Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis for Etiology Classification and Biomarker Discovery in Stroke: Advancing towards Precision Medicine
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Correlation Analysis: This approach involves assessing the pairwise correlations between omics datasets. By examining the co-variation patterns between different types of omics data, researchers can identify relationships and potential regulatory mechanisms.
- Dimensionality Reduction Techniques: Dimensionality reduction techniques, such as principal component analysis (PCA) and independent component analysis (ICA), are used to reduce the high-dimensional nature of omics data. These techniques extract relevant features and capture the major sources of variation within the data, facilitating data integration and visualization.
- Integrative Clustering: Integrative clustering methods aim to identify clusters or subgroups of samples based on the integration of multi-omics data. These techniques consider similarities and dissimilarities across different omics layers, enabling the identification of distinct molecular subtypes or phenotypes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. mRNA Expression
2.3. MicroRNA Expression
2.4. Microarray Expression of circRNAs
2.5. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling
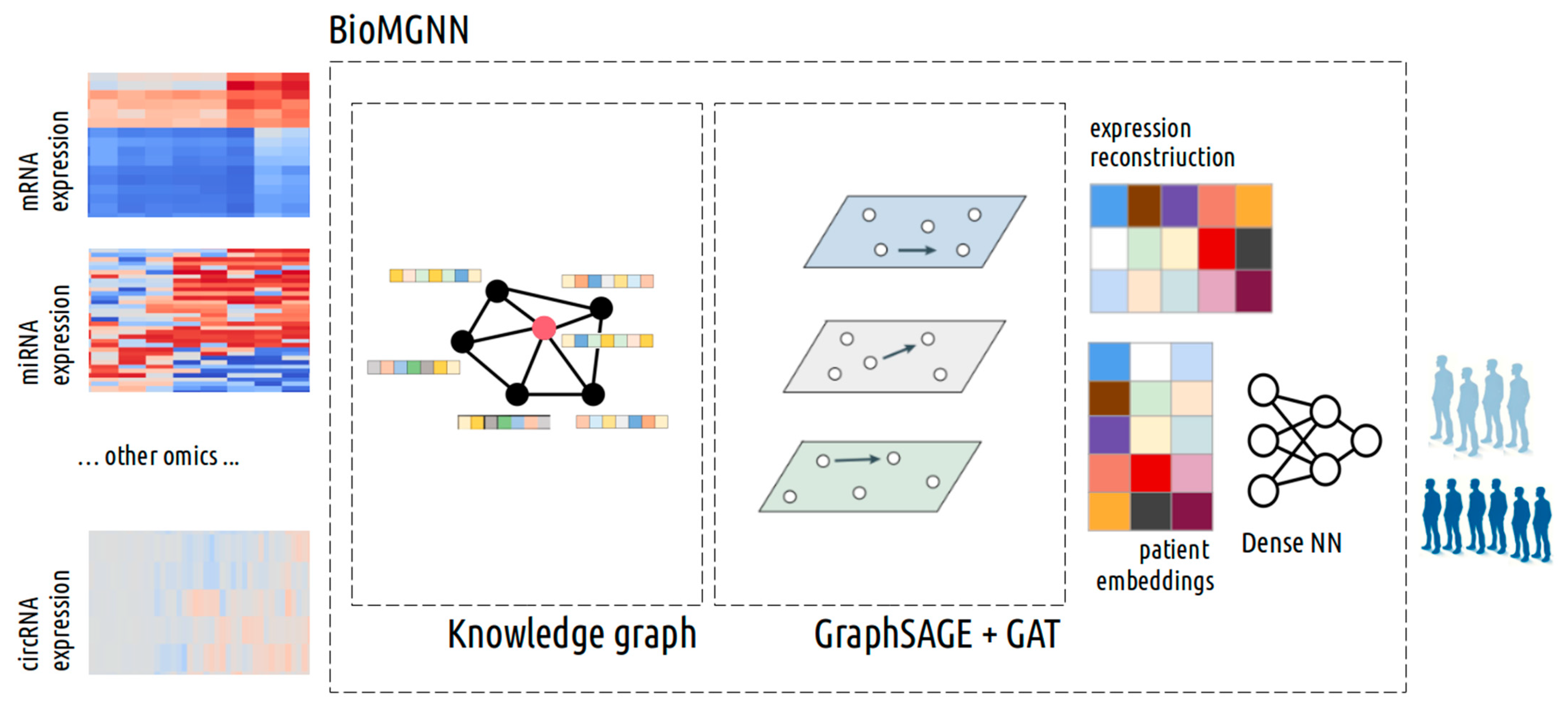
2.6. Annotation and Biomedical Knowledge Graph Construction
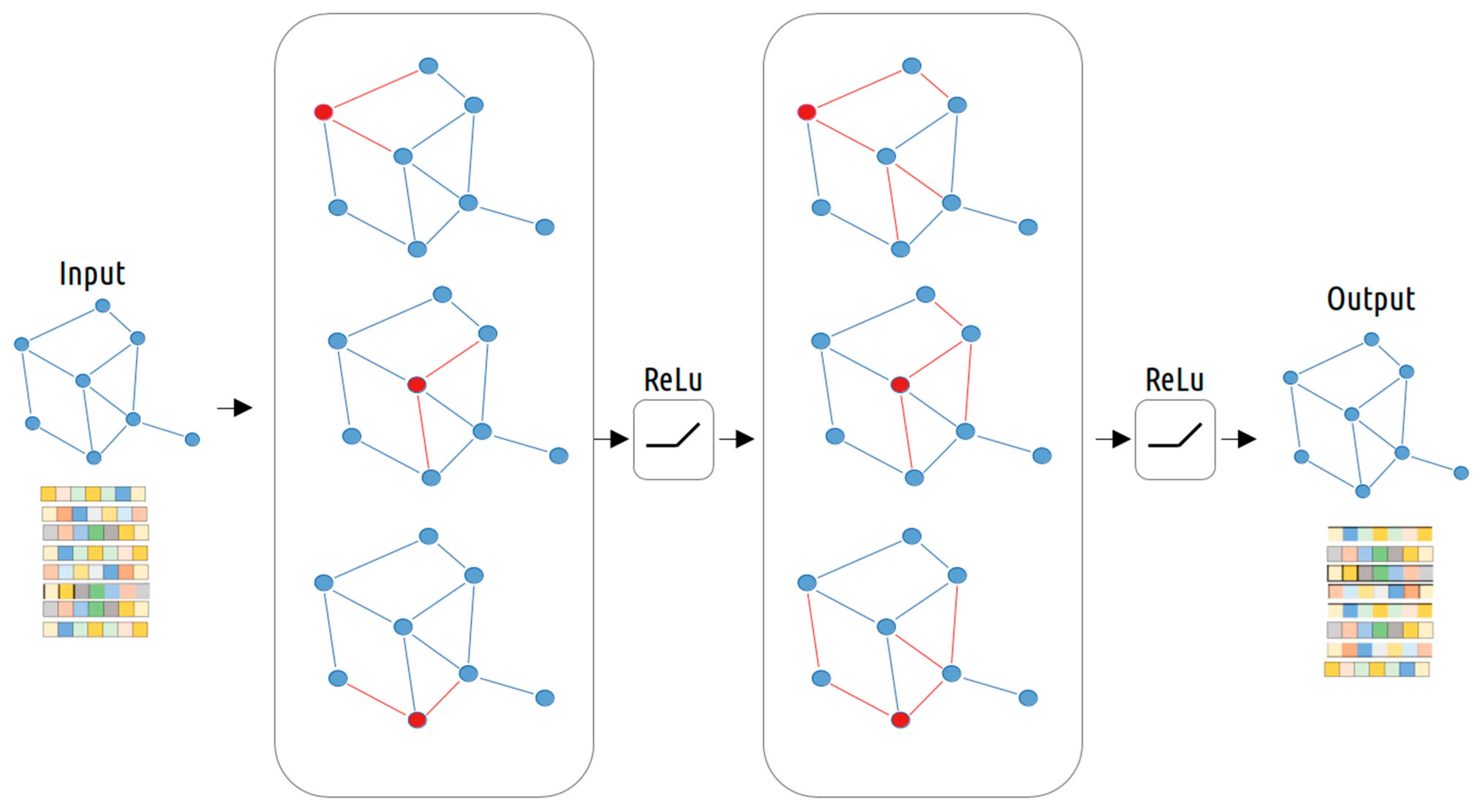
2.7. Graph-Based Multi-Omics Data Integration
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characterisation
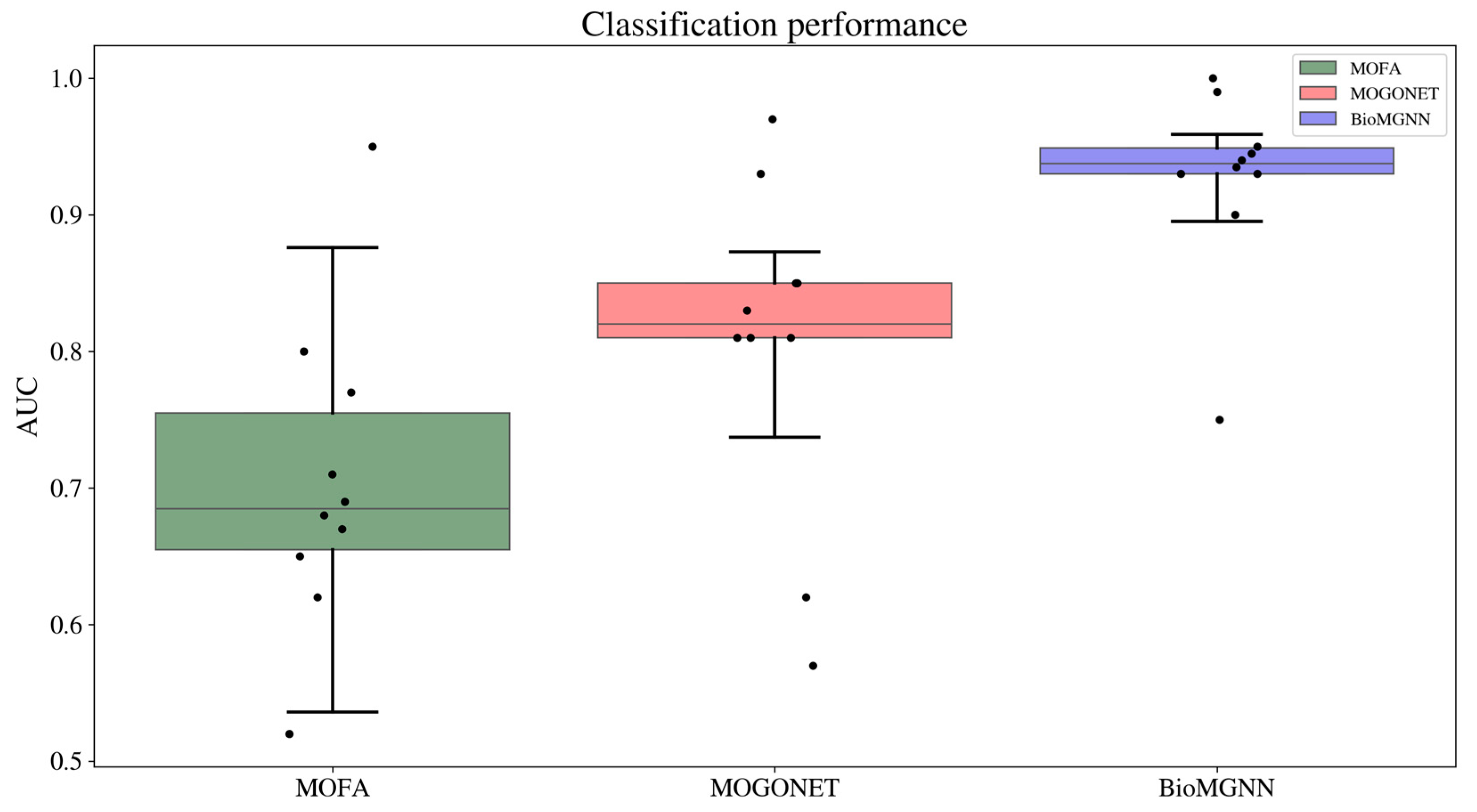
3.2. Patient Classification Task
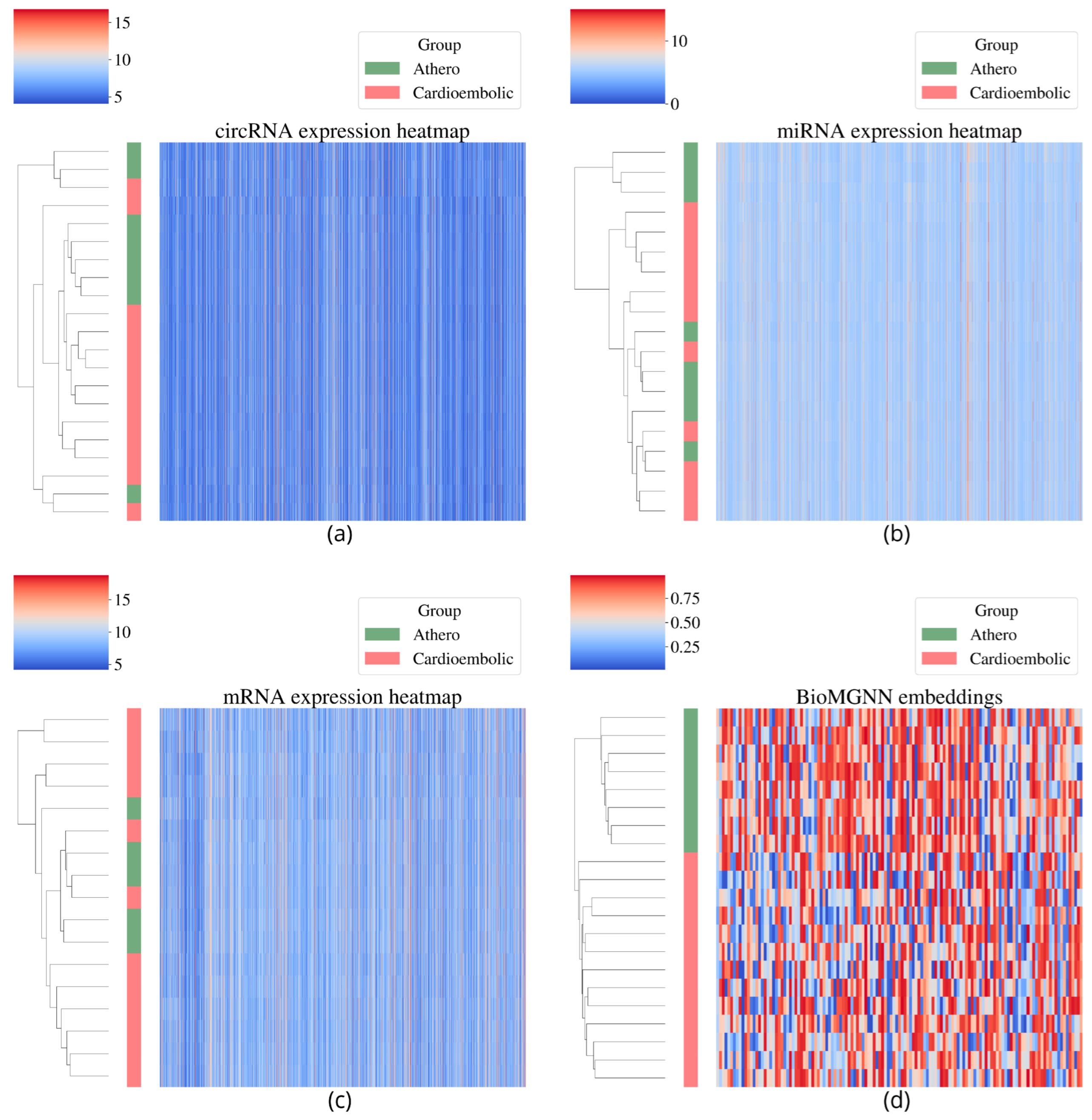
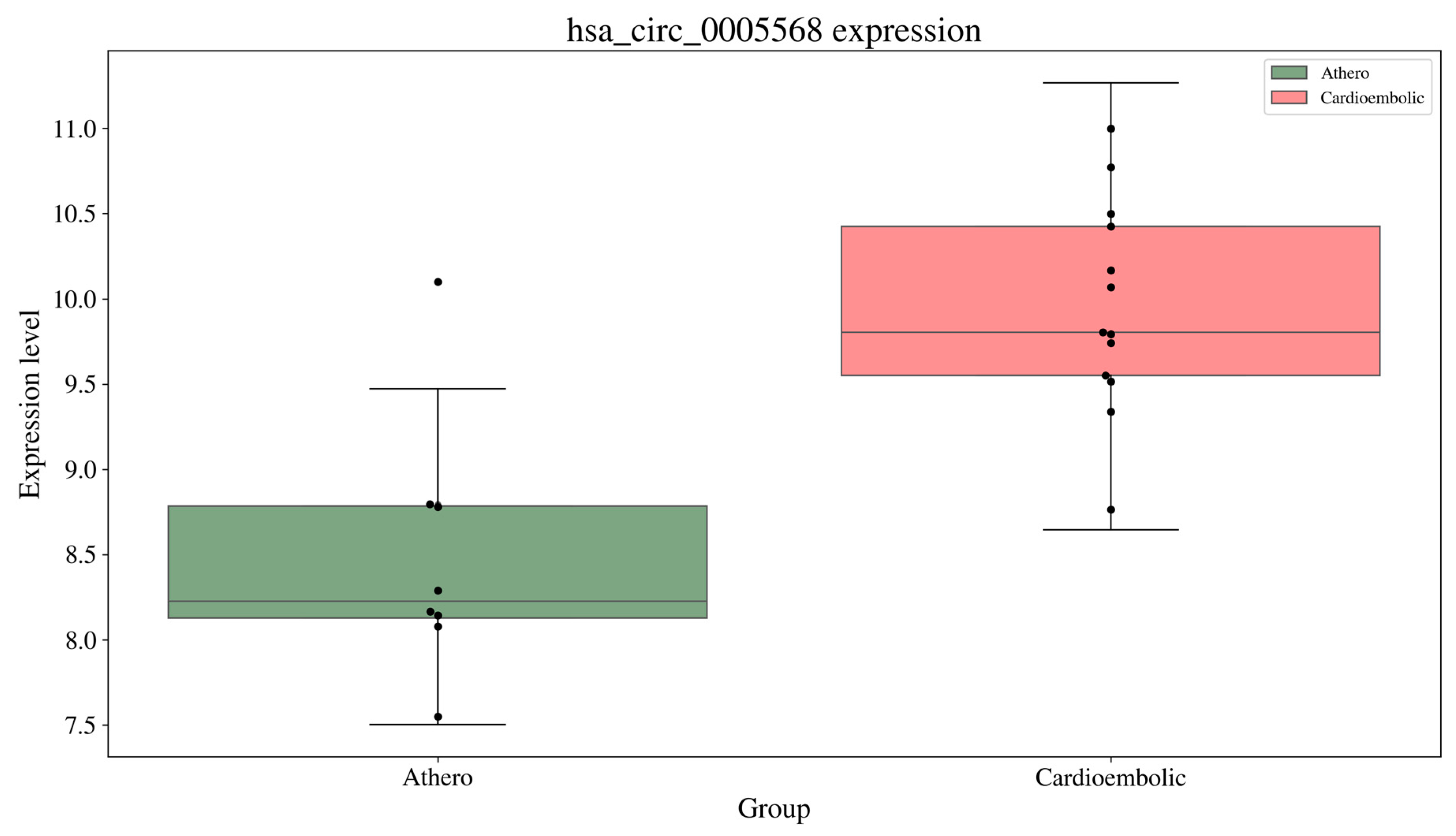
3.3. Biomarker Module Discovery
