Biology, Pathogenicity, and Genetic Diversity of the Rice Pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Heilongjiang Province, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Isolation
2.2. Pathogenicity Test
2.3. Morphological Characterization
2.4. Identification of Rice Disease Resistance
2.5. Identification and Evaluation of Tolerance to RFS Disease
2.6. Molecular Identification and Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Identification
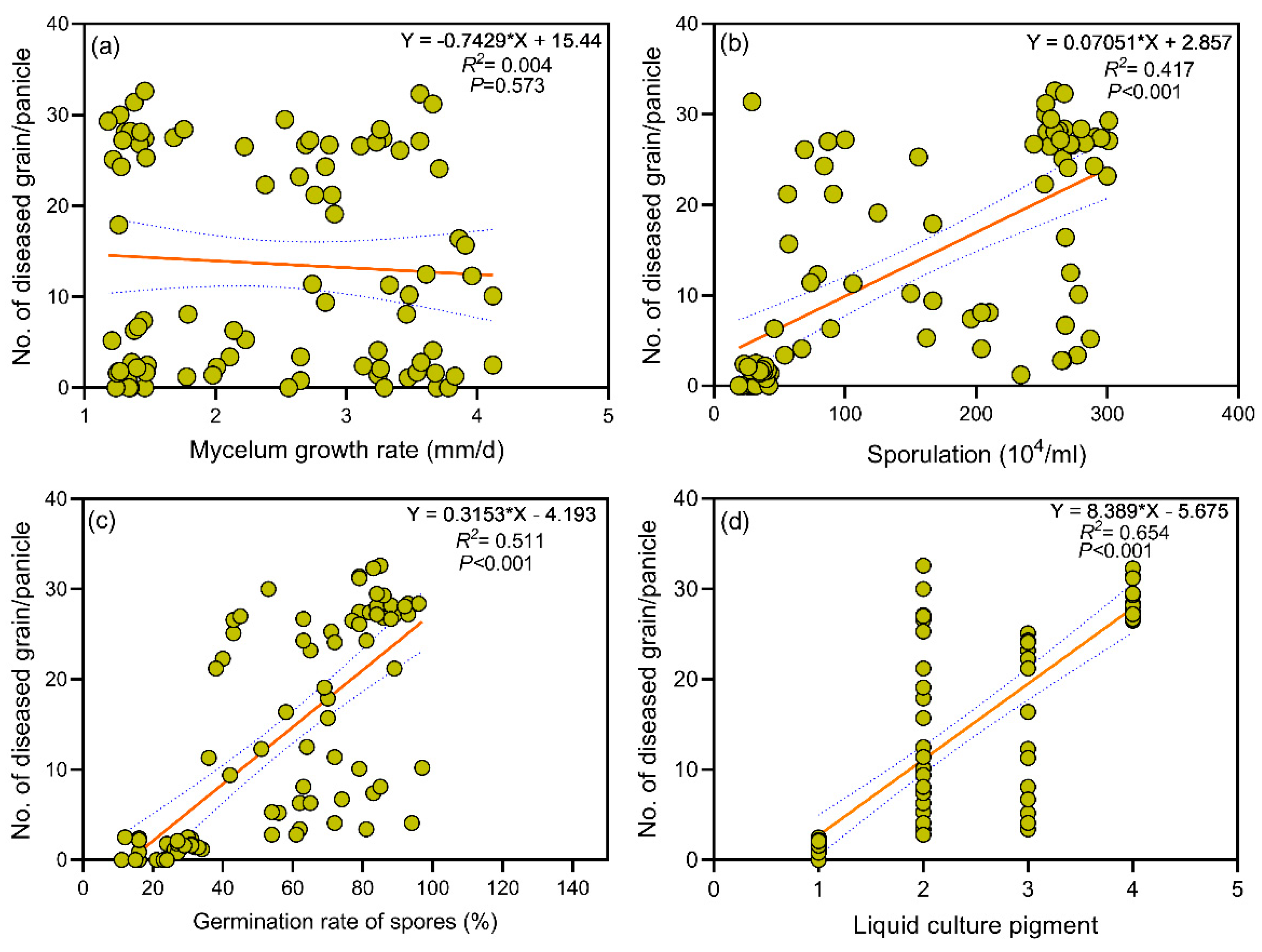
3.2. Correlation Between Biological Characteristics and Pathogenicity
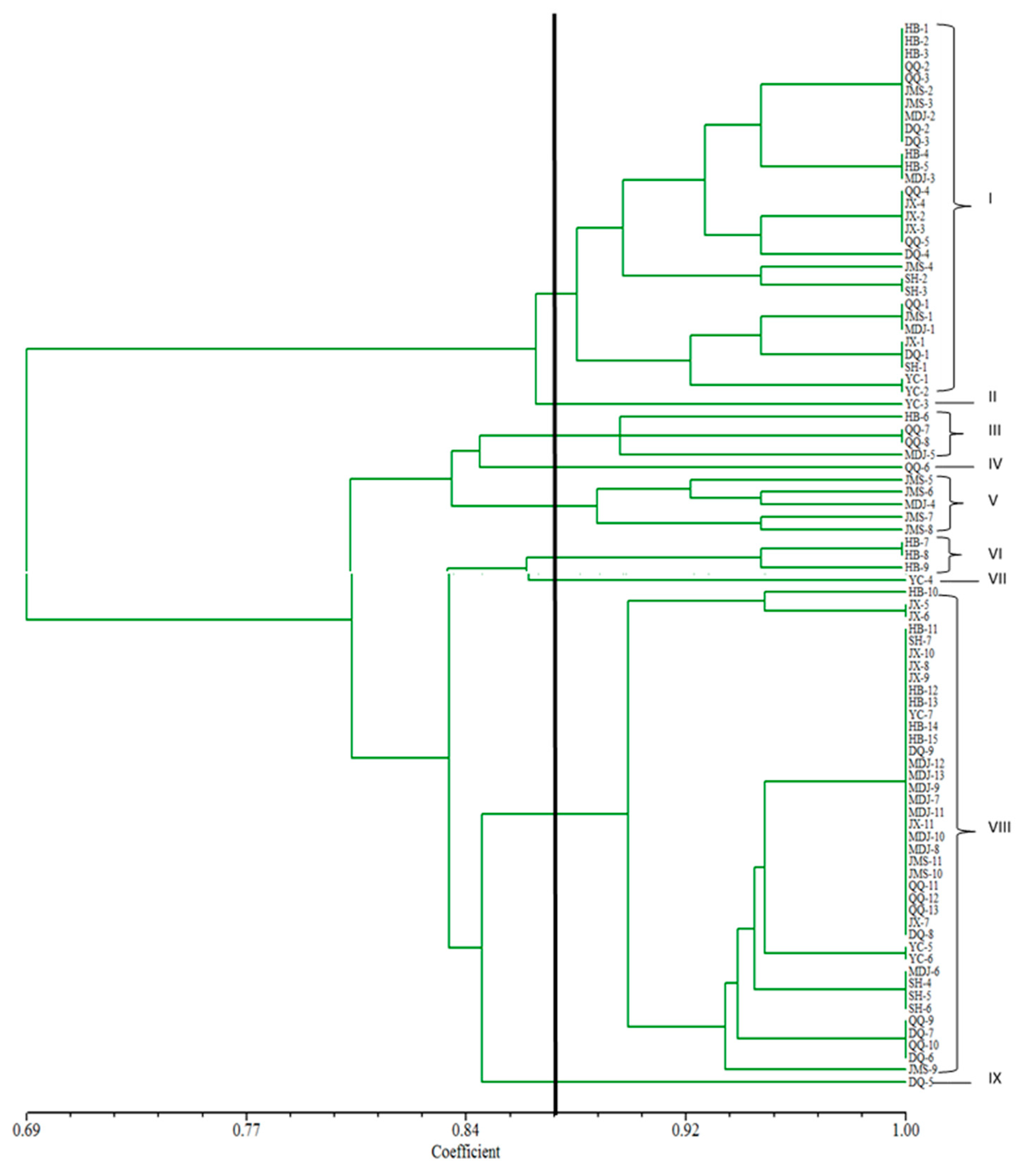
3.3. Analysis of the Clustering Situation of U. virens in Heilongjiang Province
3.4. Rep-PCR Primers Amplification
3.5. Cluster Analysis of U. virens
3.6. Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Geographical Population
3.7. Identification and Evaluation of Tolerance to RFS Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aqleem, A.; Yanping, F.; Zheng, Q.; Huizhang, Z.; Yongjian, S.; Yang, L.; Jiatao, X.; Jiasen, C.; Daohong, J. Isolation and evaluation of the biocontrol potential of Talaromyces spp. against rice sheath blight guided by soil microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5946–5961. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.R.; Zhang, S.J.; Ni, C.; Zhu, D.; Hui, G.; Qigen, D.; Ke, X.; Huo, Z. Higher relative humidity and more moderate temperatures increase the severity of rice false smut disease in the rice–crayfish coculture system. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 11, e323. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Z.; Jiyun, Y.; Anfei, F.; Jiyang, W.; Dayong, L.; Yuejiao, L.; Shanzhi, W.; Fuhao, C.; Junjie, Y.; Yongfeng, L.; et al. The essential effector SCRE1 in Ustilaginoidea virens suppresses rice immunity via a small peptide region. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 445–459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Identification of the Physiological Races of Blast Fungus in Heilongjiang Province, Resistance Monitoring of Cultivars and Mapping of an Avrirulence Gene AvrPi12. Ph.D. Thesis, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bag, M.K.; Ray, A.; Masurkar, P.; Devanna, B.N.; Parameswaran, C.; Baite, M.; Rath, P.C.; Nayak, A. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of isolates of the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in India. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.M.; Fan, J.; Jeyakumar, J.M.J. Rice false smut: An increasing threat to grain yield and quality. In Protecting Rice Grains in the Post-Genomic Era; IntechOpenn: London, UK, 2019; pp. 89–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Dangi, B. A Review on Rice False Smut, it’s Distribution, Identification and Management Practices. Acta Sci. Agric. 2020, 4, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ladhalakshmi, D.; Laha, G.S.; Ram, S.; Karthikeyan, A.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Sundaram, R.M.; Thukkaiyannan, P.; Viraktamath, B.C. Isolation and characterization of Ustilaginoidea virens and survey of false smut disease of rice in India. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.H.; Liu, W.C.; Zhu, F. Epidemic law and control technique of rice false smut in recent years. China Plant Prot. 2018, 38, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Snehlata, K.; Kumar, J. Evaluation of yield losses and management practices of false smut in rice (Oryza sativa). Indian Phytopathol. 2015, 68, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Baite, M.S.; Khokhar, M.K.; Meena, R.P. Management of False Smut Disease of Rice: A Review. In Cereal Grains; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rush, M.C.; Shahjahan, A.K.M.; Jones, J.P.; Groth, D.E. Outbreak of False Smut of Rice in Louisiana. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, M.M.M. Rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) in Egypt/Falscher Reisbrand (Ustilaginoidea virens) in Ägypten. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2004, 111, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, E.; Ashizawa, T.; Sonoda, R.; Tanaka, C. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., comb. nov., the teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens, the causal agent of rice false smut. Mycotaxon 2008, 106, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.X.; Jin, J.; Hu, D.W.; Yong, M.L.; Xu, Y.; He, L.P. Elucidation of the infection process of Ustilaginoidea virens (teleomorph: Villosiclava virens) in rice spikelets. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Juan, Y.; Yu, Q.W.; Guo, B.L.; Yan, L.; Fu, H.; Wen, M.W. Current understanding on Villosiclava virens, a unique flower-infecting fungus causing rice false smut disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Urmila, D.; Sudhi, R.D.; Rabindra, K.S. Precise disease severity assessment for false smut disease of rice. J. Phytopathol. 2015, 163, 931–940. [Google Scholar]
