The Role of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Modulating Dermal Fibroblast Activity: A Pathway to Enhanced Tissue Regeneration
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. EV Isolation and Characterization
2.4. Cell Morphology and Viability
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay via CCK8
2.6. Cell Viability Assay via MTT
2.7. Cell Migration Assay
2.8. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.9. Cytokine Assay
2.10. Growth Factor Assay
2.11. Quantitative Gene Expression Analysis by Real-Time PCR
2.12. Statistical Analysis
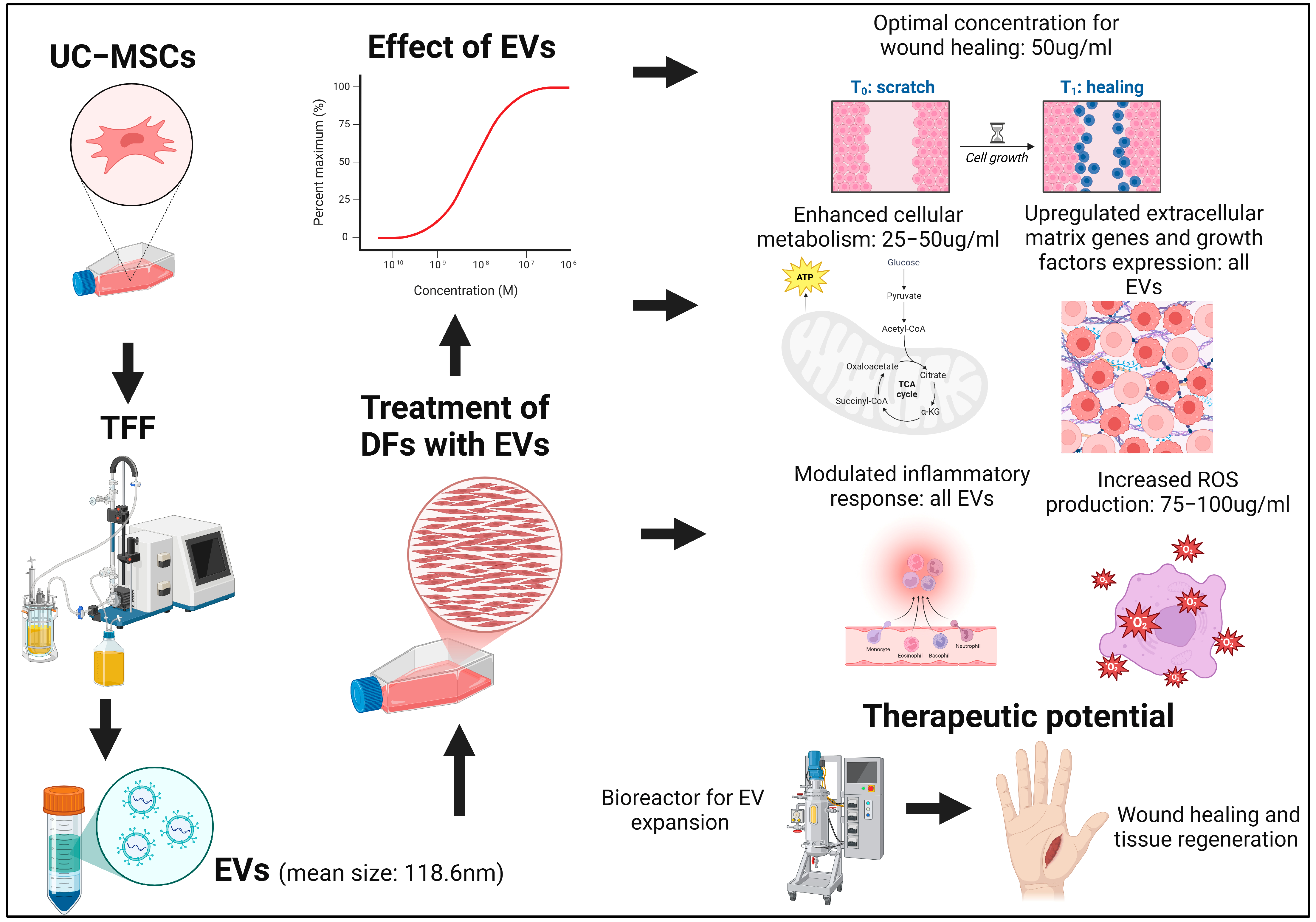
3. Results
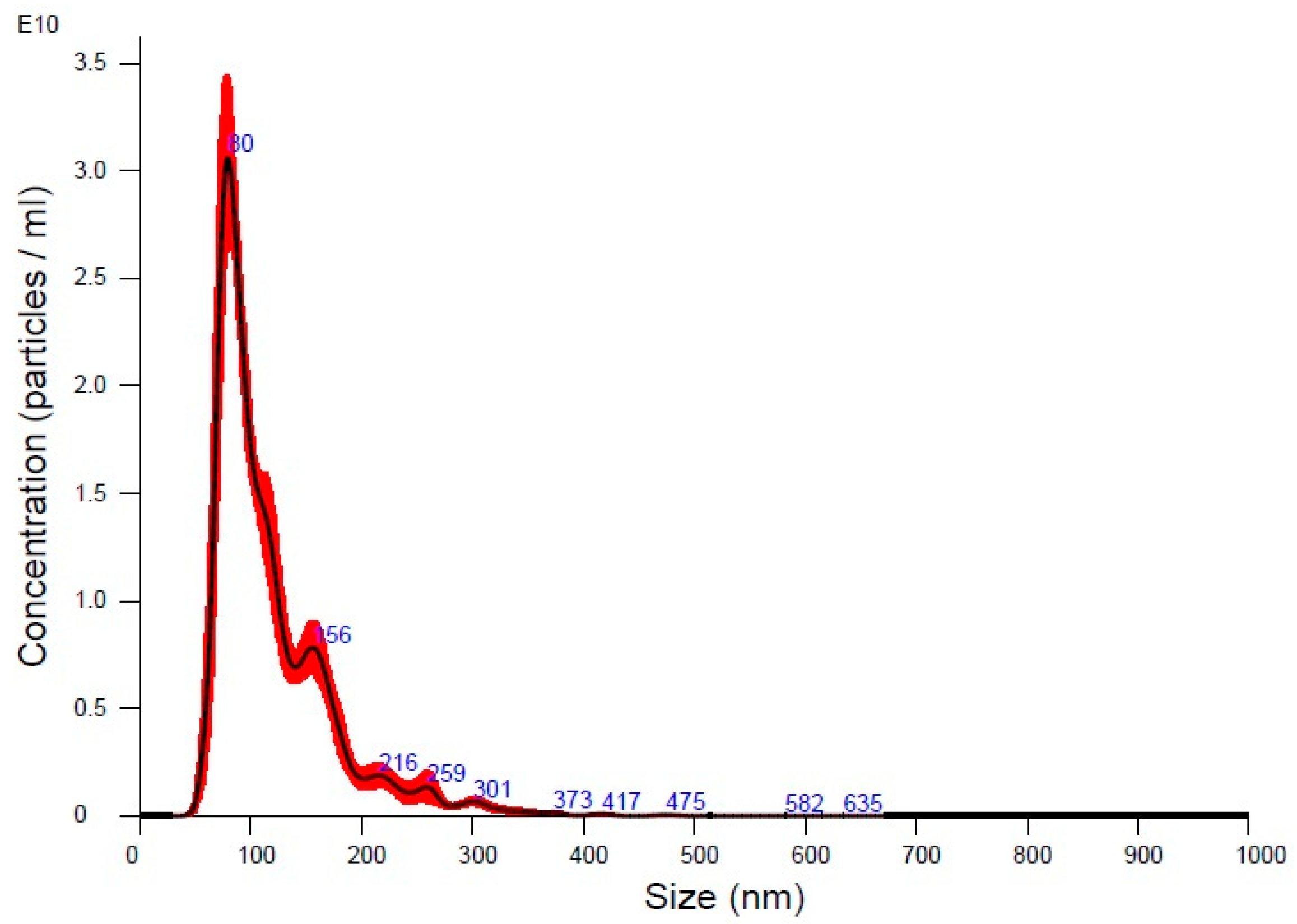
3.1. Characterization of UC-MSC-EVs
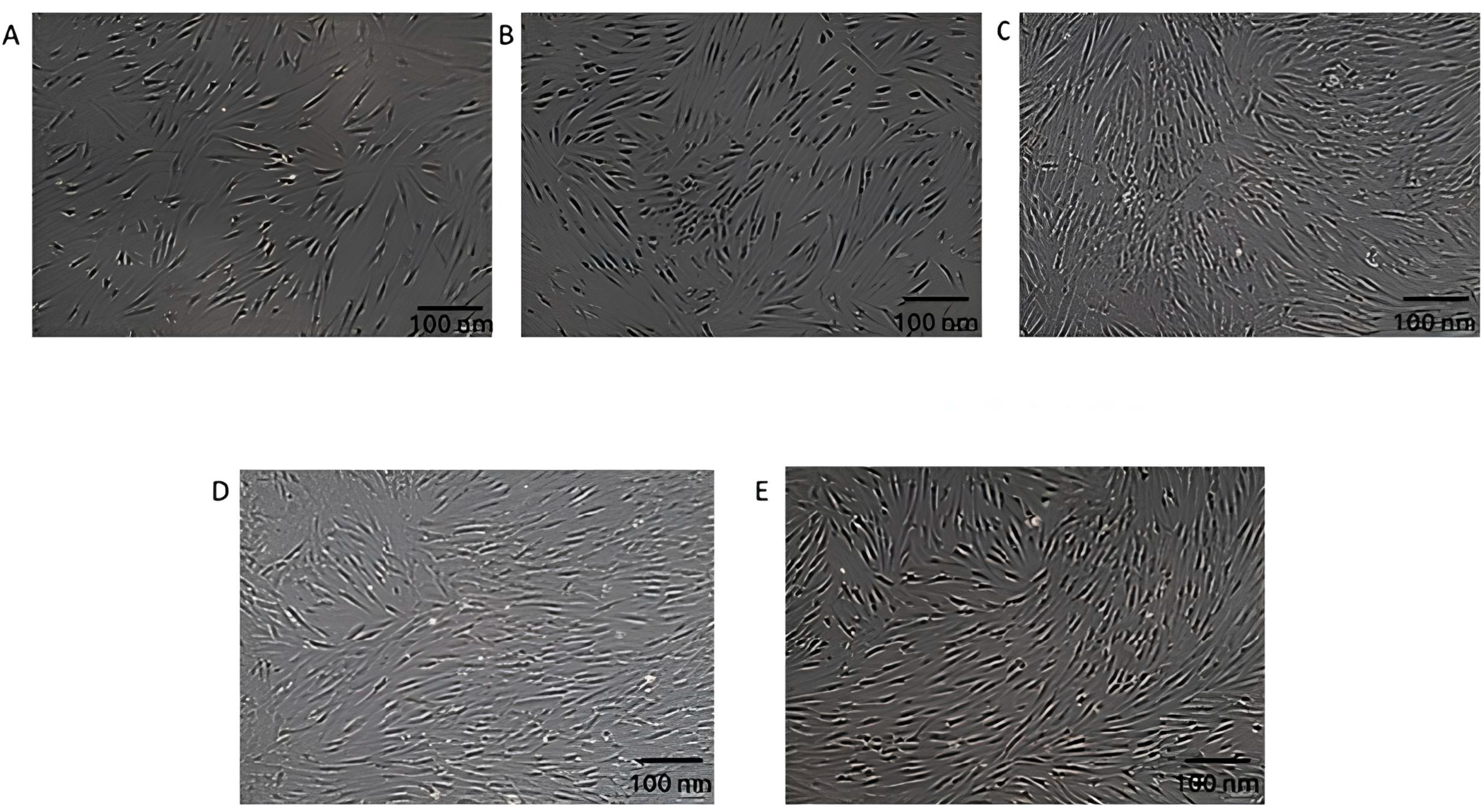
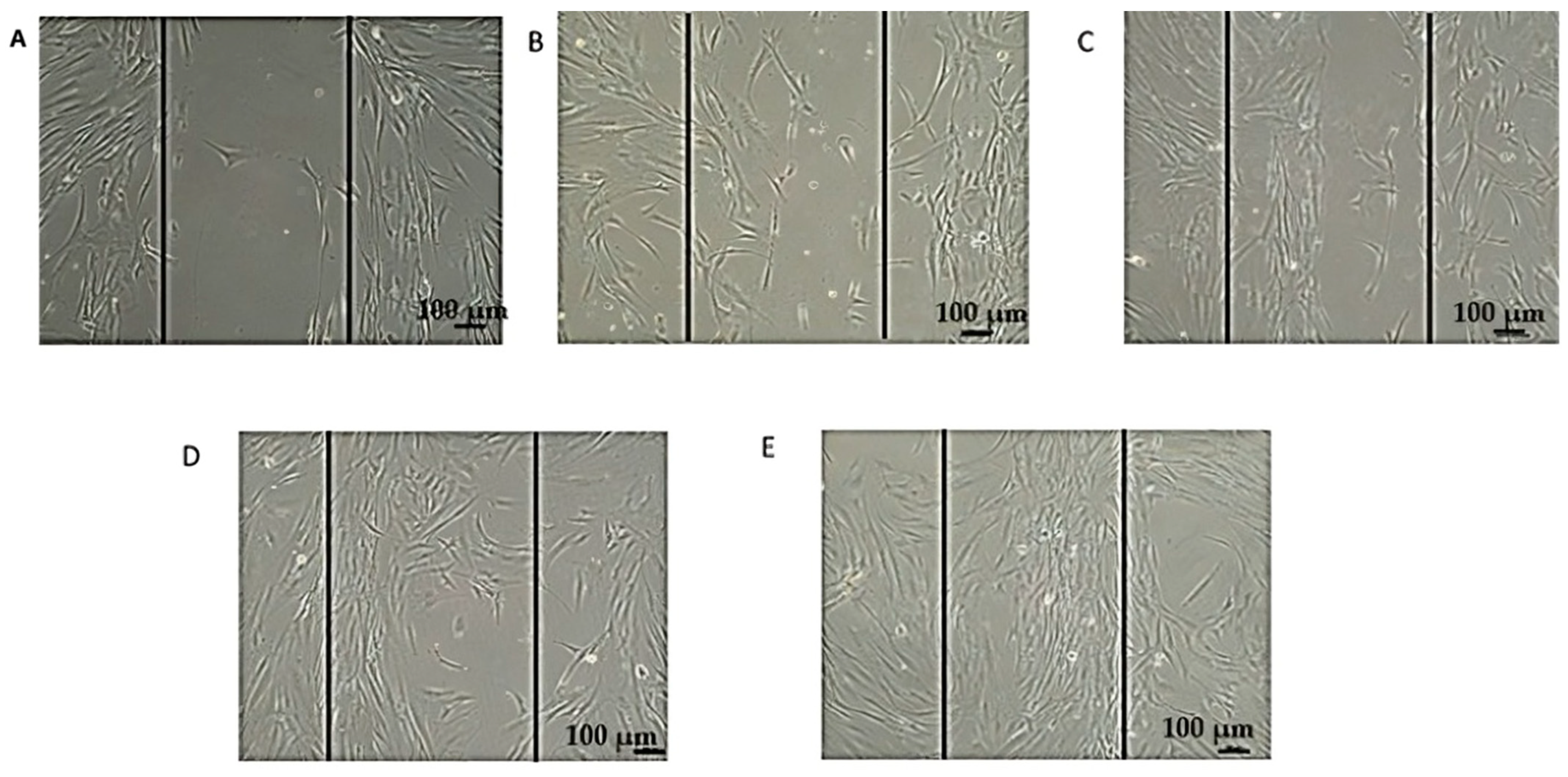
3.2. Morphological Changes in DFs After Exposure to EVs
3.3. EVs Increase Proliferation of DFs
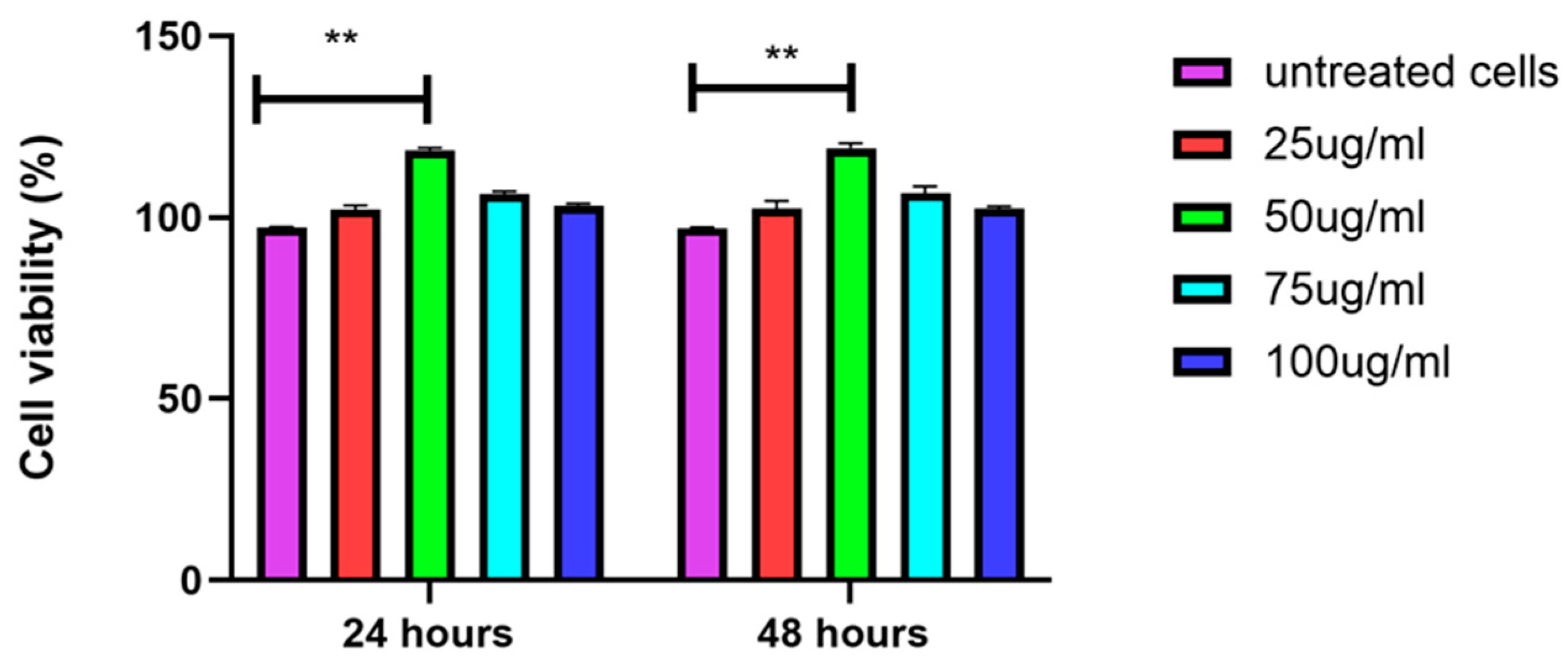
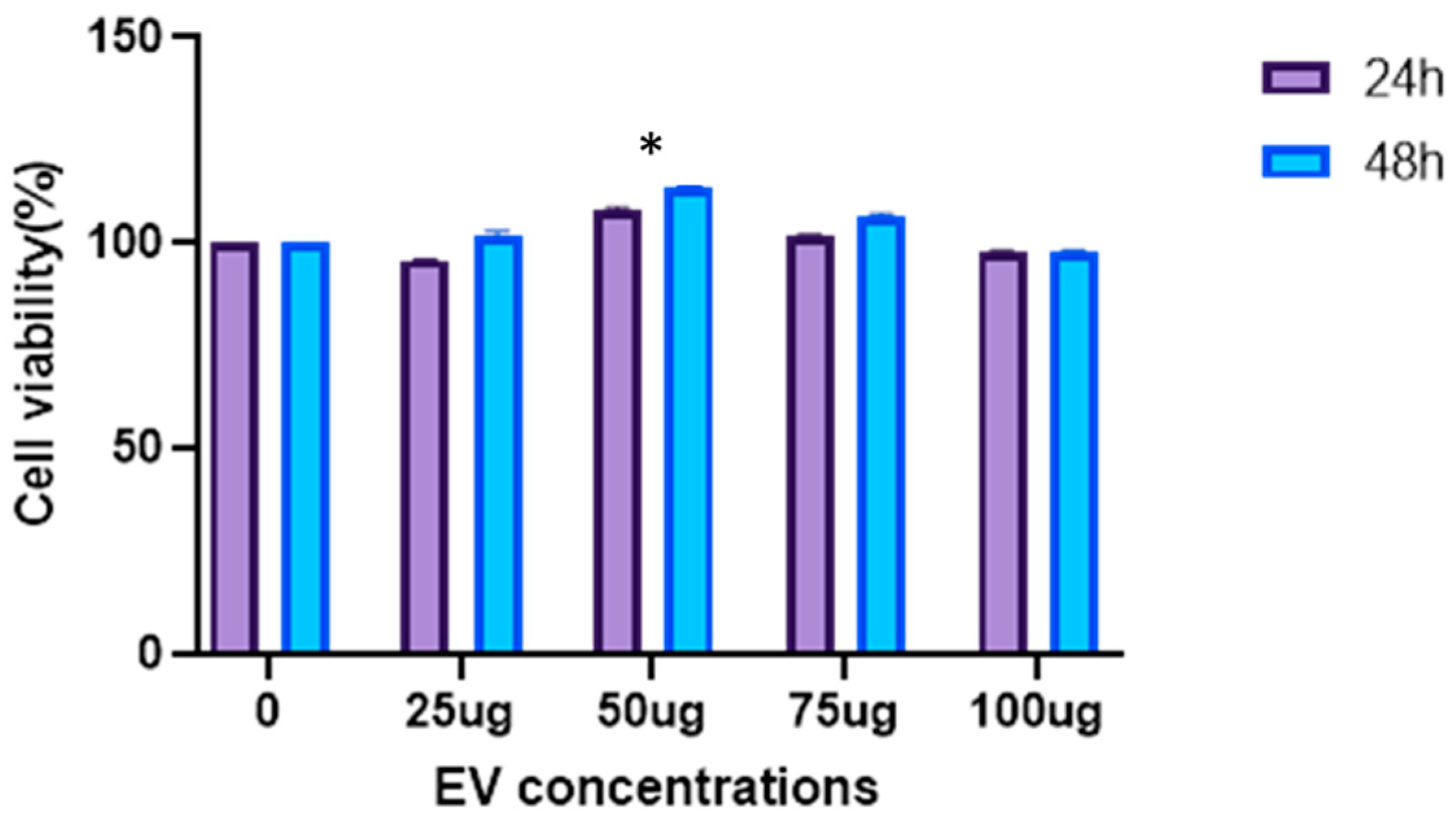
3.4. EVs Increase Viability of DFs
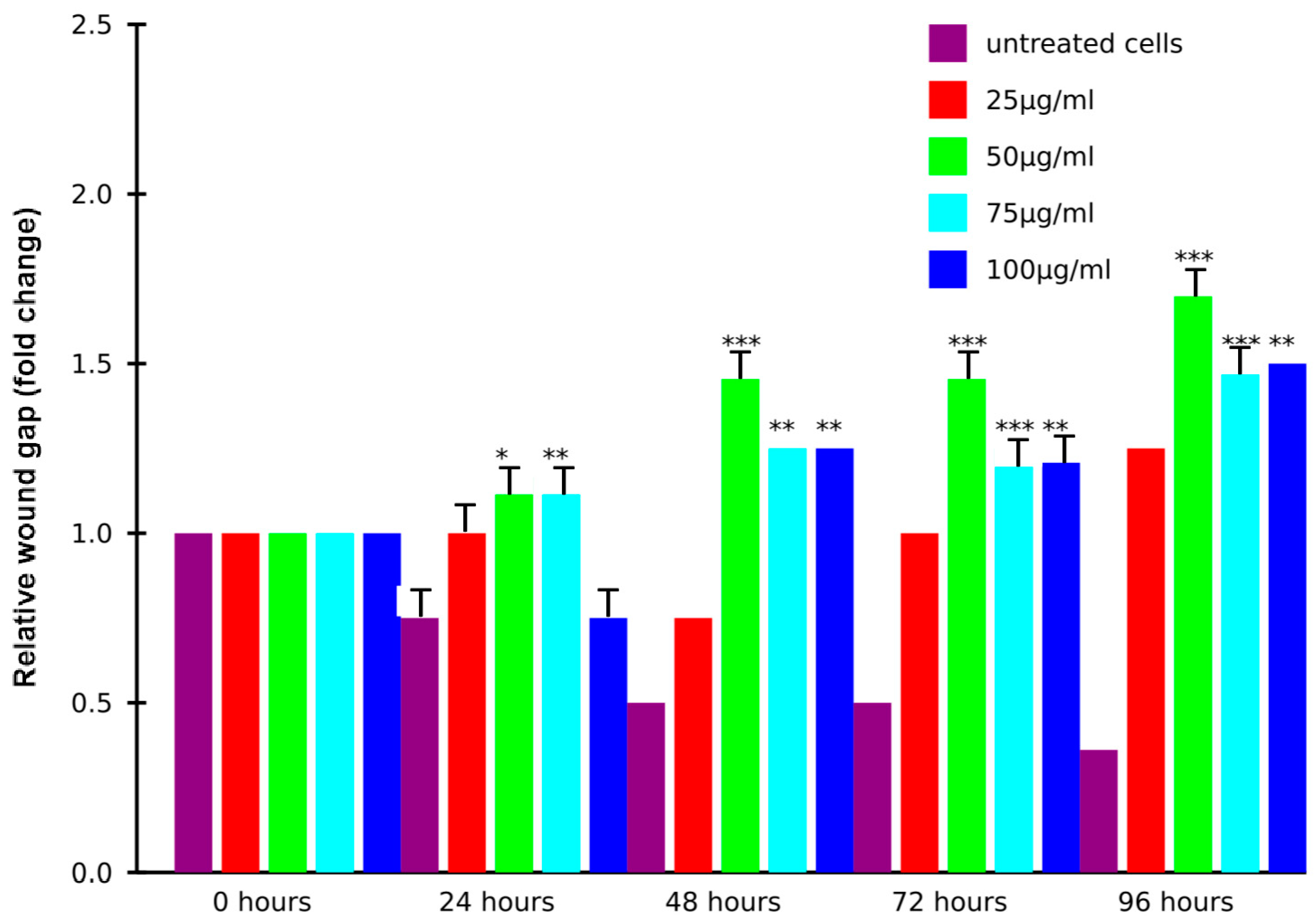
3.5. EVs Induce Migration of DFs
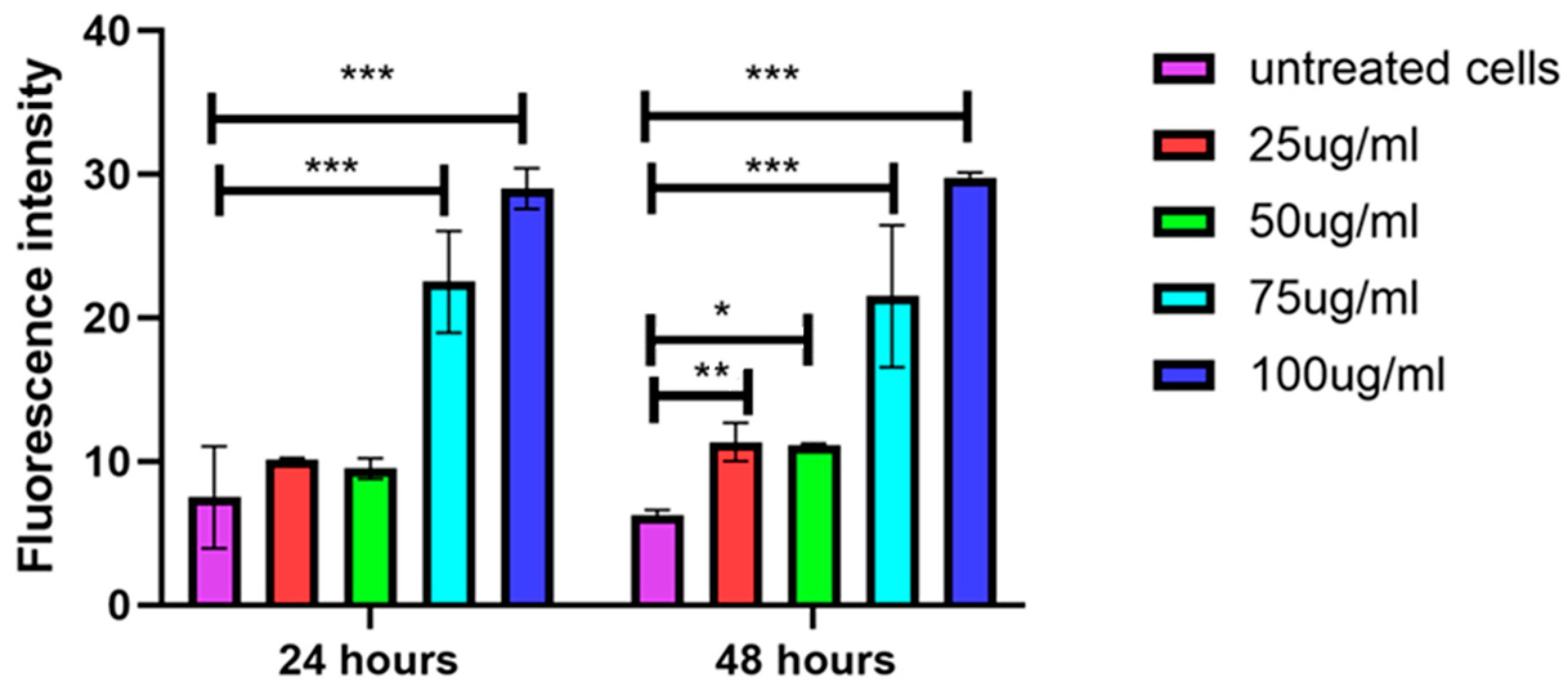
3.6. Higher Concentrations of EVs Induce Secretion of ROS
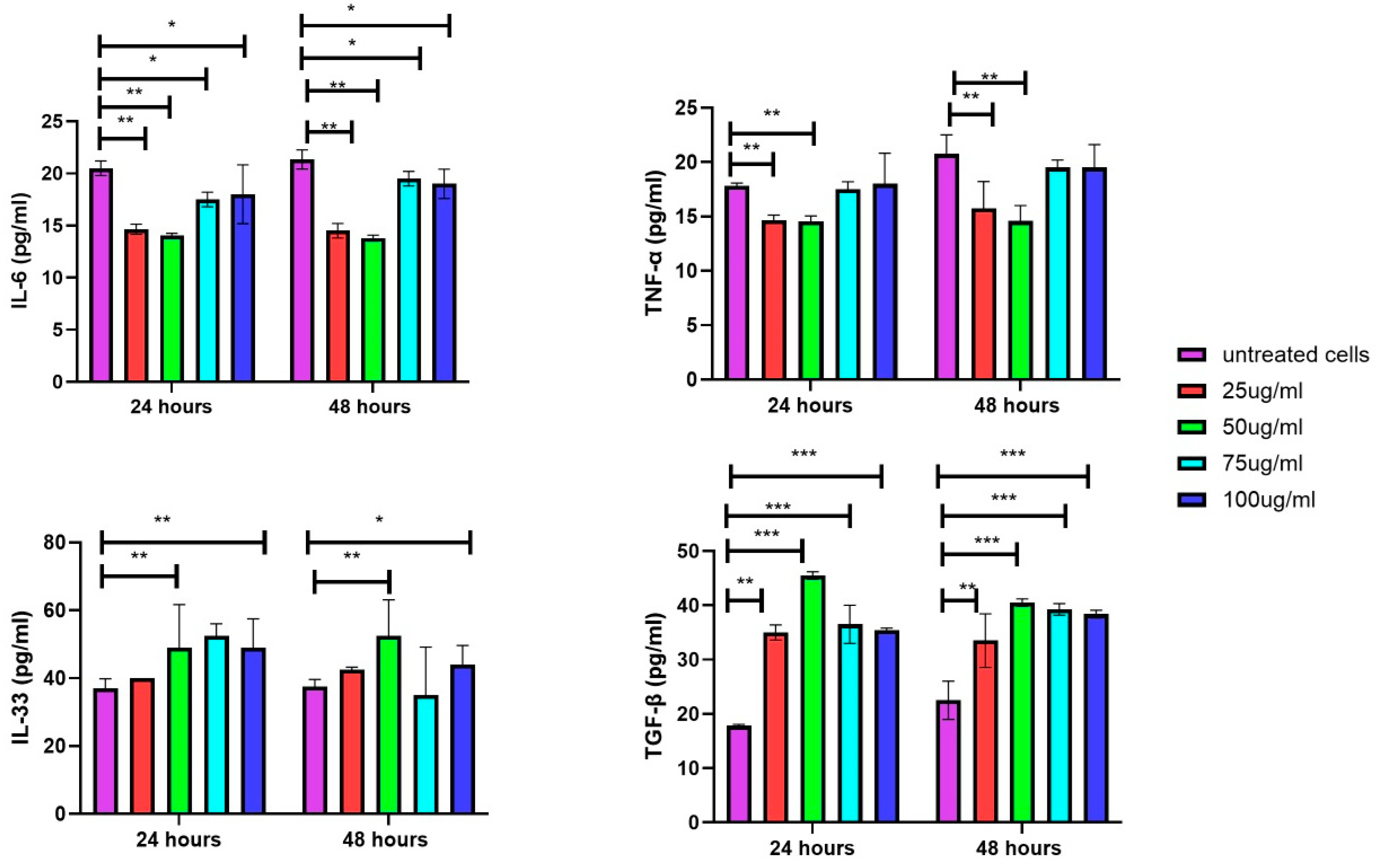
3.7. Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines in DFs upon Exposure of EVs
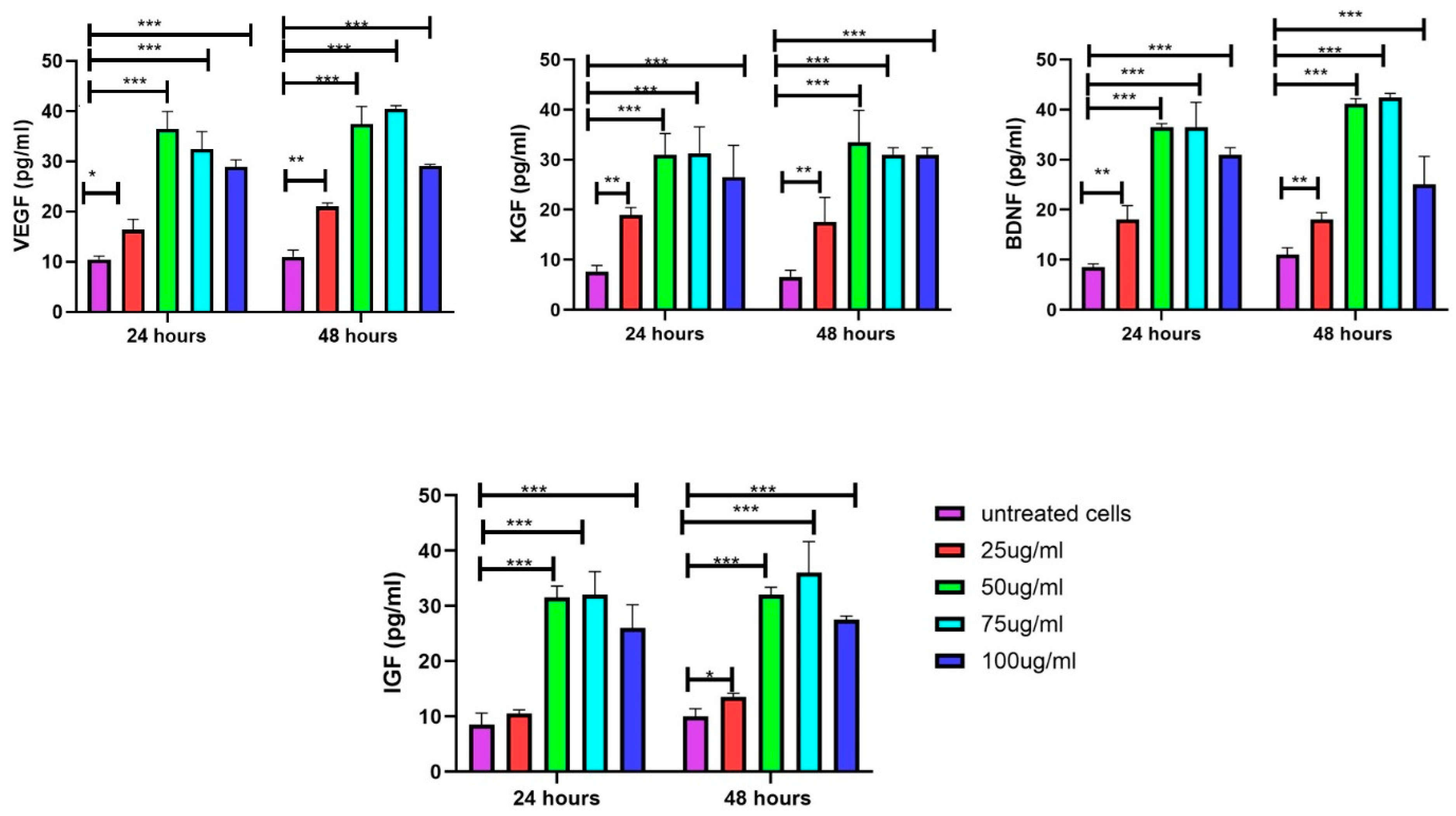
3.8. Increase in Growth Factors in DFs upon Exposure to EVs
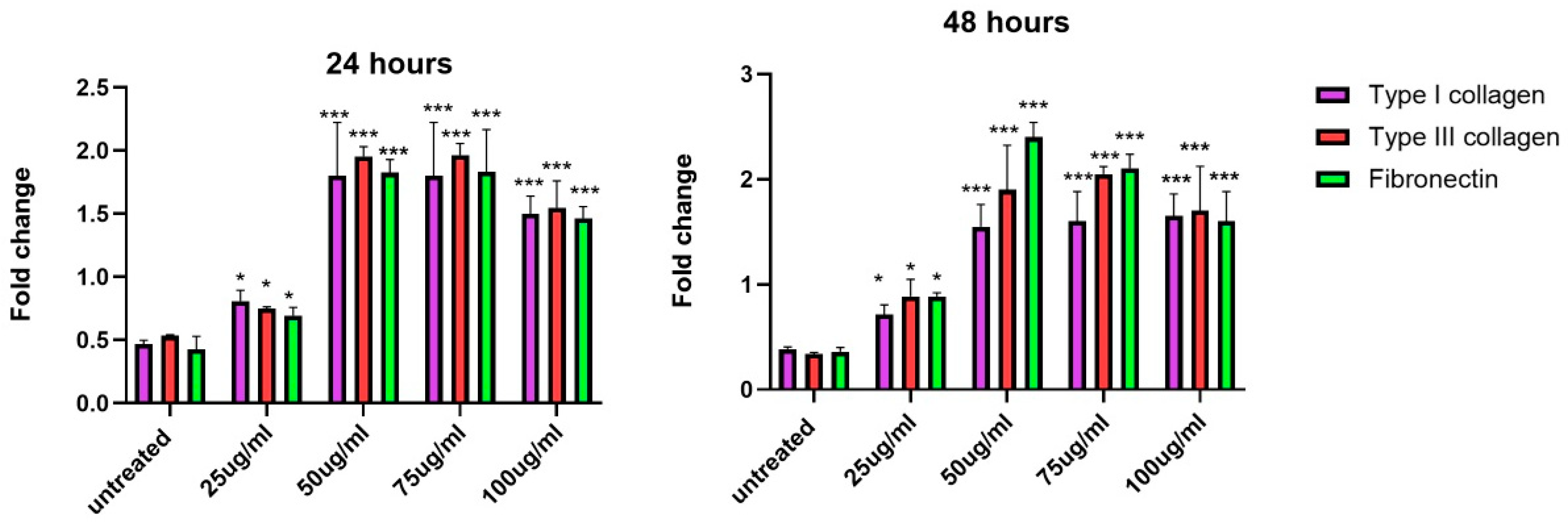
3.9. Increase in Gene Expression of Extracellular Matrix Proteins upon Exposure to EVs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhary, V.; Choudhary, M.; Bollag, W.B. Exploring Skin Wound Healing Models and the Impact of Natural Lipids on the Healing Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, R.B.; Tabor, A.J. The Role of the Extracellular Matrix (ECM) in Wound Healing: A Review. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, L.E.; Minasian, R.A.; Caterson, E.J. Extracellular Matrix and Dermal Fibroblast Function in the Healing Wound. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narauskaitė, D.; Vydmantaitė, G.; Rusteikaitė, J.; Sampath, R.; Rudaitytė, A.; Stašytė, G.; Aparicio Calvente, M.I.; Jekabsone, A. Extracellular Vesicles in Skin Wound Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Bi, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, M. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Promising Therapeutic Opportunities for Diabetic Wound Healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 4357–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttiah, B.; Ng, S.L.; Lokanathan, Y.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X. Extracellular Vesicles in Breast Cancer: From Intercellular Communication to Therapeutic Opportunities. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttiah, B.; Muhammad Fuad, N.D.; Jaafar, F.; Abdullah, N.A.H. Extracellular Vesicles in Ovarian Cancer: From Chemoresistance Mediators to Therapeutic Vectors. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, G.D.; Fonticoli, L.; Rajan, T.S.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Trubiani, O.; Pizzicannella, J.; Diomede, F. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): The Type-2 EMT in Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration and Organ Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerinck, J.; Goossens, S.; Berx, G. The epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity landscape: Principles of design and mechanisms of regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, C.; Datta, P.; Singh, Y.P.; Lo, A.; Horchler, S.; Elcheva, I.A.; Ozbolat, I.T.; Ravnic, D.J.; Koduru, S.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Use and in Bioengineering Applications. Cells 2022, 11, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varderidou-Minasian, S.; Lorenowicz, M.J. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue repair: Challenges and opportunities. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5979–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuloria, S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Dahiya, R.; Dahiya, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Kumari, U.; Sathasivam, K.; Meenakshi, D.U.; Wu, Y.S.; Sekar, M.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Regenerative Potential and Challenges. Biology 2021, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Luo, S.; Xiang, D. Extracellular vesicles derived from different sources of mesenchymal stem cells: Therapeutic effects and translational potential. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Ding, F.; et al. Improving dermal fibroblast-to-epidermis communications and aging wound repair through extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of Gstm2 mRNA. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, I.; Levy, A.; Estrach, S.; Féral, C.C.; Trentin, A.G.