3.4. Comparison with Other Biomarker Discovery Methodologies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association|Circulation. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659 (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Adams, H.P.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of Subtype of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Definitions for Use in a Multicenter Clinical Trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedi, I.; Szapáry, L.; Csécsei, P.; Csanádi, Z.; Csiba, L. Potential Biological Markers of Atrial Fibrillation: A Chance to Prevent Cryptogenic Stroke. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8153024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costamagna, G.; Bonato, S.; Corti, S.; Meneri, M. Advancing Stroke Research on Cerebral Thrombi with Omic Technologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martha, S.R.; Levy, S.H.; Federico, E.; Levitt, M.R.; Walker, M. Machine Learning Analysis of the Cerebrovascular Thrombi Lipidome in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2023, 55, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, R.; Santamaría, E.; Rubio, I.; Ausín, K.; Ostolaza, A.; Labarga, A.; Roldán, M.; Zandio, B.; Mayor, S.; Bermejo, R.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Profiling of Thrombotic Material Obtained by Endovascular Thrombectomy in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suissa, L.; Guigonis, J.-M.; Graslin, F.; Robinet-Borgomano, E.; Chau, Y.; Sedat, J.; Lindenthal, S.; Pourcher, T. Combined Omic Analyzes of Cerebral Thrombi: A New Molecular Approach to Identify Cardioembolic Stroke Origin. Stroke 2021, 52, 2892–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamtchum-Tatuene, J.; Jickling, G.C. Blood Biomarkers for Stroke Diagnosis and Management. Neuromol. Med 