Combination of Host-Associated Rummeliibacillus sp. and Microbacterium sp. Positively Modulated the Growth, Feed Utilization, and Intestinal Microbial Population of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Diet Preparation
2.2. Fish Collection, Husbandry, and Feeding Trial
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Quantification of Growth, Feed Utilization, Innate Immunity, and Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.5. Intestinal Microbiome Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of the Combined Probiotic Strains on Growth, Feed Utilization, Innate Immunity, and Serum Biochemical Parameters
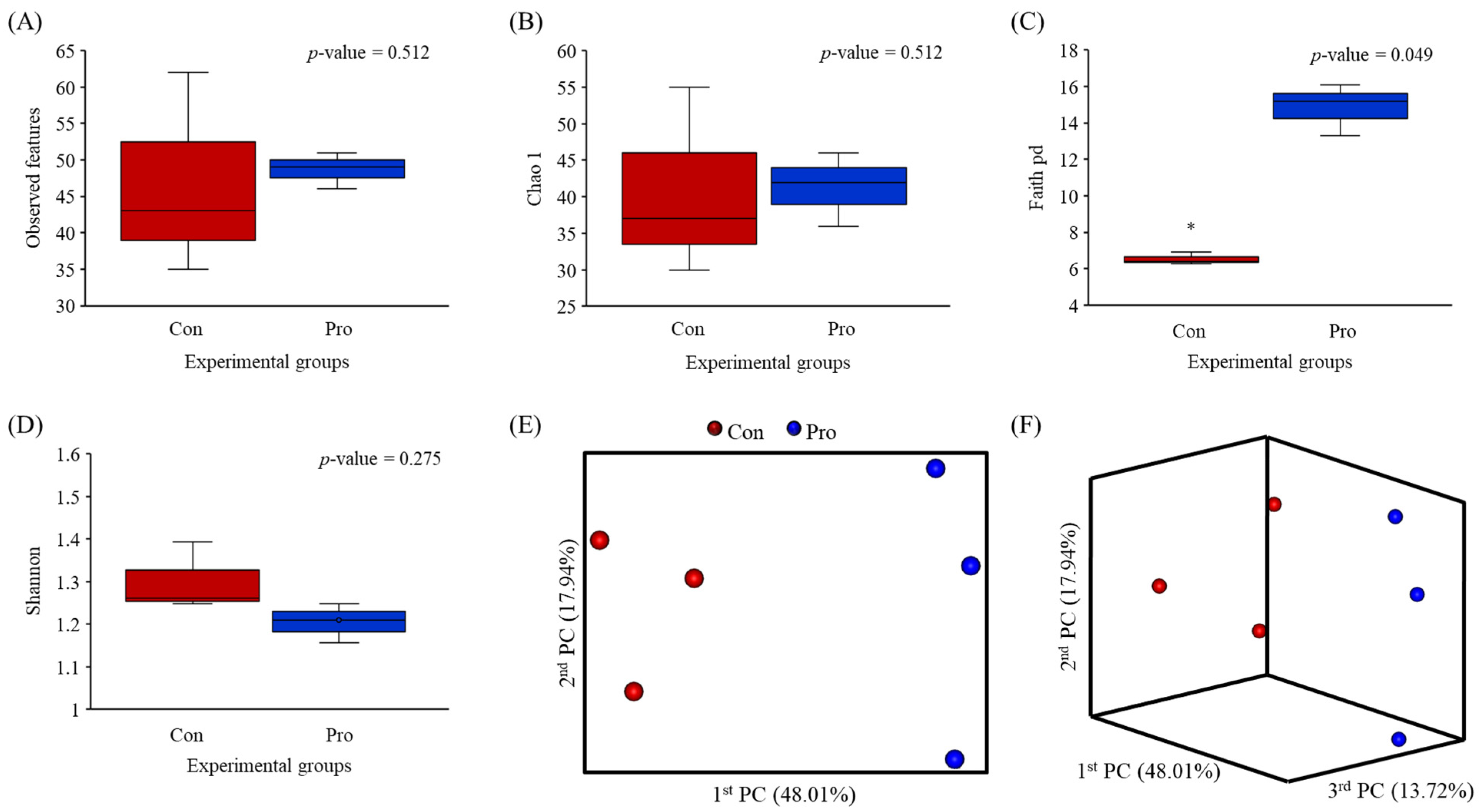
3.2. Effects of Combined Probiotics on the Alpha and Beta Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota
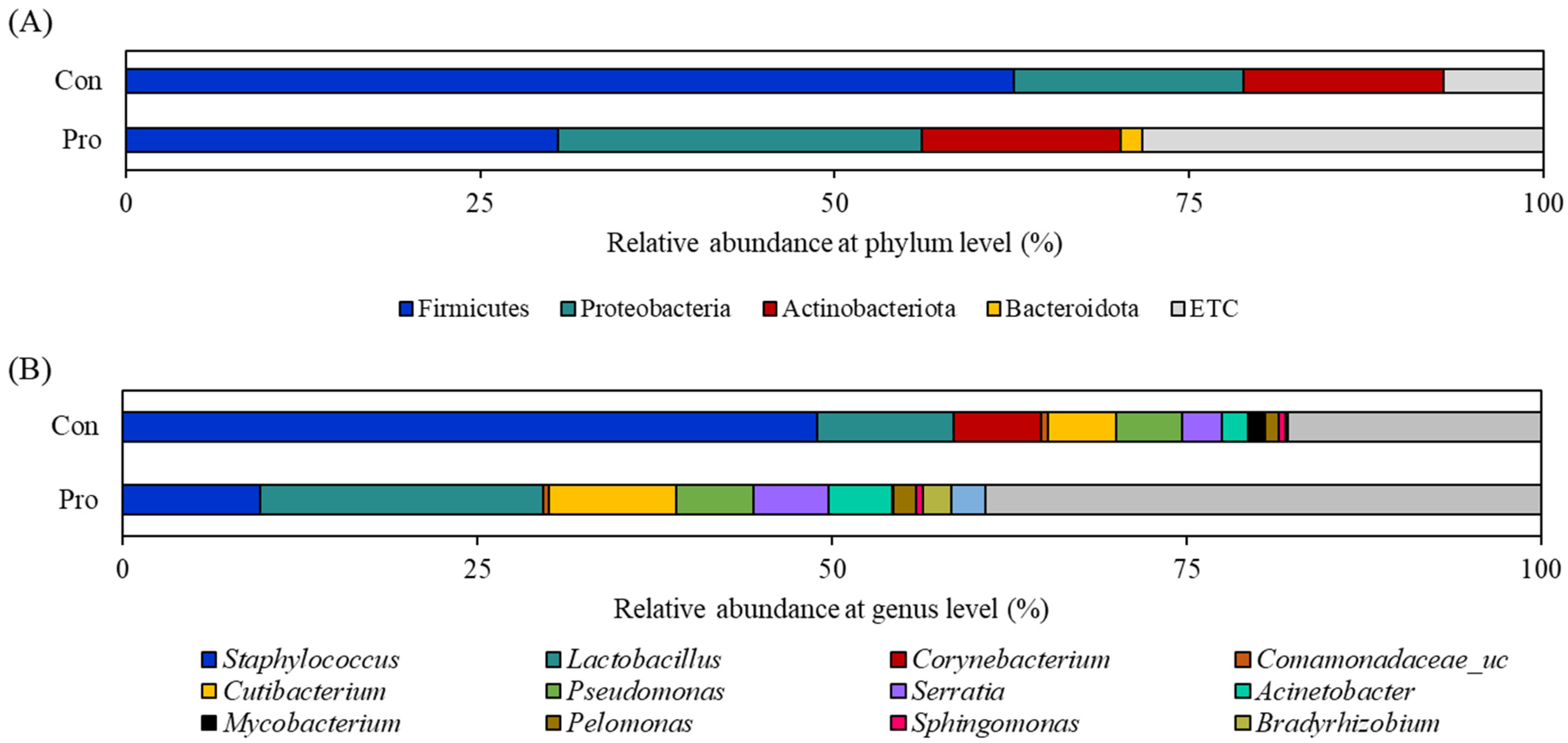
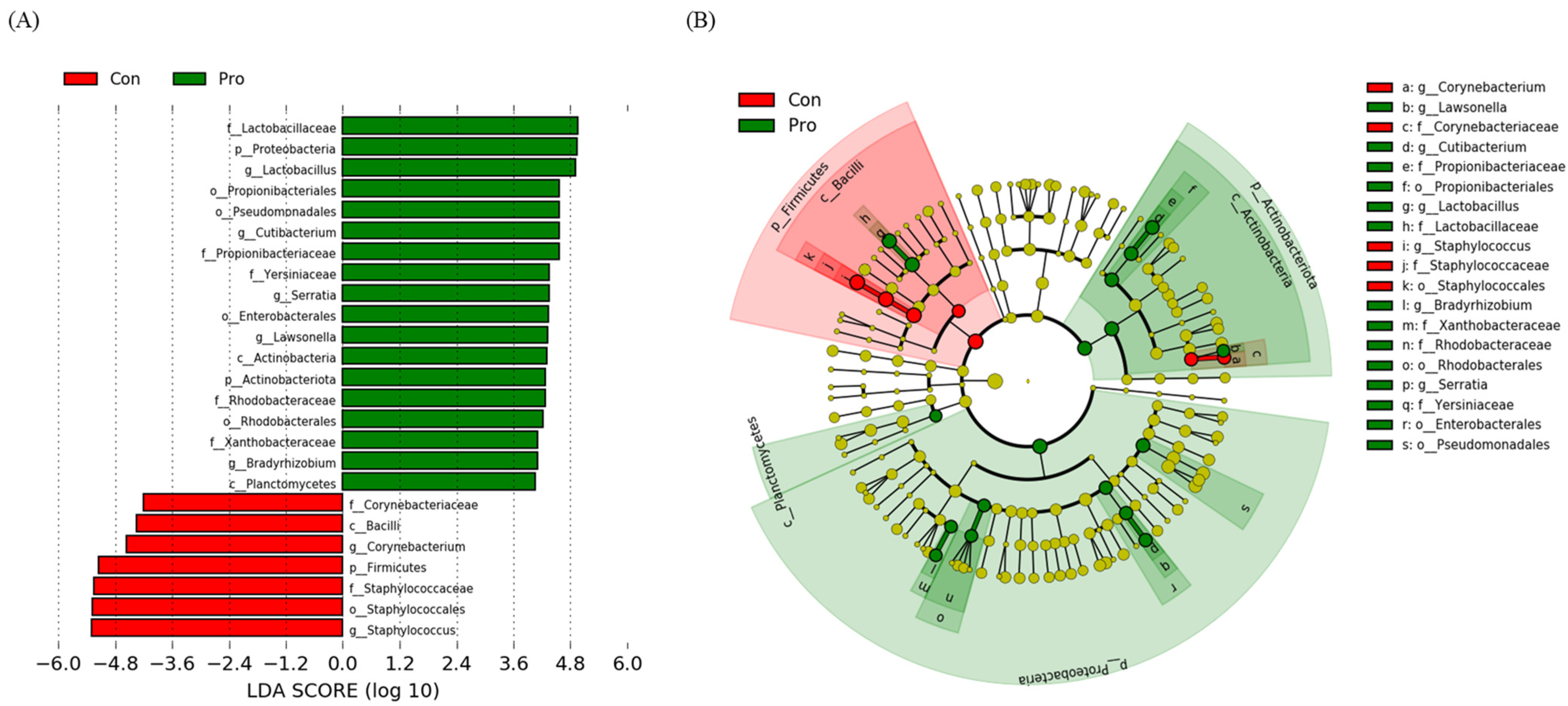
3.3. Modulation of the Relative Abundance of Microbiota at Phylum and Genus Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Survey on the Status of Fish Culture. 2021. Available online: http://kosis.kr/ (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Lee, W.; Ahn, G.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, N.; Kim, E.A.; Kim, K.N.; Jeong, J.B.; Jeon, Y.J. A Prebiotic Effect of Ecklonia cava on the Growth and Mortality of Olive Flounder Infected with Pathogenic Bacteria. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 51, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, B.R.; Kim, D.; Jeon, J.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, O.J.; Lee, J.I.; Suh, B.S.; Do, H.K.; Lee, K.H.; et al. The Effects of Combined Dietary Probiotics Lactococcus lactis BFE920 and Lactobacillus plantarum FGL0001 on Innate Immunity and Disease Resistance in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agricultural Organization; World Health Organization. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. In A Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation Report; Food and Agricultural Organization; World Health Organization: Cordoba, Argentina, 2001; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; de Blas, I.; Balcázar, J.L. Probiotics in Aquaculture: A Current Assessment. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cha, J.H.; Kim, M.G.; Shin, J.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Ji, S.C.; Lee, K.J. The Effects of Dietary Bacillus subtilis on Immune Response, Hematological Parameters, Growth Performance, and Resistance of Juvenile Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Against Streptococcus iniae. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.N.; Yun, Y.; Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; Kwon, M.J.; Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Kim, H.L. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Personality in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 374–385. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.T.; Jang, W.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, K.W.; Hur, S.W.; Lim, S.G.; Bai, S.C.; Kong, I.S. Synergistic Effects of Dietary Bacillus sp. SJ-10 Plus β-glucooligosaccharides as a Synbiotic on Growth Performance, Innate Immunity and Streptococcosis Resistance in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Rahimnejad, S.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.J. Evaluations of Bacillus spp. as Dietary Additives on Growth Performance, Innate Immunity and Disease Resistance of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Against Streptococcus iniae and as Water Additives. Aquaculture 2013, 402, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Beck, B.R.; Heo, S.B.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, K.; Do, H.; et al. Lactococcus lactis BFE920 Activates the Innate Immune System of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), Resulting in Protection Against Streptococcus iniae Infection and Enhancing Feed Efficiency and Weight Gain in Large-scale Field Studies. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, W.S.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, E.Y.; Bai, S.C.; Kong, I.S. Effects of Dietary Probiotic, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis I2, Supplementation on the Growth and Immune Response of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2013, 376, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.M.; Khosravi, S.; Kothari, D.; Lee, W.D.; Lee, B.J.; Lim, S.G.; Hur, S.W.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.K. Potential of Indigenous Bacillus spp. as Probiotic Feed Supplements in an Extruded Low-Fish-Meal Diet for Juvenile Olive Flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 244–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.T.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, B.J.; Hur, S.W.; Lim, S.G.; Kim, K.W.; Han, H.S.; Lee, E.W.; Bai, S.C.; Kong, I.S. Dietary Supplementation of Bacillus sp. SJ-10 and Lactobacillus plantarum KCCM 11322 Combinations Enhance Growth and Cellular and Humoral Immunity in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Probiotics Antimicrob. 2021, 13, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quade, M.J.; Roth, J.A. A Rapid, Direct Assay to Measure Degranulation of Bovine Neutrophil Primary Granules. Vet. Immunol. 