Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Cereibacter sphaeroides ST16 and ST26 Enhanced Soil Phosphorus Solubility, Rice Growth, and Grain Yield in Acidic-Contaminated Saline Soil
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Parameters of Evaluation
2.2.1. Soil Analysis
2.2.2. Plant Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Features of the Salinized Soil in the Rice-Shrimp Model in An Bien, An Giang
3.2. Cereibacter sphaeroides Affected the Rice Biochemistry
3.3. Cereibacter sphaeroides Affected P Dynamics and Soil Features
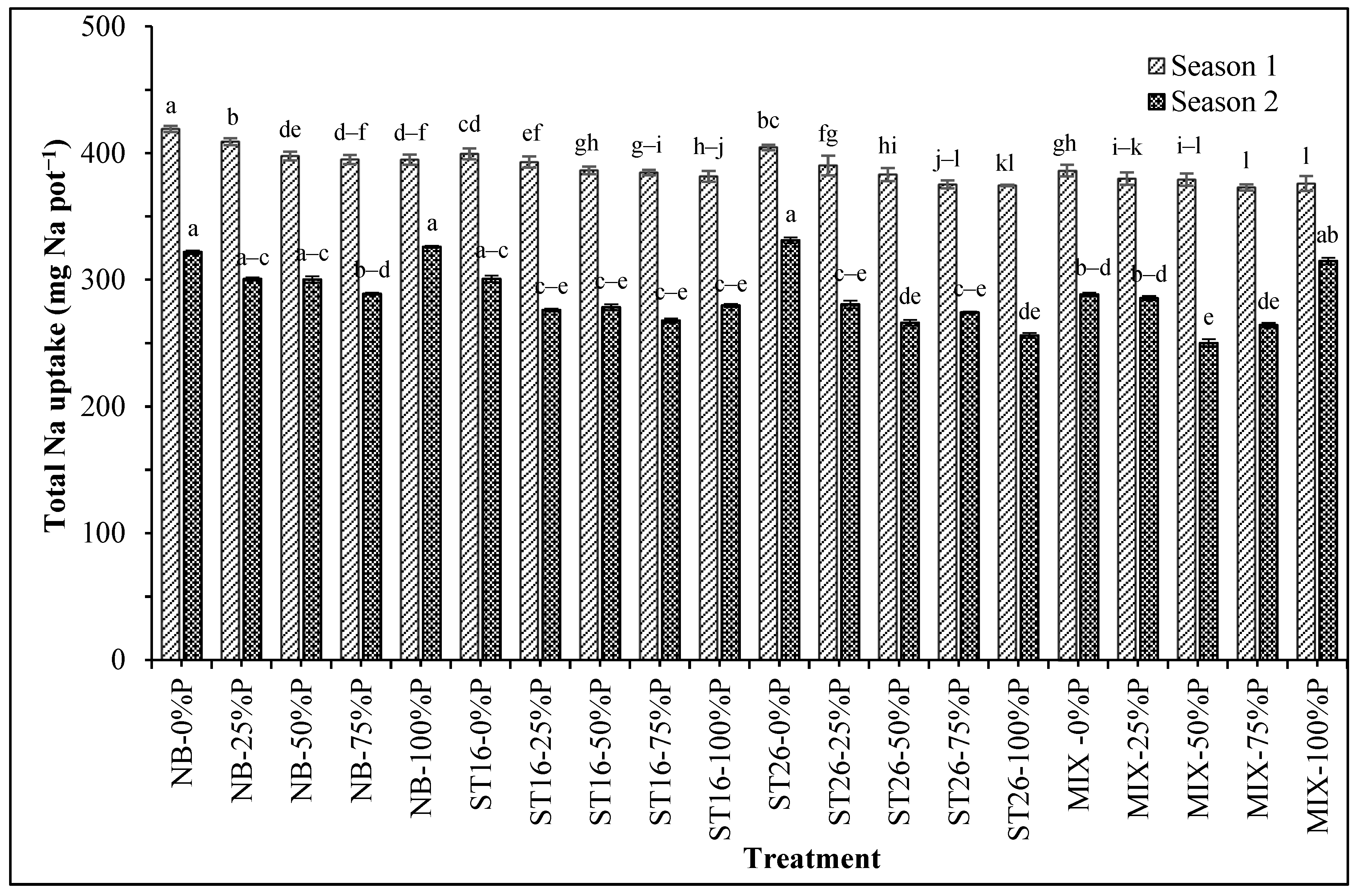
3.4. Cereibacter sphaeroides Affected P and Na Uptake in Rice Plants
3.5. Cereibacter sphaeroides Affected Rice Agronomic Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALA | 5-aminolevulinic acid |
| Al-P | Aluminum phosphate |
| Ca-P | Calcium phosphate |
| CEC | Cation exchange capacity |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| Cl | Chloride |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| EPS | Exopolymeric substances |
| Fe-P | Ferrous phosphate |
| IAA | Indole-3-acetic acid |
| Na | Sodium |
| P | Phosphate |
| PGPS | Plant growth-promoting substances |
| PNSB | Purple nonsulfur bacteria |
| SPAD | Soil and Plant Analysis Development |
References
- Loc, H.H.; Binh, D.V.; Park, E.; Shrestha, S.; Dung, T.D.; Son, V.H.; Tru, N.H.T.; Mai, N.P.; Seijger, C. Intensifying saline water intrusion and drought in the Mekong Delta: From physical evidence to policy outlooks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poelma, T.; Bayrak, M.M.; Van Nha, D.; Tran, T.A. Climate change and livelihood resilience capacities in the Mekong Delta: A case study on the transition to rice–shrimp farming in Vietnam’s Kien Giang Province. Clim. Change 2021, 164, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.N.; Huynh Van, H.; Vo Minh, H.; Tri, V.P.D. Salinity intrusion trends under the impacts of upstream discharge and sea level rise along the Co Chien River and Hau River in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Climate 2023, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Vietnam: Country Climate and Development Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, L.W.; Nguyen, N.K.; Demyan, M.S. Salinity and acid sulfate soils of the Vietnam Mekong Delta: Agricultural management and adaptation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 78, 85A–92A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.; Koch, M.; Khoi, C.M.; Braun, G.; Sebesvari, Z.; Amelung, W. Land use change from permanent rice to alternating rice-shrimp or permanent shrimp in the coastal Mekong Delta, Vietnam: Changes in the nutrient status and binding forms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, C.; Stewart-Koster, B.; Van Sang, N.; Xoan, V.B.; Tinh, N.T.N.; Sammut, J.; Burford, M.A. Rice-shrimp ecosystems in the Mekong Delta: Linking water quality, shrimp and their natural food sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlian, A.; Kurniasih, B.; Indradewa, D. Effect of saline irrigation method on the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agric. Sci. 2020, 5, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudari, A.; Mayane, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Colinet, G.; Oukarroum, A. Photosynthetic performance and nutrient uptake under salt stress: Differential responses of wheat plants to contrasting phosphorus forms and rates. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1038672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano-Armada, N.; Yañez-Yazlle, M.F.; Irazusta, V.P.; Rajal, V.B.; Moraga, N.B. Potential of Bioremediation and PGP Traits in Streptomyces as Strategies for Bio-Reclamation of Salt-Affected Soils for Agriculture. Pathogens 2020, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Fatima, T.; Mishra, J.; Mishra, I.; Verma, S.; Verma, R.; Verma, M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Verma, P.; Mishra, P.; et al. Halo-tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for improving productivity and remediation of saline soils. