1. Introduction
Since the spreading of the COVID-19 pandemic, its influence has become evident worldwide in all disciplines and sectors, e.g., social, financial, and health sectors, etc. We were clearly unprepared for such a circumstance, which was entirely unfamiliar to the current generation. Over time, it was clear that overcoming this pandemic can only be done through mass vaccination [
1].
Vaccination against infectious diseases such as SARS-CoV-2 is the most cost-effective public health intervention. In addition to individual immunization, the achievement of collective protection (so-called community immunity) for the majority of vaccine-preventable infections is also crucial to protect vulnerable groups in the population who, for various reasons, cannot be vaccinated [
2].
The currently available vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 are manufactured by one of the following technologies: (a) mRNA-based vaccines, (b) viral vector-based vaccines, (c) protein subunit vaccines, and (d) whole virus or inactivated virus vaccines [
3]. Heretofore, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved vaccines that only belong to the first two technologies (mRNA-based and viral vector-based vaccines), which aim to produce spike protein-specific antibodies [
4]. The mRNA-based technology is relatively novel in vaccine industry, and it employs molecular templates of messenger RNA (mRNA) to deliver the genetic information to produce the spike (S) glycoprotein antigen, not to deliver the antigen itself [
5]. The viral vector-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 use a non-replicating harmless version of adenovirus as a vehicle to deliver the genetic code of the S glycoprotein antigen, thus eliciting the targeted immune response [
6].
In Germany, a country with a population of around 84 million, 3,729,682 COVID-19 cases with 91,007 deaths were reported by 1 July 2021 [
7,
8]. To date, four COVID-19 vaccines had been approved in Germany; Pfizer-BioNTech (mRNA-based vaccine) approved since 21 December 2020, Moderna (mRNA-based vaccine) approved since 6 January 2021, AstraZeneca-Oxford (viral vector-based vaccine) approved since 29 January 2021, and Janssen (viral vector-based vaccine) approved since 11 March 2021 [
9].
On 1 July 2021, 926,463 vaccine doses were administered in Germany, leading to 31.487.487 people (37.9% of the total population) being fully vaccinated and 46,249,449 people (55.6%) receiving at least one vaccine dose [
10]. The German government imported -to date- 57,619,463 doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, 13,869,863 doses of AstraZeneca-Oxford, 7,641,280 doses of Moderna, and 2,893,697 doses of Janssen [
10,
11]. The Germany’s vaccination strategy prioritized healthcare workers to receive the vaccine, especially those who worked in the frontlines and treated COVID-19 patients [
11,
12].
In a recent cross-sectional study, Bauernfeind et al., 2021 investigated the opinions of the healthcare workers in Germany about COVID-19 vaccination [
13]. This study revealed that 59.5% of the surveyed subjects were willing to get vaccinated, 21.4% were hesitant, and 18.7% were against getting vaccinated, thus bolding the need for innovative strategies to tackle vaccine hesitancy and resistance drivers among German healthcare workers [
13]. Aversion to side effects had been widely recognized as one of the key drivers of vaccine hesitancy that requires transparent and independent safety evidence of the vaccines, especially the novel ones [
14].
