Paired Primary and Recurrent Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Cytogenetic Alterations, BAP1 Gene Expression Profile and Patient Outcome
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RM Patients and Samples
2.2. Molecular Analysis via Copy Number Arrays
2.3. Histological and Immunohistochemical Studies
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
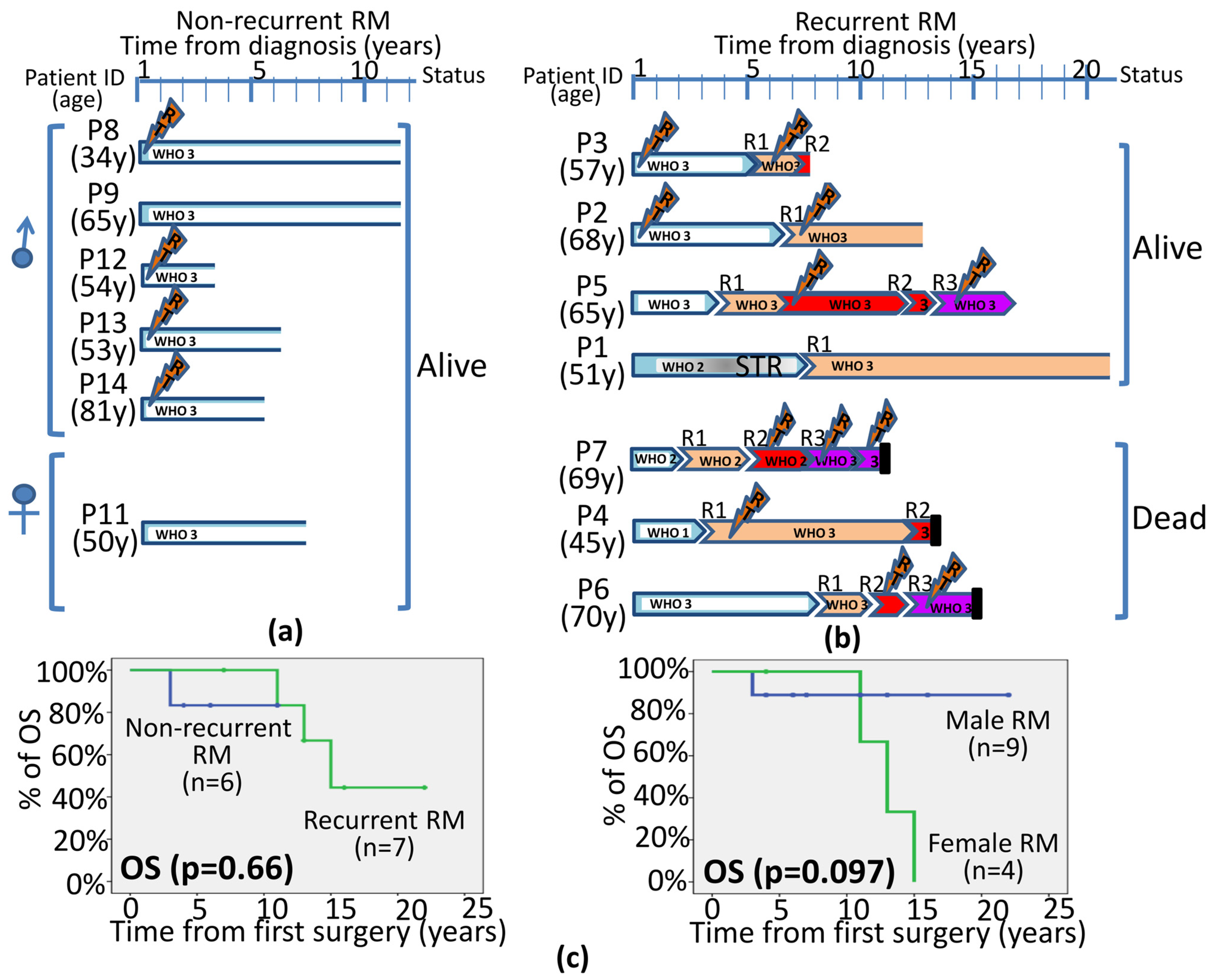
3.1. Demographics, Clinical and Histopathological Features of Recurrent vs. Non-Recurrent RM
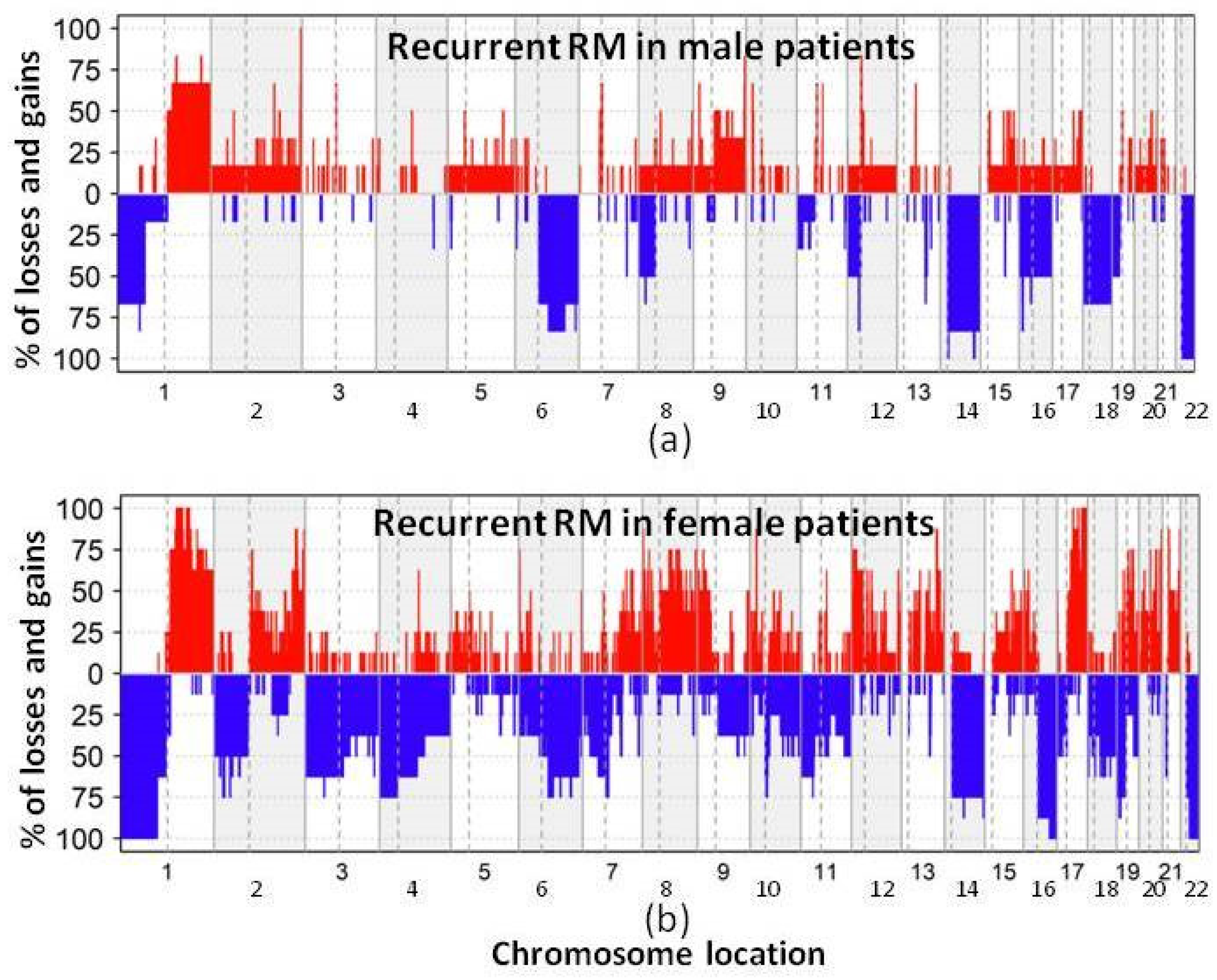
3.2. DNA Copy Number Changes in Primary Non-Recurrent vs. Recurrent RM
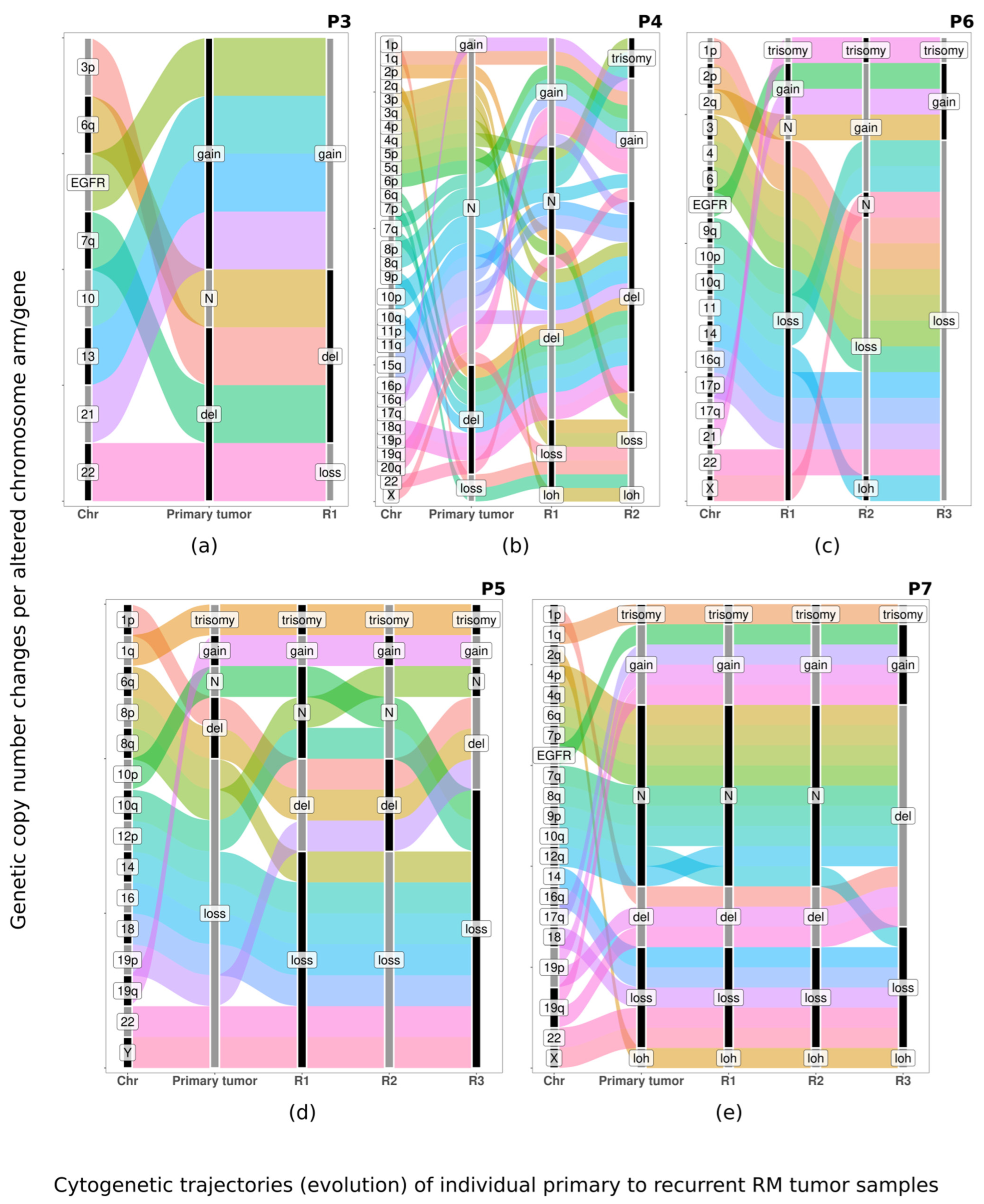
3.3. Pattern of Evolution of CNA Profiles in Paired Primary vs. Recurrent Tumors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro-oncology 2019, 21, v1–v100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaubel, R.A.; Chen, S.G.; Raleigh, D.R.; Link, M.J.; Chicoine, M.R.; Barani, I.; Jenkins, S.M.; Aleff, P.A.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Burger, P.C.; et al. Meningiomas with Rhabdoid Features Lacking Other Histologic Features of Malignancy: A Study of 44 Cases and Review of the Literature. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofrese, G.; Della Pepa, G.M.; Sabatino, G.; Esposito, G.; Puca, A.; Albanese, A. Intraparenchymal Recurrence of a Dural Meningioma: Association with Rhabdoid Alterations with Aggressive Biological and Clinical Behaviour. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 25, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Ho, J.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lin, J.-W. Rhabdoid Papillary Meningioma: A Clinicopathologic Case Series Study. Neuropathology 2011, 31, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntoon, K.; Toland, A.M.S.; Dahiya, S. Meningioma: A Review of Clinicopathological and Molecular Aspects. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 579599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, A.; Rath, G.; Mohanty, L.; Behera, P.; Mohapatro, S.; Lenka, A.; Soumendra Sahu De, S. Rhabdoid Meningioma—An Uncommon and Aggressive Variant. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2013, 5, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagli, P.; Karabagli, H.; Yavas, G. Aggressive Rhabdoid Meningioma with Osseous, Papillary and Chordoma-like Appearance. Neuropathology 2014, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyja, E.; Grajkowska, W.; Nauman, P.; Bonicki, W.; Bojarski, P.; Marchel, A. Necrotic Rhabdoid Meningiomas with Aggressive Clinical Behavior. Clin. Neuropathol. 2010, 29, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.-H. Prognostic Factors and Long-Term Outcomes of Primary Intracranial Rhabdoid Meningioma: A Systematic Review. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 196, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Zhang, G.