Contemporary Update on Clinical and Experimental Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Multi-Omics-Focused Approach to Detection and Risk Stratification
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer
2.1. Protein Biomarkers—PSA
2.2. PSA Derivatives and Related Biomarkers
2.2.1. Free PSA (fPSA)
2.2.2. Prostate Health Index (PHI)
4Kscore
2.3. Molecular Biomarkers—DNA/RNA
2.3.1. Somatic Genetic Tests, PTEN/TMPRSS2: ERG
2.3.2. Combined Prognostic Tests
PCA3
SelectMDx
ConfirmMDx
Oncotype Dx
ProMark
Prolaris
Decipher
Apifiny
3. Recent Advances in Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Single-Omics Approaches
3.1. Genomic Biomarkers
3.2. Transcriptomic Biomarkers
3.3. Proteomic Biomarkers
3.4. Epigenomic Biomarkers
3.5. Metabolomic Biomarkers
3.6. Microbiomic Biomarkers
4. Multi-Omics Approaches in Prostate Cancer
4.1. Definition and Overview of Multi-Omics
4.2. Multi-Omics Resources and Tools
4.3. Advantages of Multi-Omics Approaches in Biomarker Discovery
4.3.1. Molecular Subtyping of Prostate Cancer
4.3.2. Prognostic Biomarker Discovery
4.3.3. Single-Cell Multi-Omics
4.3.4. Spatial Multi-Omics
4.4. Clinical Applications
4.4.1. Personalized Therapy
4.4.2. Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
4.5. Challenges and Future Directions in Clinical Translation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culp, M.B.; Soerjomataram, I.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Down, L.; Barlow, M.; Bailey, S.E.; Mounce, L.T.; Merriel, S.W.; Watson, J.; Martins, T. Association between patient ethnicity and prostate cancer diagnosis following a prostate-specific antigen test: A cohort study of 730,000 men in primary care in the UK. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.-M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.-M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.-E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthes, K.L.; Limam, M.; Pestoni, G.; Held, L.; Korol, D.; Rohrmann, S. Impact of comorbidities at diagnosis on prostate cancer treatment and survival. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyll, K.; Ersvær, E.; Vlatkovic, L.; Pradhan, M.; Kildal, W.; Avranden Kjær, M.; Kleppe, A.; Hveem, T.S.; Carlsen, B.; Gill, S. Tumour heterogeneity poses a significant challenge to cancer biomarker research. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lu, X.; Shen, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X.; Yin, N.; Sun, L.; Shen, P.; Hu, C.; Jiang, H. Intratumoral heterogeneity and genetic characteristics of prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 3369–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.Y.I.; McGrath, S.; Perera, M.; Anderson, P. Chronic bacterial prostatitis leading to intrascrotal abscess after transperineal prostate biopsy. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2021, 14, e239277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, L.; Morgan, E.; Drummond, F.J.; Gavin, A. The psychological impact of prostate biopsy: Prevalence and predictors of procedure-related distress. Psycho-Oncol. 2018, 27, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, V.A.; Force, U.P.S.T. Screening for prostate cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Yang, S.-H.; Kim, A.; Kim, H.G. RNA-based biomarkers for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic response monitoring of prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 2022, 40, 105.e1–105.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, A.V.; Brito, J.M.; Yadav, K.K.; Yadav, S.S.; Tewari, A.K.; Renzulli, J. The Use of Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer Screening and Treatment. Rev. Urol. 2017, 19, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, M.W.; Salami, S.S. Biomarkers for prostate cancer detection and risk stratification. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2022, 14, 17562872221103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumbreras, B.; Parker, L.A.; Caballero-Romeu, J.P.; Gómez-Pérez, L.; Puig-García, M.; López-Garrigós, M.; García, N.; Hernández-Aguado, I. Variables Associated with False-Positive PSA Results: A Cohort Study with Real-World Data. Cancers 2022, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertok, T.; Jane, E.; Bertokova, A.; Lorencova, L.; Zvara, P.; Smolkova, B.; Kucera, R.; Klocker, H.; Tkac, J. Validating fPSA Glycoprofile as a Prostate Cancer Biomarker to Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies and Re-Biopsies. Cancers 2020, 12, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Xie, Q.; Nie, Q.W.; Ye, X. Prostate specific antigen as a biomarker for breast cancer: A meta-analysis study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4188–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhou, J.; Qu, F.; Gu, Z.; Ding, J.; Yu, Y. Modified Prostate Health Index Density Significantly Improves Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer (csPCa) Detection. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 864111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, D.A.; Chan, D.W. Biomarkers in prostate cancer: What‘s new? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, B.; Wu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Yu, Y. The modified prostate health index (PHI) outperforms PHI density in the detection of clinical prostate cancer within the PSA grey zone. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Bai, L.; Yang, Y.; Duan, J.; Gao, L. 4Kscore diagnostic value in patients with high-grade prostate cancer using cutoff values of 7.5% to 10%: A meta-analysis. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 366.e1–366.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, J.; Peacock, J.W.; Fazli, L.; Mui, A.L.; Chung, S.W.; Cox, M.E.; Monia, B.; Gleave, M.E.; Ong, C.J. Loss of PTEN is associated with progression to androgen independence. Prostate 2006, 66, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksal, I.T.; Dirice, E.; Yasar, D.; Sanlioglu, A.D.; Ciftcioglu, A.; Gulkesen, K.H.; Ozes, N.O.; Baykara, M.; Luleci, G.; Sanlioglu, S. The assessment of PTEN tumor suppressor gene in combination with Gleason scoring and serum PSA to evaluate progression of prostate carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2004, 22, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Joshua, A.M.; Cunha, I.W.; Coudry, R.A.; Fonseca, F.P.; Ludkovski, O.; Zielenska, M.; Soares, F.A.; Squire, J.A. Absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions and PTEN losses in prostate cancer is associated with a favorable outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Montironi, R.; Wang, L.; Baldrige, L.A.; Wang, J.Y.; MacLennan, G.T.; Williamson, S.R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; et al. TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion is rare compared to PTEN deletions in stage T1a prostate cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Filella, X.; Foj, L.; Milà, M.; Augé, J.M.; Molina, R.; Jiménez, W. PCA3 in the detection and management of early prostate cancer. Tumour. Biol. 2013, 34, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warli, S.M.; Warli, M.H.; Prapiska, F.F. PCA3 and TMPRSS2: ERG Urine Level as Diagnostic Biomarker of Prostate Cancer. Res. Rep. Urol. 2023, 15, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merola, R.; Tomao, L.; Antenucci, A.; Sperduti, I.; Sentinelli, S.; Masi, S.; Mandoj, C.; Orlandi, G.; Papalia, R.; Guaglianone, S.; et al. PCA3 in prostate cancer and tumor aggressiveness detection on 407 high-risk patients: A National Cancer Institute experience. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Rocco, B.; Maggi, M.; Lucarelli, G.; Falagario, U.G.; Del Giudice, F.; Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; La Civita, E.; Lasorsa, F.; et al. Beyond blood biomarkers: The role of SelectMDX in clinically significant prostate cancer identification. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, W.C.H.; de Jong, H.; Steyaert, S.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Mulders, P.F.A.; Schalken, J.A. Clinical use of the mRNA urinary biomarker SelectMDx test for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osses, D.F.; Roobol, M.J.; Schoots, I.G. Prediction Medicine: Biomarkers, Risk Calculators and Magnetic Resonance Imaging as Risk Stratification Tools in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Brown, R.E. Field effect in cancer-an update. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 39, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wojno, K.J.; Costa, F.J.; Cornell, R.J.; Small, J.D.; Pasin, E.; Van Criekinge, W.; Bigley, J.W.; Van Neste, L. Reduced Rate of Repeated Prostate Biopsies Observed in ConfirmMDx Clinical Utility Field Study. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2014, 7, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez Múgica, M.; Jalón Monzón, A. Tissue biomarkers in prostate cancer. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2022, 75, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kohaar, I.; Petrovics, G.; Srivastava, S. A Rich Array of Prostate Cancer Molecular Biomarkers: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.J.; Bjartell, A.S.; Catto, J.W.; Eggener, S.E.; Lilja, H.; Loeb, S.; Schalken, J.; Schlomm, T.; Cooperberg, M.R. Genomic Predictors of Outcome in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, D.; Goddard, A.D.; Natraj, N.; Cherbavaz, D.B.; Clark-Langone, K.M.; Snable, J.; Watson, D.; Falzarano, S.M.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Klein, E.A.; et al. Analytical validation of the Oncotype DX prostate cancer assay—A clinical RT-PCR assay optimized for prostate needle biopsies. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J. Biomarkers for prostate cancer: Prostate-specific antigen and beyond. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhr, A.; Glick, L.; Gomella, L.G. An overview of biomarkers in the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer. Can. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Berman, D.M.; Rimm, D.L.; Shipitsin, M.; Putzi, M.; Nifong, T.P.; Small, C.; Choudhury, S.; Capela, T.; Coupal, L.; et al. Development and clinical validation of an in situ biopsy-based multimarker assay for risk stratification in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipitsin, M.; Small, C.; Choudhury, S.; Giladi, E.; Friedlander, S.; Nardone, J.; Hussain, S.; Hurley, A.D.; Ernst, C.; Huang, Y.E.; et al. Identification of proteomic biomarkers predicting prostate cancer aggressiveness and lethality despite biopsy-sampling error. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, E.; Ditonno, F.; Licari, L.C.; Franco, A.; Manfredi, C.; Mossack, S.; Pandolfo, S.D.; De Nunzio, C.; Simone, G.; Leonardo, C.; et al. Tissue-Based Genomic Testing in Prostate Cancer: 10-Year Analysis of National Trends on the Use of Prolaris, Decipher, ProMark, and Oncotype DX. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschini, M.; Spahn, M.; Mattei, A.; Cheville, J.; Karnes, R.J. Incorporation of tissue-based genomic biomarkers into localized prostate cancer clinics. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erho, N.; Crisan, A.; Vergara, I.A.; Mitra, A.P.; Ghadessi, M.; Buerki, C.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Kollmeyer, T.; Fink, S.; Haddad, Z.; et al. Discovery and validation of a prostate cancer genomic classifier that predicts early metastasis following radical prostatectomy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontario, H.E. Prolaris Cell Cycle Progression Test for Localized Prostate Cancer: A Health Technology Assessment. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2017, 17, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, E.A.; Santiago-Jiménez, M.; Yousefi, K.; Robbins, B.A.; Schaeffer, E.M.; Trock, B.J.; Tosoian, J.; Haddad, Z.; Ra, S.; Karnes, R.J.; et al. Molecular Analysis of Low Grade Prostate Cancer Using a Genomic Classifier of Metastatic Potential. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.E.; Johnson, M.H.; Yousefi, K.; Davicioni, E.; Netto, G.J.; Marchionni, L.; Fedor, H.L.; Glavaris, S.; Choeurng, V.; Buerki, C.; et al. Tissue-based Genomics Augments Post-prostatectomy Risk Stratification in a Natural History Cohort of Intermediate- and High-Risk Men. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnes, R.J.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Davicioni, E.; Ghadessi, M.; Buerki, C.; Mitra, A.P.; Crisan, A.; Erho, N.; Vergara, I.A.; Lam, L.L.; et al. Validation of a genomic classifier that predicts metastasis following radical prostatectomy in an at risk patient population. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badani, K.; Thompson, D.J.; Buerki, C.; Davicioni, E.; Garrison, J.; Ghadessi, M.; Mitra, A.P.; Wood, P.J.; Hornberger, J. Impact of a genomic classifier of metastatic risk on postoperative treatment recommendations for prostate cancer patients: A report from the DECIDE study group. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den, R.B.; Santiago-Jimenez, M.; Alter, J.; Schliekelman, M.; Wagner, J.R.; Renzulli Ii, J.F.; Lee, D.I.; Brito, C.G.; Monahan, K.; Gburek, B.; et al. Decipher correlation patterns post prostatectomy: Initial experience from 2 342 prospective patients. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2016, 19, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shen, L. Advances and Trends in Omics Technology Development. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 911861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Pahwa, P.; Prakash, A.; Medhi, B. Genomic biomarkers: Unveiling the potential for precise cancer therapy response. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2023, 55, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxevanis, C.N. Biomarkers in the Era of Precision Oncology. Cancers 2023, 15, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhadi, V.K.; Armengol, G. Molecular Biomarkers in Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, W.D.; Breyer, J.P.; Johnson, S.H.; Plummer, W.D.; Smith, J.R. Prostate cancer risk variants of the HOXB genetic locus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duca, R.B.; Massillo, C.; Farré, P.L.; Graña, K.D.; Moro, J.; Gardner, K.; Lacunza, E.; De Siervi, A. Hsa-miR-133a-3p, miR-1-3p, GOLPH3 and JUP combination results in a good biomarker to distinguish between prostate cancer and non-prostate cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 997457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieronymus, H.; Murali, R.; Tin, A.; Yadav, K.; Abida, W.; Moller, H.; Berney, D.; Scher, H.; Carver, B.; Scardino, P.; et al. Tumor copy number alteration burden is a pan-cancer prognostic factor associated with recurrence and death. Elife 2018, 7, e37294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, M.; Peitzsch, C.; Gorodetska, I.; Börner, C.; Klink, B.; Dubrovska, A. Network-based analysis of prostate cancer cell lines reveals novel marker gene candidates associated with radioresistance and patient relapse. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.S.; Aggarwal, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.G.; Thomas, G.V.; Beer, T.M.; Quigley, D.A.; Foye, A.; Playdle, D.; Huang, J.; et al. Genomic Drivers of Poor Prognosis and Enzalutamide Resistance in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopsack, K.H.; Nandakumar, S.; Wibmer, A.G.; Haywood, S.; Weg, E.S.; Barnett, E.S.; Kim, C.J.; Carbone, E.A.; Vasselman, S.E.; Nguyen, B.; et al. Oncogenic Genomic Alterations, Clinical Phenotypes, and Outcomes in Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3230–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, U.; Graf, R.P.; Nussenzveig, R.H.; Fisher, V.; Tukachinsky, H.; Schrock, A.B.; Li, G.; Ross, J.S.; Sayegh, N.; Tripathi, N.; et al. SPOP Mutations as a Predictive Biomarker for Androgen Receptor Axis-Targeted Therapy in De Novo Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4917–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, L.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Ribeiro, J.R.; Carneiro, B.A.; Dizon, D.S.; Angara, K.; Mattox, T.; Wu, S.; Xiu, J.; Walker, P.; et al. Opposing Roles of SPOP Mutations in Human Prostate and Endometrial Cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, e2300088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casamassimi, A.; Federico, A.; Rienzo, M.; Esposito, S.; Ciccodicola, A. Transcriptome Profiling in Human Diseases: New Advances and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, R.; Shirley, N.; Bleackley, M.; Dolan, S.; Shafee, T. Transcriptomics technologies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, J.; Ross-Adams, H.; Pirrò, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, X.; Gadaleta, E.; Ahmad, A.S.; North, B.V.; Kammerer-Jacquet, S.F.; et al. The Transcriptomic Landscape of Prostate Cancer Development and Progression: An Integrative Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, C.; Goicoechea, I.; Goñi, A.; Schramm, M.; Armesto, M.; Arestin, M.; Manterola, L.; Tellaetxe, M.; Alberdi, A.; Nogueira, L.; et al. The Urinary Transcriptome as a Source of Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.; Rezaeian, I.; Singireddy, S.; Cavallo-Medved, D.; Porter, L.A.; Rueda, L. Transcriptomics Signature from Next-Generation Sequencing Data Reveals New Transcriptomic Biomarkers Related to Prostate Cancer. Cancer Inform. 2019, 18, 1176935119835522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Pan, J.; Huang, S.; Peng, X.; Zou, X.; Luo, Y.; Ren, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; He, P.; et al. Downregulation of miR-133a-3p promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, I.; Bylicky, M.A.; Sandfort, V.; Chopra, S.; Martello, S.; Graves, E.E.; Coleman, C.N.; Aryankalayil, M.J. The lncRNAs LINC00261 and LINC00665 are upregulated in long-term prostate cancer adaptation after radiotherapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, V.; Xu, X.; Livingstone, J.; Soares, F.; Jeon, J.; Zeng, Y.; Hua, J.T.; Petricca, J.; Guo, H.; et al. Widespread and Functional RNA Circularization in Localized Prostate Cancer. Cell 2019, 176, 831–843.e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, G. Screening and identification of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-related circRNA and miRNA in prostate cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Bansal, G.; Narang, A.; Basak, T.; Abbas, T.; Dash, D. Integrating transcriptome and proteome profiling: Strategies and applications. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanase, C.; Albulescu, R.; Neagu, M. Proteomic Approaches for Biomarker Panels in Cancer. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2016, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsogiannou, M.; Boyer, J.B.; Valdeolivas, A.; Remy, E.; Calzone, L.; Audebert, S.; Rocchi, P.; Camoin, L.; Baudot, A. Integrative proteomic and phosphoproteomic profiling of prostate cell lines. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launonen, K.M.; Paakinaho, V.; Sigismondo, G.; Malinen, M.; Sironen, R.; Hartikainen, J.M.; Laakso, H.; Visakorpi, T.; Krijgsveld, J.; Niskanen, E.A.; et al. Chromatin-directed proteomics-identified network of endogenous androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4567–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, E.V.; Pereira, B.A.; Lawrence, M.G.; Ma, X.; Rebello, R.J.; Chan, H.; Niranjan, B.; Wu, Y.; Ellem, S.; Guan, X.; et al. Proteomic Profiling of Human Prostate Cancer-associated Fibroblasts (CAF) Reveals LOXL2-dependent Regulation of the Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 18, 1410–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Gato, D.; Thysell, E.; Tyanova, S.; Crnalic, S.; Santos, A.; Lima, T.S.; Geiger, T.; Cox, J.; Widmark, A.; Bergh, A.; et al. The Proteome of Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Reveals Heterogeneity with Prognostic Implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitprez, F.; Fossati, N.; Vano, Y.; Freschi, M.; Becht, E.; Lucianò, R.; Calderaro, J.; Guédet, T.; Lacroix, L.