- Siwen, Y.; Pengwei, L.; Jiyang, W.; Dayong, L.; Dan, Z.; Cui, Y.; Dongyu, S.; Wenxian, S. Molecular mechanisms of Ustilaginoidea virens pathogenicity and their utilization in disease control. Phytopathol. Res. 2023, 5, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, R.; Sharma, V.K. Diversity analysis of northern Indian isolates of Ustilaginoidea virens. Indian Phytopathol. 2018, 71, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Kishor, K.; Amandeep, K.; Amit, K.; Pavneet, K.; Ankita, B.; Gurwinder, K.; Ishwinder, K.; Jagjeet, S.L.; Yogesh, V.; et al. High-resolution mapping of the quantitative trait locus (QTLs) conferring resistance to false smut disease in rice. J. Appl. Genet. 2022, 63, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.Q.; Pan, X.; Du, Y.; Shen, L.R.; Yu, M.N.; Yu, M.N.; Cao, H.J.; Cao, H.J.; Song, T.Q.; Song, T.Q.; et al. Pathogenicity and population structure analysis of Pyricularia oryzae in different districts of Jiangsu province, China. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Waqas, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhu, H.; Miao, J.; Gu, B.; Liu, X. Characterization of Prochloraz Resistance in Fusarium fujikuroi from Heilongjiang Province in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lu, D. Diversity Analysis of the Rice False Smut Pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Southwest China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Izumitsu, K.; Sonoda, R.; Nakazaki, T.; Tanaka, E.; Tsuda, M.; Tanaka, C. PCR-based technique for specific detection of Ustilaginoidea virens and Ephelis japonica. Phytopathology 2003, 151, 13–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bashyal, B.M.; Parmar, P.; Zaidi, N.W.; Sunani, S.K.; Prakash, G.; Aggarwal, R. Improved methodology for the isolation of false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens of rice. Indian Phytopathol. 2021, 74, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, D.G.; Pramoda, S.S.; Ramanathan, A.; Ramchander, S.; Manonmani, S.; Jeyaprakash, P.; Robin, S. Isolation, characterization and pathogenesis of Ustilaginoidea virens causing false smut disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2017, 6, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, M.L.; Deng, Q.D.; Fan, L.L.; Miao, J.K.; Lai, C.H.; Chen, H.M.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Jin, L.; et al. The role of Ustilaginoidea virens sclerotia in increasing incidence of rice false smut disease in the subtropical zone in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 150, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, L.; Gutierrez, S.; Maidana, M.; Morinigo, K. Rice false smut [Ustilaginoidea virens (Cooke) Takah. ]. Parag. Trop. Plant Res. 2016, 3, 704–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, X.; Kong, R.; Cheng, S.; Man, J.