Evaluation and Optimization Research on the Spatial Distribution of Automated External Defibrillators Based on a Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of Central Urban District of Nanjing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
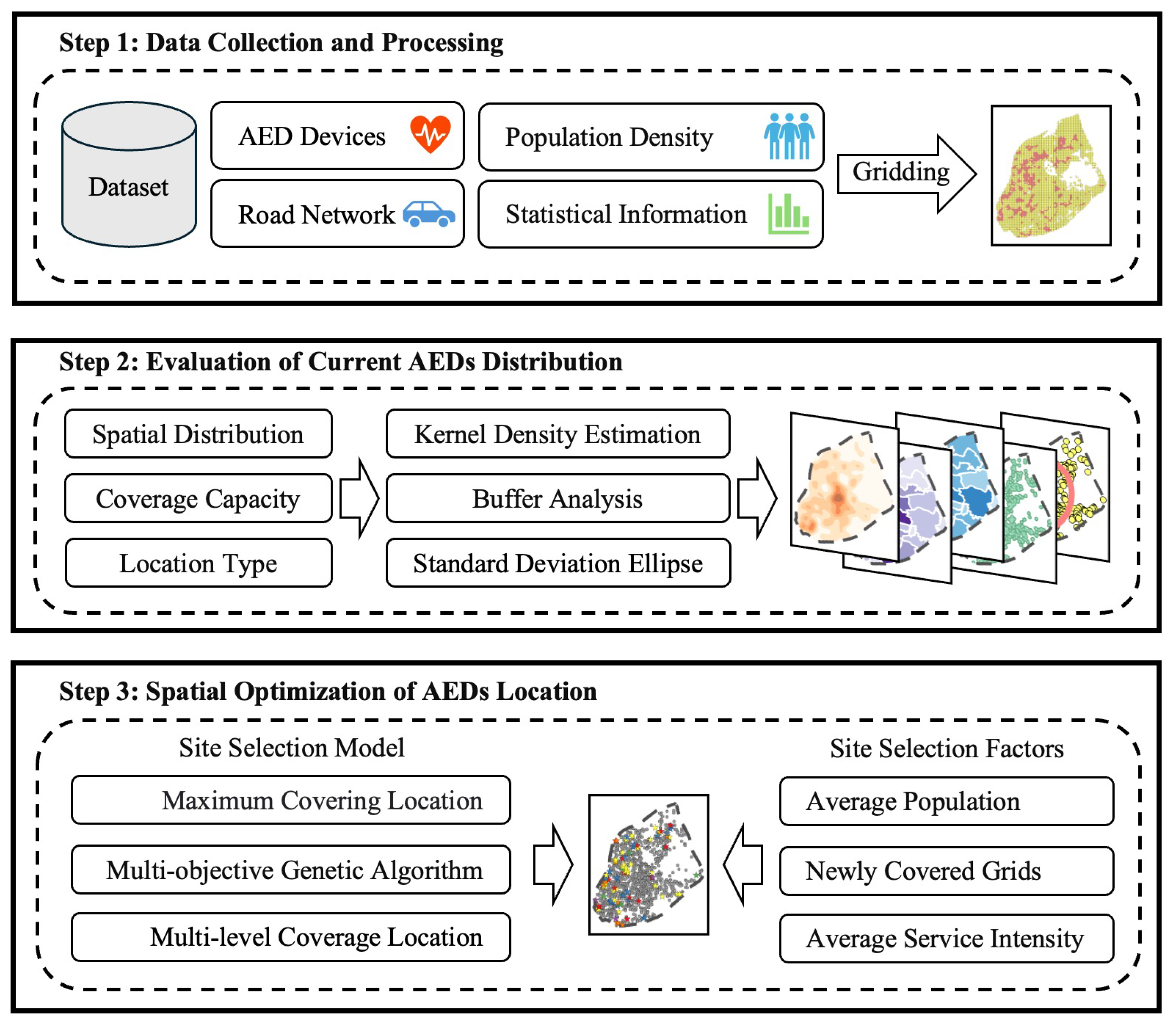
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
- AED distribution data
- Basic data on the city
- Socioeconomic data on the city
2.3. Research Method
2.3.1. Average Nearest Neighbor Index
2.3.2. Geographical Concentration Index
2.3.3. Standard Deviation Ellipse
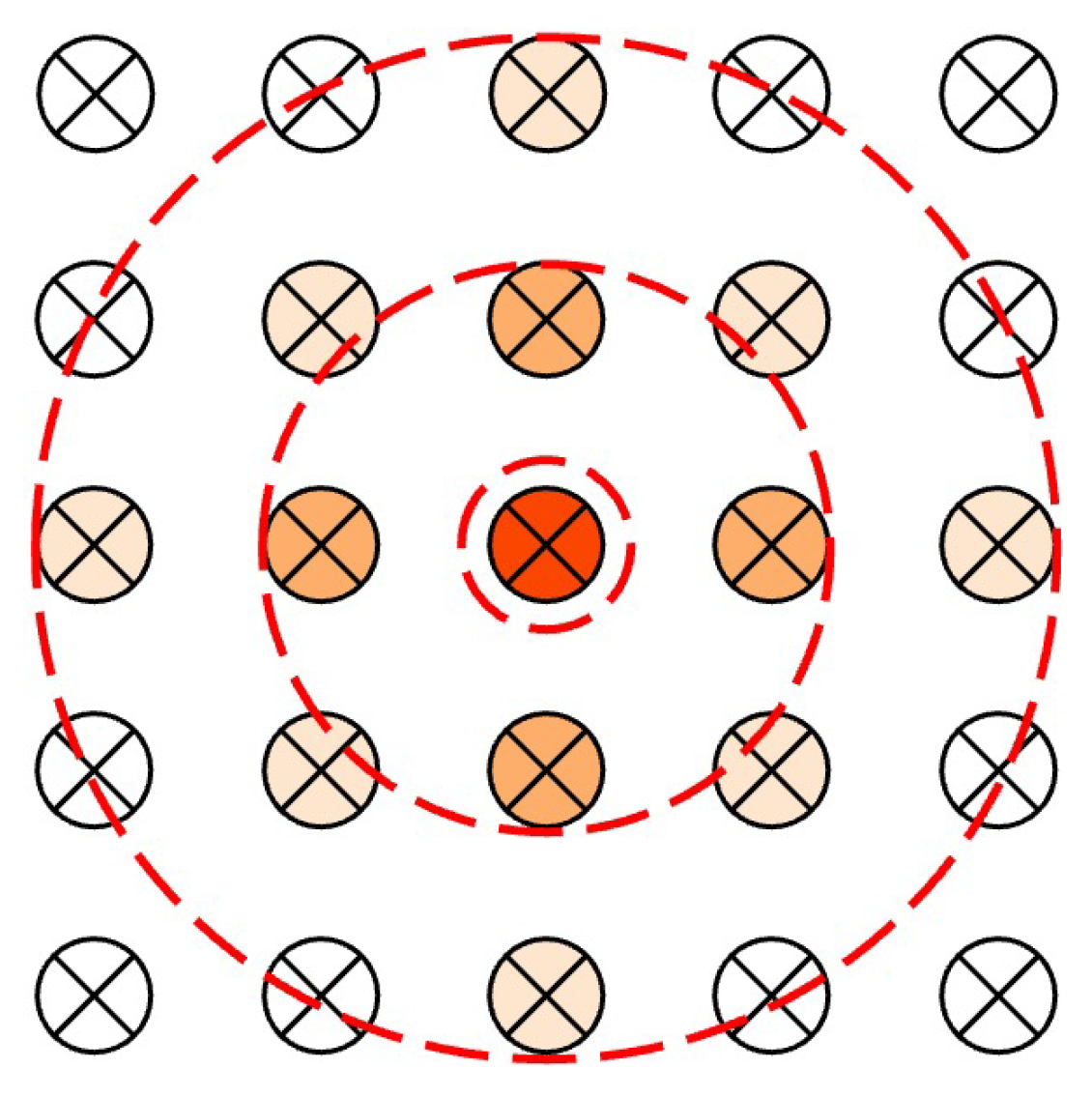
2.3.4. Kernel Density Estimation
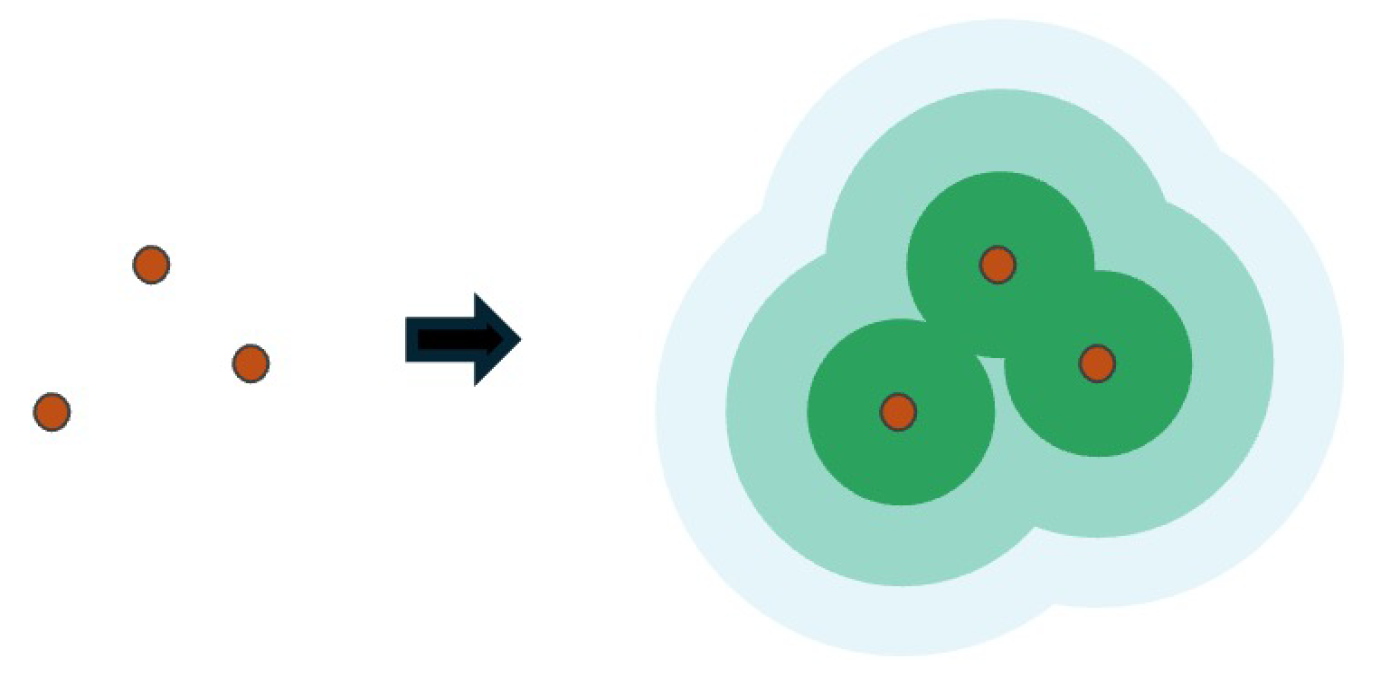
2.3.5. Buffer Analysis
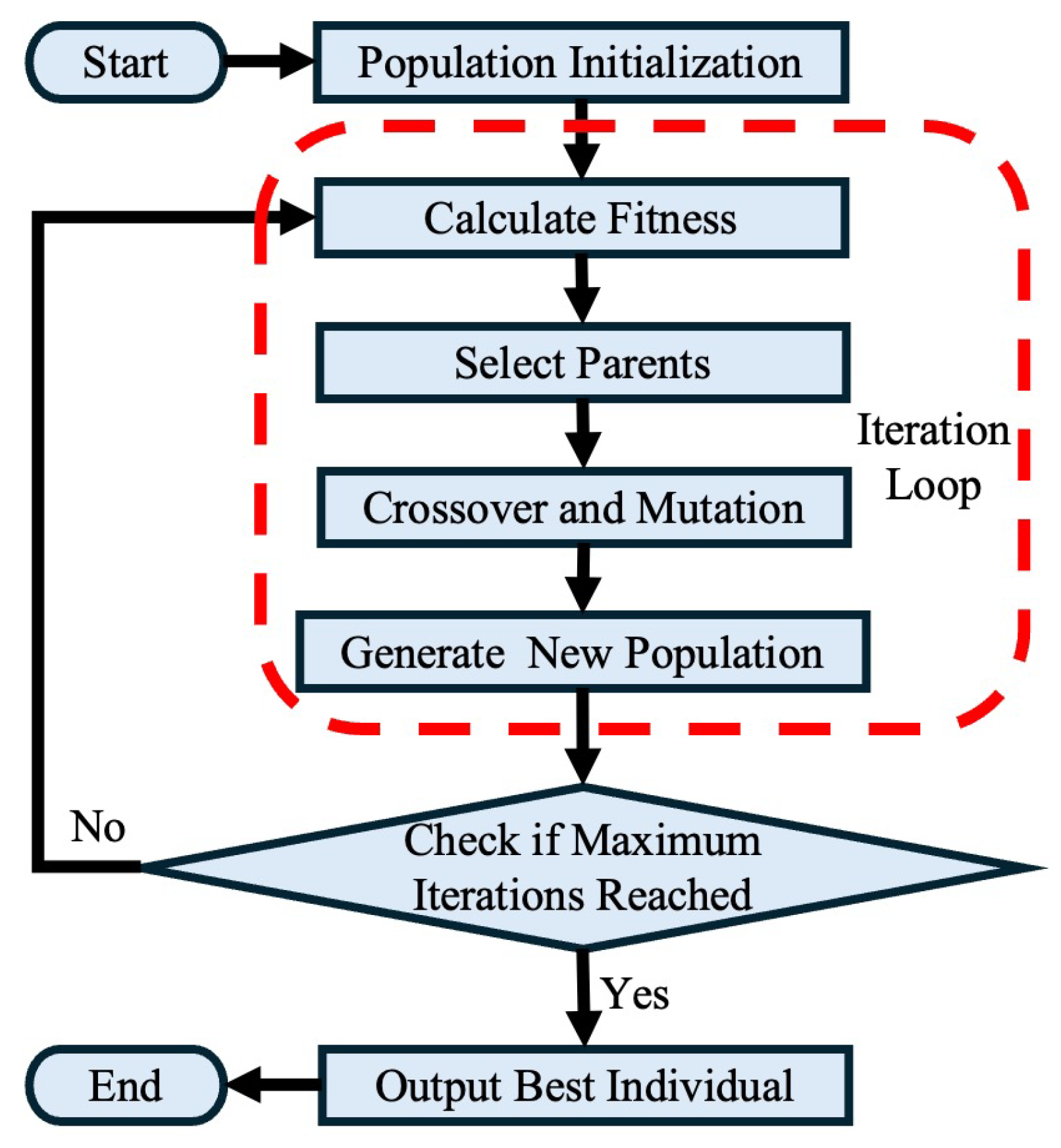
