Effects of Recurring IPC vs. rIPC Maneuvers on Exercise Performance, Pulse Wave Velocity, and Red Blood Cell Deformability: Special Consideration of Reflow Varieties
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
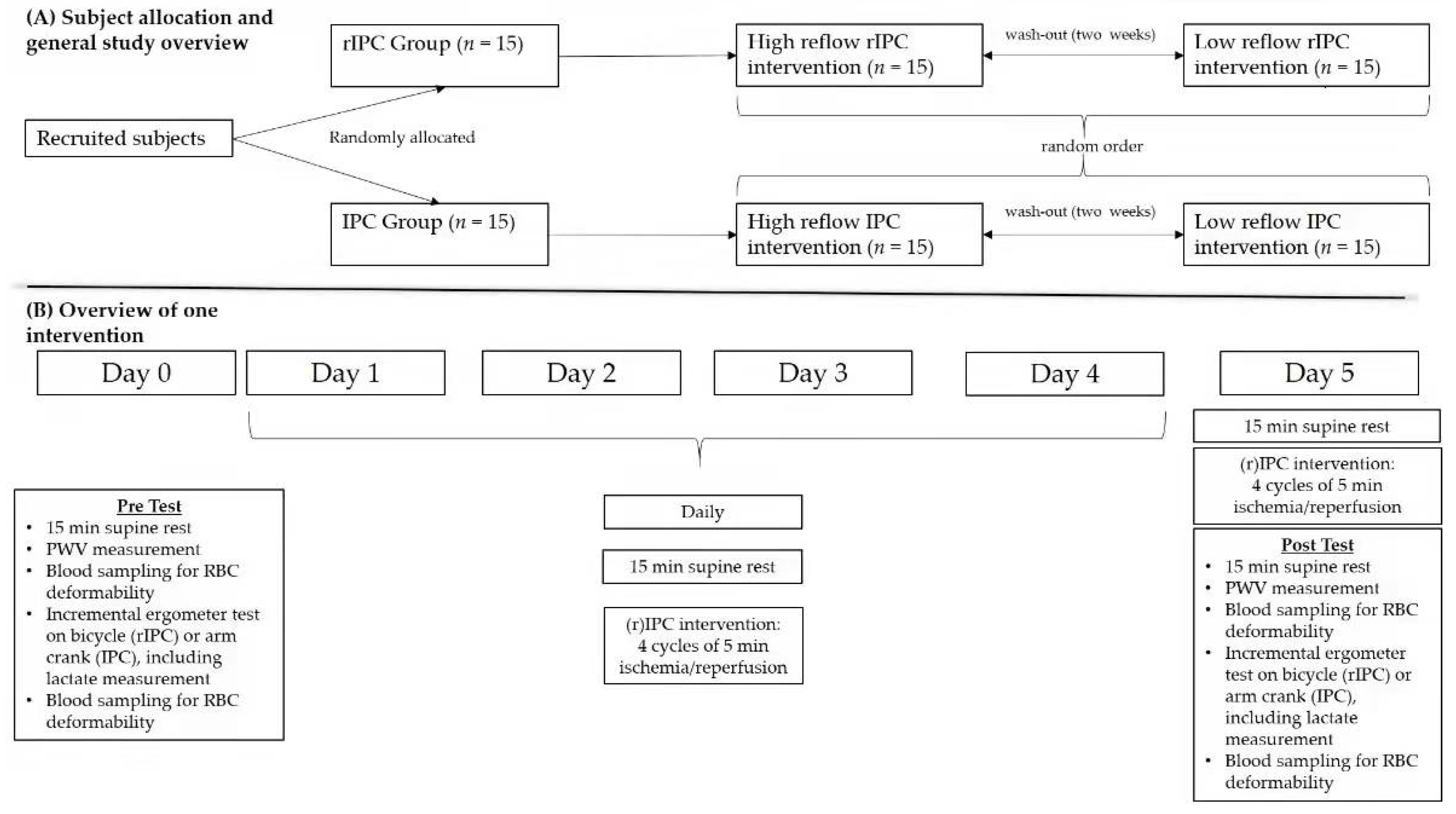
2.2. Study Design: General Information
2.3. Study Protocol: Detailed Demonstration
2.3.1. Blood Pressure and Pulse Wave Velocity Measurement
2.3.2. Initial Exercise Test, T0
2.3.3. Ischemia (Blood Occlusion)/Reperfusion Maneuver
2.3.4. Final Exercise Test, T1
2.4. Sample Measurement
2.4.1. Lactate Analysis
2.4.2. RBC Deformability Measurement
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
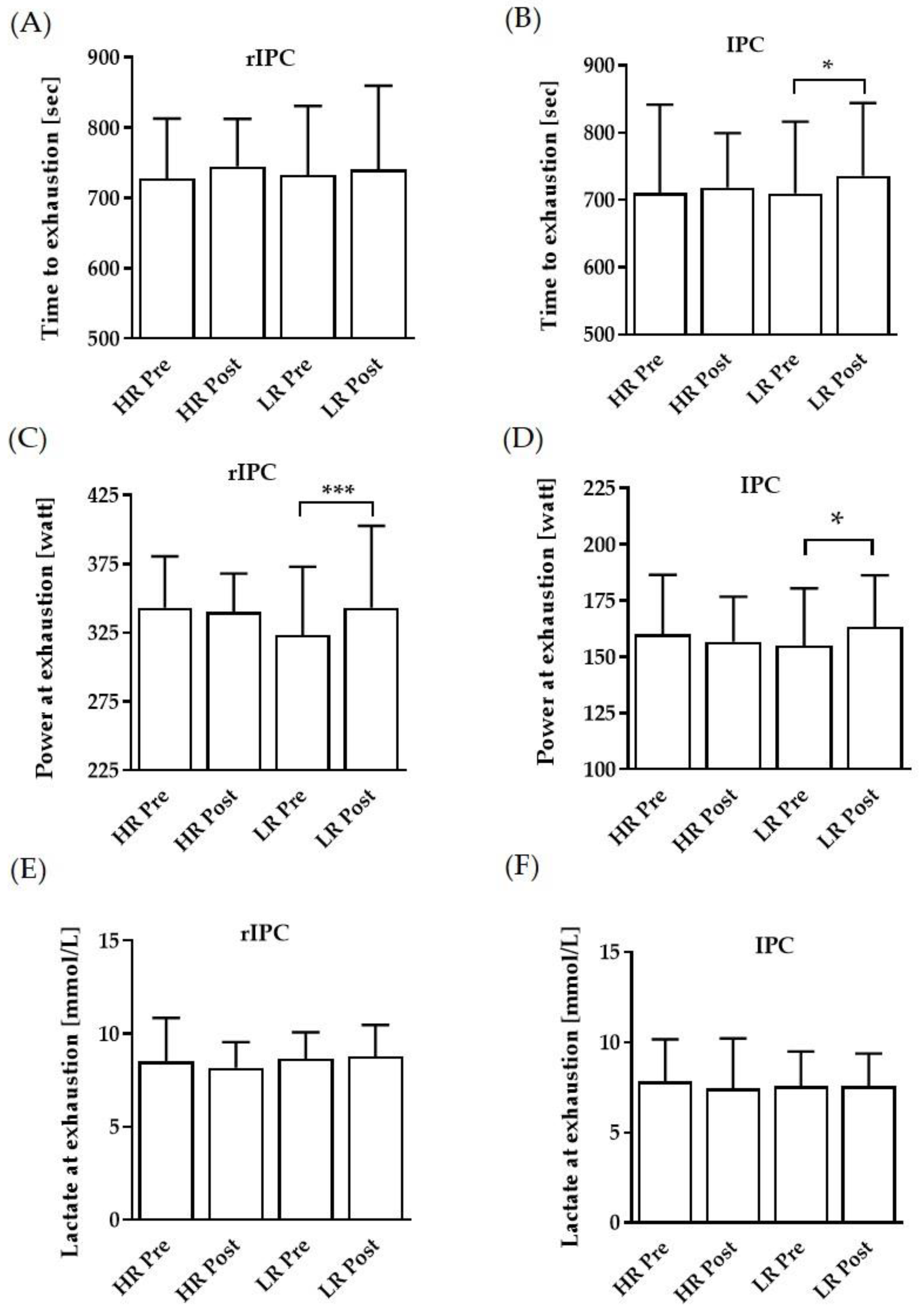
3.1. Performance Parameters
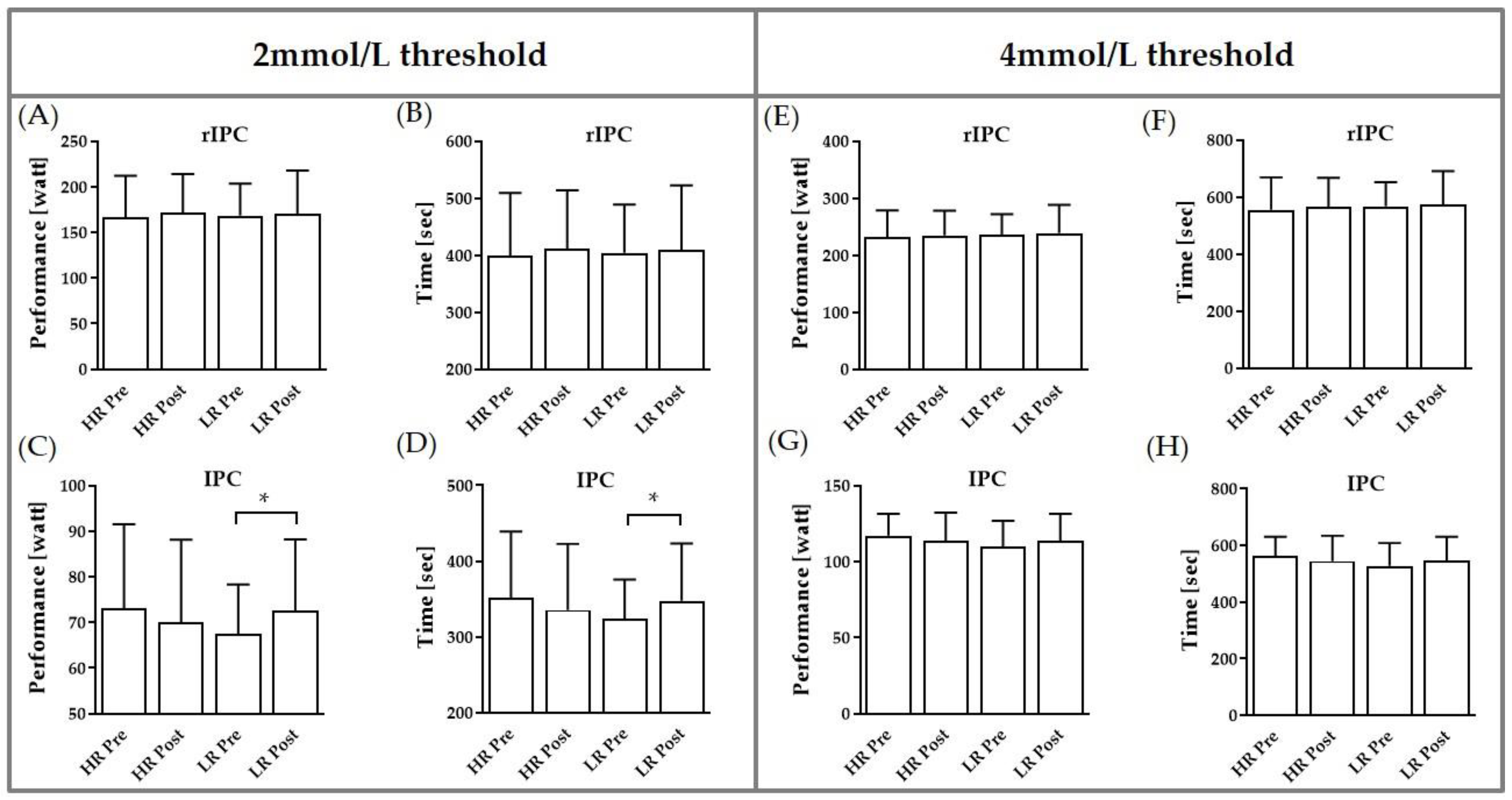
3.2. Performance at 2 and 4 mmol/L Thresholds
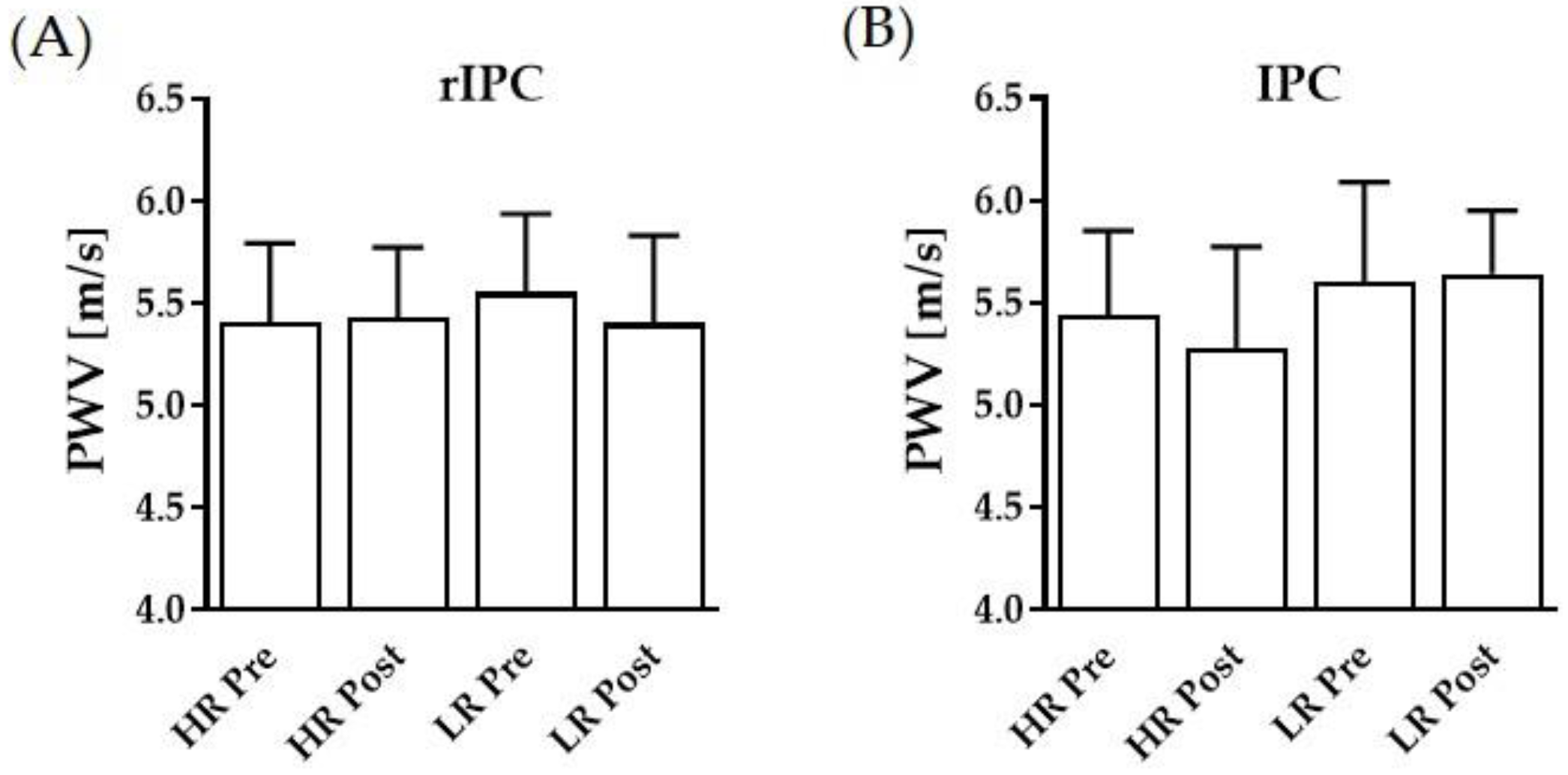
3.3. Pulse Wave Velocity and Blood Pressures
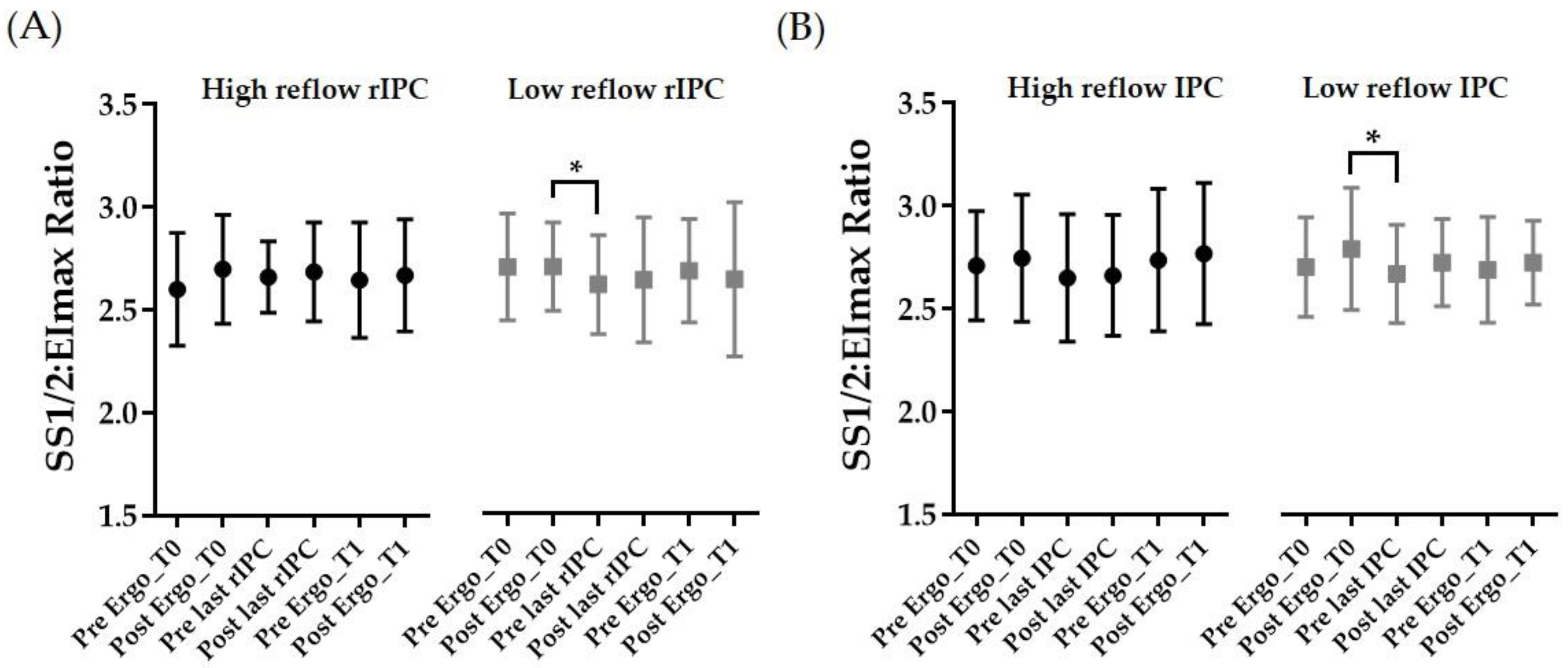
3.4. RBC Deformability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bystrom, P.; Foley, N.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.; Quesnelle, K. Ischemic preconditioning modulates ROS to confer protection in liver ischemia and reperfusion. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbanda, R.K.; Mortensen, U.M.; White, P.A.; Kristiansen, S.B.; Schmidt, M.R.; Hoschtitzky, J.A.; Vogel, M.; Sorensen, K.; Redington, A.N.; MacAllister, R. Transient limb ischemia induces remote ischemic preconditioning in vivo. Circulation 2002, 106, 2881–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, T.; Walsh, P.M.; Doran, P.P.; Mulhall, K.J. Transcriptional responses in the adaptation to ischaemia-reperfusion injury: A study of the effect of ischaemic preconditioning in total knee arthroplasty patients. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yellon, D.M.; Downey, J.M. Preconditioning the myocardium: From cellular physiology to clinical cardiology. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 1113–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinbongard, P.; Schulz, R.; Rassaf, T.; Lauer, T.; Dejam, A.; Jax, T.; Kumara, I.; Gharini, P.; Kabanova, S.; Ozüyaman, B.; et al. Red blood cells express a functional endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Blood 2006, 107, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alderton, W.K.; Cooper, C.E.; Knowles, R.G. Nitric oxide synthases: Structure, function and inhibition. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 593–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Shiva, S.; Heusch, G.; Kelm, M. Circulating nitrite contributes to cardioprotection by remote ischemic preconditioning. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, I.B.; MacCallum, H.; Cockcroft, J.R.; Webb, D.J. Inhibition of basal nitric oxide synthesis increases aortic aug-mentation index and pulse wave velocity in vivo. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bor-Kucukatay, M.; Wenby, R.B.; Meiselman, H.J.; Baskurt, O.K. Effects of nitric oxide on red blood cell deformability. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H1577–H1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grau, M.; Kollikowski, A.; Bloch, W. Remote ischemia preconditioning increases red blood cell deformability through red blood cell-nitric oxide synthase activation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2016, 63, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairbäurl, H. Red blood cells in sports: Effects of exercise and training on oxygen supply by red blood cells. