CSR, Digital Transformation, and Internal Control: Three-Way Interaction Effect on the Firm Value of Chinese Listed Companies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Stakeholder Theory, Resource-Based View, and Agency Theory
2.2. Corporate Social Responsibility
2.3. Digital Transformation
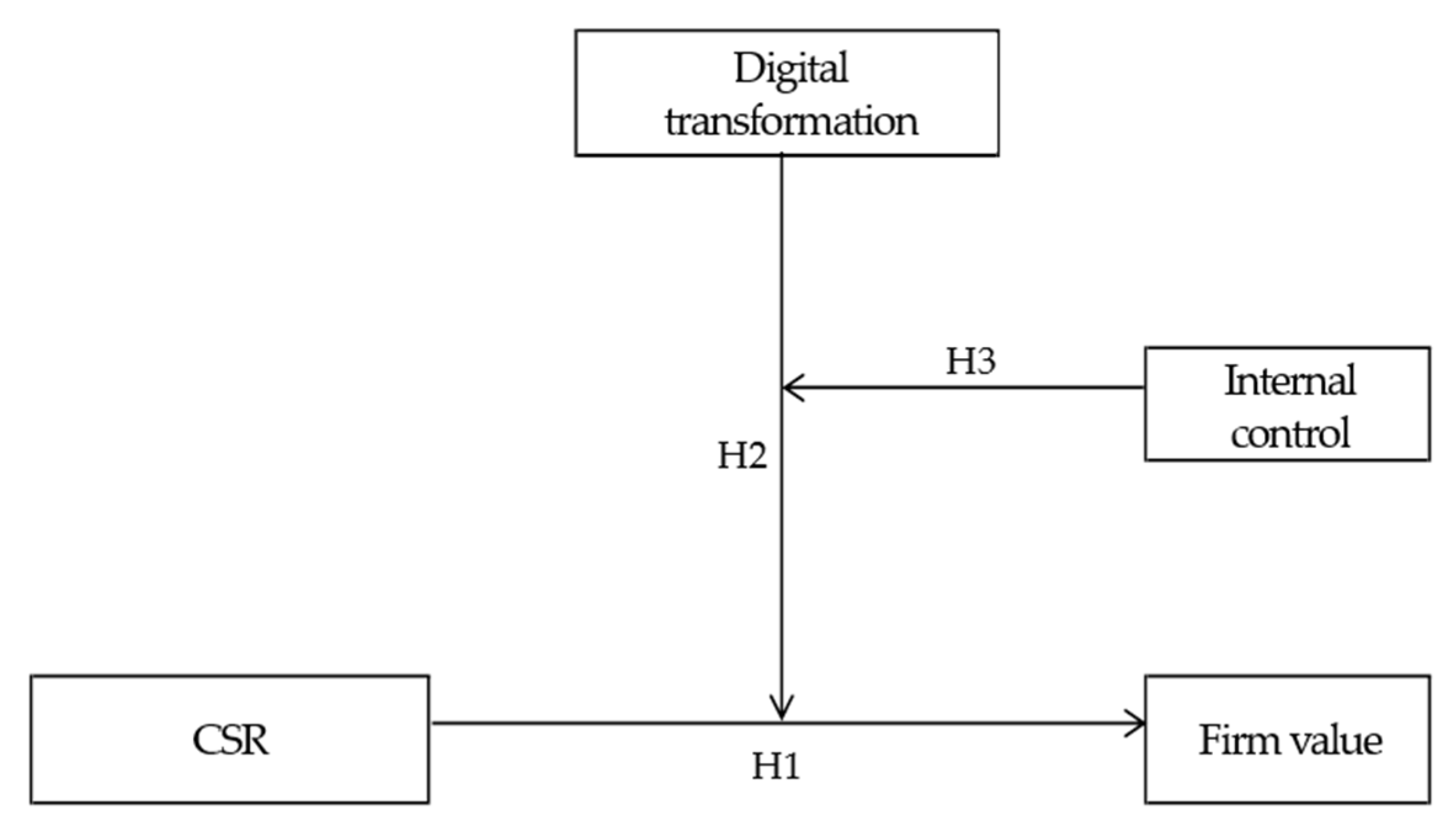
3. Research Hypotheses
3.1. Relationship between CSR and Firm Value
3.2. Moderating Effect of Digital Transformation
3.3. Three-Way Interaction Effect of Internal Control
4. Data and Measures
4.1. Data
4.2. Measures
4.2.1. Dependent Variable: Tobin’s Q
4.2.2. Independent Variable: CSR
4.2.3. Moderating Variables: Digital Transformation and Internal Control
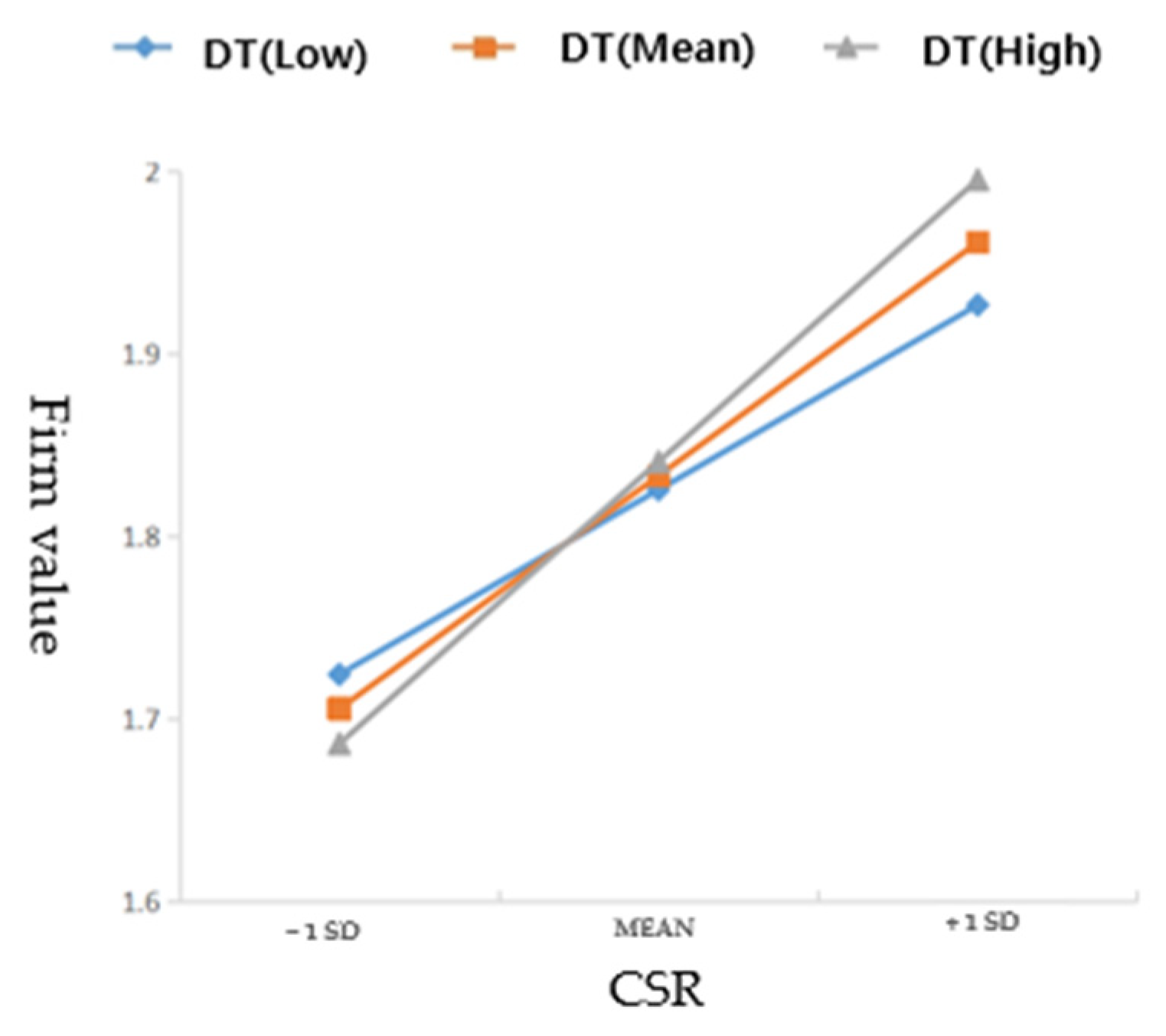
5. Analysis and Results
6. Conclusions
6.1. Key Findings
6.2. Discussion
6.3. Implications
6.4. Limitations and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.B. The pyramid of corporate social responsibility: Toward the moral management of organizational stakeholders. Bus. Horiz. 1991, 34, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jung, J. The effect of CSR attributes on CSR authenticity: Focusing on mediating effects of digital transformation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterveer, P. Promoting sustainable palm oil: Viewed from a global networks and flows perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, A.G.; Palazzo, G. The new political role of business in a globalized world: A review of a new perspective on CSR and its implications for the firm, governance, and democracy. J. Manag. Stud. 2011, 48, 899–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Harjoto, M.A. The causal effect of corporate governance on corporate social responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 106, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, J. A conceptual framework to support digital transformation in manufacturing using an integrated business process management approach. Designs 2020, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, L. The effects of digital transformation on firm performance: Evidence from China’s manufacturing sector. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wan, X.; Yao, Y. Study on the effect of digital economy on high-quality economic development in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.C.; Batten, J.A.; Ahmad, A.H.; Mohamed-Arshad, S.B.; Nordin, S.; Adzis, A.A. Does ESG certification add firm value? Financ. Res. Lett. 2021, 39, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, T.; Matt, C.; Benlian, A.; Wiesböck, F. Options for formulating a digital transformation strategy. MIS Q. Exec. 2016, 15, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Maroufkhani, P.; Tseng, M.L.; Iranmanesh, M.; Ismail, W.K.W.; Khalid, H. Big data analytics adoption: Determinants and performances among small to medium-sized enterprises. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 54, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbert, S.L. Value, rareness, competitive advantage, and performance: A conceptual-level empirical investigation of the resource-based view of the firm. Strat. Manag. J. 2008, 29, 745–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayna, T.; Striukova, L. Adaptivity and rapid prototyping: How 3D printing is changing business model innovation. In 3D Printing: Legal, Philosophical and Economic Dimension; van den Berg, B., van der Hof, S., Kosta, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K. Digital transformation of work and ESG: Perspectives on monopoly and fair trade. Risk Gov. Control Financ. Mark. Inst. 2020, 10, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.S.R.; Wäger, M. Building dynamic capabilities for digital transformation: An ongoing process of strategic renewal. Long Range Plan. 2019, 52, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y. An internal control system that includes corporate social responsibility for social sustainability in the new era. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.K. Internal control assurance, auditor reputation, and cost of equity capital: An empirical analysis based on A-share listed companies from 2009 to 2010. J Yunnan Uni Fin Econ. 2012, 8, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; An, R.; Zhong, Q. Anti-corruption, government subsidies, and investment efficiency. China J. Acc. Res. 2019, 12, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, W.C. Point of view: Corporate social responsibility in the Reagan era and beyond. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1983, 25, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yin, X.; Lee, G. The effect of CSR on corporate image, customer citizenship behaviors, and customers’ long-term relationship orientation. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 88, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoff, H.I. Corporate Strategy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Pitman: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness, P.B.; Vieito, J.P.; Wang, M. The role of board gender and foreign ownership in the CSR performance of Chinese listed firms. J. Corp. Financ. 2017, 42, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, E.T. The Theory of the Growth of the Firm; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wernerfelt, B. A resource-based view of the firm. Strat. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanpour, F. Organizational size and innovation. Organ. Stud. 1992, 13, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmon, D.G.; Hitt, M.A.; Ireland, R.D. Managing firm resources in dynamic environments to create value: Looking inside the black box. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berle, A.A.; Means, G.C. The Modern Corporation and Private Property; Macmillan: London, UK, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Rights and production functions: An application to labor-managed firms and codetermination. J. Bus. 1979, 52, 469–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, R.; Li, S.; Montoya, M. Does transitioning to a digital economy imply lower levels of corruption? Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2022, 64, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zeng, S. R&D investment, internal control and enterprise performance—An empirical study based on the listed companies in China of the core industry of the digital economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, H.R. Social Responsibility of the Businessman; Harper and Row: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.L. A Berkeley view of business and society. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1973, 16, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, D.; Berens, G.; Li, T. The impact of interactive corporate social responsibility communication on corporate reputation. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 118, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, P.C. The relationship between corporate philanthropy and shareholder wealth: A risk management perspective. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2005, 30, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, C. Competing for government procurement contracts: The role of corporate social responsibility. Strat. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 1299–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.R.; Moser, D.V. Managers’ green investment disclosures and investors’ reaction. J. Account. Econ. 2016, 61, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.; Kruschwitz, N.; Bonnet, D.; Welch, M. Embracing digital technology: A new strategic imperative. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2014, 55, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nambisan, S. Digital entrepreneurship: Toward a digital technology perspective of entrepreneurship. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2017, 41, 1029–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, F. Digital transformation and manufacturing firm performance: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Huizhi, H.; Huiyan, L.; Xiaoyi, R. Corporate digital transformation and capital market performance: Empirical evidence from stock liquidity. Manag. World 2021, 37, 130–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. The impact of digital transformation on firm’s financial performance: Evidence from China. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2024, 124, 2021–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Zomer, T.T.; Neely, A.; Martinez, V. Digital transforming capability and performance: A microfoundational perspective. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2020, 40, 1095–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Chang, R.Y.; Dang, V.T. An integrated model to explain how corporate social responsibility affects corporate financial performance. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8292–8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Yoo, J.W. When CSR matters: The moderating effect of industrial growth rate on the relationship between CSR and firm performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, B.; Shapiro, A.C. Corporate stakeholders and corporate finance. Financ. Manag. 1987, 16, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhili, H.; Dhiab, L.B. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: The case of the Saudi companies. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2019, 6, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ye, M.; Chau, K.W.; Flanagan, R. The paradoxical nexus between corporate social responsibility and sustainable financial performance: Evidence from the international construction business. CRS Environ. Manag. 2018, 25, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, M.C.; Rodrigues, L.L. Corporate social responsibility and resource-based perspectives. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 69, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, T.; Braga, V.; Correia, A.; Silva, C. Linking corporate social responsibility, cooperation and innovation: The triple bottom line perspective. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2023, 20, 244–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, D.P. Private politics, corporate social responsibility, and integrated strategy. J. Econ. Manag. Strat. 2001, 10, 7–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Bhattacharya, C.B. The debate over doing good: Corporate social performance, strategic marketing levers, and firm-idiosyncratic risk. J. Mark. 2009, 73, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.A.; Venkatraman, N.V. Digital business strategy: Toward a next generation of insights. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoopes, D.G.; Madsen, T.L.; Walker, G. Guest editors’ introduction to the special issue: Why is there a resource-based view? Toward a theory of competitive heterogeneity. Strat. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Naz, F.; Naeem, M.A.; Vigne, S.A. Is FinTech providing effective solutions to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in ASEAN countries? Econ. Anal. Pol. 2022, 75, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C. Research on the impact of digital transformation on corporate social responsibility. Contemp. Econ. Sci. 2022, 44, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Paiola, M.; Gebauer, H. Internet of things technologies, digital servitization and business model innovation in BtoB manufacturing firms. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 89, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMassah, S.; Mohieldin, M. Digital transformation and localizing the sustainable development goals (SDGs). Ecol. Econ. 2020, 169, 106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, D.; Eisenegger, M. CSR communication, corporate reputation, and the role of the news media as an agenda-setter in the digital age. Bus. Soc. 2021, 60, 1957–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcadell, F.J.; Aracil, E.; Úbeda, F. The impact of corporate sustainability and digitalization on international banks’ performance. Glob. Policy 2020, 11, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionaşcu, I.; Ionaşcu, M.; Nechita, E.; Săcărin, M.; Minu, M. Digital transformation, financial performance and sustainability: Evidence for European Union listed companies. Amfiteatru Econ. 2022, 24, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Wright, M.; Feldman, M. The digital transformation of innovation and entrepreneurship: Progress, challenges and key themes. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Su, H.; Yu, J. Digital transformation and corporate social performance: How do board independence and institutional ownership matter? Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 915583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, P.G.; De Giovanni, P. Responsible digitalization through digital technologies and green practices. CSR Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Länsiluoto, A.; Jokipii, A.; Eklund, T. Internal control effectiveness—A clustering approach. Manag. Audit. J. 2016, 31, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Sircar, S. Integrating corporate social responsibility initiatives with business strategy: A study of some Indian companies. IUP J. Corp. Gov. 2012, 11, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.D. Corporate social responsibility and internal control effectiveness. Asia-Pac. J. Financ. Stud. 2017, 46, 341–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.Z. Study on relation of internal control and enterprise value: An empirical analysis from Shanghai and Shenzhen stock markets. J. Financ. Econ. 2007, 33, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Radu, C.; Smaili, N. Alignment versus monitoring: An examination of the effect of the CSR committee and CSR-linked executive compensation on CSR performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2021, 180, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, W. Corporate social responsibility, internal control, and firm financial performance. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 977996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otley, D.; Soin, K. Management control and uncertainty. In Management Control and Uncertainty; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, G.J.; Buchholz, R.A. Research notes. Corporate social responsibility and stock market performance. Acad. Manag. J. 1978, 21, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subin, W.; Yuan, F. An empirical study on the relationship between corporate social responsibility and financial performance: Panel data analysis from stakeholder perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2008, 10, 150–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, S. Digital transformation and enterprise resilience: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnewold, L.; Lottermoser, B.G. Identification of digital technologies and digitalisation trends in the mining industry. Intern. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, W.; Zhang, T. Fintech development, firm digitalization, and bank loan pricing. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2023, 39, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fu, Y.; Kong, D. Does the digital transformation of enterprises affect stock price crash risk? Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 48, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Shen, S. Managerial shareholding and CSR: Does internal control quality matter?