Nutrient Homeostasis of Aegilops Accessions Differing in B Tolerance Level under Boron Toxic Growth Conditions
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. B Stress Induction and Harvest at Tillering Stage
2.2. ICP-AES Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ANOVA for All the Studied Root-Shoot Nutrients
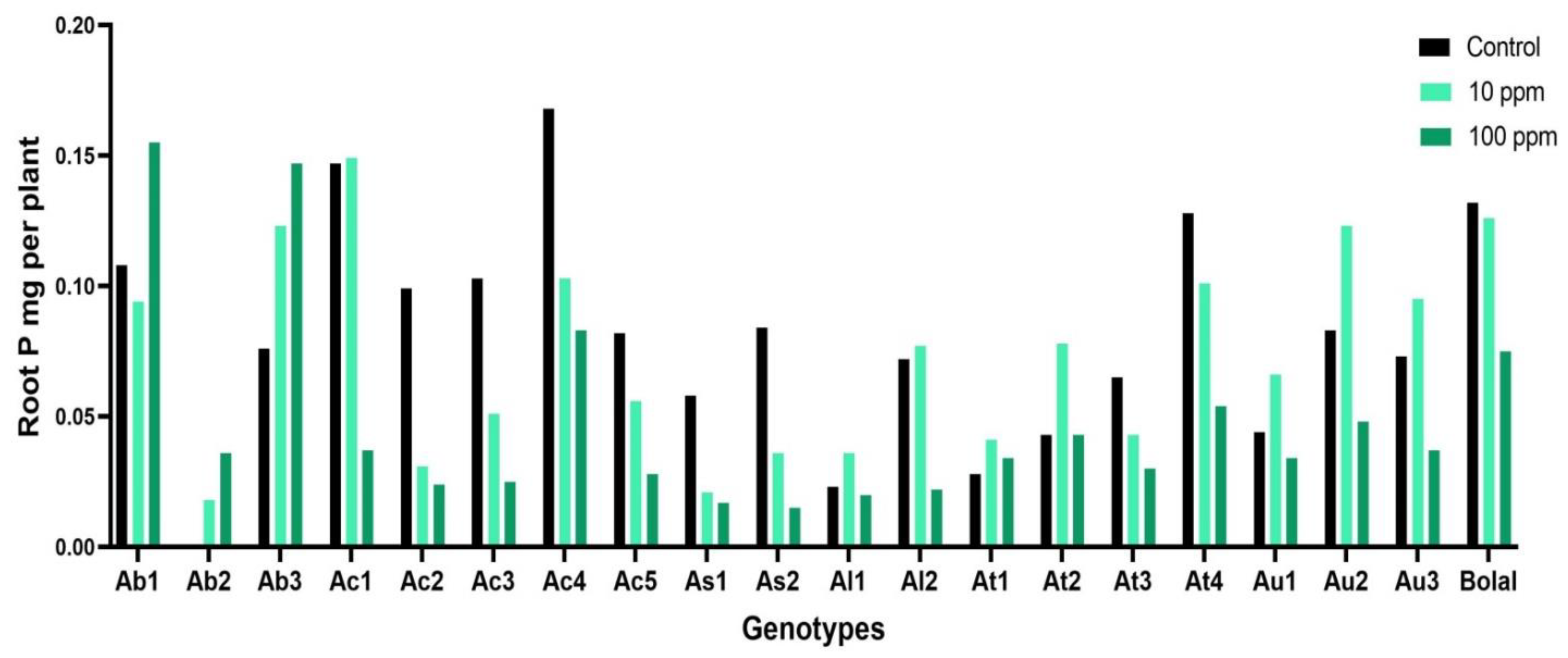
3.2. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root Phosphorus Uptake
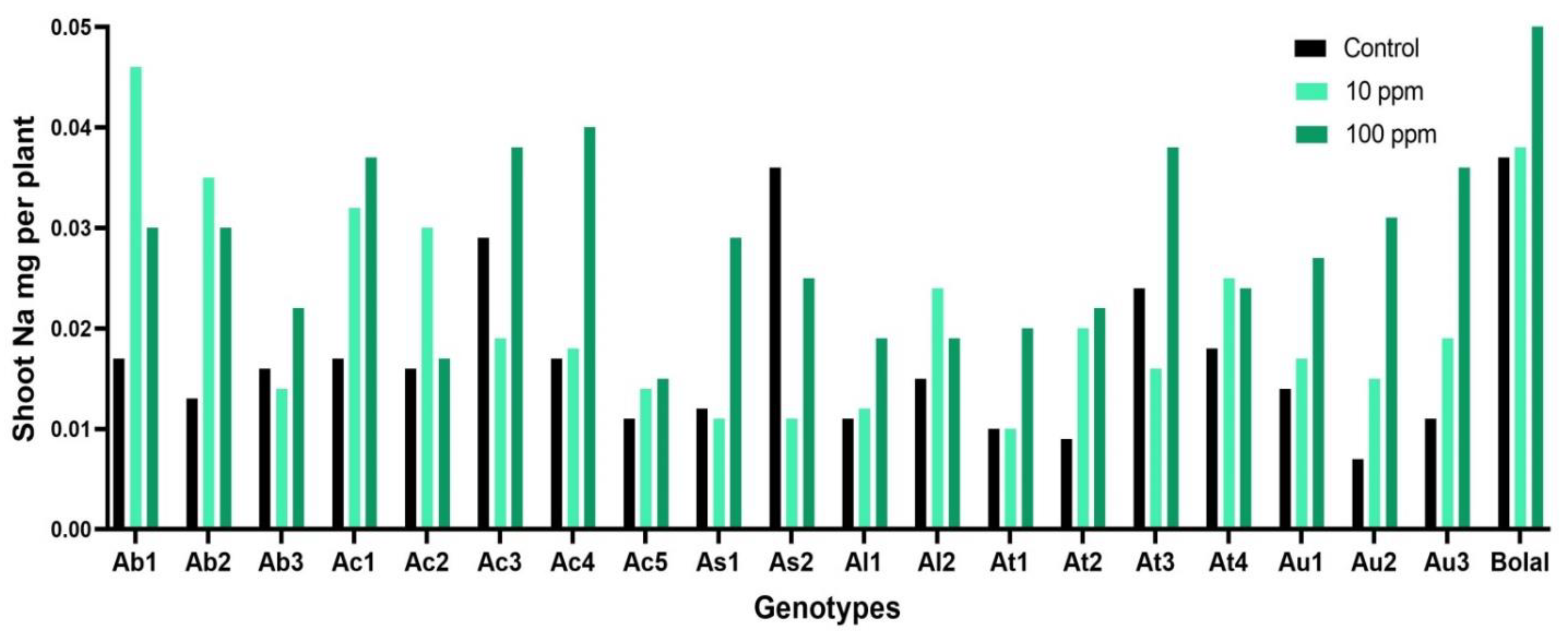
3.3. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Shoot Sodium Uptake
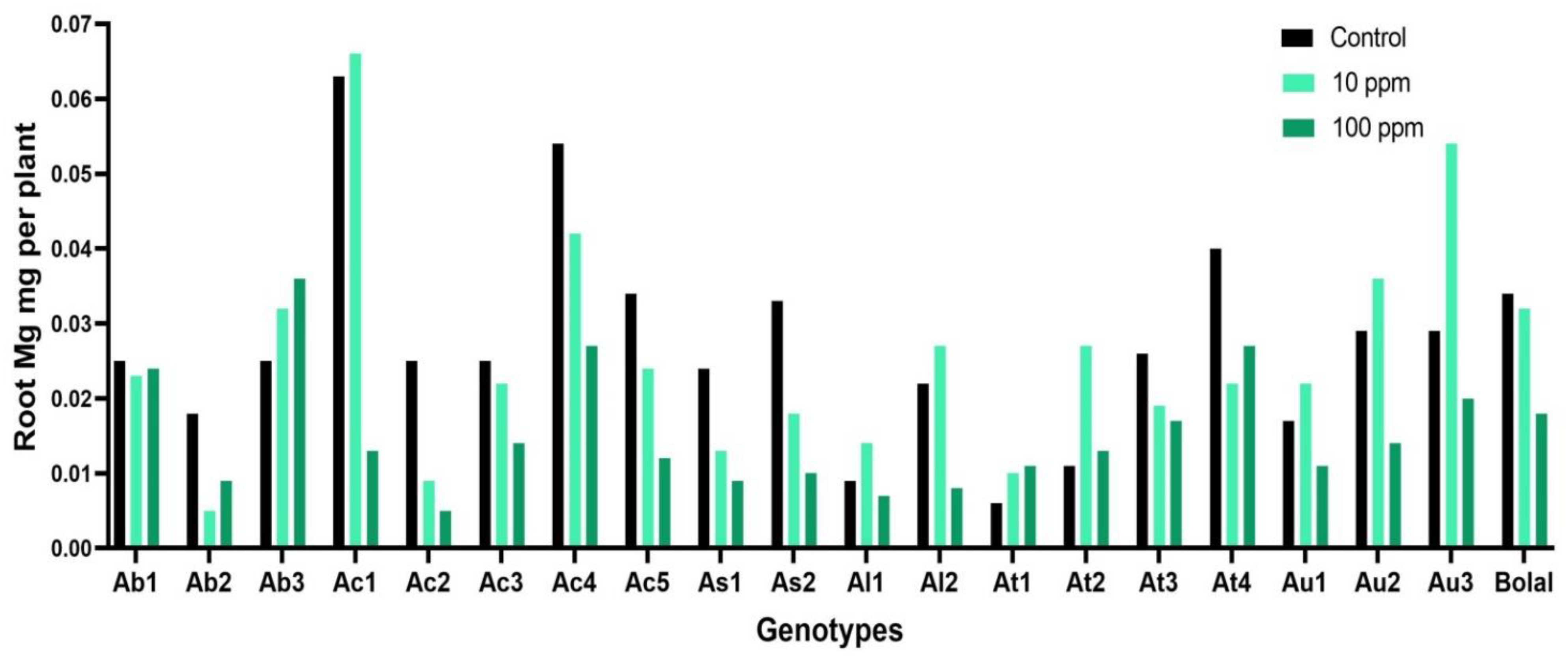
3.4. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root Magnesium Uptake
3.5. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Shoot Manganese Uptake
3.6. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root Copper Uptake
3.7. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Shoot Copper Uptake
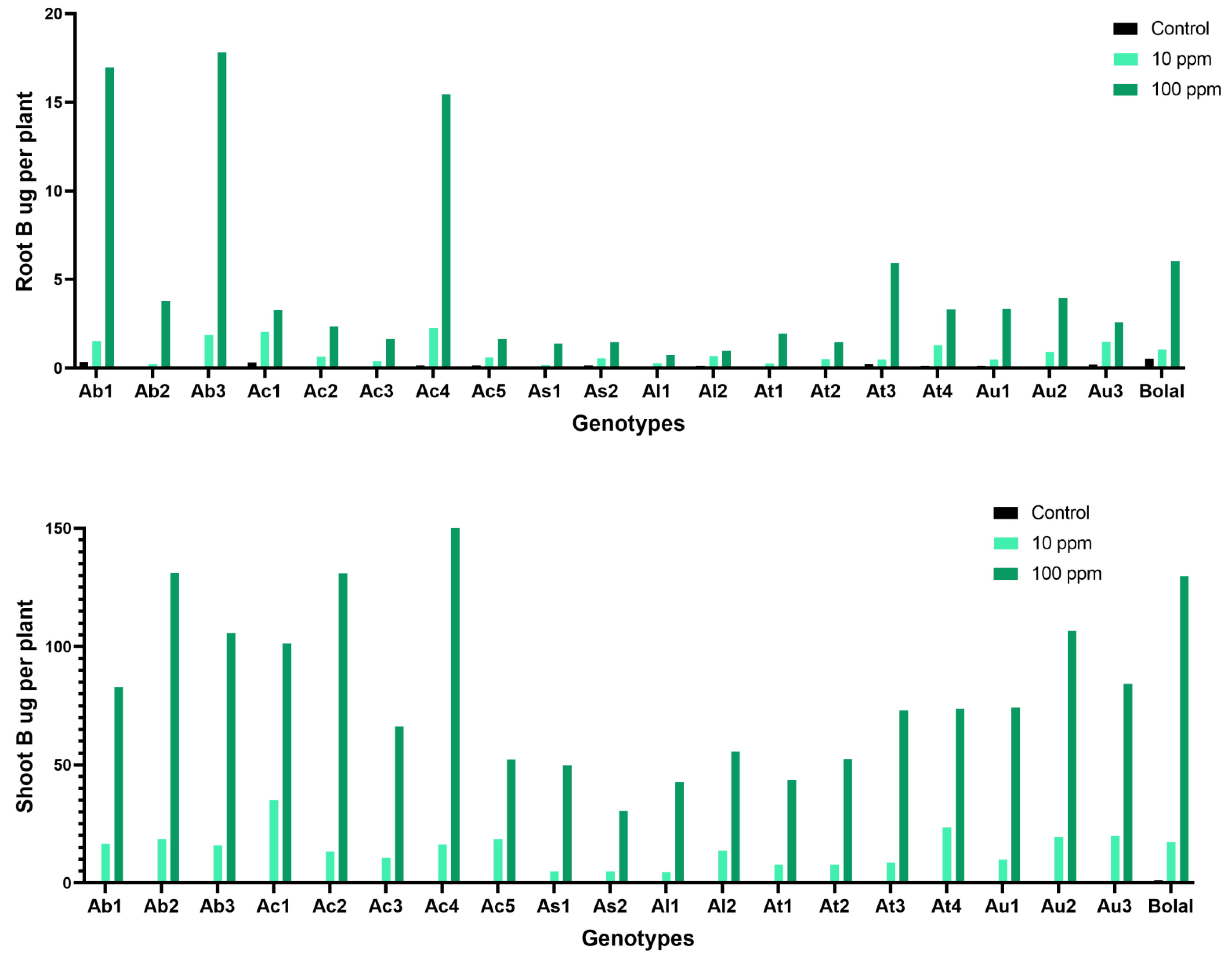
3.8. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root-Shoot B Uptake
3.9. Physiological Differences in the Aegilops Genotypes in Highly Toxic B at the Tillering Stage
3.10. Correlation among the Root-Shoot Nutrient Uptake of Aegilops Genotypes under Highly Toxic B Supply and Their Association with the Growth Parameters
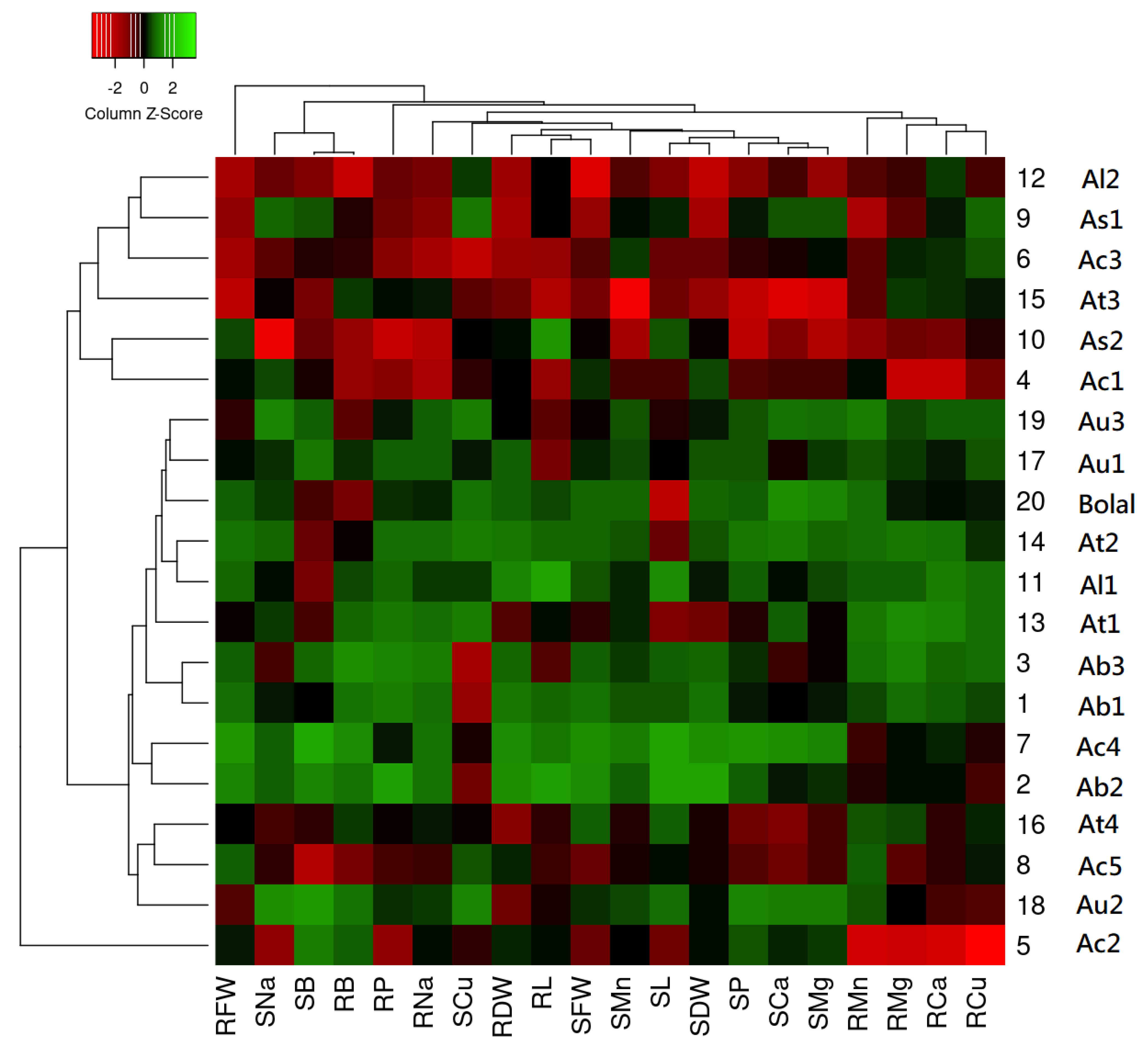
3.11. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis-Dependent Heat Map
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root Phosphorus Uptake
4.2. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Shoot Sodium Uptake
4.3. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root Magnesium Uptake
4.4. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Shoot Manganese Uptake
4.5. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root-Shoot Copper Uptake
4.6. Effect of Highly Toxic B on the Root-Shoot B Uptake
4.7. Association among the Root-Shoot Nutrient Uptake of Aegilops Genotypes under Excess B and Their Association with the Growth Parameters/Heat Map
4.8. Heat Map
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuertes-Mendizabal, T.; Bastias, E.I.; Gonzalez-Murua, C.; Gonzalez-Moro, M.B. Nitrogen Assimilation in the Highly Salt- and Boron-Tolerant Ecotype Zea mays L. Amylacea. Plants 2020, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Khan, M.K.; Hakki, E.E.; Gezgin, S.; Hamurcu, M. Combined Boron Toxicity and Salinity Stress-An Insight into Its Interaction in Plants. Plants 2019, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reid, R.J.; Hayes, J.E.; Post, A.; Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Graham, R.D. A critical analysis of the causes of boron toxicity in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquea, F.; Federici, F.; Moscoso, C.; Vega, A.; Jullian, P.; Haseloff, J.; Arce-Johnson, P. A molecular framework for the inhibition of Arabidopsis root growth in response to boron toxicity. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, M.; Degl’Innocenti, E.; Pardossi, A.; Guidi, L. Antioxidant and Photosynthetic Responses in Plants under Boron Toxicity: A Review. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brdar-Jokanovic, M. Boron Toxicity and Deficiency in Agricultural Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Fujiwara, T. Physiological roles and transport mechanisms of boron: Perspectives from plants. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2008, 456, 671–677. [Google Scholar]
