Neuroprotective Action of Humanin and Humanin Analogues: Research Findings and Perspectives
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Discovery of Humanin
2. HN and HN Analogues with Biological Activity
3. HN and HN-like Mitochondrial-Derived Peptides
4. Recent Findings on the Therapeutic Potential of HN and HN Analogues against Neurodegenerative/Neural/Brain Disorders
5. Therapeutic Potential of HN and HN Analogues against Various Other Disorders
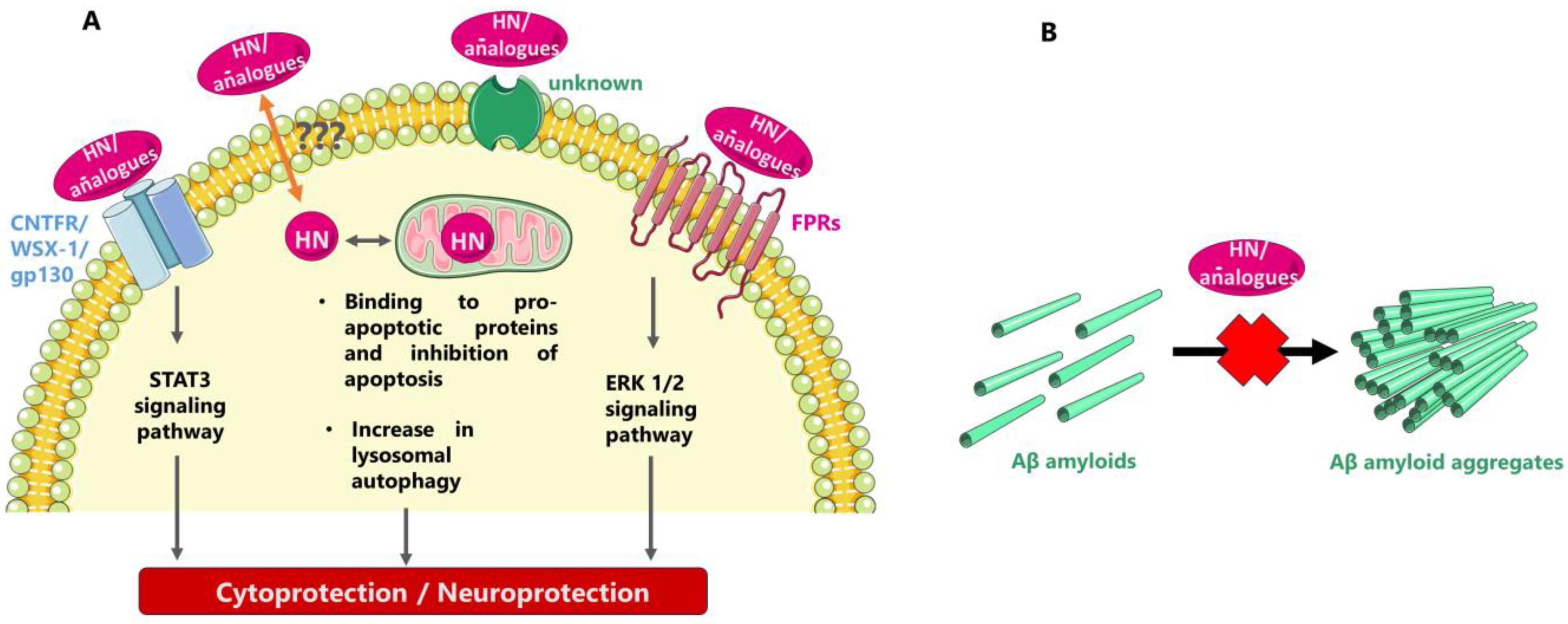
6. Possible Mode(s) of Neuroprotective/Cytoprotective Action of HN and HN Analogues
7. Routes/Formats of Exogenous Administration of HN and HN Analogues
8. HN Levels in Health, Neurodegenerative Disorders, and Aging
9. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashimoto, Y.; Ito, Y.; Niikura, T.; Shao, Z.; Hata, M.; Oyama, F.; Nishimoto, I. Mechanisms of neuroprotection by a novel rescue factor humanin from Swedish mutant amyloid precursor protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Niikura, T.; Ito, Y.; Sudo, H.; Hata, M.; Arakawa, E.; Abe, Y.; Kita, Y.; Nishimoto, I. Detailed characterization of neuroprotection by a rescue factor humanin against various Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9235–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Niikura, T.; Tajima, H.; Yasukawa, T.; Sudo, H.; Ito, Y.; Kita, Y.; Kawasumi, M.; Kouyama, K.; Doyu, M.; et al. A rescue factor abolishing neuronal cell death by a wide spectrum of familial Alzheimer’s disease genes and Abeta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6336–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, T. Humanin and Alzheimer’s disease: The beginning of a new field. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Zhai, D.; Cabezas, E.; Welsh, K.; Nouraini, S.; Satterthwait, A.C.; Reed, J.C. Humanin peptide suppresses apoptosis by interfering with Bax activation. Nature 2003, 423, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonen, M.; Liu, B.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ma, L.; Lee, K.W.; Niikura, T.; Nishimoto, I.; Cohen, P. Interaction between the Alzheimer’s survival peptide humanin and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 regulates cell survival and apoptosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13042–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nashine, S.; Kenney, M.C. Effects of mitochondrial-derived peptides (MDPs) on mitochondrial and cellular health in AMD. Cells 2020, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Niikura, T.; Nishimoto, I. Identification of essential amino acids in humanin, a neuroprotective factor against Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults. Peptides 2003, 24, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, A.; Zikos, C.; Livaniou, E.; Evangelatos, G.P. High-yield, solid-phase synthesis of humanin, an Alzheimer’s disease associated, novel 24-mer peptide which contains a difficult sequence. J. Pept. Sci. 2004, 10, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaki, D.; Zikos, C.; Evangelou, A.; Livaniou, E.; Vlassi, M.; Mikros, E.; Pelecanou, M. Solution structure of humanin, a peptide against Alzheimer’s disease-related neurotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 329, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricasole, A.; Bruno, V.; Cappuccio, I.; Melchiorri, D.; Copani, A.; Nicoletti, F. A novel rat gene encoding a Humanin-like peptide endowed with broad neuroprotective activity. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, I.; Matsuoka, M.; Niikura, T. Unravelling the role of Humanin. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sponne, I.; Fifre, A.; Koziel, V.; Kriem, B.; Oster, T.; Pillot, T. Humanin rescues cortical neurons from prion-peptide-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2004, 25, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamiya, T.; Ukai, M. [Gly(14)]-Humanin improved the learning and memory impairment induced by scopolamine in vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 1597–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Hao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Mao, N.; Miao, J.; Zhang, L. S14G-humanin improves cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid pathology in the middle-aged APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 100, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, T.; Sidahmed, E.; Hirata-Fukae, C.; Aisen, P.S.; Matsuoka, Y. A humanin derivative reduces amyloid beta accumulation and ameliorates memory deficit