The overarching aim of this study was to investigate the short-term side effects following COVID-19 vaccines reported by German healthcare workers. The primary objective was to estimate the prevalence of the side effects of both mRNA-based and viral vector-based vaccines. The secondary objectives were (a) to evaluate the demographic and medical risk factors of the COVID-19 vaccines side effects; and (b) to compare between the side effects frequency and intensity of mRNA-based versus viral vector-based vaccines.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
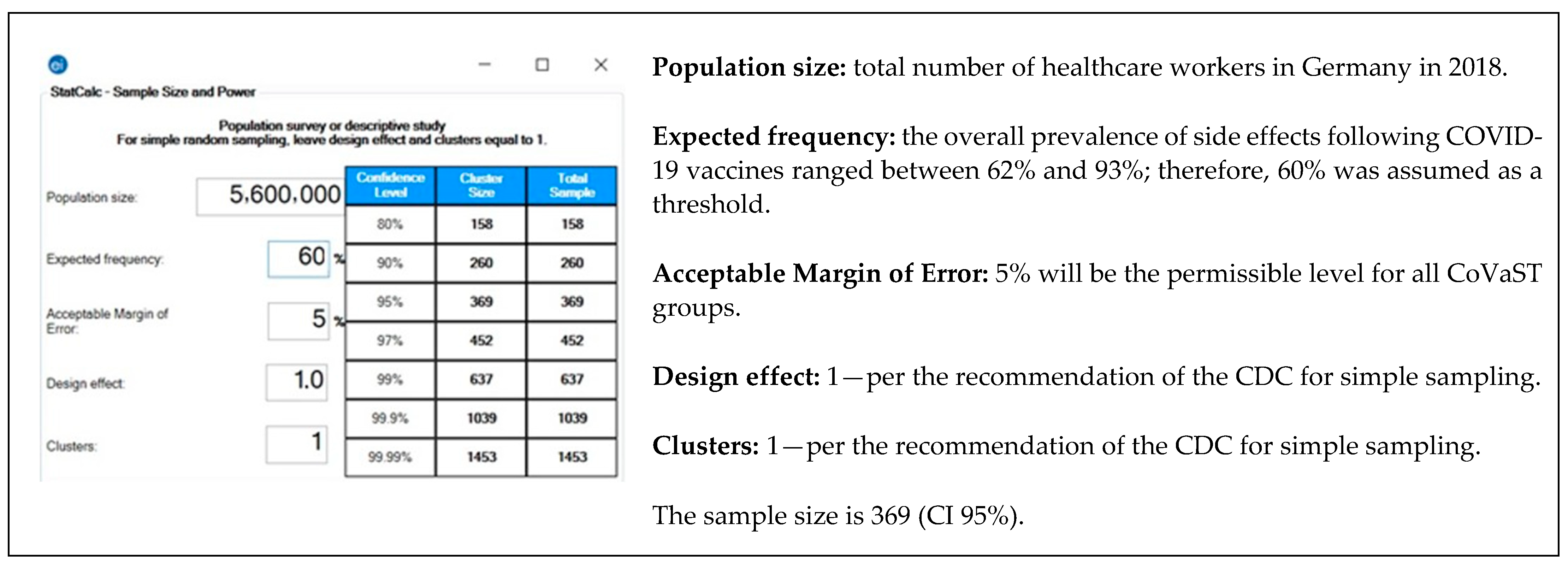
A total of 599 participants completed the SAQ properly; therefore, they were included in the final analysis. While 386 participants received Pfizer-BioNTech and 88 received Moderna (mRNA-based vaccine; n = 474), 125 received AstraZeneca-Oxford (viral vector-based vaccine; n = 125). The included participants received their first dose of the vaccines between 27 December 2020 and 30 March 2021.
The optimal sample size was reached for the total number of participants and for participants with Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. The median age of the participants was 39 years old; therefore, it was used in the downstream analyses as a cut-off for age-dependent comparisons. Out of the 474 mRNA-based vaccine recipients, 73.6% were females, 50.4% were ≤ 39 years-old, 51.3% were nurses, 40.9% had > 20 years of work experience, and 75.7% were from Schleswig-Holstein. Out of the 125 viral vector-based vaccine recipients, 67.2% were females, 50.4% were ≤ 39 years-old, 40.8% were nurses, 37.6% had 1–5 years of work experience, and 70.4% were from Schleswig-Holstein (
Table 1).
3.2. Medical Anamneses
Overall, 29.5% and 24.8% of mRNA-based vaccine and viral vector-based vaccine recipients reported at least one non-communicable disease, respectively. The most common chronic illness among mRNA-based vaccine recipients was thyroid disease (7.6%), followed by chronic hypertension (6.1%), and asthma (6.1%). Similarly, thyroid disease (8.8%) was the most common illness among viral vector-based vaccine recipients, followed by chronic hypertension (5.6%). The only significant difference between mRNA-based vaccine recipients and viral vector-based vaccine recipients (χ2 = 4.115 and 7.146; Sig. = 0.043 and 0.030) was in terms of asthma (6.1% vs. 1.6%) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (0.2% vs. 2.4%).
