Transcription Analysis for Core Networks of lncRNAs–mRNAs: Implication for Potential Role in Sterility of Crassostrea gigas
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and RNA Sequencing
2.3. lncRNA Identification and Differential Expression Analysis
2.4. Target Gene Prediction of lncRNAs and Functional Analysis of mRNAs
2.5. qRT-PCR Validation of RNA-seq Data
3. Results
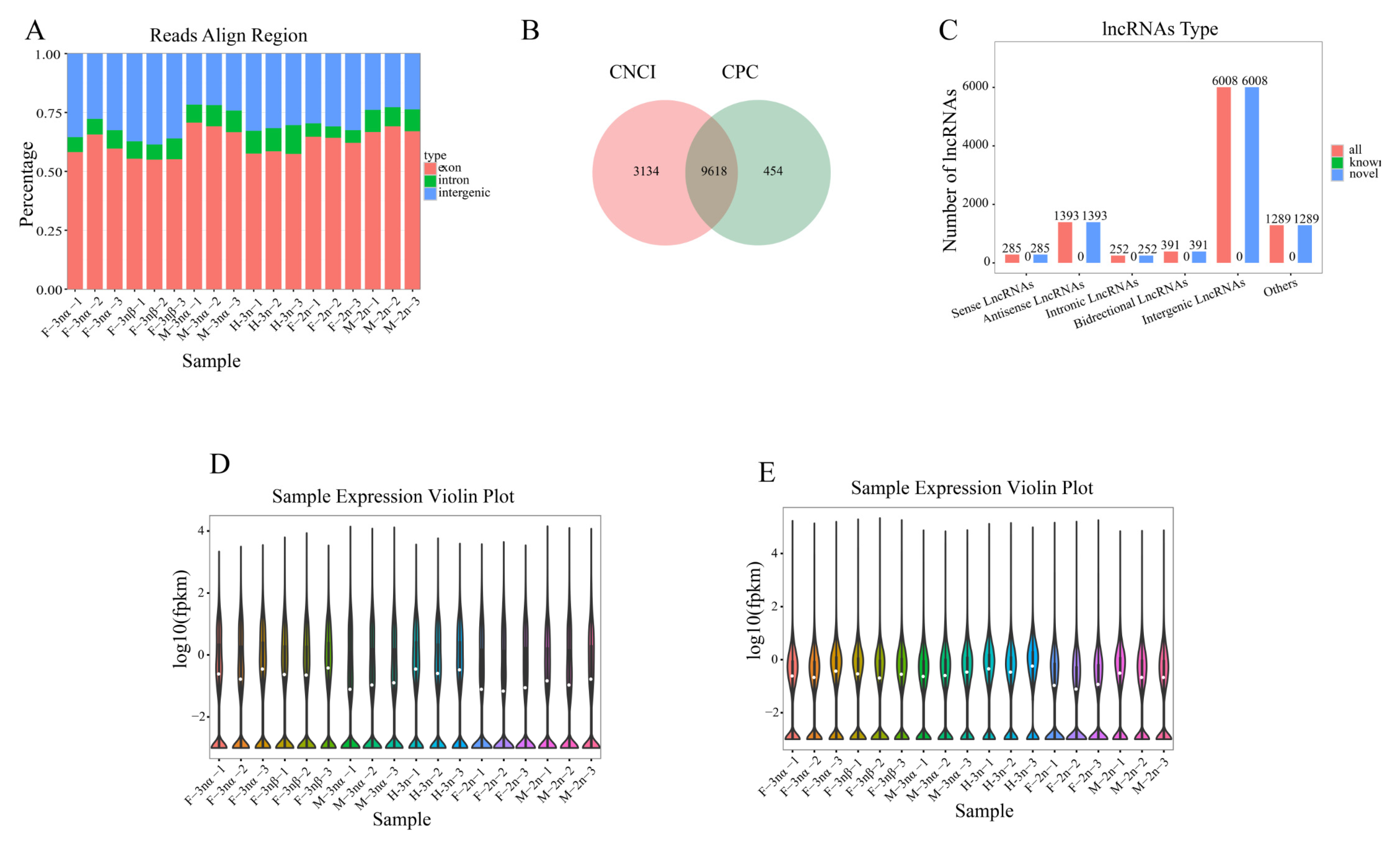
3.1. Upstream Preprocessing of RNA-Sequencing Data
3.2. Identification of DELs and DEGs
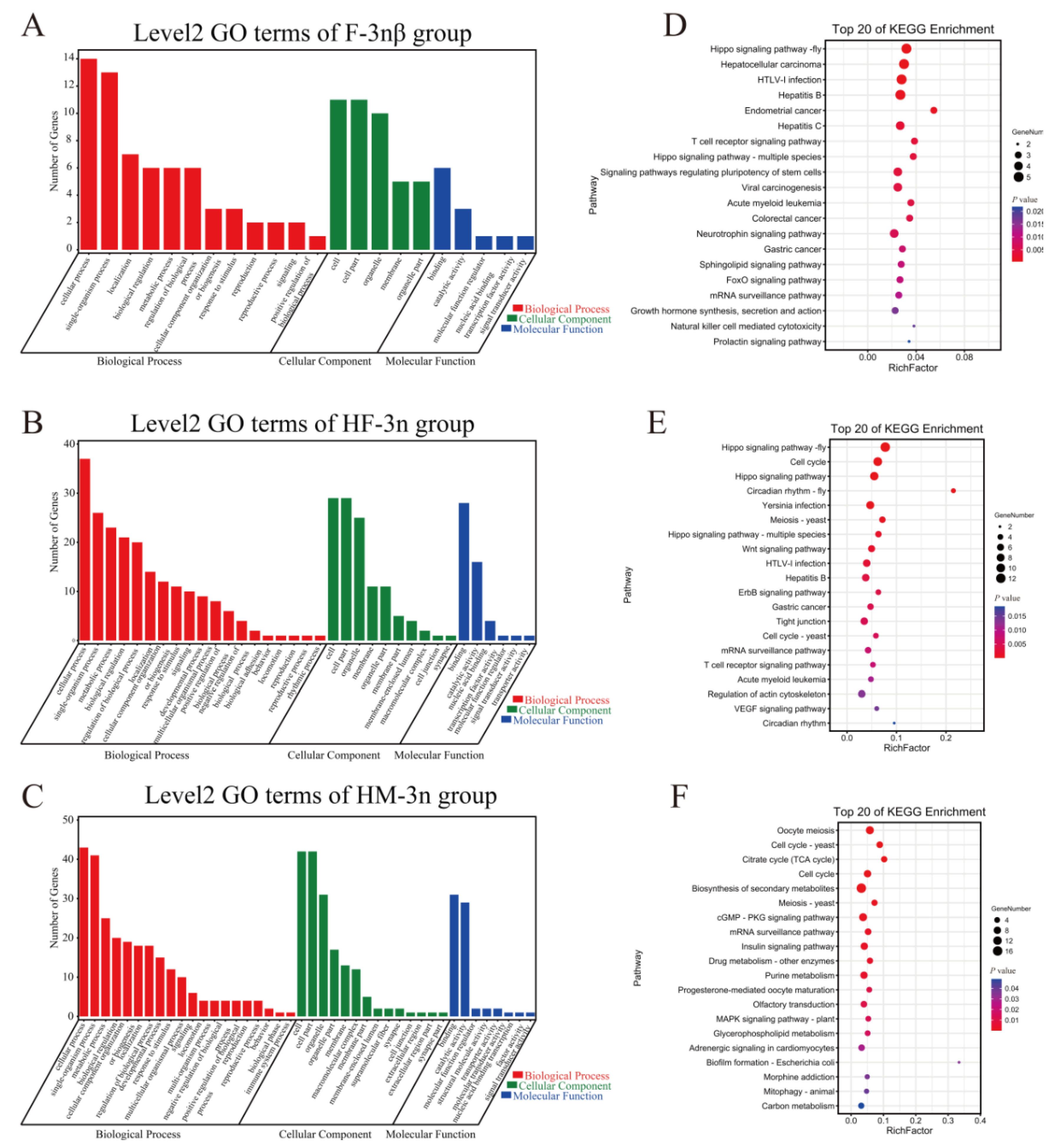
3.3. Target Gene Prediction of Differentially Expressed lncRNAs
3.4. Exploration of the Core Networks of lncRNAs–mRNAs
3.5. qRT-PCR Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, T.; Gu, W.; Liu, E.; Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, W.; Dong, F.; Xu, G. Comprehensive analysis of miRNA-mRNA/lncRNA during gonadal development of triploid female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Genomics 2021, 113, 3533–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Laurent, G.; Wahlestedt, C.; Kapranov, P. The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, W.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Pan, Z.; Li, Q. SMAD4-induced knockdown of the antisense long noncoding RNA BRE-AS contributes to granulosa cell apoptosis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lai, Z.; Jin, B.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.G.; Gu, J. Differentiation of Long Non-Coding RNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Male and Female Aedes albopictus. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, M. Transcriptome analysis provides insights into long noncoding RNAs in medaka gonads. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 39, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Zou, X.; Han, Y.; Deng, M.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Liu, D.; Li, Y. Role of mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in regulating the litter size trait in Chuanzhong black goats. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2020, 55, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouska, M.J.; Bai, H. Long noncoding RNA regulation of spermatogenesis via the spectrin cytoskeleton in Drosophila. G3 2021, 11, jkab080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L.; He, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Abnormal meiosis in fertile and sterile triploid cyprinid fish. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouaux, A.; Heude-Berthelin, C.; Sourdaine, P.; Mathieu, M.; Kellner, K. Gametogenic stages in triploid oysters Crassostrea gigas, Irregular locking of gonial proliferation and subsequent reproductive effort. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 395, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, J.L.; Allen, S.K., Jr. A classification system for gonad development in triploid Crassostrea virginica. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 735994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Li, Q. Refinement of a classification system for gonad development in the triploid oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalachev, A.V.; Yurchenko, O.V. Autophagy in nutrient storage cells of the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Tissue Cell 2019, 61, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouaux, A.; Blin, J.L.; Adeline, B.; Heude-Berthelin, C.; Sourdaine, P.; Mathieu, M.; Kellner, K. Impact of energy storage strategies on gametogenesis and reproductive effort in diploid and triploid Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas—Involvement of insulin signaling. Aquaculture 2013, 388–391, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. Variance in expression and localization of sex-related genes CgDsx, CgBHMG1 and CgFoxl2 during diploid and triploid Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas gonad differentiation. Gene 2021, 790, 145692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheilly, N.M.; Jouaux, A.; Boudry, P.; Favrel, P.; Lelong, C. Transcriptomic profiling of gametogenesis in triploid Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas: Towards an understanding of partial sterility associated with triploidy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Yu, H.; Li, Q. Integrated Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Gonads Reveal Disruption of Germ Cell Proliferation and Division, and Energy Storage in Glycogen in Sterile Triploid Pacific Oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Cells 2021, 10, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp, an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT, a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tafer, H.; Hofacker, I.L. RNAplex, a fast tool for RNA-RNA interaction search. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2657–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner Zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llera-Herrera, R.; Vazquez-Boucard, C.; Garcia-Gasca, A.; Huvet, A. Co-expression and regulation of ovarian vitellogenins in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquac. Res. 2010, 45, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broquard, C.; Saowaros, S.A.; Lepoittevin, M.; Degremont, L.; Lamy, J.B.; Morga, B.; Elizur, A.; Martinez, A.S. Gonadal transcriptomes associated with sex phenotypes provide potential male and female candidate genes of sex determination or early differentiation in Crassostrea gigas, a sequential hermaphrodite mollusc. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacca, H.; Huvet, A.; Fabioux, C.; Daniel, J.Y.; Delaporte, M.; Pouvreau, S.; Van Wormhoudt, A.; Moal, J. Molecular cloning and seasonal expression of oyster glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 140, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devlin, D.J.; Yu, Z.; Garcia, T.X.; Matzuk, M.M.; Ikawa, M. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome-edited mice reveal 10 testis-enriched genes are dispensable for male fecundity. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 105, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G.; Bao, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, N.; Lin, Z. SOHLHs Might Be Gametogenesis-Specific bHLH Transcriptional Regulation Factors in Crassostrea gigas. Front. Physio. 2019, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.G.; Su, Y.Q.; Fan, H.Y.