal transporter ZIP14 (SLC39A14). J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, A.; Lima, C.A.; Pinkus, J.L.; Pinkus, G.S.; Zon, L.I.; Robine, S.; Andrews, N.C. The iron exporter ferroportin/Slc40a1 is essential for iron homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Hepcidin and iron homeostasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adachi, M.; Kai, K.; Yamaji, K.; Ide, T.; Noshiro, H.; Kawaguchi, A.; Aishima, S. Transferrin receptor 1 overexpression is associated with tumour de-differentiation and acts as a potential prognostic indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma. Histopathology 2019, 75, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Wu, J.; Shah, B.N.; Greutelaers, K.C.; Ghosh, M.C.; Ollivierre, H.; Su, X.Z.; Thuma, P.E.; Bedu-Addo, G.; Mockenhaupt, F.P.; et al. Erythrocytic ferroportin reduces intracellular iron accumulation, hemolysis, and malaria risk. Science 2018, 359, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, E.O.; Kamilaris, T.C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Gold, P.W. Mechanisms of stress: A dynamic overview of hormonal and behavioral homeostasis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, W.; Curzytek, K.; Kubera, M.; Iciek, M.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Leskiewicz, M.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Budziszewska, B.; et al. The effect of chronic mild stress and imipramine on the markers of oxidative stress and antioxidant system in rat liver. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 30, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloomer, S.A.; Brown, K.E.; Buettner, G.R.; Kregel, K.C. Dysregulation of hepatic iron with aging: Implications for heat stress-induced oxidative liver injury. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1165–R1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Shen, H.; Li, M. Psychological stress induces hypoferremia through the IL-6-hepcidin axis in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Li, M. Glucocorticoid causes iron accumulation in liver by up-regulating expression of iron regulatory protein 1 gene through GR and STAT5. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 61, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Yang, C.; Yang, S.; He, B.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. Long-term dexamethasone exposure down-regulates hepatic TFR1 and reduces liver iron concentration in rats. Nutrients 2017, 9, 617. [Google Scholar]
- Koob, T.J.; Summers, A.P. Tendon--bridging the gap. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002, 133, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhabhar, F.S. Effects of stress on immune function: The good, the bad, and the beautiful. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Nestler, E.J. Animal models of depression: Molecular perspectives. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 7, 121–147. [Google Scholar]
- Packard, A.E.; Ghosal, S.; Herman, J.P.; Woods, S.C.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M. Chronic variable stress improves glucose tolerance in rats with sucrose-induced prediabetes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 47, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeuble, D.; Packard, A.E.B.; McKlveen, J.M.; Morano, R.; Fourman, S.; Smith, B.L.; Scheimann, J.R.; Packard, B.A.; Wilson, S.P.; James, J.; et al. Prefrontal cortex regulates chronic stress-induced cardiovascular susceptibility. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e014451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordner, Z.A.; Tamashiro, K.L. Effects of chronic variable stress on cognition and Bace1 expression among wild-type mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbet, M.; Korga, A.; Gawronska-Grzywacz, M.; Izdebska, M.; Piatkowska-Chmiel, I.; Poleszak, E.; Wrobel, A.; Matysiak, W.; Jodlowska-Jedrych, B.; Dudka, J. Chronic variable stress is responsible for lipid and DNA oxidative disorders and activation of oxidative stress response genes in the brain of rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7313090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jelenik, T.; Dille, M.; Muller-Luhlhoff, S.; Kabra, D.G.; Zhou, Z.; Binsch, C.; Hartwig, S.; Lehr, S.; Chadt, A.; Peters, E.M.J.; et al. FGF21 regulates insulin sensitivity following long-term chronic stress. Mol. Metab. 2018, 16, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Guo, S.; Li, H.; Ni, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. Identification and functional verification of microRNA-16 family targeting intestinal divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) in vitro and in vivo. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, N.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D146–D152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Fang, X.; Liu, M.; Ni, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. MiR-20b down-regulates intestinal ferroportin expression in vitro and in vivo. Cells 2019, 8, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Che, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Ke, T.; Cao, R.; Meng, S.; Li, D.; Weiming, O.; Chen, J.; et al. Effects of mild chronic intermittent cold exposure on rat organs. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahng, J.W.; Kim, N.Y.; Ryu, V.; Yoo, S.B.; Kim, B.T.; Kang, D.W.; Lee, J.H. Dexamethasone reduces food intake, weight gain and the hypothalamic 5-HT concentration and increases plasma leptin in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 581, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, D.N.; Saribekyan, H.M.; Parada, P.A.; Hanson, E.M.; Badaruddin, B.S.; Judd, J.M.; Donnay, M.E.; Padilla-Garcia, D.; Conrad, C.D. Chronic unpredictable intermittent restraint stress disrupts spatial memory in male, but not female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 383, 112519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatzkin, R.R.; Baldassaro, A.; Hayden, E. The impact of chronic stress on the predictors of acute stress-induced eating in women. Appetite 2018, 123, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A.M.; Jastreboff, A.M.; White, M.A.; Grilo, C.M.; Sinha, R. Stress, cortisol, and other appetite-related hormones: Prospective prediction of 6-month changes in food cravings and weight. Obesity 2017, 25, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Torres, M.L.; Dos Santos, C.V. Uncontrollable chronic stress affects eating behavior in rats. Stress 2019, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumolt, J.H.; Browne, R.W.; Patel, M.S.; Rideout, T.C. Malprogramming of hepatic lipid metabolism due to excessive early cholesterol exposure in adult progeny. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, A.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Han, L. Anthraquinones in the aqueous extract of Cassiae semen cause liver injury in rats through lipid metabolism disorder. Phytomedicine 2019, 64, 153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.F.; Rifaai, R.A. Preventive effect of omega-3 fatty acids in a rat model of stress-induced liver injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 11960–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataibeh, M. Cinnamon modulates biochemical alterations in rats loaded with acute restraint stress. J. Saudi. Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, S411–S414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, N.M.; Ragy, M.M.; Ahmed, S.M. Somatostatin analogue, Octreotide, improves restraint stress-induced liver injury by ameliorating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and activation of hepatic stellate cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Son, C.G. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Myelophil on restraint stress-induced liver injury in BALB/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Chu, L. Nephroprotective effect of calcium channel blockers against toxicity of lead exposure in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 218, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.N.; Sheng, Y.C.; Jiang, P.; Ji, L.L.; Xia, Y.Y.; Min, Y.; Wang, Z.T. The difference of glutathione antioxidant system in newly weaned and young mice liver and its involvement in isoline-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Gao, C.; Liu, L.; Xing, M.; Liu, L.; Yao, P. Quercetin attenuates chronic ethanol hepatotoxicity: Implication of “free” iron uptake and release. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissot, P.; Ropert, M.; Le Lan, C.; Loreal, O. Non-transferrin bound iron: A key role in iron overload and iron toxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljwaid, H.; White, D.L.; Collard, K.J.; Moody, A.J.; Pinkney, J.H. Non-transferrin-bound iron is associated with biomarkers of oxidative stress, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complications 2015, 29, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Tian, Y. Bioimaging and biosensing of ferrous ion in neurons and HepG2 cells upon oxidative stress. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataineh, H.; Pestovsky, O.; Bakac, A. pH-induced mechanistic changeover from hydroxyl radicals to iron(iv) in the Fenton reaction. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.; Avila, D.S.; da Rocha, J.B.; Aschner, M. Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: A focus on iron, manganese and mercury. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrick, L.M.; Dolan, K.G.; Romano, M.A.; Garrick, M.D. Non-transferrin-bound iron uptake in Belgrade and normal rat erythroid cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 1999, 178, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, R.; Knutson, M.D. The plasma membrane metal-ion transporter ZIP14 contributes to nontransferrin-bound iron uptake by human beta-cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C169–C175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, N.; Knutson, M.D.; Enns, C.A. The hereditary hemochromatosis protein, HFE, inhibits iron uptake via down-regulation of Zip14 in HepG2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21462–21468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meister, G. miRNAs get an early start on translational silencing. Cell 2007, 131, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castoldi, M.; Muckenthaler, M.U. Regulation of iron homeostasis by microRNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfo, I.; De Falco, L.; Asci, R.; Russo, R.; Colucci, S.; Gorrese, M.; Zollo, M.; Iolascon, A. Regulation of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) non-IRE isoform by the microRNA Let-7d in erythroid cells. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.R.; Muckenthaler, M.U. miR-148a regulates expression of the transferrin receptor 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, K.R.; Muckenthaler, M.U. miR-20a regulates expression of the iron exporter ferroportin in lung cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, T.; Salone, V.; Rederstorff, M. Dual luciferase gene reporter assays to study miRNA function. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1296, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Luo, T.; Le, G. Dietary methionine restriction upregulates endogenous H2 S via miR-328-3p: A potential mechanism to improve liver protein metabolism efficiency in a mouse model of high-fat-diet-induced obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Guo, T.; Guo, S.; Gao, J.; Ni, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. Chronic Variable Stress Induces Hepatic Fe(II) Deposition by Up-Regulating ZIP14 Expression via miR-181 Family Pathway in Rats. Biology 2021, 10, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070653
Jiang S, Guo T, Guo S, Gao J, Ni Y, Ma W, Zhao R. Chronic Variable Stress Induces Hepatic Fe(II) Deposition by Up-Regulating ZIP14 Expression via miR-181 Family Pathway in Rats. Biology. 2021; 10(7):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070653
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shuxia, Taining Guo, Shihui Guo, Jiang Gao, Yingdong Ni, Wenqiang Ma, and Ruqian Zhao. 2021. "Chronic Variable Stress Induces Hepatic Fe(II) Deposition by Up-Regulating ZIP14 Expression via miR-181 Family Pathway in Rats" Biology 10, no. 7: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070653
APA StyleJiang, S., Guo, T., Guo, S., Gao, J., Ni, Y., Ma, W., & Zhao, R. (2021). Chronic Variable Stress Induces Hepatic Fe(II) Deposition by Up-Regulating ZIP14 Expression via miR-181 Family Pathway in Rats. Biology, 10(7), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070653