2019, 21, 344–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpaz, D.; Seet, R.C.S.; Marks, R.S.; Tok, A.I.Y. Blood-Based Biomarkers Are Associated with Different Ischemic Stroke Mechanisms and Enable Rapid Classification between Cardioembolic and Atherosclerosis Etiologies. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpaz, D.; Bajpai, R.; Ng, G.J.L.; Soljak, M.; Marks, R.S.; Cheung, C.; Arumugam, T.V.; Quek, A.M.L.; Tok, A.I.Y.; Seet, R.C.S. Blood Biomarkers to Detect New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation and Cardioembolism in Ischemic Stroke Patients. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontiers|State of the Field in Multi-Omics Research: From Computational Needs to Data Mining and Sharing. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2020.610798/full (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Debette, S.; Chasman, D.I. Multiomic Approaches to Stroke: The Beginning of a Journey. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 20, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T. AIME: Autoencoder-Based Integrative Multi-Omics Data Embedding That Allows for Confounder Adjustments. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, A. Integrate Multi-Omics Data with Biological Interaction Networks Using Multi-View Factorization AutoEncoder (MAE). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wekesa, J.S.; Kimwele, M. A Review of Multi-Omics Data Integration through Deep Learning Approaches for Disease Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1199087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzel, L.; Fischer, D.S.; Günnemann, S.; Theis, F.J. Graph Representation Learning for Single-Cell Biology. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2021, 28, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandak, P.; Huang, K.; Zitnik, M. Building a Knowledge Graph to Enable Precision Medicine. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, D.; Lim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S. Biomedical Knowledge Graph Learning for Drug Repurposing by Extending Guilt-by-Association to Multiple Layers. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.; Xu, J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph Convolutional Networks: A Comprehensive Review. Comput. Soc. Netw. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Parthasarathy, S.; Moosavinasab, S.; Huang, Y.; Lin, S.M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Sun, H. Graph Embedding on Biomedical Networks: Methods, Applications and Evaluations. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.-C.; You, Z.-H.; Huang, D.-S.; Kwoh, C.K. Graph Representation Learning in Bioinformatics: Trends, Methods and Applications. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandy, J.; Daly, R. GraphOmics: An Interactive Platform to Explore and Integrate Multi-Omics Data. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razin, A.; Cedar, H. DNA Methylation and Gene Expression. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuna, M.; Urdánoz-Casado, A.; Sánchez-Ruiz de Gordoa, J.; Zelaya, M.V.; Labarga, A.; Lepesant, J.M.J.; Roldán, M.; Blanco-Luquin, I.; Perdones, Á.; Larumbe, R.; et al. DNA Methylation Signature of Human Hippocampus in Alzheimer’s Disease Is Linked to Neurogenesis. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA Biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs Are the Predominant Transcript Isoform from Hundreds of Human Genes in Diverse Cell Types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Shan, G. Circular RNAs in Eukaryotic Cells. Curr. Genom. 