ACE2 Protein Landscape in the Head and Neck Region: The Conundrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Human Tissue Specimens
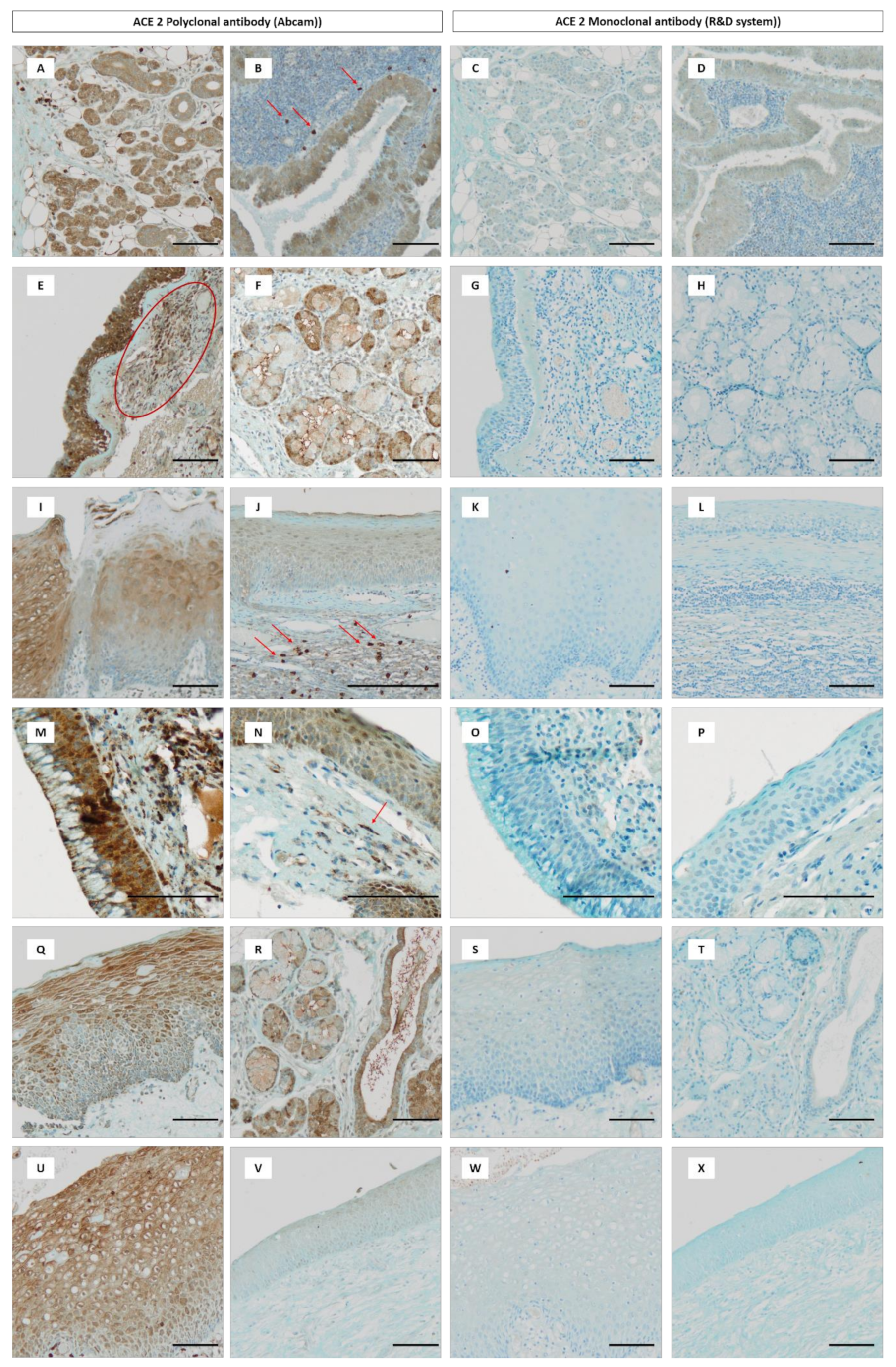
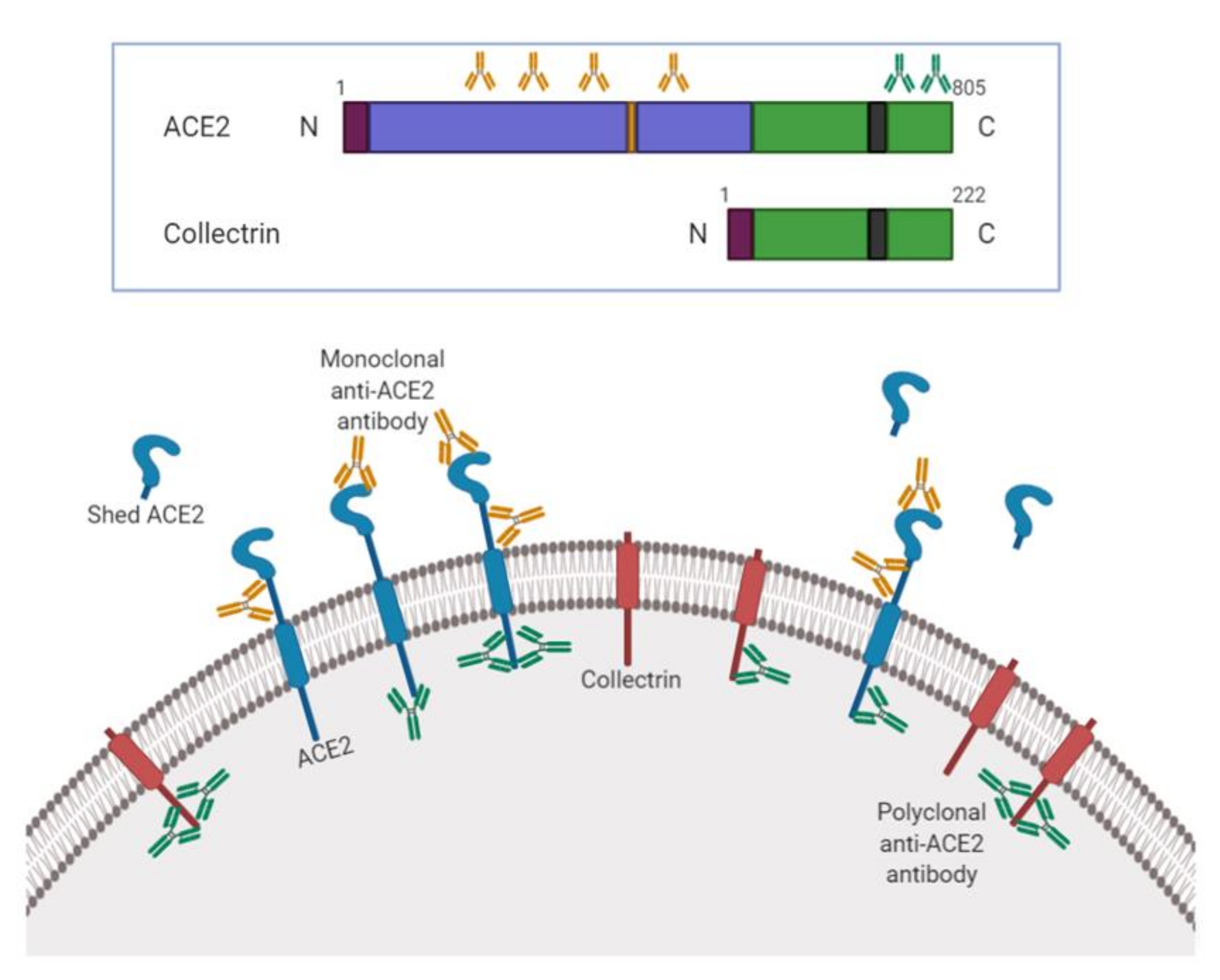
2.2. Immunohistochemistry and ACE2 Scoring
2.3. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results
3.1. ACE2 Expression in Control Tissues
3.2. ACE2 Expression in Epithelial Cells
3.3. ACE2 Expression in Blood Vessels
3.4. ACE2 Expression in Immune Inflammatory Cells and Fibroblasts
3.5. ACE2 Expression Correlation with Some Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Place, S.; Van Laethem, Y.; Cabaraux, P.; Mat, Q.; Huet, K.; Plzak, J.; Horoi, M.; Hans, S.; et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of 1,420 European Patients with mild-to-moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Shang, J.; Graham, R.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Receptor Recognition by the Novel Coronavirus from Wuhan: An Analysis Based on Decade-Long Structural Studies of SARS Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letko, M.; Marzi, A.; Munster, V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Ohto-Nakanishi, T.; Penninger, J.M. Trilogy of ACE2: A peptidase in the renin-angiotensin system, a SARS receptor, and a partner for amino acid transporters. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 128, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.J.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Xiao, R.; Lin, G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2: A double-edged sword? FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2020, 34, 6017–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; De Siati, D.R.; Horoi, M.; Le Bon, S.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Dequanter, D.; Blecic, S.; El Afia, F.; Distinguin, L.; et al. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A multicenter European study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Soc. EUFOS Affil. Ger. Soc. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Hans, S.; Barillari, M.R.; Jouffe, L.; Saussez, S. Loss of Smell and Taste in 2013 European Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhong, L.; Deng, J.; Peng, J.; Dan, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, T.; Chen, Q. High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wei, Q.; Alvarez, X.; Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, J.; Lam, P.; Zhang, L.; et al. Epithelial cells lining salivary gland ducts are early target cells of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in the upper respiratory tracts of rhesus macaques. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4025–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Gan, F.; Du, Y.; Yao, Y. Salivary Glands: Potential Reservoirs for COVID-19 Asymptomatic Infection. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-J.; Nam, K.T.; Park, H.S.; Kim, M.A.; Lafleur, B.J.; Aburatani, H.; Yang, H.-K.; Kim, W.H.; Goldenring, J.R. Gene expression profiling of metaplastic lineages identifies CDH17 as a prognostic marker in early stage gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Errarte, P.; Beitia, M.; Perez, I.; Manterola, L.; Lawrie, C.H.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; Unda, M.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. Expression and activity of angiotensin-regulating enzymes is associated with prognostic outcome in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wada, J.; Hida, K.; Tsuchiyama, Y.; Hiragushi, K.; Shikata, K.; Wang, H.; Lin, S.; Kanwar, Y.S.; Makino, H. Collectrin, a collecting duct-specific transmembrane glycoprotein, is a novel homolog of ACE2 and is developmentally regulated in embryonic kidneys. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17132–17139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wada, J. Collectrin, a homologue of ACE2, its transcriptional control and functional perspectives. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 363, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wada, J.; Yasuhara, A.; Iseda, I.; Eguchi, J.; Fukui, K.; Yang, Q.; Yamagata, K.; Hiesberger, T.; Igarashi, P.; et al. The role for HNF-1beta-targeted collectrin in maintenance of primary cilia and cell polarity in collecting duct cells. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danilczyk, U.; Sarao, R.; Remy, C.; Benabbas, C.; Stange, G.; Richter, A.; Arya, S.; Pospisilik, J.A.; Singer, D.; Camargo, S.M.R.; et al. Essential role for collectrin in renal amino acid transport. Nature 2006, 444, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, S.J.; Bröer, A.; Subramanian, N.; Tumer, E.; Cheng, Q.; Schmoll, D.; O’Mara, M.L.; Bröer, S. Molecular basis for the interaction of the mammalian amino acid transporters B0AT1 and B0AT3 with their ancillary protein collectrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24308–24325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Shah, N.; Bröer, A.; Fairweather, S.; Jiang, Y.; Schmoll, D.; Corry, B.; Bröer, S. Identification of novel inhibitors of the amino acid transporter B0 AT1 (SLC6A19), a potential target to induce protein restriction and to treat type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, D.W.; Yarski, M.; Warner, F.J.; Thornhill, P.; Parkin, E.T.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30113–30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.P.; Look, D.C.; Tan, P.; Shi, L.; Hickey, M.; Gakhar, L.; Chappell, M.C.