- Nable, R.O.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Paull, J.G. Boron toxicity. Plant Soil 1997, 193, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, S.; Nachit, M.; Ryan, J.; Hamblin, J. Phenotypic variation in boron-toxicity tolerance at seedling stage in durum wheat (Triticum durum). Euphytica 1995, 83, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Margaritopoulou, T.; Papadakis, I.E.; Araniti, F. Boron toxicity in higher plants: An update. Planta 2019, 250, 1011–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koç, C. Effects on Environment and Agriculture of Geothermal Wastewater and Boron Pollution in Great Menderes Basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 125, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rerkasem, B.; Nirantrayagul, S.; Jamjod, S. Increasing boron efficiency in international bread wheat, durum wheat, triticale and barley germplasm will boost production on soils low in boron. Field Crops Res. 2004, 86, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Mott, C. The significance of boron in plant nutrition and environment—A review. J. Agron. 2007, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, A.; Romney, E.; Alexander, G.; Kinnear, J. Phytotoxicity and some interactions of the essential trace metals iron, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, copper, and boron. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1977, 8, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leece, D. Effects of boron on the physiological activity of zinc in maize. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1978, 29, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aduayi, E. Role of boron on growth components and elemental composition of ‘Ife Plum’tomato. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1978, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, O.; Manchanda, H. Boron tolerance studies in gram and wheat grown on a sierozem sandy soil. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1979, 27, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Singh, S. Effect of applied boron on the chemical composition of lentil plants. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1983, 31, 169–170. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.P.; Dahiya, D.J.; Narwal, R.P. Boron uptake and toxicity in wheat in relation to zinc supply. Fertil. Res. 1990, 24, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, R.; Lyon, C.; Hood, S. Some effects of boron supply on the chemical composition of tomato leaflets. Plant Physiol. 1944, 19, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, N.; Mehta, B. Effects of various calcium–boron and potassium–boron ratios on the growth and chemical composition of aromatic strain of bidi tobacco. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1966, 34, 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Ohki, K. Mn and B Effects on Micronutrients and P in Cotton 1. Agron. J. 1975, 67, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emon, R.M. Screening Aegilops-Triticum species for Boron tolerance. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboobi, H.; Yucel, M.; Öktem, H.A. Cell wall uronic acid concentrations of resistant and sensitive cultivars of wheat and barley under boron toxicity. J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 24, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, M.; Schnurbusch, T.; Hayes, J.; Hay, A.; Baumann, U.; Paull, J.; Langridge, P.; Sutton, T. Molecular basis of adaptation to high soil boron in wheat landraces and elite cultivars. Nature 2014, 514, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Hamurcu, M.; Avsaroglu, Z.Z.; Ozbek, M.; Omay, A.H.; Elbasan, F.; Omay, M.R.; Gokmen, F.; Topal, A.; et al. Variability in Physiological Traits Reveals Boron Toxicity Tolerance in Aegilops Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 736614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Khan, M.K.; Hakki, E.E.; Thomas, G.; Hamurcu, M.; Gezgin, S.; Gizlenci, O.; Akkaya, M.S. Assessment of genetic variability for grain nutrients from diverse regions: Potential for wheat improvement. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, C.; Yang, E.; Yin, M.; Liu, C.; Ren, Z. Characterization of a new wheat-Aegilops biuncialis addition line conferring quality-associated HMW glutenin subunits. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, G.P.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Fritz, A.K.; Kirkham, M.B.; Gill, B.S. High Temperature Tolerance in Aegilops Species and Its Potential Transfer to Wheat. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiani, R.; Arzani, A.; Habibi, F. Physiology of salinity tolerance in Aegilops cylindrica. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, E.I.; Brown, L.K.; Olson, E.L. Fusarium head blight resistance in Aegilops tauschii. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2017, 64, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakszegi, M.; Molnár, I.; Lovegrove, A.; Darkó, É.; Farkas, A.; Láng, L.; Bedő, Z.; Doležel, J.; Molnár-Láng, M.; Shewry, P. Addition of Aegilops U and M chromosomes affects protein and dietary fiber content of wholemeal wheat flour. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, A.; Friebe, B.; Prasad, P.; Fritz, A. Evaluating heat tolerance of a complete set of wheat-Aegilops geniculata chromosome addition lines. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2018, 204, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishii, M. An Update of Recent Use of Aegilops Species in Wheat Breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suneja, Y.; Gupta, A.K.; Bains, N.S. Stress Adaptive Plasticity: Aegilops tauschii and Triticum dicoccoides as Potential Donors of Drought Associated Morpho-Physiological Traits in Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rani, K.; Raghu, B.R.; Jha, S.K.; Agarwal, P.; Mallick, N.; Niranjana, M.; Sharma, J.B.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, N.K.; Rajkumar, S.; et al. A novel leaf rust resistance gene introgressed from Aegilops markgrafii maps on chromosome arm 2AS of wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanouchi, M. The effects of phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron on the absorption and translocation of boron in several crops grown at a high concentration of boron. J. Sci. Soil Manure Jpn. 1980, 51, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Günes, A.; Alpaslan, M. Boron uptake and toxicity in maize genotypes in relation to boron and phosphorus supply. J. Plant Nutr. 2000, 23, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, F.; Chapman, J. Research note: Boron toxicity in Spanish groundnuts. Agrochemophysica 1979, 11, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sotiropoulos, T.E.; Therios, I.N.; Dimassi, K.N. Calcium application as a means to improve tolerance of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa L.) to boron toxicity. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 81, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F.J. Sodium in plants: Perception, signalling, and regulation of sodium fluxes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnasamy, K.; Bell, R.; Ma, Q. Wheat responses to sodium vary with potassium use efficiency of cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Javid, M.; Ford, R.; Norton, R.; Nicolas, M. Sodium and boron exclusion in two Brassica juncea cultivars exposed to the combined treatments of salinity and boron at moderate alkalinity. Biologia 2014, 69, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tepe, H.D.; Aydemir, T. Application of Exogenous Sodium Nitroprussid Alleviates Boron Toxicity in Wheat Seedlings: Investigation of Thiol Compounds, Macro/Micronutrient, and Polyamine Contents. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, M.; Gunes, A. Interactive effects of boron and salinity stress on the growth, membrane permeability and mineral composition of tomato and cucumber plants. Plant Soil 2001, 236, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, H.; Cikili, Y.; Dursun, S. The role of potassium in alleviating boron toxicity and combined effects on nutrient contents in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 21, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Y.S. Root development under control of magnesium availability. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e29720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovatt, C.J.; Bates, L.M. Early Effects of Excess Boron on Photosynthesis and Growth of Cucurbita pepo. J. Exp. Bot. 1984, 35, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P.; Rengel, Z. Nutrient availability in soils. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Elsevier; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 315–330. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Medina-Velo, I.A.; Cota-Ruiz, K.; Moreno-Olivas, F.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Can abiotic stresses in plants be alleviated by manganese nanoparticles or compounds? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Printz, B.; Lutts, S.; Hausman, J.F.; Sergeant, K. Copper Trafficking in Plants and Its Implication on Cell Wall Dynamics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kováčik, J.; Klejdus, B.; Hedbavny, J.; Štork, F.; Grúz, J. Modulation of Copper Uptake and Toxicity by Abiotic Stresses in Matricaria chamomilla Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6755–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.E.; Reid, R.J. Boron tolerance in barley is mediated by efflux of boron from the roots. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3376–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rehman, S.; Park, T.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, Y.W.; Yun, S.J. Inverse relationship between boron toxicity tolerance and boron contents of barley seed and root. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, S.G.; Savaghebi, G.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Amiri, R.M.; Rezaei, H. Tolerance of some wheat varieties to boron toxicity. Cereal Res. Commun. 