Assessing the Causal Association between Biological Aging Biomarkers and the Development of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
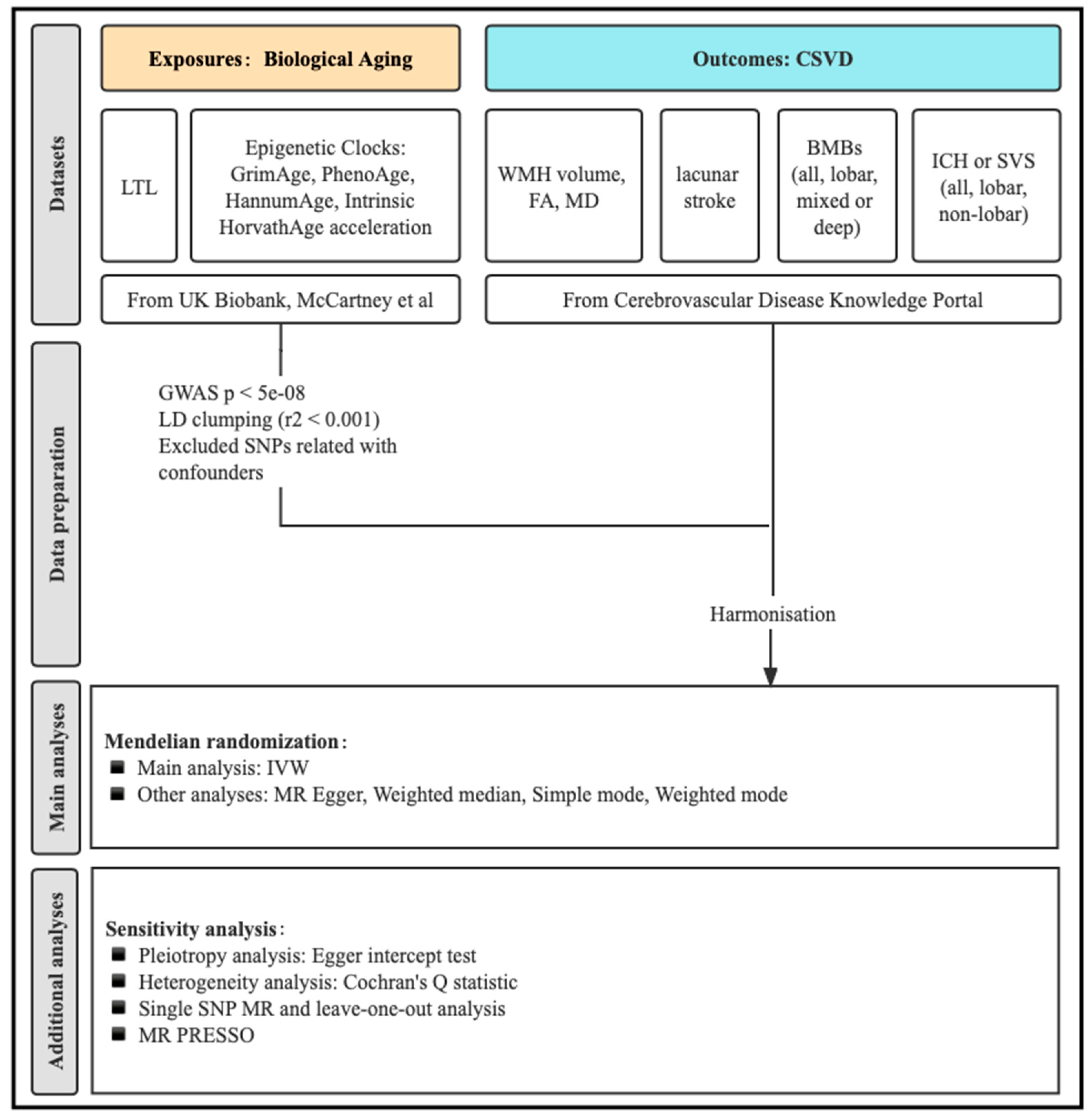
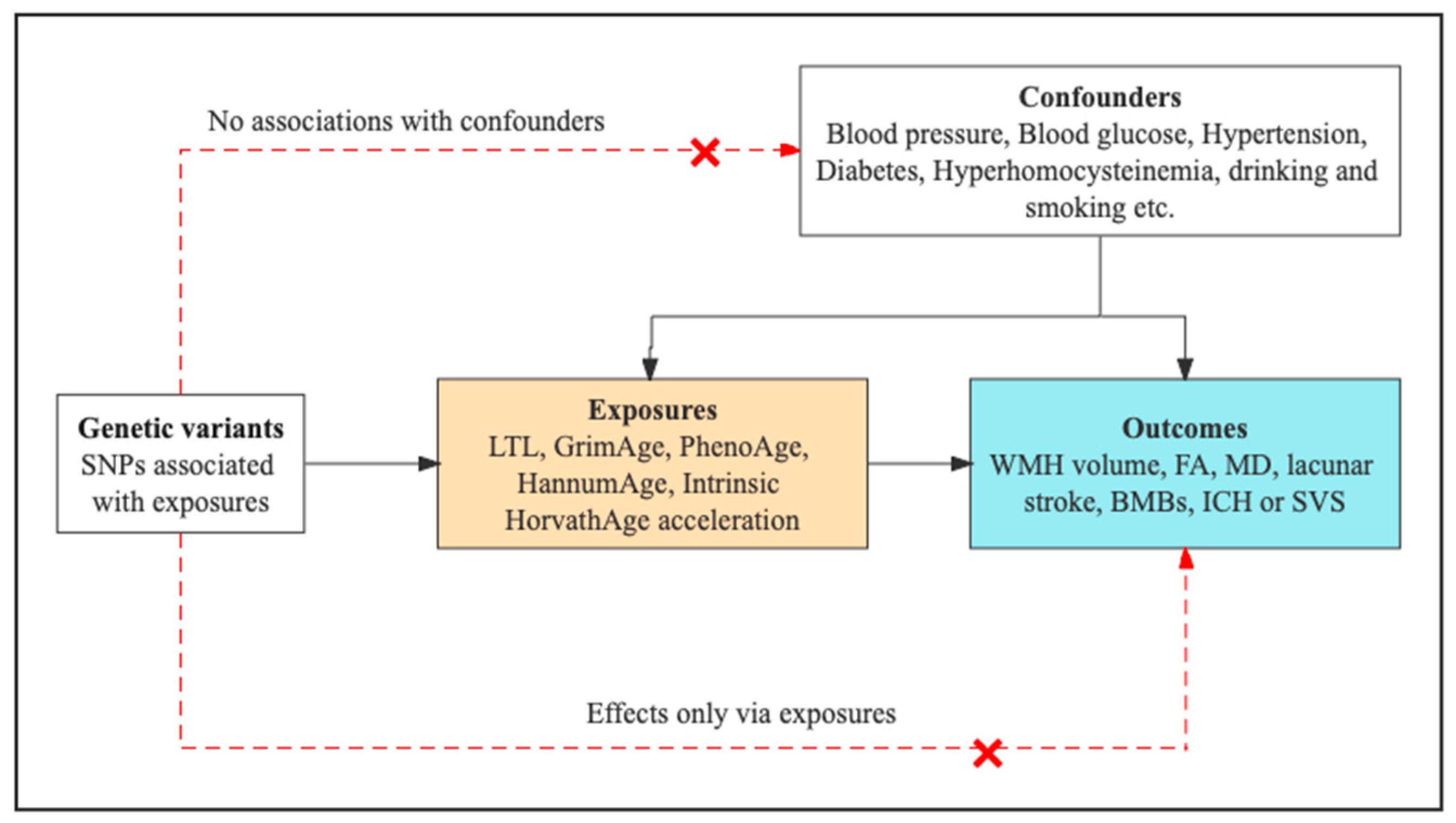
2.1. Study Design Overview
2.2. Genetic Instruments for LTL and Epigenetic Clocks
2.3. Genetic Association Data Sources for CSVD Phenotypes
2.4. MR Analyses
3. Results
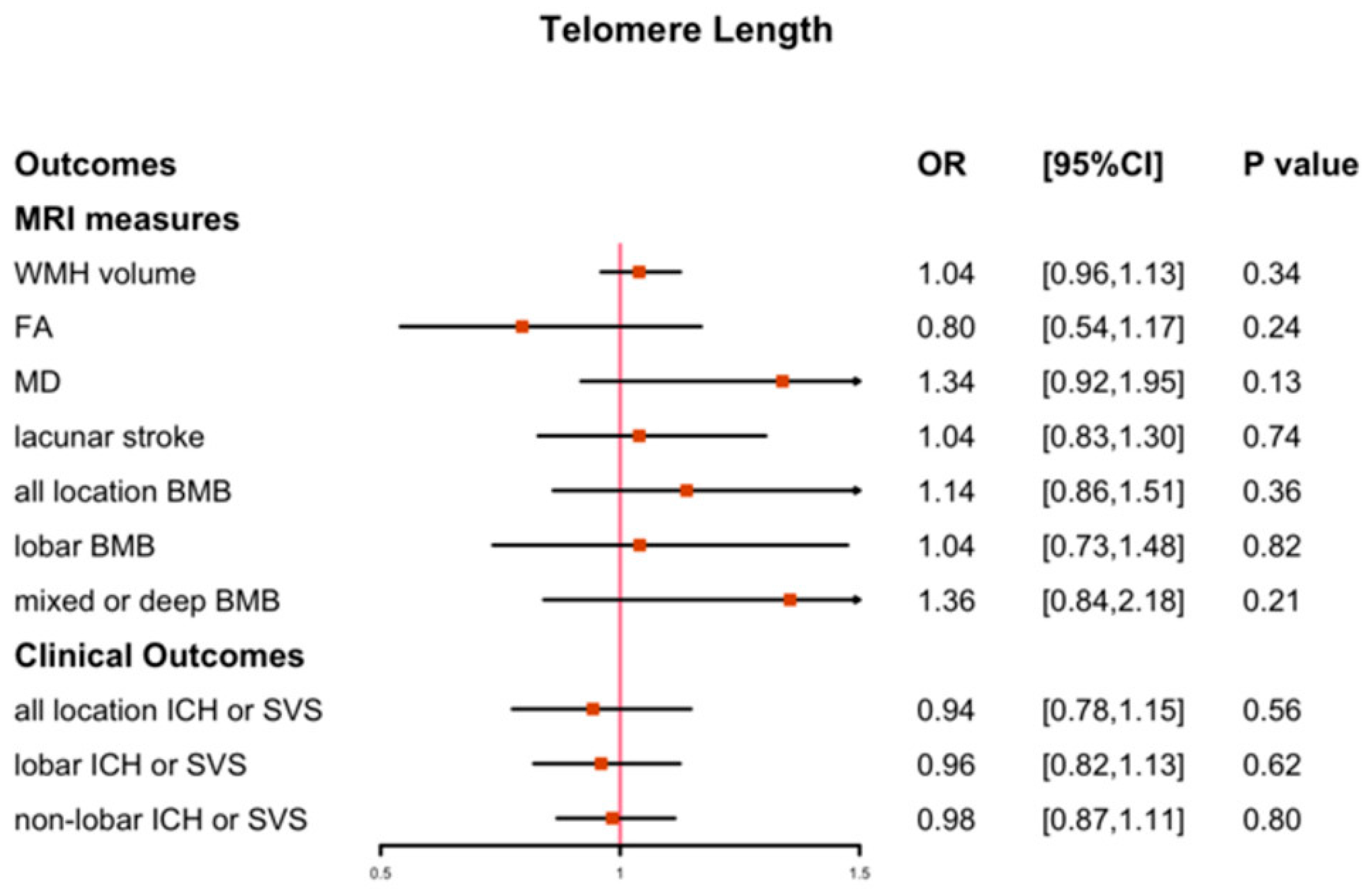
3.1. The Causal Effect of LTL on CSVD
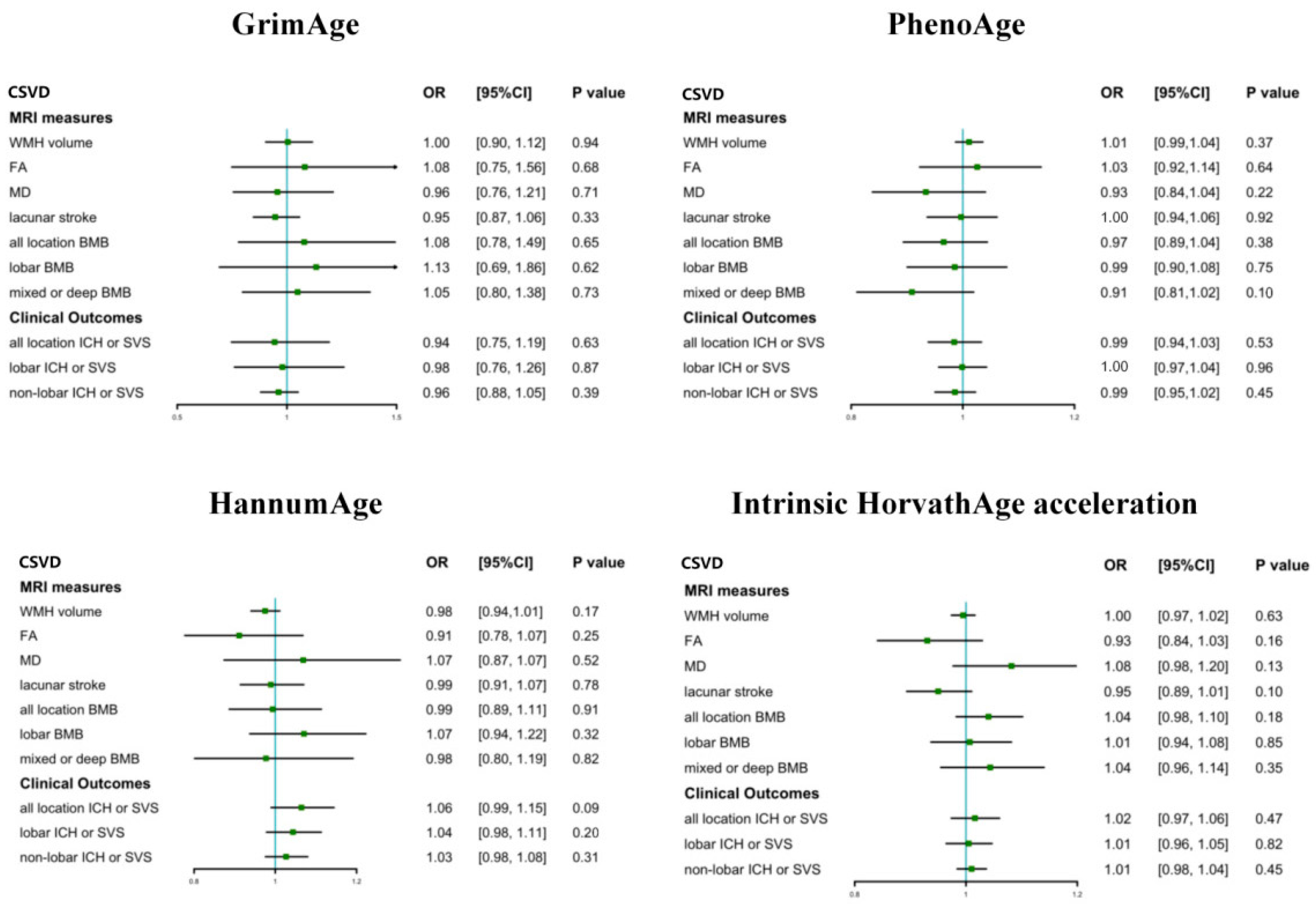
3.2. The Causal Effect of Epigenetic Clocks on CSVD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Seiler, S.; Loitfelder, M. Longitudinal change of small-vessel disease-related brain abnormalities. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.B.; Futcher, A.B.; Greider, C.W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature 1990, 345, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Zglinicki, T.; Martin-Ruiz, C.M. Telomeres as Biomarkers for Ageing and Age-Related Diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 2005, 5, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikgren, M.; Karlsson, T.; Söderlund, H.; Nordin, A.; Roos, G.; Nilsson, L.-G.; Adolfsson, R.; Norrback, K.-F. Shorter telomere length is linked to brain atrophy and white matter hyperintensities. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchy-Dicey, A.M.; Muller, C.J.; Madhyastha, T.M.; Shibata, D.; Cole, S.A.; Zhao, J.