1997, 58, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.P.; Siwicki, A.K. Basic hematology and serology for fish health programs. In Diseases in Asian aquaculture II; Shariff, M., Arthur, J.R., Subasinghe, R.P., Eds.; Philippines Fish Health Section, Asian Fisheries Society: Manila, Philippines, 1995; pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, W.J.; Hasan, M.T.; Lee, B.J.; Hur, S.W.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, E.W.; Kong, I.S. Effect of Dietary Differences on Changes of Intestinal Microbiota and Immune-related Gene Expression in Juvenile Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735442. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, I.; Abelli, L.; Bertoni, F.; Picchietti, S.; Roque, A.; Furones, D.; Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Monospecies and Multispecies Probiotic Formulations Produce Different Systemic and Local Immunostimulatory Effects in the Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.K. Probiotics and Immunity: A Fish Perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarike, E.D.; Jian, J.; Tang, J.; Cai, J.; Yu, H.; Lihua, C.; Jun, L. Influence of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Bacillus species (TCMBS) on Growth, Immune Response and Disease Resistance in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2366–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Balcázar, J.L.; Merrifield, D.L.; Carnevali, O.; Gioacchini, G.; de Blas, I.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I. Expression of Immune-related Genes in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Induced by Probiotic Bacteria During Lactococcus garvieae Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, I.; Tabassum, M.; Ahmad, T.; Zuberi, A.; Imran, M. Geotrichum candidum Enhanced the Enterococcus faecium Impact in Improving Physiology and Health of Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822) by Modulating Gut Microbiome Under Mimic Aquaculture Conditions. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, J.S.; Balasundaram, C.; Heo, M.S. Probiotics and Herbal Mixtures Enhance the Growth, Blood Constituents and Nonspecific Immune Response in Paralichthys olivaceus against Streptococcus parauberis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.T.; Kim, H.J.; Hur, S.W.; Jeong, S.M.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, S. Dietary Exogenous α-Amylase Modulates the Nutrient Digestibility, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Growth-Related Gene Expression and Diet Degradation Rate of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 1390. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari Nargesi, E.; Falahatkar, B.; Sajjadi, M.M. Dietary Supplementation of Probiotics and Influence on Feed efficiency, Growth Parameters and Reproductive Performance in Female Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Broodstock. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimnejad, S.; Guardiola, F.A.; Leclercq, E.; Esteban, M.Á.; Castex, M.; Sotoudeh, E.; Lee, S.M. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Pediococcus acidilactici MA18/5M, Galactooligosaccharide and Their Synbiotic on Growth, Innate Immunity and Disease Resistance of Rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Aquaculture 2018, 482, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fira, M.D.; Santanumurti, M.B.; Jamal, M.T.; Muttaqin, A.; Subekti, S.; Sari, P.D.W. Blood Glucose Profile as a Rapid Method for Observing Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Health Status-Case Study of Ectoparasites in Blitar, Indonesia. Rev. Bras. DE Parasitol. Vet. 2023, 32, e014622. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, N.; Wu, B.; Memon, A.M.; Mohsin, M. Probiotics and Prebiotics Associated with Aquaculture: A Review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dobaño, C.; Moncunill, G. Naturally Acquired Immunity (NAI). In Encyclopedia of Malaria; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff, S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and Foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 598–625. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Reyes-López, F.; Teles, M.; MacKenzie, S. The Response of Fish to Immunostimulant Diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 34–69. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Hu, S.Y. Improvements in the Growth Performance, Immunity, Disease Resistance, and Gut Microbiota by the Probiotic Rummeliibacillus stabekisii in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Gong, L.; Pan, L.; Li, D.; Cao, L.; Khan, T.A.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ding, X.; et al. Isolating a New Streptomyces amritsarensis N1-32 Against Fish Pathogens and Determining Its Effects on Disease Resistance of Grass Carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Hamidoghli, A.; Choi, W.; Park, Y.; Jang, W.J.; Kong, I.S.; Bai, S.C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis WB60 and Lactococcus lactis on Growth, Immune Responses, Histology and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Sadegh, T.H.; Dawood, M.A.; Dadar, M.; Sheikhzadeh, N. The