2015, 16, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidsley, R.; Y Wong, C.C.; Volta, M.; Lunnon, K.; Mill, J.; Schalkwyk, L.C. A Data-Driven Approach to Preprocessing Illumina 450K Methylation Array Data. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.M.; Cotton, A.M.; Lam, L.L.; Farré, P.; Emberly, E.; Brown, C.J.; Robinson, W.P.; Kobor, M.S. Additional Annotation Enhances Potential for Biologically-Relevant Analysis of the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip Array. Epigenet. Chromatin 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lemire, M.; Choufani, S.; Butcher, D.T.; Grafodatskaya, D.; Zanke, B.W.; Gallinger, S.; Hudson, T.J.; Weksberg, R. Discovery of Cross-Reactive Probes and Polymorphic CpGs in the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 Microarray. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA Sequences to Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.-D.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. miRTarBase Update 2022: An Informative Resource for Experimentally Validated miRNA-Target Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudekula, D.B.; Panda, A.C.; Grammatikakis, I.; De, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. CircInteractome: A Web Tool for Exploring Circular RNAs and Their Interacting Proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milacic, M.; Beavers, D.; Conley, P.; Gong, C.; Gillespie, M.; Griss, J.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D672–D678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, W.L.; Ying, R.; Leskovec, J. Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1706.02216. [Google Scholar]