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Qu, J.; Zhou, H.; Théry, C.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 bound to specific dermal fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles is protected from degradation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Halawani, A.; Mithieux, S.M.; Yeo, G.C.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Weiss, A.S. Extracellular Vesicles: Interplay with the Extracellular Matrix and Modulated Cell Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.J.; Ashraf, A.; Chung, E.J. Extracellular Vesicles as Regulators of the Extracellular Matrix. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, N.V.; Jücker, M. The Functional Role of Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Salmanian, G.; Burns, M.; Maldonado, V.; Smith, E.; Porter, R.M.; Song, Y.H.; Samsonraj, R.M. Versatility of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue repair and regenerative applications. Biochimie 2023, 207, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsa, P.; Negi, R.; Ansari, U.A.; Khanna, V.K.; Pant, A.B. Insights of Extracellular Vesicles of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Prospective Cell-Free Regenerative Medicine for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.N.; Hassan, Z.Y.Y.; Tang, Y.L.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X. Expired platelet concentrate as a source of human platelet lysate for xenogeneic-free culture of human dermal fibroblasts. Sains Malays. 2021, 50, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar]
- Burnouf, T.; Goubran, H.A. Regenerative effect of expired platelet concentrates in human therapy: An update. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 61, 103363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Greenberg, Z.F.; Serafim, M.F.; Ali, S.; Jamieson, J.C.; Traktuev, D.O.; March, K.; He, M. Understanding molecular characteristics of extracellular vesicles derived from different types of mesenchymal stem cells for therapeutic translation. Extracell. Vesicle 2024, 3, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnici, C.M.; Iannolo, G.; Cittadini, E.; Carreca, A.P.; Nascari, D.; Timoneri, F.; Bella, M.D.; Cuscino, N.; Amico, G.; Carcione, C.