Effects of Dietary Pediococcus pentosaceus on Growth Performance, Hemato-immunological Parameters and Digestive Enzyme Activities of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Bai, S.C. Use of Probiotics to Enhance Growth, Stimulate Immunity and Confer Disease Resistance to Aeromonas salmonicida in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Xu, C.; Sun, Q.; Xu, D.H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; Li, Q. Effects of Dietary poly-β-hydroxybutyrate Supplementation on the Growth, Immune Response and Intestinal Microbiota of Soiny Mullet (Liza haematocheila). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 91, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, C.; Romero, J. Fine Flounder (Paralichthys adspersus) Microbiome Showed Important Differences Between Wild and Reared Specimens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.J.; Lee, J.M.; Hasan, M.T.; Lee, B.J.; Lim, S.G.; Kong, I.S. Effects of Probiotic Supplementation of a Plant-based Protein Diet on Intestinal Microbial Diversity, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Intestinal Structure, and Immunity in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 719–727. [Google Scholar]
- Rasigade, J.P.; Vandenesch, F. Staphylococcus aureus: A Pathogen with Still Unresolved Issues. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Angert, E.R.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zou, H. Composition, Diversity, and Origin of the Bacterial Community in Grass Carp Intestine. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Canchaya, C.; Tauch, A.; Chandra, G.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Chater, K.F.; Van Sinderen, D. Genomics of Actinobacteria: Tracing the Evolutionary History of an Ancient Phylum. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 495–548. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, K.M.; Khosravi, S.; Kothari, D.; Lee, W.D.; Lim, J.M.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, K.W.; Lim, S.G.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.K. Effects of Dietary Multi-strain Probiotics Supplementation in a Low Fishmeal Diet on Growth Performance, Nutrient Utilization, Proximate Composition, Immune Parameters, and Gut Microbiota of Juvenile Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Sahandi, J.; Jafaryan, H.; Soltani, M.; Ebrahimi, P. The Use of Two Bifidobacterium Strains Enhanced Growth Performance and Nutrient Utilization of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fry. Probiotics Antimicrob. 2019, 11, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) II. Effects on Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, Intestinal Microbiota and Related Health Criteria. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups | Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, and Organosomatic Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBW (g) | WG (%) | SGR (% day−1) | FCR | PER | |