- Momanyi, B.M.; Zhou, Y.-W.; Grace-Mercure, B.K.; Temesgen, S.A.; Basharat, A.; Ning, L.; Tang, L.; Gao, H.; Lin, H.; Tang, H. SAGESDA: Multi-GraphSAGE Networks for Predicting SnoRNA-Disease Associations. Curr. Res. Struct. Biol. 2024, 7, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- PyG Documentation—Pytorch_Geometric Documentation. Available online: https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles|PNAS. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0506580102 (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Jiao, H.; Li, L.; Zheng, J. C-Myc Protects Mice from Ischemia Stroke through Elevating microRNA-200b-5p-Regulated SIRT1 Expression. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 176, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostolaza, A.; Blanco-Luquin, I.; Urdánoz-Casado, A.; Rubio, I.; Labarga, A.; Zandio, B.; Roldán, M.; Martínez-Cascales, J.; Mayor, S.; Herrera, M.; et al. Circular RNA Expression Profile in Blood According to Ischemic Stroke Etiology. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argelaguet, R.; Velten, B.; Arnol, D.; Dietrich, S.; Zenz, T.; Marioni, J.C.; Buettner, F.; Huber, W.; Stegle, O. Multi-Omics Factor Analysis—A Framework for Unsupervised Integration of Multi-omics Data Sets. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Shao, W.; Huang, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Huang, K. MOGONET Integrates Multi-Omics Data Using Graph Convolutional Networks Allowing Patient Classification and Biomarker Identification. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discovery of Multi-Dimensional Modules by Integrative Analysis of Cancer Genomic Data|Nucleic Acids Research|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/40/19/9379/2414808 (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Tenenhaus, A.; Philippe, C.; Guillemot, V.; Le Cao, K.