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.Y. Mechanisms regulating oocyte meiotic resumption, roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2037–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, C.; Kraft, R.; Sauerbruch, S.; Schultz, G.; Harteneck, C. Molecular and functional characterization of the melastatin-related cation channel TRPM3. J. Biol Chem. 2003, 278, 21493–21501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Geng, L.; Liu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide differential expression of long noncoding RNAs and mRNAs in ovarian follicles of two different chicken breeds. Genomics 2019, 111, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, C.; Wei, J.; Qin, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of three gonadal development stages reveals potential genes involved in gametogenesis of the fluted giant clam (Tridacna squamosa). BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cian, M.C.; Gregoire, E.P.; Le Rolle, M.; Lachambre, S.; Mondin, M.; Bell, S.; Guigon, C.J.; Chassot, A.A.; Chaboissier, M.C. R-spondin2 signaling is required for oocyte-driven intercellular communication and follicular growth. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2856–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Tang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhu, X.; Liang, X.; Yan, A.; Lu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Tang, D.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the different developmental stages of ovary in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis of ovary and testis reveals potential sex-related genes and pathways in spotted knifejaw Oplegnathus punctatus. Gene 2017, 637, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya, D.P.; Extavour, C.G. The Hippo pathway regulates homeostatic growth of stem cell niche precursors in the Drosophila ovary. PLoS. Genet. 2015, 11, e1004962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of sheep spermatogenesis through single-cell RNA sequencing. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.J.; Dong, X.L.; Kang, K.; Chen, H.; Dai, X.Y.; Wu, G.A.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhai, Y.F. FoxO Transcription Factor Regulate Hormone Mediated Signaling on Nymphal Diapause. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotiner, J.Y.; Wolgemuth, D.J.; Wang, P.J. Functions of cyclins and CDKs in mammalian gametogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 101, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Shen, J.; Fei, J.; Zhu, X.; Yin, M.; Zhou, J. KNDC1 Is a Predictive Marker of Malignant Transformation in Borderline Ovarian Tumors. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensa, S.; Lloyd-Lewis, B.; Sargeant, T.J.; Resemann, H.K.; Kahn, C.R.; Watson, C.J. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunits p55α and p50α regulate autophagy in vivo. FEBS. J. 2014, 281, 4557–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Fu, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Chai, M.; Chen, C.; Dai, L.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J. The possible FAT1-mediated apoptotic pathways in porcine cumulus cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.Q.; Song, Y.Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.T.; Xu, L.