-B.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Li, C.-B.; Zhang, L.-W.; Li, D.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.-T. World Health Organization Grade III (Nonanaplastic) Meningioma: Experience in a Series of 23 Cases. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e754–e762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Lin, J.-W.; Wang, H.-C.; Lee, T.-C.; Ho, J.-T.; Lin, Y.-J. Clinicopathologic Analysis of Rhabdoid Meningioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling, F.; Fodi, C.; Hoffmann, E.; Renovanz, M.; Skardelly, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Schittenhelm, J.; Honegger, J.; Tatagiba, M. The Role of Simpson Grading in Meningiomas after Integration of the Updated WHO Classification and Adjuvant Radiotherapy. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehresman, J.S.; Garzon-Muvdi, T.; Rogers, D.; Lim, M.; Gallia, G.L.; Weingart, J.; Brem, H.; Bettegowda, C.; Chaichana, K.L. The Relevance of Simpson Grade Resections in Modern Neurosurgical Treatment of World Health Organization Grade I, II, and III Meningiomas. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, e588–e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslund-Vinding, J.; Skjoth-Rasmussen, J.; Poulsgaard, L.; Fugleholm, K.; Mirian, C.; Maier, A.D.; Santarius, T.; Rom Poulsen, F.; Meling, T.; Bartek, J.J.; et al. Proposal of a New Grading System for Meningioma Resection: The Copenhagen Protocol. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, C.S.; Richardson, G.E.; Mustafa, M.A.; Taweel, B.A.; Bakhsh, A.; Kumar, S.; Keshwara, S.M.; Islim, A.I.; Mehta, S.; Millward, C.P.; et al. Volumetric Growth and Growth Curve Analysis of Residual Intracranial Meningioma. Neurosurgery 2022, 92, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemée, J.-M.; Corniola, M.V.; Da Broi, M.; Joswig, H.; Scheie, D.; Schaller, K.; Helseth, E.; Meling, T.R. Extent of Resection in Meningioma: Predictive Factors and Clinical Implications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itamura, K.; Chang, K.-E.; Lucas, J.; Donoho, D.A.; Giannotta, S.; Zada, G. Prospective Clinical Validation of a Meningioma Consistency Grading Scheme: Association with Surgical Outcomes and Extent of Tumor Resection. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbrunner, R.; Stavrinou, P.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Sahm, F.; Mawrin, C.; Weber, D.C.; Preusser, M.; Minniti, G.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Lefranc, F.; et al. EANO Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Meningiomas. Neuro-oncology 2021, 23, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, M.O.; Ryan, C.T.; Singh, R.; Lanning, R.M.; Reiner, A.S.