-A.; Grill, J.; Frouin, V. Variable Selection for Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis. Biostatistics 2014, 15, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Shannon, C.P.; Gautier, B.; Rohart, F.; Vacher, M.; Tebbutt, S.J.; Lê Cao, K.-A. DIABLO: An Integrative Approach for Identifying Key Molecular Drivers from Multi-Omics Assays. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Koo, B.; Oh, M.; Kim, T.-B.; Kim, S. GOAT: Gene-Level Biomarker Discovery from Multi-Omics Data Using Graph ATtention Neural Network for Eosinophilic Asthma Subtype. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GEO Platform | Array Name | |
|---|---|---|
| circRNA | GPL21825 | Arraystar Human CircRNA microarray V2 |
| methylation | GPL21145 | Infinium MethylationEPIC |
| microRNA | GPL19322 | miRCURY LNA microRNA Array, 7th gen |
| mRNA | GPL21185 | Agilent-072363 SurePrint G3 Human GE v3 8 × 60 K |
| Atherothrombotic (n = 8) | Cardioembolic (n = 14) | Undetermined (n = 8) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age—years, median (IQR) | 70 (55–80) | 75 (70.5–77) | 66.5 (49–77) |
| Male, n (%) | 7 (87.5) | 7 (50) | 5 (62.5) |
| High blood pressure, n (%) | 6 (75) | 12 (85.7) | 3 (37.5) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 2 (25) | 2 (14.3) | 2 (25) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 3 (37.5) | 9 (64.3) | 5 (62.5) |
| Smoker, n (%) | 4 (50) | 2 (20) | 3 (42.9) |
| Cardiopathy, n (%) | 3 (37.5) | 6 (42.9) | 0 (0) |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 0 (0) | 15 (100) | 0 (0) |
| Peripheral arteropathy, n (%) | 2 (25) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Basal mRankin, median (IQR) | 0.5 (0–1) | 0 (0–1.25) | 0 (0–0.75) |
| Basal NIHSS, median (RIQ) | 8.5 (5–18) | 20 (17–22) | 19 (18–20) |
| Significant ipsilateral carotid stenosis (%) | 8 (100) | 0 (0) | 1 (14.3) |