While 35.4% of mRNA-based vaccine recipients were taking medications regularly, only 24% of viral vector-based vaccine recipients were taking them (
χ2 = 5.853;
Sig. = 0.016). Antihypertensive drugs (12.9%) were the most common among mRNA-based vaccine recipients, followed by thyroid hormone supplements (8.9%), contraceptives (5.3%), immunosuppressive drugs (3.8%), and antidepressants (3.6%). In the viral vector-based vaccine group, thyroid hormone supplements (8.8%) were the most common medication, followed by antihypertensive drugs (5.6%), antidepressants (5.6%), antidepressants (5.6%), and contraceptives (3.2%) (
Table 2).
3.3. COVID-19-Related Anamneses
However, the vast majority of mRNA-based vaccine group (90.3%) received two doses, the vast majority of viral vector-based vaccine group (99.2%) received only one dose by the time they filled in the SAQ (
χ2 = 389.771;
Sig. < 0.001). Only four recipients of mRNA vaccine and two recipients of viral vector-based vaccine were previously infected by SARS-CoV-2. In total, 175 (29.2%) participants reported being exposed to COVID-19 patients during the last months (
Table 3).
3.4. Local and Systemic Side Effects
All local side effects, related to the injection site, were more prevalent in the mRNA-based vaccine group than the viral vector-based vaccine group. A total of 78.3% and 70.4% of mRNA-based vaccine and viral vector-based vaccine recipients reported at least one local side effect (χ2 = 3.421; Sig. = 0.064), respectively. Overall, injection site pain (75.6%) was the most prevalent local side effect, followed by injection site swelling (18%) and injection site redness (10.4%). Injection site pain (77.4% vs. 68.8%, respectively) was significantly more common in the mRNA-based vaccine group compared to the viral vector-based vaccine group (χ2 = 3.993; Sig. = 0.046).
On the contrary, all systemic side effects were more prevalent in the viral vector-based vaccine group than the mRNA-based vaccine group. A total of 87.2% and 61% of viral vector-based vaccine and mRNA-based vaccine recipients reported at least one systemic side effect (χ2 = 30.522; Sig. < 0.001), respectively. Overall, the most common systemic side effect was headache/fatigue (53.6%), followed by muscle pain (33.2%), malaise (25%), chills (23%), and joint pain (21.2%). The differences between the viral vector-based vaccine group and mRNA-based vaccine group were statistically significant (χ2 = 97.782, 106.419, 27.506, 27.292, 63.907, 16.161 and 47.501; Sig. < 0.001, < 0.001, < 0.001, < 0.001, < 0.001, < 0.001 and < 0.001, respectively) in terms of fever (48% vs. 9.9%), chills (57.6% vs. 13.9%), headache/fatigue (74.4% vs. 48.1%), muscle pain (52.8% vs. 28.1%), joint pain (47.2% vs. 14.3%), nausea (20.8% vs. 8.2%), and malaise (48.8% vs. 18.8%).
In general, 86.3% and 80% of the side effects reported by mRNA-based vaccine and viral vector-based recipients remained 1–3 days. The severe side effects that required medical attention were reported only by two (0.4%) mRNA-based vaccine recipients and four (3.2%) viral vector-based vaccine recipients (
Sig. = 0.019; 2-S Fisher’s exact test) (
Table 4).
3.5. Oral and Skin-Related Side Effects
A total of 106 (17.7%) participants reported experiencing at least one oral side effect, with 12.4% and 37.6% of mRNA-based vaccine and viral vector-based vaccine recipients being affected (χ2 = 42.967; Sig. < 0.001), respectively.
The most prevalent oral side effect was vesicles (6.3%), followed by bleeding gingiva (4.3%), halitosis (3.7%), oral paranesthesia (2.2%), swollen mucosa (2.2%), and ulcers (2%). Taste disturbance (6.4% vs. 0.8%), vesicles (12.8% vs. 4.6%), halitosis (10.4% vs. 1.9%), bleeding gingiva (12% vs. 2.3%), and xerostomia (2.4% vs. 0%) were significantly more common among viral vector-based vaccine recipients.