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 26, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuong, N.Q.; Kantachote, D.; Dung, N.T.T.; Huu, T.N.; Thuc, L.V.; Thu, L.T.M.; Quang, L.T.; Xuan, D.T.; Nhan, T.C.; Tien, P.D.; et al. Potential of potent purple nonsulfur bacteria isolated from rice-shrimp systems to ameliorate rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth and yield in saline acid sulfate soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2023, 46, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, L.S.; Wu, J.Y.; Tu, Y.K.; Chen, H.W.; Chao, Y.Y. Mitigation of salinity stress in salt-sensitive rice seedlings via phytohormone synthesis, antioxidant defence enhancement, and ion balance regulation induced by 5-aminolevulinic acid-producing purple non-sulfur bacteria. Plant Biol. 2025, 27, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Chawla, M.; Thakur, M.; Bhardwaj, R.; Wang, J.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Rinklebe, J. Bioremediation of mercury contaminated soil and water: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 1261–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G.; Banerjee, P.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Etesami, H.; Shaw, A.K.; Huang, Y.H.; Huang, H.B.; Chen, C.Y. Management of phosphorus in salinity-stressed agriculture for sustainable crop production by salt-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria—A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Lur, H.-S.; Liu, C.-T. From Lab to Farm: Elucidating the beneficial roles of photosynthetic bacteria in sustainable agriculture. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Sundar, L.S.; Tu, Y.K.; Chao, Y.Y. Exploring the potential of purple non-sulfur bacteria strains A3-5 and F3-3 in sustainable agriculture: A study on nutrient solubilization, plant growth promotion, and acidic stress tolerance. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, K.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Anoxygenic phototrophic purple non-sulfur bacteria: Tool for bioremediation of hazardous environmental pollutants. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dat, L.T.; Xuan, L.N.T.; Nhan, T.C.; Quang, L.T.; Khuong, N.Q. Isolating, selecting, and identifying Na+, H+, Al3+, Fe2+, Mn2+-resistant purple non-sulfur bacteria solubilizing insoluble phosphorus compounds from salt-contaminated acid sulfate soil for rice-shrimp system. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2024, 18, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horneck, D.A.; Sullivan, D.M.; Owen, J.S.; Hart, J.M. Soil Test Interpretation Guide; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Metson, A.J. Methods of Chemical Analysis for Soil Survey Samples. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cu, N.X.; Dung, B.T.N.; Duc, L.; Hiep, T.K.; Tranh, C.V. Analysis of soil minerals. In Methods in Analyzing Soil, Water, and Fertilizer for Crops, Khoa, L.V., Ed.; Viet Nam Education Publishing House: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2000; Volume Chapter 6, pp. 78–99. [Google Scholar]