| Hemorrhagic transformation, n (%) | 5 (62.5) | 4 (28.6) | 2 (25) |
| Discharge mRankin, median (IQR) | 4.5 (2–6) | 4 (2–5) | 3 (0.5–5) |
| BioMGNN | miRNA | circRNA | Methyl | mRNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| accuracy | 0.95 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.77 |
| precision | 0.93 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.77 |
| recall | 0.95 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.77 |
| F1 score | 0.96 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.78 | 0.86 |
| AUC | 0.95 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labarga, A.; Martínez-Gonzalez, J.; Barajas, M. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis for Etiology Classification and Biomarker Discovery in Stroke: Advancing towards Precision Medicine. Biology 2024, 13, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050338
Labarga A, Martínez-Gonzalez J, Barajas M. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis for Etiology Classification and Biomarker Discovery in Stroke: Advancing towards Precision Medicine. Biology. 2024; 13(5):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050338
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabarga, Alberto, Judith Martínez-Gonzalez, and Miguel Barajas. 2024. "Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis for Etiology Classification and Biomarker Discovery in Stroke: Advancing towards Precision Medicine" Biology 13, no. 5: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050338
APA StyleLabarga, A., Martínez-Gonzalez, J., & Barajas, M. (2024). Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis for Etiology Classification and Biomarker Discovery in Stroke: Advancing towards Precision Medicine. Biology, 13(5), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050338