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nader, E.; Monedero, D.; Robert, M.; Skinner, S.; Stauffer, E.; Cibiel, A.; Germain, M.; Hugonnet, J.; Scheer, A.; Joly, P.; et al. Impact of a 10 km running trial on eryptosis, red blood cell rheology, and electrophysiology in endurance trained athletes: A pilot study. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomschi, F.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M. Impact of Type of Sport, Gender and Age on Red Blood Cell Deformability of Elite Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connes, P.; Simmonds, M.J.; Brun, J.-F.; Baskurt, O.K. Exercise hemorheology: Classical data, recent findings and unresolved issues. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2013, 53, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean-St-Michel, E.; Manlhiot, C.; Li, J.; Tropak, M.; Michelsen, M.M.; Schmidt, M.R.; McCrindle, B.W.; Wells, G.D.; Redington, A.N. Remote preconditioning improves maximal performance in highly trained athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, L.; Jacobs, I. Methodological Variations Contributing to Heterogenous Ergogenic Responses to Ischemic Preconditioning. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 656980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.F.; de Aguiar, R.A.; Lisbôa, F.D.; Pereira, K.L.; Cruz, R.S.; Caputo, F. Ischemic Preconditioning and Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomschi, F.; Ottmann, H.; Niemann, D.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M. Ischemic Preconditioning im Leistungssport: Wie weit ist die Forschung? Leistungssport 2021, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi, M. Ischemic preconditioning: Potential impact on exercise performance and underlying mechanisms. J. Phys. Fit. Sports Med. 2017, 6, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.