Taxonomic Composition and Salinity Tolerance of Macrozoobenthos in Small Rivers of the Southern Arid Zone of the East European Plain
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Characteristics of Watercourses
2.3. Field Sampling
2.4. Species Identification
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
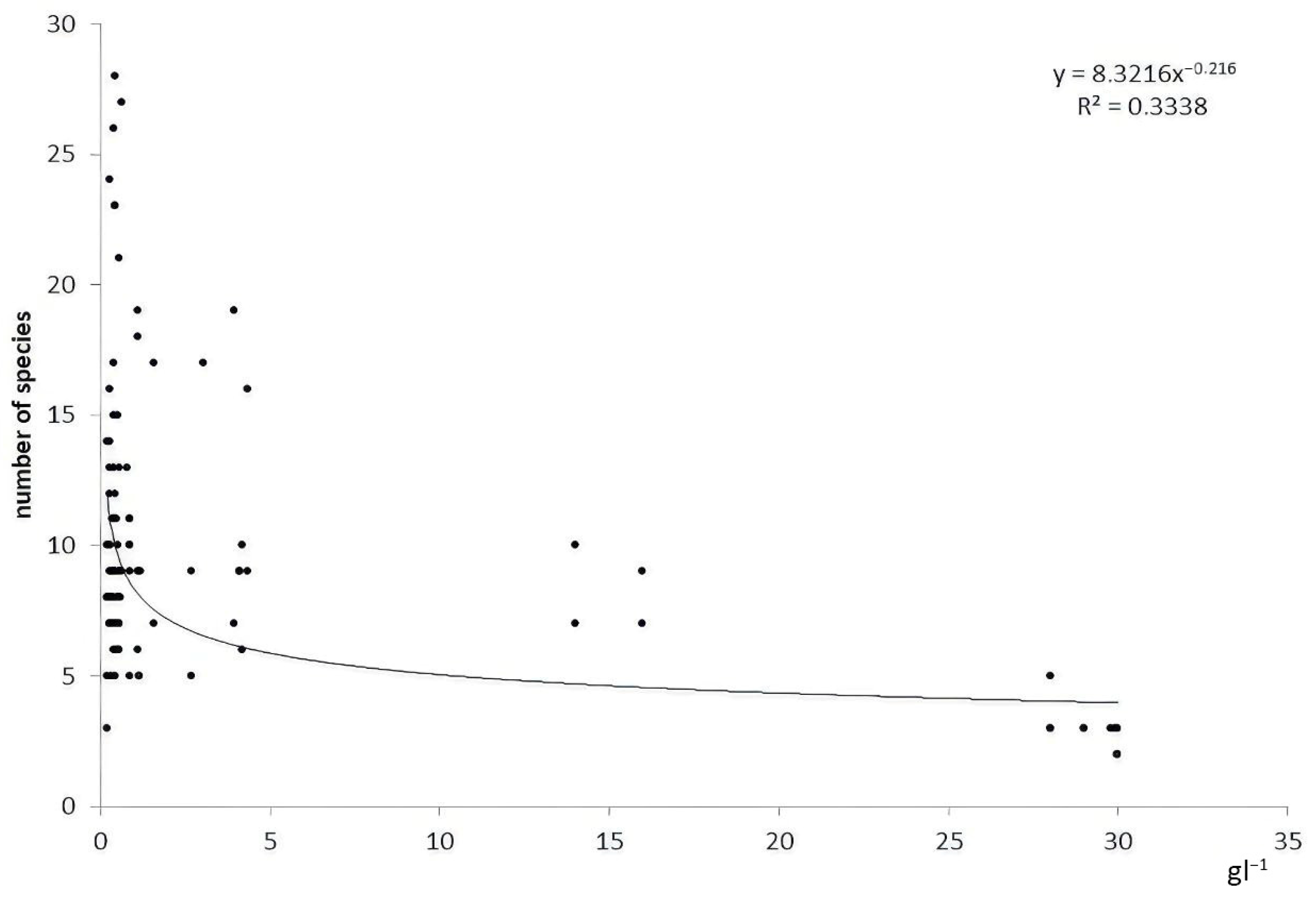
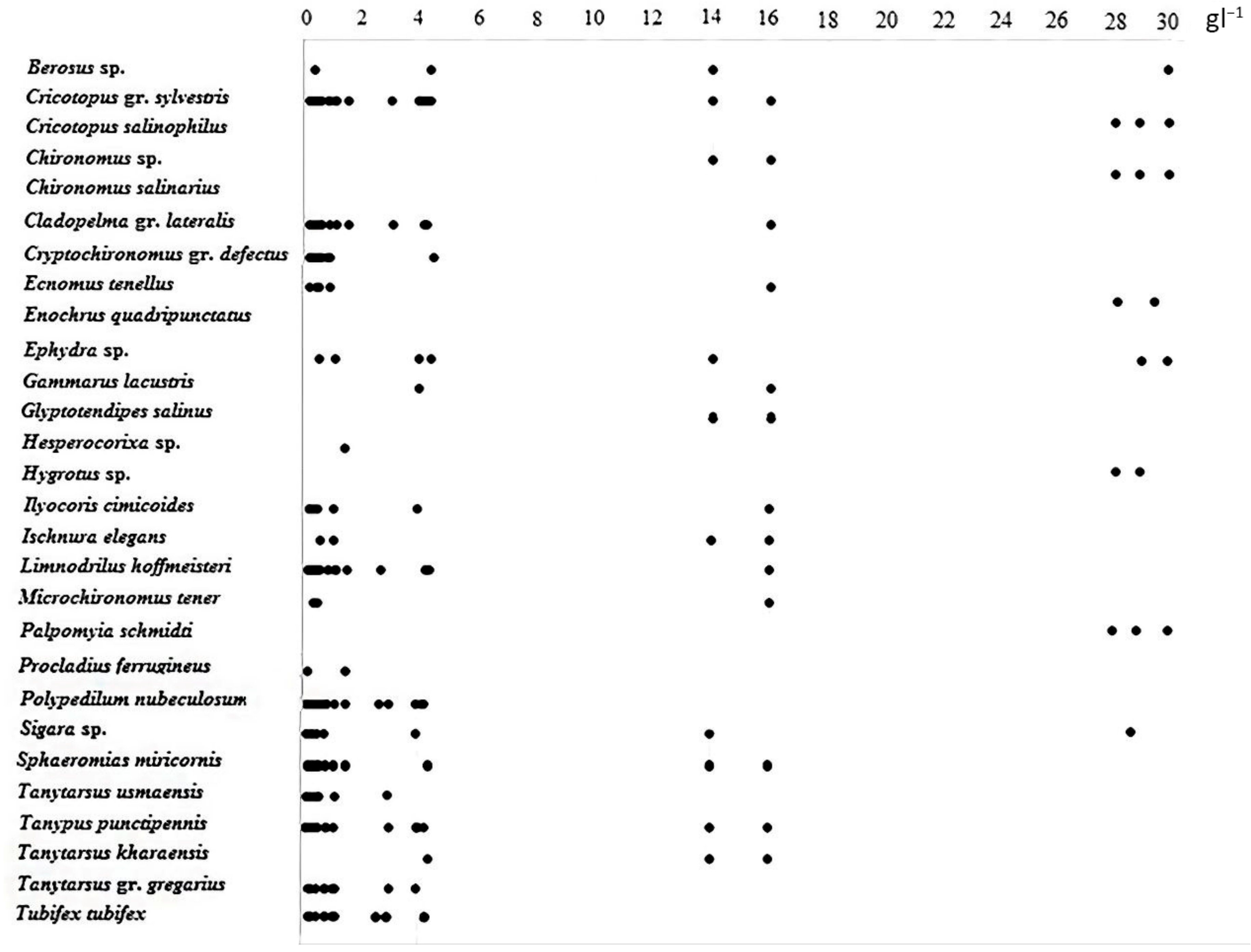
3.1. Fauna Structure and Species Richness
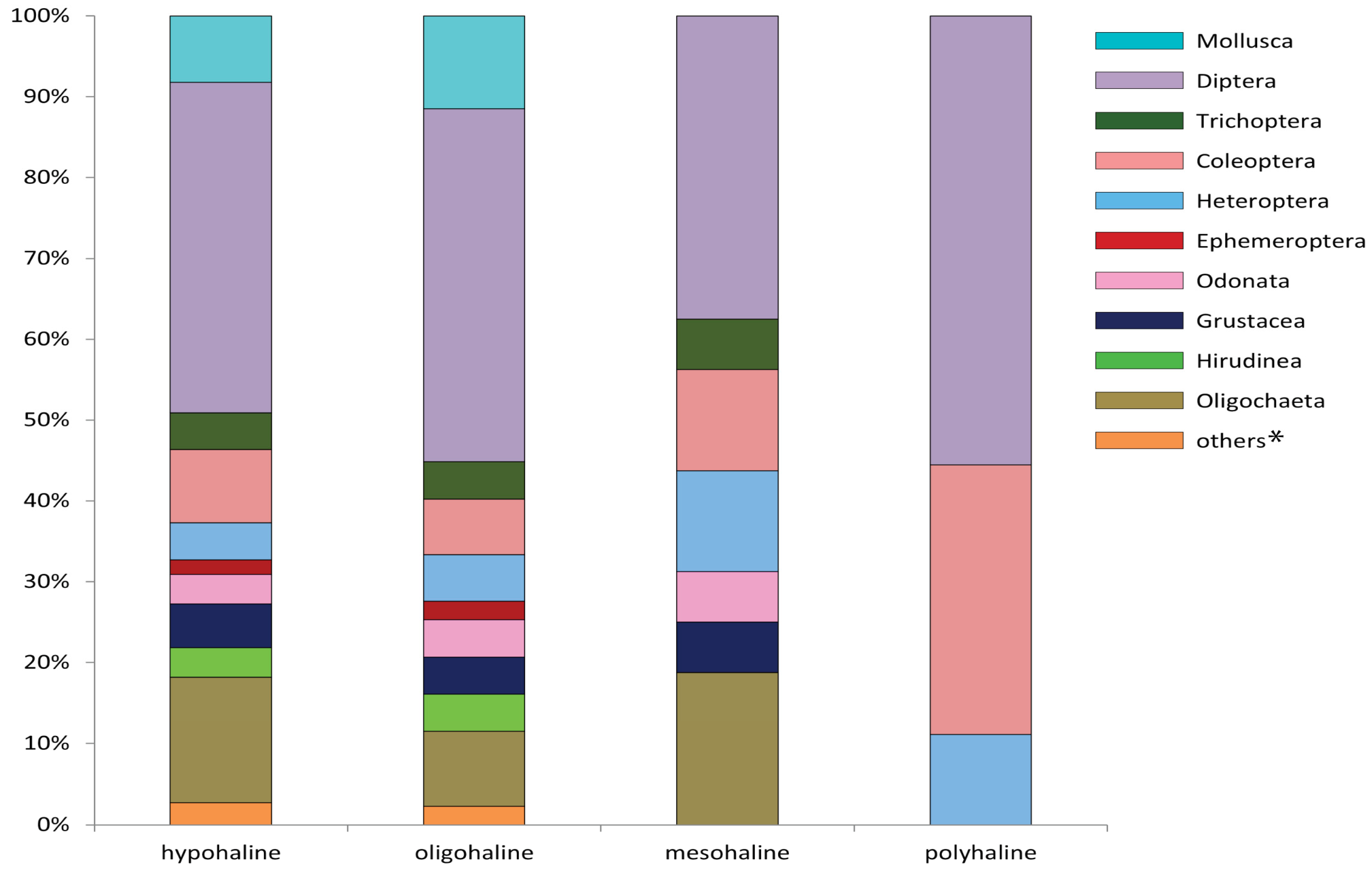
3.2. Distribution of Taxonomic Groups
3.3. Benthic Assemblages in Rivers of Different Salinity
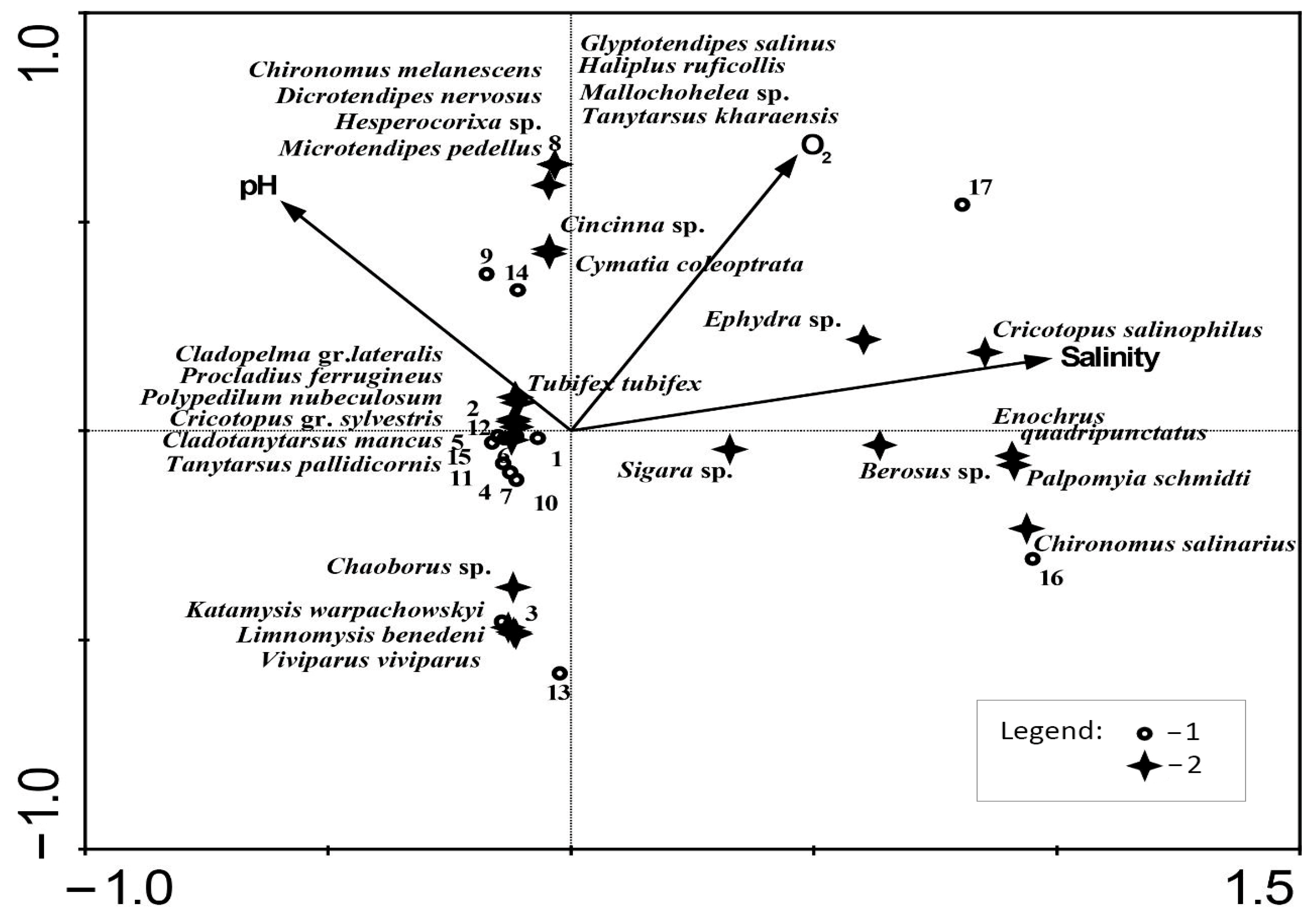
3.4. Relationships between Macrozoobenthos Distribution and Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, J.R. Predicting combined effects of land use and climate change on river and stream salinity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowa, A.; Krodkiewska, M.; Halabowski, D. How Does Mining Salinisation Gradient Affect the Structure and Functioning of Macroinvertebrate Communities? Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsov, V.M. (Ed.) The Roshydromet 3d Assessment Report on Climate Change and Its Consequences on the Territory of the Russian Federation; Science-Intensive Technologies: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2022; 676p. Available online: https://www.meteorf.gov.ru/upload/pdf_download/compressed.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2023). (In Russian)
- The WMO Report on State of the Climate in Europe 2021; WMO-No. 1304; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; 52p, Available online: https://library.wmo.int/index.php?lvl=notice_display&id=22152#.ZFywgXbP3IV (accessed on 25 April 2023). (In Russian)
- Molenda, T. Natural and Anthropogenic Conditions of Physical and Chemical Water Changes in Post-Mining Aquatic Areas of Upper Silesian Region and Its Neighbouring Area; Uniw. Śląski: Katowice, Poland, 2011; 134p. [Google Scholar]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Kefford, B.; Piscart, C.; Prat, N.; Schäfer, R.B.; Schulz, C.J. Salinisation of rivers: An urgent ecological issue. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subetto, D.A.; Nazarova, L.B.; Pestryakova, L.A.; Syrykh, L.S.; Andronikov, A.V.; Biskaborn, B.; Diekmann, B.; Kuznetsov, D.D.; Sapelko, T.V.; Grekov, I.M. Palaeolimnological studies in Russian Northern Eurasia: A review. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 4, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, R.J.; Langdon, P.G.; Doncaster, C.P.; Dearing, J.A.; Wang, R.; Nazarova, L.B.; Medeiros, A.S.; Brooks, S.J. Metrics of structural change as indicators of chironomid community stability in high latitude lakes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 249, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, G.M.; Burns, D.A.; Driscoll, C.T.; Jenkins, J.C.; Mitchell, M.J.; Rustad, L.; Haeuber, R. Who needs environmental monitoring? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovatyuk, L.V.; Zinchenko, T.D.; Nazarova, L.B. Macrozoobenthic communities of the saline Bolshaya Samoroda River (Lower Volga region, Russia): Species composition, density, biomass and production. Aquat. Ecol. 2020, 54, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumke, T.; Ksenofontova, M.; Pestryakova, L.; Nazarova, L.; Hubberten, H.-W. Limnological characteristics of lakes in the lowlands of Central Yakutia, Russia. J. Limnol. 2007, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palagushkina, O.V.; Nazarova, L.B.; Wetterich, S.; Shirrmaister, L. Diatoms of modern bottom sediments in Siberian Arctic. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2012, 5, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefford, B.J.; Buchwalter, D.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Davis, J.; Duncan, R.P.; Hoffmann, A.; Thompson, R. Salinized rivers: Degraded systems or new habitats for salttolerant faunas? Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20151072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskaborn, B.K.; Nazarova, L.; Pestryakova, L.A.; Syrykh, L.; Funck, K.; Meyer, H.; Chapligin, B.; Vyse, S.; Gorodnichev, R.; Zakharov, E.; et al. Spatial distribution of environmental indicators in surface sediments of Lake Bolshoe Toko, Yakutia, Russia. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4023–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, F.A. (Ed.) Geology of the USSR: Rostov, Volgograd, Astrakhan Regions and Kalmyk ASSR. Geological Description; Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1970; 667p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Badyukova, E.N. History of fluctuations of the Caspian Sea level in the Pleistocene (Was there a Great Khvalyn transgression?). Bull. Comm. Study Quat. Period 2015, 74, 111–120. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kotlyakov, V.M. (Ed.) National Atlas of Russia; Volume 2: Nature. Ecology; Roskartografiya: Moscow, Russia, 2007; 495p, Available online: https://nationalatlas.ru/tom2/ (accessed on 25 April 2023). (In Russian)
- Edelgeriev, R.S.H. (Ed.) National Report “Global Climate and Soil Cover of Russia: Desertification and Land Degradation, Institutional, Infrastructural, Technological Adaptation Measures (Agriculture and Forestry)”; MBA Publishing House LLC: Moscow, Russia, 2019; Volume 2, 476p, Available online: https://esoil.ru/publications/books/nacdoklclimat.html (accessed on 25 April 2023). (In Russian)
- Cherenkova, E.A.; Sidorova, M.V. On the impact of insufficient atmospheric moistening on the low annual discharge of large rivers in European Russia. Water Res. 2021, 48, 351–360. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapanov, M.K. Environmental Implications of Climate Warming for the Northern Caspian Region. Arid Ecosyst. 2018, 8, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotokrylin, A.N.; Titkova, T.B.; Cherenkova, E.A. Characteristics of the spring-summer droughts during the dry and wet periods in the South of European Russia. Arid Ecosyst. 