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.; Su, G.; et al. Global distribution of ustiloxins in rice and their male-biased hepatotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 118992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H. Development of Generic Immuno-Magnetic Bead-Based Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay for Ustiloxins in Rice Coupled with Enrichment. Toxins 2021, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.P.; Song, J.W.; Liu, E.M.; Liu, N.X.; Wang, J.H.; Xiao, Q.M. Analysis of genetic diversity of Ustilaginoidea virens in Hunan. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. 2008, 34, 694–697. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, W.; Shu, Z.; Liu, M.G.; Lin, X.S.; Liu, H.J.; Peng, Y.L.; Huang, J.B.; Xi, C. Genetic diversity analysis reveals that geographical environment plays a more important role than rice cultivar in Villosiclava virens population selection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Zhiyi, C.; Hu, J.; Yin, X.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y. Genetic diversity and pathogenicity of Ustilaginoidea virens isolated from different rice false smut balls of a diseased spike. Acta Phytophyl. 2013, 43, 561–573. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Gu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Hsiang, T.; Luo, C.; Huang, J. Genetic analysis of the population structure of the rice false smut fungus, Villosiclava virens, in China using microsatellite markers mined from a genome assembly. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Wang, S.T.; Yao, J.N.; Du, Y.X.; Chen, F.R. Analysis of genetic diversity of Ustilaginoidea virens from Fujian province based on RAPD markers. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2011, 19, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, A.F.; Fu, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Fu, Y.H.; Qin, Y.B.; Bai, Z.X.; Tan, Z.; Cai, J.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Sichuan-Chongqing region. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Strain Number | Region | Mycelial Growth Rate (mm/d) | Sporulation (104/mL) | Germination Rate of Spores (%) | Liquid Culture Color | No. of Diseased Grain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-1 | Harbin | 3.56 ± 0.12 | 301 ± 20.06 | 89 ± 8.93 | YG | 27.1 ± 2.11 |
| B-2 | Harbin | 1.78 ± 0.21 | 234 ± 17.87 | 34 ± 3.23 | W | 1.2 ± 0.21 |
| HB-3 | Harbin | 1.21 ± 0.34 | 287 ± 18.76 | 56 ± 4.56 | DG | 5.2 ± 2.12 |