-F.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Hsu, W.-C.; Chen, C.; Pan, C.-H. Local and Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Sprint Interval Exercise Performance in Team Sport Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incognito, A.V.; Burr, J.F.; Millar, P.J. The Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Human Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, F.; Curnier, D.Y. Can anaerobic performance be improved by remote ischemic preconditioning? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhevaara, V.; Sovijärvi, A.; Ilmarinen, J.; Teräslinna, P. Differences in cardiorespiratory responses during and after arm crank and cycle exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1990, 138, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, F.; Brenig, J.; Müller, R.; Behrens, H.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M. Moderate exercise promotes human RBC-NOS activity, NO production and deformability through Akt kinase pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeman, M.R.; Dobbe, J.G.; Ince, C. The Laser-assisted Optical Rotational Cell Analyzer (LORCA) as red blood cell aggregometer. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2001, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Hardeman, M.R.; Uyuklu, M.; Ulker, P.; Cengiz, M.; Nemeth, N.; Shin, S.; Alexy, T.; Meiselman, H.J. Parameterization of red blood cell elongation index—Shear stress curves obtained by ektacytometry. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2009, 69, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Meiselman, H.J. Analyzing shear stress-elongation index curves: Comparison of two approaches to simplify data presentation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2004, 31, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, O.; Evans, D.T.; Waldron, M.; Coussens, A.; Patterson, S.D. Seven-day ischaemic preconditioning improves muscle efficiency during cycling. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.; Petersen, C.; Ferguson, H.; Blackwell, G.; Rickerby, S. Lack of a Dose Response from 7 Days of Ischemic Preconditioning in Moderately trained Cyclists. Sports Med. Int. Open 2018, 2, E91–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.G.; Jones, H.; Gregson, W.; Atkinson, G.; Cable, N.T.; Thijssen, D.H.J. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on lactate accumulation and running performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riksen, N.P.; Smits, P.; Rongen, G.A. Ischaemic preconditioning: From molecular characterisation to clinical application—Part I. Neth. J. Med. 2004, 62, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, C.Y.; Yang, R.Z.; Zong, A.; Xu, N.; Boyd, B.; Forrest, C.R. Acute ischaemic preconditioning protects against skeletal muscle infarction in the pig. Cardiovasc. Res. 1995, 29, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, O.; Waldron, M.; Pattison, J.R.; Patterson, S.D. Enhanced Local Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Capacity and Microvascular Blood Flow Following 7-Day Ischemic Preconditioning in Healthy Humans. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 298, 229–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertuglia, S. Preconditioning and Shear Stress in the Microcirculation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2006, 2, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinandy, P.; Schulz, R. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yellon, D.M.; Alkhulaifi, A.M.; Pugsley, W.B. Preconditioning the human myocardium. Lancet 1993, 342, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connes, P.; Tripette, J.; Mukisi-Mukaza, M.; Baskurt, O.K.; Toth, K.; Meiselman, H.J.; Hue, O.; Antoine-Jonville, S. Relationships between hemodynamic, hemorheological and metabolic responses during exercise. Biorheology 2009, 46, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Jung, W.-S.; Park, W.; Park, H.-Y. Twelve Weeks of Combined Resistance and Aerobic Exercise Improves Cardiometabolic Biomarkers and Enhances Red Blood Cell Hemorheological Function in Obese Older Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.A.; Martin, D.T.; Telford, R.D.; Ballas, S.K. Greater erythrocyte deformability in world-class endurance athletes. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, H2188–H2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szanto, S.; Mody, T.; Gyurcsik, Z.; Babjak, L.B.; Somogyi, V.; Barath, B.; Varga, A.; Matrai, A.A.; Nemeth, N. Alterations of Selected Hemorheological and Metabolic Parameters Induced by Physical Activity in Untrained Men and Sportsmen. Metabolites 2021, 11, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomschi, F.; Niemann, D.; Bloch, W.; Predel, H.-G.; Grau, M. Ischemic Preconditioning Enhances Performance and Eryth-rocyte Deformability of Responders. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.M.; Millar, P.J.; Burr, J.F. Blunted Cardiac Output from Overtraining Is Related to Increased Arterial Stiffness. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomschi, F.; Ottmann, H.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M.; Predel, H.