2015, 43, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torun, B.; Kalayci, M.; Ozturk, L.; Torun, A.; Aydin, M.; Cakmak, I. Differences in Shoot Boron Concentrations, Leaf Symptoms, and Yield of Turkish Barley Cultivars Grown on Boron-Toxic Soil in Field. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 26, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaoğlu, M.; Gezgin, S.; Topal, A.; Sade, B.; Dural, H. Gypsophila sphaerocephala Fenzl ex Tchihat.: A boron hyperaccumulator plant species that may phytoremediate soils with toxic B levels. Turk. J. Bot. 2004, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Torun, A.A.; Yazici, A.; Erdem, H.; ÇAKMAK, İ. Genotypic variation in tolerance to boron toxicity in 70 durum wheat genotypes. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2006, 30, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Khan, M.K.; Hamurcu, M.; Yilmaz, F.G.; Gezgin, S. Boron Toxicity: An Insight on Its Influence on Wheat Growth. In Metal Toxicology Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 417–432. [Google Scholar]
- Metwally, A.; El-Shazoly, R.; Hamada, A.M. Effect of boron on growth criteria of some wheat cultivars. J. Biol. Earth Sci. 2012, 2, B1–B9. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayci, M.; Alkan, A.; Cakmak, I.; Bayramoğlu, O.; Yilmaz, A.; Aydin, M.; Ozbek, V.; Ekiz, H.; Ozberisoy, F. Studies on differential response of wheat cultivars to boron toxicity. Euphytica 1998, 100, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.A.; Taban, N.; Taban, S. Effect of calcium on the alleviation of boron toxicity and localization of boron and calcium in cell wall of wheat. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2009, 37, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, C.; Tuna, A.L.; Dikilitas, M.; Ashraf, M.; Koskeroglu, S.; Guneri, M. Supplementary phosphorus can alleviate boron toxicity in tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 121, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, F.; Strong, J.; Rhoades, J.; Keren, R. Effects of salinity and varying boron concentrations on boron uptake and growth of wheat. Plant Soil 1987, 97, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.; Alston, A. The effects of salt and boron on growth of wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1992, 43, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, C.M.; Poss, J.A. Wheat response to interactive effects of boron and salinity. J. Plant Nutr. 2000, 23, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.E.; Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M.; Poss, J.A.; Suarez, D.L. Salinity’s influence on boron toxicity in broccoli: II. Impacts on boron uptake, uptake mechanisms and tissue ion relations. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, T.; Iqbal, M.M.; Akhtar, J.; Saqib, M.; Ali, M.; Zafar, M.I.; Dell, B.; Datta, R.; Ansari, M.J.; Danish, S.; et al. Carbohydrate Partitioning, Growth and Ionic Compartmentalisation of Wheat Grown under Boron Toxic and Salt Degraded Land. Agronomy 2022, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedeh, H.; Antoni, S.; Cocciaglia, L.; Ciccolini, V. Molecular and Physiological Effects of Magnesium-Polyphenolic Compound as Biostimulant in Drought Stress Mitigation in Tomato. Plants 2022, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Hamurcu, M.; Ozbek, M.; Omay, M.R.; Gokmen, F.; Topal, A.; Gezgin, S. Effects of High Boron on the Nutrients Uptake of Aegilops Genotypes Differing in Their B Tolerance Level. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 11, 75. [Google Scholar]