| HB-4 | Harbin | 3.13 ± 0.07 | 23 ± 9.67 | 16 ± 1.34 | W | 2.4 ± 1.01 |
| HB-5 | Harbin | 1.22 ± 0.13 | 266 ± 31.45 | 43 ± 9.12 | DG | 25.1 ± 3.21 |
| HB-6 | Harbin | 3.69 ± 0.03 | 28 ± 5.34 | 11 ± 4.56 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| HB-7 | Harbin | 1.68 ± 0.06 | 291 ± 32.11 | 79 ± 11.23 | DY | 27.5 ± 3.21 |
| HB-8 | Harbin | 2.64 ± 0.09 | 300 ± 16.67 | 65 ± 13.45 | DG | 23.2 ± 2.34 |
| HB-9 | Harbin | 1.46 ± 0.11 | 26 ± 6.67 | 16 ± 4.56 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| HB-10 | Harbin | 3.28 ± 0.23 | 265 ± 12.34 | 82 ± 8.69 | DY | 27.4 ± 6.12 |
| HB-11 | Harbin | 1.31 ± 0.06 | 254 ± 9.08 | 84 ± 7.44 | DY | 28.1 ± 3.45 |
| HB-12 | Harbin | 3.48 ± 0.08 | 150 ± 11.34 | 97 ± 3.54 | YG | 10.2 ± 2.34 |
| HB-13 | Harbin | 2.65 ± 0.05 | 277 ± 20.03 | 62 ± 2.56 | YG | 3.4 ± 1.22 |
| HB-14 | Harbin | 2.23 ± 0.14 | 162 ± 8.97 | 54 ± 2.21 | YG | 5.3 ± 1.12 |
| HB-15 | Harbin | 3.61 ± 0.25 | 272 ± 13.45 | 64 ± 2.11 | YG | 12.5 ± 4.56 |
| QQ-1 | Qiqihar | 1.27 ± 0.18 | 253 ± 21.33 | 53 ± 1.98 | YG | 30.1 ± 5.12 |
| QQ-2 | Qiqihar | 2.22 ± 0.17 | 256 ± 17.89 | 77 ± 7.02 | DY | 26.5 ± 2.11 |
| QQ-3 | Qiqihar | 3.66 ± 0.08 | 67 ± 4.32 | 72 ± 6.97 | YG | 4.1 ± 1.12 |
| QQ-4 | Qiqihar | 3.78 ± 0.19 | 22 ± 3.21 | 21 ± 2.32 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| QQ-5 | Qiqihar | 4.12 ± 0.22 | 278 ± 16.76 | 79 ± 6.77 | YG | 10.1 ± 1.32 |
| QQ-6 | Qiqihar | 3.11 ± 0.08 | 273 ± 15.32 | 43 ± 3.21 | YG | 26.6 ± 2.34 |
| QQ-7 | Qiqihar | 1.35 ± 0.16 | 30 ± 5.43 | 11 ± 2.34 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| QQ-8 | Qiqihar | 2.89 ± 0.17 | 56 ± 6.32 | 89 ± 7.89 | YG | 21.2 ± 3.23 |
| QQ-9 | Qiqihar | 2.38 ± 0.2 | 252 ± 21.44 | 40 ± 2.33 | DG | 22.3 ± 2.34 |
| QQ-10 | Qiqihar | 2.11 ± 0.21 | 54 ± 9.02 | 81 ± 5.43 | DG | 3.4 ± 0.41 |
| QQ-11 | Qiqihar | 2.01 ± 0.25 | 35 ± 8.77 | 31 ± 2.34 | W | 2.3 ± 0.22 |
| QQ-12 | Qiqihar | 1.26 ± 0.27 | 167 ± 12.34 | 70 ± 6.43 | YG | 17.9 ± 3.21 |
| QQ-13 | Qiqihar | 1.33 ± 0.15 | 32 ± 3.45 | 16 ± 4.56 | W | 0.9 ± 0.23 |
| JMS-1 | Jiamusi | 1.38 ± 0.06 | 29 ± 2.34 | 79 ± 3.23 | DY | 31.4 ± 9.23 |
| JMS-2 | Jiamusi | 1.34 ± 0.16 | 32 ± 3.12 | 23 ± 2.12 | W | 0 ± 0. |
| JMS-3 | Jiamusi | 1.46 ± 0.17 | 295 ± 23.12 | 82 ± 4.56 | DY | 27.4 ± 3.21 |
| JMS-4 | Jiamusi | 1.98 ± 0.24 | 43 ± 4.65 | 32 ± 2.12 | W | 1.4 ± 0.11 |
| JMS-5 | Jiamusi | 3.24 ± 0.07 | 204 ± 3.42 | 94 ± 5.67 | DG | 4.1 ± 1.16 |
| JMS-6 | Jiamusi | 3.46 ± 0.08 | 210 ± 14.56 | 63 ± 3.23 | DG | 8.1 ± 3.22 |
| JMS-7 | Jiamusi | 1.42 ± 0.26 | 283 ± 16.54 | 86 ± 4.34 | DY | 26.8 ± 7.21 |
| JMS-8 | Jiamusi | 1.38 ± 0.28 | 89 ± 6.78 | 62 ± 2.45 | YG | 6.3 ± 1.23 |
