The Shortening of Leukocyte Telomere Length Contributes to Alzheimer’s Disease: Further Evidence from Late-Onset Familial and Sporadic Cases
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
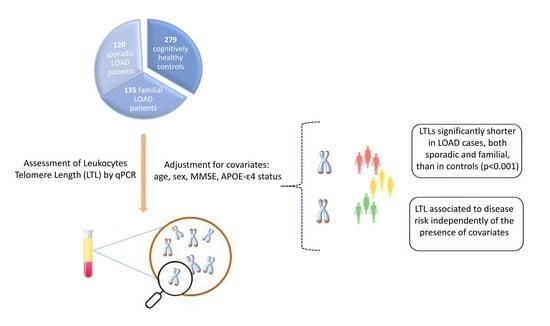
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Leukocyte Telomere Length (LTL)
2.5. APOE Genotyping
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.T.; Ma, Y.H.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. The Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s Disease Modifiable Risk Factors and Prevention. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 8, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossiello, F.; Jurk, D.; Passos, J.F.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Telomere dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthon, R.M.; Smith, K.R.; O’Brien, E.; Sivatchenko, A.; Kerber, R.A. Association between telomere length in blood and mortality in people aged 60 years or older. Lancet 2003, 361, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviv, A.; Shay, J.W. Reflections on telomere dynamics and ageing-related diseases in humans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ezquerro, J.D.; Rodríguez-Castañeda, A.; Ortiz-Ramírez, M.; Sánchez-García, S.; Rosas-Vargas, H.; Sánchez-Arenas, R.; García-De la Torre, P. Oxidative Stress, Telomere Length, and Frailty in an Old Age Population. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2020, 71, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiao, F.; Kong, Q.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y. Telomere Length: A Potential Biomarker for the Risk and Prognosis of Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkiadaki, P.; Nikitovic, D.; Kalliantasi, K.; Sarandi, E.; Thanasoula, M.; Stivaktakis, P.; Nepka, C.; Spandidos, D.; Theodoros, T.; Tsatsakis, A. Telomere length and telomerase activity in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 19, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Seimiya, H. Revisiting Telomere Shortening in Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, B.; Gispert, J.D.; Guigo, R.; Navarro, A.; Vilor-Tejedor, N.; Crous-Bou, M. Genetically predicted telomere length and its relationship with neurodegenerative diseases and life expectancy. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 4251–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, C.; Kong, J. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- Boccardi, V.; Arosio, B.; Cari, L.; Bastiani, P.; Scamosci, M.; Casati, M.; Ferri, E.; Bertagnoli, L.; Ciccone, S.; Rossi, P.D.; et al. Beta-carotene, telomerase activity and Alzheimer’s disease in old age subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, D.A.; González-Giraldo, Y.; López-Quintero, C.; Castro-Vega, L.J.; Barreto, G.E.; Perry, G. Meta-analysis of Telomere Length in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honig, L.S.; Schupf, N.; Lee, J.H.; Tang, M.X.; Mayeux, R. Shorter telomeres are associated with mortality in those with APOE ϵ4 and dementia. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, L.; Porter, V.R.; Valenzuela, H.F.; Zhu, X.; Reback, E.; Masterman, D.; Cummings, J.L.; Effros, R.B. Telomere shortening in T cells correlates with Alzheimer’s disease status. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarabino, D.; Broggio, E.; Gambina, G.; Corbo, R.M. Leukocyte telomere length in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease patients. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 98, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikgren, M.; Karlsson, T.; Nilbrink, T.; Nordfjall, K.; Hultdin, J.; Sleegers, K.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; Nyberg, L.; Roos, G.; Nilsson, L.G.; et al. APOE epsilon4 is associated with longer telomeres, and longer telomeres among epsilon4 carriers predicts worse episodic memory. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, S.; Blasco, M.A.; Siedlak, S.L.; Harris, P.L.R.; Moreira, P.I.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Telomeres and telomerase in Alzheimer’s disease: Epiphenomena or a new focus for therapeutic strategy? Alzheimers Dement. 2006, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekry, D.; Herrmann, F.R.; Irminger-Finger, I.; Ortolan, L.; Genet, C.; Vitale, A.M.; Michel, J.P.; Gold, G.; Krause, K.H. Telomere length is not predictive of dementia or MCI conversion in the oldest old. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekry, D.; Herrmann, F.R.; Irminger-Finger, I.; Graf, C.; Genet, C.; Vitale, A.M.; Michel, J.P.; Gold, G.; Krause, K.H. Telomere length and ApoE polymorphism in mild cognitive impairment, degenerative and vascular dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 299, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, Y.; Kikukawa, M.; Hanyu, H.; Koyama, S.; Shimizu, S.; Umahara, T.; Sakurai, H.; Iwamoto, T.; Ohyashiki, K.; Ohyashiki, J.H. Association between ApoE Phenotypes and Telomere Erosion in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movérare-Skrtic, S.; Johansson, P.; Mattsson, N.; Hansson, O.; Wallin, A.; Johansson, J.O.