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Tabar, V.; Gutin, P.H. Predictors of Treatment Response and Survival Outcomes in Meningioma Recurrence with Atypical or Anaplastic Histology. Neurosurgery 2018, 82, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterberger, A.; Nguyen, T.; Duong, C.; Kondajji, A.; Kulinich, D.; Yang, I. Meta-Analysis of Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Intracranial Atypical and Malignant Meningiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 152, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, S.-W.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, M.-S.; Kang, H.; Dho, Y.-S.; Seo, Y.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.-K. Adjuvant Radiotherapy versus Observation Following Gross Total Resection for Atypical Meningioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, C.; Philbrick, B.D.; Adamson, D.C. Meningioma: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.; Barani, I.; Chamberlain, M.; Kaley, T.J.; McDermott, M.; Raizer, J.; Schiff, D.; Weber, D.C.; Wen, P.Y.; Vogelbaum, M.A. Meningiomas: Knowledge Base, Treatment Outcomes, and Uncertainties. A RANO Review. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q.; Hawasli, A.H.; Huang, J.; Chicoine, M.R.; Kim, A.H. An Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithm for the Management of WHO Grade II and III Meningiomas. Neurosurg. Focus 2015, 38, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q.; Gong, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhong, P.; Che, X.; Jiang, C.; Huang, F.; Zheng, K.; Li, S.; et al. Clinicopathological Analysis of Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Report of 12 Cases and a Systematic Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2013, 79, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, M.; Li, J.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, S. Intraspinal Rhabdoid Meningioma Metastasis to the Liver. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydzewski, N.R.; Lesniak, M.S.; Chandler, J.P.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Pollom, E.; Tate, M.C.; Bloch, O.; Kruser, T.; Dalal, P.; Sachdev, S. Gross Total Resection and Adjuvant Radiotherapy Most Significant Predictors of Improved Survival in Patients with Atypical Meningioma. Cancer 2018, 124, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birua, G.J.S.; Sadashiva, N.; Konar, S.; Rao, S.; Shukla, D.; Krishna, U.; Saini, J.; Santosh, V. Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Clinicopathological Analysis of a Rare Variant of Meningioma. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnoni, L.; Aburas, S.; Giraffa, M.; Russo, I.; Chiarella, V.; Paolini, S.; Tini, P.; Minniti, G. Radiation Therapy for Atypical and Anaplastic Meningiomas: An Overview of Current Results and Controversial Issues. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 3019–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, P.H.; Sousa, P.; Otero, A.; Goncalves, J.M.; Ruiz, L.; Lopes, M.C.; de Oliveira, C.; Orfao, A.; Tabernero, M.D. Proposal for a New Risk Stratification Classification for Meningioma Based on Patient Age, WHO Tumor Grade, Size, Localization, and Karyotype. Neuro-oncology 2014, 16, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Shu, K.; Lei, T. Analysis of Prognostic Factors of World Health Organization Grade Ⅲ Meningiomas. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 593073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, M.D.; Maillo, A.; Nieto, A.B.; Diez-Tascon, C.; Lara, M.; Sousa, P.; Otero, A.; Castrillo, A.; Patino-Alonso Mdel, C.; Espinosa, A.; et al. Delineation of Commonly Deleted Chromosomal Regions in Meningiomas by High-Density Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Genotyping Arrays. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2012, 51, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido Ruiz, P.A.; González-Tablas, M.; Pasco Peña, A.; Zelaya Huerta, M.V.; Ortiz, J.; Otero, Á.; Corchete, L.A.; Ludeña, M.D.; Caballero Martínez, M.C.; Córdoba Iturriagagoitia, A.; et al. Clinical, Histopathologic and Genetic Features of Rhabdoid Meningiomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, J.; Hoffman, S.E.; Tavakol, S.; Woodward, E.; Maury, E.A.; Bhave, V.; Greenwald, N.F.; Nassiri, F.; Aldape, K.; Zadeh, G.; et al. A Molecularly Integrated Grade for Meningioma. Neuro-oncology 2022, 24, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Abedalthagafi, M.; Vaubel, R.A.; Merrill, P.H.; Nayyar, N.; Gill, C.M.; Brewster, R.; Bi, W.L.; Agarwalla, P.K.; Thorner, A.R.; et al. Germline and Somatic BAP1 Mutations in High-Grade Rhabdoid Meningiomas. Neuro-oncology 2017, 19, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Harbour, J.W.; Brugarolas, J.; Bononi, A.; Pagano, I.; Dey, A.; Krausz, T.; Pass, H.I.; Yang, H.; Gaudino, G. Biological Mechanisms and Clinical Significance of BAP1 Mutations in Human Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1103–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Santagata, S. BAP1 Mutations in High-Grade Meningioma: Implications for Patient Care. Neuro-oncology 2017, 19, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanpay, A.C.; Barkley, A.; White-Dzuro, G.A.; Cimino, P.J.; Gonzalez-Cuyar, L.F.; Lockwood, C.; Halasz, L.M.; Hisama, F.M.; Ferreira, M. Giant Pediatric Rhabdoid Meningioma Associated with a Germline BAP1 Pathogenic Variation: A Rare Clinical Case. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.N.; Gardner, U.G.; Yaney, A.; Prevedello, D.M.; Koboldt, D.C.; Thomas, D.L.; Mardis, E.R.; Palmer, J.D. Germline BAP1 Mutation in a Family with Multi-Generational Meningioma with Rhabdoid Features: A Case Series and Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 721712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, G.; Liestøl, K.; Van Loo, P.; Moen Vollan, H.K.; Eide, M.B.; Rueda, O.M.; Chin, S.