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; McCray, P.B. Ectodomain shedding of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in human airway epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L84–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.-Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Do, A.; Vicencio, A. Nasal Gene Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Children and Adults. JAMA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Ma, L.; Wu, D.; Gao, J.; Chen, G.; Li, H. Systematic profiling of ACE2 expression in diverse physiological and pathological conditions for COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakladar, J.; Shende, N.; Li, W.T.; Rajasekaran, M.; Chang, E.Y.; Ongkeko, W.M. Smoking-Mediated Upregulation of the Androgen Pathway Leads to Increased SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, D.H.; Tsukahara, T.; Weinreb, C.; Lipovsek, M.; den Berge, K.V.; Gong, B.; Chance, R.; Macaulay, I.C.; Chou, H.; Fletcher, R.; et al. Non-neuronal expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry genes in the olfactory system suggests mechanisms underlying COVID-19-associated anosmia. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butowt, R.; Bilinska, K. SARS-CoV-2: Olfaction, Brain Infection, and the Urgent Need for Clinical Samples Allowing Earlier Virus Detection. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilinska, K.; Jakubowska, P.; Von Bartheld, C.S.; Butowt, R. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Entry Proteins, ACE2 and TMPRSS2, in Cells of the Olfactory Epithelium: Identification of Cell Types and Trends with Age. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shen, W.; Rowan, N.R.; Kulaga, H.; Hillel, A.; Ramanathan, M.; Lane, A.P. Elevated ACE2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: Implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Michel, J.; Radulesco, T.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Vaira, L.A.; Riu, G.D.; Sowerby, L.J.; Hopkins, C.; Saussez, S. Clinical and Radiological Evaluations of COVID-19 Patients with Anosmia: Preliminary Report. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Bécavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-López, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertram, S.; Heurich, A.; Lavender, H.; Gierer, S.; Danisch, S.; Perin, P.; Lucas, J.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Pöhlmann, S.; Soilleux, E.J. Influenza and SARS-coronavirus activating proteases TMPRSS2 and HAT are expressed at multiple sites in human respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.P.; Look, D.C.; Shi, L.; Hickey, M.; Pewe, L.; Netland, J.; Farzan, M.