More than three-fourths (75.6%) of oral side effects emerged within the first week after vaccination. The most common site for ulcers, vesicles and blisters were labial/buccal mucosa (43.2%), followed by lips (29.5%) and tongue (27.3%). Tongue (57.1%) and labial/buccal mucosa (57.1%) were the common sites for white/red plaque (
Table 5).
A total of 21 (3.5%) participants reported experiencing at least one skin-related side effect, with 3% and 5.6% of mRNA-based vaccine and viral vector-based vaccine recipients being affected (Sig. = 0.171; 2-S Fisher’s exact test), respectively.
The most prevalent skin-related side effect was rash (2.8%), followed by urticaria (0.7%), and angioedema (0.7%). The most common affected sites were face (57.1%), followed by upper limb (38.1%), and lower limb (19%) (
Table 6).
3.6. COVID-19 Vaccines Side Effects by Gender
The local side effects were almost equally distributed between female (78.2%) and male (77.9%) participants who received mRNA-based vaccines. On the other hand, the females who received the viral vector-based vaccine had a significantly higher prevalence of local side effects (χ2 = 5.989; Sig. = 0.014) compared to their male counterparts, 77.4% vs. 56.1, respectively.
Similarly, the difference between female and male participants in terms of systemic side effects was not statistically significant in the case of mRNA-based vaccines (χ2 = 1.868; Sig. = 0.172), but it was statistically significant in the case of the viral vector-based vaccine (χ2 = 4.578; Sig. = 0.032).
In the mRNA-based vaccine group, females had higher prevalence of fever (10.6% vs. 7.4%), chills (14.9% vs. 11.5), headache/fatigue (51.3% vs. 38.5%), muscle pain (28.4% vs. 27%), joint pain (15.8% vs. 9.8%), and lymphadenopathy (10.3% vs. 4.9%) than males (
Figure 2).
In the viral vector-based vaccine group, females had higher prevalence of fever (53.6% vs. 36.6%), chills (60.7% vs. 51.2%), headache/fatigue (81% vs. 61%), muscle pain (56% vs. 46.3%), joint pain (52.4% vs. 36.6%), nausea (22.6% vs. 17.1%), and malaise (51.2% vs. 43.9%) (
Figure 3).
The severe side effects were exclusively reported by females (n = 2) in the mRNA-based vaccine, and in the viral vector-based vaccine, the female:male ratio was 3:1. Oral side effects affected males slightly more than females in the mRNA-based vaccine group (14.8% vs. 11.7%) and the viral vector-based vaccine group (39% vs. 36.9%). In the mRNA-based vaccine group, all the skin-related side effects were reported by females (
Table 7).
3.7. COVID-19 Vaccines Side Effects by Age
The local side effects were almost equally distributed between the younger age group (≤ 39 years-old) and the older age group (≤ 39 years-old) participants who received mRNA-based vaccines (78.7% vs. 77.9%, respectively) and the viral vector-based vaccine (73% vs. 67.7%, respectively).
The difference between the younger age group and older age group participants in terms of systemic side effects was statistically significant in case of mRNA-based vaccines (χ2 = 8.281; Sig. = 0.004), but it was not statistically significant in case of the viral vector-based vaccine (χ2 = 1.075; Sig. = 0.300). While the younger age group was more affected by systemic side effects following mRNA-based vaccines (67.4% vs. 54.5%), they were less affected by systemic side effects following viral vector-based vaccine (84.1% vs. 90.3%) compared to the older age group.
In the mRNA-based vaccine group, the younger age group had a significantly higher level of headache/fatigue (
χ2 = 11;
Sig. = 0.001) and joint pain (
χ2 = 7.882;
Sig. = 0.005) than the older age group (
Figure 4).
In the viral vector-based vaccine group, the older age group had a higher prevalence of most of the investigated systemic side effects but without statistical significance. The largest difference between the age groups was in the case of chills (10.5%), followed by fever (10.3%), and joint pain (8.7%) (
Figure 5).
