Global and Conditional Disruption of the Igf-I Gene in Osteoblasts and/or Chondrocytes Unveils Epiphyseal and Metaphyseal Bone-Specific Effects of IGF-I in Bone
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
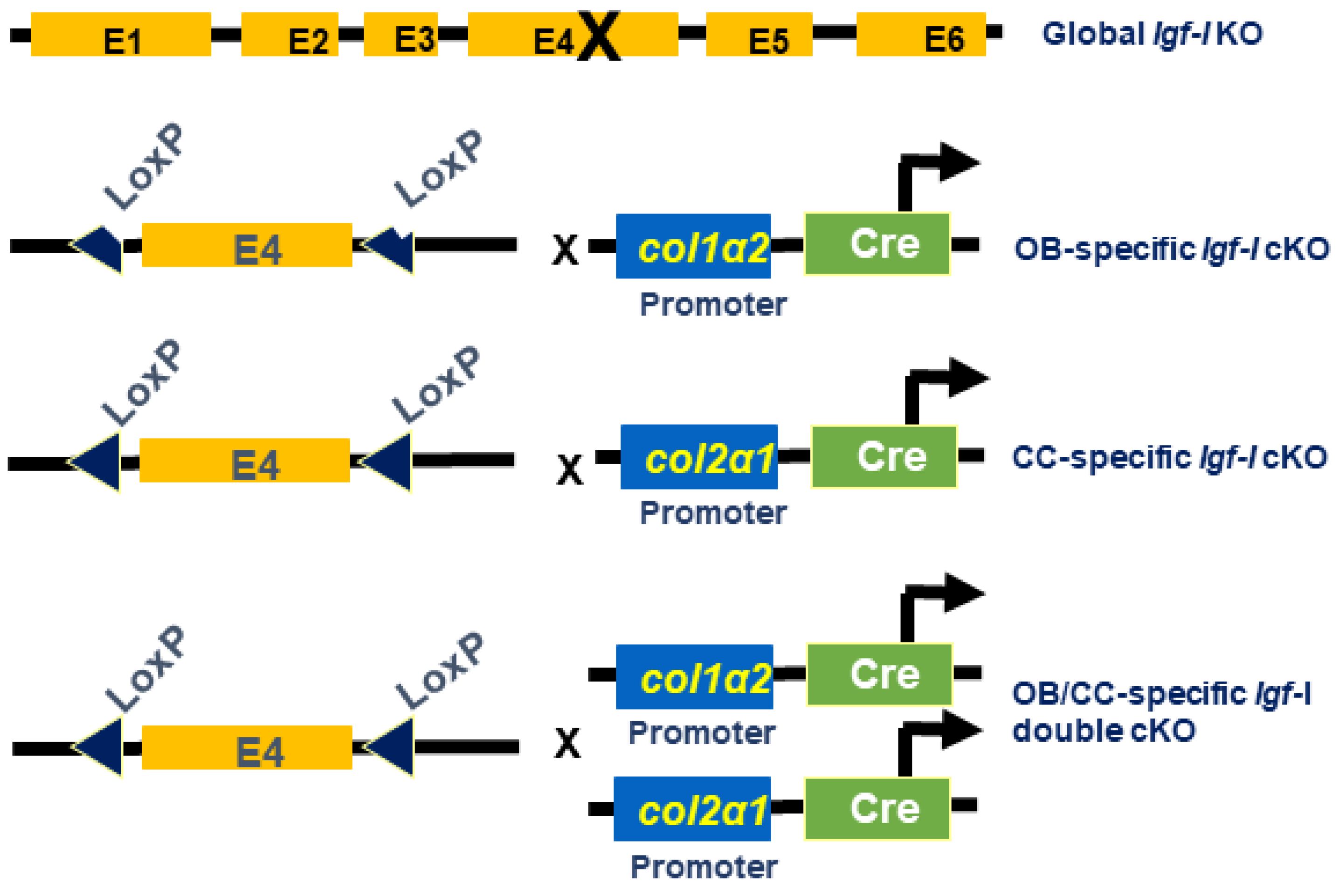
2.1. Generation of Igf-I KO Mice
2.2. MicroCT Evaluation
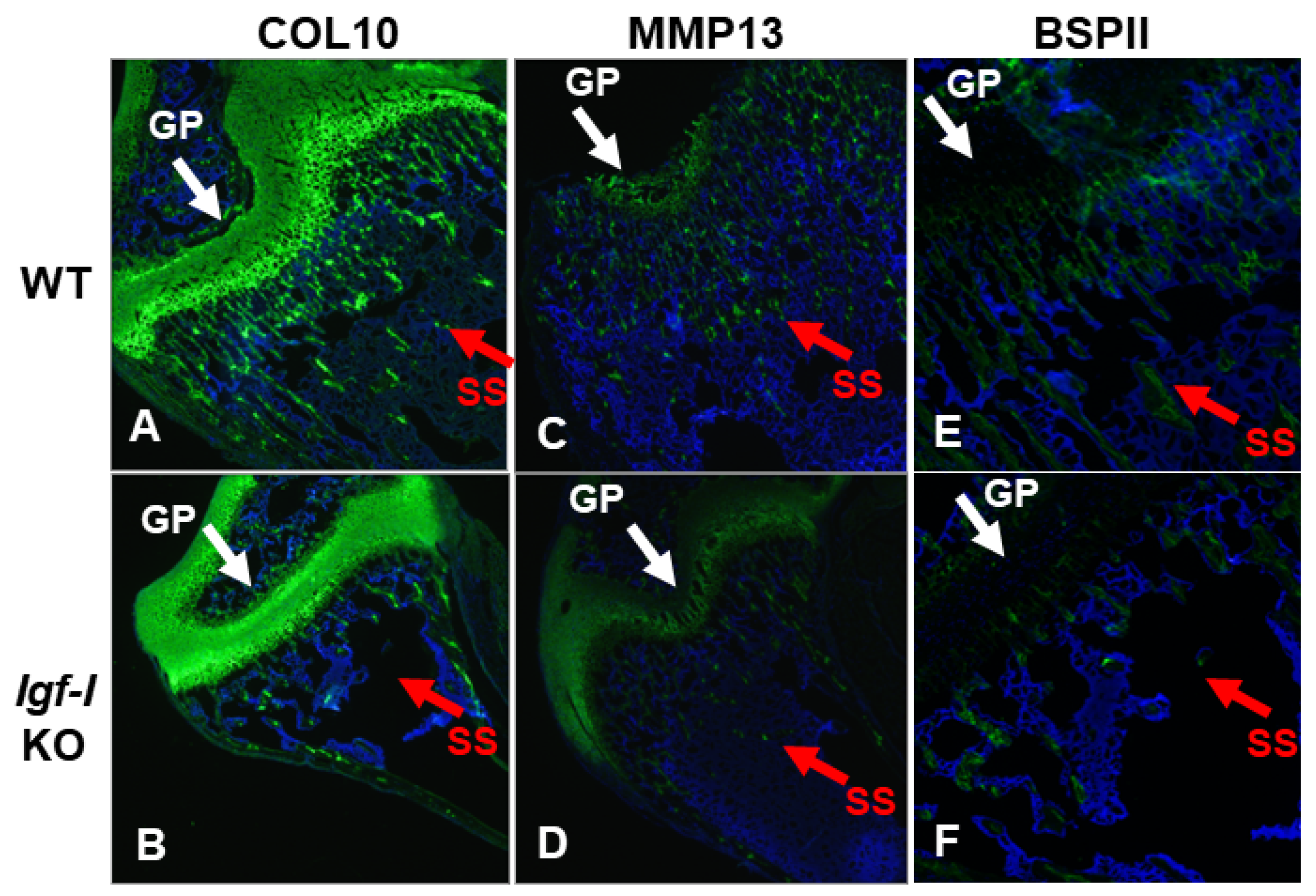
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
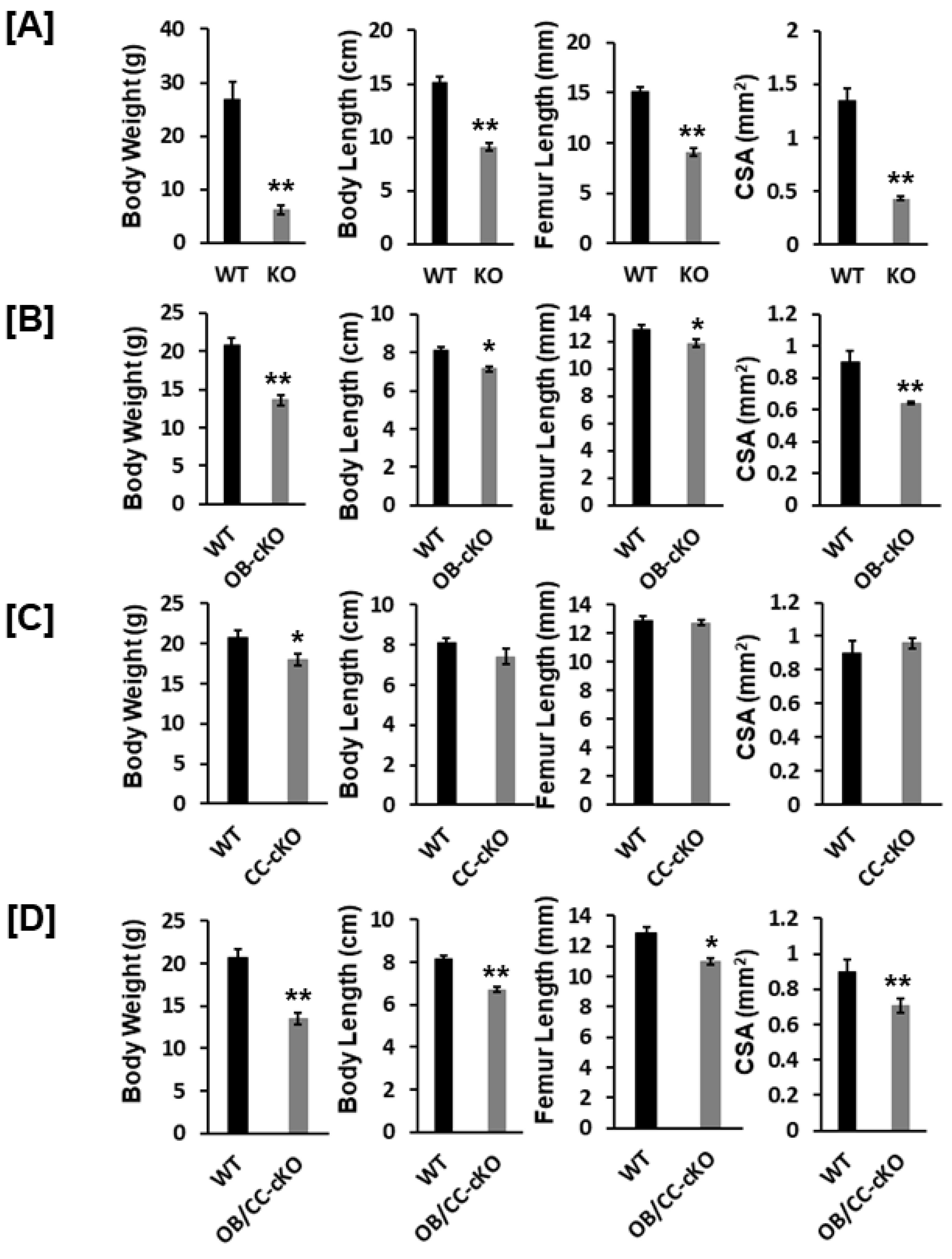
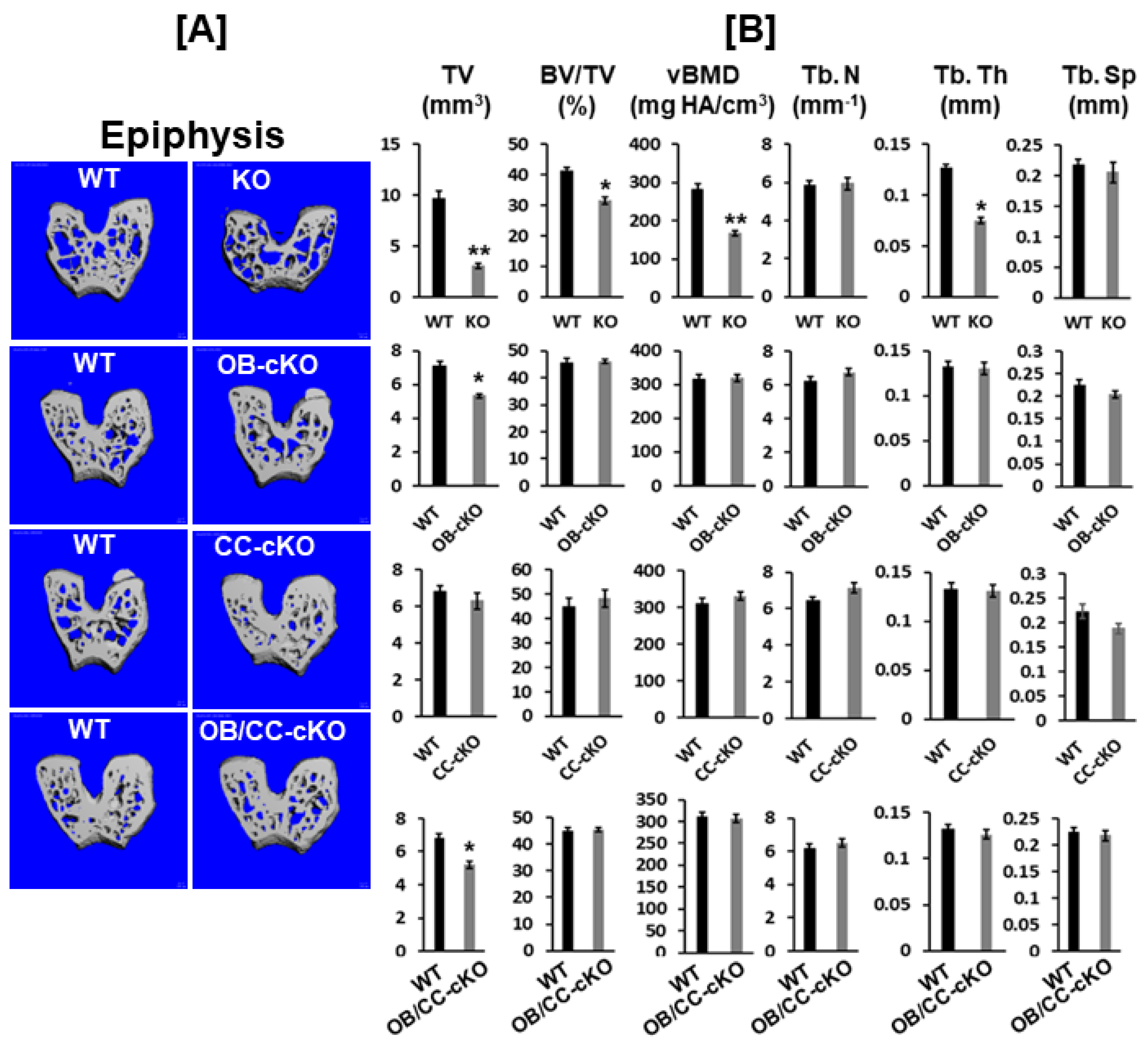
3.1. Bone Size at the Epiphysis Is Reduced in Mice with Global and Osteoblastic-Specific Disruption of the Igf-I Gene but Not in Chondrocyte-Specific Conditional KO Mice
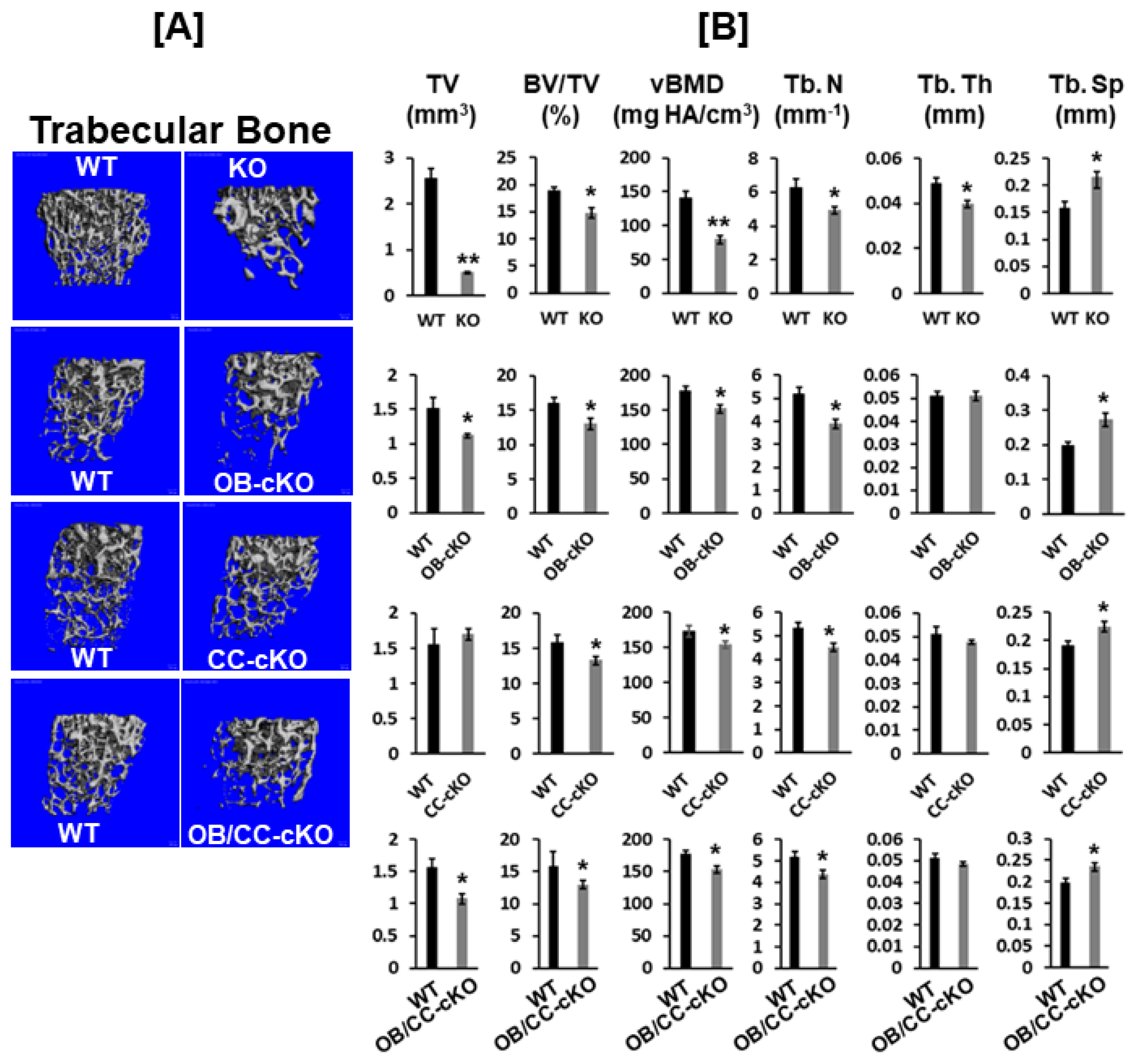
3.2. Trabecular Bone Volume and vBMD Are Reduced at the Secondary Spongiosa of the Distal Femur in Mice with the Disruption of the Igf-I Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powell-Braxton, L.; Hollingshead, P.; Warburton, C.; Dowd, M.; Pitts-Meek, S.; Dalton, D.; Gillett, N.; Stewart, T.A. IGF-I is required for normal embryonic growth in mice. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Monier-Faugere, M.C.; Langub, M.C.; Geng, Z.; Nakayama, T.; Pike, J.W.; Chernausek, S.D.; Rosen, C.J.; Donahue, L.R.; Malluche, H.H.; et al. Targeted overexpression of insulin-like growth factor I to osteoblasts of transgenic mice: Increased trabecular bone volume without increased osteoblast proliferation. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, C.M.; Brommage, R.; Deleon, L.; Adams, S.; Rosen, D.; Sommer, A. Benefit of systemically administered rhIGF-I and rhIGF-I/IGFBP-3 on cancellous bone in ovariectomized rats. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1994, 9, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libanati, C.; Baylink, D.J.; Lois-Wenzel, E.; Srinvasan, N.; Mohan, S. Studies on the potential mediators of skeletal changes occurring during puberty in girls. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.T.; Lv, Z.T.; Zhou, C.K.; Mao, C.; Sheng, W.B. Association between IGF-1 polymorphisms and risk of osteoporosis in Chinese population: A meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kineman, R.D.; Del Rio-Moreno, M.; Sarmento-Cabral, A. 40 Years of IGF1: Understanding the tissue-specific roles of IGF1/IGF1R in regulating metabolism using the Cre/loxP system. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T187–T198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bikle, D.D.; Chang, W. Autocrine and Paracrine Actions of IGF-I Signaling in Skeletal Development. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakar, S.; Liu, J.L.; Stannard, B.; Butler, A.; Accili, D.; Sauer, B.; LeRoith, D. Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7324–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjogren, K.; Liu, J.L.; Blad, K.; Skrtic, S.; Vidal, O.; Wallenius, V.; LeRoith, D.; Tornell, J.; Isaksson, O.G.; Jansson, J.O.; et al. Liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is the principal source of IGF-I in blood but is not required for postnatal body growth in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7088–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjogren, K.; Jansson, J.O.; Isaksson, O.G.; Ohlsson, C. A model for tissue-specific inducible insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) inactivation to determine the physiological role of liver-derived IGF-I. Endocrine 2002, 19, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazowski, D.A.; Fraher, L.J.; Hodsman, A.; Steer, B.; Modrowski, D.; Han, V.K. Regional variation of insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression in mature rat bone and cartilage. Bone 1994, 15, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Chin, E.; Zhou, J.; Bondy, C.A. Cellular patterns of insulin-like growth factor system gene expression in murine chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Govoni, K.; Donahue, L.R.; Kesavan, C.; Wergedal, J.; Long, C.; Bassett, J.H.; Gogakos, A.; Wojcicka, A.; Williams, G.R.; et al. Genetic evidence that thyroid hormone is indispensable for prepubertal IGF-I expression and bone acquisition in mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, K.E.; Wergedal, J.E.; Florin, L.; Angel, P.; Baylink, D.J.; Mohan, S. Conditional deletion of IGF-I in collagen type 1{alpha}2 (Col1{alpha}2) expressing cells results in postnatal lethality and a dramatic reduction in bone accretion. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5706–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, K.E.; Lee, S.K.; Chung, Y.S.; Behringer, R.R.; Wergedal, J.E.; Baylink, D.J.; Mohan, S. Disruption of insulin-like growth factor-I expression in type IIalphaI collagen-expressing cells reduces bone length and width in mice. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 30, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Muller, R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortebjerg, R.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Frystyk, J. Insulin growth factor binding proteins as therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotwein, P. Mapping the growth hormone--Stat5b--IGF-I transcriptional circuit. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Arnao, J.; Miell, J.P.; Ross, R.J. Influence of thyroid hormones on the GH-IGF-I axis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 4, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, A.M.; Engels, M.A.; Boerma, G.J.; Krenning, E.P.; De Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M. Changes in bone mineral density, body composition, and lipid metabolism during growth hormone (GH) treatment in children with GH deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett-Connor, E.; Goodman-Gruen, D. Gender differences in insulin-like growth factor and bone mineral density association in old age: The Rancho Bernardo Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.A.; Burger, H.; Stolk, R.P.; Grobbee, D.E.; de Jong, F.H.; Lamberts, S.W.; Pols, H.A. Gender-specific relationship between serum free and total IGF-I and bone mineral density in elderly men and women. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 138, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Kuribayashi, F.; Chihara, K. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, and IGFBP-3 in osteoporotic patients with and without spinal fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, D.; Grgurevic, L.; Erjavec, I.; Razdorov, G.; Brkljacic, J.; Orlic, I.; Plancak, D. Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-7 on gene expression of bone morphogenetic protein-4, dentin matrix protein-1, insulin-like growth factor-I and -II in cementoblasts in vitro. Coll. Antropol. 2012, 36, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Baker, J.; Perkins, A.S.; Robertson, E.J.; Efstratiadis, A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 1993, 75, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; von der Mark, K.; Henry, S.; Norton, W.; Adams, H.; de Crombrugghe, B. Chondrocytes Transdifferentiate into Osteoblasts in Endochondral Bone during Development, Postnatal Growth and Fracture Healing in Mice. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakar, S.; Werner, H.; Rosen, C.J. Insulin-like growth factors: Actions on the skeleton. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T115–T137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, J.; Windahl, S.H.; Sjogren, K.; Koskela, A.; Tuukkanen, J.; Ohlsson, C. Liver-derived IGF-I regulates cortical bone mass but is dispensable for the osteogenic response to mechanical loading in female mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E138–E144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.H.; Baylink, D.J.; Sheng, M.H. Osteocyte-derived insulin-like growth factor-I is not essential for bone repletion response in mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.W.; Rundle, C.H.; Zhou, X.D.; Baylink, D.J.; Sheng, M.H. Conditional deletion of IGF-I in osteocytes unexpectedly accelerates bony union of the fracture gap in mice. Bone 2016, 92, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| KO Cell Type | Mechanism | Bone Size | Trabecular Bone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Every cell type (global) | Endocrine and local action | Reduced | Reduced |
| Osteoblasts | Local action | Reduced | Reduced |
| Chondrocytes | Local action | No change | Reduced |
| Osteoblasts/chondrocytes | Local action | Reduced | Reduced |
| Hepatocytes | Local action | Reduced | No change |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, W.; Kesavan, C.; Pourteymoor, S.; Mohan, S. Global and Conditional Disruption of the Igf-I Gene in Osteoblasts and/or Chondrocytes Unveils Epiphyseal and Metaphyseal Bone-Specific Effects of IGF-I in Bone. Biology 2023, 12, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091228
Xing W, Kesavan C, Pourteymoor S, Mohan S. Global and Conditional Disruption of the Igf-I Gene in Osteoblasts and/or Chondrocytes Unveils Epiphyseal and Metaphyseal Bone-Specific Effects of IGF-I in Bone. Biology. 2023; 12(9):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091228
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Weirong, Chandrasekhar Kesavan, Sheila Pourteymoor, and Subburaman Mohan. 2023. "Global and Conditional Disruption of the Igf-I Gene in Osteoblasts and/or Chondrocytes Unveils Epiphyseal and Metaphyseal Bone-Specific Effects of IGF-I in Bone" Biology 12, no. 9: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091228
APA StyleXing, W., Kesavan, C., Pourteymoor, S., & Mohan, S. (2023). Global and Conditional Disruption of the Igf-I Gene in Osteoblasts and/or Chondrocytes Unveils Epiphyseal and Metaphyseal Bone-Specific Effects of IGF-I in Bone. Biology, 12(9), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091228





