Sex Variations in Retinal Microcirculation Response to Lower Body Negative Pressure
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
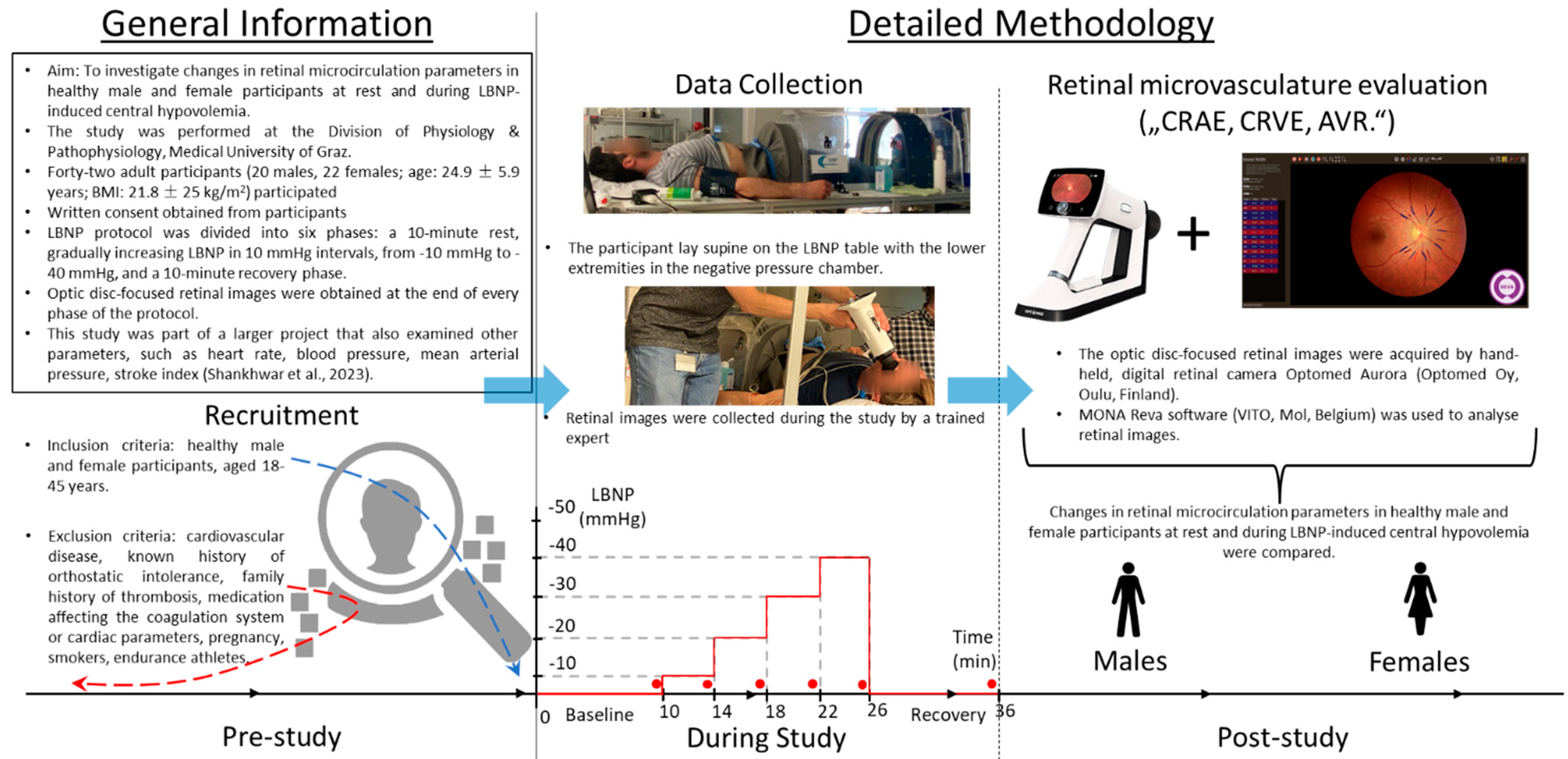
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Size Calculation
2.2. Participants
2.3. LBNP Protocol
2.4. Microcirculation Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Retinal Microcirculation Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. Retinal Microcirculation Measurements
4.2. Differences in Males vs. Females
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hargens, A.R.; Whalen, R.T.; Watenpaugh, D.E.; Schwandt, D.F.; Krock, L.P. Lower body negative pressure to provide load bearing in space. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1991, 62, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.P.; Thornton, W.E. Space shuttle inflight and postflight fluid shifts measured by leg volume changes. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1987, 58, A91-6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Blaber, A.P.; Hinghofer-Szalkay, H.; Convertino, V.A. Lower Body Negative Pressure: Physiological Effects, Applications, and Implementation. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 807–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Evans, J.; Schneider, S.; von der Wiesche, M.; Mulder, E.; Rössler, A.; Hinghofer-Szalkay, H.; Blaber, A.P. Effects of Individualized Centrifugation Training on Orthostatic Tolerance in Men and Women. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convertino, V.A.; Schlotman, T.E.; Akers, K.S.; Nessen, S.C.; Mansur, D.E.; Campos, M.O.; Mattos, J.D.; Paiva, A.C.S.; Rocha, M.P.; Videira, R.L.R.; et al. Gender differences in autonomic functions associated with blood pressure regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1998, 275, R1909–R1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deciuceis, C.; Porteri, E.; Rizzoni, D.; Rizzardi, N.; Paiardi, S.; Boari, G.E.; Miclini, M.; Zani, F.; Muiesan, M.L.; Donato, F.; et al. Structural Alterations of Subcutaneous Small-Resistance Arteries May Predict Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoni, D.; Porteri, E.; Boari, G.E.; De Ciuceis, C.; Sleiman, I.; Muiesan, M.L.; Castellano, M.; Miclini, M.; Agabiti-Rosei, E. Prognostic Significance of Small-Artery Structure in Hypertension. Circulation 2003, 108, 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Klein, R.; Sharrett, A.R.; Duncan, B.B.; Couper, D.J.; Klein, B.E.; Hubbard, L.D.; Nieto, F.J. For the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study Retinal Arteriolar Diameter and Risk for Hypertension. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.K.; Witteman, J.C.; Vingerling, J.R.; Breteler, M.M.; Hofman, A.; de Jong, P.T. Retinal Vessel Diameters and Risk of Hypertension. Hypertension 2006, 47, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, Y.; Kawasaki, R.; Wang, J.J.; Wong, T.Y.; Mitchell, P.; Daimon, M.; Oizumi, T.; Kato, T.; Kawata, S.; Kayama, T.; et al. Retinal Arteriolar Narrowing Predicts 5-Year Risk of Hypertension in Japanese People: The Funagata Study. Microcirculation 2010, 17, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Wong, T.Y. Retinal vascular manifestations of metabolic disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Mitchell, P. Hypertensive Retinopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2310–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.; Mitchell, P. The eye in hypertension. Lancet 2007, 369, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Kamineni, A.; Klein, R.; Sharrett, A.R.; Klein, B.E.; Siscovick, D.S.; Cushman, M.; Duncan, B.B. Quantitative Retinal Venular Caliber and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Older Persons. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Liew, G.; Klein, R.; Rochtchina, E.; Knudtson, M.D.; Klein, B.E.; Wong, T.Y.; Burlutsky, G.; Mitchell, P. Retinal vessel diameter and cardiovascular mortality: Pooled data analysis from two older populations. Eur. Hear. J. 2007, 28, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerma, E.C.; van der Voort, P.H.J.; Spronk, P.E.; Ince, C. Relationship between sublingual and intestinal microcirculatory perfusion in patients with abdominal sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, J.K.; Ruemmler, R.; Hartmann, E.K.; Ziebart, A.; Ludwig, M.; Patzak, A.; Xia, N.; Li, H.; Pfeiffer, N.; Gericke, A. Responses of retinal arterioles and ciliary arteries in pigs with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 184, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.R.; Kim, Y.; Park, T.; Oh, W.Y.; Yune, H.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, Y.H.; Kim, K. 1423: Microcirculatory alterations in hemorrhagic shock and sepsis with optical coherence tomography. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkiene, J.; Pranskuniene, Z.; Patasius, M.; Trumpaitis, J.; Boerma, E.C.; Pranskunas, A. Alterations of retinal vessels in patients with sepsis. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2019, 34, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, K.; Liisanantti, J.H.; Hautala, N.; Koskenkari, J.; Kamakura, R.; Herzig, K.H.; Syrjälä, H.; Ala-Kokko, T.I. Retinal arterial blood flow and retinal changes in patients with sepsis: Preliminary study using fluorescein angiography. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloň, A.; Steuber, B.; Neshev, R.; Schmid-Zalaudek, K.; De Boever, P.; Bergmann, E.; Picha, R.; Fredriksen, P.M.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Goswami, N. Vascular Responses following Light Therapy: A Pilot Study with Healthy Volunteers. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloň, A.; Neshev, R.; Teraž, K.; Šimunič, B.; Peskar, M.; Marušič, U.; Pišot, S.; Šlosar, L.; Gasparini, M.; Pišot, R.; et al. A pilot study: Exploring the influence of COVID-19 on cardiovascular physiology and retinal microcirculation. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 150, 104588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankhwar, V.; Urvec, J.; Steuber, B.; Zalaudek, K.S.; Bergauer, A.; Alsuwaidi, H.; Du Plessis, S.; Alsheikh-Ali, A.; Kellett, C.; Bayoumi, R.; et al. Association of gender with cardiovascular and autonomic responses to central hypovolemia. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1211774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; De Boever, P.; Gerrits, N.; Akhtar, N.; Saqqur, M.; Ponirakis, G.; Gad, H.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Shuaib, A.; Faber, J.E.; et al. Retinal vessel multifractals predict pial collateral status in patients with acute ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åneman, A.; Pettersson, A.; Eisenhofer, G.; Friberg, P.; Holm, M.; Von Bothmer, C.; Fändriks, L. Sympathetic and renin-angiotensin activation during graded hypovolemia in pigs: Impact on mesenteric perfusion and duodenal mucosal function. Shock 1997, 8, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toung, T.; Reilly, P.M.; Fuh, K.C.; Ferris, R.; Bulkley, G.B. Mesenteric vasoconstriction in response to hemorrhagic shock. Shock 2000, 13, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, A.; Sperber, G.O. Control of retinal and choroidal blood flow. Eye 1990, 4, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Shen, Y.-M.; Jiang, M.-N.; Lou, X.-F.; Shen, Y. Ocular Blood Flow Autoregulation Mechanisms and Methods. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koep, J.L.; Taylor, C.E.; Coombes, J.S.; Bond, B.; Ainslie, P.N.; Bailey, T.G. Autonomic control of cerebral blood flow: Fundamental comparisons between peripheral and cerebrovascular circulations in humans. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, V.H.; Velten, M.; Heyob, K.M.; Wold, L.E.; Rogers, L.K.; Chavez, G.C.S.C.; Li, B.-Y.; Glazebrook, P.A.; Kunze, D.L.; Schild, J.H.; et al. Sex and the cardiovascular system: The intriguing tale of how women and men regulate cardiovascular function differently. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2007, 31, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.K.; de Jong, F.J.; Vingerling, J.R.; Witteman, J.C.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M.; de Jong, P.T. Are Retinal Arteriolar or Venular Diameters Associated with Markers for Cardiovascular Disorders? The Rotterdam Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willikens, S.; Zitron, E.; Scholz, E.; Scherer, D.; Seyler, C.; Waegelein, M.; Kalinowski, T.; Katus, H.; Karle, C.; Duong, G. Retinal Arterio-Venule-Ratio (AVR) in the cardiovascular risk management of hypertension. Eur. Hear. J. 2013, 34, P5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Meuer, S.M.; Hubbard, L.D. Retinal Vessel Diameters and Their Associations with Age and Blood Pressure. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4644–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Roessler, A.; Lackner, H.K.; Schneditz, D.; Grasser, E.; Hinghofer-Szalkay, H.G. Heart rate and stroke volume response patterns to augmented orthostatic stress. Clin. Auton. Res. 2009, 19, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Females | Males |
|---|---|---|
| N | 16 | 11 |
| Age [y] | 22.4 ± 2.7 | 24.2 ± 4.2 |
| Weight [kg] | 58.7 ± 7.3 | 75.1 ± 8.3 |
| Height [cm] | 167.3 ± 6.6 | 181.6 ± 6.9 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 21.0 ± 1.9 | 22.8 ± 2.4 |
| Time Point | Baseline | LBNP-40 | Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females |
| CRAE [μm] | 140.81 ± 13.26 | 146.90 ± 11.70 | 142.18 ± 10.42 | 149.74 ± 13.84 | 141.34 ± 13.54 | 147.41 ± 13.05 |
| CRVE [μm] | 203.97 ± 20.52 | 210.13 ± 23.03 | 205.44 ± 19.03 | 210.45 ± 19.39 | 207.77 ± 18.66 | 211.40 ± 20.68 |
| AVR | 0.69 ± 0.07 | 0.70 ± 0.07 | 0.71 ± 0.06 | 0.71 ± 0.05 | 0.68 ± 0.07 | 0.70 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saloň, A.; Vladic, N.; Schmid-Zalaudek, K.; Steuber, B.; Hawliczek, A.; Urevc, J.; Bergauer, A.; Pivec, V.; Shankhwar, V.; Goswami, N. Sex Variations in Retinal Microcirculation Response to Lower Body Negative Pressure. Biology 2023, 12, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091224
Saloň A, Vladic N, Schmid-Zalaudek K, Steuber B, Hawliczek A, Urevc J, Bergauer A, Pivec V, Shankhwar V, Goswami N. Sex Variations in Retinal Microcirculation Response to Lower Body Negative Pressure. Biology. 2023; 12(9):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091224
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaloň, Adam, Nikola Vladic, Karin Schmid-Zalaudek, Bianca Steuber, Anna Hawliczek, Janez Urevc, Andrej Bergauer, Vid Pivec, Vishwajeet Shankhwar, and Nandu Goswami. 2023. "Sex Variations in Retinal Microcirculation Response to Lower Body Negative Pressure" Biology 12, no. 9: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091224
APA StyleSaloň, A., Vladic, N., Schmid-Zalaudek, K., Steuber, B., Hawliczek, A., Urevc, J., Bergauer, A., Pivec, V., Shankhwar, V., & Goswami, N. (2023). Sex Variations in Retinal Microcirculation Response to Lower Body Negative Pressure. Biology, 12(9), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091224