| GenBank Code | Site of Origin | Abbreviation Code | Ploidy | Genome | Taxon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGB 026218 | Adıyaman, Turkey | Ab1 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops biuncialis |
| TGB 026219 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | Ab2 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops biuncialis |
| TGB 037313 | Gaziantep, Turkey | Ab3 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops biuncialis |
| TGB 037373 | Gaziantep, Turkey | Ac1 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops columnaris |
| TGB 038488 | Ankara, Turkey | Ac2 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops columnaris |
| TGB 037489 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | Ac3 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops columnaris |
| TGB 000107 | Adıyaman, Turkey | Ac4 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops columnaris |
| TR 57295 | Van, Turkey | Ac5 | 4x | UUMM | Aegilops columnaris |
| TGB 037791 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | As1 | 2x | SS | Aegilops speltoides |
| TR 62174 | Gaziantep, Turkey | As2 | 2x | SS | Aegilops speltoides |
| TGB 000803 | Mersin, Turkey | Al1 | 2x | SS | Aegilops ligustica |
| TR 39488 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | Al2 | 2x | SS | Aegilops ligustica |
| TGB 037311 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | At1 | 4x | CCUU | Aegilops triuncialis |
| TGB 037355 | Adıyaman, Turkey | At2 | 4x | CCUU | Aegilops triuncialis |
| TGB 037376 | Gaziantep, Turkey | At3 | 4x | CCUU | Aegilops triuncialis |
| TR 72224 | Adıyaman, Turkey | At4 | 4x | CCUU | Aegilops triuncialis |
| TGB 037353 | Erzincan, Turkey | Au1 | 2x | UU | Aegilops umbellulata |
| TGB 037356 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | Au2 | 2x | UU | Aegilops umbellulata |
| TR 72200 | Şanlıurfa, Turkey | Au3 | 2x | UU | Aegilops umbellulata |
| Bolal 2973 | Turkey | Bolal | 6x | AABBDD | Triticum aestivum |
| Studied Traits | Code | % of Total Variation | p-Value | Control vs. 10 ppm | Control vs. 100 ppm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotypes | Treatment | Genotypes | Treatment | Mean Difference | Adjusted p-Value | Mean Difference | Adjusted p-Value | ||
| Root Calcium | RCa | 60.4 | 3.7 | *** | ns | 0.010 | ns | 0.017 | ns |
| Shoot Calcium | SCa | 53.5 | 1.8 | * | ns | 0.002 | ns | 0.017 | ns |
| Root Phosphorus | RP | 59.6 | 11.1 | *** | ** | 0.007 | ns | 0.033 | ** |
| Shoot Phosphorus | SP | 72.8 | 2.4 | **** | ns | −0.007 | ns | 0.048 | ns |
| Root Sodium | RNa | 46.6 | 2.3 | ns | ns | 0.005 | ns | 0.003 | ns |
| Shoot Sodium | SNa | 48.2 | 20.2 | ** | **** | −0.004 | ns | −0.013 | **** |
| Root Magnesium | RMg | 54.6 | 15.9 | *** | *** | 0.002 | ns | 0.012 | *** |
| Shoot Magnesium | SMg | 73.5 | 1.7 | **** | ns | 0.000 | ns | 0.009 | ns |
| Root Manganese | RMn | 72.5 | 2.3 | **** | ns | 0.026 | ns | 0.240 | ns |
| Shoot Manganese | SMn | 67.7 | 7.3 | **** | ** | 0.014 | ns | 0.712 | * |
| Root Copper | RCu | 82.3 | 2.5 | **** | ns | 0.321 | ns | 0.600 | * |
| Shoot Copper | SCu | 51.6 | 8.9 | ** | * | 0.111 | ns | 0.518 | * |
| Root Boron | RB | 27.1 | 31.1 | ns | **** | −0.728 | ns | −4.649 | **** |