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. Axin-1 Regulates Meiotic Spindle Organization in Mouse Oocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginanova, V.; Golubkova, E.; Kliver, S.; Bychkova, E.; Markoska, K.; Ivankova, N.; Tretyakova, I.; Evgen’ev, M.; Mamon, L. Testis-specific products of the Drosophila melanogaster sbr gene, encoding nuclear export factor 1, are necessary for male fertility. Gene 2016, 577, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashpa, R.; Vazquez-Pianzola, P.; Colombo, M.; Hernandez, G.; Beuchle, D.; Berger, F.; Peischl, S.; Bruggmann, R.; Suter, B. Cbp80 is needed for the expression of piRNA components and piRNAs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurasz, P.; Yurkova, N.; Kirshenbaum, L.; Stewart, D.J. VEGF masks BNIP3-mediated apoptosis of hypoxic endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2011, 14, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel-Espíndola, F.; Maldonado, R.; Mancilla, H.; vander Stelt, K.; Acuña, A.I.; Covarrubias, A.; López, C.; Angulo, C.; Castro, M.A.; Slebe, J.C.; et al. Muscle glycogen synthase isoform is responsible for testicular glycogen synthesis: Glycogen overproduction induces apoptosis in male germ cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, M.; Jang, S.; Ni, C.; Buszczak, M. The Dynamic Regulation of mRNA Translation and Ribosome Biogenesis During Germ Cell Development and Reproductive Aging. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 710186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickel, J.S.; Chen, L.; Hayward, J.; Yeap, S.L.; Alkers, A.E.; Chan, R.C. Structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins promote homolog-independent recombination repair in meiosis crucial for germ cell genomic stability. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ergul, M.; Bakar-Ates, F. RO3280, A Novel PLK1 Inhibitor, Suppressed the Proliferation of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells Through the Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest at G2/M Point. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, K. Sperm flagella, comparative and phylogenetic perspectives of protein components. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 17, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Transcript Name | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) | Amplification Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSTRG.28339.2 | F: TGTAGCAATGGGCAAACCAGA R: GCTAGGCCAGGTCCACTAAC | 109 | 1.930 |
| Tex36 | F: TCCCGTAGATGCCGATTT R: AGGACTTGGGTCGGTGTTC | 88 | 2.002 |
| MSTRG.39041.2 | F: TGTTTTGGACAAACCCAACGG R: TAATACGGTCACCGCAGCAT | 131 | 2.186 |
| MSTRG.22725.2 | F: TGCTTCAAGACCAAATGCGG R: AGTCCCGCGGACATTTACAG | 118 | 2.074 |
| MSTRG.3451.1 | F: TAAATGTGGAGGACCACGCC R: ACGACCATGACCTTTGCCTC | 121 | 1.934 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, S. Transcription Analysis for Core Networks of lncRNAs–mRNAs: Implication for Potential Role in Sterility of Crassostrea gigas. Biology 2022, 11, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030378
Wang H, Yu H, Li Q, Liu S. Transcription Analysis for Core Networks of lncRNAs–mRNAs: Implication for Potential Role in Sterility of Crassostrea gigas. Biology. 2022; 11(3):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030378
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huihui, Hong Yu, Qi Li, and Shikai Liu. 2022. "Transcription Analysis for Core Networks of lncRNAs–mRNAs: Implication for Potential Role in Sterility of Crassostrea gigas" Biology 11, no. 3: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030378
APA StyleWang, H., Yu, H., Li, Q., & Liu, S. (2022). Transcription Analysis for Core Networks of lncRNAs–mRNAs: Implication for Potential Role in Sterility of Crassostrea gigas. Biology, 11(3), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030378