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNAs of Human Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells May Activate Endogenous VEGF-A to Promote Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Chen, Y.A.; Ke, C.C.; Chiu, S.J.; Jeng, F.S.; Chen, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Yang, B.H.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, F.S.; et al. Multiplexed Molecular Imaging Strategy Integrated with RNA Sequencing in the Assessment of the Therapeutic Effect of Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Osteoporosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 7813–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Takakura, Y. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: Extracellular vesicles as therapeutic targets and agents. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 242, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, A.L.; Johansson, K.; Mossberg, M.; Kahn, R.; Karpman, D. Exosomes and microvesicles in normal physiology, pathophysiology, and renal diseases. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Extracellular microvesicles/exosomes: Discovery, disbelief, acceptance, and the future? Leukemia 2020, 34, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mambro, T.; Pellielo, G.; Agyapong, E.D.; Carinci, M.; Chianese, D.; Giorgi, C.; Morciano, G.; Patergnani, S.; Pinton, P.; Rimessi, A. The Tricky Connection between Extracellular Vesicles and Mitochondria in Inflammatory-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasai, A.; Jay, J.W.; Jupiter, D.; Wolf, S.E.; El Ayadi, A. Role of Exosomes in Dermal Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142 Pt A, 662–678.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalirfardouei, R.; Gholoobi, A.; Vahabian, M.; Mahdipour, E.; Afzaljavan, F. Therapeutic role of extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells in cutaneous wound models: A systematic review. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garima Sharma, D.; Kumar, A.; Mostafavi, E. Extracellular vesicle-based biovectors in chronic wound healing: Biogenesis and delivery approaches. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 32, 822–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarcinella, A.; Femminò, S.; Brizzi, M.F. Extracellular Vesicles: Emergent and Multiple Sources in Wound Healing Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitti, M.; Marengo, B.; Furfaro, A.L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Marinari, U.M.; Domenicotti, C.; Traverso, N. Hormesis and Oxidative Distress: Pathophysiology of Reactive Oxygen Species and the Open Question of Antioxidant Modulation and Supplementation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasugi, M.; Okada, R.; Takahashi, A.; Virya Chen, D.; Watanabe, S.; Hara, E. Small extracellular vesicles secreted from senescent cells promote cancer cell proliferation through EphA2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi, K.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Esfahani, H.; Zandsalimi, K.; Shahidi, F.K.; Abrahamse, H. Accelerating skin regeneration and wound healing by controlled ROS from photodynamic treatment. Inflamm. Regen. 2022, 42, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardaweel, S.K.; Gul, M.; Alzweiri, M.; Ishaqat, A.; ALSalamat, H.A.; Bashatwah, R.M. Reactive Oxygen Species: The Dual Role in Physiological and Pathological Conditions of the Human Body. Eurasian J. Med. 2018, 50, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dipietro, L.A. Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, S.G. Hall of Fame among Pro-inflammatory Cytokines: Interleukin-6 Gene and Its Transcriptional Regulation Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer-Geissler, J.C.J.; Schwingenschuh, S.; Zacharias, M.; Einsiedler, J.; Kainz, S.; Reisenegger, P.; Holecek, C.; Hofmann, E.; Wolff-Winiski, B.; Fahrngruber, H.; et al. The Impact of Prolonged Inflammation on Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, K.T.; Li, S.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, H.T.; Hu, D.H. Effects of exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on inflammatory response of mouse RAW264.7 cells and wound healing of full-thickness skin defects in mice. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi 2022, 38, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Xu, Q. Effect of gingival mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on inflammatory macrophages in a high-lipid microenvironment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 94, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Joo, H.S.; Hong, E.B.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.M. Therapeutic Application of Exosomes in Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, M.; Fan, Q.; Li, C.; Zhou, X. Therapeutic potential of exosome-based personalized delivery platform in chronic inflammatory diseases. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Pan, M.; Xu, X.; Du, L.; Rao, X.; Fu, G.; Lv, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, P.; et al. Interleukin-33 Potentiates TGF-β Signaling to Regulate Intestinal Stem Cell Regeneration After Radiation Injury. Cell Transplant. 2023, 32, 9636897231177377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Fan, T.; Xiao, C.; Tian, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molofsky, A.B.; Savage, A.K.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-33 in Tissue Homeostasis, Injury, and Inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.E.; Han, G.; Lim, N.R.; Kim, E.H.; Jang, Y.; Cho, H.; Jang, H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Harnessing the Natural Healing Power of Colostrum: Bovine Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Colostrum Facilitating the Transition from Inflammation to Tissue Regeneration for Accelerating Cutaneous Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Li, H.; Shen, J. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5911–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.; Lana, J.F.; Onishi, K.; Buford, D.; Peng, J.; Mahmood, A.; Fonseca, L.F.; van Zundert, A.; Podesta, L. Angiogenesis and Tissue Repair Depend on Platelet Dosing and Bioformulation Strategies Following Orthobiological Platelet-Rich Plasma Procedures: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilgus, T.A.; Matthies, A.M.; Radek, K.A.; Dovi, J.V.; Burns, A.L.; Shankar, R.; DiPietro, L.A. Novel function for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 on epidermal keratinocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidova-Rice, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Herman, I.M. Acute and impaired wound healing: Pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 2: Role of growth factors in normal and pathological wound healing: Therapeutic potential and methods of delivery. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2012, 25, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, X.H.; Do, P.T.X.; Dang, V.D.; Dam, P.T.M.; Bui, H.T.H.; Trinh, M.Q.; Vu, D.M.; et al. Differential Wound Healing Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Originated From Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue and Umbilical Cord Under Serum- and Xeno-Free Condition. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, H.; Bi, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Huang, Y.; Peng, B.; et al. Bioengineered MSC-derived exosomes in skin wound repair and regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1029671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekaev, N.N.; Borzykh, O.B.; Medvedev, G.V.; Pushkin, D.V.; Petrova, M.M.; Petrov, A.V.; Dmitrenko, D.V.; Karpova, E.I.; Demina, O.M.; Shnayder, N.A. The Role of Extracellular Matrix in Skin Wound Healing. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Rai, V.; Agrawal, D.K. Regulation of Collagen I and Collagen III in Tissue Injury and Regeneration. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 7, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Chiang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: A next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ling, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, L. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration by Modulating Multiple Cellular Changes: A Brief Review. Genes 2023, 14, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Xue, Y.; Zhan, B.; Lai, Z.; Huang, W.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Research progress of extracellular vesicles and exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of oxidative stress-related diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1238789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, V.; Roy, V.; Paré, B.; Goulet, C.R.; Deschênes, L.T.; Berthod, F.; Bolduc, S.; Gros-Louis, F. Tridimensional cell culture of dermal fibroblasts promotes exosome-mediated secretion of extracellular matrix proteins. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, G.; Guo, Y.; Tang, H.; Shi, Y.; Bian, X.; Zhu, M.; Kang, X.; Zhou, M.; Lyu, J.; et al. Exosomes from tendon stem cells promote injury tendon healing through balancing synthesis and degradation of the tendon extracellular matrix. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5475–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Type I collagen | AAGGAGGCCAGGTAGAAAGG | TGAGGATCAGGGGAAGGAGG |
| Type III collagen | GGGAGGAGGAGGAGGAGGAGG | TCACAGTGAGGAGAGGAGGA |
| Fibronectin | ATGGCGGAGTGGGATGGTGG | TGCTGTGGAGTGTGACAGTGG |
| Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | CTGAGGAGCAGGGGGGAGAA | AAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTT |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean Particle Size | 119.2 ± 2.0 nm |
| Mode Particle Size | 81.5 ± 2.8 nm |
| Standard Deviation (SD) | 55.1 ± 2.6 nm |