- Landon, J.R. Booker Agricultural Soil Manual: A Handbook for Soil Survey and Agricultural Land Evaluation in the Tropics and Subtropics; Booker Agricultural International Limited: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuong, N.Q.; Huu, T.N.; Nhan, T.C.; Tran, H.N.; Tien, P.D.; Xuan, L.N.T.; Kantachote, D. Two strains of Luteovulum sphaeroides (purple nonsulfur bacteria) promote rice cultivation in saline soils by increasing available phosphorus. Rhizosphere 2021, 20, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, T.T.C.; Loan, H.T.P.; Nghia, P.T. The selection for iron-rich rich variety OM 5451. J. Sci. Technol. Min. Agri. Rural Dev. 2011, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3–Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, R. Formulae for determination of chlorophyllous pigments extracted with N, N-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol. 1982, 69, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.A.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil. 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRRI (International Network for Genetic Evaluation of Rice). Standard Evaluation System for Rice; IRRI: Los Baños, Philippines, 1996. Available online: http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/images/docs/rice-standard-evaluation-system.pdf. (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Houba, V.J.G.; Van der Lee, J.J.; Novozamsky, I. Soil and Plant Analysis, Part 5; Wageningen Agricultural University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil. 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Barrow, N.J. Soil pH-nutrient relationships: The diagram. Plant Soil. 2023, 486, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.N.T.; Huyen, N.P.T.; Thu, L.T.M.; Thuy, V.T.B.; Tuan, L.M.; Quang, L.T.; Dao, N.T.X.; Thuc, L.V.; Khuong, N.Q. Supplementation of P-solubilizing purple nonsulfur bacteria, Rhodopseudomonas palustris improved soil fertility, P nutrient, growth, and yield of Cucumis melo L. Open Agric. 2024, 9, 20220247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Khairun, Y.; Rahman, M.M.; Shivakoti, G.P. Production economics as an indicator for sustainable development of shrimp farming. Asia-Pac. J. Rural. Dev. 2010, 20, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.F.; Ahmed, O.H.; Jalloh, M.B.; Omar, L.; Kwan, Y.M.; Musah, A.A.; Poong, K.H. Soil nutrient retention and pH buffering capacity are enhanced by calciprill and sodium silicate. Agronomy 2022, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Rasul, F.; Shahzad, S.; Wu, C.; Shao, J.; Huang, G.; Li, R.; Almari, S.; et al. Soil acidification and salinity: The importance of biochar application to agricultural soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1206820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunkaew, T.; Kantachote, D.; Nitoda, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Ritchie, R.J. Characterization of exopolymeric substances from selected Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains and their ability to adsorb sodium ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Qian, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, J.; Lu, B.; He, Y.; Tang, S.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms increase soil phosphorus availability: A review. Geomicrobiol. J. 2024, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuong, N.Q.; Sakpirom, J.; Oanh, T.O.; Thuc, L.V.; Thu, L.T.M.; Xuan, D.T.; Quang, L.T.; Xuan, L.N.T. Isolation and characterization of novel potassium-solubilizing purple nonsulfur bacteria from acidic paddy soils using culture-dependent and culture-independent techniques. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.; Khan, M.A.; Lee, K.E.; Kang, S.M.; Dhungana, S.K.; Bhusal, N.; Lee, I.J. The halotolerant rhizobacterium-Pseudomonas koreensis MU2 enhances inorganic silicon and phosphorus use efficiency and augments salt stress tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L.). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, S.; Hua, Q.; Qiu, C.; Wu, P.; Liu, X.; Lin, X. The long-term effects of using phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and photosynthetic bacteria as biofertilizers on peanut yield and soil bacteria community. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 693535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, A.; Chen, Z.; Luo, X.; Kong, D.; Zhang, F.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Luo, L. Improvement of salinity tolerance in water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Nie, F.; Liu, Q. OsLPR5 encoding ferroxidase positively regulates the tolerance to salt stress in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, N.D.; Dao, D.T.H.; Dung, N.H.; Nhung, V.T.T.; Vu, P.A.; Loan, L.Q.; Diep, H.T.; Luu, P.T.; Khanh, H.Q. Isolation and characterization of novel Rhodobacter spp. with the sodium removal ability from mangrove forest sediment in Southeast Vietnam. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2022, 2022, 202012575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talubaghi, M.J.; Daliri, M.S.; Mazloum, P.; Rameeh, V.; Mousavi, A. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological and biochemical parameters and activities of antioxidative enzymes of rice cultivars. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Prasad, S.M. 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) regulates photosynthetic performance and nitrogen metabolism status in UV-B challenged Cajanus cajan L. seedlings. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A. Role of nitrogen (N) in plant growth, photosynthesis pigments, and N use efficiency: A review. Agrisost 2022, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, K.S.; Sundar, L.S.; Chao, Y.Y. Foliar application of Rhodopseudomonas palustris enhances the rice crop growth and yield under field conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poury, N.; Seifi, E.; Alizadeh, M. Effects of salinity and proline on growth and physiological characteristics of three olive cultivars. Gesunde Pflanzen 2023, 75, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spormann, S.; Nadais, P.; Sousa, F.; Pinto, M.; Martins, M.; Sousa, B.; Fidalgo, F.; Soares, C. Accumulation of proline in plants under contaminated soils-Are we on the same page? Antioxidants 2023, 12, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, S.M.; Abolhassani, M.; Hadian-Deljou, M.; Feyzi, H.; Akbari, A.; Rasouli, F.; Koçak, M.Z.; Kulak, M.; Gohari, G.G. Proline-functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles (GO-Pro NPs): A new engineered nanoparticle to ameliorate salinity stress on grape (Vitis vinifera L. cv Sultana). Plant Stress 2023, 7, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.; Khadhir, F.Z. Effects of salinity on growth and proline content on bean and alfalfa. J. Appl. Life Sci. Environ. 2021, 2, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, R.; Uchida, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Sonoda, F.; Tsunoda, K.; Nagata, H.; Nagata, D.; Koga, A.; Goto, M.; Maki, T.A.; et al. Effects of seed bio-priming by purple non-sulfur bacteria (PNSB) on the root development of rice. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, E.M.; Kour, B.; Ramya, S.; Krishna, P.D.; Nazla, K.A.; Sudheer, K.; Anith, K.N.; Jisha, M.S.; Ramakrishnan, B. Rice in acid sulphate soils: Role of microbial interactions in crop and soil health management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Pei, M.; Fu, J.; Ji, H.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, X. Enhanced rice yields are related to pronounced shifts in soil resident bacterial community structures in response to Rhodopseudomonas palustris and Bacillus subtilis inoculation. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhuong, V.T.X.; Minh, N.T.; Tri, D.H.; Tung, N.C.T.; Ky, H.; Trang, N.T.D. Salt tolerance of rice varieties at the germination and seedling stages. Vietnam J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 20, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar]