| JMS-9 | Jiamusi | 1.36 ± 0.15 | 266 ± 18.91 | 61 ± 3.02 | YG | 2.8 ± 1.45 |
| JMS-10 | Jiamusi | 3.83 ± 0.24 | 40 ± 4.23 | 28 ± 2.12 | W | 1.3 ± 0.23 |
| JMS-11 | Jiamusi | 1.28 ± 0.13 | 290 ± 23.12 | 81 ± 7.21 | DG | 24.3 ± 2.34 |
| MDJ-1 | Mudanjiang | 2.14 ± 0.21 | 46 ± 4.32 | 65 ± 2.12 | YG | 6.3 ± 1.09 |
| MDJ-2 | Mudanjiang | 3.23 ± 0.06 | 87 ± 2.12 | 45 ± 3.21 | YG | 27 ± 4.56 |
| MDJ-3 | Mudanjiang | 1.26 ± 0.23 | 32 ± 1.32 | 24 ± 2.12 | W | 1.8 ± 0.18 |
| MDJ-4 | Mudanjiang | 1.45 ± 0.18 | 196 ± 12.43 | 83 ± 6.21 | YG | 7.4 ± 2.23 |
| MDJ-5 | Mudanjiang | 1.76 ± 0.16 | 267 ± 14.22 | 93 ± 4.54 | DY | 28.4 ± 3.45 |
| MDJ-6 | Mudanjiang | 3.47 ± 0.23 | 38 ± 9.32 | 26 ± 3.45 | W | 1.1 ± 0.22 |
| MDJ-7 | Mudanjiang | 2.91 ± 0.17 | 125 ± 3.02 | 69 ± 5.61 | YG | 19.1 ± 2.34 |
| MDJ-8 | Mudanjiang | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 42 ± 2.12 | 16 ± 2.21 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| MDJ-9 | Mudanjiang | 2.65 ± 0.11 | 40 ± 2.32 | 27 ± 1.23 | W | 0.8 ± 0.34 |
| MDJ-10 | Mudanjiang | 2.84 ± 0.24 | 167 ± 8.45 | 42 ± 3.21 | YG | 9.4 ± 2.33 |
| MDJ-11 | Mudanjiang | 3.86 ± 0.08 | 268 ± 10.22 | 58 ± 2.34 | DG | 16.4 ± 4.34 |
| MDJ-12 | Mudanjiang | 1.35 ± 0.01 | 263 ± 9.32 | 88 ± 5.67 | DY | 28.2 ± 6.11 |
| MDJ-13 | Mudanjiang | 1.47 ± 0.12 | 156 ± 4.22 | 71 ± 4.53 | YG | 25.3 ± 3.21 |
| YC-1 | Yichun | 1.46 ± 0.11 | 260 ± 5.67 | 85 ± 5.65 | YG | 32.6 ± 4.23 |
| YC-2 | Yichun | 2.56 ± 0.03 | 19 ± 2.11 | 24 ± 4.57 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| YC-3 | Yichun | 3.96 ± 0.3 | 79 ± 4.23 | 51 ± 3.24 | DG | 12.3 ± 3.22 |
| YC-4 | Yichun | 3.24 ± 0.28 | 35 ± 2.13 | 33 ± 2.14 | W | 1.4 ± 0.19 |
| YC-5 | Yichun | 2.69 ± 0.19 | 272 ± 10.05 | 63 ± 3.42 | YG | 26.7 ± 2.34 |
| YC-6 | Yichun | 1.79 ± 0.14 | 204 ± 9.88 | 85 ± 5.62 | YG | 8.1 ± 3.22 |
| YC-7 | Yichun | 1.48 ± 0.17 | 32 ± 1.23 | 30 ± 2.11 | W | 2.5 ± 1.21 |
| JX-1 | Jixi | 1.47 ± 0.07 | 41 ± 2.34 | 31 ± 2.31 | W | 1.7 ± 0.67 |
| JX-2 | Jixi | 2.84 ± 0.18 | 84 ± 4.56 | 63 ± 3.21 | DG | 24.3 ± 5.67 |
| JX-3 | Jixi | 2.74 ± 0.19 | 74 ± 5.61 | 72 ± 2.43 | YG | 11.4 ± 3.34 |
| JX-4 | Jixi | 2.87 ± 0.22 | 244 ± 13.22 | 88 ± 3.22 | DY | 26.7 ± 2.14 |
| JX-5 | Jixi | 3.91 ± 0.27 | 57 ± 3.23 | 70 ± 2.22 | YG | 15.7 ± 2.23 |
| JX-6 | Jixi | 1.25 ± 0.07 | 38 ± 10.12 | 31 ± 1.47 | W | 1.6 ± 0.08 |
| JX-7 | Jixi | 3.26 ± 0.23 | 280 ± 20.34 | 96 ± 7.32 | DY | 28.4 ± 2.12 |
| JX-8 | Jixi | 2.72 ± 0.19 | 100 ± 3.44 | 93 ± 6.72 | DY | 27.2 ± 3.21 |
| JX-9 | Jixi | 3.33 ± 0.12 | 106 ± 5.65 | 36 ± 4.35 | DG | 11.3 ± 2.11 |