| Shoot Boron | SB | 15.0 | 58.7 | ns | **** | −13.790 | ns | −88.590 | **** |
| Code | SDW | RDW | SCa | RCa | SP | RP | SNa | RNa | SMg | RMg | SMn | RMn | SCu | RCu | SB | RB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ab1 | 6 | −28 | −20 | 20 | −28 | 31 | 45 | 50 | −20 | −4 | −5 | −21 | −167 | 2 | 99.26 | 98.08 |
| Ab2 | 31 | −9 | −13 | −37 | 4 | 100 | 58 | 58 | −12 | −95 | −1 | −104 | −124 | −123 | 99.61 | 98.18 |
| Ab3 | 0 | −47 | −39 | 26 | −17 | 48 | 27 | 78 | −32 | 32 | −24 | 33 | −192 | 36 | 99.50 | 99.36 |
| Ac1 | −7 | −92 | −42 | −251 | −78 | −300 | 53 | −212 | −49 | −395 | −103 | −65 | −80 | −173 | 99.20 | 90.11 |
| Ac2 | −20 | −76 | −11 | −287 | −2 | −313 | 4 | −27 | −7 | −404 | −55 | −393 | −78 | −492 | 99.58 | 97.29 |
| Ac3 | −48 | −192 | −29 | −10 | −62 | −303 | 22 | −204 | −23 | −76 | −25 | −156 | −229 | 10 | 99.17 | 93.70 |
| Ac4 | 20 | −13 | 38 | −17 | 50 | −102 | 58 | 58 | 26 | −100 | 40 | −131 | −68 | −92 | 99.81 | 99.08 |
| Ac5 | −30 | −79 | −57 | −74 | −80 | −195 | 30 | −71 | −49 | −188 | −75 | 7 | −11 | −37 | 98.64 | 91.35 |
| As1 | −82 | −206 | 5 | −29 | −30 | −242 | 60 | −158 | 0 | −183 | −48 | −300 | 23 | 32 | 99.43 | 94.02 |
| As2 | −27 | −90 | −69 | −131 | −170 | −457 | −47 | −236 | −117 | −210 | −213 | −241 | −52 | −89 | 99.03 | 90.12 |
| Al1 | −19 | −20 | −19 | 56 | 1 | −17 | 41 | 13 | −5 | −25 | −35 | 9 | −19 | 44 | 98.95 | 96.66 |
| Al2 | −98 | −193 | −45 | −5 | −120 | −227 | 20 | −130 | −91 | −156 | −107 | −152 | −21 | −116 | 98.91 | 86.93 |
| At1 | −54 | −131 | 6 | 60 | −55 | 16 | 50 | 48 | −33 | 42 | −37 | 41 | 30 | 38 | 99.09 | 97.48 |
| At2 | −4 | −28 | 26 | 37 | 24 | 1 | 61 | 53 | 8 | 17 | −9 | 29 | 31 | −18 | 99.02 | 94.73 |
| At3 | −71 | −149 | −145 | −11 | −181 | −115 | 37 | −19 | −146 | −54 | −350 | −165 | −108 | −44 | 98.94 | 96.28 |
| At4 | −28 | −175 | −71 | −72 | −94 | −137 | 26 | −19 | −50 | −44 | −81 | −11 | −62 | −31 | 99.15 | 96.20 |
| Au1 | −6 | −49 | −30 | −27 | −3 | −27 | 48 | 31 | −10 | −54 | −17 | −9 | −40 | 9 | 99.56 | 96.07 |
| Au2 | −20 | −148 | 24 | −87 | 35 | −71 | 76 | 8 | 20 | −109 | −12 | −10 | 37 | −131 | 99.72 | 97.99 |
| Au3 | −19 | −96 | 18 | 19 | −5 | −100 | 71 | 37 | 11 | −45 | −4 | 52 | 29 | 23 | 99.46 | 92.57 |
| Bolal | 0 | −53 | 38 | −36 | −1 | −76 | 51 | −9 | 24 | −91 | 5 | 25 | 16 | −39 | 99.09 | 91.34 |
| T Parameter | SDW | RDW | SCa | RCa | SP | RP | SNa | RNa | SMg | RMg | SMn | RMn | SCu | RCu | SB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDW | 0.85 ** | ||||||||||||||
| p-value | 0.000 | ||||||||||||||
| SCa | 0.39 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||
| p-value | 0.089 | 0.187 | |||||||||||||
| RCa | −0.09 | 0.07 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
| p-value | 0.696 | 0.764 | 0.519 | ||||||||||||
| SP | 0.60 ** | 0.51 * | 0.85 ** | 0.15 | |||||||||||
| p-value | 0.005 | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.521 | |||||||||||
| RP | 0.44 | 0.49 * | 0.29 | 0.64 ** | 0.53 * | ||||||||||
| p-value | 0.053 | 0.027 | 0.210 | 0.002 | 0.016 | ||||||||||
| SNa | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.53 * | 0.35 | 0.63 ** | 0.63 ** | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.360 | 0.615 | 0.016 | 0.135 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| RNa | 0.49 * | 0.56 * | 0.34 | 0.47 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.89 ** | 0.51 * | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.025 | 0.010 | 0.142 | 0.034 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.021 | ||||||||