| Soil Characteristic | Unit | Value | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pHH2O | - | 3.82 ± 0.05 | Low | Horneck et al. [20] |
| pHKCl | - | 3.69 ± 0.08 | Highly acidic | Horneck et al. [20] |
| EC | mS cm−1 | 6.59 ± 0.11 | Only suitable for certain crops | Horneck et al. [20] |
| Ntotal | %N | 0.196 ± 0.09 | Low | Metson [21] |
| NH4+ | mg kg−1 | 49.8 ± 1.25 | Optimum | Horneck et al. [20] |
| Ptotal | %P2O5 | 0.021 ± 0.009 | Poor | Cu et al. [22] |
| Psoluble | mg kg−1 | 85.0 ± 3.22 | High | Horneck et al. [20] |
| Al-P | mgkg−1 | 14.5 ± 0.22 | - | - |
| Fe-P | mgkg−1 | 105.3 ± 2.24 | - | - |
| Ca-P | mgkg−1 | 85.0 ± 4.65 | - | - |
| CEC | meq 100 g−1 | 9.71 ± 0.20 | Low | Landon [23] |
| Na+ | meq 100 g−1 | 3.02 ± 0.08 | High | Horneck et al. [20] |
| K+ | meq 100 g−1 | 0.683 ± 0.05 | High | Horneck et al. [20] |
| Ca2+ | meq 100 g−1 | 3.07 ± 0.11 | - | - |
| Mg2+ | meq 100 g−1 | 2.82 ± 0.06 | Extremely high | Horneck et al. [20] |
| Factor | SPAD | Chlorophyll | Proline | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | a | b | A + b | (µmol g−1 DW) | ||
| Days | Days | Days | Days | (µg g−1 Fresh Leaf Weight) | |||||
| Season 1 | |||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 39.2 | 38.8 b | 38.0 a | 37.9 | 4.78 b | 2.60 a | 7.50 a | 31.0 a |
| 25 | 39.5 | 39.1 ab | 37.2 bc | 38.5 | 5.35 a | 2.44 b | 7.74 a | 29.8 b | |
| 50 | 39.3 | 38.8 b | 37.0 c | 38.6 | 5.17 a | 2.09 c | 7.21 b | 29.1 b | |
| 75 | 39.8 | 39.4 a | 37.7 ab | 38.4 | 5.14 a | 1.81 d | 6.88 c | 29.5 b | |
| 100 | 39.8 | 39.0 b | 37.6 ab | 38.4 | 5.21 a | 1.82 d | 7.03 bc | 29.4 b | |
| Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 39.4 b | 38.9 | 36.9 b | 38.0 b | 4.18 c | 3.14 a | 7.31 b | 31.2 a |
| ST16 | 40.0 a | 39.0 | 36.6 b | 38.8 a | 5.72 a | 2.43 b | 8.15 a | 30.6 a | |
| ST26 | 39.5 ab | 39.2 | 38.3 a | 38.6 ab | 5.67 a | 1.44 d | 7.17 b | 28.7 b | |
| MIX | 39.2 b | 39.0 | 38.1 a | 38.2 ab | 4.94 b | 1.59 c | 6.46 c | 28.5 b | |
| P (A) | ns | ns | * | ns | * | * | * | * | |
| P (B) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| P (A × B) | ns | ns | * | ns | * | * | * | ns | |
| CV (%) | 2.37 | 1.55 | 2.14 | 2.63 | 5.55 | 9.33 | 5.09 | 3.83 | |
| Season 2 | |||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 35.8 bc | 40.6 | 37.2 | 34.7 d | 3.56 b | 1.89 a | 5.45 | 34.8 a |
| 25 | 36.5 a | 40.9 | 37.6 | 35.2 cd | 3.84 a | 1.76 b | 5.60 | 34.1 ab | |
| 50 | 35.3 d | 40.6 | 37.2 | 35.8 ab | 3.81 a | 1.73 b | 5.54 | 33.4 ab | |
| 75 | 36.0 b | 40.9 | 37.5 | 36.3 a | 3.78 a | 1.78 b | 5.56 | 34.3 ab | |
| 100 | 35.4 cd | 40.7 | 37.5 | 35.6 bc | 3.77 a | 1.69 b | 5.46 | 33.1 b | |
| Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 34.9 c | 40.3 b | 36.9 b | 34.4 c | 3.49 c | 1.93 a | 5.42 b | 37.3 a |
| ST16 | 35.7 b | 41.0 a | 37.5 a | 35.1 b | 3.70 b | 1.71 b | 5.41 b | 32.5 b | |
| ST26 | 37.2 a | 41.2 a | 37.6 a | 36.1 a | 4.03 a | 1.70 b | 5.72 a | 32.5 b | |
| MIX | 35.3 bc | 40.4 b | 37.5 a | 36.6 a | 3.79 b | 1.75 b | 5.54 b | 33.5 b | |
| P (A) | * | ns | ns | * | * | * | ns | * | |
| P (B) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| P (A × B) | * | ns | * | * | ns | * | * | * | |
| CV (%) | 1.87 | 1.83 | 2.08 | 2.14 | 5.27 | 7.12 | 4.11 | 5.49 | |
| Factors | pHH2O | pHKCl | CEC | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | meq 100 g−1 | |||||||||||||
| Season 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 4.63 | 3.57 | 18.4 | 1.92 a | 1.534 e | 16.4 a | 3.27 | |||||||
| 25 | 4.71 | 3.60 | 18.8 | 1.84 b | 1.562 d | 16.1 ab | 3.32 | ||||||||
| 50 | 4.74 | 3.64 | 18.4 | 1.84 b | 1.627 c | 15.7 abc | 3.35 | ||||||||
| 75 | 4.51 | 3.54 | 19.1 | 1.74 c | 1.691 b | 15.4 c | 3.37 | ||||||||
