Beneficial Effects of Infiltration of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Endometrium
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
1.1.1. PRP Definition and Classification
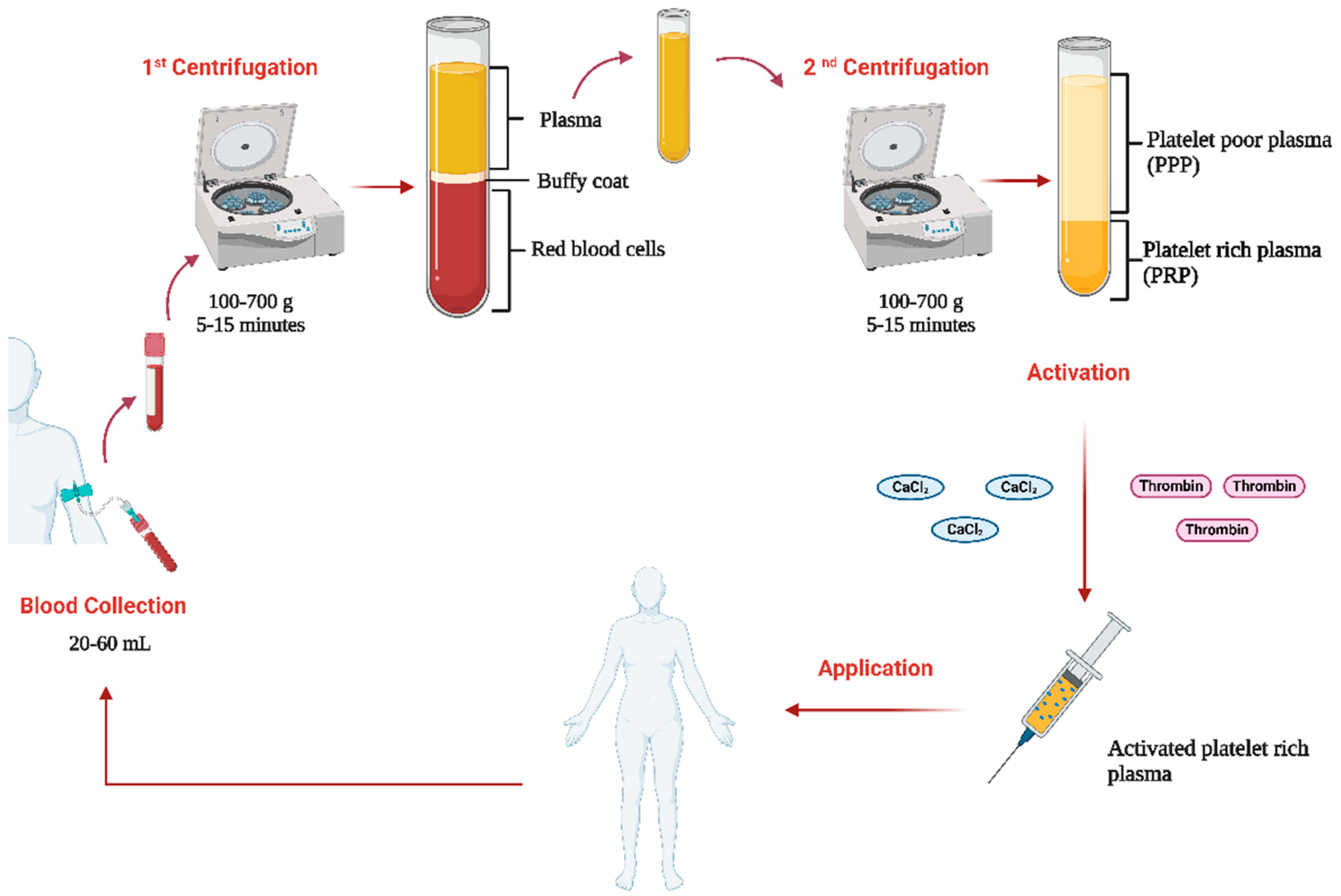
1.1.2. PRP Preparation Protocols
1.2. Clinical Applications
1.3. Reproductive Medicine Applications
2. Materials and Methods
3. Research Findings
3.1. PRP Composition
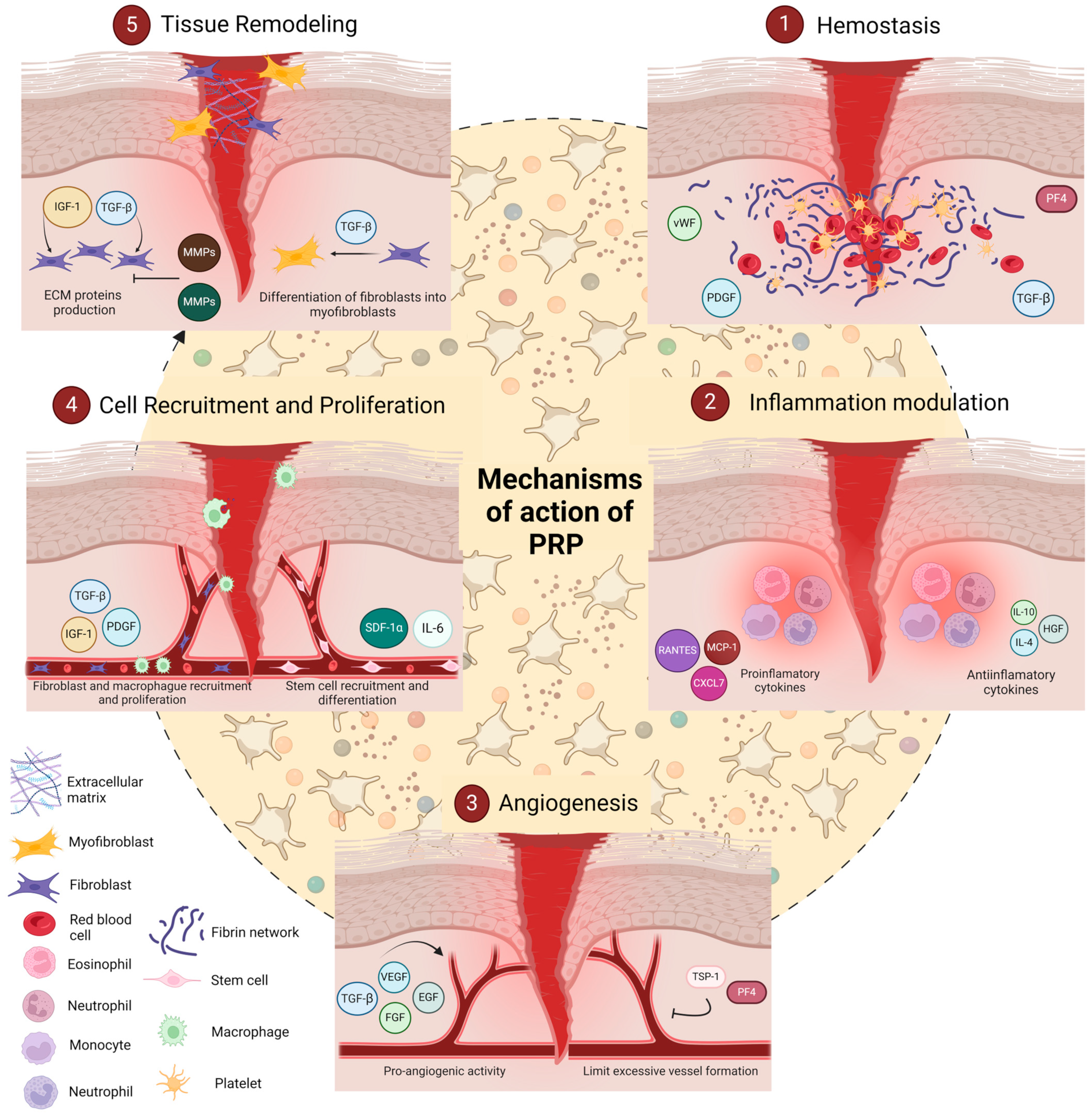
3.2. Mechanisms of PRP
3.2.1. Hemostasis
3.2.2. Inflammation Modulation
3.2.3. Angiogenesis
3.2.4. Cell Recruitment and Proliferation
3.2.5. Tissue Remodelling
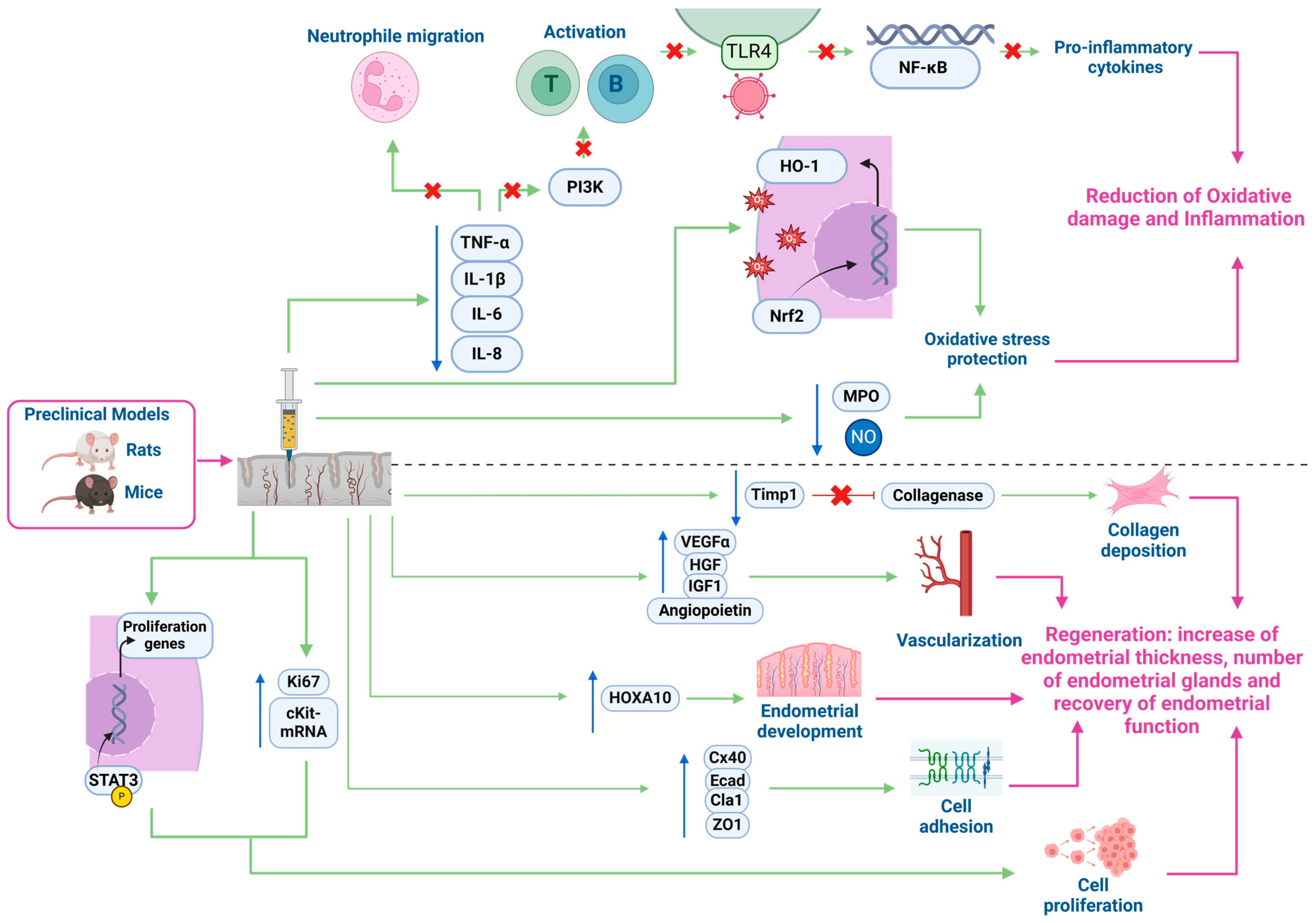
3.3. Mechanisms of Action in the Endometrium
3.3.1. Preclinical In Vivo and In Vitro Models
3.3.2. Clinical Trials
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Word | Abbreviation | Word |
| α-SMA | Alpha-smooth muscle actin | L-PRP | Leukocyte- and platelet-rich plasma |
| ACD-A | Citrate dextrose A | L-PRF | Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin |
| Adm | Adrenomedullin gen | LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| AS | Asherman syndrome | MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| ATP/ADP | Adenosine Triphosphate/Adenosine Diphosphate | Mg2+ | Magnesium Ion |
| Ca2+ | Calcium Ion | MIP-1α | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 1 Alpha |
| CaCl2 | Calcium chloride | MMP-1, -2, -9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 1, 2, and 9 |
| CD40-L | CD40 Ligand | MPO | Mieloperoxidase |
| CCL | C-C motif chemokine ligands | MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| CK18 | Cytokeratin 18 | Mt2-MMP | Membrane type 2 matrix metalloproteinase gen |
| CK19 | Cytokeratin 19 | NAP-2 | Neutrophil Activating Peptide 2 |
| cKit-Mrna | c-Kit tyrosine kinase receptor messenger RNA | NF-κβ | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| CXCL | Chemokine C-X-C motif ligand | NO | Nitric oxide |
| CTGF | Connective Tissue Growth Factor | Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| Cx40 | Connexin 40 | PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| Ecad | E-cadherin | PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix | PF4 | Platelet factor 4 |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | PPP | Platelet-poor plasma |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor | P-PRF | Platelet-rich fibrin |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor | PRGF | Plasma rich in growth factors |
| GFs | Growth factors | PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor | P-PRP | Pure platelet-rich plasma |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 | RANTES | Regulated upon activation, normal T cells expressed and secreted |
| HOXA10 | Homeobox A10 | RIF | Recurrent implantation failure |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 | SDF-1α | Stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha |
| IGF-A | Insulin-like growth factor A | STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 Beta | TE | Thin endometrium |
| IL-4 | Interleukin 4 | TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 | Timp1 | Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases 1 gen |
