CDC6 as a Key Inhibitory Regulator of CDK1 Activation Dynamics and the Timing of Mitotic Entry and Progression
Abstract
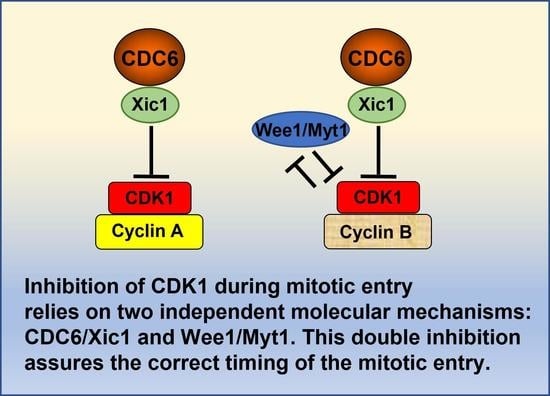
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Activation of CDK1 by Association with Cyclins A and B and Its Concomitant Inhibition by Wee1/Myt1 Kinases Post-Translational Modifications
3. Role of PLK1 in CDK1 Activation upon Mitotic Entry
4. Role of Aurora A/Bora Complex in CDK1 Activation through PLK1
5. Role of Nuclear Transport in CDK1 Activation and Function
6. CDC6 as an Upstream Regulator of CDK1 through Its Inhibition
7. Regulation of CDC6 by PP2A
8. Role of PP2A-Greatwall/Mastl Pathway in Potential CDC6 Regulation
9. A Model of CDC6 Involvement in CDK1 Activation
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, A.W.; Kirschner, M.W. Cyclin Synthesis Drives the Early Embryonic Cell Cycle. Nature 1989, 339, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.W.; Solomon, M.J.; Kirschner, M.W. The Role of Cyclin Synthesis and Degradation in the Control of Maturation Promoting Factor Activity. Nature 1989, 339, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotzer, M.; Murray, A.W.; Kirschner, M.W. Cyclin Is Degraded by the Ubiquitin Pathway. Nature 1991, 349, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochegger, H.; Klotzbücher, A.; Kirk, J.; Howell, M.; le Guellec, K.; Fletcher, K.; Duncan, T.; Sohail, M.; Hunt, T. New B-Type Cyclin Synthesis Is Required between Meiosis I and II during Xenopus Oocyte Maturation. Development 2001, 128, 3795–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Ferrell, J.E. The Roles of Cyclin A2, B1, and B2 in Early and Late Mitotic Events. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 3149–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pomerening, J.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Ferrell, J.E. Systems-Level Dissection of the Cell-Cycle Oscillator: Bypassing Positive Feedback Produces Damped Oscillations. Cell 2005, 122, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marteil, G.; Gagné, J.P.; Borsuk, E.; Richard-Parpaillon, L.; Poirier, G.G.; Kubiak, J.Z. Proteomics Reveals a Switch in CDK1-Associated Proteins upon M-Phase Exit during the Xenopus Laevis Oocyte to Embryo Transition. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK Inhibitors: Positive and Negative Regulators of G1-Phase Progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Dika, M.; Wechselberger, L.; Djeghout, B.; Benouareth, D.E.; Jęderka, K.; Lewicki, S.; Zdanowski, R.; Prigent, C.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. Mitotic Timing Is Differentially Controlled by A-and B-Type Cyclins and by CDC6 Associated with a Bona Fide CDK Inhibitor Xic1 in Xenopus Laevis Cell-Free Extract. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2021, 65, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Dika, M. Régulation de La Phase M Du Cycle Cellulaire Par CDK1, PP2A et CDC6. 1. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rennes 1, Rennes, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- El Dika, M.; Laskowska-Kaszub, K.; Koryto, M.; Dudka, D.; Prigent, C.; Tassan, J.P.; Kloc, M.; Polanski, Z.; Borsuk, E.; Kubiak, J.Z. CDC6 Controls Dynamics of the First Embryonic M-Phase Entry and Progression via CDK1 Inhibition. Dev. Biol. 2014, 396, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debowski, M.; El Dika, M.; Malejczyk, J.; Zdanowski, R.; Prigent, C.; Tassan, J.P.; Kloc, M.; Lachowicz, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. Flexibility vs. Robustness in Cell Cycle Regulation of Timing of M-Phase Entry in Xenopus Laevis Embryo Cell-Free Extract. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 60, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dębowski, M.; Szymańska, Z.; Kubiak, J.Z.; Lachowicz, M. Mathematical Model Explaining the Role of CDC6 in the Diauxic Growth of CDK1 Activity during the M-Phase of the Cell Cycle. Cells 2019, 8, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borsuk, E.; Jachowicz, J.; Kloc, M.; Tassan, J.P.; Kubiak, J.Z. Role of Cdc6 during Oogenesis and Early Embryo Development in Mouse and Xenopus Laevis. In Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 59, pp. 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Delmolino, L.M.; Saha, P.; Dutta, A. Multiple Mechanisms Regulate Subcellular Localization of Human CDC6. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26947–26954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrilla, A.; Barber, M.; Majem, B.; Castellví, J.; Morote, J.; Sánchez, J.L.; Pérez-Benavente, A.; Segura, M.F.; Gil-Moreno, A.; Santamaria, A. Aurora Borealis (Bora), Which Promotes Plk1 Activation by Aurora A, Has an Oncogenic Role in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrilla, A.; Cirillo, L.; Thomas, Y.; Gotta, M.; Pintard, L.; Santamaria, A. Mitotic Entry: The Interplay between Cdk1, Plk1 and Bora. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, Y.; Cirillo, L.; Panbianco, C.; Martino, L.; Tavernier, N.; Schwager, F.; Van Hove, L.; Joly, N.; Santamaria, A.; Pintard, L. Cdk1 Phosphorylates SPAT-1/Bora to Promote Plk1 Activation in C. Elegans and Human Cells. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavernier, N.; Thomas, Y.; Vigneron, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Orlicky, S.; Mader, P.; Regmi, S.; Van Hove, L.; Levinson, N.; Gasmi-Seabrook, G. Bora Phosphorylation Substitutes in Trans for T-Loop Phosphorylation in Aurora A to Promote Mitotic Entry. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, S.; Sundermann, L.; Labbé, J.-C.; Pintard, L.; Radulescu, O.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. Cyclin A-Cdk1-Dependent Phosphorylation of Bora Is the Triggering Factor Promoting Mitotic Entry. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, W.; Aprelia, M.; García-Santisteban, I.; Kool, J.; Xu, Y.; Medema, R. Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 during the DNA Damage Response Is Mediated through Loss of Aurora A Recruitment by Bora. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joukov, V.; De Nicolo, A. Aurora-PLK1 Cascades as Key Signaling Modules in the Regulation of Mitosis. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaar4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larouche, M.; Kachaner, D.; Wang, P.; Normandin, K.; Garrido, D.; Yao, C.; Cormier, M.; Johansen, K.M.; Johansen, J.; Archambault, V. Spatiotemporal Coordination of Greatwall-Endos-PP2A Promotes Mitotic Progression. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202008145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillan, A.; Tavernier, N.; Pintard, L. [The kiss of life: Aurora A embraces the phosphate of its cofactor Bora to trigger mitotic entry]. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavernier, N.; Sicheri, F.; Pintard, L. Aurora A Kinase Activation: Different Means to Different Ends. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeper, D.S.; Parker, L.L.; Ewen, M.; Toebes, M.; Hall, F.; Xu, M.; Zantema, A.; Van der Eb, A.; Piwnica-Worms, H. A-and B-type Cyclins Differentially Modulate Substrate Specificity of Cyclin-cdk Complexes. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, J. Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases: A Biochemical View. Biochem. J. 1995, 308, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, J.; Hunter, T. Human Cyclins A and B1 Are Differentially Located in the Cell and Undergo Cell Cycle-Dependent Nuclear Transport. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 115, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton-Fessler, S.; Parker, L.L.; Geahlen, R.L.; Piwnica-Worms, H. Mechanisms of P34cdc2 Regulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booher, R.N.; Holman, P.S.; Fattaey, A. Human Myt1 Is a Cell Cycle-Regulated Kinase That Inhibits Cdc2 but Not Cdk2 Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 22300–22306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fesquet, D.; Labbé, J.C.; Derancourt, J.; Capony, J.P.; Galas, S.; Girard, F.; Lorca, T.; Shuttleworth, J.; Dorée, M.; Cavadore, J.C. The MO15 Gene Encodes the Catalytic Subunit of a Protein Kinase That Activates Cdc2 and Other Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs) through Phosphorylation of Thr161 and Its Homologues. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, R.Y.; Yamashita, K.; Adamczewski, J.P.; Hunt, T.; Shuttleworth, J. The Cdc2-Related Protein P40MO15 Is the Catalytic Subunit of a Protein Kinase That Can Activate P33cdk2 and P34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.J.; Harper, J.W.; Shuttleworth, J. CAK, the P34cdc2 Activating Kinase, Contains a Protein Identical or Closely Related to P40MO15. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.P.; Morgan, D.O. A Novel Cyclin Associates with MO15/CDK7 to Form the CDK-Activating Kinase. Cell 1994, 78, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhu, K.; Reed, S.I.; Richardson, H.; Russell, P. Human Homolog of Fission Yeast Cdc25 Mitotic Inducer Is Predominantly Expressed in G2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5139–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galaktionov, K.; Beach, D. Specific Activation of Cdc25 Tyrosine Phosphatases by B-Type Cyclins: Evidence for Multiple Roles of Mitotic Cyclins. Cell 1991, 67, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, A.; Igarashi, M.; Jinno, S.; Suto, K.; Okayama, H. An Additional Homolog of the Fission Yeast Cdc25+ Gene Occurs in Humans and Is Highly Expressed in Some Cancer Cells. New Biol. 1991, 3, 959–968. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli, B.G.; De Souza, C.P.; Tonks, I.D.; Clark, J.M.; Hayward, N.K.; Ellem, K.A. Cytoplasmic Accumulation of Cdc25B Phosphatase in Mitosis Triggers Centrosomal Microtubule Nucleation in HeLa Cells. J. Cell Sci 1996, 109 Pt 5, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammer, C.; Wagerer, S.; Saffrich, R.; Mertens, D.; Ansorge, W.; Hoffmann, I. The Cdc25B Phosphatase Is Essential for the G2/M Phase Transition in Human Cells. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111 Pt 16, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, I.; Clarke, P.R.; Marcote, M.J.; Karsenti, E.; Draetta, G. Phosphorylation and Activation of Human Cdc25-C by Cdc2--Cyclin B and Its Involvement in the Self-Amplification of MPF at Mitosis. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Arai, H.; Nishihara, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Watanabe, N.; Hunter, T.; Osada, H. M-Phase Kinases Induce Phospho-Dependent Ubiquitination of Somatic Wee1 by SCFbeta-TrCP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4419–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Kozono, D.; Deraska, P.; Branigan, T.; Dunn, C.; Zheng, X.-F.; Parmar, K.; Nguyen, H.; DeCaprio, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; et al. CHK1 Inhibitor Blocks Phosphorylation of FAM122A and Promotes Replication Stress. Mol. Cell. 2020, 80, 410–422.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meyer, A.N.; Donoghue, D.J. Nuclear Localization of Cyclin B1 Mediates Its Biological Activity and Is Regulated by Phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gheghiani, L.; Loew, D.; Lombard, B.; Mansfeld, J.; Gavet, O. PLK1 Activation in Late G2 Sets Up Commitment to Mitosis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumagai, A.; Dunphy, W.G. Purification and Molecular Cloning of Plx1, a Cdc25-Regulatory Kinase from Xenopus Egg Extracts. Science 1996, 273, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrieu, A.; Brassac, T.; Galas, S.; Fisher, D.; Labbé, J.C.; Dorée, M. The Polo-like Kinase Plx1 Is a Component of the MPF Amplification Loop at the G2/M-Phase Transition of the Cell Cycle in Xenopus Eggs. J. Cell Sci 1998, 111 Pt 12, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.W.; Erikson, E.; Li, C.; Maller, J.L. Activated Polo-like Kinase Plx1 Is Required at Multiple Points during Mitosis in Xenopus Laevis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 4262–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elia, A.E.H.; Cantley, L.C.; Yaffe, M.B. Proteomic Screen Finds PSer/PThr-Binding Domain Localizing Plk1 to Mitotic Substrates. Science 2003, 299, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima-Morimoto, F.; Taniguchi, E.; Nishida, E. Plk1 Promotes Nuclear Translocation of Human Cdc25C during Prophase. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailly, E.; Bornens, M. Cell Biology. Centrosome and Cell Division. Nature 1992, 355, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, E.; Dorée, M.; Nurse, P.; Bornens, M. P34cdc2 Is Located in Both Nucleus and Cytoplasm; Part Is Centrosomally Associated at G2/M and Enters Vesicles at Anaphase. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3985–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, M.; Lindon, C.; Nigg, E.A.; Pines, J. Active Cyclin B1-Cdk1 First Appears on Centrosomes in Prophase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, L.M.; Tsekova, R.T.; Xu, X.; Stern, D.F. The Plk1 Polo Box Domain Mediates a Cell Cycle and DNA Damage Regulated Interaction with Chk2. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krämer, A.; Mailand, N.; Lukas, C.; Syljuåsen, R.G.; Wilkinson, C.J.; Nigg, E.A.; Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. Centrosome-Associated Chk1 Prevents Premature Activation of Cyclin-B-Cdk1 Kinase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golsteyn, R.M.; Mundt, K.E.; Fry, A.M.; Nigg, E.A. Cell Cycle Regulation of the Activity and Subcellular Localization of Plk1, a Human Protein Kinase Implicated in Mitotic Spindle Function. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 129, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.A.; Nigg, E.A. Antibody Microinjection Reveals an Essential Role for Human Polo-like Kinase 1 (Plk1) in the Functional Maturation of Mitotic Centrosomes. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.W.; Erikson, E.; Taieb, F.E.; Maller, J.L. The Polo-like Kinase Plx1 Is Required for Activation of the Phosphatase Cdc25C and Cyclin B-Cdc2 in Xenopus Oocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Vugt, M.A.T.M.; Brás, A.; Medema, R.H. Polo-like Kinase-1 Controls Recovery from a G2 DNA Damage-Induced Arrest in Mammalian Cells. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, N.; Noatynska, A.; Panbianco, C.; Martino, L.; Van Hove, L.; Schwager, F.; Léger, T.; Gotta, M.; Pintard, L. Cdk1 Phosphorylates SPAT-1/Bora to Trigger PLK-1 Activation and Drive Mitotic Entry in C. Elegans Embryos. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavernier, N.; Panbianco, C.; Gotta, M.; Pintard, L. Cdk1 Plays Matchmaker for the Polo-like Kinase and Its Activator SPAT-1/Bora. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2394–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, G.; Yu, H. Cyclin A Turns on Bora to Light the Path to Mitosis. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giet, R.; Uzbekov, R.; Cubizolles, F.; Le Guellec, K.; Prigent, C. The Xenopus Laevis Aurora-Related Protein Kinase PEg2 Associates with and Phosphorylates the Kinesin-Related Protein XlEg5. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15005–15013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berdnik, D.; Knoblich, J.A. Drosophila Aurora-A Is Required for Centrosome Maturation and Actin-Dependent Asymmetric Protein Localization during Mitosis. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutertre, S.; Cazales, M.; Quaranta, M.; Froment, C.; Trabut, V.; Dozier, C.; Mirey, G.; Bouché, J.-P.; Theis-Febvre, N.; Schmitt, E.; et al. Phosphorylation of CDC25B by Aurora-A at the Centrosome Contributes to the G2-M Transition. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macůrek, L.; Lindqvist, A.; Lim, D.; Lampson, M.A.; Klompmaker, R.; Freire, R.; Clouin, C.; Taylor, S.S.; Yaffe, M.B.; Medema, R.H. Polo-like Kinase-1 Is Activated by Aurora A to Promote Checkpoint Recovery. Nature 2008, 455, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, A.; Coppinger, J.A.; Jang, C.-Y.; Yates, J.R.; Fang, G. Bora and the Kinase Aurora a Cooperatively Activate the Kinase Plk1 and Control Mitotic Entry. Science 2008, 320, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, E.H.Y.; Santamaria, A.; Silljé, H.H.W.; Nigg, E.A. Plk1 Regulates Mitotic Aurora A Function through BetaTrCP-Dependent Degradation of HBora. Chromosoma 2008, 117, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meyer, A.N.; Donoghue, D.J. Requirement for Phosphorylation of Cyclin B1 for Xenopus Oocyte Maturation. Mol. Biol. Cell 1995, 6, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumi, T.; Maller, J.L. Phosphorylation of Xenopus Cyclins B1 and B2 Is Not Required for Cell Cycle Transitions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, J.; Hunter, T. The Differential Localization of Human Cyclins A and B Is Due to a Cytoplasmic Retention Signal in Cyclin B. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 3772–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Hardy, S.; Morgan, D.O. Nuclear Localization of Cyclin B1 Controls Mitotic Entry after DNA Damage. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toyoshima, F.; Moriguchi, T.; Wada, A.; Fukuda, M.; Nishida, E. Nuclear Export of Cyclin B1 and Its Possible Role in the DNA Damage-Induced G2 Checkpoint. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2728–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Song, H.; Walsh, S.; Bardes, E.S.; Kornbluth, S. Combinatorial Control of Cyclin B1 Nuclear Trafficking through Phosphorylation at Multiple Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3604–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyoshima-Morimoto, F.; Taniguchi, E.; Shinya, N.; Iwamatsu, A.; Nishida, E. Polo-like Kinase 1 Phosphorylates Cyclin B1 and Targets It to the Nucleus during Prophase. Nature 2001, 410, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Eckerdt, F.; Bereiter-Hahn, J.; Kurunci-Csacsko, E.; Kaufmann, M.; Strebhardt, K. Cooperative Phosphorylation Including the Activity of Polo-like Kinase 1 Regulates the Subcellular Localization of Cyclin B1. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8282–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, M.; Barnes, E.A.; Ollendorff, V.; Donoghue, D.J. Cyclin F Regulates the Nuclear Localization of Cyclin B1 through a Cyclin-Cyclin Interaction. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagting, A.; Jackman, M.; Simpson, K.; Pines, J. Translocation of Cyclin B1 to the Nucleus at Prophase Requires a Phosphorylation-Dependent Nuclear Import Signal. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.D.; Yang, J.; Truant, R.; Kornbluth, S. Nuclear Import of Cdk/Cyclin Complexes: Identification of Distinct Mechanisms for Import of Cdk2/Cyclin E and Cdc2/Cyclin B1. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchkovich, K.; Duffy, L.A.; Harlow, E. The Retinoblastoma Protein Is Phosphorylated during Specific Phases of the Cell Cycle. Cell 1989, 58, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, J.; Matsushime, H.; Hiebert, S.W.; Ewen, M.E.; Sherr, C.J. Direct Binding of Cyclin D to the Retinoblastoma Gene Product (PRb) and PRb Phosphorylation by the Cyclin D-Dependent Kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brehm, A.; Miska, E.A.; McCance, D.J.; Reid, J.L.; Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T. Retinoblastoma Protein Recruits Histone Deacetylase to Repress Transcription. Nature 1998, 391, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, R.; McKeon, F. Mutations of Phosphorylation Sites in Lamin A That Prevent Nuclear Lamina Disassembly in Mitosis. Cell 1990, 61, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courvalin, J.; Segil, N.; Blobel, G.; Worman, H. The Lamin B Receptor of the Inner Nuclear Membrane Undergoes Mitosis-Specific Phosphorylation and Is a Substrate for P34cdc2-Type Protein Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 19035–19038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blangy, A.; Lane, H.A.; d’Hérin, P.; Harper, M.; Kress, M.; Nigg, E.A. Phosphorylation by P34cdc2 Regulates Spindle Association of Human Eg5, a Kinesin-Related Motor Essential for Bipolar Spindle Formation in Vivo. Cell 1995, 83, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, M.C.; Tutter, A.V.; Cvetic, C.; Gilbert, C.H.; Prokhorova, T.A.; Walter, J.C. MCM2-7 Complexes Bind Chromatin in a Distributed Pattern Surrounding the Origin Recognition Complex in Xenopus Egg Extracts. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33049–33057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randell, J.C.W.; Bowers, J.L.; Rodríguez, H.K.; Bell, S.P. Sequential ATP Hydrolysis by Cdc6 and ORC Directs Loading of the Mcm2-7 Helicase. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Stillman, B. ATPase-Dependent Cooperative Binding of ORC and Cdc6 to Origin DNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weinreich, M.; Liang, C.; Stillman, B. The Cdc6p Nucleotide-Binding Motif Is Required for Loading Mcm Proteins onto Chromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, B.O.; Lukas, J.; Sørensen, C.S.; Bartek, J.; Helin, K. Phosphorylation of Mammalian CDC6 by Cyclin A/CDK2 Regulates Its Subcellular Localization. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsasser, S.; Lou, F.; Wang, B.; Campbell, J.L.; Jong, A. Interaction between Yeast Cdc6 Protein and B-Type Cyclin/Cdc28 Kinases. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calzada, A.; Sacristán, M.; Sánchez, E.; Bueno, A. Cdc6 Cooperates with Sic1 and Hct1 to Inactivate Mitotic Cyclin-Dependent Kinases. Nature 2001, 412, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Örd, M.; Venta, R.; Möll, K.; Valk, E.; Loog, M. Cyclin-Specific Docking Mechanisms Reveal the Complexity of M-CDK Function in the Cell Cycle. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 76–89.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venta, R.; Valk, E.; Örd, M.; Košik, O.; Pääbo, K.; Maljavin, A.; Kivi, R.; Faustova, I.; Shtaida, N.; Lepiku, M.; et al. A Processive Phosphorylation Circuit with Multiple Kinase Inputs and Mutually Diversional Routes Controls G1/S Decision. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yim, H.; Erikson, R.L. Cell Division Cycle 6, a Mitotic Substrate of Polo-like Kinase 1, Regulates Chromosomal Segregation Mediated by Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 and Separase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19742–19747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duderstadt, K.E.; Berger, J.M. AAA+ ATPases in the Initiation of DNA Replication. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 43, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, V.; Li, C.X.; Tackett, A.J.; Wasch, R.; Chait, B.T.; Rout, M.P.; Cross, F.R. Genetic and Biochemical Evaluation of the Importance of Cdc6 in Regulating Mitotic Exit. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4592–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monod, J. The Growth of Bacterial Cultures. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1949, 3, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Z.; Meng, T.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Schatten, H.; Qiao, J.; Sun, Q.; Qian, W. CDC6 Regulates Both G2/M Transition and Metaphase-to-anaphase Transition during the First Meiosis of Mouse Oocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virshup, D.M.; Shenolikar, S. From Promiscuity to Precision: Protein Phosphatases Get a Makeover. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, V.; Longin, S.; Goris, J. PP2A Holoenzyme Assembly: In Cauda Venenum (the Sting Is in the Tail). Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, S.; Ikeo, S.; Gannon, J.; Hunt, T. Regulated Activity of PP2A-B55 Delta Is Crucial for Controlling Entry into and Exit from Mitosis in Xenopus Egg Extracts. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castilho, P.V.; Williams, B.C.; Mochida, S.; Zhao, Y.; Goldberg, M.L. The M Phase Kinase Greatwall (Gwl) Promotes Inactivation of PP2A/B55delta, a Phosphatase Directed against CDK Phosphosites. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 4777–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrigno, P.; Langan, T.A.; Cohen, P. Protein Phosphatase 2A1 Is the Major Enzyme in Vertebrate Cell Extracts That Dephosphorylates Several Physiological Substrates for Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinases. Mol. Biol. Cell 1993, 4, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer-Jaekel, R.E.; Ohkura, H.; Gomes, R.; Sunkel, C.E.; Baumgartner, S.; Hemmings, B.A.; Glover, D.M. The 55 Kd Regulatory Subunit of Drosophila Protein Phosphatase 2A Is Required for Anaphase. Cell 1993, 72, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer-Jaekel, R.E.; Ohkura, H.; Ferrigno, P.; Andjelkovic, N.; Shiomi, K.; Uemura, T.; Glover, D.M.; Hemmings, B.A. Drosophila Mutants in the 55 KDa Regulatory Subunit of Protein Phosphatase 2A Show Strongly Reduced Ability to Dephosphorylate Substrates of P34cdc2. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107 Pt 9, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goris, J.; Hermann, J.; Hendrix, P.; Ozon, R.; Merlevede, W. Okadaic Acid, a Specific Protein Phosphatase Inhibitor, Induces Maturation and MPF Formation in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes. Febs Lett. 1989, 245, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karaïskou, A.; Cayla, X.; Haccard, O.; Jessus, C.; Ozon, R. MPF Amplification in Xenopus Oocyte Extracts Depends on a Two-Step Activation of Cdc25 Phosphatase. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 244, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rime, H.; Jessus, C.; Ozon, R. Estramustine Phosphate Inhibits Germinal Vesicle Breakdown and Induces Depolymerization of Microtubules in Mouse Oocyte. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. (1980) 1988, 28, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, A.; Labbé, J.C.; Barakat, H.; Cavadore, J.C.; Dorée, M. Okadaic Acid Mimics a Nuclear Component Required for Cyclin B-Cdc2 Kinase Microinjection to Drive Starfish Oocytes into M Phase. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 115, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.R.; Hoffmann, I.; Draetta, G.; Karsenti, E. Dephosphorylation of Cdc25-C by a Type-2A Protein Phosphatase: Specific Regulation during the Cell Cycle in Xenopus Egg Extracts. Mol. Biol. Cell 1993, 4, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maton, G.; Lorca, T.; Girault, J.-A.; Ozon, R.; Jessus, C. Differential Regulation of Cdc2 and Aurora-A in Xenopus Oocytes: A Crucial Role of Phosphatase 2A. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Félix, M.A.; Cohen, P.; Karsenti, E. Cdc2 H1 Kinase Is Negatively Regulated by a Type 2A Phosphatase in the Xenopus Early Embryonic Cell Cycle: Evidence from the Effects of Okadaic Acid. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, A.M.; Zolnierowicz, S.; Stapleton, A.E.; Goebl, M.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Pringle, J.R. CDC55, a Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Gene Involved in Cellular Morphogenesis: Identification, Characterization, and Homology to the B Subunit of Mammalian Type 2A Protein Phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5767–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zyl, W.; Huang, W.; Sneddon, A.A.; Stark, M.; Camier, S.; Werner, M.; Marck, C.; Sentenac, A.; Broach, J.R. Inactivation of the Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory Subunit A Results in Morphological and Transcriptional Defects in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Yang, H.; Hallberg, E.; Hallberg, R. Molecular Genetic Analysis of Rts1p, a B’ Regulatory Subunit of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Protein Phosphatase 2A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 3242–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossio, V.; Yoshida, S. Spatial Regulation of Cdc55-PP2A by Zds1/Zds2 Controls Mitotic Entry and Mitotic Exit in Budding Yeast. J. Cell Biol 2011, 193, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, F.; Arndt, K.T. The Role of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Type 2A Phosphatase in the Actin Cytoskeleton and in Entry into Mitosis. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 2745–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, W.; Gentry, M.; Hallberg, R.L. Loss of a Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory Subunit (Cdc55p) Elicits Improper Regulation of Swe1p Degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8143–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossio, V.; Michimoto, T.; Sasaki, T.; Ohbayashi, I.; Kikuchi, Y.; Yoshida, S. Nuclear PP2A-Cdc55 Prevents APC-Cdc20 Activation during the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minshull, J.; Straight, A.; Rudner, A.D.; Dernburg, A.F.; Belmont, A.; Murray, A.W. Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulates MPF Activity and Sister Chromatid Cohesion in Budding Yeast. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Burke, D.J. Cdc55p, the B-Type Regulatory Subunit of Protein Phosphatase 2A, Has Multiple Functions in Mitosis and Is Required for the Kinetochore/Spindle Checkpoint in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lianga, N.; Williams, E.C.; Kennedy, E.K.; Doré, C.; Pilon, S.; Girard, S.L.; Deneault, J.-S.; Rudner, A.D. A Wee1 Checkpoint Inhibits Anaphase Onset. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Queralt, E.; Lehane, C.; Novak, B.; Uhlmann, F. Downregulation of PP2A(Cdc55) Phosphatase by Separase Initiates Mitotic Exit in Budding Yeast. Cell 2006, 125, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visintin, R.; Hwang, E.S.; Amon, A. Cfi1 Prevents Premature Exit from Mitosis by Anchoring Cdc14 Phosphatase in the Nucleolus. Nature 1999, 398, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, R.; Chen, S.L.; Shou, W.; Mah, A.S.; Alexandru, G.; Nasmyth, K.; Annan, R.S.; Carr, S.A.; Deshaies, R.J. Phosphorylation by Cyclin B-Cdk Underlies Release of Mitotic Exit Activator Cdc14 from the Nucleolus. Science 2004, 305, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shou, W.; Seol, J.H.; Shevchenko, A.; Baskerville, C.; Moazed, D.; Chen, Z.W.; Jang, J.; Shevchenko, A.; Charbonneau, H.; Deshaies, R.J. Exit from Mitosis Is Triggered by Tem1-Dependent Release of the Protein Phosphatase Cdc14 from Nucleolar RENT Complex. Cell 1999, 97, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomson, B.N.; Rahal, R.; Reiser, V.; Monje-Casas, F.; Mekhail, K.; Moazed, D.; Amon, A. Regulation of Spo12 Phosphorylation and Its Essential Role in the FEAR Network. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, Y.; Yung, P.Y.K.; Huo, L.; Liang, C. Cdc14p Resets the Competency of Replication Licensing by Dephosphorylating Multiple Initiation Proteins during Mitotic Exit in Budding Yeast. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philip, J.; Örd, M.; Silva, A.; Singh, S.; Diffley, J.F.; Remus, D.; Loog, M.; Ikui, A.E. Cdc6 Is Sequentially Regulated by PP2A-Cdc55, Cdc14, and Sic1 for Origin Licensing in S. Cerevisiae. Elife 2022, 11, e74437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi-Ayachi, A.; Labbe, J.-C.; Burgess, A.; Vigneron, S.; Strub, J.-M.; Brioudes, E.; Van-Dorsselaer, A.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. The Substrate of Greatwall Kinase, Arpp19, Controls Mitosis by Inhibiting Protein Phosphatase 2A. Science 2010, 330, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Vigneron, S.; Brioudes, E.; Labbé, J.-C.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. Loss of Human Greatwall Results in G2 Arrest and Multiple Mitotic Defects Due to Deregulation of the Cyclin B-Cdc2/PP2A Balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12564–12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneron, S.; Brioudes, E.; Burgess, A.; Labbé, J.-C.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. Greatwall Maintains Mitosis through Regulation of PP2A. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneron, S.; Robert, P.; Hached, K.; Sundermann, L.; Charrasse, S.; Labbé, J.-C.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. The Master Greatwall Kinase, a Critical Regulator of Mitosis and Meiosis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 60, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupré, A.-I.; Haccard, O.; Jessus, C. The Greatwall Kinase Is Dominant over PKA in Controlling the Antagonistic Function of ARPP19 in Xenopus Oocytes. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Vigneron, S.; Robert, P.; Strub, J.M.; Cianferani, S.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. Greatwall Dephosphorylation and Inactivation upon Mitotic Exit Is Triggered by PP1. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hached, K.; Goguet, P.; Charrasse, S.; Vigneron, S.; Sacristan, M.P.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. ENSA and ARPP19 Differentially Control Cell Cycle Progression and Development. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Galas, S.; Goldberg, M.L. Greatwall Kinase Participates in the Cdc2 Autoregulatory Loop in Xenopus Egg Extracts. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Dika, M.; Dudka, D.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. CDC6 as a Key Inhibitory Regulator of CDK1 Activation Dynamics and the Timing of Mitotic Entry and Progression. Biology 2023, 12, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060855
El Dika M, Dudka D, Kloc M, Kubiak JZ. CDC6 as a Key Inhibitory Regulator of CDK1 Activation Dynamics and the Timing of Mitotic Entry and Progression. Biology. 2023; 12(6):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060855
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Dika, Mohammed, Damian Dudka, Malgorzata Kloc, and Jacek Z. Kubiak. 2023. "CDC6 as a Key Inhibitory Regulator of CDK1 Activation Dynamics and the Timing of Mitotic Entry and Progression" Biology 12, no. 6: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060855
APA StyleEl Dika, M., Dudka, D., Kloc, M., & Kubiak, J. Z. (2023). CDC6 as a Key Inhibitory Regulator of CDK1 Activation Dynamics and the Timing of Mitotic Entry and Progression. Biology, 12(6), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060855