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and CD8(+) T-cell Infiltrate are Associated with Clinical Progression in Patients with Node-positive Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conteduca, V.; Ku, S.Y.; Puca, L.; Slade, M.; Fernandez, L.; Hess, J.; Bareja, R.; Vlachostergios, P.J.; Sigouros, M.; Mosquera, J.M.; et al. SLFN11 Expression in Advanced Prostate Cancer and Response to Platinum-based Chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Peng, A. Cancer epigenetics: From laboratory studies and clinical trials to precision medicine. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liu, Y. DNA methylation in human diseases. Genes. Dis. 2018, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-C.; Okino, S.T.; Dahiya, R. DNA methylation in prostate cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2004, 1704, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, G. Markers of clinical utility in the differential diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, S143–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaraswamy, A.; Welker Leng, K.R.; Westbrook, T.C.; Yates, J.A.; Zhao, S.G.; Evans, C.P.; Feng, F.Y.; Morgan, T.M.; Alumkal, J.J. Recent Advances in Epigenetic Biomarkers and Epigenetic Targeting in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkach, Y.; Zarbl, R.; Bauer, S.; Ritter, M.; Ellinger, J.; Hauser, S.; Hüser, L.; Klauck, S.M.; Altevogt, P.; Sültmann, H. DNA promoter methylation and ERG regulate the expression of CD24 in prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Li, C.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X. Identification of prostate cancer specific methylation biomarkers from a multi-cancer analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Petricca, J.; Ye, W.; Guan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, N.; Gong, L.; Shen, S.Y.; Hua, J.T.; Crumbaker, M. The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized and metastatic prostate tumors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngollo, M.; Lebert, A.; Daures, M.; Judes, G.; Rifai, K.; Dubois, L.; Kemeny, J.-L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Bignon, Y.-J.; Guy, L. Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratchian, M.; Tiwari, R.; Khalighi, S.; Chakravarthy, A.; Yuan, W.; Berk, M.; Li, J.; Guerinot, A.; de Bono, J.; Makarov, V. H3K9 methylation drives resistance to androgen receptor–antagonist therapy in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114324119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.F.; Michishita-Kioi, E.; Xi, Y.; Tasselli, L.; Kioi, M.; Moqtaderi, Z.; Tennen, R.I.; Paredes, S.; Young, N.L.; Chen, K. SIRT7 links H3K18 deacetylation to maintenance of oncogenic transformation. Nature 2012, 487, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.; Massa, F.; Kaminski, L.; Clavel, S.; Djabari, Z.; Robert, G.; Laurent, K.; Michiels, J.-F.; Durand, M.; Ricci, J.-E. Sirtuin 7: A new marker of aggressiveness in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small molecule metabolites: Discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segers, K.; Declerck, S.; Mangelings, D.; Heyden, Y.V.; Eeckhaut, A.V. Analytical techniques for metabolomic studies: A review. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 2297–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.K.; Ma, M.H.; Tse, H.F.; Yeung, K.F.; Tsang, H.F.; Chu, M.K.M.; Kan, C.M.; Cho, W.C.S.; Ng, L.B.W.; Chan, L.W.C. The applications of metabolomics in the molecular diagnostics of cancer. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratlin, J.L.; Serkova, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.G. Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franko, A.; Shao, Y.; Heni, M.; Hennenlotter, J.; Hoene, M.; Hu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Birkenfeld, A.L. Human prostate cancer is characterized by an increase in urea cycle metabolites. Cancers 2020, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudka, I.; Thysell, E.; Lundquist, K.; Antti, H.; Iglesias-Gato, D.; Flores-Morales, A.; Bergh, A.; Wikström, P.; Gröbner, G. Comprehensive metabolomics analysis of prostate cancer tissue in relation to tumor aggressiveness and TMPRSS2-ERG fusion status. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braadland, P.R.; Giskeødegård, G.; Sandsmark, E.; Bertilsson, H.; Euceda, L.R.; Hansen, A.F.; Guldvik, I.J.; Selnæs, K.M.; Grytli, H.H.; Katz, B. Ex vivo metabolic fingerprinting identifies biomarkers predictive of prostate cancer recurrence following radical prostatectomy. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Niu, L.; Li, L.; Li, T.; Duan, L.; He, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, L.; Wu, X.; Luo, C. Identification of the metabolic signatures of prostate cancer by mass spectrometry-based plasma and urine metabolomics analysis. Prostate 2021, 81, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Liu, H.; Xie, L.-X.