Cognitive Phenotypic Plasticity: Environmental Enrichment Affects Learning but Not Executive Functions in a Teleost Fish, Poecilia reticulata
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Environmental Enrichment Treatment
2.3. Inhibitory Control
2.4. Learning
2.5. Cognitive Flexibility
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
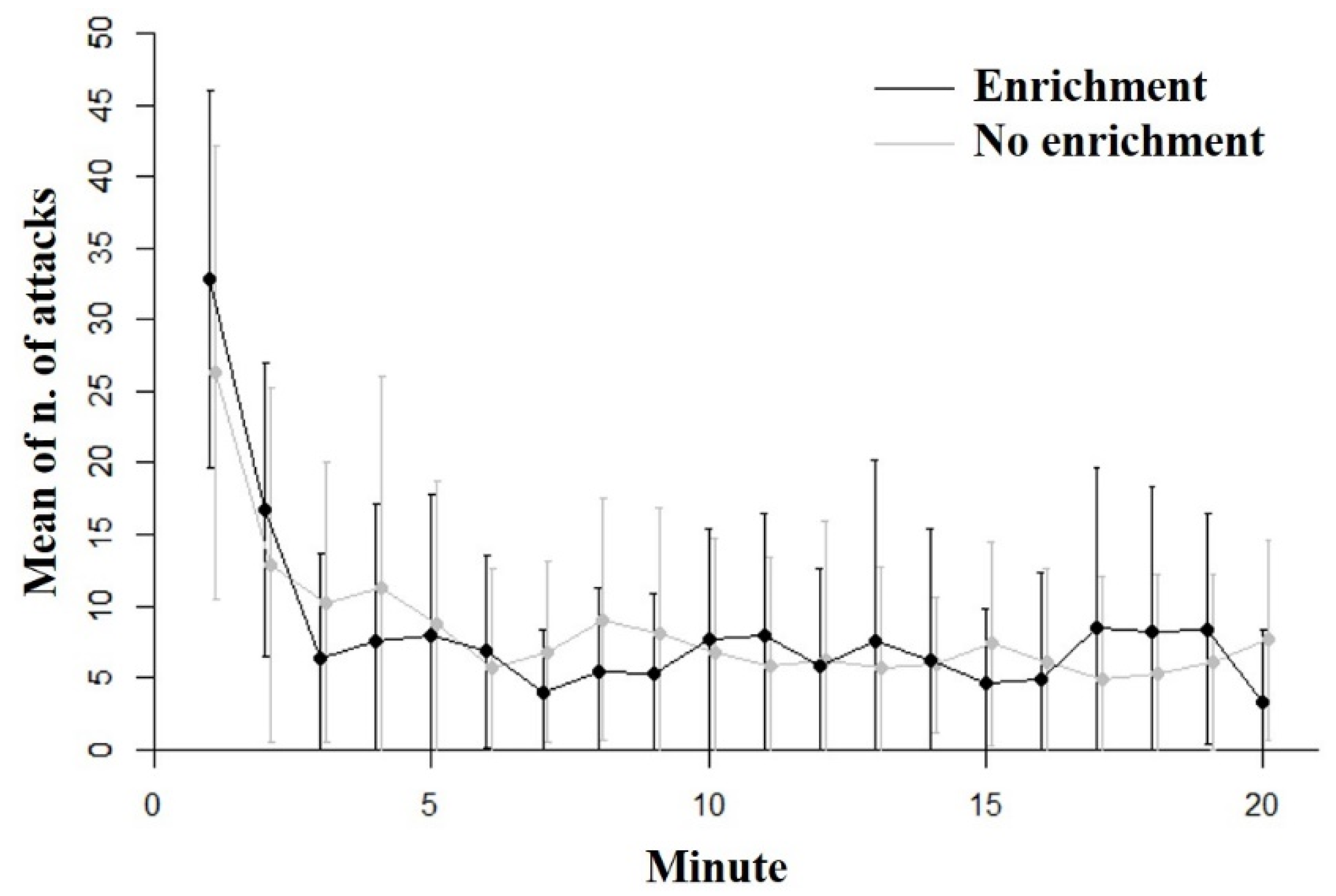
3.1. Inhibitory Control
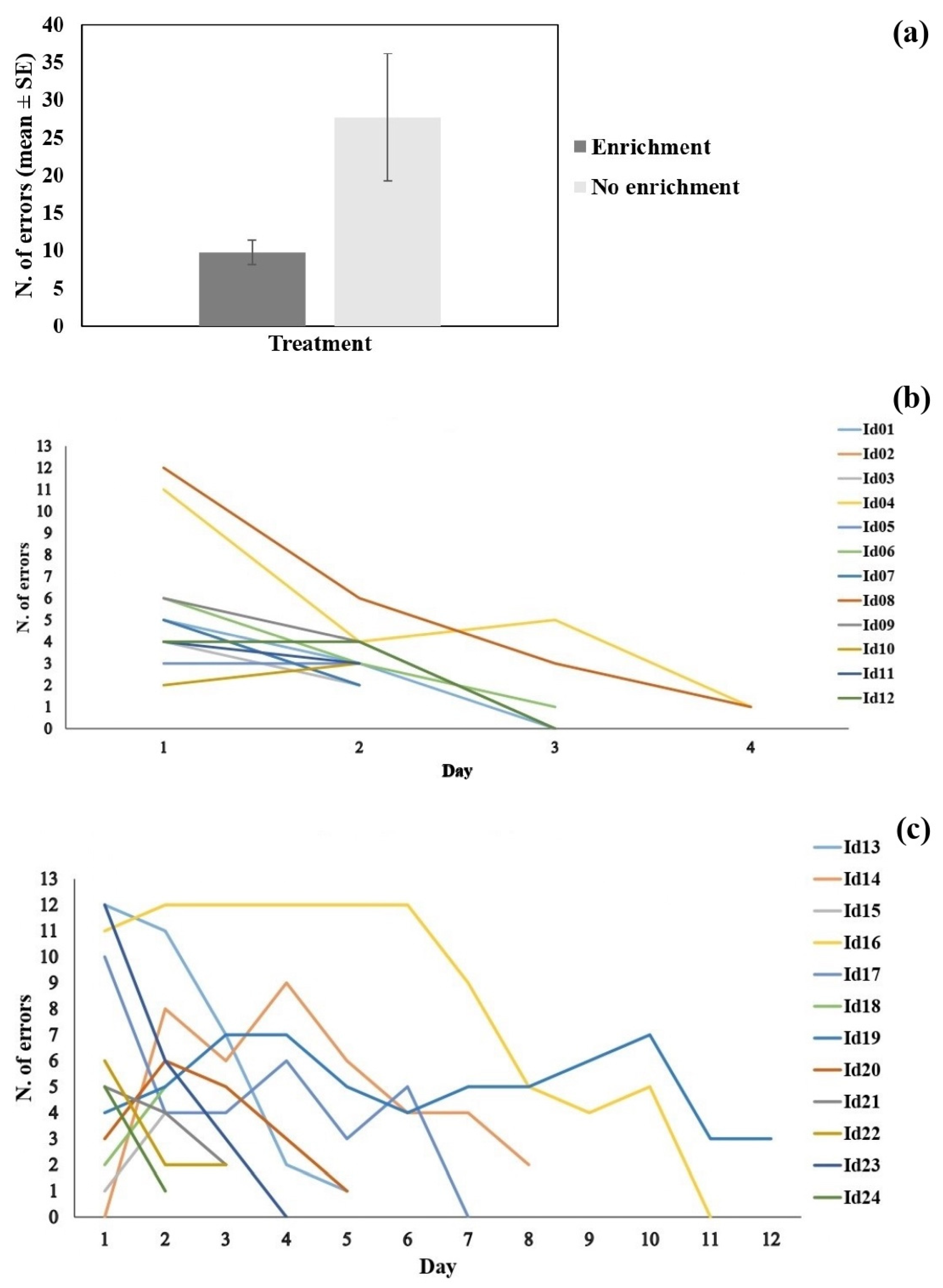
3.2. Learning
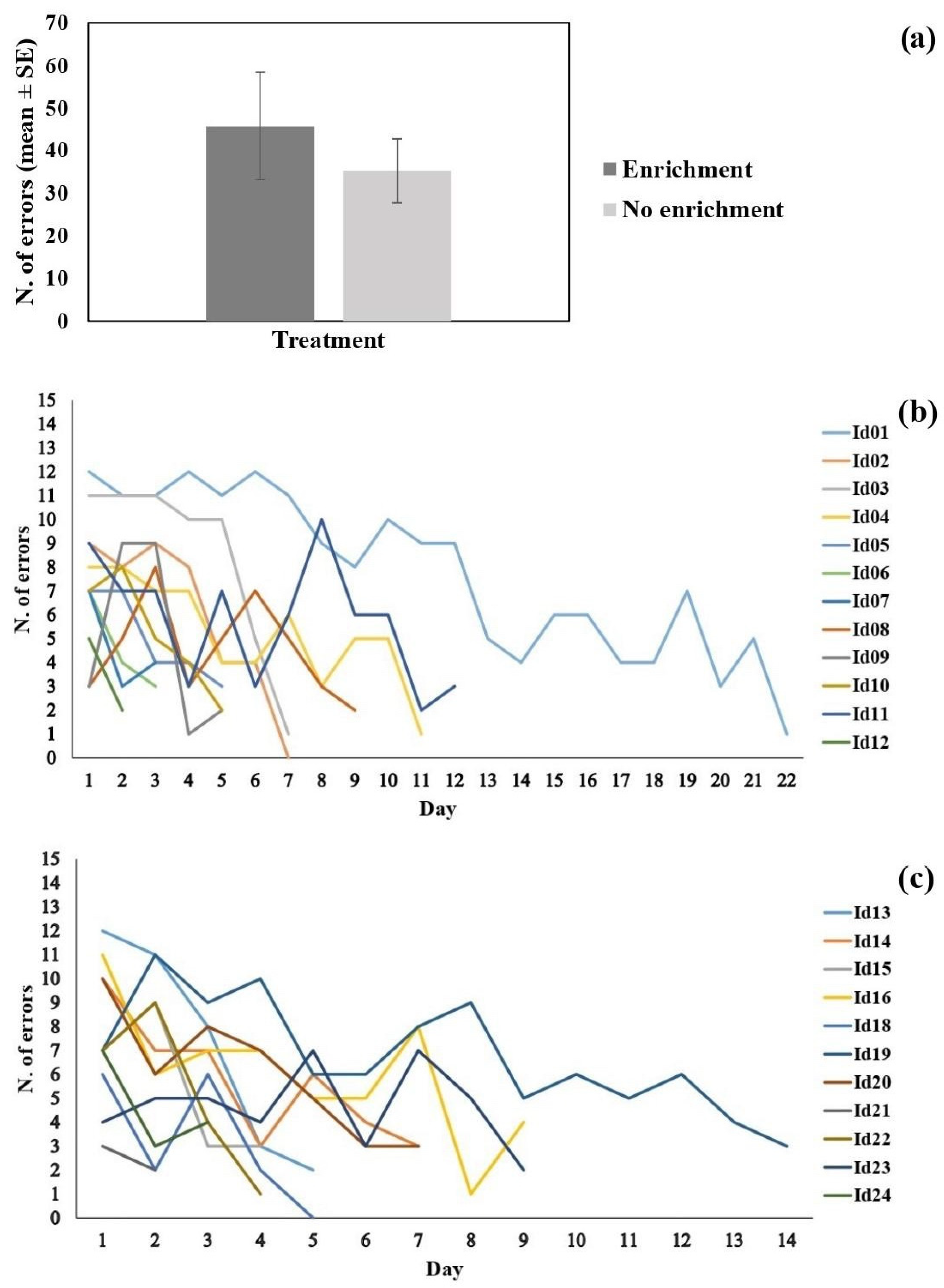
3.3. Cognitive Flexibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ban, S.D.; Boesch, C.; Janmaat, K.R. Taï chimpanzees anticipate revisiting high-valued fruit trees from further distances. Anim. Cogn. 2014, 17, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, P.A.U.L.; Reznick, D.N. Patterns and analysis of adaptive phenotypic plasticity in animals. In Phenotypic Plasticity: Functional and Conceptual Approaches, 1st ed.; DeWitt, T.J., Scheiner, S.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 126–150. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, J.L. Predation and relative helmet size in cyclomorphic Daphnia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 53, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tollrian, R. Predator-induced helmet formation in Daphnia cucullata (Sars). Arch. Hydrobiol. 1990, 119, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, I.A. Environment and plasticity of myogenesis in teleost fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2249–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McPeek, M.A. Morphological evolution mediated by behavior in the damselflies of two communities. Evolution 1995, 49, 749–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, J.; Svanbäck, R.; Eklöv, P. Effects of resource level and habitat type on behavioral and morphological plasticity in Eurasian perch. Oecologia 2007, 152, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culumber, Z.W.; Shepard, D.B.; Coleman, S.W.; Rosenthal, G.G.; Tobler, M. Physiological adaptation along environmental gradients and replicated hybrid zone structure in swordtails (Teleostei: Xiphophorus). J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 25, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Ren, Z.; Han, F.; Tan, X.; Xiang, Z.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. Genomic mechanisms of physiological and morphological adaptations of limestone langurs to karst habitats. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 952–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binning, S.A.; Ros, A.F.; Nusbaumer, D.; Roche, D.G. Physiological plasticity to water flow habitat in the damselfish, Acanthochromis polyacanthus: Linking phenotype to performance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girvan, J.R.; Braithwaite, V.A. Population differences in spatial learning in three–spined sticklebacks. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, B.B.; Ward, A.J.; Krause, J. Schooling and learning: Early social environment predicts social learning ability in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, E.F.; Morand-Ferron, J.; Hinks, A.E.; Quinn, J.L. Cognitive ability influences reproductive life history variation in the wild. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauchard, L.; Angers, B.; Boogert, N.J.; Lenarth, M.; Bize, P.; Doligez, B. An experimental test of a causal link between problem-solving performance and reproductive success in wild great tits. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotrschal, A.; Taborsky, B. Environmental change enhances cognitive abilities in fish. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebbesson, L.O.E.; Braithwaite, V.A. Environmental effects on fish neural plasticity and cognition. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 2151–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, L.C.; Wheeler, P. The expensive-tissue hypothesis: The brain and the digestive system in human and primate evolution. Curr. Anthropol. 1995, 36, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrschal, A.; Rogell, B.; Bundsen, A.; Svensson, B.; Zajitschek, S.; Brännström, I.; Kolm, N. Artificial selection on relative brain size in the guppy reveals costs and benefits of evolving a larger brain. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sewall, K.B. Social complexity as a driver of communication and cognition. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvanes, A.G.V.; Moberg, O.; Ebbesson, L.O.; Nilsen, T.O.; Jensen, K.H.; Braithwaite, V.A. Environmental enrichment promotes neural plasticity and cognitive ability in fish. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G. Environmental enrichment, new neurons and the neurobiology of individuality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, Z.J.; Tropepe, V. Using teleost fish to discern developmental signatures of evolutionary adaptation from phenotypic plasticity in brain structure. Front. Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbia, P.S.; Brown, C. Environmental enrichment influences spatial learning ability in captive-reared intertidal gobies (Bathygobius cocosensis). Anim. Cogn. 2019, 22, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, D.A.; Utne-Palm, A.C.; Jakobsen, P.J.; Braithwaite, V.A.; Jensen, K.H.; Salvanes, A.G. Enrichment promotes learning in fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 412, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, A.; Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bisazza, A. Guppies in the puzzle box: Innovative problem-solving by a teleost fish. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2021, 75, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrillo, C.; Dadda, M.; Serena, G.; Bisazza, A. Use of number by fish. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierszewski, S.; Bleckmann, H.; Schluessel, V. Cognitive abilities in Malawi cichlids (Pseudotropheus sp.): Matching-to-sample and image/mirror-image discriminations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Manabe, K.; Bisazza, A. Guppies learn faster to discriminate between red and yellow than between two shapes. Ethology 2019, 125, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, T.; Witte, K. Sex differences in color discrimination and serial reversal learning in mollies and guppies. Curr. Zool. 2019, 65, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bisazza, A. Discrimination reversal learning reveals greater female behavioural flexibility in guppies. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrazzini, M.E.M.; Bisazza, A.; Agrillo, C.; Lucon-Xiccato, T. Sex differences in discrimination reversal learning in the guppy. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Montalbano, G.; Bertolucci, C. Personality traits covary with individual differences in inhibitory abilities in 2 species of fish. Curr. Zool. 2020, 66, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montalbano, G.; Bertolucci, C.; Lucon-Xiccato, T. Measures of inhibitory control correlate between different tasks but do not predict problem-solving success in a fish, Poecilia reticulata. Intelligence 2020, 82, 101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A. Executive functions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fong, S.; Buechel, S.D.; Boussard, A.; Kotrschal, A.; Kolm, N. Plastic changes in brain morphology in relation to learning and environmental enrichment in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata). J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shettleworth, S.J. Cognition, Evolution, and Behaviour, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Spierer, L.; Chavan, C.; Manuel, A.L. Training-induced behavioral and brain plasticity in inhibitory control. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olivotto, I.; Rollo, A.; Sulpizio, R.; Avella, M.; Tosti, L.; Carnevali, O. Breeding and rearing the Sunrise Dottyback Pseudochromis flavivertex: The importance of live prey enrichment during larval development. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, V.A.; Bergendahl, I.A. The effects of early life experience on behavioural development in captive fish species. In The Welfare of Fish; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Olivotto, I.; Di Stefano, M.; Rosetti, S.; Cossignani, L.; Pugnaloni, A.; Giantomassi, F.; Carnevali, O. Live prey enrichment, with particular emphasis on HUFAs, as limiting factor in false percula clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris, Pomacentridae) larval development and metamorphosis: Molecular and biochemical implications. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 2011, 159, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.D.; Kisko, T.M.; Witt, S.H.; Rietschel, M.; Schwarting, R.K.; Wöhr, M. Long-term environmental impact on object recognition, spatial memory and reversal learning capabilities in Cacna1c-haploinsufficient rats. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 4113–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bertolucci, C. Guppies show rapid and lasting inhibition of foraging behaviour. Behav. Process. 2019, 164, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Petrazzini, M.E.M.; Agrillo, C.; Bisazza, A. Guppies discriminate between two quantities of food items but prioritize item size over total amount. Anim. Behav. 2015, 107, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Santacà, M.; Petrazzini, M.E.M.; Agrillo, C.; Dadda, M. Guppies, Poecilia reticulata, perceive a reversed Delboeuf illusion. Anim. Cogn. 2019, 22, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaney, W.; Kendal, J.; Capon, H.; Brown, C.; Laland, K.N. Familiarity facilitates social learning of foraging behaviour in the guppy. Anim. Behav. 2001, 62, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makino, H.; Masuda, R.; Tanaka, M. Environmental stimuli improve learning capability in striped knifejaw juveniles: The stage-specific effect of environmental enrichment and the comparison between wild and hatchery-reared fish. Fish. Sci. 2015, 81, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.P.; Wang, H.; Feng, R.; Kyin, M.; Tsien, J.Z. Differential effects of enrichment on learning and memory function in NR2B transgenic mice. Neuropharmacology 2001, 41, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.S.; Long, N.; Pigino, G.; Brady, S.T.; Lazarov, O. Molecular mechanisms of environmental enrichment: Impairments in Akt/GSK3β, neurotrophin-3 and CREB signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemenson, G.D.