-G. Brachial and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness in adult elite athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingwell, B.A. Large artery stiffness: Implications for exercise capacity and cardiovascular risk. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Taebling, M.; Oberhoffer, R. Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Has No Short-Term Effect on Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, and Arterial Stiffness in Healthy Young Adults. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Ueda, K.; Goto, C.; Jitsuiki, D.; Nishioka, K.; Umemura, T.; Noma, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Chayama, K.; Higashi, Y. Repetition of ischemic preconditioning augments endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans: Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide and endothelial progenitor cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, L.; Pedone, C.; Mondì, A.; Nunziata, E.; Antonelli Incalzi, R. Effect of local and remote ischemic preconditioning on endothelial function in young people and healthy or hypertensive elderly people. Atherosclerosis 2011, 219, 750–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Peripheral BP | Pre | Post | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR Sys (mmHg) | RR Dias (mmHg) | RR Sys (mmHg) | RR Dias (mmHg) | ||
| IPC | Low Reflow | 127.3 (9.5) | 70.7 (6.3) | 130.0 (14.8) | 71.6 (9.7) |
| High Reflow | 123.1 (9.5) | 68.6 (7.2) | 121.0 (9.5) | 69.1 (6.2) | |
| rIPC | Low Reflow | 125.0 (7.1) | 69.7 (7.6) | 125.7 (7.6) | 68.6 (8.7) |
| High Reflow | 126.0 (12.7) | 69.0 (7.8) | 127.3 (11.9) | 70.6 (7.7) | |
| Central BP | Pre | Post | |||
| RR Sys (mmHg) | RR Dias (mmHg) | RR Sys (mmHg) | RR Dias (mmHg) | ||