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Buchwald, D. Telomere length and magnetic resonance imaging findings of vascular brain injury and central brain atrophy: The strong heart study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, C.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Hui, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W. The association of telomere attrition with first-onset stroke in Southern Chinese: A case-control study and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampawar, P.; Schmidt, R.; Schmidt, H. Leukocyte Telomere Length Is Related to Brain Parenchymal Fraction and Attention/Speed in the Elderly: Results of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampawar, P.; Schmidt, R.; Schmidt, H. Telomere length and brain aging: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 80, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S.; Raj, K. DNA methylation-based biomarkers and the epigenetic clock theory of ageing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Wilson, J.G.; Reiner, A.P.; Aviv, A.; Raj, K.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Li, Y.; Stewart, J.D.; et al. DNA methylation GrimAge strongly predicts lifespan and healthspan. Aging 2019, 11, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.E.; Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Chen, B.H.; Assimes, T.L.; Bandinelli, S.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Li, Y.; et al. An epigenetic biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging 2018, 10, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrory, C.; Fiorito, G.; Hernandez, B.; Polidoro, S.; O’Halloran, A.M.; Hever, A.; Ni Cheallaigh, C.; Lu, A.T.; Horvath, S.; Vineis, P.; et al. GrimAge Outperforms Other Epigenetic Clocks in the Prediction of Age-Related Clinical Phenotypes and All-Cause Mortality. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, R.F.; Stevenson, A.J.; Cox, S.R.; McCartney, D.L.; Harris, S.E.; Seeboth, A.; Higham, J.; Sproul, D.; Taylor, A.M.; Redmond, P.; et al. An epigenetic predictor of death captures multi-modal measures of brain health. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3806–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, A.; Zhao, X.; Grove, M.L.; Bressler, J.; Gottesman, R.F.; Guan, W.; Pankow, J.S.; Boerwinkle, E.; Mosley, T.H.; Fornage, M. Cerebral white matter hyperintensities on MRI and acceleration of epigenetic aging: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Clin. Epigenet. 2017, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, K.; Carless, M.A.; Kulkarni, H.; Curran, J.E.; Sprooten, E.; Knowles, E.E.; Mathias, S.; Göring, H.H.; Yao, N.; Olvera, R.L.; et al. Epigenetic Age Acceleration Assessed with Human White-Matter Images. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4735–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouliaras, L.; Pishva, E.; Haapakoski, R.; Zsoldos, E.; Mahmood, A.; Filippini, N.; Burrage, J.; Mill, J.; Kivimäki, M.; Lunnon, K.; et al. Peripheral DNA methylation, cognitive decline and brain aging: Pilot findings from the Whitehall II imaging study. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Holmes, M.V. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Small, D.S.; Thompson, S.G. A review of instrumental variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2017, 26, 2333–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Brommer, B.; Tian, X.; Krishnan, A.; Meer, M.; Wang, C.; Vera, D.L.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, D.; Bonkowski, M.S.; et al. Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision. Nature 2020, 588, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-H.; Hayano, M.; Griffin, P.T.; Amorim, J.A.; Bonkowski, M.S.; Apostolides, J.K.; Salfati, E.L.; Blanchette, M.; Munding, E.M.; Bhakta, M.; et al. Loss of epigenetic information as a cause of mammalian aging. Cell 2023, 186, 305–326.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Smith, G.D. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, V.; Wang, Q.; Allara, E.; Musicha, C.; Kaptoge, S.; Stoma, S.; Jiang, T.; Hamby, S.E.; Braund, P.S.; Bountziouka, V.; et al. Polygenic basis and biomedical consequences of telomere length variation. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney, D.L.; Min, J.L.; Richmond, R.C.; Lu, A.T.; Sobczyk, M.K.; Davies, G.; Broer, L.; Guo, X.; Jeong, A.; Jung, J.; et al. Genome-wide association studies identify 137 genetic loci for DNA methylation biomarkers of aging. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persyn, E.; Hanscombe, K.B.; Howson, J.M.M.; Lewis, C.M.; Traylor, M.; Markus, H.S. Genome-wide association study of MRI markers of cerebral small vessel disease in 42,310 participants. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traylor, M.; Persyn, E.; Tomppo, L.; Klasson, S.; Abedi, V.; Bakker, M.K.; Torres, N.; Li, L.; Bell, S.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; et al. Genetic basis of lacunar stroke: A pooled analysis of individual patient data and genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knol, M.J.; Lu, D.; Traylor, M.; Adams, H.H.H.; Romero, J.R.J.; Smith, A.V.; Fornage, M.; Hofer, E.; Liu, J.; Hostettler, I.C.; et al. Association of common genetic variants with brain microbleeds: A genome-wide association study. Neurology 2020, 95, e3331–e3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Marini, S.; Pera, J.; Norrving, B.; Jimenez-Conde, J.; Roquer, J.; Fernandez-Cadenas, I.; Tirschwell, D.L.; Selim, M.; Brown, D.; et al. Genome-wide association study of cerebral small vessel disease reveals established and novel loci. Brain 2019, 142, 3176–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian Randomization Analysis with Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G.; CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorska, O.O.; Burgess, S. Mendelian Randomization: An R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, G.; McCrory, C.; Robinson, O.; Carmeli, C.; Ochoa-Rosales, C.; Zhang, Y.; Colicino, E.; Dugué, P.-A.; Artaud, F.; McKay, G.J.; et al. Socioeconomic position, lifestyle habits and biomarkers of epigenetic aging: A multi-cohort analysis. Aging 2019, 11, 2045–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, G.; Polidoro, S.; Dugue, P.