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Svensson, J. Leukocyte Telomere Length (LTL) is reduced in stable mild cognitive impairment but low LTL is not associated with conversion to Alzheimer’s Disease: A pilot study. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, L.; Hilal, S.; Sedaghat, S.; Broer, L.; Licher, S.; Arp, P.P.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Ikram, M.K.; Ikram, M.A. Telomere Length and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Rotterdam Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 73, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.O.; Boardman, L.A.; Cha, R.H.; Pankratz, V.S.; Johnson, R.A.; Druliner, B.R.; Christianson, T.J.H.; Roberts, L.R.; Petersen, R.C. Short and long telomeres increase risk of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 141–142, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocco, P.; Barale, R.; Rose, G.; Rizzato, C.; Santoro, A.; de Rango, F.; Carrai, M.; Fogar, P.; Monti, D.; Biondi, F.; et al. Population-specific association of genes for telomere-associated proteins with longevity in an Italian population. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. Mini-mental state. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, E.; Binetti, G.; Bianchetti, A.; Rozzini, R.; Trabucchi, M. Mini-Mental State Examination: A normative study in Italian elderly population. Eur. J. Neurol. 1996, 3, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Galasko, D.; Kosaka, K.; Perry, E.K.; Dickson, D.W.; Hansen, L.A.; Salmon, D.P.; Lowe, J.; Mirra, S.S.; Byrne, E.J.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): Report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 1996, 47, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englund, B.; Brun, A.; Gustafson, L.; Passant, U.; Mann, D.; Neary, D.; Snowden, J.S. Clinical and neuropathological criteria for frontotemporal dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 416–418. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, G.C.; Tatemichi, T.K.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Cummings, J.L.; Masdeu, J.C.; Garcia, J.H.; Amaducci, L.; Orgogozo, J.M.; Brun, A.; Hofman, A.; et al. Vascular dementia: Diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN InternationalWorkshop. Neurology 1993, 43, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, R.; Olivieri, F.; Sirolla, C.; Spazzafumo, L.; Rippo, M.R.; Marra, M.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Ceriello, A.; Antonicelli, R.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Leukocyte telomere length is associated with complications of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2011, 28, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthon, R.M. Telomere measurement by quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenham, P.R.; Newton, C.R.; Price, W.H. Analysis of apolipoprotein E genotypes by the Amplification Refractory Mutation System. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrieri, G.; Bonafè, M.; de Luca, M.; Rose, G.; Varcasia, O.; Bruni, A.; Maletta, R.; Nacmias, B.; Sorbi, S.; Corsonello, F.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups and APOE4 allele are non-independent variables in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Genet. 2001, 108, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Hendrie, H.C.; Hall, K.S.; Hui, S. The relationships between age, sex, and the incidence of dementia and Alzheimer disease: A meta-analysis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J. The age factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Aldrete, L.; Moser, M.V.; Putignano, G.; Ferretti, M.T.; Schumacher Dimech, A.; Santuccione Chadha, A. Sex and gender considerations in Alzheimer’s disease: The Women’s Brain Project contribution. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1105620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.G.; Epel, E.S.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.H.; Rasgon, N.L. Relationship between leukocyte telomere length, telomerase activity, and hippocampal volume in early aging. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Song, C.; Karlsson, R.; Tillander, A.; Reynolds, C.A.; Pedersen, N.L.; Hägg, S. Telomere length shortening and alzheimer disease–a mendelian randomization study. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1202–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, H. Leukocyte telomere length shortening and Alzheimer’s disease etiology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 69, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller Madrid, A.; Rasmussen, K.L.; Rode, L.