The severe side effects were exclusively reported by the younger age group (
n = 2) in the mRNA-based vaccine, and in the viral vector-based vaccine, the older age group:younger age group ratio was 3:1. Oral side effects affected the younger age group slightly more than the older age group in the mRNA-based vaccine group (13.8% vs. 11.1%) and the viral vector-based vaccine group (41.3% vs. 33.9%) (
Table 8).
3.8. Risk Factors of COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effects
On performing binary logistic regression for the demographic and medical risk factors, female gender (only for viral vector vaccine), the younger age group, chronic illnesses (only for viral vector vaccine), and medications were associated with an increased odds ratio (OR) of COVID-19 vaccine side effects, however not statistically significant. The previous infection statistically significantly increased OR of side effects for both vaccine types 21.310 for mRNA-based vaccine and 7.721 for viral vector-based vaccine.
Female participants were 3.429 times (CI 95%: 0.910–12.912) more likely to experience side effects after viral vector-based vaccine than their male counterparts. The participants with chronic illnesses and taking medications were 2.173 times (CI 95%: 0.571–8.270) and 3.6 times (CI 95%: 0.965–13.428) more likely to experience side effects after the viral vector-based vaccine (
Table 9).
In the mRNA-based vaccine group, females had OR of 1.338 times (CI 95%: 0.881–2.032) for systemic side effects and OR of 1.021 times (CI 95%: 0.621–1.679) for local side effects. The younger age group had OR of 1.725 times (CI 95%: 1.188–2.505) for systemic side effects and OR of 1.047 times (CI 95%: 0.677–1.621) for local side effects. The chronic illnesses increased the OR for systemic side effects slightly; similarly, the medications increased the OR for local side effects slightly (
Table 10).
In the viral vector-based vaccine group, females had OR of 3.094 times (CI 95%: 1.061–9.022) for systemic side effects and OR of 2.677 times (CI 95%: 1.202–5.965) for local side effects. The participants with chronic illnesses had OR of 2.016 times (CI 95%: 0.667–7.094) for systemic side effects and OR of 1.182 times (CI 95%: 0.492–2.836) for local side effects. The participants taking medications regularly had OR of 2.125 times (CI 95%: 0.701–6.441) for systemic side effects and OR of 2.739 times (CI 95%: 1.162–6.455) for local side effects (
Table 11).
4. Discussion
This post-marketing study demonstrated that 88.1% of the surveyed German healthcare workers reported at least one side effect after receiving COVID-19 vaccines; 87.1% following mRNA-based vaccines and 92% following the viral vector-based vaccine.
The cross-vaccine comparison of our sample data revealed that mRNA-based vaccines were associated with more frequent local side effects (78.3% vs. 70.4%); while the viral vector-based vaccine was associated with more frequent systemic side effects (87.2% vs. 61%). The largest post-marketing study to date of COVID-19 vaccines analyzed the side effects of BNT162b2 (mRNA-based vaccine) and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (viral vector-based vaccine) reported by UK inhabitants using the COVID-19 Symptom Study app (ZOE Global, London, UK) [
29,
30]. Our results are consistent with the findings of this UK study; as the mRNA-based vaccine was associated with a higher prevalence of local side effects (71.7% vs. 58.7%), while the viral vector-based vaccine was associated with a higher prevalence of systemic side effects (33.7% vs. 20%) among the British population [
30]. Similarly, Mathioudakis et al., 2021 found that local side effects were more frequent in the mRNA-based vaccine group, while the systemic side effects were more frequent in the viral vector-based vaccine group [
31]. Abu-Hammad et al., 2021 found that the mRNA-based vaccine was significantly associated with local side effects, while the viral vector-based vaccine was associated with systemic side effects among Jordanian healthcare workers [
32]. On the contrary, Alhazmi et al., 2021 found no significant difference in terms of local side effects among vaccinated individuals in Saudi Arabia; however, the viral vector-based vaccine was still significantly associated with an increased risk of systemic side effects [
33].