| 100 | 4.62 | 3.55 | 19.2 | 1.68 d | 1.794 a | 15.4 c | 3.37 | ||||||||
| Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 4.23 c | 3.54 | 18.1 | 1.84 a | 1.546 d | 16.0 | 3.24 b | |||||||
| ST16 | 4.98 a | 3.61 | 19.0 | 1.78 b | 1.641 c | 15.8 | 3.36 a | ||||||||
| ST26 | 4.50 b | 3.54 | 19.1 | 1.80 ab | 1.662 b | 15.6 | 3.34 a | ||||||||
| MIX | 4.87 a | 3.63 | 18.9 | 1.76 b | 1.718 a | 15.8 | 3.39 a | ||||||||
| P (A) | ns | ns | ns | * | * | * | ns | ||||||||
| P (B) | * | ns | ns | * | * | ns | * | ||||||||
| P (A × B) | ns | ns | ns | * | * | ns | ns | ||||||||
| CV (%) | 8.13 | 4.28 | 4.28 | 3.26 | 1.49 | 6.01 | 3.71 | ||||||||
| Season 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 5.53 | 3.87 | 16.9 | 0.145 a | 0.871 e | 15.3 d | 3.29 c | |||||||
| 25 | 5.54 | 3.89 | 16.0 | 0.127 b | 0.990 d | 16.3 c | 3.44 b | ||||||||
| 50 | 5.64 | 3.99 | 16.0 | 0.113 c | 1.079 c | 19.3 b | 3.47 b | ||||||||
| 75 | 5.53 | 3.84 | 16.8 | 0.100 d | 1.191 b | 20.3 a | 3.74 a | ||||||||
| 100 | 5.59 | 4.07 | 16.8 | 0.093 d | 1.220 a | 20.5 a | 3.62 a | ||||||||
| Phosphate -solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 5.27 c | 3.82 | 16.0 | 0.172 a | 0.952 c | 18.0 c | 3.14 c | |||||||
| ST16 | 5.83 a | 3.99 | 17.2 | 0.092 c | 1.056 b | 17.8 c | 3.62 b | ||||||||
| ST26 | 5.45 b | 3.92 | 16.5 | 0.093 c | 1.123 a | 18.5 b | 3.56 b | ||||||||
| MIX | 5.71 a | 4.00 | 16.3 | 0.105 b | 1.149 a | 19.1 a | 3.74 a | ||||||||
| P (A) | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||
| P (B) | * | ns | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||
| P (A × B) | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | ns | ||||||||
| CV (%) | 4.27 | 7.35 | 11.12 | 9.47 | 4.14 | 1.46 | 4.91 | ||||||||
| Factors | EC | N total | P total | NH4+ | Psoluble | Fe-P | Ca-P | Al-P | |||||||
| mS cm−1 | % | mg kg−1 | |||||||||||||
| Season 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 4.78 e | 0.215 | 0.043 | 231.1 c | 4.94 e | 151.3 d | 164.1 e | 140.9 d | ||||||
| 25 | 4.88 d | 0.216 | 0.042 | 234.1 b | 5.29 d | 156.8 c | 171.7 d | 146.1 c | |||||||
| 50 | 4.93 c | 0.224 | 0.044 | 235.4 b | 5.69 c | 162.7 b | 174.2 c | 148.8 b | |||||||
| 75 | 4.97 b | 0.220 | 0.044 | 239.8 a | 5.87 b | 165.2 a | 179.7 b | 150.0 b | |||||||
| 100 | 5.00 a | 0.218 | 0.042 | 241.4 a | 6.26 a | 167.0 a | 189.2 a | 158.0 a | |||||||
| Phosphate -solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 5.55 a | 0.218 | 0.043 | 228.5 d | 4.64 d | 174.4 a | 193.5 a | 164.4 a | ||||||
| ST16 | 5.06 b | 0.216 | 0.043 | 234.5 c | 5.71 c | 166.8 b | 174.6 b | 152.7 b | |||||||
| ST26 | 4.56 c | 0.223 | 0.044 | 238.4 b | 5.92 b | 161.4 c | 169.2 c | 140.9 c | |||||||
| MIX | 4.49 d | 0.217 | 0.043 | 244.1 a | 6.16 a | 139.8 d | 165.8 d | 137.1 d | |||||||
| P (A) | * | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| P (B) | * | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| P (A × B) | ns | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| CV (%) | 0.67 | 7.85 | 8.36 | 1.01 | 3.92 | 1.85 | 1.45 | 2.15 | |||||||
| Season 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 4.26 e | 0.201 | 0.038 | 119.2 c | 27.4 e | 118.0 e | 66.3 e | 16.3 c | ||||||
| 25 | 4.35 d | 0.201 | 0.036 | 124.5 b | 28.2 d | 120.6 d | 67.7 d | 16.6 c | |||||||
| 50 | 4.47 c | 0.210 | 0.038 | 125.7 b | 28.7 c | 122.5 c | 69.7 c | 17.2 b | |||||||
| 75 | 4.52 b | 0.193 | 0.036 | 128.2 a | 29.1 b | 127.8 b | 76.1 b | 17.4 b | |||||||
| 100 | 4.62 a | 0.199 | 0.038 | 130.4 a | 31.0 a | 130.1 a | 81.3 a | 20.6 a | |||||||
| Phosphate -solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 5.31 a | 0.205 | 0.038 | 115.3 d | 27.2 d | 133.9 a | 78.3 a | 26.0 a | ||||||
| ST16 | 4.28 b | 0.209 | 0.036 | 123.6 c | 27.9 c | 125.9 b | 76.0 b | 17.8 b | |||||||