| IPC | Low Reflow | 119.7 (10.9) | 71.9 (6.8) | 118.8 (13.1) | 70.3 (7.5) |
| High Reflow | 114.2 (11.5) | 70.0 (6.2) | 112.0 (13.3) | 70.4 (7.0) | |
| rIPC | Low Reflow | 116.7 (9.3) | 70.3 (7.8) | 113.6 (11.3) | 70.3 (7.7) |
| High Reflow | 112.7 (11.5) | 71.0 (8.4) | 113.3 (9.9) | 73.0 (8.9) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grau, M.; Seeger, B.; Mozigemba, L.; Roth, R.; Baumgartner, L.; Predel, H.-G.; Bloch, W.; Tomschi, F. Effects of Recurring IPC vs. rIPC Maneuvers on Exercise Performance, Pulse Wave Velocity, and Red Blood Cell Deformability: Special Consideration of Reflow Varieties. Biology 2022, 11, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020163
Grau M, Seeger B, Mozigemba L, Roth R, Baumgartner L, Predel H-G, Bloch W, Tomschi F. Effects of Recurring IPC vs. rIPC Maneuvers on Exercise Performance, Pulse Wave Velocity, and Red Blood Cell Deformability: Special Consideration of Reflow Varieties. Biology. 2022; 11(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrau, Marijke, Benedikt Seeger, Lukas Mozigemba, Roland Roth, Luca Baumgartner, Hans-Georg Predel, Wilhelm Bloch, and Fabian Tomschi. 2022. "Effects of Recurring IPC vs. rIPC Maneuvers on Exercise Performance, Pulse Wave Velocity, and Red Blood Cell Deformability: Special Consideration of Reflow Varieties" Biology 11, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020163
APA StyleGrau, M., Seeger, B., Mozigemba, L., Roth, R., Baumgartner, L., Predel, H.-G., Bloch, W., & Tomschi, F. (2022). Effects of Recurring IPC vs. rIPC Maneuvers on Exercise Performance, Pulse Wave Velocity, and Red Blood Cell Deformability: Special Consideration of Reflow Varieties. Biology, 11(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020163