| SMg | 0.51 * | 0.37 | 0.90 ** | 0.13 | 0.95 ** | 0.40 | 0.62 ** | 0.45 * | |||||||
| p-value | 0.019 | 0.108 | 0.000 | 0.600 | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.003 | 0.045 | |||||||
| RMg | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.92 ** | 0.18 | 0.73 ** | 0.31 | 0.61 ** | 0.14 | ||||||
| p-value | 0.712 | 0.554 | 0.651 | 0.000 | 0.442 | 0.000 | 0.178 | 0.004 | 0.564 | ||||||
| SMn | 0.52 * | 0.38 | 0.86 ** | 0.22 | 0.88 ** | 0.43 | 0.50 * | 0.43 | 0.91 ** | 0.22 | |||||
| p-value | 0.018 | 0.098 | 0.000 | 0.363 | 0.000 | 0.053 | 0.024 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.359 | |||||
| RMn | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.54 * | 0.27 | 0.66 ** | 0.48 * | 0.52 * | 0.27 | 0.65 ** | 0.36 | ||||
| p-value | 0.130 | 0.171 | 0.372 | 0.012 | 0.242 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.017 | 0.245 | 0.002 | 0.122 | ||||
| SCu | −0.20 | −0.09 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.25 | −0.03 | 0.11 | 0.20 | |||
| p-value | 0.388 | 0.712 | 0.074 | 0.806 | 0.429 | 0.939 | 0.160 | 0.694 | 0.280 | 0.918 | 0.660 | 0.402 | |||
| RCu | −0.10 | −0.05 | 0.00 | 0.83 ** | −0.04 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.78 ** | 0.10 | 0.61 ** | 0.05 | ||
| p-value | 0.669 | 0.831 | 0.992 | 0.000 | 0.872 | 0.067 | 0.234 | 0.501 | 0.926 | 0.000 | 0.671 | 0.004 | 0.835 | ||
| SB | 0.46 * | 0.21 | 0.48 * | −0.16 | 0.64 ** | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.56 * | −0.06 | 0.49 * | −0.17 | −0.13 | −0.27 | |
| p-value | 0.041 | 0.373 | 0.031 | 0.503 | 0.002 | 0.337 | 0.121 | 0.125 | 0.010 | 0.808 | 0.028 | 0.469 | 0.594 | 0.245 | |
| RB | 0.45 * | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.51 * | 0.62 ** | 0.31 | 0.71 ** | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.11 | −0.28 | 0.03 | 0.58 ** |
| p-value | 0.043 | 0.109 | 0.462 | 0.337 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.181 | 0.000 | 0.109 | 0.065 | 0.189 | 0.633 | 0.232 | 0.910 | 0.007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Hamurcu, M.; Germ, M.; Yilmaz, F.G.; Ozbek, M.; Avsaroglu, Z.Z.; Topal, A.; Gezgin, S. Nutrient Homeostasis of Aegilops Accessions Differing in B Tolerance Level under Boron Toxic Growth Conditions. Biology 2022, 11, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081094
Khan MK, Pandey A, Hamurcu M, Germ M, Yilmaz FG, Ozbek M, Avsaroglu ZZ, Topal A, Gezgin S. Nutrient Homeostasis of Aegilops Accessions Differing in B Tolerance Level under Boron Toxic Growth Conditions. Biology. 2022; 11(8):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081094
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Mohd. Kamran, Anamika Pandey, Mehmet Hamurcu, Mateja Germ, Fatma Gokmen Yilmaz, Merve Ozbek, Zuhal Zeynep Avsaroglu, Ali Topal, and Sait Gezgin. 2022. "Nutrient Homeostasis of Aegilops Accessions Differing in B Tolerance Level under Boron Toxic Growth Conditions" Biology 11, no. 8: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081094
APA StyleKhan, M. K., Pandey, A., Hamurcu, M., Germ, M., Yilmaz, F. G., Ozbek, M., Avsaroglu, Z. Z., Topal, A., & Gezgin, S. (2022). Nutrient Homeostasis of Aegilops Accessions Differing in B Tolerance Level under Boron Toxic Growth Conditions. Biology, 11(8), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081094