While the vast majority of governments rely on more than one vaccine in their mass-vaccination strategies, there is a lack of evidence on the comparative side effects of different COVID-19 vaccines [
34,
35]. The current evidence is limited by a series of constraints, including unequal sample size across the study groups, lack of normal distribution of demographic and medical risk factors across the study groups, and lack of attention to the onset of each side effect [
30,
31,
32,
33,
36]. Vaccine selectivity can be defined as “the discriminatory attitudes towards certain types of vaccines based on their target contagion or manufacturing technology that yields heterogeneous acceptance levels of recommended vaccines”. Understandably, public health researchers might be diverted from comparing the side effects of different COVID-19 vaccines to avoid triggering vaccine selectivity through misinterpretation of their results. Nevertheless, the infodemic related to vaccine safety has been pragmatically targeting specific types of COVID-19 vaccines to increase vaccine hesitancy or trigger public selectivity against these vaccines [
37,
38]. Therefore, it is imperative to expand in the cross-vaccine comparison research while sticking to the highest standards of epidemiologic methodology to synthesize rigorous evidence that should fairly inform the public and individuals’ decision of vaccination.
The younger age (≤39 years-old) group were 1.122 times (CI 95%: 0.683–1.842) more likely to experience side effects compared to the older age (>39 years-old) group. The age-related differences in our sample were only statistically significant in case of systemic side effects that affected the mRNA-based vaccine recipients (67.4% vs. 54.5%;
Sig. = 0.004). Nonetheless, the older age group had more systemic side effects following viral vector-based vaccine than the younger group. Menni et al., 2021 found that the British individuals aged 55 years or below had significantly higher prevalence of side effects following both mRNA-based and viral vector-based vaccines [
30]. Similarly, Jordanian healthcare workers (≤45 years-old) and UAE inhabitants (≤49 years-old) reported more side effects following COVID-19 vaccination [
32,
39]. Mazur et al., 2021 found that the incidence of post-vaccination oral side effects decreases in the older age groups among the included European healthcare workers [
36]. In Czech Republic and Turkey, the younger healthcare workers reported a higher incidence of short-term side effects following BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccines, respectively, compared to their older colleagues [
20,
22]. In contrast to the supposition that “the younger you are, the more likely to experience side effects”, El-Shitany et al., 2021 found that the Saudi individuals aged 60 years or above had a significantly higher level of local side effects, especially injection site pain (80.8% vs. 68.6%;
Sig. = 0.0056) compared to their younger counterparts who received BNT162b2 vaccine [
40].
The increased odds of side effects among young adults can be explained by the fact that these side effects are a by-product of the exuberant production of type I interferon (IFN-I) that occurs to initiate an effective immune response to the invading pathogen [
41]. The generation of IFN-I in females and younger adults was found to be more potent [
41,
42]. The pre-marketing (phase III) and post-marketing (phase IV) studies of COVID-19 vaccines used heterogonous cut-off points for the age-related analyses of vaccines reactogenicity and side effects. While the phase III trials used the retirement age cut-offs, e.g., 55 years-old and 65 years-old, some phase IV studies were inclined to use the median age of their own surveyed samples in order to compare the prevalence of post-vaccination side effects [
20,
30,
40]. Both approaches are unequivocally effective in evaluating and communicating age-related differences; nevertheless, harmonizing vaccine safety reports, especially those from independent institutions, became a methodological must. Therefore, the findings of this study call for developing consensus guidelines for reporting COVID-19 vaccine side effects and effectiveness.
Female participants in our study had OR of 0.833 (CI 95%: 0.441–1.573) and 3.429 (CI 95%: 0.910–12.912) to experience side effects following mRNA-based vaccines and viral vector-based vaccine, respectively, thus indicating that viral vector-based vaccines impact females more significantly, while mRNA-based vaccines had no statistically significant lower OR in females. We can hypothesize that if an optimal sample size was reached for the viral vector-based vaccine this result would be more likely also statistically significant. Interestingly, all side effects were more common among female recipients of viral vector-based vaccine except injection site redness and lymphadenopathy, which were slightly more common among male recipients. Alghamdi et al., 2021 found within a viral vector-based vaccine recipients sample that the prevalence of post-vaccination side effects was significantly higher in females than males [
43]. They also found that the onset of side effects occurrence is faster in females, and also the intensity of side effects and the rate of pain killer consumption were significantly higher in females [
43]. The female predominance was also reported in mRNA-based vaccines and inactivated virus vaccines [
20,
22,
40].