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.-H. High-throughput metabolomics enables biomarker discovery in prostate cancer. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobi, A.; Qian, F.; Lugade, A.A.; Odunsi, K. Tryptophan catabolism and cancer immunotherapy targeting IDO mediated immune suppression. Tumor Immune Microenviron. Cancer Progress. Cancer Ther. 2017, 1036, 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-M.; Mahon, K.L.; Weir, J.M.; Mundra, P.A.; Spielman, C.; Briscoe, K.; Gurney, H.; Mallesara, G.; Marx, G.; Stockler, M.R.; et al. A distinct plasma lipid signature associated with poor prognosis in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunrinola, G.A.; Oyewale, J.O.; Oshamika, O.O.; Olasehinde, G.I. The Human Microbiome and Its Impacts on Health. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8045646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The human microbiome project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjo, R.; Sabbah, D.A.; Al Bawab, A.Q. Unlocking the Potential of the Human Microbiome for Identifying Disease Diagnostic Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, E.; White, J.R.; Yu, S.H.; Kulac, I.; Ertunc, O.; De Marzo, A.M.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Mangold, L.A.; Partin, A.W.; Sfanos, K.S. Profiling the Urinary Microbiome in Men with Positive versus Negative Biopsies for Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Wu, D.C.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, J.W.; Juan, Y.S.; Li, C.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lee, H.Y. Exploring the Association between Gut and Urine Microbiota and Prostatic Disease including Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer Using 16S rRNA Sequencing. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernigoni, N.; Zagato, E.; Calcinotto, A.; Troiani, M.; Mestre, R.P.; Calì, B.; Attanasio, G.; Troisi, J.; Minini, M.; Mosole, S.; et al. Commensal bacteria promote endocrine resistance in prostate cancer through androgen biosynthesis. Science 2021, 374, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.M.; Shrestha, E.; Peiffer, L.B.; Sfanos, K.S. The microbiome in prostate inflammation and prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Alwine, J.C.; Wei, Z.; Tian, T.; Shih, N.; Sperling, C.; Guzzo, T.; Feldman, M.D.; Robertson, E.S. Microbiome signatures in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, A.R.; Ferreira, M.V.; Mota, R.M.; Ferrasi, A.C.; Pardini, M.I.; Rabenhorst, S.H. Gastric adenocarcinoma and Helicobacter pylori: Correlation with p53 mutation and p27 immunoexpression. Cancer Epidemiol. 2010, 34, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Ikegawa, S.; Alves, J.M.; Zhou, B.; Kobayashi, A.; Iida, T.; Mitamura, K.; Tanabe, G.; Serrano, M.; De Guzman, A.; et al. Clostridium scindens: A human gut microbe with a high potential to convert glucocorticoids into androgens. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2437–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersanelli, M.; Mosca, E.; Remondini, D.; Giampieri, E.; Sala, C.; Castellani, G.; Milanesi, L. Methods for the integration of multi-omics data: Mathematical aspects. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17 (Suppl. S2), 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naithani, N.; Sinha, S.; Misra, P.; Vasudevan, B.; Sahu, R. Precision medicine: Concept and tools. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2021, 77, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danckaert, W.; Spaas, M.; Sundahl, N.; De Bruycker, A.; Fonteyne, V.; De Paepe, E.; De Wagter, C.; Vanhaecke, L.; Ost, P. Microbiome and metabolome dynamics during radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2023, 189, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedias, C.; Marie, H.; Pageneck, C.; Glory, J.; Vincent, A.; Lawrence, A.; Olaitan, I.A.; David, E. Multi-omics data integration approach identifies potential biomarkers for Prostate cancer. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.K.; Ha, Y.S.; Lee, J.N.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Chun, S.Y.; Kwon, T.G.; Lee, S. Comparative Proteome Profiling and Mutant Protein Identification in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Cells by Quantitative Mass Spectrometry-based Proteogenomics. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wei, G.H.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, S.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Su, H.; et al. Whole-genome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Prostate Cancer Identify New Genetic Alterations Driving Disease Progression. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Lue, H.W.; Podolak, J.