| JX-10 | Jixi | 1.4 ± 0.05 | 39 ± 2 | 16 ± 2.33 | W | 2.2 ± 0.23 |
| JX-11 | Jixi | 1.18 ± 0.02 | 301 ± 17.21 | 86 ± 7.45 | DY | 29.3 ± 4.22 |
| DQ-1 | Daqing | 3.56 ± 0.18 | 267 ± 16.71 | 83 ± 2.66 | DY | 32.3 ± 4.67 |
| DQ-2 | Daqing | 2.76 ± 0.15 | 91 ± 5.21 | 38 ± 2.11 | DG | 21.2 ± 4.56 |
| DQ-3 | Daqing | 4.12 ± 0.31 | 32 ± 12.2 | 12 ± 1.22 | W | 2.5 ± 0.22 |
| DQ-4 | Daqing | 1.43 ± 0.07 | 260 ± 15.21 | 92 ± 9.23 | DY | 28.1 ± 3.12 |
| DQ-5 | Daqing | 3.54 ± 0.12 | 28 ± 4.5 | 24 ± 3.02 | W | 1.7 ± 0.11 |
| DQ-6 | Daqing | 3.66 ± 0.16 | 253 ± 11.21 | 79 ± 4.22 | DY | 31.2 ± 2.11 |
| DQ-7 | Daqing | 2.53 ± 0.18 | 257 ± 12.23 | 84 ± 2.31 | DY | 29.5 ± 3.21 |
| DQ-8 | Daqing | 3.29 ± 0.19 | 22 ± 5.23 | 15 ± 1.13 | W | 0 ± 0 |
| DQ-9 | Daqing | 3.71 ± 0.26 | 270 ± 13.45 | 72 ± 5.23 | DG | 24.1 ± 2.33 |
| SH-1 | Suihua | 1.27 ± 0.03 | 37 ± 3.12 | 27 ± 2.33 | W | 1.8 ± 0.12 |
| SH-2 | Suihua | 3.68 ± 0.24 | 35 ± 2.12 | 29 ± 3.21 | W | 1.6 ± 0.22 |
| SH-3 | Suihua | 3.57 ± 0.21 | 265 ± 14.23 | 54 ± 4.56 | YG | 2.8 ± 0.67 |
| SH-4 | Suihua | 1.41 ± 0.04 | 268 ± 15.67 | 74 ± 6.44 | DG | 6.7 ± 1.21 |
| SH-5 | Suihua | 1.29 ± 0.05 | 264 ± 24.23 | 84 ± 7.11 | DY | 27.2 ± 3.24 |
| SH-6 | Suihua | 3.41 ± 0.26 | 69 ± 6.34 | 79 ± 6.43 | YG | 26.1 ± 4.23 |
| SH-7 | Suihua | 3.26 ± 0.17 | 26 ± 3.23 | 27 ± 2.33 | W | 2.1 ± 0.78 |
| Region | No. of Samples | Observed Number of Alleles | Effective Number of Alleles | Nei’s Gene Diversity Index | Shannon Information Index | No. of Polymorphic Loci | No. of Polymorphic Loci (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbin | 15 | 1.7423 | 1.5467 | 0.3793 | 0.4769 | 23 | 40.4% |
| Qiqihar | 13 | 1.7264 | 1.5249 | 0.3576 | 0.4563 | 21 | 36.8% |
| Jiamusi | 11 | 1.5869 | 1.3836 | 0.2394 | 0.3403 | 13 | 22.8% |
| Mudanjiang | 13 | 1.6657 | 1.4694 | 0.3002 | 0.4069 | 17 | 29.8% |
| Yichun | 7 | 1.4896 | 1.2942 | 0.1121 | 0.2434 | 10 | 17.5% |
| Jixi | 11 | 1.5742 | 1.3724 | 0.2289 | 0.3376 | 11 | 19.3% |
| Daqing | 9 | 1.6873 | 1.4869 | 0.3231 | 0.4279 | 18 | 31.6% |
| Suihua | 7 | 1.6214 | 1.4268 | 0.2679 | 0.3763 | 15 | 26.3% |
| Average | 11 | 1.6367 | 1.4381 | 0.2761 | 0.3832 | 16 | 28.1% |
| Total | 86 | 1.7646 | 1.5608 | 0.3998 | 0.4979 | 25 | 43.9% |
| Number | Rice Varieties | Average Disease Head Rate% | Classification of Disease Resistance | Number | Rice Varieties | Average Disease Head Rate% | Classification of Disease Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suijing 15 | 2.2 | R | 21 | Pine japonica 19 | 17.2 | S |
| 2 | Mudanjiang 35 | 2.2 | R | 22 | Pine japonica 9 | 17.2 | S |
| 3 | Dragon japonica 60 | 0.9 | R | 23 | Dragon japonica 61 | 17.2 | S |