2020, 10, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubarev, D.I.; Levitskaya, N.G.; Derevyagin, S.S. Influence of Climate Change on Soil Degradation in Arid Zones of the Volga Region. Arid Ecosyst. 2022, 12, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, S.V. Climate-induced changes in the annual river runoff and its components in European Russia. Izv. Akad. Nauk Ser. Geogr. 2011, 6, 78–86. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shumova, N.A. Water resources and hydrothermal moistening conditions in the Lower Volga basin. Arid Ecosyst. 2015, 5, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzmina, J.V.; Treshkin, S.E. Climate changes in the basin of the Lower Volga and their influence on the ecosystem. Arid Ecosyst. 2014, 4, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Zarfl, C.; Robinson, C. Rivers of Europe, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; 942p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkov, F.N.; Gvozdetsky, N.A. Physical Geography of the USSR, 5th ed.; Volume 1: General Overview. The European Part of the USSR. Caucasus; Higher School: Moscow, Russia, 1986; 376p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alekseevsky, N.I.; Evstigneev, V.M.; Koronkevich, N.I.; Yasinsky, S.V.; Isaev, A.A.; Simonov, J.G.; Kruzhalin, V.I.; Simonova, T.J.; Paramonov, S.G.; Dolgov, S.V.; et al. Small Rivers of the Volga Basin; Alekseevsky, N.I., Ed.; Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 1998; 233p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Matishov, G.G.; Golubeva, N.I. The Significance of Arid and Semiarid Zones in the System of Modern Land Use Management in Russia. In Current State and Technologies of Monitoring of Arid and Semiarid Ecosystems in the South of Russia; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; SSC RAS Publishing: Rostov-On-Don, Russia, 2010; pp. 11–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Danilov-Danilyan, V.I.; Pryazhinskaya, V.G. (Eds.) Economic and Territorial Aspects of Water Management in Russia; RASHN: Moscow, Russia, 2013; 311p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bening, A.L. To the study of the bottom life of the Volga River. Monogr. Volga Biol. Stn. Saratov Nat. Soc. 1924, 1, 1–398. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Brekhov, O.G. Review of the fauna of predatory aquatic Coleoptera of the semidesert zone of the Lower Volga region. Izv. Volgogr. Peduniver. 2003, 3, 93–101. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Brekhov, O.G. Ecological and Faunal Analysis of Coleoptera (Coleoptera, Hydrophilidae, Haliplidae, Noteridae, Dytiscidae) Aquatic Ecosystems of the Urbanized Territory of the Steppe Zone of Southwest Russia (on the Example of the City of Volgograd). Ph.D. Thesis, Volgograd State University, Volgograd, Russia, 2002. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gorelov, V.P.; Golokolenova, T.B.; Kuchishkina, N.V.; Shevlyakov, T.P. Hydrobiological Characteristics of Water Objects of the Elton Lake Region (Based on the Materials of 2003). In Biodiversity and Problems of Nature Management in the Elton Lake Region; Chernobai, V.F., Ed.; PrinTerra: Volgograd, Russia, 2006; pp. 23–36. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Anikin, V.V.; Ugolnikova, E.V. Dragonflies (Insecta, Odonata) of the valleys of small rivers of the Saratov region. Ecology of aquatic invertebrates. In Proceedings of the International Conference Dedicated to the 100th Anniversary of the Birth of F.D. Mordukhai-Boltovsky, Yaroslavl, Russia, 30 October–1 November 2010; Krylov, A.V., Rivier, I.K., Eds.; Printhouse: Yaroslavl, Russia; p. 16. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy, M.D.F. A Classification of the Biogeographical Provinces of the World; IUCN Occasional Paper no. 18; IUCN: Morges, Switzerland, 1975; 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Belik, V.P. (Ed.) Red Data Book of the Volgograd Region, 2nd ed.; Volume 1: Animals; LLC Izdat-print: Voronezh, Russia, 2017; 216p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, V.Z. (Ed.) Educational and Historical Atlas of the Saratov Region; Saratov State University: Saratov, Russia, 2013; 143p, Available online: https://geoportal.rgo.ru/catalog/regionalnye-atlasy/uchebno-kraevedcheskiy-atlas-saratovskoy-oblasti (accessed on 25 April 2023). (In Russian)
- Brylyov, V.A. (Ed.) Geographical Atlas of the Volgograd Region, 2nd ed.; Planeta: Moscow, Russia, 2014; 64p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pryakhina, S.I.; Ormeli, E.I. Agroclimatic Characterisation of the Seasons of the Year in Saratov Region. Izv. Saratov Univ. Ser. Earth Sci. 2018, 18, 243–247. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Characteristics of the River Basin. In Scheme of Integrated Use and Protection of Water Bodies of the Volga River Basin; Approved by the order no. 233 on 14.08.2015; Lower Volga Basin Water Management Committee: Volgograd, Russia, 2015; Volume 1, 105p. (In Russian)
- Kalioujnaia, I.J.; Kalioujnaia, N.S. Wetlands of the Elton Region; Regional Center for Biodiversity Study & Conservation: Volgograd, Russia, 2005; 28p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zinchenko, T.D.; Gladyshev, M.I.; Makhutova, O.N.; Sushchik, N.N.; Kalachova, G.S.; Golovatyuk, L.V. Saline rivers provide arid landscapes with a considerable amount of biochemically valuable production of chironomid (Diptera) larvae. Hydrobiologia 2014, 722, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovatyuk, L.V.; Shitikov, V.K. Salinity Tolerance of Macrozoobenthic Taxa in Small Rivers of the Lake Elton Basin. Russ. J. Ecol. 2016, 47, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalioujnaia, I.J.; Kalioujnaia, N.S.; Leummens, H.J.L. Experience of using cartographic methods and GIS in the design of biosphere reserve “Lake Elton”. InterCarto InterGIS 2019, 25 Pt 1, 337–351. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Water Register. Available online: https://textual.ru/gvr/ (accessed on 25 April 2023). (In Russian).