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Serawat, A.; Alumkal, J.J.; Fiehn, O.; Thomas, G.V. Multi-Omics Analyses Detail Metabolic Reprogramming in Lipids, Carnitines, and Use of Glycolytic Intermediates between Prostate Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Prostate Adenocarcinoma. Metabolites 2019, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Han, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Chao, F.; Song, Z.; Chen, G. Deep Learning-Based Multi-Omics Integration Robustly Predicts Relapse in Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 893424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiebish, M.A.; Cullen, J.; Mishra, P.; Ali, A.; Milliman, E.; Rodrigues, L.O.; Chen, E.Y.; Tolstikov, V.; Zhang, L.; Panagopoulos, K.; et al. Multi-omic serum biomarkers for prognosis of disease progression in prostate cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antman, E.; Weiss, S.; Loscalzo, J. Systems pharmacology, pharmacogenetics, and clinical trial design in network medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2012, 4, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Liu, T. Investigating the Multi-Target Pharmacological Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa Willd Acting on Prostate Cancer: A Network Pharmacology Approach. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q.; Taly, V.; Tan, F. Integrative analysis of multi-omics data for liquid biopsy. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Centenera, M.M.; Hodgson, J.T.; Nguyen, E.V.; Butler, L.M.; Daly, R.J.; Nguyen, L.K. A Boolean-based machine learning framework identifies predictive biomarkers of HSP90-targeted therapy response in prostate cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1094321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carels, N.; Sgariglia, D.; Junior, M.G.V.; Lima, C.R.; Carneiro, F.R.G.; Silva, G.F.D.; Silva, F.; Scardini, R.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Andrade, C.V.; et al. A Strategy Utilizing Protein-Protein Interaction Hubs for the Treatment of Cancer Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, V.J.; Bandrowski, A.E.; Pepin, A.S.; Gonzalez, B.J.; Desfeux, A. OMICtools: An informative directory for multi-omic data analysis. Database 2014, 2014, bau069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Huang, H.D.; Hsu, J.B.; Chang, T.H. Biomarker Identification through Multiomics Data Analysis of Prostate Cancer Prognostication Using a Deep Learning Model and Similarity Network Fusion. Cancers 2021, 13, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salachan, P.V.; Rasmussen, M.; Ulhoi, B.P.; Jensen, J.B.; Borre, M.; Sorensen, K.D. Spatial whole transcriptome profiling of primary tumor from patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.J.; Li, S.H.; Wei, L.L.; Luo, B.; He, R.Q.; Xia, S. Role of miR-452-5p in the tumorigenesis of prostate cancer: A study based on the Cancer Genome Atl(TCGA), Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and bioinformatics analysis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, H. Identification of prognosis biomarkers of prostatic cancer in a cohort of 498 patients from TCGA. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2019, 43, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Fan, W.; Luo, H.; Zhu, X. The emerging roles of artificial intelligence in cancer drug development and precision therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, A.P.; Anderson, P.C. Predicting drug activity against cancer cells by random forest models based on minimal genomic information and chemical properties. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, H.K.; Xu, H.J.; Hu, D.K.; Hankey, W.; Chen, L.; Xiao, J.; Liang, C.Z.; Zhao, B.; Xu, L.F. Single-cell analysis revealing the metabolic landscape of prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2024, 26, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, R.; Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Single-cell omics traces the heterogeneity of prostate cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Dang, H.X.; Zhang, M.; Quigley, D.A.; Feng, F.Y.; Maher, C.A. Single cell-transcriptomic analysis informs the lncRNA landscape in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. NPJ Genom. Med. 2024, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, S.; Huang, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Integrative multi-omics and drug-response characterization of patient-derived prostate cancer primary cells. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vargas Roditi, L.; Jacobs, A.; Rueschoff, J.H.; Bankhead, P.; Chevrier, S.; Jackson, H.W.; Hermanns, T.; Fankhauser, C.D.; Poyet, C.; Chun, F.; et al. Single-cell proteomics defines the cellular heterogeneity of localized prostate cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Wang, W.; Abudurexiti, M.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Shi, G.; Du, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Tan, C.; et al. Integration Analysis of Single-Cell Multi-Omics Reveals Prostate Cancer Heterogeneity. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2305724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raufaste-Cazavieille, V.; Santiago, R.; Droit, A. Multi-omics analysis: Paving the path toward achieving precision medicine in cancer treatment and immuno-oncology. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 962743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.; Murphy, B.T.; Boyce, S.; Flynn, L.; Gilgunn, S.; O‘Rourke, C.J.; Rooney, C.; Stöckmann, H.; Walsh, A.L.; Finn, S. Integrating biomarkers across omic platforms: An approach to improve stratification of patients with indolent and aggressive prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Hai, Y.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Hu, X.; Zou, X.; Hao, J. Integrative multi-omics analysis unveils stemness-associated molecular subtypes in prostate cancer and pan-cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic significance. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Xiao, D.; Li, F.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Zeng, H.; Zheng, J.; Lai, W. Multi-omics analysis reveals a macrophage-related marker gene signature for prognostic prediction, immune landscape, genomic heterogeneity, and drug choices in prostate cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1122670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.-Q.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, S.; Wang, X. EZH2 as a prognostic factor and its immune implication with molecular characterization in prostate cancer: An integrated multi-omics in silico analysis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Niraula, D.; Gates, E.D.H.; Fu, J.; Luo, Y.; Nyflot, M.J.; Bowen, S.R.; El Naqa, I.M.; Cui, S. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in precision oncology: A review on enhancing discoverability through multiomics integration. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Roy, S.; Vengadesan, K.; Gupta, D. Multi-omics approach for identifying CNV-associated lncRNA signatures with prognostic value in prostate cancer. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, M.M.; Li, Y.; Chu, L.W.; Haile, R.W.; Whittemore, A.S.; Han, S.S.; Moore, S.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Andrulis, I.L.; John, E.M. Metabolomic profiles in breast cancer: A pilot case-control study in the breast cancer family registry. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Abugessaisa, I.; Maier, D.; Teschendorff, A.; Merkenschlager, M.; Gisel, A.; Ballestar, E.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E.; Conesa, A.; Tegnér, J. Data integration in the era of omics: Current and future challenges. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
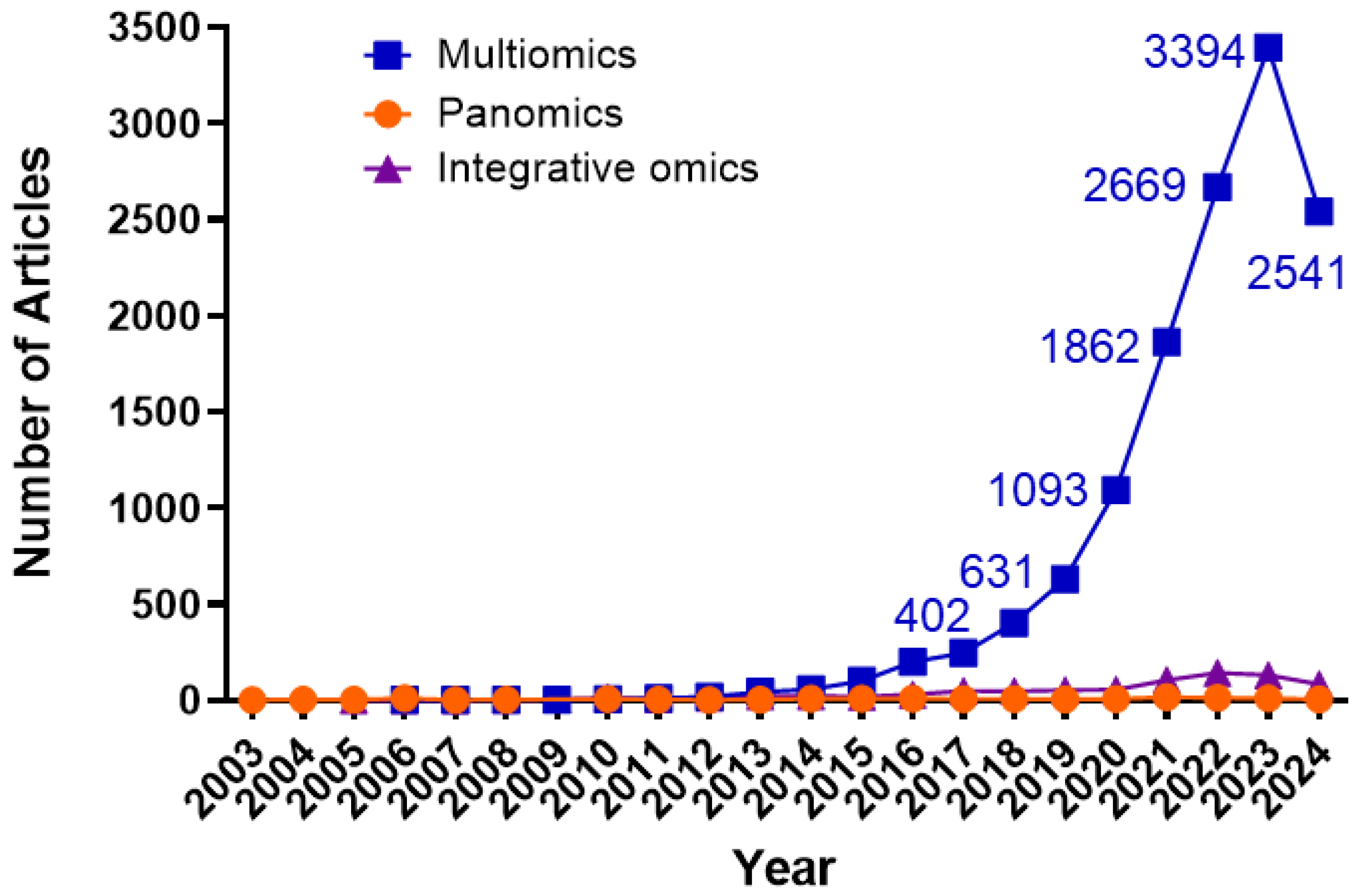
| Omics Approach | Number of Publications in Cancer | Number of Publications in Prostate Cancer | Years of Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics | 424,352 | 17,357 | 1951–2024 |
| Transcriptomics | 99.833 | 4899 | 1982–2024 |
| Proteomics | 44,766 | 1995 | 1996–2024 |
| Microbiomics | 19,232 | 364 | 1979–2024 |
| Metabolomics | 16,066 | 793 | 2000–2024 |
| Epigenomics | 11,053 | 477 | 1975–2024 |
| Multi-omics | 5782 | 158 | 2009–2024 |
| Integrative Omics | 5582 | 174 | 2007–2024 |
| Panomics | 4870 | 147 | 2005–2024 |
| Metagenomics | 2333 | 35 | 2006–2024 |
| Lipidomics | 2173 | 120 | 2003–2024 |
| Phosphoproteomics | 2057 | 73 | 2001–2024 |
| Glycoproteomics | 703 | 58 | 2005–2024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hachem, S.; Yehya, A.; El Masri, J.; Mavingire, N.; Johnson, J.R.; Dwead, A.M.; Kattour, N.; Bouchi, Y.; Kobeissy, F.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; et al. Contemporary Update on Clinical and Experimental Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Multi-Omics-Focused Approach to Detection and Risk Stratification. Biology 2024, 13, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100762
Hachem S, Yehya A, El Masri J, Mavingire N, Johnson JR, Dwead AM, Kattour N, Bouchi Y, Kobeissy F, Rais-Bahrami S, et al. Contemporary Update on Clinical and Experimental Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Multi-Omics-Focused Approach to Detection and Risk Stratification. Biology. 2024; 13(10):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100762
Chicago/Turabian StyleHachem, Sana, Amani Yehya, Jad El Masri, Nicole Mavingire, Jabril R. Johnson, Abdulrahman M. Dwead, Naim Kattour, Yazan Bouchi, Firas Kobeissy, Soroush Rais-Bahrami, and et al. 2024. "Contemporary Update on Clinical and Experimental Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Multi-Omics-Focused Approach to Detection and Risk Stratification" Biology 13, no. 10: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100762
APA StyleHachem, S., Yehya, A., El Masri, J., Mavingire, N., Johnson, J. R., Dwead, A. M., Kattour, N., Bouchi, Y., Kobeissy, F., Rais-Bahrami, S., Mechref, Y., Abou-Kheir, W., & Woods-Burnham, L. (2024). Contemporary Update on Clinical and Experimental Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Multi-Omics-Focused Approach to Detection and Risk Stratification. Biology, 13(10), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100762