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Perlman, S.; McCray, P.B. ACE2 receptor expression and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection depend on differentiation of human airway epithelia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14614–14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olender, T.; Keydar, I.; Pinto, J.M.; Tatarskyy, P.; Alkelai, A.; Chien, M.-S.; Fishilevich, S.; Restrepo, D.; Matsunami, H.; Gilad, Y.; et al. The human olfactory transcriptome. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.J.; Okuda, K.; Edwards, C.E.; Martinez, D.R.; Asakura, T.; Dinnon, K.H.; Kato, T.; Lee, R.E.; Yount, B.L.; Mascenik, T.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Reverse Genetics Reveals a Variable Infection Gradient in the Respiratory Tract. Cell 2020, 182, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.A.; Kurtenbach, S.; Sargi, Z.B.; Harbour, J.W.; Choi, R.; Kurtenbach, S.; Goss, G.M.; Matsunami, H.; Goldstein, B.J. Single-cell analysis of olfactory neurogenesis and differentiation in adult humans. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajuthi, S.P.; Sharma, N.K.; Chou, J.W.; Palmer, N.D.; McWilliams, D.R.; Beal, J.; Comeau, M.E.; Ma, L.; Calles-Escandon, J.; Demons, J.; et al. Mapping adipose and muscle tissue expression quantitative trait loci in African Americans to identify genes for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, R.; Hernandez, K.; Huang, L.; Luke, J.J. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression by clinical, HLA, immune, and microbial correlates across 34 human cancers and matched normal tissues: Implications for SARS-CoV-2 COVID-19. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluimer, J.C.; Gasc, J.M.; Hamming, I.; van Goor, H.; Michaud, A.; van den Akker, L.H.; Jütten, B.; Cleutjens, J.; Bijnens, A.P.J.J.; Corvol, P.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and activity in human carotid atherosclerotic lesions. J. Pathol. 2008, 215, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z.; Giani, J.F.; Cao, D.-Y.; Bernstein, E.A.; Shen, X.Z. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikmet, F.; Méar, L.; Edvinsson, Å.; Micke, P.; Uhlén, M.; Lindskog, C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Peng, J.; Li, X.; Deng, X.; Geng, Z.; Shen, Z.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, Y.; et al. Detection of 2019-nCoV in Saliva and Characterization of Oral Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlen, M.; Bandrowski, A.; Carr, S.; Edwards, A.; Ellenberg, J.; Lundberg, E.; Rimm, D.L.; Rodriguez, H.; Hiltke, T.; Snyder, M.; et al. A proposal for validation of antibodies. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Localization | Number of cases (n) | Pathology | Lesion-free Epithelia | Pathologic state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinus | 10 | Chronic Rhinosinusitis | Respiratory | Benign |