| IL-8 | Interleukin 8 | TIMPs | Inhibitors of metalloproteinases |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 | TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| IVF | In vitro fertilization | TLR4/NF-Κb | Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor κB |
| JAM-A, JAM-C | Junctional Adhesion Molecule A, C | TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| K+ | Potassium Ion | TSP-1 | Thrombospondin-1 |
| Ki67 | Ki-67 nuclear proliferation antigen gen | VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| LFA-2 | Lymphocyte Function-associated Antigen 2 | vWF | von Willebrand factor |
| Lox | Lysil oxidase gen | ZO1 | Zona occludens-1 |
References
- Alves, R.; Grimalt, R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2018, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, A.; Ruiz-Santiago, F.; García-Espinosa, J. Platelet-rich plasma: Myth or reality? Radiologia 2018, 60, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delong, J.M.; Russell, R.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Platelet-rich plasma: The PAW classification system. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalon, J.; Chateau, A.L.; Bertrand, B.; Louis, M.L.; Silvestre, A.; Giraudo, L.; Veran, J.; Sabatier, F. DEPA classification: A proposal for standardising PRP use and a retrospective application of available devices. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.; Alsousou, J.; Andia, I.; Burnouf, T.; Dohan Ehrenfest, D.; Everts, P.; Langer, H.; Magalon, J.; Marck, R.; Gresele, P. The use of platelets in regenerative medicine and proposal for a new classification system: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, C.; Roffi, A.; Grigolo, B.; Mariani, E.; Pratelli, L.; Merli, G.; Kon, E.; Marcacci, M.; Filardo, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The Choice of Activation Method Affects the Release of Bioactive Molecules. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6591717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachito, D.V.; Bagattini, A.M.; de Almeida, A.M.; Mendrone-Júnior, A.; Riera, R. Technical Procedures for Preparation and Administration of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Related Products: A Scoping Review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 598816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeny, J.; Grossman, B.J.; Brecher, M. Blood collection, storage, and component preparation methods. In Technical Manual, 13th ed.; Krager, S., Ed.; American Association of Blood Banks: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 955–958. [Google Scholar]
- Dashore, S.; Chouhan, K.; Nanda, S.; Sharma, A. Preparation of platelet-rich plasma: National IADVL PRP taskforce recommendations. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 12, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.F.; Stessuk, T.; Camargo IC, C.; Sabeh Junior, N.; Santos, L.D.; Ribeiro-Paes, J.T. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Methodological aspects and clinical applications. Platelets 2014, 26, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, C.S. Blood coagulation: Evidence of an antagonist to factor VI in platelet-rich human plasma. Nature 1954, 173, 723–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-rich plasma: New performance understandings and therapeutic considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-González, D.J.; Méndez-Bolaina, E.; Trejo-Bahena, N.I. Platelet-rich plasma peptides: Key for regeneration. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 2012, 532519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mościcka, P.; Przylipiak, A. History of autologous platelet-rich plasma: A short review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 2712–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.R.; Gallego, M.A.P.; García-Denche, J.T. Plasma rico en plaquetas: Fundamentos biológicos y aplicaciones en cirugía maxilofacial y estética facial. Rev. Española Cirugía Oral Maxilofac. 2012, 34, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, I.; Sáenz, A.; Arévalo, A.; Roussel, S.; Pérez-Moreiras, I.; Artiñano, E.; Martínez-Peñuela, A.; Esquide, J.; Aspiroz, A.; Camacho, I. Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on heart infarction in sheep. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2013, 83, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave, B.; Li, F. Nanosecond pulse electric field activation of platelet-rich plasma reduces myocardial infarct size and improves left ventricular mechanical function in the rabbit heart. J. Extra-Corpor. Technol. 2012, 44, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawdat, H.I.; Tawdy, A.M.; Hegazy, R.A.; Zakaria, M.M.; Allam, R.S. Autologous platelet-rich plasma versus readymade growth factors in skin rejuvenation: A split face study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 16, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.C.; Lin, D.Z.; Lee, S.L.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.J.; Chiu, W.K. Assisted therapy with platelet-rich plasma for burn patients: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Burns 2021, 47, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zouhbi, A.; Yammine, J.; Hemdanieh, M.; Korbani, E.T.; Nassereddine, M. Utility of platelet-rich plasma therapy in the management of meniscus injuries: A narrative review. Orthop. Rev. 2024, 16, 94240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.A.V.; Tran, T.T.P.; Luong, N.T.M. Antimicrobial effect of platelet-rich plasma against Porphyromonas gingivalis. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 7329103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahli, E.; Özmert, E.; Günel, M.D.; Atilla, H. Evaluation of the efficacy of subtenon autologous platelet-rich plasma therapy in patients with retinitis pigmentosa and factors affecting response to the treatment. Int. Ophthalmol. 2024, 44, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Arnalich-Montiel, F.; Rodriguez, A.E. The role of “eye platelet rich plasma” (E-PRP) for wound healing in ophthalmology. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharara, F.I.; Lelea, L.L.; Rahman, S.; Klebanoff, J.S.; Moawad, G.N. A narrative review of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in reproductive medicine. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, W.T.; McBain, J.; Rogers, P. What is the contribution of embryo-endometrial asynchrony to implantation failure? J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2016, 33, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasius, A.; Smit, J.G.; Torrance, H.L.; Eijkemans, M.J.C.; Mol, B.W.; Opmeer, B.C.; Broekmans, F.J.M. Endometrial thickness and pregnancy rates after IVF: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2014, 20, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibeh, N.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Madani, J.; Pourakbari, R.; Yousefi, M.; Ahmadian Heris, J. Cell-based therapy in thin endometrium and Asherman syndrome. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.E.; Hartman, M.; Hartman, A. Management of thin endometrium in assisted reproduction: A clinical practice guideline from the Canadian Fertility and Andrology Society. Reprod. BioMedicine Online 2019, 39, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar, M.; Tabibnejad, N.; Tabatabaie, A.A. The thin endometrium in assisted reproductive technology: An ongoing challenge. Middle East Fertil. Soc. J. 2018, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Teng, X. New advances in the treatment of thin endometrium. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1269382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, L.N.; Pang, J.; Chen, J.; Liang, X. Autologous platelet-rich plasma infusion improves clinical pregnancy rate in frozen embryo transfer cycles for women with thin endometrium. Medicine 2019, 98, e14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Mettler, L.; Jain, S.; Meshram, S.; Günther, V.; Alkatout, I. Management of a thin endometrium by hysteroscopic instillation of platelet-rich plasma into the endomyometrial junction: A pilot study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efendieva, Z.; Vishnyakova, P.; Apolikhina, I.; Artemova, D.; Butov, K.; Kalinina, E.; Fedorova, T.; Tregubova, A.; Asaturova, A.; Fatkhudinov, T.; et al. Hysteroscopic injections of autologous endometrial cells and platelet-rich plasma in patients with thin endometrium: A pilot randomized study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 945. [Google Scholar]
- Puente Gonzalo, E.; Alonso Pacheco, L.; Vega Jiménez, A.; Vitale, S.G.; Raffone, A.; Laganà, A.S. Intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma for severe Asherman syndrome: A cutting-edge approach. Updates Surg. 2021, 73, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanova, L.; Cedars, M.I.; Huddleston, H.G. Platelet-rich plasma in the management of asherman syndrome: Case report. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Eguren, A.; Bueno-Fernandez, C.; Gómez-Álvarez, M.; Francés-Herrero, E.; Pellicer, A.; Bellver, J.; Seli, E.; Cervelló, I. Evolution of biotechnological advances and regenerative therapies for endometrial disorders: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2024, 30, 584–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Cheng, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X. Autologous platelet-rich plasma intrauterine perfusion to improve pregnancy outcomes after implantation failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2022, 48, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet α-granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qi, J.; Sun, Y. Platelet-rich plasma as a potential new strategy in the endometrium treatment in assisted reproductive technology. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 707584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, J.N.; Italiano, J.E. Platelets: Production, morphology and ultrastructure. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 210, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulou, M.; Dai, C.; Tan, X.; Wen, X.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Liu, Y. Hepatocyte growth factor exerts its anti-inflammatory action by disrupting nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubkowska, A.; Dolegowska, B.; Banfi, G. Growth factor content in PRP and their applicability in medicine. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26 (Suppl. S1), 3S–22S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polasek, J. Platelet secretory granules or secretory lysosomes? Platelets 2005, 16, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amalia, L. The role of platelet-selectin as a marker of thrombocyte aggregation on cerebral sinus venous thrombosis. J. Blood Med. 2022, 13, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus-Bell, E.; Mangin, P.H. The relative importance of platelet integrins in hemostasis, thrombosis and beyond. Haematologica 2023, 108, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J.; Browder, T.; Palmblad, J. Angiogenesis research: Guidelines for translation to clinical application. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W. Sorting machineries: How platelet-dense granules differ from α-granules. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognasse, F.; Laradi, S.; Berthelot, P.; Bourlet, T.; Marotte, H.; Mismetti, P.; Garraud, O.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H. Platelet inflammatory response to stress. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleator, J.H.; Zhu, W.Q.; Vaughan, D.E.; Hamm, H.E. Differential regulation of endothelial exocytosis of P-selectin and von Willebrand factor by protease-activated receptors and cAMP. Blood 2006, 107, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.E.; Puskas, B.L.; Mandelbaum, B.R.; Gerhardt, M.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Platelet-rich plasma: From basic science to clinical applications. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Sanchez, M.; Maffulli, N. Tendon healing and platelet-rich plasma therapies. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.A.M.; Knape, J.T.A.; Weibrich, G.; Schönberger, J.P.A.M.; Hoffmann, J.; Overdevest, E.P.; Box, H.A.M.; van Zundert, A. Platelet-rich plasma and platelet gel: A review. J. Extra-Corpor. Technol. 2006, 38, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, M.A.; Diacovo, T.G.; Emsley, J.; Liddington, R.; Handin, R.I. Mapping the glycoprotein Ib-binding site in the von Willebrand factor A1 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19098–19105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, I.; D’Ascenzo, S.; MacChiarelli, G.; Dolo, V. In vitro evidence supporting applications of platelet derivatives in regenerative medicine. Blood Transfus. 2020, 18, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, K.K.; Barro, V.; Muller, B.; Terada, S.; Fu, F.H. Evaluation of the effects of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involved in the healing of sports-related soft tissue injuries. Iowa Orthop. J. 2012, 32, 150–163. [Google Scholar]