- Mordukhai-Boltovsky, F.D. (Ed.) Methods of Studying Biogeocenoses of Inland Reservoirs; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1975; 240p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholm, T. Chironomidae of Holarctic Region: Keys and Diagnoses. Part 1. Larvae. Entomol. Scand. Suppl. 1983, 19, 19–457. [Google Scholar]
- Moller Pillot, H.K.M. De Larven der Nederlandse Chironomidae (Diptera). Tanypodinae, Chironomini. Nederl Faun Meded. 1984, 1, 1–277. [Google Scholar]
- Moller Pillot, H.K.M. De Larven der Nederlandse Chironomidae (Diptera: Orthocladiinae). Nederl Faun Meded. 1984, 1, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, P.E. Part 1: Diamesinae, Prodiamesinae and Orthocladiinae. In A Key to the Larval Chironomidae and Their Instars from Austrian Danube Region Streams and Rivers; Federal Institute for Water Quality of the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Wien, Austria, 1993; 513p. [Google Scholar]
- Timm, T. A Guide to the Freshwater Oligochaeta and Polychaeta of Northern and Central Europe. Lauterbornia 2009, 66, 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Soldán, T. The Mayflies of Europe (Ephemeroptera); Apollo Books: Ollerup, Denmark, 2012; pp. 1–781. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, J.H.; Rogers, D.C. (Eds.) Ecology and General Biology. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier Inc.: London, UK, 2015; Volume I, 1118p. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, J.H.; Rogers, D.C. (Eds.) Keys to Nearctic Fauna. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier Inc.: London, UK, 2016; Volume II, 762p. [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS Editorial Board. World Register of Marine Species. 2023. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; Ower, G.; Hernández Robles, D.R.; Plata Corredor, C.A.; Stjernegaard Jeppesen, T.; Örn, A.; Vandepitte, L.; Hobern, D.; et al. Catalogue of Life Checklist (Version 2023-08-17). Catalogue of Life. Available online: https://www.catalogueoflife.org/ (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Venice System. Symposium on the Classification of Brackish Waters, Venice, Italy, 8–14 April 1958. Arch. Oceanogr. Limnol. 1958, 11, 1–248. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.J.; Birks, H.J.B. Chironomid-inferred air temperatures from late-glacial and Holocene sites in north-west Europe: Progress and problems. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2001, 20, 1723–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barley, E.M.; Walker, I.R.; Kurek, J.; Cwynar, L.C.; Mathewes, R.W.; Gajewski, K.; Finney, B.P. A northwest North American training set: Distribution of freshwater midges in relation to air temperature and lake depth. J. Paleolimnol. 2006, 36, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; 880p. [Google Scholar]
- Birks, H.J.B. Quantitative Palaeoenvironmental Reconstructions. In Statistical Modelling of Quaternary Science Data. Technical Guide 5; Maddy, D., Brew, J.S., Eds.; Quaternary Research Association: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 161–254. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F. Ordination. In Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology; Jongman, R.H.G., ter Braak, C.J.F., van Tongeren, O.F.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 69–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002; 500p. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F. Update Notes: CANOCO Version 3.10; Agricultural Mathematics Group; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1990; 36p. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, R.A. Malacofauna of Different Types of Reservoirs and Watercourses of the Samara Region; Cassandra: Togliatti, Russia, 2017; 103p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Juggins, S. Quantitative reconstructions in palaeolimnology: New paradigm or sick science? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 64, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Environmental threats to salts lakes and the likely status of inland saline ecosystems. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, S.D.; Attrill, M.J.; Arshad, A. Seasonality in macroinvertebrate community composition across a neglected ecological boundary, the freshwater-estuarine transition zone. Aquat. Ecol. 1998, 32, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfgren, S. The chemical effects of de-icing salt on soil and stream water of five catchments in southeast Sweden. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscart, C.; Lecerf, A.; Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Moreteau, J.-C.; Beisel, J.-N. Biodiversity patterns along a salinity gradient: The case of net-spinning caddisflies. Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 2235–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscart, C.; Moreteau, J.C.; Beisel, J.N. Biodiversity and structure of macroinvertebrate communities along a small permanent salinity gradient (Meurthe River, France). Hydrobiologia 2005, 551, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, J.; Millán, A.; Hernández, J.; Gutiérrez, C.; Abellán, P.; Sánchez, D.; Ruiz, M. Response of biotic communities to salinity changes in a Mediterranean hyper stream. Saline Syst. 2006, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zinchenko, T.D.; Golovatyuk, L.V.; Abrosimova, E.V.; Popchenko, T.V. Macrozoobenthos in saline rivers in the Lake Elton basin: Spatial and temporal dynamics. Inland Water Biol. 2017, 10, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, T.D.; Golovatyuk, L.V.; Zagorskaya, E.P. Structural Organization of Macrozoobenthos Communities of Lowland Rivers under Anthropogenic Influence. In Bioindication of the Ecological State of Lowland Rivers; Bukharin, O.V., Rosenberg, G.S., Eds.; Science: Moscow, Russia, 2007; pp. 113–128. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Golovatyuk, L.V. Macrozoobenthos of Lowland Rivers of the Lower Volga Basin: Taxonomic Diversity, Structural Indicators, Spatial Distribution. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Biology of Inland Waters of RAS, Borok, Russia, 2023. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Nazarova, L.B.; Self, A.E.; Brooks, S.J.; Solovieva, N.; Syrykh, L.S.; Dauvalter, V.A. Chironomid fauna of the lakes from the Pechora River basin (East of European part of Russian Arctic): Ecology and reconstruction of recent ecological changes in the region. Cont. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 4, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonov, N.V. (Ed.) Lower Volga Region. In Handbook on Water Resources of the USSR; Publication of the State Hydrological Institute and the Central Bureau of Water Cadastre: Leningrad, Russia, 1934; Volume V, 681p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Golovatyuk, L.V.; Shitikov, V.K.; Zinchenko, T.D. Spatial distribution of diversity of bottom communities of logical systems of the Middle and Lower Volga region. Princ. Ecol. 2021, 2, 38–53. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remane, A. Die Brackwasserfauna. Zool. Anz. 1934, 7, 34–74. [Google Scholar]
- Aladin, N.V. The concept of relativity and plurality of barrier salinity zones. Zhurnal Obs. Biol. 1988, 49, 825–833. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Khlebovich, V.V. Ecology of an Individual (Essays on Phenotypic Adaptations of Animals); Zoological Institute of RAS: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2012; 143p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hart, B.T.; Bailey, P.; Edwards, R.; Hortle, K.; James, K.; Mcmahon, A.; Meredith, C.; Swadling, K. A review of the saltsensitivity of the Australian freshwater biota. Hydrobiologia 1991, 210, 105–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leland, H.V.; Fend, S.V. Benthic invertebrate distributions in the San Joaquin River, California, in relation to physical and chemical factors. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, A.; Velasco, J.; Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C.; Arribas, P.; Picazo, F.; Sánchez-Fernández, D.; Abellán, P. Mediterranean saline streams in southeast Spain: What do we know? J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V. Aquatic Insect Ecology. Part 1: Biology and Habitat; J. Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2002; 456p. [Google Scholar]
- Zerguine, K. Chironomidae (Diptera: Insecta) of temporary salt lakes in the eastern Hauts Plateaux of Algeria. Experiment 2014, 25, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, W.R.; Halse, S.A.; Scanlon, M.D.; Smith, M.J. Distributions and environmental tolerances of aquatic macroinvertebrate families in the agricultural zone of southwestern Australia. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2001, 20, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, J.C.; Kefford, B.J. Effects of Salinity on Stream Ecosystems: Improving Models for Macroinvertebrates. In CSIRO Land and Water Technical Report 22/05; Canberra, Australia, 2005; 64p, Available online: https://publications.csiro.au/rpr/pub?list=BRO&pid=procite:c0930011-a85c-470f-aaa5-d579380600aa (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Bunn, S.E.; Davies, P.M. Community structure of macroinvertebrate fauna and water quality of saline river system in south-western Australia. Hydrobiologia 1992, 248, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Mayenco, A. Freshwater macroinvertebrate distribution in two basins with different salinity gradients (Guadalete and Guadaira river basins, south-western Spain). Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1994, 3, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivosheina, M.G. Morphological and Ecological Mechanisms of of Hydrobionts Larvae of Diptera (Insecta, Diptera) to Resist to Extreme Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution of RAS, Moscow, Russia, 2004. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Krivosheina, M.G. On feeding insects with cyanobacteria. Paleontol. J. 2008, 6, 26–29. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Prat, N. Macroinvertebrate community in the lower Ebro river (NE Spain). Hydrobiologia 1994, 86, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhteev, V.V.; Lopatovskaya, O.G.; Okuneva, G.L.; Pomazkova, G.I.; Samoilova, E.A.; Rozhkova, N.A. Ecological description of the sodium chloride mineral springs in the Kirenga River basin and the upper reaches of the Lena River: 1. General characteristics of the springs and their hydrofauna. Inland Water Biol. 2017, 10, 331–341. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.D.; Williams, N.E.; Cao, Y. Road salt contamination of groundwater in a major metropolitan area and development of a biological index to monitor its impact. Water Res. 1999, 34, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefford, B.J.; Papas, P.J.; Nugegoda, D. Relative salinity tolerance of macroinvertebrates from the Barwon River, Victoria, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, T.D.; Makarchenko, M.A.; Makarchenko, E.A. A new species of genus Cricotopus van der Wulp (Diptera, Chironomidae) from a saline river of the Elton Lake basin (Volgograd Region, Russia). Eurasian Entomol. J. 2009, 8, 83–88. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zorina, O.V.; Zinchenko, T.D. A new species of genus Tanytarsus van der Wulp (Diptera, Chironomidae) from a saline river of the Elton Lake basin (Volgograd region, Russia). Eurasian Entomol. J. 2009, 8, 105–110. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Szadziewski, R.; Golovatyuk, L.V.; Sontag, E.; Urbanek, A.; Zinchenko, T.D. All stages of the Palaearctic predaceous midge Palpomyia schmidti Goetghebuer, 1934 (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4137, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No | River | Stream Order | Coordinates of the River Mouth, N, E | Catchment Area, km2 | Length, km | Average Stream Slope, ‰ | Current Velocity, m s−1 | Salinity Min−Max, g L−1 | Salinity Class | Salinity Average g L−1 | Dissolved O2, mg L−1 | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volga River basin | ||||||||||||
