Efficacy of Single and Multi-Strain Probiotics on In Vitro Strain Compatibility, Pathogen Inhibition, Biofilm Formation Capability, and Stress Tolerance
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Methods to Determine the Antimicrobial Effect of MSPs
2.1.1. Broth Culture
2.1.2. Antagonistic Assay—Well Diffusion Assay
2.1.3. Compatibility Assessment by Well Diffusion Assay
2.1.4. Co-Culture Assay of MSP with Pathogens
2.2. Properties of MSPs
2.2.1. Biofilm Formation
2.2.2. Resistance to High Temperature
2.2.3. Tolerance of MSP towards Different pH
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
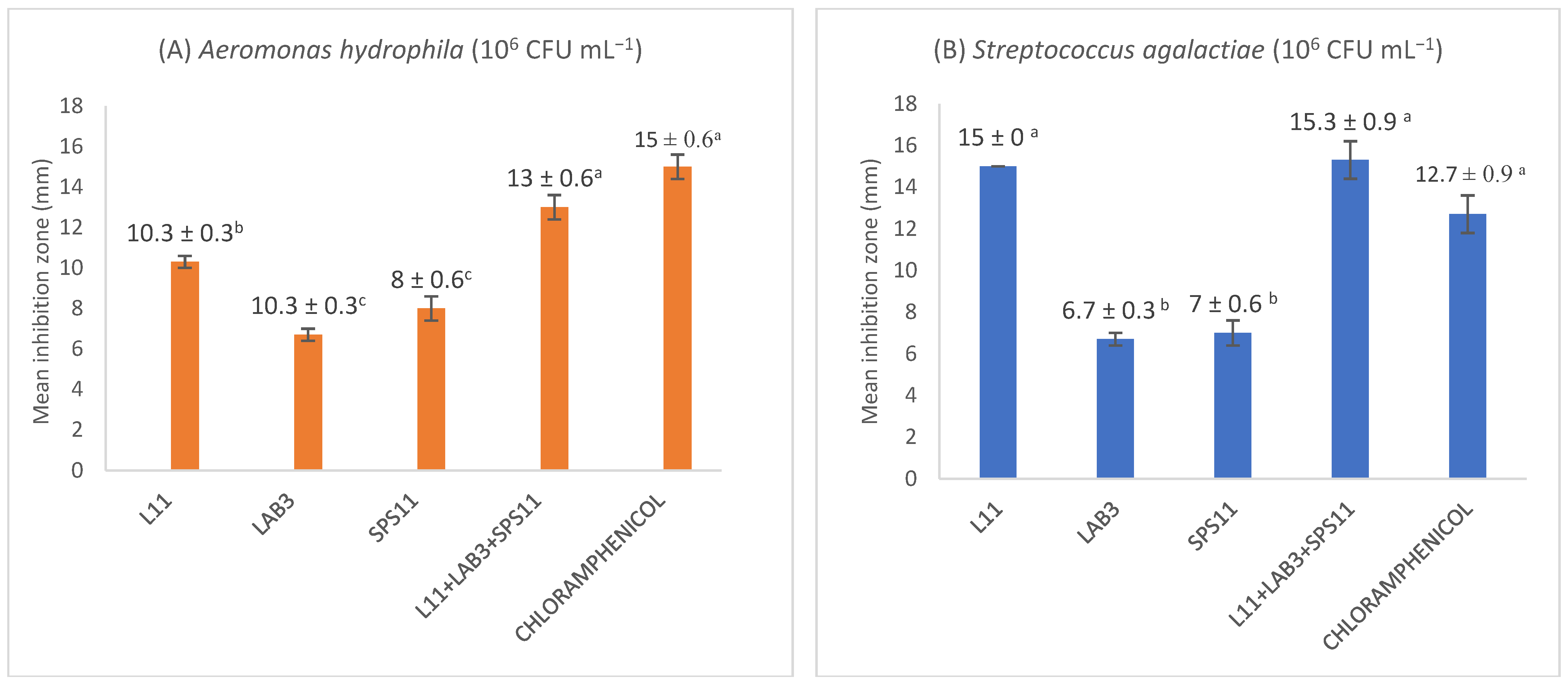
3.1. Antagonistic Assay
3.2. Compatibility Assay between Strains
3.3. Co-Culture Assay
3.4. Biofilm Formation
3.5. Resistance of Single-Strain Probiotics (SSPs) to High Temperatures
3.6. Tolerance of MSP towards Different pH Values
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, N.T.; Yang, W.; Nguyen, X.T.; Zhang, M.; Ma, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, K.G.; Li, S. Application of heat-killed probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Dawood, M.A.; Ringø, E.; Ahmadifar, E.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics used to control vibriosis in fish: A review. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, N.; Wang, H.P.; Yao, H.; Abou-ElGheit, E. Mixed Bacillus species enhance the innate immune response and stress tolerance in yellow perch subjected to hypoxia and air-exposure stress. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoah, K.; Huang, Q.C.; Tan, B.P.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Dong, X.H. Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus coagulans ATCC 7050, improves the growth performance, intestinal morphology, microflora, immune response, and disease confrontation of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, C.M.; Williams, M.A.; Carrias, A.; Ran, C.; Newman, M.; Tweedie, J.; Allison, E.; Jescovitch, L.N.; Wilson, A.E.; Terhune, J.S.; et al. Bacillus velezensis AP193 exerts probiotic effects in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and reduces aquaculture pond eutrophication. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.L.; Shiu, Y.L.; Chiu, C.S.; Huang, S.L.; Liu, C.H. Screening probiotic candidates for a mixture of probiotics to enhance the growth performance, immunity, and disease resistance of Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch), against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Esteban, M.Á. Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 10, 950–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, H.M.; Koning, C.J.; Mulder, L.; Rombouts, F.M.; Beynen, A.C. Monostrain, multistrain and multispecies probiotics—A comparison of functionality and efficacy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 96, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Invernici, M.M.; Furlaneto, F.A.; Messora, M.R. Effectiveness of multi-strain versus single-strain probiotics: Current status and recommendations for the future. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoji, I.D.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Okpeku, M.; Adeleke, M.A. Multi-strain probiotics: Synergy among isolates enhances biological activities. Biology 2021, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azrin, N.A.R.; Yuzine, E.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Karim, M. The efficacy of potential probiont Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain L11 in protecting artemia nauplii and blue crab juveniles against Vibrio harveyi infection. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 13, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masduki, F.; Min, C.C.; Karim, M. Characterization of Enterococcus hirae isolated from the intestine of seabass (Lates Calcarifer) as a new potential probiotic against pathogenic Vibrios. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3962–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabidi, A.; Rosland, N.A.; Yaminudin, J.; Karim, M. In vitro assessment of bacterial strains associated with microalgae as potential probiotics. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2021, 44, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosland, N.A.; Ikhsan, N.; Min, C.C.; Yusoff, F.M.; Karim, M. Influence of symbiotic probiont strains on the growth of amphora and chlorella and its potential protections against Vibrio spp. in artemia. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3901–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengpipat, S.; Rueangruklikhit, T.; Piyatiratitivorakul, S. Evaluations of lactic acid bacteria as probiotics for juvenile seabass Lates calcarifer. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseeharan, B.A.R.P.; Ramasamy, P. Control of pathogenic Vibrio spp. by Bacillus subtilis BT23, a possible probiotic treatment for black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddey, J.A.; Flegg, C.P.; Day, C.J.; Beacham, I.R.; Peak, I.R. Temperature-regulated microcolony formation by Burkholderia pseudomallei requires pilA and enhances association with cultured human cells. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5374–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.H.; Kim, J.M.; Nam, H.M.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.M. Screening lactic acid bacteria from swine origins for multistrain probiotics based on in vitro functional properties. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, M.; Raja, M.; Perumal, P. Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822). Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.A.R.; Alves, L.L.; Barros, F.A.L.; Cordeiro, C.A.M.; Meneses, J.O.; Santos, T.B.R.; Santos, C.C.M.; Paixão, P.E.G.; Nogueira Filho, R.M.; Martins, M.L.; et al. Comparative effects of using a single strain probiotic and multi-strain probiotic on the productive performance and disease resistance in Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2022, 550, 737855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, T.; Praveenraj, J.; Kiruba-Sankar, R.; Haridas, H.; Kumar, S.; Varghese, B. Effects of single and multi-strain probiotics on the growth, hemato-immunological, enzymatic activity, gut morphology and disease resistance in Rohu, Labeo rohita. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao Joe, J.T.; Shi Sung, H.T.; Wu, J.L.; Lai, Y.S.; Lu, M.W. Dietary administration of novel multistrain probiotics from healthy grouper intestines promotes the intestinal immune response against NNV infection. Life 2021, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, G.; Rafiee, G.; Tavabe, K.R.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Dawood, M.A. The enrichment of diet with beneficial bacteria (single-or multi-strain) in biofloc system enhanced the water quality, growth performance, immune responses, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, N.; Ren, T.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Bai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ding, J. The effect of a multi-strain probiotic on growth performance, non-specific immune response, and intestinal health of juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ringø, E.; Ángeles Esteban, M.; Dadar, M.; Dawood, M.A.; Faggio, C. Host-associated probiotics: A key factor in sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, C.; Romero, J. The microbiome of Seriola lalandi of wild and aquaculture origin reveals differences in composition and potential function. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillinger, M.; Weber, B.; Standen, B.; Schmid, M.C.; Kesselring, J.C. Multi-strain probiotics show increased protection of intestinal epithelial cells against pathogens in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Ahmed, Y.A.G.; Ghareeb, A.A.A.; Mohamed, M.F. Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Ravi, D. Probiotic bacteria as growth promoter and biocontrol agent against Aeromonas hydrophila in Catla catla (Hamilton, 1822). Indian J. Fish. 2011, 58, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Melo-Bolívar, J.F.; Ruiz Pardo, R.Y.; MEHume, V.D.L. Multistrain probiotics use in main commercially cultured freshwater fish: A systematic review of evidence. Rev Aquac. 2021, 13, 1758–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.H.; Daud, H.M.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Hassim, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.M.; Bakar, S.N.A.; Srisapoome, P. Short-and long-term probiotic effects of Enterococcus hirae isolated from fermented vegetable wastes on the growth, immune responses, and disease resistance of hybrid catfish (Clarias gariepinus × Clarias macrocephalus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 114, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, L.; Telli, G.S.; de Carla Dias, D.; Goncalves, G.S.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Natori, M.M.; Hamed, S.B.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Effect of feeding strategy of probiotic Enterococcus faecium on growth performance, hematologic, biochemical parameters and non-specific immune response of Nile tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masduki, F.; Zakaria, T.; Min, C.C.; Karim, M. Evaluation of Enterococcus hirae LAB3 as potential probiont against Vibrio harveyi in Artemia nauplii and Asian seabass larvae (Lates calcarifer) cultures. J. Environ. Biol. 2020, 41, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, J.; Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Austin, B. The development of probiotics for the control of multiple bacterial diseases of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2007, 30, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogananth, N.; Akila, M.; Ali, M.A.; Jayaprakashvel, M.; Muthezhilan, R. Determination of probiotic bacteria from intestine of Sparisoma viride and bioencapsulation of Artemia salina with probionts. Res. J. Microbiol. 2020, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.; Lu, Y.; Abarike, E.D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sakyi, M.E. In vitro assessment of the probiotic characteristics of three Bacillus species from the gut of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins. 2020, 12, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.; Banerjee, G.; Dan, S.K.; Ghosh, K.; Ray, A.K. Evaluation of in vivo probiotic efficiency of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in Labeo rohita challenged by pathogenic strain of Aeromonas hydrophila MTCC 1739. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thy, H.T.T.; Tri, N.N.; Quy, O.M.; Fotedar, R.; Kannika, K.; Unajak, S.; Areechon, N. Effects of the dietary supplementation of mixed probiotic spores of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 54A, and Bacillus pumilus 47B on growth, innate immunity and stress responses of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.M.; El-Sayed, A.F.M.; Mahmoud, M.M. Effects of a novel marine probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum AH 78, on growth performance and immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, A.; Banerjee, A.; Mandal, A.; Khan, M.A.; Mohapatra, P.K.D. Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the intestine of Clarias batrachus for probiotic organism. In Proceedings of the Zoological Society; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2019; Volume 72, pp. 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Chean, M.Y.B.; Puvanasundram, P.; Yaminudin, J.; Karim, M. Evaluation of antagonism activity and control of Vibrio alginolyticus in artemia culture using mixed probiotic. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2021, 44, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Flores, M. The use of probiotic in aquaculture: An overview. Int. Res. J. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, C.M.C.; Gibson, G.R.; Rowland, I. In vitro evaluation of single-and multi-strain probiotics: Inter-species inhibition between probiotic strains, and inhibition of pathogens. Anaerobe. 2012, 18, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseling, W.; Wittka, S.; Kroll, S.; Soltmann, C.; Kegler, P.; Kunzmann, A.; Riss, H.W.; Lohmeyer, M. Functionalised ceramic spawning tiles with probiotic Pseudoalteromonas biofilms designed for clownfish aquaculture. Aquaculture 2015, 446, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M. Beneficial biofilm formation by industrial bacteria Bacillus subtilis and related species. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulden, E.F.; Hall, M.R.; Pereg, L.L.; Høj, L. Identification of an antagonistic probiotic combination protecting ornate spiny lobster (Panulirus ornatus) larvae against Vibrio owensii infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Rantala, M.; Hallamaa, K.; Nohynek, L.; Virkajärvi, I.; Mättö, J. Stationary-phase acid and heat treatments for improvement of the viability of probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Su, X.; Yun, L.; Shen, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, G.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Chang, X. Evaluation of probiotic characteristics and whole genome analysis of Bacillus velezensis R-71003 isolated from the intestine of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) for its use as a probiotic in aquaculture. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Lin, L.; Wang, G.; Elsadek, M.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; et al. Evaluating the probiotic potential and adhesion characteristics of Bacillus spp. isolated from the intestine of Rhynchocypris lagowskii Dybowski. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 747–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.P. Isolation, identification and characterization of Lactobacillus on black tiger shrimp. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Dev. 2014, 1, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Getachew, T. Stomach pH, feeding rhythm and ingestion rate in Oreochromis niloticus L. (Pisces: Cichlidae) in Lake Awasa, Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia. 1989, 174, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, R.M.; Selim, K.M.; El-Sayed, H.M.; El-Hady, M.A. In vitro selection and identification of potential probiotics isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins. 2018, 10, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.K.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.A.; Dhama, K.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: An overview. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriwulan, A.A.; Rantetondok, A.; Anshary, H. Screening and application of lactic acid bacteria isolated from vanamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) intestine as a probiotic potential for tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). AACL Bioflux 2019, 12, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar]