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Bojesen, S.E. Observational and genetic studies of short telomeres and Alzheimer’s disease in 67,000 and 152,000 individuals: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lu, L.; Ma, Z.; Wu, S. Genetically predicted telomere length and its relationship with Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 595864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, A.; Li, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. New Insights in Amyloid Beta Interactions with Human Telomerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilsbury, A.; Miwa, S.; Attems, J.; Saretzki, G. The Role of Telomerase Protein TERT in Alzheimer’s Disease and in Tau-Related Pathology In Vitro. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, V.S.; Deo, P.; Chua, A.; Thomas, P.; Fenech, M. Shorter Telomere Length in Carriers of APOE-ε4 and High Plasma Concentration of Glucose, Glyoxal and Other Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenhaar, F.S.; Josefsson, M.; Adolfsson, A.N.; Landfors, M.; Kauppi, K.; Hultdin, M.; Adolfsson, R.; Degerman, S.; Pudas, S. Short leukocyte telomeres predict 25-year Alzheimer’s disease incidence in non-APOE ε4-carriers. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, A.M.; Deary, I.J.; Gardner, J.; Kimura, M.; Lu, X.; Spector, T.D.; Aviv, A.; Cherkas, L.F. Leukocyte telomere length is associated with cognitive performance in healthy women. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochstrasser, T.; Marksteiner, J.; Humpel, C. Telomere length is age-dependent and reduced in monocytes of Alzheimer patients. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huo, Y.R.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Ji, Y. Telomere Shortening in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 46, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, E.R.; Dumitrescu, L.; Seto, M.; Nudelman, K.N.H.; Buckley, R.F.; Gifford, K.A.; Saykin, A.J.; Jefferson, A.J.; Hohman, T.J. Telomere length associations with cognition depend on Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 5, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, S.-H.; Choi, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Jang, J.W.; Park, K.W.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Yoon, B.; et al. Telomere shortening reflecting physical aging is associated with cognitive decline and dementia conversion in mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease. Aging 2020, 12, 4407–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukens, J.N.; van Deerlin, V.; Clark, C.M.; Xie, S.X.; Johnson, F.B. Comparisons of telomere lengths in peripheral blood and cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimes Dement. 2009, 5, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| LOAD | Controls (n = 279) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sporadic (n = 120) | Familial (n = 135) | All Patients (n = 255) | p-Value * | ||
| Age (mean ± SD) | 76.9 ± 2.75 | 77.86 ± 2.77 | 77.41 ± 2.80 | 73.67 ± 5.49 | <0.001 |
| Males (%) | 37.5 | 37.0 | 37.3 | 52.7 | <0.001 |
| Age onset (mean ± SD) | 73.9 ± 5.40 | 73.72 ± 4.44 | 73.80 ± 5.41 | - | |
| MMSE ** (mean ± SD) | 14.34 ± 5.72 | 14.48 ± 5.01 | 14.42 ± 5.35 | 24.75 ± 3.73 | <0.001 |
| APOE-ε4 carriers (%) | 38.3 | 43.7 | 41.2 | 8.6 | <0.001 |
| Variables | OR (95% CI) * | p-Value | Nagelkerke R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sporadic LOAD | |||
| MMSE scores | 0.70 (0.65–0.76) | <0.001 | 0.712 |
| LogTS ratio | 0.03 (0.006–0.15) | <0.001 | |
| APOE-ε4 status | 5.89 (2.47–13.99) | <0.001 | |
| Age | 1.11 (1.03–1.19) | 0.008 | |
| Familial LOAD | |||
| MMSE scores | 0.69 (0.64–0.75) | <0.001 | 0.734 |
| LogTS ratio | 0.09 (0.02–0.40) | <0.001 | |
| APOE-ε4 status | 4.33 (1.88–9.96) | <0.001 | |
| Age | 1.13 (1.04–1.22) | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crocco, P.; De Rango, F.; Dato, S.; La Grotta, R.; Maletta, R.; Bruni, A.C.; Passarino, G.; Rose, G. The Shortening of Leukocyte Telomere Length Contributes to Alzheimer’s Disease: Further Evidence from Late-Onset Familial and Sporadic Cases. Biology 2023, 12, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101286
Crocco P, De Rango F, Dato S, La Grotta R, Maletta R, Bruni AC, Passarino G, Rose G. The Shortening of Leukocyte Telomere Length Contributes to Alzheimer’s Disease: Further Evidence from Late-Onset Familial and Sporadic Cases. Biology. 2023; 12(10):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101286
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrocco, Paolina, Francesco De Rango, Serena Dato, Rossella La Grotta, Raffaele Maletta, Amalia Cecilia Bruni, Giuseppe Passarino, and Giuseppina Rose. 2023. "The Shortening of Leukocyte Telomere Length Contributes to Alzheimer’s Disease: Further Evidence from Late-Onset Familial and Sporadic Cases" Biology 12, no. 10: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101286
APA StyleCrocco, P., De Rango, F., Dato, S., La Grotta, R., Maletta, R., Bruni, A. C., Passarino, G., & Rose, G. (2023). The Shortening of Leukocyte Telomere Length Contributes to Alzheimer’s Disease: Further Evidence from Late-Onset Familial and Sporadic Cases. Biology, 12(10), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101286