The more vigorous immune response and the lower pain threshold of females are suggested hypotheses to explain the gender-based differences in self-reported COVID-19 vaccines side effects [
44,
45]. The selection bias and the information bias may also play a key role in the emergence of gender-based differences; therefore, gender-adjusted analyses are indispensable in studying the self-reported outcomes of COVID-19 vaccines. Females were consistently associated with an increased risk of side effects following viral vaccines, including influenza, measles–mumps–rubella combination vaccine (MMR), attenuated Japanese encephalitis, and attenuated Dengue vaccines [
44,
46]. Future research should focus on the gender-based differences of COVID-19 vaccines side effects.
Injection site pain was the most prevalent local side effect in our sample (75.6%), followed by injection swelling (18%) and injection site redness (10.4%). The same order was found in both vaccines, the UK, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and the Czech Republic [
20,
30,
32,
40]. In general, all the systemic side effects were significantly more common among viral vector-based vaccine recipients than mRNA-based vaccine recipients.
The most common systemic side effect among our mRNA-based vaccine recipients was headache/fatigue (48.1%), followed by muscle pain (28.1%), malaise (18.8%), joint pain (14.3%), chills (13.9%), and fever (9.9%). In the safety report of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for BNT162b2 vaccine, headache/fatigue (44.1%) was the most common systemic side effect reported by the phase III volunteers, followed by muscle pain (25.4%), chills (19.7%), joint pain (15%), and fever (7.9%) [
24]. The CDC report of mRNA-1273 vaccine revealed that headache/fatigue (47.8%) was the most common systemic side effect, followed by muscle pain (40%), joint pain (29%), chills (25.3%), and fever (7.9%) [
25]. The prevalence of mRNA-based vaccine systemic side effects in our sample was lower than what was reported in the phase III trials [
24,
25]. The similar finding was reported by the UK study were the side effects prevalence among the app user being significantly lower than the manufacturers’ reports [
30]. Contrarily, Riad et al., 2021 found that the post-marketing prevalence of BNT162b2 side effects among Czech healthcare workers was higher than what was reported by the manufacturer [
20].
The most common systemic side effect among our viral vector-based vaccine recipients was headache/fatigue (74.4%), followed by chills (57.6%), muscle pain (52.8%), malaise (48.8%), fever (48%), and joint pain (47.2%). In the safety report of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine, headache (52.7%), fatigue (53%), malaise (44.4%), muscle pain (43.9%), fever (41.1%), chills (32.2%), and joint pain (26.6%) [
26]. The increased prevalence of side effects among our sample can be explained by the fact that the frequency of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 side effects decreases after the second dose while our sample participants received only the first dose [
26].
Manfredi et al., 2021 reported a case of a middle-aged female recipient of BNT162b2 vaccine who presented to their clinic with diffuse ulcerative lesions on the floor of the mouth associated with angular cheilitis and erythema of the tongue after two days of her first dose [
47]. Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) as a constituent component of the mRNA-based vaccine was suspected to trigger these oral side effects [
47,
48]. Azzi et al., 2021 reported another case of a middle-aged female recipient of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 with diffuse, erythematous and swollen red lesions on her buccal mucosa, tongue, gingiva and palate [
49]. Heterozygous Factor V Leiden mutation was suspected to be the trigger of the thromboembolic events that were experienced by the patient, in addition to being a predisposing factor for the oral mucositis episode that followed the COVID-19 vaccination [
49,
50]. Oral mucosal lesions were increasingly reported in COVID-19 patients in the last months; therefore, the oral side effects of COVID-19 vaccines may mimic the COVID-19-associated oral symptoms [
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59].