in triple transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, X.J.; Han, W.N.; Li, Q.S.; Wang, Z.J.; Wu, M.N.; Yang, W.; Qi, J.S. [Gly14]-Humanin protects against amyloid β peptide-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Nagahama, M.; Maruyama, T.; Niikura, T. Humanin ameliorates diazepam-induced memory deficit in mice. Neuropeptides 2017, 62, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Nagahama, M.; Abe, Y.; Niikura, T. Humanin affects object recognition and gliosis in short-term cuprizone-treated mice. Neuropeptides 2017, 66, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaki, D.; Zikos, C.; Evangelou, A.; Livaniou, E.; Vlassi, M.; Mikros, E.; Pelecanou, M. Solution structure of Ser14Gly-humanin, a potent rescue factor against neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashita, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Niikura, T.; Tajima, H.; Yamagishi, Y.; Ishizaka, M.; Kawasumi, M.; Chiba, T.; Kanekura, K.; Yamada, M.; et al. Two serine residues distinctly regulate the rescue function of humanin, an inhibiting factor of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurotoxicity: Functional potentiation by isomerization and dimerization. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsanousi, N.; Sugiki, T.; Furuita, K.; So, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Fujiwara, T.; Kojima, C. Solution NMR structure and inhibitory effect against amyloid-β fibrillation of humanin containing a d-isomerized serine residue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, T.; Yamada, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Sato, M.; Sasabe, J.; Kita, Y.; Terashita, K.; Aiso, S.; Nishimoto, I.; Matsuoka, M. Development of a femtomolar-acting humanin derivative named colivelin by attaching activity-dependent neurotrophic factor to its N terminus: Characterization of colivelin-mediated neuroprotection against Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10252–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzumdar, R.H.; Huffman, D.M.; Atzmon, G.; Buettner, C.; Cobb, L.J.; Fishman, S.; Budagov, T.; Cui, L.; Einstein, F.H.; Poduval, A.; et al. Humanin: A novel central regulator of peripheral insulin action. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.P.; Keni, J.; Wan, J.; Mehta, H.; Anene, F.; Jia, Y.; Lue, Y.H.; Swerdloff, R.; Cobb, L.J.; Wang, C.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of humanin and its analogues in male rodents. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3739–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, C.; Chen, B.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, L.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. HNGF6A inhibits oxidative stress-induced MC3T3-E1 cell apoptosis and osteoblast phenotype inhibition by targeting circ_0001843/miR-214 pathway. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.; Lerner-Yardeni, J.; Meridor, D.; Kasher, R.; Nathan, I.; Parola, A.H. Humanin derivatives inhibit necrotic cell death in neurons. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Shi, H.; He, Y.; Yuan, L.; Qu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, H.; Qi, J. Colivelin ameliorates impairments in cognitive behaviors and synaptic plasticity in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 59, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.N.; Zhou, L.W.; Wang, Z.J.; Han, W.N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.J.; Tong, J.Q.; Qi, J.S. Colivelin ameliorates amyloid β peptide-induced impairments in spatial memory, synaptic plasticity, and calcium homeostasis in rats. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunesová, G.; Hlavácek, J.; Patocka, J.; Evangelou, A.; Zikos, C.; Benaki, D.; Paravatou-Petsotas, M.; Pelecanou, M.; Livaniou, E.; Slaninova, J. The multiple T-maze in vivo testing of the neuroprotective effect of humanin analogues. Peptides 2008, 29, 1982–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, A.; Zikos, C.; Benaki, D.; Pelecanou, M.; Bouziotis, P.; Papadopoulos, M.; Borovickova, L.; Vesela, I.; Elbert, T.; Kunesová, G.; et al. In vitro binding and in vivo biodistribution studies of the neuroprotective peptide humanin using [125I]humanin derivatives. Peptides 2009, 30, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostomoiri, M.; Zikos, C.; Benaki, D.; Triantis, C.; Sagnou, M.; Paravatou-Petsotas, M.; Papadaki, A.; Boleti, H.; Papadopoulos, M.; Pirmettis, I.; et al. New labeled derivatives of the neuroprotective peptide colivelin: Synthesis, characterization, and first in vitro and in vivo applications. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 567, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostomoiri, M.; Evangelou, A.; Zikos, C.; Benaki, D.; Pelecanou, M.; Livaniou, E. Development of Biotinylated Derivatives of Humanin and Colivelin and Use in ELISA-Type Assays with the β-Amyloid Peptide. In Peptides 2014, Proceedings of the 33rd European Peptide Symposium, Sofia, Bulgaria, 31 August–5 September 2014; Naydenova, E., Rajpanova, T., Danalev, D., Eds.; Bulgarian Peptide Society: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2014; pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, Y.C.; Lee, N.H.; Lee, R.K.; Shim, J.H.; Glimcher, L.H.; Mook-Jung, I.; Cheong, E.; Kim, W.K.; et al. Amelioration of neurodegenerative diseases by cell death-induced cytoplasmic delivery of humanin. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilon, C.; Gitlin-Domagalska, A.; Lahiani, A.; Yehoshua-Alshanski, S.; Shumacher-Klinger, A.; Gilon, D.; Taha, M.; Sekler, I.; Hoffman, A.; Lazarovici, P. Novel humanin analogs confer neuroprotection and myoprotection to neuronal and myoblast cell cultures exposed to ischemia-like and doxorubicin-induced cell death insults. Peptides 2020, 134, 170399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Bao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Yang, P.; Xu, S.; Yu, F.; Meng, R.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Cholinergic neuron targeting nanosystem delivering hybrid peptide for combinatorial mitochondrial therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11455–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Bojarska, J.; Chai, T.T.; Elnagdy, S.; Kaczmarek, K.; Matsoukas, J.; New, R.; Parang, K.; Lopez, O.P.; Parhiz, H.; et al. A global review on short peptides: Frontiers and perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P. Humanin: A harbinger of mitochondrial-derived peptides? Trends Endocrinol. Metabol. 2013, 24, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazafa, A.; Batool, A.; Ahmad, S.; Amjad, M.; Chaudhry, S.N.; Asad, J.; Ghuman, H.F.; Khan, H.M.; Naeem, M.; Ghani, U. Humanin: A mitochondrial-derived peptide in the treatment of apoptosis-related diseases. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.W.; Namkung, J. Expression profile of mouse Gm20594, nuclear-encoded humanin-like gene. J. Lifestyle Med. 2021, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijenayake, S.; Storey, K.B. Oxidative damage? Not a problem! The characterization of humanin-like mitochondrial peptide in anoxia tolerant freshwater turtles. Protein J. 2021, 40, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijenayake, S.; Storey, K.B. The role of humanin in natural stress tolerance: An underexplored therapeutic avenue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bug, D.S.; Subbotina, T.F.; Narkevich, A.N.; Petukhova, N.V.; Zhloba, A.A. Evolutionary reconstruction of MT-RNR2 gene demonstrates a diverse compositional landscape of humanin in vertebrates. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 59, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, H.; Miller, B.; Kim, S.J.; Leelaprachakul, N.; Kikuchi, N.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P. Novel insights into mitochondrial DNA: Mitochondrial microproteins and mtDNA variants modulate athletic performance and age-related diseases. Genes 2023, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.; Kim, S.J.; Kumagai, H.; Mehta, H.H.; Xiang, W.; Liu, J.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P. Peptides derived from small mitochondrial open reading frames: Genomic, biological, and therapeutic implications. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 393, 112056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.; Kim, S.J.; Kumagai, H.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P. Mitochondria-derived peptides in aging and healthspan. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, L.J.; Lee, C.; Xiao, J.; Yen, K.; Wong, R.G.; Nakamura, H.K.; Mehta, H.H.; Gao, Q.; Ashur, C.; Huffman, D.M.; et al. Naturally occurring mitochondrial-derived peptides are age-dependent regulators of apoptosis, insulin sensitivity, and inflammatory markers. Aging 2016, 8, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamarai Kannan, H.; Issac, P.K.; Dey, N.; Guru, A.; Arockiaraj, J. A review on mitochondrial derived peptide humanin and small humanin-like peptides and their therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2023, 29, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Tran, L.T.; NamKoong, C.; Choi, H.J.