2.3.6. Coverage Site Selection Model Based on Genetic Algorithm
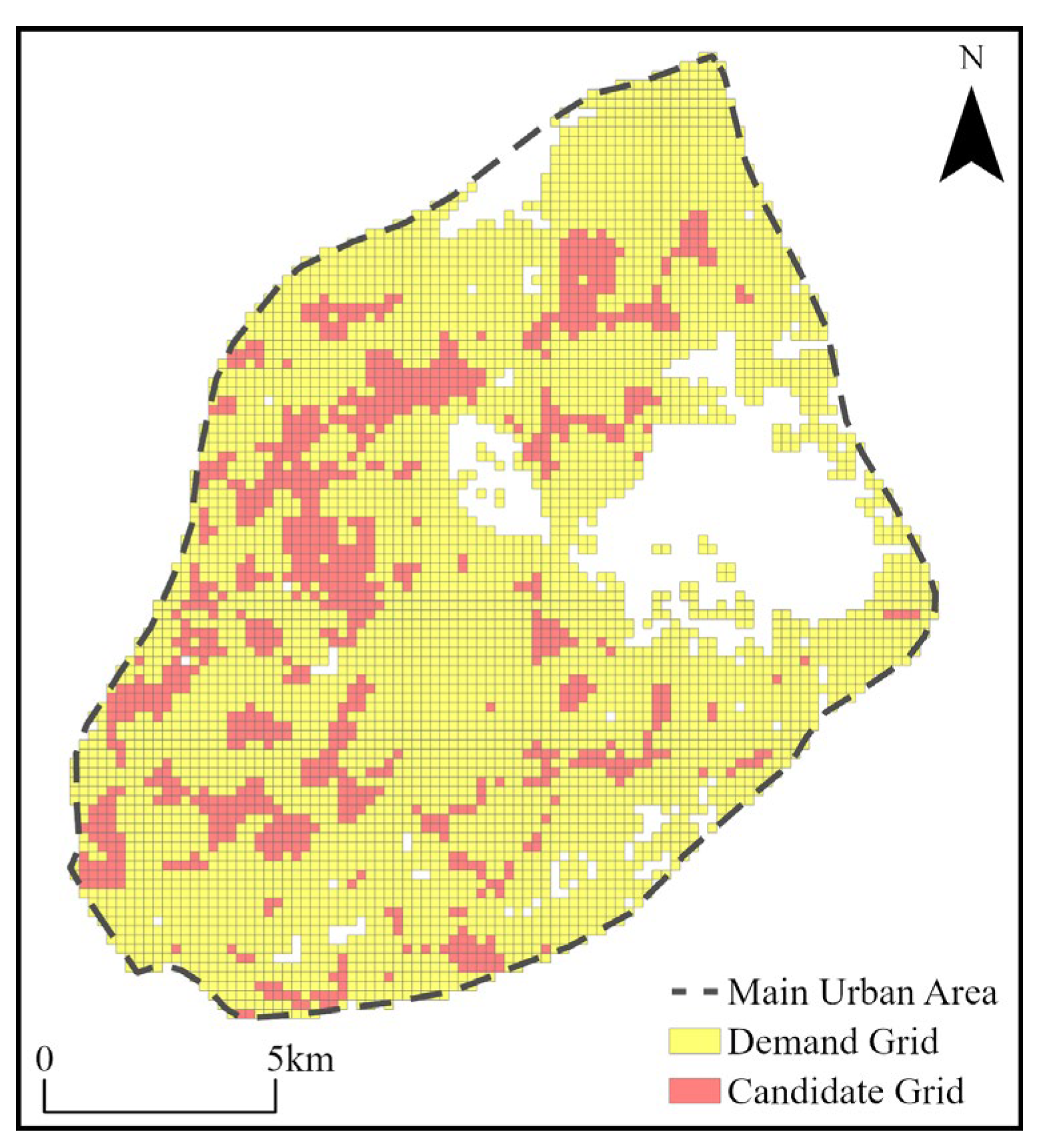
- Site selection model input
- Objective function construction
- Output of genetic algorithm
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Distribution of AEDs
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution Patterns
3.1.2. Spatial Coverage Patterns
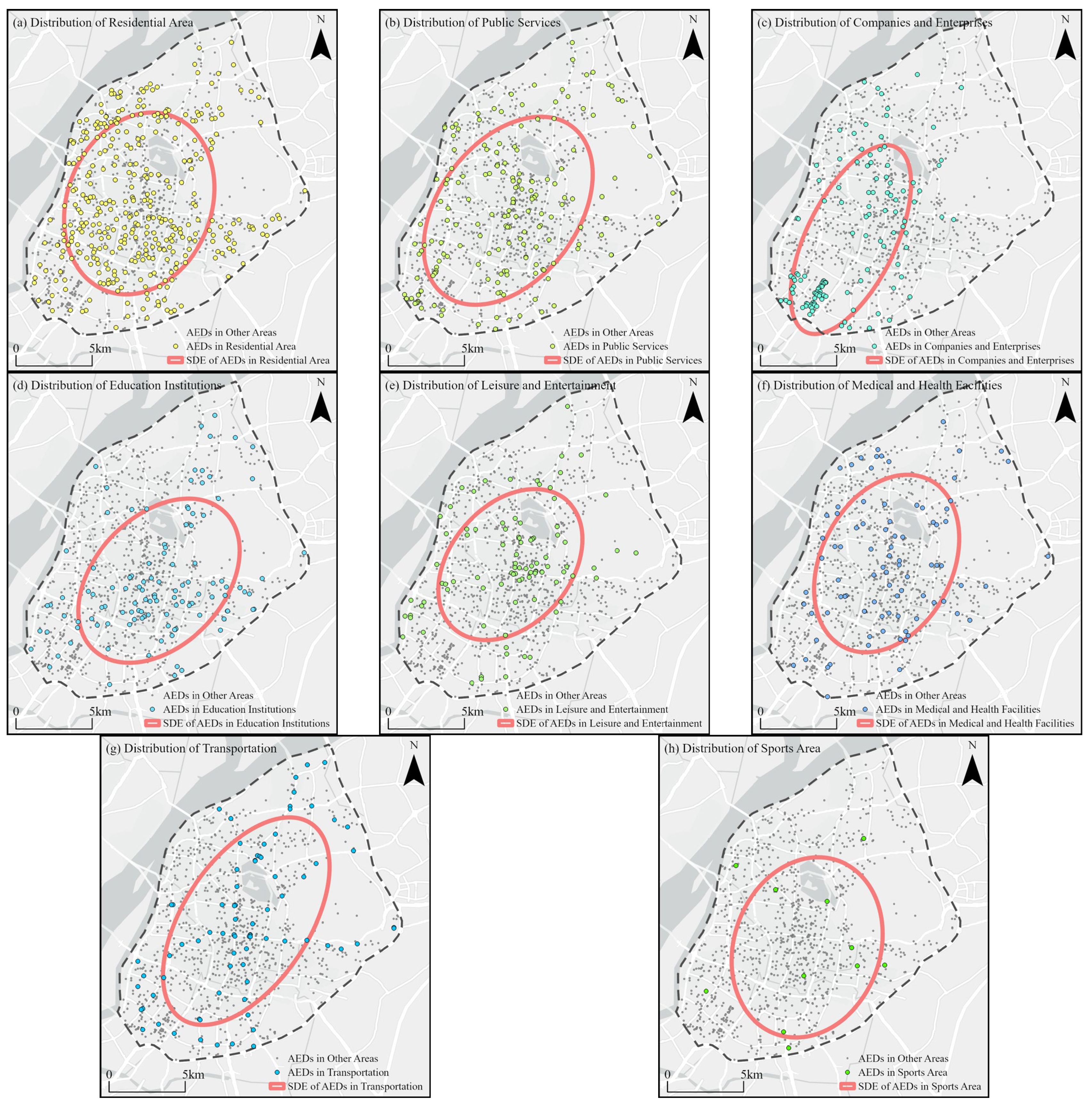
3.1.3. Types of Distribution Locations
- (1)
- Spatial distribution: AEDs demonstrate a clustered distribution, radiating outward from the central area, with better distribution on the southwest side compared to the northeast. At the street level, distribution balance is poor, with a generally low number of AEDs and significant density differences. This pattern reflects differences in urban functional zones and population density, indicating that certain areas, especially in the northeast, have an insufficient number of devices.
- (2)
- Coverage capacity: The overall coverage of AEDs, in terms of both area and population, is relatively consistent, with a coverage rate of around 90% within a 400 m range. However, the coverage rates within 200 m and 100 m ranges are only 50% and 20%, respectively, indicating substantial room for improvement, particularly in emergency response times. This is especially relevant for areas with high population density and high-risk zones, where increasing the density of AEDs is crucial to ensuring timely access to life-saving equipment.
- (3)
- Venue types: AEDs in residential areas and public service facilities account for more than half of the distribution. AEDs in corporate and educational institutions are concentrated in specific areas, with a bias towards the southwest and southeast sides, respectively. Leisure and entertainment AEDs are centralized in the central region, while AEDs in medical and health facilities are primarily located in communities with higher elderly populations. While transportation hubs are adequately equipped, AEDs in sports venues are scarce, and their availability needs to be significantly increased to address potential high-risk sports scenarios associated with sporting activities.