-F.; Russell, R.; Baumbusch, L.O.; Caldas, C.; et al. Copynumber: Efficient Algorithms for Single- and Multi-Track Copy Number Segmentation. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermel, C.H.; Schumacher, S.E.; Hill, B.; Meyerson, M.L.; Beroukhim, R.; Getz, G. GISTIC2.0 Facilitates Sensitive and Confident Localization of the Targets of Focal Somatic Copy-Number Alteration in Human Cancers. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, J.R.; Ziman, R.; Yuen, R.K.C.; Feuk, L.; Scherer, S.W. The Database of Genomic Variants: A Curated Collection of Structural Variation in the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D986–D992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bi, W.L.; Aizer, A.; Hua, L.; Tian, M.; Den, J.; Tang, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Atypical and Anaplastic Meningioma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’steen, L.; Amdur, R.J.; Morris, C.G.; Mendenhall, W.M. Challenging the Concept That Late Recurrence and Death from Tumor are Common after Fractionated Radiotherapy for Benign Meningioma. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyre, M.; Gauchotte, G.; Giry, M.; Froehlich, S.; Pallud, J.; Graillon, T.; Bielle, F.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Varlet, P.; Figarella-Branger, D.; et al. De Novo and Secondary Anaplastic Meningiomas: A Study of Clinical and Histomolecular Prognostic Factors. Neuro-oncology 2018, 20, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzevick, J.; Gibson, A.; Tatman, P.; Emerson, S.; Ferreira, M. WHO Grade III Meningioma: De Novo Tumors Show Improved Progression Free Survival as Compared to Secondary Progressive Tumors. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 91, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.C.; Pisapia, D.J.; Ramakrishna, R.; Schwartz, T.H.; Pannullo, S.C.; Knisely, J.P.S.; Chiang, G.C.; Ivanidze, J.; Stieg, P.E.; Liechty, B.; et al. Outcomes Following Upfront Radiation versus Monitoring in Atypical Meningiomas: 16-Year Experience at a Tertiary Medical Center. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Silvani, A.; Tramacere, I.; Farinotti, M.; Legnani, F.; Pinzi, V.; Pollo, B.; Erbetta, A.; Gaviani, P. Long Term Follow up in 183 High Grade Meningioma: A Single Institutional Experience. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Landry, A.P.; Nassiri, F.; Merali, Z.A.; Patel, Z.; Lee, G.; Rogers, L.; Zuccato, J.A.; Voisin, M.R.; Munoz, D.; et al. Outcomes and Predictors of Response to Fractionated Radiotherapy as Primary Treatment for Intracranial Meningiomas. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 41, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclef, L.; Ahmed, O.; Estavoyer, B.; Larrivée, B.; Labrecque, N.; Nijnik, A.; Affar, E.B. Roles and Mechanisms of BAP1 Deubiquitinase in Tumor Suppression. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, F.; Liu, J.; Patil, V.; Mamatjan, Y.; Wang, J.Z.; Hugh-White, R.; Macklin, A.M.; Khan, S.; Singh, O.; Karimi, S.; et al. A Clinically Applicable Integrative Molecular Classification of Meningiomas. Nature 2021, 597, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, S.; Nassiri, F.; Bi, W.L.; Dunn, I.F.; Hanemann, C.O.; Horbinski, C.M.; Hashizume, R.; James, C.D.; Mawrin, C.; Noushmehr, H.; et al. Molecular and Translational Advances in Meningiomas. Neuro-oncology 2019, 21, i4–i17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Stichel, D.; Hielscher, T.; Sievers, P.; Berghoff, A.S.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Euskirchen, P.; Blume, C.; Patel, A.; et al. Integrated Molecular-Morphologic Meningioma Classification: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis, Retrospectively and Prospectively Validated. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3839–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, P.; Gonzalez-Tablas, M.; Otero, A.; Pascual, D.; Ruiz, L.; Miranda, D.; Sousa, P.; Goncalves, J.M.; Lopes, M.C.; Orfao, A.; et al. Genetic/Molecular Alterations of Meningiomas and the Signaling Pathways Targeted. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10671–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Tablas, M.; Prieto, C.; Arandia, D.; Jara-Acevedo, M.; Otero, Á.; Pascual, D.; Ruíz, L.; Álvarez-Twose, I.; García-Montero, A.C.; Orfao, A.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals Recurrent but Heterogeneous Mutational Profiles in Sporadic WHO Grade 1 Meningiomas. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 740782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, M.; Jara-Acevedo, M.; Nieto, A.B.; Caballero, A.R.; Otero, A.; Sousa, P.; Goncalves, J.; Domingues, P.H.; Orfao, A. Association between Mutation of the NF2 Gene and Monosomy 22 in Menopausal Women with Sporadic Meningiomas. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzawa, S.; Nishihara, H.; Tanaka, S. Genetic Landscape of Meningioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016, 33, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, P.; Hielscher, T.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Reuss, D.E.; Berghoff, A.S.; Neidert, M.C.; Wirsching, H.-G.; Mawrin, C.; Ketter, R.; et al. CDKN2A/B Homozygous Deletion Is Associated with Early Recurrence in Meningiomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, V.; Lu, R.; Mirchia, K.; Van Ziffle, J.; Devine, P.; Lee, J.; Phillips, J.J.; Perry, A.; Raleigh, D.R.; Lucas, C.-H.G.; et al. Loss of P16 Expression Is a Sensitive Marker of CDKN2A Homozygous Deletion in Malignant Meningiomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 145, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.B.; English, C.W.; Chen, W.C.; Athukuri, P.; Bayley, J.C.; Brandt, V.L.; Shetty, A.; Hadley, C.C.; Choudhury, A.; Lu, H.-C.; et al. Even Heterozygous Loss of CDKN2A/B Greatly Accelerates Recurrence in Aggressive Meningioma. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 145, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