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Cheon, M.; Chung, C.; Hwang, J.; Lim, H.H.; et al. Mitochondria-derived peptide SHLP2 regulates energy homeostasis through the activation of hypothalamic neurons. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H. Intranasal delivery of mitochondrial protein humanin rescues cell death and promotes mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Theranostics 2023, 13, 3330–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.E.; Sun, G.; Bautista Garrido, J.; Obertas, L.; Mobley, A.S.; Ting, S.M.; Zhao, X.; Aronowski, J. The mitochondria-derived peptide humanin improves recovery from intracerebral hemorrhage: Implication of mitochondria transfer and microglia phenotype change. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, R.; Bautista-Garrido, J.; Ozaki, D.; Sun, G.; Obertas, L.; Mobley, A.S.; Kim, G.S.; Aronowski, J.; Jung, J.E. Transplantation of astrocytic mitochondria modulates neuronal antioxidant defense and neuroplasticity and promotes functional recovery after intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 7001–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arneson, D.; Zhang, G.; Ahn, I.S.; Ying, Z.; Diamante, G.; Cely, I.; Palafox-Sanchez, V.; Gomez-Pinilla, F.; Yang, X. Systems spatiotemporal dynamics of traumatic brain injury at single-cell resolution reveals humanin as a therapeutic target. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegawa, N.; Kozuka, A.; Morita, N.; Murakami, M.; Sasakawa, N.; Niikura, T. Humanin derivative, HNG, enhances neurotransmitter release. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, W.; Wu, B.; Du, H. Humanin protects cortical neurons from calyculin A-induced neurotoxicities by increasing PP2A activity and SOD. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Jeyaraj, M.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, J.H. Mitochondrial peptide humanin protects silver nanoparticles-induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma cancer cells (SH-SY5Y). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; Jin, W.N.; Shi, F.D. Colivelin rescues ischemic neuron and axons involving JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Neuroscience 2019, 416, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Jia, N.; Zhong, Y.; Shang, X. S14G-humanin alleviates insulin resistance and increases autophagy in neurons of APP/PS1 transgenic mouse. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3111–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, K.; Wan, J.; Mehta, H.H.; Miller, B.; Christensen, A.; Levine, M.E.; Salomon, M.P.; Brandhorst, S.; Xiao, J.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Humanin prevents age-related cognitive decline in mice and is associated with improved cognitive age in humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wan, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Sun, G.; Ji, Y.; Lu, J.; et al. The neurovascular protective effect of S14G-humanin in a murine MCAO model and brain endothelial cells. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradduzza, D.; Congiargiu, A.; Chen, Z.; Cruciani, S.; Zinellu, A.; Carru, C.; Medici, S. Humanin and its pathophysiological roles in aging: A systematic review. Biology 2023, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabravolski, S.A. Mitochondria-derived peptides in healthy ageing and therapy of age-related diseases. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2023, 136, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Miller, B.; Kumagai, H.; Silverstein, A.R.; Flores, M.; Yen, K. Mitochondrial-derived peptides in aging and age-related diseases. GeroScience 2021, 43, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasiak, J. Senescence in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nashine, S.; Cohen, P.; Chwa, M.; Lu, S.; Nesburn, A.B.; Kuppermann, B.D.; Kenney, M.C. Humanin G (HNG) protects age-related macular degeneration (AMD) transmitochondrial ARPE-19 cybrids from mitochondrial and cellular damage. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Kannan, R. Mechanisms of protection of retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidant injury by humanin and other mitochondrial-derived peptides: Implications for age-related macular degeneration. Redox. Biol. 2020, 37, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtscher, J.; Soltany, A.; Visavadiya, N.P.; Burtscher, M.; Millet, G.P.; Khoramipour, K.; Khamoui, A.V. Mitochondrial stress and mitokines in aging. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Pappas, P.D.; Theodoridis, T.D.; Vavilis, D. Humanin and diabetes mellitus: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hu, X.; Bennett, S.; Xu, J.; Mai, Y. The molecular structure and role of humanin in neural and skeletal diseases, and in tissue regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 823354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, L.D. Mitochondrial peptides-appropriate options for therapeutic exploitation. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Meloux, A.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Role of humanin, a mitochondrial-derived peptide, in cardiovascular disorders. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 113, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.W.; Wang, S.R.; Liu, Z.H.; Cao, Y.J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.F.; Xie, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Gly [14]-Humanin inhibits ox-LDL uptake and stimulates cholesterol efflux in macrophage-derived foam cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, C.F.; Asad, A.S.; Nicola Candia, A.J.; Gottardo, M.F.; Moreno Ayala, M.A.; Theas, M.S.; Seilicovich, A.; Candolfi, M. Mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin as therapeutic target in cancer and degenerative diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lue, Y.; Swerdloff, R.; Wan, J.; Xiao, J.; French, S.; Atienza, V.; Canela, V.; Bruhn, K.W.; Stone, B.; Jia, Y.; et al. The potent humanin analogue (HNG) protects germ cells and leucocytes while enhancing chemotherapy-induced suppression of cancer metastases in male mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, E.; Wickström, M.; Perup, L.S.; Johnsen, J.I.; Eksborg, S.; Kogner, P.; Sävendahl, L. Protective role of humanin on bortezomib-induced bone growth impairment in anticancer treatment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P. New role for the mitochondrial peptide humanin: Protective agent against chemotherapy-induced side effects. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximov, V.; Martynenko, A.; Hunsmann, G.; Tarantul, V. Mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene encodes a functional peptide, a potential drug for Alzheimer’s disease and target for cancer therapy. Med. Hypotheses 2002, 59, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Ayala, M.A.; Gottardo, M.F.; Zuccato, C.F.; Pidre, M.L.; Nicola Candia, A.J.; Asad, A.S.; Imsen, M.; Romanowski, V.; Creton, A.; Isla Larrain, M.; et al. Humanin promotes tumor progression in experimental triple negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, M.F.; Pidre, M.L.; Zuccato, C.; Asad, A.S.; Imsen, M.; Jaita, G.; Candolfi, M.; Romanowski, V.; Seilicovich, A. Baculovirus-based gene silencing of Humanin for the treatment of pituitary tumors. Apoptosis 2018, 23, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Chen, S.; Tseng, L.M.; Lee, H.C. Role of the mitochondrial stress response in human cancer progression. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2020, 245, 861–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njomen, E.; Evans, H.G.; Gedara, S.H.; Heyl, D.L. Humanin peptide binds to insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) and regulates its interaction with importin-β. Protein Pept. Lett. 2015, 22, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Luciano, F.; Zhu, X.; Guo, B.; Satterthwait, A.C.; Reed, J.C. Humanin binds and nullifies Bid activity by blocking its activation of Bax and Bak. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15815–15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.W.; Liu, D.X. Humanin decreases mitochondrial membrane permeability by inhibiting the membrane association and oligomerization of Bax and Bid proteins. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.L.; Johnson, S.; Bleck, C.K.E.; Lee, D.Y.; Tjandra, N. Humanin selectively prevents the activation of pro-apoptotic protein BID by sequestering it into fibers. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 18226–18238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Devgan, A.; Miller, B.; Lee, S.M.; Kumagai, H.; Wilson, K.A.; Wassef, G.; Wong, R.; Mehta, H.H.; Cohen, P.; et al. Humanin-induced autophagy plays important roles in skeletal muscle function and lifespan extension. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Tasset, I. Humanin enhances the cellular response to stress by activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 10832–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Tasset, I.; Diaz, A.; Anguiano, J.; Tas, E.; Cui, L.; Kuliawat, R.; Liu, H.; Kühn, B.; Cuervo, A.M.; et al. Humanin is an endogenous activator of chaperone-mediated autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.; Iribarren, P.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, N.; Yu, Z.X.; Le, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.M. Humanin, a newly identified neuroprotective factor, uses the G protein-coupled formylpeptide receptor-like-1 as a functional receptor. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7078–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Habata, Y.; Hosoya, M.; Nishi, K.; Fujii, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Hinuma, S. N-Formylated humanin activates both formyl peptide receptor-like 1 and 2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Hashimoto, Y. Humanin and the receptors for humanin. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Guerrero, N.; Wassef, G.; Xiao, J.; Mehta, H.H.; Cohen, P.; Yen, K. The mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin activates the ERK1/2, AKT, and STAT3 signaling pathways and has age-dependent signaling differences in the hippocampus. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46899–46912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.I.; Rezzola, S.; Tobia, C.; Coltrini, D.; Belleri, M.; Mitola, S.; Corsini, M.; Sandomenico, A.; Caporale, A.; Ruvo, M.; et al. D-Peptide analogues of Boc-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe-COOH induce neovascularization via endothelial N-formyl peptide receptor 3. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, L.; Vieten, S.; Brödel, S.; Endres, K.; Bufe, B. Emerging contributions of formyl peptide receptors to neurodegenerative diseases. Biol. Chem. 2022, 403, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.L.; Li, J.Z.; Feng, Z.B.; Ma, G.L.; Gong, L.; Li, C.L.; Zhang, C.; Li, K. Humanin rescues cultured rat cortical neurons from NMDA-induced toxicity not by NMDA receptor. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 341529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.Z.; Song, T.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Ma, G.L.; Zhang, H.; Li, K. Humanin rescues cultured rat cortical neurons from NMDA-induced toxicity through the alleviation of mitochondrial dysfunction. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.P.; Bilousova, T.; Spilman, P.; Vadivel, K.; Bai, D.; Elias, C.J.; Evseenko, D.; John, V. A Small molecule mimetic of the humanin peptide as a candidate for modulating NMDA-induced neurotoxicity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiankhaw, K.; Chattipakorn, K.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Roles of humanin and derivatives on the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases and cognition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Ding, Y.; Sha, Y.; Hu, B.; Nie, S. Humanin peptides block calcium influx of rat hippocampal neurons by altering fibrogenesis of Abeta(1-40). Peptides 2003, 24, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftei, M.; Tian, X.; Manea, M.; Exner, T.E.; Schwanzar, D.; von Arnim, C.A.; Przybylski, M. Interaction structure of the complex between neuroprotective factor humanin and Alzheimer’s β-amyloid peptide revealed by affinity mass spectrometry and molecular modeling. J. Pept. Sci. 2012, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.K.; Teranishi, K.; Lobo, F.; Isas, J.M.; Xiao, J.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P.; Langen, R. The mitochondrial-derived peptides, humaninS14G and small humanin-like peptide 2, exhibit chaperone-like activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, Z.A.; Teranishi, K.; Okada, A.K.; Langen, R.; Shea, J.E. The mitochondrial peptide humanin targets but does not denature amyloid oligomers in type II diabetes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14168–14179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chua, C.C.; Gao, J.; Hamdy, R.C.; Chua, B.H. Humanin is a novel neuroprotective agent against stroke. Stroke 2006, 37, 2613–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gong, S.; Feng, L.; Zhong, Y.; Pang, Z. The proton permeability of self-assembled polymersomes and their neuroprotection by enhancing a neuroprotective peptide across the blood-brain barrier after modification with lactoferrin. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3250–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Lu, W.; Yin, Q.; Gao, H.; Jiang, X. Self-assembled polymersomes conjugated with lactoferrin as novel drug carrier for brain delivery. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgul, M.; Nesburn, A.B.; Nasralla, N.; Katz, B.; Taylan, E.; Kuppermann, B.D.; Kenney, M.C. Stability determination of intact humanin-G with characterizations of oxidation and dimerization patterns. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhao, S.; Tang, L. Humanin levels in human seminal plasma and spermatozoa are related to sperm quality. Andrology 2019, 7, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Zhou, F.; Tang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ke, D.; Cheng, G.; Xia, W.; Zhang, L.; et al. Follicular fluid humanin concentration is related to ovarian reserve markers and clinical pregnancy after IVF-ICSI: A pilot study. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2019, 38, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Weidling, I.; Koppel, S.; Menta, B.; Perez Ortiz, J.; Kalani, A.; Wilkins, H.M.; Swerdlow, R.H. Detection of mitochondria-pertinent components in exosomes. Mitochondrion 2020, 55, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M.; Ridolfo, F.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Schillaci, F.A.; Caniglia, S.; Lanuzza, B.; Cantone, M.; Ferri, R. Humanin gene expression in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, K.; Mehta, H.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lue, Y.; Hoang, J.; Guerrero, N.; Port, J.; Bi, Q.; Navarrete, G.; Brandhorst, S.; et al. The mitochondrial derived peptide humanin is a regulator of lifespan and healthspan. Aging 2020, 12, 11185–11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Protective Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients with Vascular Dementia. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wan, J.; Miyazaki, B.; Fang, Y.; Guevara-Aguirre, J.; Yen, K.; Longo, V.; Bartke, A.; Cohen, P. IGF-I regulates the age-dependent signaling peptide humanin. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zárate, S.C.; Traetta, M.E.; Codagnone, M.G.; Seilicovich, A.; Reinés, A.G. Humanin, a mitochondrial-derived peptide released by astrocytes, prevents synapse loss in hippocampal neurons. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Ostan, R.; Fabbri, C.; Santoro, A.; Guidarelli, G.; Vitale, G.; Mari, D.; Sevini, F.; Capri, M.; Sandri, M.; et al. Human Aging and Longevity Are Characterized by High Levels of Mitokines. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S. Aducanumab: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, S.M. Lecanemab: First approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. Landmark Alzheimer’s drug approval confounds research community. Nature 2021, 594, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilakopoulou, V.; Karachaliou, C.E.; Evangelou, A.; Zikos, C.; Livaniou, E. Peptide-based vaccines for neurodegenerative diseases: Recent endeavors and future perspectives. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.H.; Ahmad, K.; Saeed, M.; Alharbi, A.M.; Barreto, G.E.; Ashraf, G.M.; Choi, I. Peptide based therapeutics and their use for the treatment of neurodegenerative and other diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Gracia, P.; Navarro, S.; Peña-Díaz, S.; Pujols, J.; Cremades, N.; Pallarès, I.; Ventura, S. α-Helical peptidic scaffolds to target α-synuclein toxic species with nanomolar affinity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: Current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Code Name | Primary Structure | Evaluation in In Vitro/In Vivo Experimental Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| HN | MAPRGFSCLLLLTSEIDLPVKRRA | +/+ | [1,2,3] |
| HNG | MAPRGFSCLLLLTGEIDLPVKRRA | +/+ | [1,2,3] |
| HN-D-Ser14 | MAPRGFSCLLLLTsEIDLPVKRRA | +/− | [21] |
| HNGF6A | MAPRGASCLLLLTGEIDLPVKRRA | +/− | [26] |
| AGA-(C8R)HNG17 | PAGASRLLLLTGEIDLP | +/+ | [23] |
| CL | SALLRSIPAPAGASRLLLLTGEIDLP | +/+ | [23] |
| des-Leu-CL | SALLRSIPAPAGASRLLL_TGEIDLP | −/+ | [30] |
| tHN-C3 | Hph-1 &-KKRLGLPGDEVDMAPRGFSCLLLLTSEIDLPVKRRA | +/+ | [34] |
| HUJInin | YNAPVSIPQPAGASRLLLLTGEIDLP | +/− | [35] |
| c[D-Ser14-HN] | c *(MAPAGASRLLLLTsEIDLPVKRRA) | +/− | [35] |
| HNSS | R(d)-Dmt #-KFGG-MAPRGFSCLLLLTGEIDLPVKRRA | +/+ | [36] |