| D10 (10% of particles below) | 72.5 ± 1.7 nm |
| D50 (Median particle size) | 101.1 ± 2.2 nm |
| D90 (90% of particles below) | 184.8 ± 4.9 nm |
| Particle Concentration | 1.83 × 1012 ± 1.66 × 1011 particles/mL |
| Particles per Frame | 100.0 ± 9.1 |
| Centers Detected per Frame | 114.8 ± 10.8 |
| Concentration of EVs (µg/mL) | Morphological Features | Cell Density | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (Control) | Elongated, spindle-shaped morphology, with a well-spread appearance. | Normal | Typical fibroblast morphology observed in untreated cells. |
| 25 | Similar elongated, spindle-shaped morphology to control cells. | Slight increase | Cell density shows a minor increase compared to untreated cells, with no noticeable morphological changes. |
| 50 | Denser population, with enhanced spindle-like and healthier appearance. | Significant increase | Optimal concentration, resulting in reduced intercellular space and enhanced cell proliferation. |
| 75 | Retains fibroblast-like elongated morphology. | Comparable to 50 µg/mL | No further improvement in cell density or morphology compared to 50 µg/mL. |
| 100 | Similar fibroblast-like morphology as at 75 µg/mL. | Comparable to 50 µg/mL | No additional enhancement in morphology or cell density. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barathan, M.; Ham, K.J.; Wong, H.Y.; Law, J.X. The Role of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Modulating Dermal Fibroblast Activity: A Pathway to Enhanced Tissue Regeneration. Biology 2025, 14, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020150
Barathan M, Ham KJ, Wong HY, Law JX. The Role of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Modulating Dermal Fibroblast Activity: A Pathway to Enhanced Tissue Regeneration. Biology. 2025; 14(2):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarathan, Muttiah, Kow Jack Ham, Hui Yin Wong, and Jia Xian Law. 2025. "The Role of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Modulating Dermal Fibroblast Activity: A Pathway to Enhanced Tissue Regeneration" Biology 14, no. 2: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020150
APA StyleBarathan, M., Ham, K. J., Wong, H. Y., & Law, J. X. (2025). The Role of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Modulating Dermal Fibroblast Activity: A Pathway to Enhanced Tissue Regeneration. Biology, 14(2), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020150