3.2. Optimization Strategy for the Distribution of AEDs
3.2.1. Analysis of Parameter Settings
3.2.2. Analysis of Site Selection Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Spatial Optimization Research
4.2. Planning Policy Recommendation
4.3. Study Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stokes, N.A.; Scapigliati, A.; Trammell, A.R.; Parish, D.C. The effect of the AED and AED programs on survival of individuals, groups and populations. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2012, 27, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.C.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, C.C.; Kuo, C.L.; Fan, I.C.; Ho, C.K.; Liu, I.; Chan, T.C. Spatial decision on allocating automated external defibrillators (AED) in communities by multi-criterion two-step floating catchment area (MC2SFCA). Int. J. Health Geogr. 2016, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Widener, M.J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.C. Identification of priority areas for public-access automated external defibrillators (AEDs) in metropolitan areas: A case study in Hangzhou, China. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 154, 102922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, B.; Ge, P.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.-S.; Wu, Y. Current status of support for automated external defibrillators (AEDs) in public places and factors influencing their sse in China: A cross-sectional study. J. Public Health 2023, 32, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, P.; Pinch, S. Urban Social Geography: An Introduction; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.C.; Li, H.; Lebovic, G.; Tang, S.K.; Chan, J.Y.; Cheng, H.C.; Morrison, L.J.; Brooks, S.C. Identifying locations for public access defibrillators using mathematical optimization. Circulation 2013, 127, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.C.; Demirtas, D.; Kwon, R.H. Optimizing the deployment of public access defibrillators. Manag. Sci. 2016, 62, 3617–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tao, G.; Shi, J.; Shen, M.; Zhu, Z.H. A lithium-ion battery degradation prediction model with uncertainty quantification for its predictive maintenance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 3650–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Ren, X.; Guo, S. Evaluation of public service facilities in 19 large cities in China from the perspective of supply and demand. Land 2022, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yan, J.; Dai, T. A multi-scale approach mapping spatial equality of urban public facilities for urban design. Heliyon 2023, 9, E18281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y. Measuring the differences of public health service facilities and their influencing factors. Land 2021, 10, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Huang, L.; Zhai, T.; Zhu, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, C. A challenge of sustainable urbanization: Mapping the equity of urban public facilities in multiple dimensions in Zhengzhou, China. Land 2023, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Feng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, F. Assessing regional public service facility accessibility using multisource geospatial data: A case study of underdeveloped areas in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Guo, C.; Sun, P. Study on rationality of public fitness service facilities in Beijing based on GIS. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xu, Z.; You, L.; Wu, Z. Assessing equal rights in obtaining urban public primary school services with case studies of Hangzhou in China. Habitat Int. 2022, 119, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, L.; Kanjilal, B. Measuring spatial equity and access to maternal health services using enhanced two step floating catchment area method (E2SFCA)—A case study of the Indian Sundarbans. Int. J. Equity Health 2016, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ran, Q.; Yao, S.; Ding, L. Evaluation and optimization of the layout of community public service facilities for the elderly: A case study of Hangzhou. Land 2023, 12, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Examining accessibility to medical resources for urban older adults with common diseases using multisource data: A case study of Beijing. J. Urban Plann. Dev. 2023, 149, 05023031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Geertman, S.; Hooimeijer, P.; Xu, W. Accessibility-based equity of public facilities: A case study in Xiamen, China. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2021, 14, 947–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.; Roberts, H.E.; McEachan, R.R.C.; Dallimer, M. Contrasting distributions of urban green infrastructure across social and ethno-racial groups. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 175, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi, B.; Mansourianfar, M.H.; Haghshenas, H.; Kim, I. Multimodal accessibility-based equity assessment of urban public facilities distribution. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kwan, M.-P.; Kan, Z. Analyzing disparities in transit-based healthcare accessibility in the Chicago Metropolitan Area. Can. Geogr. Géographe Can. 2021, 66, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, C.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Research on optimizing the location and layout of national emergency material reserve. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Z. The location optimization of urban shared new energy vehicles based on P-Median model: The example of Xuzhou City, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, F.; Kwan, M.-P.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Equalizing the spatial accessibility of emergency medical services in Shanghai: A trade-off perspective. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 92, 101745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Hu, M.; Zheng, J.; Tang, T. Site selection of fire stations in large cities based on actual spatiotemporal demands: A case study of Nanjing City. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Location selection for regional logistics center based on particle swarm optimization. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lai, Z.; Huang, C. Optimizing spatial location and service capacity of new schools toward maximum equity in the distribution of educational resources. J. Urban Plann. Dev. 2023, 149, 04023027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, N. Decision-dependent multiobjective multiperiod stochastic model for parking location analysis in sustainable cities: Evidence from a real case. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2022, 148, 05021052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Guo, B.; Yan, Z. Multi-criterion spatial optimization of future police stations based on urban expansion and criminal behavior characteristics. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, Q. Model for public car park layout based on dynamic multiperiodic parking demands. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 04018031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, Y. Study on location of bus stop in subway service area based on residents’ travel accessibility. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.L.; Demirtas, D.; Brooks, S.C.; Morrison, L.J.; Chan, T.C. Overcoming spatial and temporal barriers to public access defibrillators via optimization. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Fernández, S.; Martínez-Falero, E.; Peribáñez, J.R.; Ezquerra, A. GIS-based simulated annealing algorithm for the optimum location of fire stations in the Madrid region, Spain: Monitoring the Collapse Index. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Qin, Q.; Sun, T.; Wang, M.Y.; Liu, Q.L. Comprehensive evaluation model for resettlement site selection in karst areas using multiobjective particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 113759–113769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chu, K.C.; Lee, J.T.; Kao, C.Y. Optimal deployment of automated external defibrillators in a long and narrow environment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0264098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, G.; Maria Antonia, B.; Piero Maria, B.; Andrea, P.; Guido Francesco, V.; Enrico Gianluca, C. Development of a novel framework to propose new strategies for automated external defibrillators deployment targeting residential out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: Application to the city of Milan. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mu, L.; Zhang, D.; Rajbhandari-Thapa, J.; Chen, Z.; Pagán, J.A.; Li, Y.; Son, H.; Liu, J. Spatiotemporal optimization for the placement of automated external defibrillators using mobile phone data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeby, D.; Staeger, P.; Dami, F. How to improve automated external defibrillator placement for out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: A case study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Gao, F.; Feng, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W. Observed Equity and Driving Factors of Automated External Defibrillators: A Case Study Using WeChat Applet Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, D. Training Experience Is an Important Factor Affecting Willingness for Bystander CPR and Awareness of AED: A Survey of Residents from a Province in Central China in 2023. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1459590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yuan, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, M.; Hu, C. Public Knowledge and Willingness in the Use of Public Access Defibrillation of Hubei Province in China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicine 2024, 103, e36928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Red Cross Society of China. Nanjing Promotes the Construction of AED Safe Community. 2022. Available online: https://www.redcross.org.cn/html/2022-06/86853.html (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- The Supreme People’s Procuratorate of the People’s Republic of China. The Representative Committee Called for Enhancing the Legal Provision Utilized by AED Allocation Management. 2024. Available online: https://www.spp.gov.cn/zdgz/202403/t20240305_647438.shtml (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Yangtze River Delta Science Data Center, National Science and Technology Infrastructure of China. National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure. 2015. Available online: http://nnu.www.geodata.cn (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Bureau 2023. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Chiu, C.-Y.; Prayoonwong, A.; Liao, Y.-C. Learning to index for nearest neighbor search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumais, G.; Ellison, G.; Glaeser, E.L. Geographic concentration as a dynamic process. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2002, 84, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Global and local: Measuring geographical concentration of China’s manufacturing industries. Prof. Geogr. 2014, 66, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wei, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Pang, C. Explore the mitigation mechanism of urban thermal environment by integrating geographic detector and standard deviation ellipse (SDE). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Shan, J.; Ding, L.; Ye, P.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N. Urban road network expansion and its driving variables: A case study of Nanjing City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Wu, Y.; Luo, W.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Jing, N. HiBuffer: Buffer analysis of 10-million-scale spatial data in real time. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, R.; Revelle, C. The maximal covering location problem. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1974, 32, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulver, A.; Wei, R.; Mann, C. Locating AED enabled medical drones to enhance cardiac arrest response times. Prehosp. Emerg. Care 2016, 20, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, R.L. The planar maximal covering location problem. J. Reg. Sci. 1984, 24, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.C.B.; da Cunha, J.R.R.; da Silva, J.P.C. Estimation of pedestrian walking speeds on footways. Proc. Inst. Civil Eng. Munic. Eng. 2014, 167, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Shen, L.; Liu, M.; Ma, D. Modelling speed–flow relationships for bicycle traffic flow. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2017, 170, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.; Berglund, E.; Djärv, T.; Nordberg, P.; Claesson, A.; Forsberg, S.; Nord, A.; Tan, H.L.; Ringh, M. A Brisk Walk—Real-Life Travelling Speed of Lay Responders in out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. Resuscitation 2020, 151, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, T.D.; Roe, D.J.; Cretin, S.; Spaite, D.W.; Larsen, M.P. Estimating Effectiveness of Cardiac Arrest Interventions. Circulation 1997, 96, 3308–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.P.; Eisenberg, M.S.; Cummins, R.O.; Hallstrom, A. Predicting Survival from Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Graphic Model. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1993, 22, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning; Addison Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Lu, S.; Liao, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Han, X. AED Inequity among Social Groups in Guangzhou. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zibo, C.; Lian, X.; Zhang, Y. Location Optimization of Emergency Medical Facilities for Public Health Emergencies in Megacities Based on Genetic Algorithm. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 3330–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, B.; Gama Dessavre, D.; Kraus, K.; Ramirez-Marquez, J.E. Optimal placement of public-access AEDs in urban environments. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 90, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, A.; Afshar-Nadjafi, B.; Amiri, M. A Two-Stage Optimization Approach for Healthcare Facility Location- Allocation Problems with Service Delivering Based on Genetic Algorithm. Int. J. Public Health 2023, 68, 1605015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, J. A Dual-Population Based Evolutionary Algorithm for Multi-Objective Location Problem under Uncertainty of Facilities. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 7692–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, E.; Rabajante, J.; Tubay, J.; Lapitan, A.; Madrid, V.R. A Multi-Objective Site Selection Model for Evacuation Centers in Taguig City, Philippines. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 8303–8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, W.; He, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, N. Emergency logistics centers site selection by multi-criteria decision-making and GIS. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 96, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.L.F.; Karlsson, L.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Morrison, L.J.; Folke, F.; Chan, T.C.Y. Spatiotemporal AED optimization is generalizable. Resuscitation 2018, 131, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

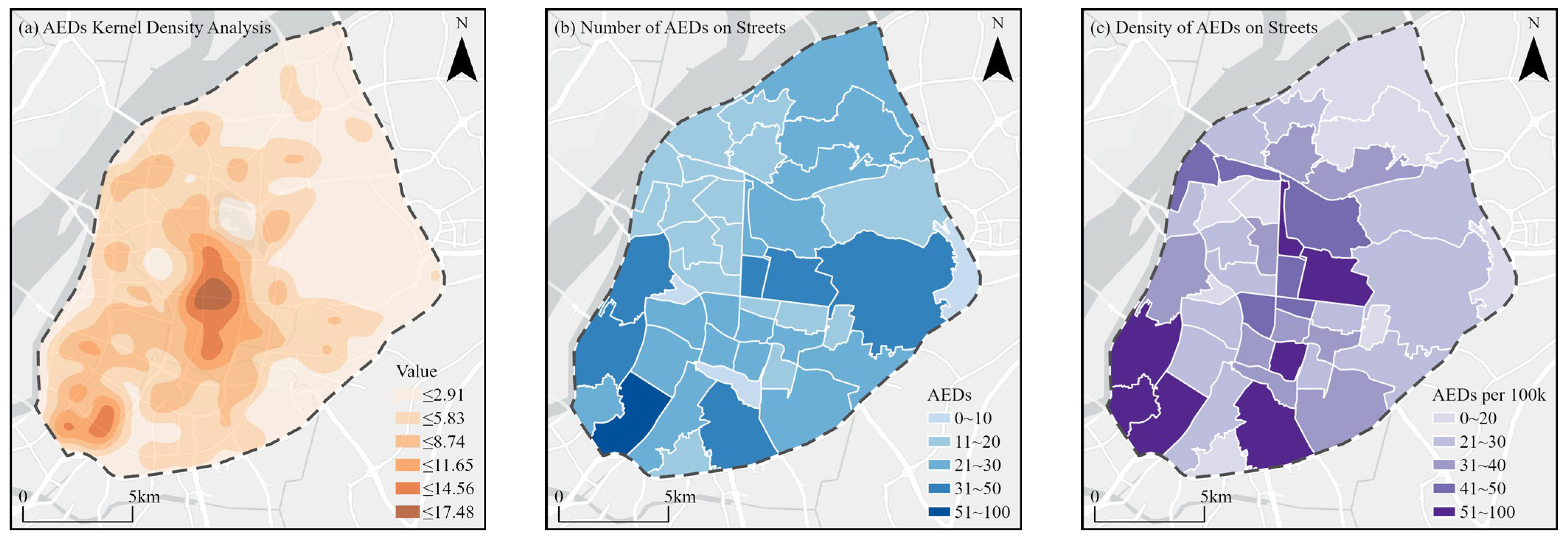
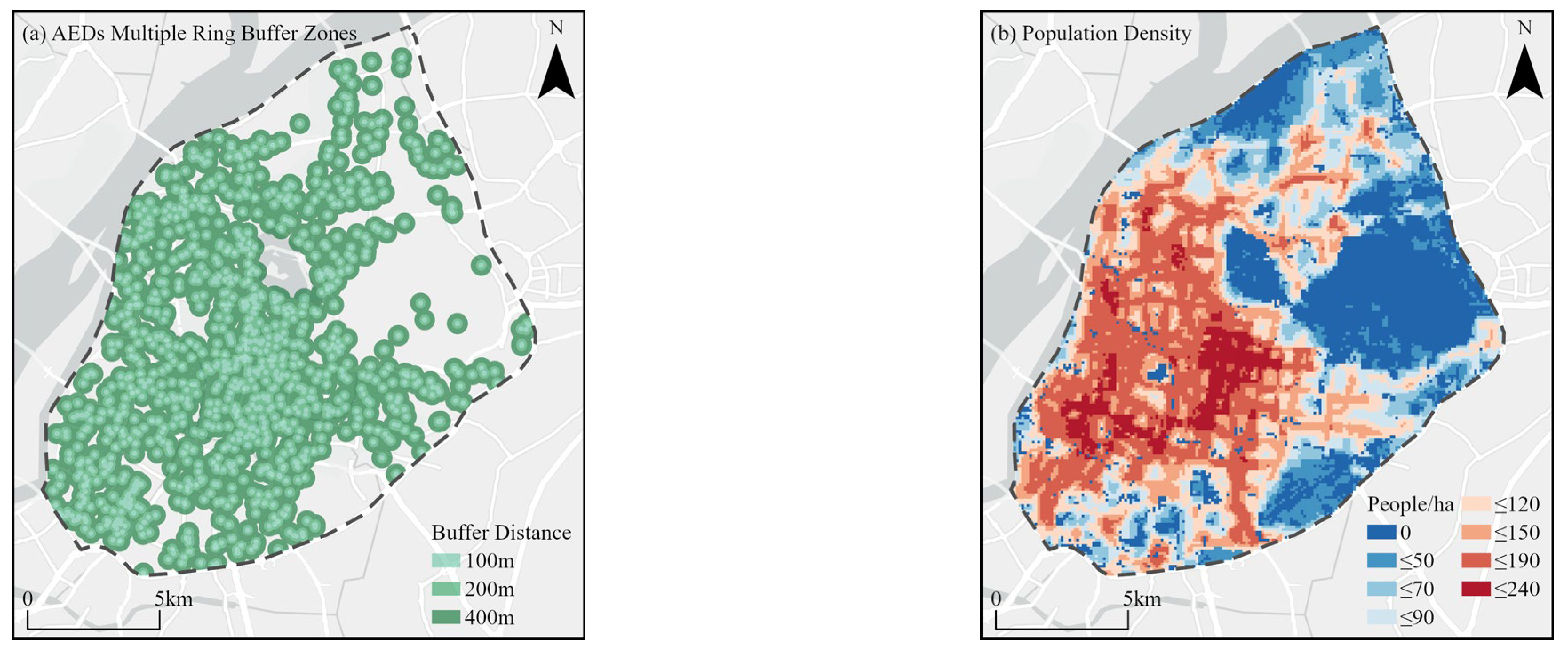
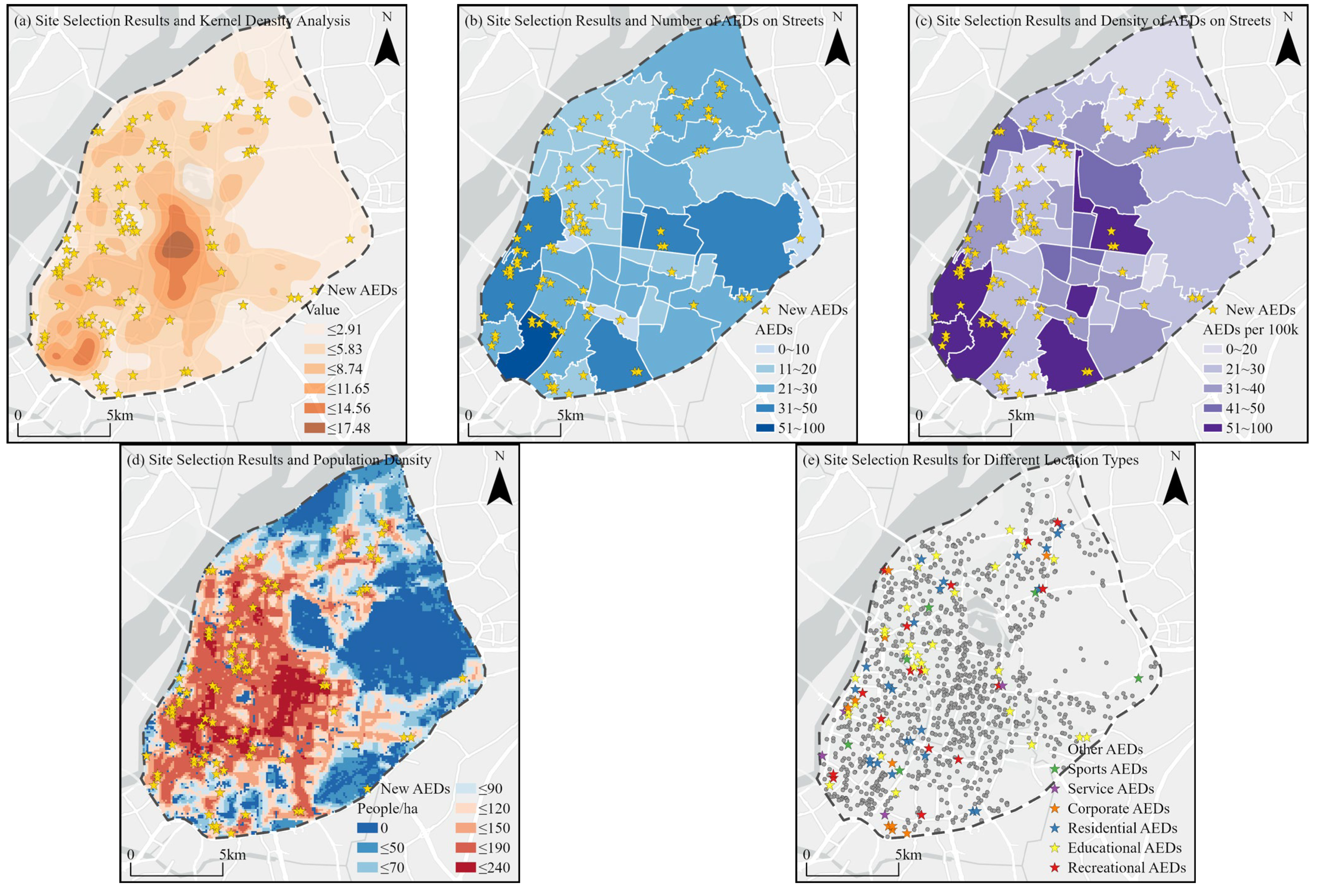
| AEDs Quantity | Quantity at Street Level | Density of AEDs (per 100,000 People) | Quantity of Street |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 3 | 0~20 | 8 |
| 11~20 | 17 | 21~30 | 13 |
| 21~30 | 16 | 31~40 | 9 |
| 31~50 | 6 | 41~50 | 6 |
| 51~100 | 1 | 51~100 | 7 |
| Type | Quantity | Percentage/% | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential area | 350 | 33.98 | 1 |
| Public services | 173 | 16.80 | 2 |
| Companies and enterprises | 123 | 11.94 | 3 |
| Educational institutions | 112 | 10.87 | 4 |
| Leisure and entertainment | 93 | 9.03 | 5 |
| Medical and health facilities | 89 | 8.64 | 6 |
| Transportation | 79 | 7.67 | 7 |
| Sports area | 11 | 1.07 | 8 |
| Number of Newly Add AEDs | Adaptation | Newly Add Quantity/Unit | Change of Coverage Rate/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 m | 400 m | 200 m | 400 m | ||
| 10 | 117.47 | 50 | 80 | 0.95 | 1.51 |
| 20 | 298.09 | 99 | 138 | 1.87 | 2.61 |
| 30 | 403.84 | 147 | 172 | 2.78 | 3.25 |
| 40 | 468.56 | 189 | 184 | 3.57 | 3.48 |
| 50 | 537.99 | 232 | 203 | 4.39 | 3.84 |
| 60 | 593.94 | 275 | 218 | 5.20 | 4.12 |
| 70 | 639.75 | 311 | 227 | 5.88 | 4.29 |
| 80 | 687.87 | 328 | 251 | 6.20 | 4.75 |
| 90 | 734.28 | 381 | 247 | 7.21 | 4.67 |
| 100 | 771.08 | 406 | 252 | 7.68 | 4.77 |
| 110 | 793.65 | 439 | 261 | 8.30 | 4.94 |
| 120 | 827.34 | 481 | 262 | 9.10 | 4.96 |
| Newly Add Quantity | Adaptation | Newly Add Coverage/Unit | Change of Coverage Rate/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m | 200 m | 400 m | 100 m | 200 m | 400 m | ||
| 90 | 734.28 | 90 | 381 | 247 | 1.70 | 7.21 | 4.67 |
| Spatial Coverage Rate/% | Population Coverage Rate/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m | 200 m | 400 m | 100 m | 200 m | 400 m | |
| Before optimization | 15.96 | 48.65 | 90.22 | 17.40 | 50.77 | 87.95 |
| After optimization | 17.52 | 53.67 | 95.60 | 19.57 | 56.03 | 92.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Na, J.; Chen, W. Evaluation and Optimization Research on the Spatial Distribution of Automated External Defibrillators Based on a Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of Central Urban District of Nanjing, China. Systems 2025, 13, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13010064
Shi G, Liu J, Chen C, Zhang J, Xu J, Chen Y, Na J, Chen W. Evaluation and Optimization Research on the Spatial Distribution of Automated External Defibrillators Based on a Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of Central Urban District of Nanjing, China. Systems. 2025; 13(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Ge, Jiahang Liu, Chuang Chen, Jingran Zhang, Jinghai Xu, Yu Chen, Jiaming Na, and Wei Chen. 2025. "Evaluation and Optimization Research on the Spatial Distribution of Automated External Defibrillators Based on a Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of Central Urban District of Nanjing, China" Systems 13, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13010064
APA StyleShi, G., Liu, J., Chen, C., Zhang, J., Xu, J., Chen, Y., Na, J., & Chen, W. (2025). Evaluation and Optimization Research on the Spatial Distribution of Automated External Defibrillators Based on a Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of Central Urban District of Nanjing, China. Systems, 13(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13010064