| ST26 | 4.13 c | 0.200 | 0.036 | 129.5 b | 29.3 b | 119.5 c | 72.6 c | 14.9 c | |||||||
| MIX | 4.06 d | 0.190 | 0.038 | 133.9 a | 31.2 a | 115.9 d | 62.0 d | 11.7 d | |||||||
| P (A) | * | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| P (B) | * | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| P (A × B) | * | ns | ns | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| CV (%) | 1.30 | 15.04 | 10.29 | 2.68 | 1.20 | 1.99 | 2.40 | 3.27 | |||||||
| Factor | Biomass | Na Content | Na Uptake | Total Na Uptake | P Content | P Uptake | Total P Uptake | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem–Leaf | Grain | Stem–Leaf | Grain | Stem–Leaf | Grain | Stem–Leaf | Grain | Stem–Leaf | Grain | ||||
| g pot −1 | % | mg Na pot−1 | % | mg P pot−1 | |||||||||
| Season 1 | |||||||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 12.0 e | 15.1 e | 1.63 a | 1.15 a | 203.9 a | 198.4 a | 402.4 a | 0.188 a | 0.281 a | 21.7 c | 42.6 b | 65.1 cd |
| 25 | 12.4 d | 15.9 d | 1.55 b | 1.13 ab | 201.3 b | 191.8 b | 393.0 b | 0.176 b | 0.252 b | 22.5 c | 40.6 b | 62.3 d | |
| 50 | 13.0 c | 16.9 c | 1.52 c | 1.12 ab | 196.1 c | 190.5 b | 386.6 c | 0.192 a | 0.245 bc | 22.5 c | 42.0 b | 67.1 bc | |
| 75 | 13.5 b | 19.4 b | 1.54 bc | 1.11 b | 195.2 c | 186.7 c | 381.9 d | 0.167 c | 0.238 bc | 25.1 b | 46.9 a | 69.3 b | |
| 100 | 14.2 a | 20.8 a | 1.54 bc | 1.10 b | 195.3 c | 186.4 c | 381.7 d | 0.189 a | 0.235 c | 26.8 a | 48.8 a | 75.6 a | |
| Phosphate -solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 11.8 d | 11.8 d | 1.62 a | 1.21 a | 205.3 a | 197.8 a | 403.2 a | 0.184 b | 0.222 b | 21.6 c | 26.1 c | 47.8 d |
| ST16 | 12.8 c | 18.7 c | 1.56 b | 1.13 b | 197.9 b | 191.1 b | 389.0 b | 0.177 c | 0.257 a | 22.7 b | 47.7 b | 70.4 cd | |
| ST26 | 13.3 b | 19.1 b | 1.54 b | 1.07 c | 195.6 c | 190.0 b | 385.6 c | 0.193 a | 0.260 a | 25.5 a | 48.3 b | 73.9 b | |
| MIX | 14.3 a | 20.9 a | 1.50 c | 1.08 c | 194.7 c | 184.2 c | 378.8 d | 0.175 c | 0.262 a | 25.0 a | 54.4 a | 79.5 a | |
| P (A) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| P (B) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| P (A × B) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| CV (%) | 3.03 | 2.61 | 2.43 | 4.21 | 1.32 | 1.67 | 1.07 | 5.82 | 7.89 | 6.39 | 8.48 | 6.39 | |
| Season 2 | |||||||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 21.4 e | 20.5 e | 0.766 a | 0.722 a | 164.1 a | 146.5 a | 310.5 a | 0.140 d | 0.141 c | 30.1 d | 28.9 e | 59.0 d |
| 25 | 21.9 d | 21.6 d | 0.731 b | 0.585 b | 159.9 bc | 125.9 b | 285.8 bc | 0.158 c | 0.141 bc | 34.8 c | 30.7 d | 65.5 c | |
| 50 | 23.0 c | 22.5 c | 0.664 c | 0.544 bc | 151.9 d | 121.8 b | 273.7 c | 0.169 ab | 0.150 a | 38.8 b | 33.8 c | 72.7 b | |
| 75 | 24.1 b | 24.0 b | 0.653 c | 0.491 c | 156.6 c | 117.3 b | 273.8 c | 0.164 bc | 0.149 a | 39.9 b | 35.7 b | 75.6 b | |
| 100 | 24.9 a | 25.7 a | 0.655 c | 0.518 c | 162.2 ab | 132.0 b | 294.2 b | 0.174 a | 0.146 ab | 43.7 a | 37.6 a | 79.2 a | |
| Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 21.4 d | 20.7 d | 0.766 a | 0.699 a | 163.9 a | 143.7 a | 307.6 a | 0.138 b | 0.135 b | 29.6 c | 28.0 c | 57.7 c |
| ST16 | 22.5 c | 22.5 c | 0.679 b | 0.576 b | 152.4 c | 128.2 b | 280.6 b | 0.168 a | 0.148 a | 37.7 b | 33.4 b | 71.1 b | |
| ST26 | 23.8 b | 23.6 b | 0.688 b | 0.512 c | 162.7 a | 118.9 b | 281.6 b | 0.172 a | 0.151 a | 41.3 a | 35.7 a | 77.1 a | |
| MIX | 24.6 a | 24.7 a | 0.641 c | 0.501 c | 156.7 b | 123.9 b | 280.6 b | 0.166 a | 0.147 a | 41.2 a | 36.3 a | 75.8 a | |
| P (A) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| P (B) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| P (A × B) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| CV (%) | 1.17 | 1.25 | 3.02 | 14.2 | 3.15 | 15.11 | 6.96 | 5.48 | 4.90 | 5.82 | 5.52 | 6.56 | |