| Tonsil | 10 | Recurrent tonsillitis or snoring | Stratified Squamous | Benign |
| Salivary Gland | 10 | Normal Salivary Gland and/or Whartin tumor | Acini and Ducts or Oncocytic columnar cells | Benign |
| Glottic Larynx (Vocal Cord) | 10 | Nodules or Polyps | Stratified Squamous/Respiratory | Benign |
| Supraglottic Larynx | 10 | Tumor | Stratified Squamous | Malignant |
| Oral Cavity | 10 | Tumor | Stratified Squamous | Malignant |
| Pharynx | 10 | Tumor | Stratified Squamous | Malignant |
| N | Median | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE2 score | 61 | 5 (0–6) | - |
| Gender (F/M) | 15/34 | 0.26 | |
| Tobacco (No/Yes) | 24/23 | 0.86 | |
| Diabetes (No/Yes) | 42/5 | 0.15 | |
| Arterial Hypertenstion (No/Yes) | 36/11 | 0.17 | |
| Blood pressure Medication (No/Yes) | 45/2 | 0.15 |
| Epithelial Cells | Endothelial Cells (Vessels) | Glands | Inflammatory Cells | Fibroblasts | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinuses | 5 | 4 | 5 | + | + |
| Tonsils | 4 | 0 | 0 | ++ | - |
| Salivary Glands | 5 | 0 | 0 | ++ | - |
| Oral Cavity | 5 | 2 | 0 | + | + |
| Pharynx | 2 | 2 | 3 | + | - |
| Vocal Cords | 5 | 2 | 0 | + | + |
| Larynx | 4 | 4 | 6 | + | + |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Descamps, G.; Verset, L.; Trelcat, A.; Hopkins, C.; Lechien, J.R.; Journe, F.; Saussez, S. ACE2 Protein Landscape in the Head and Neck Region: The Conundrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biology 2020, 9, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080235
Descamps G, Verset L, Trelcat A, Hopkins C, Lechien JR, Journe F, Saussez S. ACE2 Protein Landscape in the Head and Neck Region: The Conundrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biology. 2020; 9(8):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080235
Chicago/Turabian StyleDescamps, Géraldine, Laurine Verset, Anne Trelcat, Claire Hopkins, Jérome R. Lechien, Fabrice Journe, and Sven Saussez. 2020. "ACE2 Protein Landscape in the Head and Neck Region: The Conundrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Biology 9, no. 8: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080235
APA StyleDescamps, G., Verset, L., Trelcat, A., Hopkins, C., Lechien, J. R., Journe, F., & Saussez, S. (2020). ACE2 Protein Landscape in the Head and Neck Region: The Conundrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biology, 9(8), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080235