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Environmental enrichment and neurogenesis: From mice to humans. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 4, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Tsai, M.J. The role of BETA2/NeuroD1 in the development of the nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 30, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, C.; Braithwaite, V.A.; Nilsson, J.; Nilsen, T.O.; Teien, H.C.; Handeland, S.O.; Ebbesson, L.O. Aluminum exposure impacts brain plasticity and behavior in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderhaeghen, P. Wnts blow on NeuroD1 to promote adult neuron production and diversity. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, T.; Hsieh, J.; Muotri, A.; Yeo, G.; Warashina, M.; Lie, D.C.; Gage, F.H. Wnt-mediated activation of NeuroD1 and retro-elements during adult neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Bai, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X. Effects of environmental enrichment on the welfare of juvenile black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii: Growth, behavior and physiology. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzina, A.; Kalogiannis, D.; Dalla, C.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z.; Chadio, S.; Karakatsouli, N. Blue substrate modifies the time course of stress response in gilthead seabream Sparus aurata. Aquaculture 2014, 420, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, B.N.; Heath, J.W.; Heath, D.D.; Bernier, N.J. Effects of early rearing environment and breeding strategy on social interactions and the hormonal response to stressors in juvenile Chinook salmon. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogert, N.J.; Lachlan, R.F.; Spencer, K.A.; Templeton, C.N.; Farine, D.R. Stress hormones, social associations and song learning in zebra finches. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawley, W.R.; Grissom, E.M.; Barratt, H.E.; Conrad, T.S.; Dohanich, G.P. The effects of biological sex and gonadal hormones on learning strategy in adult rats. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 105, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, C.; Cooper, G.F. Development of the brain depends on the visual environment. Nature 1970, 228, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.J.; Taylor, J.; De Leaniz, C.G. Environmental enrichment reduces maladaptive risk-taking behavior in salmon reared for conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.L.; Küchler, A.; Damasio, T.; Noble, D.W.; Byrne, R.W.; Whiting, M.J. Learning ability is unaffected by isolation rearing in a family-living lizard. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, T.J.; Fernandez, S.M.; Frick, K.M. Different types of environmental enrichment have discrepant effects on spatial memory and synaptophysin levels in female mice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2005, 83, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Montalbano, G.; Reddon, A.; Bertolucci, C. Social environment affects inhibitory control via developmental plasticity in a fish. Anim. Behav. 2022, 183, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila Pouca, C.; Mitchell, D.J.; Lefèvre, J.; Vega-Trejo, R.; Kotrschal, A. Early predation risk shapes adult learning and cognitive flexibility. Oikos 2021, 130, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Montalbano, G.; Frigato, E.; Loosli, F.; Foulkes, N.S.; Bertolucci, C. Medaka as a model for seasonal plasticity: Photoperiod-mediated changes in behaviour, cognition, and hormones. Horm. Behav. under review.
- Zeleznikow-Johnston, A.; Burrows, E.L.; Renoir, T.; Hannan, A.J. Environmental enrichment enhances cognitive flexibility in C57BL/6 mice on a touchscreen reversal learning task. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, E.L.; Hare, B.; Nunn, C.L.; Addessi, E.; Amici, F.; Anderson, R.C.; Boogert, N.J. The evolution of self-control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2140–E2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalbano, G.; Bertolucci, C.; Lucon-Xiccato, T. Cognitive Phenotypic Plasticity: Environmental Enrichment Affects Learning but Not Executive Functions in a Teleost Fish, Poecilia reticulata. Biology 2022, 11, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010064
Montalbano G, Bertolucci C, Lucon-Xiccato T. Cognitive Phenotypic Plasticity: Environmental Enrichment Affects Learning but Not Executive Functions in a Teleost Fish, Poecilia reticulata. Biology. 2022; 11(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalbano, Giulia, Cristiano Bertolucci, and Tyrone Lucon-Xiccato. 2022. "Cognitive Phenotypic Plasticity: Environmental Enrichment Affects Learning but Not Executive Functions in a Teleost Fish, Poecilia reticulata" Biology 11, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010064
APA StyleMontalbano, G., Bertolucci, C., & Lucon-Xiccato, T. (2022). Cognitive Phenotypic Plasticity: Environmental Enrichment Affects Learning but Not Executive Functions in a Teleost Fish, Poecilia reticulata. Biology, 11(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010064