| Factor | Plant Height | Panicle Length | Panicle Number pot−1 | Grain Number Panicle−1 | 1000-Grain Weight | Filled Grain Percentage | Yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (panicles) | (grains) | (g) | (%) | (g pot−1) | |||
| Season 1 | ||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 88.8 e | 20.4 | 18.3 e | 77.5 | 21.9 | 66.2 e | 16.1 e |
| 25 | 91.0 d | 20.0 | 20.2 d | 66.5 | 21.7 | 67.2 d | 17.3 d | |
| 50 | 92.2 c | 20.0 | 21.0 c | 67.7 | 21.8 | 70.8 c | 18.8 c | |
| 75 | 93.9 b | 20.6 | 22.0 b | 74.6 | 22.1 | 73.8 b | 20.0 b | |
| 100 | 95.0 a | 21.0 | 23.0 a | 76.8 | 22.1 | 77.5 a | 21.6 a | |
| Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 86.8 d | 19.1 b | 16.9 d | 60.1 b | 21.8 | 66.4 d | 14.7 d |
| ST16 | 92.4 c | 20.7 a | 20.5 c | 75.2 a | 22.2 | 70.8 c | 18.3 c | |
| ST26 | 93.4 b | 20.8 a | 22.5 b | 75.2 a | 21.7 | 71.9 b | 19.7 b | |
| MIX | 96.1 a | 20.9 a | 23.6 a | 80.0 a | 22.0 | 75.2 a | 22.2 a | |
| P (A) | * | ns | * | ns | ns | * | * | |
| P (B) | * | * | * | * | ns | * | * | |
| P (A × B) | * | ns | * | ns | ns | * | * | |
| CV (%) | 1.33 | 6.37 | 2.95 | 20.60 | 3.11 | 1.14 | 3.01 | |
| Season 2 | ||||||||
| Phosphate fertilizer percentage (A) (%) | 0 | 89.3 d | 18.8 | 18.5 e | 66.9 | 22.9 | 89.4 d | 20.9 e |
| 25 | 89.8 c | 18.7 | 19.0 d | 65.2 | 23.0 | 90.5 c | 21.5 d | |
| 50 | 91.1 b | 18.4 | 19.6 c | 63.9 | 23.3 | 90.8 c | 23.9 c | |
| 75 | 91.5 b | 18.9 | 20.2 b | 65.8 | 23.4 | 91.2 b | 24.3 b | |
| 100 | 92.4 a | 19.0 | 21.4 a | 64.1 | 23.6 | 92.5 a | 27.0 a | |
| Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (B) | NB | 88.9 d | 18.6 | 17.2 d | 65.4 | 23.1 | 87.4 d | 21.1 d |
| ST16 | 90.8 c | 19.2 | 19.6 c | 66.3 | 23.1 | 90.8 c | 22.6 c | |
| ST26 | 91.4 b | 18.7 | 20.6 b | 65.4 | 23.4 | 91.2 b | 23.6 b | |
| MIX | 92.0 a | 18.7 | 21.5 a | 63.6 | 23.4 | 94.1 a | 26.7 a | |
| P (A) | * | ns | * | ns | ns | * | * | |
| P (B) | * | ns | * | ns | ns | * | * | |
| P (A × B) | * | ns | * | ns | ns | * | * | |
| CV (%) | 0.69 | 4.87 | 2.49 | 9.86 | 3.66 | 0.60 | 1.88 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dat, L.T.; Chinh, L.T.; Xuan, L.N.T.; Quang, L.T.; Thao, P.T.P.; Xuan, D.T.; Thu, L.T.M.; Trong, N.D.; Nguyen, T.T.K.; Khuong, N.Q. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Cereibacter sphaeroides ST16 and ST26 Enhanced Soil Phosphorus Solubility, Rice Growth, and Grain Yield in Acidic-Contaminated Saline Soil. Biology 2025, 14, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040443
Dat LT, Chinh LT, Xuan LNT, Quang LT, Thao PTP, Xuan DT, Thu LTM, Trong ND, Nguyen TTK, Khuong NQ. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Cereibacter sphaeroides ST16 and ST26 Enhanced Soil Phosphorus Solubility, Rice Growth, and Grain Yield in Acidic-Contaminated Saline Soil. Biology. 2025; 14(4):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040443
Chicago/Turabian StyleDat, Le Tien, Le Thi Chinh, Ly Ngoc Thanh Xuan, Le Thanh Quang, Pham Thi Phuong Thao, Do Thi Xuan, Le Thi My Thu, Nguyen Duc Trong, Tran Trong Khoi Nguyen, and Nguyen Quoc Khuong. 2025. "Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Cereibacter sphaeroides ST16 and ST26 Enhanced Soil Phosphorus Solubility, Rice Growth, and Grain Yield in Acidic-Contaminated Saline Soil" Biology 14, no. 4: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040443
APA StyleDat, L. T., Chinh, L. T., Xuan, L. N. T., Quang, L. T., Thao, P. T. P., Xuan, D. T., Thu, L. T. M., Trong, N. D., Nguyen, T. T. K., & Khuong, N. Q. (2025). Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Cereibacter sphaeroides ST16 and ST26 Enhanced Soil Phosphorus Solubility, Rice Growth, and Grain Yield in Acidic-Contaminated Saline Soil. Biology, 14(4), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040443