-A.; Kivimaki, M.; Ponzi, E.; Matullo, G.; Guarrera, S.; Assumma, M.B.; Georgiadis, P.; Kyrtopoulos, S.A.; et al. Social adversity and epigenetic aging: A multi-cohort study on socioeconomic differences in peripheral blood DNA methylation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, G.; Pedron, S.; Ochoa-Rosales, C.; McCrory, C.; Polidoro, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dugué, P.-A.; Ratliff, S.; Zhao, W.N.; McKay, G.J.; et al. The Role of Epigenetic Clocks in Explaining Educational Inequalities in Mortality: A Multicohort Study and Meta-analysis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, B.; Mu, Y.; Ding, Z. Assessing the Causal Association between Biological Aging Biomarkers and the Development of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Biology 2023, 12, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050660
Lin B, Mu Y, Ding Z. Assessing the Causal Association between Biological Aging Biomarkers and the Development of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Biology. 2023; 12(5):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Biying, Yuzhu Mu, and Zhongxiang Ding. 2023. "Assessing the Causal Association between Biological Aging Biomarkers and the Development of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study" Biology 12, no. 5: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050660
APA StyleLin, B., Mu, Y., & Ding, Z. (2023). Assessing the Causal Association between Biological Aging Biomarkers and the Development of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Biology, 12(5), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050660