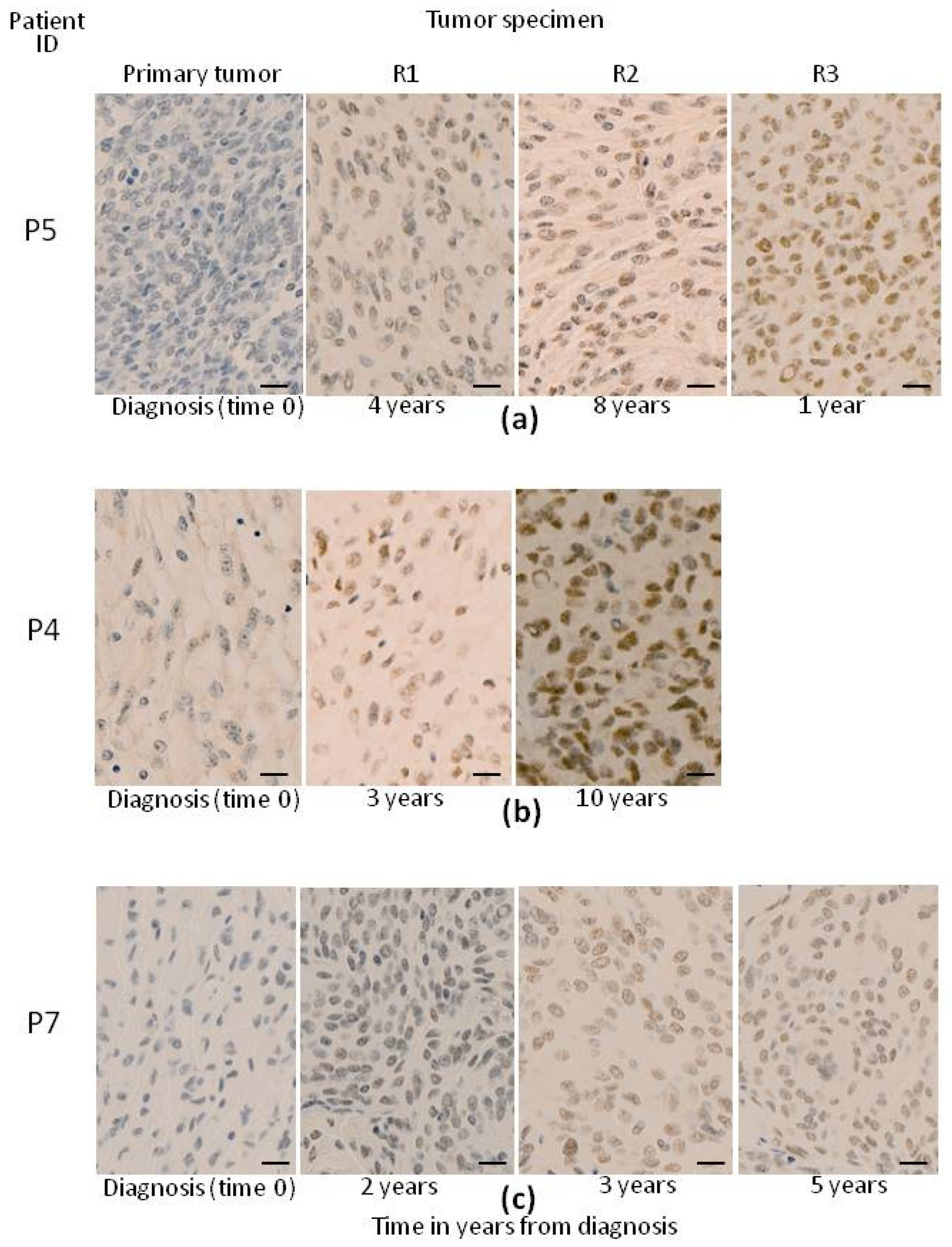
| Disease Features | Diagnosis | p-Value | Recurrences of RM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Recurrent (n = 8) | Recurrent (n = 7) Ө | R1 (n = 7) | R2 # (n = 4) | R3 (n = 3) | |||
| Age * (range) | 59 (34–81) | 61 (45–69) | 0.9 | 69 (48–75) | 72 (58–74) | 78 (73–79) | 0.06 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Man (n = 10) | 75% | 57% | 57% | 40% | 33% | ||
| Woman (n = 5) | 25% | 43% | 0.4 | 43% | 60% | 67% | 0.7 |
| % of rhabdoid cells | |||||||
| <50% (n = 7; 4 m & 3 w) | 25% | 71% | 43% | 75% | 33% | ||
| >50% (n = 8; 6 m & 2 w) | 75% | 29% | 0.07 | 57% | 25% | 67% | 0.5 |
| WHO grade | |||||||
| 1 | 0 | 14% | 0% | 0% | 0% | ||
| 2 | 0 | 72% | 0.003 | 14% | 25% | 0% | 0.6 |
| 3 | 100% | 14% | 86% | 75% | 100% | ||
| BAP1 expression (n = 26) & | 100% | 33% | 0.02 | 71% | 100% | 100% | 0.3 |
| Follow-Up Features | Diagnosis | p-Value | RM Recurrences | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Recurrent RM (n = 8) | Recurrent RM (n = 7) | R1 (n = 7) | R2 (n = 4) $ | R3 (n = 3) | ||||
| Treatment | ||||||||
| Surgery: | % GTR | 88% | 86% | 0.9 | 100% | 50% | 0% | 0.03 |
| % STR | 12% | 14% | 0% | 50% | 100% | |||
| % Radiotherapy | 50% | 29% | 0.4 | 43% | 50% | 67% | 0.2 | |
| Follow up (years) * | 6 (3–11) | 13 (7–22) | 0.008 | 5 (2–9) | 3 (1–9) | 3 (<1–5) | 0.01 | |
| Time to recurrence # | - | - | - | 68 (20–114) | 33 (21–118) | 53 (9–71) | 0.2 | |
| % of deaths | 14% ɛ | 43% | 0.5 | 0% | 20% | 67% | 0.05 | |
| CNA | Chr Location [N. of Genes] | RM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Type | Non-Recurrent (n = 8) | Recurrent (n = 6) * | |||
| Frequency | q-Value | Frequency | q-Value | |||
| Broad | Loss | 1p [2121] | 2/8 (25%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 |
| 14q [1341] | 1/8 (12%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | ||
| 18p [143] | 1/8 (12%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | ||
| 18q [446] | 1/8 (12%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | ||
| 19p [995] | 5/8 (62%) | <0.0001 | 1/6 (17%) | - | ||
| 19q [1709] | 4/8 (50%) | 0.003 | 0/6 (0%) | - | ||
| 21p [13] | 0/8 (0%) | - | 3/6 (50%) | 0.03 | ||
| 22q [921] | 8/8 (100%) | <0.0001 | 6/6 (100%) | <0.0001 | ||
| Gain | 20p [355] | 3/8 (38%) | 0.04 | 1/6 (17%) | - | |
| 21p [13] | 3/8 (38%) | 0.0006 | 1/6 (17%) | - | ||
| 21q [509] | 3/8 (38%) | 0.03 | 1/6 (17%) | - | ||
| Focal | Gain | 17q22 [1] | 0/8 (0%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.03 |
| CNA | Chr Location [N. of Genes] | Diagnosis | First Relapse | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Type | Frequency | q-Value | Frequency | q-Value | |