—Evidence from China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaiseh, M.E. Do firm size and financial performance affect corporate social responsibility disclosure: Employees’ and environmental dimensions? Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2015, 12, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, L.S.; Ilo, B.M.; Lawal, F.K. The effect of firm size on performance of firms in Nigeria. Aestimatio IEB Int. J. Financ. 2017, 15, 68–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dahmash, F.N. Size effect on company profitability: Evidence from Jordan. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Sci. 2015, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loderer, C.F.; Waelchli, U. Firm Age and Performance. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1342248 (accessed on 30 April 2010).
- Mirza, S.A.; Javed, A. Determinants of financial performance of a firm: Case of Pakistani stock market. J. Econ. Financ. 2013, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoogh, J.; Swärd, P. The Impact of Tangible Assets on Capital Structure—An Analysis of Swedish Listed Companies. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2015. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2077/39577 (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Hsu, P.H.; Lee, H.H.; Liu, A.Z.; Zhang, Z. Corporate innovation, default risk, and bond pricing. J. Corp. Financ. 2015, 35, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. The social responsibility of a business is to increase its profits. In The New York Times Magazine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Asogwa, C.I.; Ugwu, O.C.; Okereke, G.K.; Samuel, A.; Igbinedion, A.; Uzuagu, A.; Abolarinwa, S.I. Corporate social responsibility intensity: Shareholders’ value adding or destroying? Cogent Bus. Manag. 2020, 7, 1826089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Jung, S.; Young, J. Do CSR activities increase firm value? Evidence from the Korean market. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, F.; Mustilli, M.; Varrone, N. The impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) knowledge on corporate financial performance: Evidence from the European banking industry. J. Knowl. Manag. 2019, 23, 110–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.Y.; Fairhurst, A.; Wesley, S. Corporate social responsibility: A review of the top 100 US retailers. Corp. Rep. Rev. 2009, 12, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgreen, A.; Swaen, V.; Johnston, W.J. Corporate social responsibility: An empirical investigation of U.S. organizations. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 85, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J. Corporate governance, corporate social responsibility and corporate performance. J. Manag. Organ. 2010, 16, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z. The impact of digital transformation on corporate innovation: Roles of analyst coverage and internal control. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2024, 45, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.J.; Fernandes, C.I.; Ferreira, F.A. To be or not to be digital, that is the question: Firm innovation and performance. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 101, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dimensions of Digitalization | Corresponding Text Word |
|---|---|
| Artificial intelligence technology | Machine learning, artificial intelligence, face recognition, business intelligence, identity verification, deep learning, biometrics, image understanding, semantic search, voice recognition, intelligent robotics, intelligent data analysis, autonomous driving, natural voice processing |
| Blockchain technology | Bitcoin, distributed computing, consensus mechanism, federated chain, decentralization. |