| 1 | Solenaya Kuba | 2 | 50°47′, 46°66′ | 2.03 | 98 | 0.56 | 0.005 | 0.38–3.96 | hypohaline–oligohaline | 1.94 | 8.7 | 8.01 |
| 2 | Bizyuk | 2 | 50°74′, 46°46′ | 0.71 | 54 | 1.08 | 0.005 | 0.27–0.43 | hypohaline | 0.33 | 6.5 | 8.28 |
| 3 | Tarlyk | 1 | 51°01′, 46°15′ | 0.63 | 51 | 1.59 | 0.03 | 0.27–0.61 | hypohaline–oligohaline | 0.42 | 4.6 | 8.1 |
| 4 | Yama 1 | 2 | 50°19′, 46°26′ | 0.38 | 39 | 0.56 | 0.005 | 0.18–0.41 | hypohaline | 0.3 | 8.3 | 8.3 |
| 5 | Zhidkaya Solyanka | 2 | 50°79′, 47°04′ | 0.39 | 39 | 0.67 | 0.005 | 0.27–0.47 | hypohaline | 0.34 | 8.2 | 8.5 |
| 6 | Kuba | 2 | 50°19′, 46°25′ | 0.36 | 37 | 0.62 | 0.005 | 0.87–1.2 | oligohaline | 0.93 | 6.7 | 8.08 |
| 7 | Vodyanka | 2 | 50°12′, 47°12′ | 0.25 | 30 | 0.84 | 0.005 | 0.19–0.29 | hypohaline | 0.48 | 6.5 | 8.0 |
| 8 | Otrozhina | 2 | 50°46′, 46°73′ | 0.20 | 27 | 0.77 | 0.004 | 0.56–16 | oligohalinemesohaline | 7.8 | 9.0 | 8.8 |
| 9 | Solyanka 2 | 3 | 50°76′, 46°97′ | 0.20 | 27 | 1.11 | 0.005 | 0.52–0.56 | oligohaline | 0.54 | 7.2 | 9.0 |
| 10 | Yama | 2 | 50°97′, 47°14′ | 0.13 | 21 | 0.75 | 0.005 | 0.27–0.39 | hypohaline | 0.35 | 8.1 | 8.06 |
| 11 | Solyanka 3 | 2 | 50°13′, 46°20′ | 0.12 | 20 | 0.68 | 0.005 | 0.38–0.52 | hypohaline–oligohaline | 0.45 | 5.6 | 8.05 |
| 12 | Gorkaya | 2 | 50°35′, 46°54′ | 0.07 | 16 | 0.84 | 0.005 | 0.41–1.14 | hypohaline–oligohaline | 0.89 | 8.6 | 8.4 |
| 13 | Kochetnaya | 1 | 52°15′, 50°78′ | 0.06 | 14 | 1.97 | 0.01 | 0.53–1.1 | oligohaline | 0.82 | 7.7 | 7.0 |
| 14 | Solyanka 1 | 2 | 50°47′, 46°53′ | 0.06 | 14 | 1.21 | 0.005 | 4.12–4.34 | oligohaline | 4.22 | 8.8 | 8.8 |
| 15 | Gashon | 2 | 50°97′, 46°91′ | 0.05 | 13 | 1.51 | 0.005 | 0.42–0.8 | hypohaline–oligohaline | 0.56 | 6.1 | 8.1 |
| Lake Elton basin | ||||||||||||
| 16 | Solyanka | 1 | 49°10′, 46°35′ | 0.018 | 6.7 | 5.52 | 0.12 | 28–30 | polyhaline | 28.7 | 12.6 | 7.5 |
| 17 | Chernavka | 1 | 49°12′, 46°40′ | 0.018 | 5.2 | 5.38 | 0.23 | 28–30 | polyhaline | 28.5 | 8.2 | 7.2 |
| Taxonomic Groups | Genus, Species | |
|---|---|---|
| Volga River basin | ||
| Phylum Mollusca | Class Gastropoda | Anisus sp., Bithynia tentaculata (Linnaeus, 1758), Cincinna piscinalis (Müller, 1774), Cincinna sp., Lymnaea auricularia (Linnaeus, 1758), L. intermedia (Lamark, 1822), L. ovata (Draparnaud, 1805), Lymnaea sp., L. stagnalis (Linnaeus, 1758), Planorbis planorbis (Linnaeus, 1758), and Viviparus viviparus (Linnaeus, 1758) |
| Class Bivalvia | Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas, 1771), Euglesa sp., Musculium sp., and Neopisidium sp. | |
| Phylum Annelida Class Clitellata | Subclass Oligochaeta | Dero digitata (Müller, 1773), D. obtusa Udekem, 1855, Enchytraeus albidus Henle, 1837, Limnodrilus claparedeanus Ratzel, 1868, L. hoffmeisteri Claparede, 1862, L. udekemianus Claparede, 1862, Lumbriculus variegatus (Müller, 1773), Nais barbata Müller, 1773, N. communis Piguet, 1906, N. pardalis Piquet, 1906, N. pseudobtusa Piguet, 1906, N. variabilis Piguet, 1906, Ophidonais serpentina (Müller, 1773), Stylaria lacustris (Linnaeus, 1767), Tubifex tubifex (Müller, 1773), and Uncinais uncinata (Oersted, 1842) |
| Order Hirudinea | Helobdella stagnalis (Linnaeus, 1758), Hemiclepsis marginata (Müller, 1774) Herpobdella octoculata (Linnaeus, 1758), and Piscicola geometra (Linnaeus, 1761) | |
| Phylum Arthropoda | Subphylum Crustacea | Asellus aquaticus (Linne, 1758), Gammarus lacustris Sars, 1863, Chaetogammarus warpachowskyi (Sars, 1894), Katamysis warpachowskyi G.O. Sars,1893, Limnomysis benedeni Czerniavsky, 1882, Paramysis intermedia (Czerniavsky, 1882), P. lacustris (Czerniavsky, 1882), and Pterocuma rostrata (G.O. Sars, 1894) |
| Phylum Arthropoda Class Insecta | Order Odonata | Anax imperator Leach, 1815, Enallagma cyathigerum Charpentier, 1840, Erythromma najas (Hansemann, 1823), Ischnura elegans Vanderlinden, 1823, Lestes sponsa (Hansemann, 1823), Orthetrum cancellatum (Linnaeus, 1758), Sympecma fusca (Vanderlinden., 1823), and Sympetrum depressiusculum (Sélys, 1841) |
| Order Ephemeroptera | Caenis robusta (Eaton, 1884), Cloeon gr. dipterum, C. simile Eaton, 1870 | |
| Order Heteroptera | Cymatia coleoptrata (Fabricius, 1777), Gerris lacustris (Linnaeus, 1758), Hesperocorixa sp., Ilyocoris cimicoides (Linnaeus, 1758), Mesovelia furcata Mulsant et Rey, 1852, Micronecta sp., Microvelia sp., Notonecta glauca glauca Linnaeus, 1758, Plea minutissima Leach, 1817, Ranatra linearis Linnaeus, 1758, and Sigara sp. | |
| Order Coleoptera | Bagous argillaceus Gyllenhal, 1836, Berosus sp., Cybister sp., Donacia crassipes Fabricius, 1775, Haliplus ruficollis (De Geer, 1774), Haliplus sp., Helophorus paraminutus Angus, 1986, Hyphydrus ovatus (Linnaeus, 1761), Laccobius sp., Laccophilus sp., Noterus clavicornis (De Geer, 1774), Ochthebius sp., Paracymus aeneus (Germar, 1824), Peltodytes caesus (Duftschmid, 1805), Enochrus quadripunctatus (Herbs, 1797), and Hygrotus sp. | |
| Order Megaloptera | Sialis sordida Klingstedt, 1932 | |
| Order Trichoptera | Agraylea multipunctata Curtis, 1834, Cyrnus flavidus MacLachlan, 1864, Ecnomus tenellus (Rambur, 1842), Hydroptila sp., Leptocerus tineiformis Curtis, 1834, Oecetis furva (Rambur, 1842), and Phryganea bipunctata (Retzius, 1783) | |
| Order Lepidoptera | Parapoynx stratiotata Linnaeus, 1758 | |