| Broad | Loss | 1p [2121] | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | 4/6 (67%) | <0.001 |
| 6q [839] | 3/6 (50%) | 0.07 | 3/6 (50%) | 0.051 | ||
| 14q [1341] | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | 4/6 (67%) | 0.001 | ||
| 16q [702] | 2/6 (33%) | - | 3/6 (50%) | 0.025 | ||
| 18p [143] | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | 4/6 (67%) | 0.007 | ||
| 18q [446] | 4/6 (67%) | 0.004 | 4/6 (67%) | 0.006 | ||
| 19p [995] | 1/6 (17%) | - | 3/6 (50%) | 0.047 | ||
| 21p [13] | 3/6 (50%) | 0.027 | 3/6 (50%) | 0.045 | ||
| 22q [921] | 6/6 (100%) | <0.001 | 6/6 (100%) | <0.001 | ||
| Gain | 1q [1955] | 3/6 (50%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.002 | |
| 17q [1592] | 3/6 (50%) | - | 4/6 (67%) | 0.003 | ||
| Focal | Gain | 17q22 [1] (55,403,923–57,333,858) | 4/6 (67%) | 0.031 | 0/6 (0%) | 0/6 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrido Ruiz, P.A.; Rodriguez, Á.O.; Corchete, L.A.; Zelaya Huerta, V.; Pasco Peña, A.; Caballero Martínez, C.; González-Carreró Fojón, J.; Catalina Fernández, I.; López Duque, J.C.; Zaldumbide Dueñas, L.; et al. Paired Primary and Recurrent Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Cytogenetic Alterations, BAP1 Gene Expression Profile and Patient Outcome. Biology 2024, 13, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050350
Garrido Ruiz PA, Rodriguez ÁO, Corchete LA, Zelaya Huerta V, Pasco Peña A, Caballero Martínez C, González-Carreró Fojón J, Catalina Fernández I, López Duque JC, Zaldumbide Dueñas L, et al. Paired Primary and Recurrent Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Cytogenetic Alterations, BAP1 Gene Expression Profile and Patient Outcome. Biology. 2024; 13(5):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050350
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrido Ruiz, Patricia Alejandra, Álvaro Otero Rodriguez, Luis Antonio Corchete, Victoria Zelaya Huerta, Alejandro Pasco Peña, Cristina Caballero Martínez, Joaquín González-Carreró Fojón, Inmaculada Catalina Fernández, Juan Carlos López Duque, Laura Zaldumbide Dueñas, and et al. 2024. "Paired Primary and Recurrent Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Cytogenetic Alterations, BAP1 Gene Expression Profile and Patient Outcome" Biology 13, no. 5: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050350
APA StyleGarrido Ruiz, P. A., Rodriguez, Á. O., Corchete, L. A., Zelaya Huerta, V., Pasco Peña, A., Caballero Martínez, C., González-Carreró Fojón, J., Catalina Fernández, I., López Duque, J. C., Zaldumbide Dueñas, L., Mosteiro González, L., Astudillo, M. A., Hernández-Laín, A., Camacho Urkaray, E. N., Viguri Diaz, M. A., Orfao, A., & Tabernero, M. D. (2024). Paired Primary and Recurrent Rhabdoid Meningiomas: Cytogenetic Alterations, BAP1 Gene Expression Profile and Patient Outcome. Biology, 13(5), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13050350