In our sample, 17.7% of the participants reported at least one oral side effect, with mucosal lesions being the most commonly reported side effects, followed by bleeding gingiva (4.3%), halitosis (3.7%), and oral paranesthesia (2.2%), and taste disturbance (2%). It is worthy of mentioning that oral paranesthesia and taste disturbance were not solicited in our original questionnaire, even though the participants reported it voluntarily in the additional comment boxes. Therefore, we suggest that the actual prevalence of oral paranesthesia and taste disturbance can be higher than what we report in this study. The participants referred to oral paranesthesia by keywords, such as tongue tingling, mouth-tingling, and pins and needles sensation, e.g., while they referred to the taste disturbance by keywords like metallic taste, taste change, salty taste, and unpleasant taste, etc.
A large registry-based study by McMahon et al., 2021 revealed that mRNA-based vaccines were associated with a myriad of skin-related side effects that mimicked the SARS-CoV-2 infection [
60]. In our sample 17 (2.8%) participants reported experiencing rash after vaccination, 4 (0.7%) reported urticaria, and 4 (0.7%) reported angioedema. The most common location of skin-related side effects was face (57.1%), followed by upper limb (38.1%), and lower limb (19%). However, there is a paucity of focus on the less common side effects, such as skin-related side effects by the phase IV trials of COVID-19 vaccines, and there is an emerging number of individual case reports and case series for recently vaccinated individuals with skin-related side effects [
61].
4.1. Strengths
This is the first study to evaluate the side effects of COVID-19 vaccines among the German population to the best of the authors’ knowledge. This study is one of the few studies that aims to enhance our emerging knowledge about the risk factors of COVID-19 vaccines side effects by inquiring and analyzing the self-reported side effects across various demographic and medical parameters [
20,
21,
22,
30,
31,
40,
62].
Another contribution of this study is its focus on the less reported side effects, e.g., the oral and skin-related ones, which were not solicited in the manufacturers’ reports of the phase III trials. However, the less common side effects being mild to moderate, may act as a trigger for a vaccine hesitancy or vaccine resistance position by the vaccinated individuals or their household and acquaintances because they were not clearly explained a priori. The optimal sample size was reached for a total number of participants and for participants with Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.
4.2. Limitations
The first limitation of this study is that the vast majority of viral vector-based vaccine recipients received only the first dose by the time they filled in the questionnaire; therefore, it was not possible to compare between the first and the second dose side effects. However, this corresponds with the public health strategy to extend the period between the first and second dose, especially among viral vector-based vaccines. Another limitation is because we did not ask about the timing of each inquired side effect, whether it was after the first dose, second dose, or both doses. The software used for data collection, KoBoToolbox, does not enable the researchers to learn the number of form visitors (potential respondents) which is the denominator of the response rate equation; therefore, we could not calculate the response rate in our study.
While this study, like typical post-marketing (phase IV) trials, relies primarily on the self-reported outcomes of the respondents, it had targeted healthcare workers as they are deemed to retain substantial levels of health literacy. The optimal sample size was not reached for the number of participants with Moderna and AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccines. This limitation should be seen in the context of the national vaccination strategy that limited the number of healthcare workers who received Moderna and AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccines.
4.3. Implications
This study implies that future research of COVID-19 vaccine safety should focus on cross-vaccine comparison as it can deliver timely and critical messages to the public. The findings of this study strengthen the call for consensus guidelines for reporting the independent studies of COVID-19 reactogenicity and side effects to overcome the growing heterogeneity among the reports of different research groups worldwide.
The age and gender-related differences of local and systemic side effects prevalence and incidence warrant further investigation. The less common side effects, e.g., oral and skin-related side effects, should be widely tracked by independent vaccine safety studies. The onset of each side effect and its duration should be precisely inquired about in future vaccine safety studies.
The findings of this study serve as independent evidence on the safety of COVID-19 vaccines that should encourage the public to take informed decisions for getting vaccinated, as the non-serious side effects we found were of limited duration (1–3 days),mainly related to the injection site and not interfering with the daily routine.