- Andia, I.; Sánchez, M.; Maffulli, N. Joint pathology and platelet-rich plasma therapies. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flad, H.-D.; Brandt, E. Platelet-derived chemokines: Pathophysiology and therapeutic aspects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2010, 67, 2363–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.F.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Mosaner, T.; Lana, J.F. The regenerative mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma: A review. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandercappellen, J.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. The role of the CXC chemokines platelet factor-4 (CXCL4/PF-4) and its variant (CXCL4L1/PF-4var) in inflammation, angiogenesis and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Szukiewicz, D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 561459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, C.J.; Leibovich, S.J. Regulation of macrophage polarization and wound healing. Adv. Wound Care 2012, 1, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andia, I.; Abate, M. Platelet-rich plasma: Underlying biology and clinical correlates. Regen. Med. 2013, 8, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A.T.; Nurden, P.; Sanchez, M.; Andia, I.; Anitua, E. Platelets and wound healing. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 2008, 13, 3532–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, P.; Kirchhoff, K.; Bekeran, S.; Bauer, A.-T.; von Isenburg, S.; Dornseifer, U.; Machens, H.-G.; Schilling, A.F.; Hadjipanayi, E. Comparative Evaluation of the Angiogenic Potential of Hypoxia Preconditioned Blood-Derived Secretomes and Platelet-Rich Plasma: An In Vitro Analysis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.E.; Zurakowski, D.; Italiano, J.E.; Michel, L.V.; Fox, L.; Klement, G.L.; Folkman, J. Normal ranges of angiogenesis regulatory proteins in human platelets. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.; Ii, G.F.; Rothenberg, J.; Mautner, K.; Everts, P.A.; Ii, G.F.; Rothenberg, J.; Mautner, K. The rationale of autologously prepared bone marrow aspirate concentrate for use in regenerative medicine applications. In Regenerative Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P. Wound healing—Aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.J.; Ralphs, J.R. The response of foetal annulus fibrosus cells to growth factors: Modulation of matrix synthesis by TGF-β1 and IGF-1. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 136, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, M.; Martínez, C.; Martínez, J.; Smith, P.C. Effects of platelet-rich and -poor plasma on the reparative response of gingival fibroblasts. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Li, L.; Tang, J.; Cheng, B. The anti-photoaging effects of pre- and post-treatment of platelet-rich plasma on UVB-damaged HaCaT keratinocytes. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 97, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hire, J.M.; Evanson, J.L.; Johnson, P.C.; Zumbrun, S.D.; Guyton, M.K.; McPherson, J.C.; Bojescul, J.A. Variance of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) concentrations in activated, concentrated platelets from healthy male donors. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2014, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Horikawa, T.; Takamizawa, S.; Ochiai, A.; Kawamura, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Sugiyama, R. Transcriptomic profiling analysis of human endometrial stromal cells treated with autologous platelet-rich plasma. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2023, 22, e12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Hao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L. Platelet rich plasma alleviates endometritis induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice via inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 91, e13833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Yang, Z.; Xue, P.; Liu, X. Nrf2/HO-1 pathway is involved the anti-inflammatory action of intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma against lipopolysaccharides in endometritis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2022, 44, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.Y.; Myoung, S.M.; Choe, J.M.; Kim, T.; Cheon, Y.P.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, H. Effects of autologous platelet-rich plasma on regeneration of damaged endometrium in female rats. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshersagar, J.; Kawale, A.A.; Tardalkar, K.; Damle, M.N.; Chaudhari, L.R.; Sharma, R.; Joshi, M.G. Activated platelet-rich plasma accelerate endometrial regeneration and improve pregnancy outcomes in murine model of disturbed endometrium. Cell Tissue Bank. 2024, 25, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Yoon, J.A.; Yoon, S.Y.; Park, M.; Lee, W.S.; Lyu, S.W.; Song, H. Human platelet-rich plasma facilitates angiogenesis to restore impaired uterine environments with asherman’s syndrome for embryo implantation and following pregnancy in mice. Cells 2022, 11, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Sánchez, J.; Sánchez, W.; Vielma, V. Platelet-rich plasma as an adjuvant in the endometrial preparation of patients with refractory endometrium. JBRA Assist. Reprod. 2018, 22, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadehmodarres, S.; Salehpour, S.; Saharkhiz, N.; Nazari, L. Treatment of thin endometrium with autologous platelet-rich plasma: A pilot study. JBRA Assist. Reprod. 2017, 21, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, M.; Ihana, T.; Kurosawa, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Tsutsumi, O. Intrauterine administration of platelet-rich plasma improves embryo implantation by increasing the endometrial thickness in women with repeated implantation failure: A single-arm self-controlled trial. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2020, 19, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enatsu, Y.; Enatsu, N.; Kishi, K.; Otsuki, J.; Iwasaki, T.; Okamoto, E.; Kokeguchi, S.; Shiotani, M. Clinical outcome of intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma in patients with recurrent implantation failure. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2021, 21, e12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Mou, S.; Zhao, H.; Fang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Sha, T.; Ding, J.; Hao, C. Investigation of platelet-rich plasma in increasing proliferation and migration of endometrial mesenchymal stem cells and improving pregnancy outcome of patients with thin endometrium. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 7403–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, P.; Mai, H.; Guo, Q.; Guo, J.; Liang, X.; Chen, P. How platelet-rich plasma (PRP) intra-uterine injection improve endometrial receptivity of intrauterine adhesions in women: A time-series-based self-controlled study. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2023, 156, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boychuk, A.V.; Kotsabyn, N.V.; Yakymchuk, J.B.; Nikitina, I.M. Pregravid preparation of women with chronic endometritis in IVF cycles. Wiad. Lek. 2024, 77, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanova, L.; Sundaram, V.; Kao, C.N.; Letourneau, J.M.; Manvelyan, E.; Cedars, M.I.; Huddleston, H.G. Autologous platelet-rich plasma treatment for moderate-severe Asherman syndrome: The first experience. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 2955–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandulwadkar, S.; Mishra, S.; Gupta, S. Successful application of combined autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells and platelet-rich plasma in a case of severe asherman syndrome and subsequent in vitro fertilization conception. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 14, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alonso-Frías, P.; Francés-Herrero, E.; Bueno-Fernandez, C.; Gómez-Álvarez, M.; Agustina-Hernández, M.; Cervelló, I.; Cozzolino, M. Beneficial Effects of Infiltration of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Endometrium. Biology 2025, 14, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040319
Alonso-Frías P, Francés-Herrero E, Bueno-Fernandez C, Gómez-Álvarez M, Agustina-Hernández M, Cervelló I, Cozzolino M. Beneficial Effects of Infiltration of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Endometrium. Biology. 2025; 14(4):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040319
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlonso-Frías, Paula, Emilio Francés-Herrero, Clara Bueno-Fernandez, María Gómez-Álvarez, Marcos Agustina-Hernández, Irene Cervelló, and Mauro Cozzolino. 2025. "Beneficial Effects of Infiltration of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Endometrium" Biology 14, no. 4: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040319
APA StyleAlonso-Frías, P., Francés-Herrero, E., Bueno-Fernandez, C., Gómez-Álvarez, M., Agustina-Hernández, M., Cervelló, I., & Cozzolino, M. (2025). Beneficial Effects of Infiltration of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Endometrium. Biology, 14(4), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040319