| No | Isolate | Name | Genbank Accession Number | Host | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L11 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | MN096657 | Portunus pelagicus (Blue swimmer crab) | [12] |
| 2 | LAB3 | Enterococcus hirae | MK757970 | Lates calcarifer (Asian seabass) | [13] |
| 3 | SPS11 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | MK757974 | Spirulina sp. (Microalgae) | [14] |
| 4 | NAS32 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus | MK757973 | Nannochloropsis sp. (Microalgae) | [14] |
| 5 | A1 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | MK764897 | Amphora sp. (Microalgae) | [15] |
| No | Isolates | Host | Provided by |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Oreochromis sp. | Laboratory of Aquatic Animal Health and Therapeutics, Institute of Biosciences, UPM |
| 2 | Streptococcus agalactiae type 3 | Oreochromis sp. | Immunology Laboratory, Department of Aquaculture, Faculty of Agriculture, UPM |
| 3 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain VPK1 | Epinephelus fuscoguttus | Laboratory of Aquatic Animal Health and Therapeutics, Institute of Biosciences, UPM |
| 4 | Vibrio harveyi strain VH1 | Epinephelus fuscoguttus |
| Interval | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates | 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 |
| L11 | 0.688 ± 0.22 ab | 0.303 ± 0.08 b | 2.68 ± 0.17 b | 5.54 ± 0.37 b |
| LAB3 | 0.273 ± 0.18 bc | 0.170 ± 0.02 b | 0.151 ± 0.04 cd | 0.151 ± 0.01 c |
| SPS11 | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | 0.264 ± 0.04 b | 0.0594 ± 0.01 d | 0.098 ± 0.02 c |
| A. hydrophila | 1.05 ± 0.03 d | 1.41 ± 0.03 c | 0.615 ± 0.03 c | 0.551 ± 0.15 c |
| S. agalactiae | 0.052 ± 0.01 c | 0.198 ± 0.04 b | 0.124 ±0.03 d | 0.445 ± 0.03 c |
| MSP1 | 0.138 ±0.01 c | 0.509 ± 0.16 b | 3.42 ± 0.17 a | 10.09 ± 0.4 a |
| Interval | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates | 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 |
| SPS11 | 0.219 ± 0.06 b | 0.485 ± 0.03 ab | 1.01 ± 0.13 ab | 1.65 ± 0.16 bc |
| NAS32 | 0.128 ± 0.02 b | 0.172 ± 0.00 d | 0.413 ± 0.03 c | 1.29 ± 0.13 cd |
| A1 | 0.118 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.00 d | 0.633 ± 0.05 bc | 2.10 ± 0.24 b |
| V. parahaemolyticus | 1.01 ± 0.03 a | 0.609 ±0.08 a | 1.07 ± 0.12 a | 1.13 ± 0.12 cd |
| V. harveyi | 0.177 ± 0.01 b | 0.208 ± 0.03 cd | 0.655 ± 0.09 bc | 0.793 ± 0.09 d |
| MSP2 | 0.123 ± 0.02 b | 0.396 ± 0.06 bc | 0.927 ± 0.03 a | 3.46 ± 0.01 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puvanasundram, P.; Chong, C.M.; Sabri, S.; Yusoff, M.S.M.; Lim, K.C.; Karim, M. Efficacy of Single and Multi-Strain Probiotics on In Vitro Strain Compatibility, Pathogen Inhibition, Biofilm Formation Capability, and Stress Tolerance. Biology 2022, 11, 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111644
Puvanasundram P, Chong CM, Sabri S, Yusoff MSM, Lim KC, Karim M. Efficacy of Single and Multi-Strain Probiotics on In Vitro Strain Compatibility, Pathogen Inhibition, Biofilm Formation Capability, and Stress Tolerance. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111644
Chicago/Turabian StylePuvanasundram, Puvaneswari, Chou Min Chong, Suriana Sabri, Md Sabri Mohd Yusoff, Keng Chin Lim, and Murni Karim. 2022. "Efficacy of Single and Multi-Strain Probiotics on In Vitro Strain Compatibility, Pathogen Inhibition, Biofilm Formation Capability, and Stress Tolerance" Biology 11, no. 11: 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111644
APA StylePuvanasundram, P., Chong, C. M., Sabri, S., Yusoff, M. S. M., Lim, K. C., & Karim, M. (2022). Efficacy of Single and Multi-Strain Probiotics on In Vitro Strain Compatibility, Pathogen Inhibition, Biofilm Formation Capability, and Stress Tolerance. Biology, 11(11), 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111644