| Cloud computing technology | EB-level storage, multi-party secure computing, brain-like computing, stream computing, green computing, in-memory computing, cognitive computing, converged architecture, graph computing, Internet of Things, information physical systems, billion concurrency, cloud computing |
| Big data technology | Mixed reality, data visualization, data mining, text mining, virtual reality, heterogeneous data, augmented reality, credit investigation |
| Digital technology applications | B2B, B2C, C2B, C2C, fintech, NFC payment, 020, third-party payment, e-commerce, industrial Internet, Internet finance, Internet healthcare, fintech, open banking, quantitative finance, digital finance, digital marketing, netlink, unstaffed retail, mobile Internet, mobile payment, smart agriculture, smart wear, smart grid, smart environmental protection, smart home, smart transportation, smart customer service, smart energy, smart investment, smart cultural travel, smart medical, smart marketing |
| Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firm value | 1.83 | 0.64 | 1 | |||||||
| CSR | 1.80 | 0.85 | 0.210 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Digital transformation | 8.35 | 19.37 | −0.038 | −0.011 | 1 | |||||
| Internal control | 6.34 | 1.21 | 0.031 | 0.311 ** | 0.072 ** | 1 | ||||
| Firm age | 12.14 | 7.46 | −0.420 ** | 0.009 | −0.010 | 0.020 | 1 | |||
| Firm size | 22.46 | 1.28 | −0.564 ** | 0.162 ** | 0.151 ** | 0.156 ** | 0.466 ** | 1 | ||
| Fixed asset ratio | 0.24 | 0.14 | −0.206 ** | −0.041 | −0.232 ** | −0.027 | 0.109 ** | 0.125 ** | 1 | |
| Debt ratio | 0.45 | 0.17 | −0.521 ** | −0.272 ** | 0.069 ** | −0.042 | 0.216 ** | 0.463 ** | 0.043 | 1 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 1904 | β(t) | β(t) | β(t) | β(t) |
| Dependent variable | Firm value | |||
| Firm age | −0.192 *** (−9.971) | −0.173 *** (−9.251) | −0.174 *** (−9.285) | −0.169 *** (−8.989) |
| Firm size | −0.305 *** (−14.369) | −0.389 *** (−17.738) | −0.392 *** (−17.561) | −0.410 *** (−18.006) |
| Fixed asset ratio | −0.133 *** (−7.739) | −0.120 *** (−7.189) | −0.117 *** (−6.792) | −0.112 *** (−6.502) |
| Debt ratio | −0.333 *** (−17.371) | −0.243 *** (−12.014) | −0.246 *** (−12.137) | −0.243 *** (−12.007) |
| CSR | 0.202 *** (11.050) | 0.151 *** (5.583) | 0.283 * (2.249) | |
| Digital transformation | −0.076 * (−1.988) | 0.264 (1.300) | ||
| CSR × Digital transformation | 0.110 * (2.570) | −0.670 ** (−2.610) | ||
| Internal control | 0.034 (0.636) | |||
| CSR × Internal control | −0.140 (−0.954) | |||
| Digital transformation × Internal control | −0.354 (−1.583) | |||
| CSR × Digital transformation × Internal control | 0.816 ** (2.936) | |||
| R2 | 0.453 | 0.486 | 0.488 | 0.493 |
| Adj R2 | 0.452 | 0.485 | 0.486 | 0.490 |
| F value | 393.086 *** | 358.941 *** | 258.079 *** | 167.180 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, J.W.; Fan, B.; Chang, Y.J. CSR, Digital Transformation, and Internal Control: Three-Way Interaction Effect on the Firm Value of Chinese Listed Companies. Systems 2024, 12, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12070236
Yoo JW, Fan B, Chang YJ. CSR, Digital Transformation, and Internal Control: Three-Way Interaction Effect on the Firm Value of Chinese Listed Companies. Systems. 2024; 12(7):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12070236
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Jae Wook, Bu Fan, and Yu Jin Chang. 2024. "CSR, Digital Transformation, and Internal Control: Three-Way Interaction Effect on the Firm Value of Chinese Listed Companies" Systems 12, no. 7: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12070236
APA StyleYoo, J. W., Fan, B., & Chang, Y. J. (2024). CSR, Digital Transformation, and Internal Control: Three-Way Interaction Effect on the Firm Value of Chinese Listed Companies. Systems, 12(7), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12070236