| Order Diptera | Ablabesmyia monilis (Linnaeus, 1758), A. phatta (Eggert, 1863), Ablabesmyia sp., Anopheles sp., Bezzia sp., Chaoborus sp., Cricotopus gr. sylvestris, Chironomus melanescens Keyl, 1961, Ch. parathummi Keyl, 1961, Ch. plumosus (Linnaeus, 1758), Chironomus sp., Ch. salinarius Kieffer 1915, Cladopelma gr. lateralis, Cladotanytarsus mancus (Walker, 1856), Corynoneura coronata Edwards, 1924, C. scutellata Winnertz, 1846, Cricotopus caducus Hirvenoja, 1973, C. salinophilus Zinchenko, Makarchenko et Makarchenko, 2009, C. gr. sylvestris, Cricotopus sp., Cryptochironomus gr. defectus, Culicoides sp., Dasyhelea sp., Dicrotendipes nervosus (Staeger, 1939), D. notatus (Meigen, 1818), Endochironomus albipennis (Meigen, 1830), E. impar (Walker, 1856), Ephydra sp., Fleuria lacustris Kieffer, 1924, Glyptotendipes barbipes (Staeger, 1839), G. glaucus (Meigen, 1818), G. gripekoveni (Kieffer, 1913), G. paripes Edwards, 1929, G. salinus Michailova, 1987, Guttipelopia guttipennis (Wulp, 1974), Lauterborniella agrayloides (Kieffer, 1911), Macropelopia nebulosa (Meigen, 1804), Mallochohelea setigera (Loew, 1864), Mallochohelea sp., Microchironomus tener (Kieffer, 1918), Microtendipes pedellus (de Geer, 1776), Mochlonyx sp., Nanocladius bicolor (Zetterstedt, 1838), Odontomyia sp., Palpomyia sp., Palpomyia schmidti Goetghebuer, 1934, Paratanytarsus confusus Palmen, 1960, P. gr. lauterborni, Paratanytarsus sp., Parachironomus varus Goetghebuer, 1921, Podura aquatica Linnaeus, 1758, Polypedilum nubeculosum (Meigen, 1804), P. bicrenatum Kieffer, 1921, P. pedestre (Meigen, 1830), P. sordens (van der Wulp, 1874), Procladius ferrugineus (Kieffer, 1918), P. choreus (Meigen, 1804), Psectrocladius flavus (Johannsen, 1905), P. sordidellus (Zetterstedt, 1838), Sphaeromias pictus (Meigen, 1818), Stictochironomus crassiforceps Kieffer, 1922, S. rosenschöldi (Zetterstedt, 1781), Tanypus punctipennis (Meigen, 1818), Tanytarsus usmaënsis Pagast, 1931, T. gr. gregarius, and T. kharaensis Zorina et Zinchenko, 2009 | |
| Lake Elton basin | ||
| Phylum Arthropoda Class Insecta | Order Heteroptera | Sigara sp. |
| Order Coleoptera | Enochrus quadripunctatus (Herbs, 1797), Berosus sp., Hygrotus sp. | |
| Order Diptera | Chironomus salinarius Kieffer 1915, Cricotopus salinophilus Zinchenko, Makarchenko et Makarchenko, 2009, Ephydra sp., Palpomyia schmidti Goetghebuer, 1934, and Tanytarsus kharaensis Zorina et Zinchenko, 2009 | |
| River | Ol * | Hi | Ml | Cr | Ep | Od | He | Tr | Co | Ch | Di | Others | In Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volga River basin | |||||||||||||
| Solenaya Kuba | 9 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 29 | 6 | - | 72 |
| Bizyuk | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| Tarlyk | 9 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 25 | 2 | 2 | 65 |
| Yama 1 | 5 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 15 | 2 | - | 30 |
| Zhidkaya Solyanka | 8 | - | 3 | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 18 | - | 1 | 34 |
| Kuba | 5 | - | - | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 3 | 1 | 35 |
| Vodyanka | 7 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 19 | 3 | - | 39 |
| Otrozhina | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 27 | 4 | 1 | 56 |
| Solyanka 2 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 24 |
| Yama | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 3 | 18 | 1 | - | 37 |
| Solyanka 3 | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | 14 | 2 | - | 23 |
| Gorkaya | 4 | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 17 | - | 2 | 26 |
| Kochetnaya | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 6 | - | 3 | 16 | 6 | 2 | 49 |
| Solyanka 1 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 16 | 1 | - | 24 |
| Gashon | 3 | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 12 | - | - | 19 |
| Lake Elton basin | |||||||||||||
| Chernavka | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 8 |
| Solyanka | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 6 |
| Full Data Set | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 |
| Eigenvalues | 0.900 | 0.218 | 0.216 | 0.169 |
| Cumulative % variance of taxon data | 32.8 | 40.8 | 48.6 | 54.8 |
| Significance (probability) of axis | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Sum of all unconstrained eigenvalues | 2.743 | |||
| Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 2.126 | |||
| Three Significant Variables | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 |
| Eigenvalues | 0.891 | 0.193 | 0.165 | 0.149 |
| Cumulative % variance of taxon data | 32.5 | 39.5 | 45.6 | 51.0 |
| Significance (probability) of axis | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Sum of all unconstrained eigenvalues | 2.743 | |||
| Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 1.494 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golovatyuk, L.V.; Nazarova, L.B.; Kalioujnaia, I.J.; Grekov, I.M. Taxonomic Composition and Salinity Tolerance of Macrozoobenthos in Small Rivers of the Southern Arid Zone of the East European Plain. Biology 2023, 12, 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091271
Golovatyuk LV, Nazarova LB, Kalioujnaia IJ, Grekov IM. Taxonomic Composition and Salinity Tolerance of Macrozoobenthos in Small Rivers of the Southern Arid Zone of the East European Plain. Biology. 2023; 12(9):1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091271
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolovatyuk, Larisa V., Larisa B. Nazarova, Irina J. Kalioujnaia, and Ivan M. Grekov. 2023. "Taxonomic Composition and Salinity Tolerance of Macrozoobenthos in Small Rivers of the Southern Arid Zone of the East European Plain" Biology 12, no. 9: 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091271
APA StyleGolovatyuk, L. V., Nazarova, L. B., Kalioujnaia, I. J., & Grekov, I. M. (2023). Taxonomic Composition and Salinity Tolerance of Macrozoobenthos in Small Rivers of the Southern Arid Zone of the East European Plain. Biology, 12(9), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091271