| HN/HN Analogue | Disorder/Pathological Symptom Simulated | In Vitro Cellular Model/In Vitro Beneficial Effects | In Vivo Animal Model/In Vivo Beneficial Effects/Main Route of Administration | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN | Parkinson’s disease (PD) | SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma and PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cell lines/ Neuroprotection through mitochondrial biogenesis | Mouse models of PD/Neuroprotection and behavioral recovery/ i.n. administration | [50] |
| HNSS | Alzheimer’s disease (AD) | HT22 neuronal cells overexpressing FGFR1/Inhibition of experimentally induced intracellular and mitochondrial ROS production | 3xTg-AD mice/ Mitochondrial rescue, inhibition of Aβ deposition and tau hyperphosphorylation, amelioration of memory defect and neuronal damage/ i.v. administration through a specially developed delivery system | [36] |
| HN | ICH | Rat primary cerebral cortical astrocyte and microglia cultures/ Promotion of a “reparative” microglia phenotype characterized by enhanced phagocytosis and reduced proinflammatory responses | C57BL/6J mouse model of ICH induced by intrastriatal injection of autologous blood/ Reduction of neurological deficits, and improvement of hematoma clearance/ i.p. or i.n. administration | [51] |
| HN | Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) | ICH-like cellular model induced in primary rodent neuron cultures/ HN upregulated phosphorylation of STAT3 and increased Mn-SOD expression in neurons under ICH-like injury and prevented ROS-overexpression | C57BL6/J mouse and Sprague Dawley rat models of ICH/ Systemic transplantation of astrocytic mitochondria (which contain HN) in ICH promotes antioxidative protection and assists in functional recovery by enhancing Mn-SOD-mediated neuronal antioxidant defense and neuroplasticity in the brain | [52] |
| HN | Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) | - | Mouse model of mTBI/Reversal of cognitive impairment through restoration of metabolic pathways within astrocytes/ i.p. administration | [53] |
| HNG | Impairment of object memory | PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells/ Enhancement of regulated neuronal exocytosis | Normal mice/ Improvement of object memory/ i.p. administration | [54] |
| HN | Neuronal cell death | Cortical neuron neurotoxicity model induced by calyculin A (CA)/ HN preincubation preserved cell viability, alleviated oxidative stress, blocked tau overphosphorylation, and protected neurons against CA-induced insults | - | [55] |
| HUJInin and c(D-Ser14-HN) | Stroke | Ischemia–reperfusion injury cellular model induced in PC12 cell cultures using ischemia-like oxygen–glycose-deprivation–reoxygenation insult and SH-SY5Y neuronal cell cultures exposed to pathological H2O2 oxidative stress/ Cell neuroprotection | - | [35] |
| HN | Neuronal cell death | SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line/Neuroprotection against neurotoxicity induced by silver nanoparticles | - | [56] |
| CL | Stroke | - | C57BL/6 middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mouse model/ Decrease in the neurological deficits, improvement of motor and cognitive functions, improvement of infarct lesion/ i.p. administration | [57] |
| HNG | AD | - | APP/PS1 mice/ Improvement of cognitive function/ i.p. administration | [58] |
| HNG | Age-related cognitive decline | SH-SY5Y cells/ Neuroprotective effect against Aβ mitochondrial toxicity | C57Bl/6N mice/ Improvement of cognitive ability of old-age mice/ i.p. administration | [59] |
| HNG | Stroke | Mouse brain endothelial cells bEnd.3/ Cytoprotection under oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) conditions | Mouse MCAO stroke model/ Amelioration of cerebral infarction and suppression of various inflammatory cytokines/ i.p. administration | [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karachaliou, C.-E.; Livaniou, E. Neuroprotective Action of Humanin and Humanin Analogues: Research Findings and Perspectives. Biology 2023, 12, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121534
Karachaliou C-E, Livaniou E. Neuroprotective Action of Humanin and Humanin Analogues: Research Findings and Perspectives. Biology. 2023; 12(12):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121534
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarachaliou, Chrysoula-Evangelia, and Evangelia Livaniou. 2023. "Neuroprotective Action of Humanin and Humanin Analogues: Research Findings and Perspectives" Biology 12, no. 12: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121534
APA StyleKarachaliou, C.-E., & Livaniou, E. (2023). Neuroprotective Action of Humanin and Humanin Analogues: Research Findings and Perspectives. Biology, 12(12), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121534