| 4 | Suijing 14 | 4.2 | MR | 24 | Dragon japonica 53 | 17.1 | S |
| 5 | Dragon japonica 56 | 4.1 | MR | 25 | Dragon japonica 47 | 17.2 | S |
| 6 | Dragon japonica 55 | 3.4 | MR | 26 | Dragon japonica 39 | 18.2 | S |
| 7 | Dragon japonica 43 | 4.5 | MR | 27 | Dragon japonica 21 | 17.1 | S |
| 8 | Dragon japonica 31 | 4.1 | MR | 28 | Long Yang 11 | 18.4 | S |
| 9 | Pine japonica 2 | 4.2 | MR | 29 | Dragon Rice 18 | 27.4 | HS |
| 10 | Pine japonica 1 | 5.1 | MR | 30 | Suijing 18 | 25.3 | HS |
| 11 | Cultivated rice 12 | 6.1 | MR | 31 | Pine japonica 22 | 25.4 | HS |
| 12 | Dragon Rice 21 | 8.1 | MS | 32 | Pine japonica 18 | 26.1 | HS |
| 13 | Suijing 4 | 9.2 | MS | 33 | Pine japonica 16 | 26.3 | HS |
| 14 | Dragon japonica 58 | 11.2 | MS | 34 | Dongnong 425 | 25.3 | HS |
| 15 | Dragon japonica 54 | 9.6 | MS | 35 | Dragon japonica 59 | 27.1 | HS |
| 16 | Dragon japonica 51 | 7.4 | MS | 36 | Dragon japonica 57 | 26.3 | HS |
| 17 | Dragon japonica 50 | 10.7 | MS | 37 | Dragon japonica 52 | 27.4 | HS |
| 18 | Dragon japonica 46 | 8.5 | MS | 38 | Dragon japonica 25 | 26.6 | HS |
| 19 | Dragon japonica 29 | 8.2 | MS | 39 | Five excellent rice 4 | 30 | HS |
| 20 | Dragon japonica 1 | 8.2 | MS | 40 | Loose and sticky 1 | 26.3 | HS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, P.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Nihal, N.; Yang, M.; Ni, Z.; Haseeb, Y.; Hou, L.; Lv, A.; Zhang, J. Biology, Pathogenicity, and Genetic Diversity of the Rice Pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Heilongjiang Province, China. Biology 2025, 14, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010046
Guo P, Xu X, Ma Y, Nihal N, Yang M, Ni Z, Haseeb Y, Hou L, Lv A, Zhang J. Biology, Pathogenicity, and Genetic Diversity of the Rice Pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Heilongjiang Province, China. Biology. 2025; 14(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Peng, Xiaofeng Xu, Yue Ma, Niaz Nihal, Mingxiu Yang, Zhe Ni, Younis Haseeb, Lei Hou, Anqi Lv, and Junhua Zhang. 2025. "Biology, Pathogenicity, and Genetic Diversity of the Rice Pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Heilongjiang Province, China" Biology 14, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010046
APA StyleGuo, P., Xu, X., Ma, Y., Nihal, N., Yang, M., Ni, Z., Haseeb, Y., Hou, L., Lv, A., & Zhang, J. (2025). Biology, Pathogenicity, and Genetic Diversity of the Rice Pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Heilongjiang Province, China. Biology, 14(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010046