| Con | 31.55 ± 0.50 a | 192.95 ± 6.79 a | 1.92 ± 0.04 a | 1.23 ± 0.04 b | 1.60 ± 0.08 a |
| Pro | 35.98 ± 1.05 b | 233.31 ± 6.80 b | 2.15 ± 0.04 b | 1.02 ± 0.04 a | 1.93 ± 0.11 b |
| Groups | Serum Biochemical Parameters | |||
| ALT | AST | TG | TC | |
| Con | 108.33 ± 14.57 | 46.33 ± 5.69 | 16.67 ± 2.08 | 147.33 ± 12.22 |
| Pro | 102.33 ± 16.26 | 45.33 ± 3.21 | 17.00 ± 3.61 | 138.67 ± 9.71 |
| Groups | Nonspecific immune parameters | |||
| SOD | RB | MPO | AP | |
| Con | 37.11 ± 5.38 | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.07 a | 72.33 ± 6.81 |
| Pro | 41.68 ± 4.83 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | 1.19 ± 0.22 b | 81.67 ± 9.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, D.-I.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, T.-R.; Hasan, M.T.; Lee, E.-W.; Jang, W.J. Combination of Host-Associated Rummeliibacillus sp. and Microbacterium sp. Positively Modulated the Growth, Feed Utilization, and Intestinal Microbial Population of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Biology 2023, 12, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111443
Lee S-J, Kim SH, Noh D-I, Lee Y-S, Kim T-R, Hasan MT, Lee E-W, Jang WJ. Combination of Host-Associated Rummeliibacillus sp. and Microbacterium sp. Positively Modulated the Growth, Feed Utilization, and Intestinal Microbial Population of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Biology. 2023; 12(11):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su-Jeong, So Hee Kim, Da-In Noh, Young-Sun Lee, Tae-Rim Kim, Md Tawheed Hasan, Eun-Woo Lee, and Won Je Jang. 2023. "Combination of Host-Associated Rummeliibacillus sp. and Microbacterium sp. Positively Modulated the Growth, Feed Utilization, and Intestinal Microbial Population of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)" Biology 12, no. 11: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111443
APA StyleLee, S.-J., Kim, S. H., Noh, D.-I., Lee, Y.-S., Kim, T.-R., Hasan, M. T., Lee, E.-W., & Jang, W. J. (2023). Combination of Host-Associated Rummeliibacillus sp. and Microbacterium sp. Positively Modulated the Growth, Feed Utilization, and Intestinal Microbial Population of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Biology, 12(11), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111443






